#abolition journal
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Hundreds Riot in Tennessee Prison Over Food Shortages, Take 3 Correctional Officers Hostage (The Worker)
published june 14th, 2025
i want you to read this, and understand that these people had no choice but to riot, because otherwise they were going to die
and then i also want you to think about how even the declassified CIA documents admitted the soviets fed their prisoners. and i want you to understand that while communists DO value human life, they also understand that if you do not feed your prisoners, this is inevitable.
this will continue to happen so long as the usamerican imperial regime does not feed its prisoners. we need to be organizing with people on the inside and people on the outside to find a VIABLE ROUTE to tear these boxes down, for good. to tear them down as many times as it takes such that they are never rebuilt. our people are starving in there. they are starving, and desperate, and struggling, and through trial and error, with their own bodies, in tithes of blood, they are showing the rest of us the path to victory
it is beyond time those of us lucky enough to be outside the big house had skin in the game
and if we are deported for trying, we will set those prisons on fire from the inside
#us pol#prison abolition#incarceration#2025#i do not yet have a good tag scheme for this i am pretty new to journalism so bear with me
44 notes
·
View notes
Text
this is how a gang operates. these are shakedowns
#tiktok#police#police abolition#police abuse#airport#airport security#us department of justice#the fourth amendment#journalism
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Was reading some lists of traits of "cluster B" disorders and my takeaway was "wow, society really can't stand people who are industrious and diligent on their own terms" considering how much those kinds of things would come up. Of course it does - people who know their worth and throw themselves headlong into what they consider important rather than what others tell them is important make shitty wage slaves.
When I read these lists, they read like they're written by the same kind of people who irrationally hate cats for not being dogs. And I'm a dog person myself - I don't dislike any other animals, dogs are just my favorite, probably because I can relate to them (I, too, am a socially inquisitive animal who has a "go hard or go home" approach when it comes to trust).
Am I "dangerous" because I can't be happy with an understimulating life and social environment? Am I "destructive" and "selfish" and "irresponsible" for quitting an arguably-comfortable, consistent retail position to take care of pets and deliver food by commission, which leaves me time and freedom to take care of personal affairs between clients throughout my workday? I don't think so, and neither should you.
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Journal entry from January:
Same shit, different day.
God, I wish I was a boy. Yeah, I got the penis envy well enough. Yeah, I wish I was muscular all around, like some guys tend to be. Yeah, I wish guys would see me as a guy. Yeah, whatever.
I attended a [CENSORED] hockey game tonight. My father's school friends were there— I think when he says "daughter", they expect a "girl"— not exactly whatever the fuck I am.
I see the cheerleaders, first— all young blondes in cleavage-cropped tops— they are there just to be looked at. They barely cheer— just some vague arm gestures to the newest Olivia Rodrigo song— cheering is not the point of them anymore. They are to be pleasing, to be looked at. To be so feminine, you harmoniously succeed at the task of being a woman.
I see the boys, second— the hockey players, the fast, highly able boys — they're meant to be looked at, too, but only by merit of their skill. Only by the jerseys on their backs, & how fast they strip the puck from one another. To be so skilled that people value you for that in itself. To be so domineering in competition, that you've made it here— to Princeton, to Quinnipiac— to D1, to a contract, to a spectacle on the big screen. To be so able— to be so masculine.
& I sit there, an odd duck out. I remember how I loved to play ice hockey. I remember how good it felt to be good at it. I wonder why God did not make me a boy— it would've been so easy to keep up.
& I think about how boys love each other. I think about being on an ice hockey team— 15 boys, sweating, turned on and ready to go. I think of how divine it would be, to be a pretty boy surrounded by other pretty boys. I think of how they smack their heads together— I think of the unexpected closeness had when the person next to you scores a goal— when both of you have nothing else to do but swing into each other, invading breaths and tossing arms around in celebration. To be a boy, able to invade a boy's space.
To not be a girl— to not be treated with difference or fragility. To be a boy— where you both freely, languidely wrestle with each other— to be evenly matched, to feel the tension of competition surging within you. To feel that animal inside of you dominate, just for a split second. To transmute that beast into tension, into connection, into action.
& I sit here wondering why this is not me. Perhaps it would all be too simple— no grievances are afforded to this class of person in America— and where there is no struggle, there is no depth. Perhaps this was all masterfully orchestrated, to become me.
To be Achilles as well as Patroclus. To be wholly, divinely even.
That's the thing though! We've enscribed these preconceived notions of our gender onto ourselves, and onto our bodies; men have the privilege of being the "normal" body, & so their internal connections and their external actions are not scrutinized in the way that women, or the woman-adjacent person is. A man has a penis, and if you don't have it, you're not quite a man. Whatever you are, you have a vagina! A weaker body; tits for the looking; butt for the grabbing. When men have tits, they don't have tits. When a boy touches a boy, it is acceptable. When whatever I am does anything, I am immediately evaluated in phenotype to be determined as a vagina-haver; a woman-adjacent; a "whatever," with a vagina; a "whatever" that is at least, certainly not an actual man.
& so all my interactions are contextualized as such. & so my life is determined by that which none of us can adequately control, that actively misrepresents.
The boy's club, the Quinnipiac boy's hockey team. I know in soberation that it is not a club I genuinely would or should miss being in: it is all a façade in the face of patriarchy, an elaborate show borne from 5,000 years of atrocious normativity. The boys are no longer pretty when a slur slips from their mouth— they are not pretty when one sweet-talks assault— they are not pretty when they don't like you, when they reject what they see. A boy's club nine times out of ten deals with the imperial overpresence of patriarchal-induced misogyny (and one must add in some white supremacy if it's a white-boy's-club). These are not spaces I should feel drawn to, because the fantasy is absolutely not real.
Why does the fantasy persist then? Probably just because of what we've already discussed— a man is the fixed status of normalcy, of indifference, of congruency. To be a man is to be nothing at all. To have a penis is to be a man, which is the standard of individually recognized human. To have a vagina is to be exactly inverse— you are then other, differentiated, and something. And when you are something, you are to be seen. When you are nothing, there is nothing TO see.
What the forg. Moving on, I must go wash my face. Goodnight all, I hope you said it back.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
watching this lit such a fire in me. why do we do this? genuinely, the feeling that overtook me when i heard them cheering -- i know that feeling, why do we do this to people? i've seen a lot and i can't imagine a human being who deserves this.
i hope that interview made them feel seen. and i hope that one day we live in a world where we don't lock people up because we don't want to deal with them.
y'all HAVE to watch this...interview??? with the inmates of the prison where luigi mangione is being held.
the reporter is standing outside the prison walls, while the inmates are inside watching the news, and collectively screaming out one-word answers to questions loud enough to be heard by the reporter.
I've never seen anything like it
60K notes
·
View notes
Text
https://www.joinjeremy.org/about-3 Jeremy Busby is a wrongfully convicted incarcerated journalist who has faced near constant retaliation from TDCJ officials. Please take action to demand #SafetyForJeremy and #JoinJeremy.
0 notes
Text




The Little Honourings Journal is accepting submissions from now until June 3. We eagerly await reading through your creations!
#writing#journal#poetrty#poems on tumblr#creative writing#publish#publishing#mentalhealth#mentalillness#psychsurvivor#madstudies#abolition#criticalpsych#criticalpsychiatry
1 note
·
View note
Text
HAHAHAHAHAHAHAHAHAHAHAHAHAHAHAHAHAHA!!!
GET REKT, RADFEMS!


#vice#journalism#press#journalistic integrity#jezebel#journalistic ethics#ethics#yellow journalism#radblr#radical feminism#gender critical#radical feminists do interact#male violence#rad fems do interact#radical feminist#radical feminist safe#radical feminist community#radical feminists do touch#gender abolition#terfblr
251 notes
·
View notes
Text

ID: [A drawing of a giant, disintegrating American flag with someone hanging on and swinging from the dangling threads of the flag. Text reads: What, to the American Incarcerated Person, is your Fourth of July? The Marshall Project.]
“I’m a federal transgender inmate, and I’ve been incarcerated since 2010. Being a double minority — a transgender and a Black person — the Fourth of July is nothing but a good meal in the chow hall.
Growing up, I didn’t know that I was on a pipeline to prison. I remember being harassed by police in the streets of Galveston, Texas, standing on the corner with my friends. Then I would watch other young people standing on the corners in their White neighborhoods who didn’t get harassed.
There’s this profound song called “Scholarship 2 the Pen” by a rapper in Houston named ‘Lil Keke. Like the title suggests, I didn’t grow up hearing about college or how I could get financial aid. Instead, I went into a Scared Straight program, which didn’t do anything but show me what prison was like. Meanwhile, in more suburban and White neighborhoods, kids heard questions like, “What college are you going to? Who are you going to intern for?” It was no surprise that I eventually caught a case.
Today, with Donald Trump in office, it seems like they’re rolling back all of our rights. I’m incarcerated here with a lot of Black men who were literally sitting in front of the television when Trump was getting elected saying, Oh, he’s gonna let us out of jail. I told them, “No, he’s not. He does not care about you.”
All of this is why the Fourth of July is nothing more to me than a big hamburger with all the fixings, a ‘brat or two, some watermelon, and some type of ice cream dish.
- Ayana Satyagrahi in What, to the American Incarcerated Person, is your Fourth of July? From the Marshall Project
441 notes
·
View notes
Text
It's a consistent rule that media which conspicuously and deliberately refuses to engage with a social issue functionally supports the Status Quo. Sometimes this is an intentional strategy by someone who consciously holds this position but feels insecure with openly expressing it, but other times it's simply the natural outcome of presenting things in this way regardless of the creators intent. Like I've been reading a little about agricultural reform movements in the South Eastern USA before the US civil war, and the general refusal of the most popular agricultural journals to even mention slavery (i.e. the very bedrock of the Southern agricultural system) was clearly a way to support it without getting embroiled in the controversy around abolition that was raging among white settlers in the decades leading up to the war. This excerpt sums it up pretty well:
Considering the Southern Cultivator's resolution to "be exclusively devoted to Southern Agriculture" and its abundant references to planters and plantations, the journal remained remarkably silent about slavery in its first ten years. The editors had abundant reasons to ignore the subject. First, because agricultural journals relied on the exchange of information across multiple national and transatlantic networks, a preoccupation with slavery threatened to alienate critical partnerships. For this reason, agricultural publications both above and below the Mason-Dixon Line tempered their treatment of slavery. Like the Southern Cultivator, the Albany Cultivator, a northern journal with a large southern readership in the 1830s and 1840s, discussed plantations without often mentioning slaves. In both journals, "planters" and "plantations" served as euphemisms for slave owners and slave-labor landscapes Further, agricultural writers made a living by finding and addressing problems, and the editors of southern agricultural journals, even if so inclined, could not afford to suggest that slavery was a problem. Rather, the Southern Cultivator and similar publications mimicked mainstream agricultural philosophy by espousing the idea that the appearance and productivity of agrarian landscapes were an extension of the character and behavior of the landed proprietor. The Southern Cultivator thus bypassed questions of the utility and economy of slavery by focusing its critique on planters and their mismanagement of plantations. In 1849, in a rare direct engagement with national slavery debates, Daniel Lee declared to readers that "[t]he evils of defective system of husbandry—one that makes the soil poorer instead of richer—are mistakenly charged to the account of slave labor when they ought to be ascribed to the misdirection of such labor." The Southern Cultivator thus was a clearinghouse for the various ways planters could use agriculture, architecture, and horticulture to redirect slaves' labor into more culturally and economically productive channels. The journal was not a platform for critiquing or reforming the labor system itself
Philip Herrington (2012) Agricultural and Architectural Reform in the Antebellum South: Fruitland at Augusta, Georgia, The Journal of Southern History vol 78. No 4.
175 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hi long-time lurker, first time follower. When you say the hardliners still profit from their connections to Fall Out Boy, does that mean in a “name-dropping” way or do you think FOB is actively doing things for them?
To answer your question in very narrow and brief way, this guy I will call R (for the sake of this post) wrote a very long feature article on Fall Out Boy's origins as well as other stuff too. Another guy called S owned the label they put Evening Out on.
In the 90s, R used to make zines and be in bands with this guy I'll call S (for the sake of this post). S owned the label Fall Out Boy put Evening Out on. Both of them identified with a movement that held very extreme beliefs that were both positive and harmful. In these zines, they often advocated for the extermination of gay people, insisted gay people were indoctrinating children, compared abortion to the Holocaust, believed women should not be allowed to access birth control, and wrote offensive things about women who disagreed with their views, such as calling them "lard cunts." They also advocated for positive things like racial justice, police abolition, and environmental preservation.
Andy was in a band with S when he was like 15 years old and a lot of the zines were put out in association with this band. When Pete was like 14 and a literal child, he was in a band that probably identified with this movement, and a lot of his other bands were not explicitly identified with this movement, but shared a lot of scene real estate with them. I'm pretty sure R and S were like 5 years older.
As Pete and Andy became young adults (17-19), they started their own bands that focused entirely on positive things like racial justice or veganism, but still shared spaces with bands who held certain beliefs about abortion, birth control, women, and gay people. Then, as actual adults (21-23), they started Fall Out Boy, which sought to be positive and inclusive to everyone, and later used Fall Out Boy's influence to advocate for both pro-choice and pro-gay activism.
They ended up not wanting to release Evening Out on S's label, and while they have never gotten too explicit about it and have primarily focused on the quality of the demos, I am pretty sure a big part of it was S's beliefs. Evening Out came out on the label anyway, it made a bunch of money, and a lot of that money was used to fuel this subculture, which they were not okay with but did not have a choice in because they signed a contract with S to further the band.
As decades progressed, R and S slowly dialed back the more problematic elements of their beliefs a lot. R became a journalist at the same publication as the ghostwriter of Pete's book, most likely while still identifying with this movement. S is often quoted as an authority on Fall Out Boy.
In 2013, R wrote what is one of the most influential and widely circulated pieces of journalism on Fall Out Boy's history. In 2023, Fall Out Boy re-released this piece as a book. They made a lot of edits, which included removing a misogynistic comment from Pete as well as references to politics in hardcore. Around when they did this, scans of the piece on Reddit that had been widely viewed and circulated for the last decade were taken down due to copyright. This piece quoted from S a lot, and S is often quoted as an authority on FOB in general. R definitely profited from the release of this book though he is no longer affiliated with the movement discussed in this post, and he probably wrote a lot of other journalism about FOB, and he probably got into journalism partially through publishing these hateful zines about women and gay people.
I'm focusing on R and S in this post for the sake of giving examples to provide simplicity because they are some of the biggest names, but benefits of Fall Out Boy's legacy carries over to a lot of people associated with hardcore, and I think Fall Out Boy's hardcore roots are often sanitized in order to protect Fall Out Boy's image as well as hardcore's image, especially in relation to women and feminism.
And that's often not good when most people dominating music history are straight men, and people like R who was arguably part of a hate group are the ones who get to decide which perspectives are and are not included in seemingly "objective" documents like oral histories, which is often problematic as these documents posit that women just didn't exist, when in reality, Riot Grrrl and hardcore existed at the same time and were often reacting to each other on issues like race and women's rights. Obviously, there are problematic elements of Riot Grrrl too.
Anyway, it's often treated as if women or gay people in emo didn't exist and never accomplished anything because "They were no women at Warped because they weren't good enough to play" "There were no women on X label/tour/whatever because they weren't good enough" "There were no girls in bands in the 90s" "That girl's band isn't "really" emo so she doesn't matter and she shouldn't be in the book" And there's no consideration of how major players in "emo" viewing feminists as "lard cunts," or things like that thing about that guy who ran Warped intentionally pairing up bands with MCR with homophobic bands to cause heckling and drama, impacted who is considered "really emo" today and which smaller male bands have been chosen as important, legacy acts despite not being commercially successful, versus how female fronted bands that aren't commercially successful are dismissed as failures that don't matter, and how this is currently impacting things like WWWY or the Warped comeback.
And fans of MCR, FOB, and Panic often do not engage with these discussions in a constructive way, partially due to how they are wholly informed by (see above discourse about The Narrative).
Someone wrote a 250 page zine mostly about the movement I've discussed and touches on Fall Out Boy's relation to it and made it available for free, it's very well written and well cited as well as taking a very balanced perspective.
84 notes
·
View notes
Note
Sorry if this is a little out of your wheelhouse, but I have to write an essay due in April apart of my collegework, and I want to do it on the movie “Sing Sing” - particularly its view of/representation of the Prison System and Black men, and the correlations the two have (ie the way Black people are disproportionately targeted). I wanted to know if you knew of any academic articles or books which discuss the relationship between Prisons/ Prisoners and Black men? The stereotypes attributed to them or the overlap between stereotypes of Prisoners and Black men, the way Black men are expected to act especially in those sorts of environments, etc. I've done looking of my own to collect sources, but I figured I'd ask anyways to try and get more to help with forming a better/more insightful essay 😅 Thank you, and have a nice day!
Widening your scope a little to prison abolition overall will give you context as to the history and the environment, plus some familiar names to go to for their written works for your more specific questions (e.g. why that environment forces Black men to behave a certain way, how certain stereotypes about Blackness and Black men lend themselves to creating the mass social consent of capturing and imprisoning Black bodies).
The New Jim Crow by Michelle Alexander is always a go to; @embodiedfutures used to run the BFP page that has an archive full of prison abolition resources (They have so much literature on everything!!)
106 notes
·
View notes
Text
Honestly it's INSANELY funny that a post is going around rn about the Life of Faith dolls cause I remember when they were being sold. My conservative Christian mom even said "Hmm. That might be a bit culty for us. Also the Elsie Dinsmore books are racist trash," bought me a pretty journal from the local Christian bookstore, and that was that. Me and my friend Annie did a deep-dive on them a few months back just in our own DMs so for those curious about how bad this gets, here's some fun facts:
The company was started by Christian Homeschoolers™ (not "homeschoolers who are christian." Christian Homeschoolers and all the stereotypes that entails) in the mid-90s but went bankrupt in 2010. They based them around the old Elsie Dinsmore books, starring a girl who was so pious she would rather die than not pray to God or smth like that. The dolls hands can be clasped in prayer and they all came with mini Bibles
The dolls were Elsie Dinsmore, the daughter of a fucking plantation owner; Millie Keith, her cousin whose doll was a clear ripoff of Kirsten Larson; Violet Travilla, Elsie's daughter; Laylie Colbert, a fucking slave doll (but it's ok because the white girls converted her to Christianity); and Kathleen McKenzie, a Great Depression bitch.
This is a screencap from the defunct official site. Note how only Laylie looks like she could be from pre-90s LMAO.
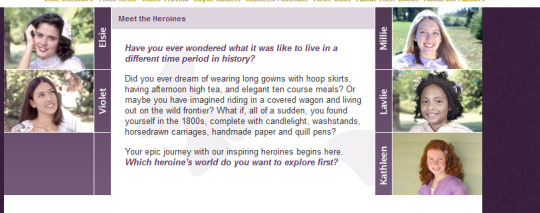
Elsie Dinsmore books were originally published between 1867-1905. They are generally considered so bad that even hardcore Evangelicals consider them boring at best. The doll line EDITED the books to be less racist actually. Yes, the doll line that calls the slaves "Plantation-Dwellers" actually edited racist shit out of the books. I recall a bit where Elsie told a slave girl that she would be white in Heaven. They also cut out a bit where her Dad beats her with a riding crop.
Yes, she does marry her Dad's Friend. They did not cut this part out.
DINSMORE, YOU BRUTE
Millie's books were somehow both more and less racist. Millie and her family were abolitionists who helped runaway slaves but also one of her brothers marries a Mexican girl after the two of them were, and I quote, "captured by Indians and presumed dead."
IIRC, Elsie and Violet happen to be in Europe when the Civil War happens and they just kinda stay there to avoid the consequences of their actions. When they come back they are threatened by the KKK but I don't remember why. I DO remember that they spent Elsie's money on rebuilding plantations, because clearly THAT is where our priorities have to lie
The Violet and Laylie books are fanfiction. I don't think Kathleen's have anything to do with Elsie at all.
Oh, did I say books? Laylie only got one book, one nightgown, and some accessories for her collection. Kathleen, who was released a year later, got a shitton of stuff. Like, a mountain of stuff. I wonder what the difference between them is
I'm pretty sure Laylie's book does involve her escaping slavery but I never read it so idk. I do know that it plays heavily into Millie as her White Savior™ teaching her about God and how to read or whatever. I think Millie also teaches her about abolition which is fucking wild. Imagine a white girl explaining abolition to a slave
It's like they took everything American Girl did right when making Addy and said "we need to do the opposite of all of this"
Kathleen is both a ripoff of American Girl's Kit Kittredge and Girls of Many Lands's Kathleen (yep, same name and appearance).
The reason this line exists is the original Christian Homeschoolers considered American Girl to be pro-lesbian and pro-abortion. No American Girl didnt have any references to homosexuality or abortion at the time. Their first canon queer characters were in 2021 (Kira's gay aunts). As @jabberwockypie put it, everyone flipped out because AG partnered with Girls Inc "to fund after-school science programs and stuff" and god forbid, amirite?
And, yes, the red eye defect persists. It is SO funny
Here's an archived site about the collection, and another post about it by @dollysattictreasures. Anyway if anyone was given a Laylie doll as a child by your overly-religious parents, go give her a hug for me. And a gun
141 notes
·
View notes
Text
In 1833, Parliament finally abolished slavery in the British Caribbean, and the taxpayer payout of £20 million in “compensation” [paid by the government to slave owners] built the material, geophysical (railways, mines, factories), and imperial infrastructures of Britain [...]. Slavery and industrialization were tied by the various afterlives of slavery in the form of indentured and carceral labor that continued to enrich new emergent industrial powers [...]. Enslaved “free” African Americans predominately mined coal in the corporate use of black power or the new “industrial slavery,” [...]. The labor of the coffee - the carceral penance of the rock pile, “breaking rocks out here and keeping on the chain gang” (Nina Simone, Work Song, 1966), laying iron on the railroads - is the carceral future mobilized at plantation’s end (or the “nonevent” of emancipation). [...] [T]he racial circumscription of slavery predates and prepares the material ground for Europe and the Americas in terms of both nation and empire building - and continues to sustain it.
Text by: Kathryn Yusoff. "White Utopia/Black Inferno: Life on a Geologic Spike". e-flux Journal Issue #97. February 2019.
---
When the Haitian Revolution erupted [...], slaveholding regimes around the world grew alarmed. In response to a series of slave rebellions in its own sugar colonies, especially in Jamaica, the British Empire formally abolished slavery in the 1830s. [...] Importing indentured labor from Asia emerged as a potential way to maintain the British Empire’s sugar plantation system. In 1838 John Gladstone, father of future prime minister William E. Gladstone, arranged for the shipment of 396 South Asian workers, bound to five years of indentured labor, to his sugar estates in British Guiana. The experiment [...] inaugurated [...] "a new system of [...] [indentured servitude]," which would endure for nearly a century. [...] Desperate to regain power and authority after the war [and abolition of chattel slavery in the US], Louisiana’s wealthiest planters studied and learned from their Caribbean counterparts. [...] Thousands of Chinese workers landed in Louisiana between 1866 and 1870, recruited from the Caribbean, China and California. [...] When Congress debated excluding the Chinese from the United States in 1882, Rep. Horace F. Page of California argued that the United States could not allow the entry of “millions of cooly slaves and serfs.”
Text by: Moon-Ho Jung. "Making sugar, making 'coolies': Chinese laborers toiled alongside Black workers on 19th-century Louisiana plantations". The Conversation. 13 January 2022.
---
The durability and extensibility of plantations [...] have been tracked most especially in the contemporary United States’ prison archipelago and segregated urban areas [...], [including] “skewed life chances, limited access to health [...], premature death, incarceration [...]”. [...] [In labor arrangements there exists] a moral tie that indefinitely indebts the laborers to their master, [...] the main mechanisms reproducing the plantation system long after the abolition of slavery [...]. [G]enealogies of labor management […] have been traced […] linking different features of plantations to later economic enterprises, such as factories […] or diamond mines […] [,] chartered companies, free ports, dependencies, trusteeships [...].
Text by: Irene Peano, Marta Macedo, and Colette Le Petitcorps. "Introduction: Viewing Plantations at the Intersection of Political Ecologies and Multiple Space-Times". Global Plantations in the Modern World: Sovereignties, Ecologies, Afterlives (edited by Petitcrops, Macedo, and Peano). Published 2023.
---
Louis-Napoleon, still serving in the capacity of president of the [French] republic, threw his weight behind […] the exile of criminals as well as political dissidents. “It seems possible to me,” he declared near the end of 1850, “to render the punishment of hard labor more efficient, more moralizing, less expensive […], by using it to advance French colonization.” [...] Slavery had just been abolished in the French Empire [...]. If slavery were at an end, then the crucial question facing the colony was that of finding an alternative source of labor. During the period of the early penal colony we see this search for new slaves, not only in French Guiana, but also throughout [other European] colonies built on the plantation model.
Text by: Peter Redfield. Space in the Tropics: From Convicts to Rockets in French Guiana. 2000.
---
To control the desperate and the jobless, the authorities passed harsh new laws, a legislative program designed to quell disorder and ensure a pliant workforce for the factories. The Riot Act banned public disorder; the Combination Act made trade unions illegal; the Workhouse Act forced the poor to work; the Vagrancy Act turned joblessness into a crime. Eventually, over 220 offences could attract capital punishment - or, indeed, transportation. […] [C]onvict transportation - a system in which prisoners toiled without pay under military discipline - replicated many of the worst cruelties of slavery. […] Middle-class anti-slavery activists expressed little sympathy for Britain’s ragged and desperate, holding […] [them] responsible for their own misery. The men and women of London’s slums weren’t slaves. They were free individuals - and if they chose criminality, […] they brought their punishment on themselves. That was how Phillip [commander of the British First Fleet settlement in Australia] could decry chattel slavery while simultaneously relying on unfree labour from convicts. The experience of John Moseley, one of the eleven people of colour on the First Fleet, illustrates how, in the Australian settlement, a rhetoric of liberty accompanied a new kind of bondage. [Moseley was Black and had been a slave at a plantation in America before escaping to Britain, where he was charged with a crime and shipped to do convict labor in Australia.] […] The eventual commutation of a capital sentence to transportation meant that armed guards marched a black ex-slave, chained once more by the neck and ankles, to the Scarborough, on which he sailed to New South Wales. […] For John Moseley, the “free land” of New South Wales brought only a replication of that captivity he’d endured in Virginia. His experience was not unique. […] [T]hroughout the settlement, the old strode in, disguised as the new. [...] In the context of that widespread enthusiasm [in Australia] for the [American] South (the welcome extended to the Confederate ship Shenandoah in Melbourne in 1865 led one of its officers to conclude “the heart of colonial Britain was in our cause”), Queenslanders dreamed of building a “second Louisiana”. [...] The men did not merely adopt a lifestyle associated with New World slavery. They also relied on its techniques and its personnel. [...] Hope, for instance, acquired his sugar plants from the old slaver Thomas Scott. He hired supervisors from Jamaica and Barbados, looking for those with experience driving plantation slaves. [...] The Royal Navy’s Commander George Palmer described Lewin’s vessels as “fitted up precisely like an African slaver [...]".
Text by: Jeff Sparrow. “Friday essay: a slave state - how blackbirding in colonial Australia created a legacy of racism.” The Conversation. 4 August 2022.
#abolition#tidalectics#multispecies#ecology#intimacies of four continents#ecologies#confinement mobility borders escape etc#homeless housing precarity etc#plantation afterlives#archipelagic thinking#geographic imaginaries#kathryn yusoff#katherine mckittrick#sylvia wynter#fred moten#achille mbembe#indigenous pedagogies#black methodologies
221 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hi! A lot has already been written about Robespierre's relationship with both Camille and Saint-Just, but I would be really curious to learn more about his relationship with Pétion that you've mentioned!
Specifically if there is any evidence that we know of that indicates any strong feelings or possible romantic involvement. I'd also be interested to know how their relationship transformed over time, since they ultimately ended up on opposing sides?
Thank you in advance citoyen!

Pétion and Robespierre met for the very first time after the convening of the Estates General in May 1789 to which both had been elected members, Pétion in March, Robespierre in April. Using Oeuvres complètes de Maximilien Robespierre, I’ve tracked the first instance of the two getting mentioned together to May 20 1789, when the journal Le Point du Jour describes a debate on the publication of municipal minutes both have taken part in:
In the debates occasioned by this motion, great talents already known, such as those of MM. Target and Mirabeau fulfilled the expectations one had created. Others, like those of MM. Barnave, Chapelier, Pétion de Villeneuve and Robespierre, manifested themselves in a striking manner.
Using the same source, along with Poursuivre la Révolution : Robespierre et ses amis à la Constituante (1994), it can be observed that Pétion and Robespierre from this moment up until the closing of the National Assembly in September 1791 fought side by side in a number of big discussions — the question of war and peace (May 16-22 1790) where both supported the motion that the Assembly alone should hold the right to declare war and king should be deprived of it, the colonies (May 11-15 1791), where both were among the 27 deputies speaking in favor of free men of color, the organisation of the national guard (27-28 april 1791), a body to which they argued both active and passive citizens should belong, the abolition of lettres de cachet (13-16 March 1790) as well as that of the silver mark and land ownership (August 1791), the non-eligibility of National Assembly deputies to the next Legislature (May 16 1791) an idea Robespierre himself had come up with, and the question of the death penalty (May 30 1791), were both were among the rare ones to ask for its complete and total abolition. Pétion and Robespierre are found agreeing on a multitude of smaller topics as well, such as the sanction of the Declaration of the Rights of Man (October 2 1789), the treatment of bishops in office (June 22 1790), the inviolability of deputies (June 25 1790), the massacres of La Glacière (16-18 November 1790), police functions (December 28 and December 30 1790), the power of the colonial committee (January 11 1791) the organisation of the justice system (February 5 1791), the organization of administrative bodies (March 3 1791), an extradition request from the court of Vienna (March 5 1791), appointment of national treasury administrators (March 9 1791), the judgment of disputes in electoral matters (March 13 1791), the right to inheritance (April 1 1791) and the right to petition (May 9 and May 10 1791).
All these shared battles of course led to the two often getting mentioned side by side in the evergrowing press. Over the first two years of the National Assembly’s existence, these mentions mostly just consist of Pétion and Robespierre both getting listed as two of several deputies of the far left, alongside people such as Mirabeau, Barnave, Lameth, Duport, Buzot, and Grégoire. The first instance of someone describing Pétion and Robespierre as a unit while also seperating them from their fellow radical deputies that I’ve found is from December 13 1790, when Desmoulins writes the following in number 55 of his Révolutions de France et de Brabant:
One cannot speak about Robespierre without thinking about Péthion [sic].
This tying together of the two deputies and their cause was in the following months to do nothing but grow among the journalists. Desmoulins himself would go on to declare that ”it is only Péthion and Robespierre that I have constantly praised, because every man of good faith will agree that they have always been irreproachable” (number 69, March 21 1791) and that ”we must always come back […] to the system of Robespierre and Péthion: perish the colonies, rather than the principles!” (number 77, May 16 1791). In number 472 (May 28 1791) of of l’Ami du Peuple, Marat describes the National Assembly as consisting of ”two hundred men too narrow-minded to know what they are, and one or two honest men who have never wanted anything other than the general good. Such are Péthion [sic] and especially Robespierre,” and three days later, in number 475, he reveals that ”If I were tribune of the people […] I would give Péthion [sic] and especially Robespierre a civic crown.” In number 783(October 2 1791) of Le Patriote Français, Brissot called Pétion and Robespierre ”the two Catos of the Constituent” and a few days later Louis Marie Prudhomme expressed himself in similar terms, writing ”Péthion [sic], Robespierre and the small group of their like, did not fail to embarrass their adversaries so powerful in number and means: more than once their presence reminded that of Cato to the licentious spectators of Rome” (Révolutions de Paris, number 117).
The image of the two as inseparable was even stronger in the different Jacobin clubs scattered across the land. On April 17 1791 it was discovered that one of them had placed busts of Pétion and Robespierre next to that of the recently deceased Mirabeau, contrary to the rule that no busts of living people would be displayed in the clubs. On July 13 1791, one M. Sigaud read a letter to the parisian Jacobin club signed by 300 people wanting to ”give thanks to MM. Pétion and Robespierre, for having announced the greatest courage in the defense of the people. They will threaten you with daggers, with death: fear nothing, their daggers will only be able to penetrate you through the rampart of our bodies. Our arms, our hearts, our lives, everything is yours.” Two weeks after that, July 25 1791 Tallien exclaimed to the same club that ”Where Pétion and Robespierre are, are the true friends of the Constitution,” and three months later, October 10 1791, he held a speech where he said that ”the names of Pétion, of Robespierre, and of of those who, like them, have well served their fatherland, must be the rallying sign of all patriots; we always see them on the path of honor, and, by following in their footsteps, we are sure not to go astray.” On April 30 1792, Simond told the jacobins that ”MM Pétion and Robespierre” were the best revolutionaires, ”because there are no individuals who have figured like them in our revolutionary splendors.” In Nouveau Tableau de Paris (1797), Louis Sebastien Mercier remembered how Pétion had been the ”inseparable friend of Robespierre, their principles were then so consistent and their intimacy so marked, that they were called the two fingers of the hand. They continued to be placed under the same accolade until the end of 1792,” while Robespierre’s sister Charlotte wrote in her memoirs (1834) that her brother during the National Assembly ”was closest with Pétion, whose popularity then equaled his. They […] fought for the cause of the people, like two generous imitators who looked to surpass each other in noble sentiments.”
In spite of all this, it’s not until December 1790 I’ve been able to for the first time find Pétion and Robespierre together with a backdrop that’s not political, as they on the 25th and 27th of that month signed the wedding contract and attended the wedding ceremony of Camille and Lucile Desmoulins, Camille reporting to his father that ”I had as witnesses Péthion [sic] and Robespierre, the elite of the National Assembly, Sillery, who wanted to be there, and my two colleagues Brissot de Warwille and Mercier, the elite among the journalists. […] The dinner was at my house, only M. and Mdm Duplessis, their daughter Adèle, the witnesses and the celebrant.” Two months later, March 3 1791, Sillery writes to the same Camille that ”Madame de Sillery is coming to dine at my house with Pétion and Robespierre, I dare to ask your lovable and beautiful wife to do me this honor as well.” Yet another month later, April 3 1791, Robespierre made the motion that the recently deceased Mirabeau be buried in the Panthéon. In his memoirs (written 1793), Brissot claimed that ”Pétion reproached [Robespierre] for it the same day, he reproached him for it in my presence.” According to number 72 of Révolutions de France et de Brabant, Pétion was indeed the only deputy that didn’t attend Mirabeau’s funeral on April 5 1791. Finally, in 1850, Louis Philippe told John Wilson Croker that he at some point during the National Assembly had been at a dinner where the two deputies where — ”Pétion was big and fat, good-humoured and talkative, but heavy withal. He talked on, Robespierre said not a word, and I took little notice of him, he looked like a cat lapping vinegar. Pétion was rallying him on being so taciturn and farouche, and said they must find him a wife to apprivoiser him: upon which Robespierre opened his mouth for the first and last time with a kind of scream, ”I will never marry!” (The Croker Papers: the Correspondence and Diaries of the late right honourable John Wilson Croker… (1885) volume 3, page 209).
On June 10 1791, Robespierre was elected to become the future public prosecutor of the Paris criminal tribunal. Three days later, Pétion was chosen as president of the same body, after the first three elected deputies had all resigned. These new posts are the subject of the very first conserved letter exchanged between the two, dated 15 June 1791. Pétion writes the following to Robespierre using vouvoiement, the form the two are always recorded to have used with one another:
You probably know, my friend, about my appointment. I accept. I don't count having you as a colleague as something small. What scared Duport away is what attracts me. I looked for you in the hall and didn't see you. I wanted to go to your house, but I said to myself: I won't find him, he never dines at home. Buzot is a substitute and accepts. Be well, all yours. This Wednesday evening. Pétion.
There’s also the following letter from Pétion to Robespierre, that it too has to do with the latter’s position as public prosecutor. It is unfortunately undated, but Correspondance inédite de Maximilien et Augustin Robespierre (1910) traces it to June 1791 as well:
My friend, I violate the decrees, I become solicitor. It is true that my offense is not within the competence of the assembly. I ask you in the name of my relative, my friend and my host the right to supply medicine to the poor sick prisoners. I was told that this concession was within your competence. I don’t know anything about it. All yours. This Friday evening.
Just six days after Pétion had penned the first letter down, June 21, Paris woke up to the discovery that the royal family had fled the capital during the night. In number 82 of Révolutions de France et de Brabant, Desmoulins described how he and others the very same day had brought a woman with information to give about the escape to the Jacobin Club, in the hopes that her testimony would get Robespierre to denounce Lafayette and Bailly. At first, Robespierre seems quite willing to go through with this, but when Pétion shows up and shows his disapproval of the idea he is quickly taken aback:
The section immediately named a deputation of 12 members, and we took this woman to the National Assembly. Robespierre and Buzot, whom we consulted, were carried away by the assured countenance of the witness, and by the whole of the testimony; but they were greatly perplexed as to the measures to be taken. All the members of the assembly were against revolutionaries, some without knowing it, but many knowingly, and the others out of fear. We will be, they said, pushed back from the tribune, referred to the research committee, and our accusation will be entered in this mortuary register of denunciations. Péthion [sic] came, and increased the embarrassment, and stopped Robespierre, who, at first, was quite disposed to take away the reputation of Bailly and La Fayette by assault.
In her memoirs, Madame Roland claimed to the very same day have seen Brissot and Robespierre at Pétion’s house (on rue du Faubourg-Saint-Honoré n. 6, today roughly a one hour walk from Robespierre’s apartment on rue de Saintonge 30) discussing the flight:
I was struck by the terror with which [Robespierre] seemed to be overcome on the day of the king's flight to Varennes; I found him in the afternoon at Pétion’s; where he said with concern that the royal family would not have taken this course without having a coalition in Paris which would order the Saint-Barthélemy of the patriots, and that he expected to be dead within twenty-four hours. Pétion and Brissot said, on the contrary, that the flight of the king was his loss, and that it was necessary to take advantage of it; that the dispositions of the people were excellent; that it would be better enlightened on the perfidy of the court by this approach than it would have been by the wisest of writings; that it was obvious to everyone, by this fact alone, that the king did not want the constitution he had sworn to; that it was time to ensure a more homogeneous one, and that it was necessary to prepare minds for the Republic. Robespierre, sneering as usual and biting his nails, asked what a Republic was!
In the night between June 21 and 22 the royal family was stopped in Varennes, and the next day Pétion, alongside Barnave and Maubourg, left the capital to escort them back. They reached Paris again on June 25. The escape attempt resulted in massive discontentment and demands that the king abdicate. On July 15, a petition written by a certain Massoulard, asking the assembly to suspend “all determination on the fate of Louis XVI until the well-pronounced wish of the entire Empire has been expressed” was brought to the National Assembly. In Lettre de J. Pétion à ses Commettans sur les Circonstances Actuelles, released later the same month, Pétion described how he and Robespierre had held these petitioners off, saying that since the Assembly had voted to keep the king on the throne the very same day, a petition was out of order:
I will say, since the occasion presents itself, that only once in this affair was a relationship established between the citizens gathered on the 15th of this month at the Champ-de-Mars and myself. These citizens had drawn up a petition for the National Assembly; commissioners carried them; they were charged with speaking to those who had risen against the project of the committees, to Grégoire, Robespierre, Prieur and myself, to be their organs with the assembly, and to negotiate their entry to the bar. M. Robespierre and I left the room to listen to these commissioners; and we told them that this petition was useless, that the decree [to keep the king on the throne] had just been passed. They asked us for a word to see that they had fulfilled their mission; we wrote a letter which breathes the love of order, of peace, and which, I believe, has been able to prevent misfortunes.
When Pétion, Robespierre and Rœderer entered the Jacobin club’s evening session the very same day they got covered in applause. Both were there again on both July 16, putting their signatures on a letter to the sister societies in the provinces about liberty of the press and the elections for the upcoming Legislative Assembly, as well as on July 17 and 18, this time dealing with the mass walkout (that left the two and a handful more as the only National Assembly deputies still members of the Jacobins) following the founding of the Feuillants club the previous day. Desmoulins, who was also present at the session on the 17th, stated that he didn’t want any writing to say the Jacobins were splitting from the National Assembly since, ”certainly, where MM. Robespierre and Pétion are, there is no split with the National Assembly.”
Pétion would later recall how afraid Robespierre had been during these days. In J. P. Brissot, député à la Convention nationale, à tous les républicains de France; sur la société des Jacobins de Paris (1792) Brissot even accused Robespierre of having ”secretly proposed fleeing to Marseille to Pétion.” If that is a charge that should be taken with a grain of salt, it was nevertheless during these same days Robespierre changed address and took cover with the Duplay family on Rue Saint-Honoré 366. In her old days, the family’s youngest daughter Élisabeth claimed Pétion would frequent the house ”in the early days.” The year after the move Robespierre himself would nevertheless write that it wasn’t until August 7 1792 Pétion for the first time set his foot in the house (see below).
On September 30 1791, the National Assembly was finally closed to be replaced by the Legislative Assembly. Several journals described the triumphant exit Pétion and Robespierre made from there the very same day, getting met by cheers, applauds and cries of joy from a huge crowd who offered them so called ”civic crowns,” before the two climbed into a carriage (a ”humble” one according to Révolutions de France et de Brabant) and rode off together to the sound of fanfares. Here is the description given by Le Thermomètre du Jour:
Pétion and Robespierre came out last, arm in arm. Citizens with oak crowns tied with tricolor ribbons in their hands embraced them and said to them: ”Receive the price of your good citizenship and your incorruptibility; we give, by crowning you, the signal to posterity”; and the applause, the bravos, the shouts of ”long live Pétion and Robespierre! Long live the spotless deputies!” mingled with the chords of military music placed on the terrace of the foliage, filled all hearts with the sweetest intoxication. In vain, the two legislators wanted to hide from these testimonies of public recognition: as they fled, a young lady whom they met on the stairs which lead to the storage room said to them: ”allow at least that my child embraces you”; and this they could not resist. To escape the chorus of applause who were pursuing them, the two deputies, who had taken refuge in a house in the rue Saint-Honoré, got into a carriage. Immediately, in the delirium of enthusiasm, the horses were unhitched, and a thousand biases hastened to drag the carriage; degrading idolatry, of which those who were the object of it were afflicted and indignant. At this moment the honorable Robespierre, seized with holy indignation, hastily alighted from the carriage.��“Citizens, he said, what are you doing? What humiliating posture will you take? Is this the price of my work for you for two years? Don't you already remember that you are a free people?” And he quickly got back into the carriage where his worthy colleague was. The attitude and admiration of the citizens at this moment cannot be described: sublime spectacle! You make delicious tears flow. One let the carriage roll off to the sound of fanfares, applause, cries and the most energetic blessings. May those who could have deserved such a triumph dry up in spite, comparing this excess of gratitude to the silence of contempt, or to the curses of hatred who accompanied them. Above all, may this touching example produce Pétions and Robespierres in the new legislation.
This celebration might very well have been the follow-up of an intervention made at the Jacobin club on September 25 by one Varnet, who asked for ”a civic feast rewarded by the grateful parties to MM. Robespierre, Péthion [sic], etc, much more fraternal than all these royal celebrations which recall the ancient idolatry of the Badauds.” These would not be the homages paid to the two in the wake of the closing of the National Assembly. On October 9, the Jacobin club of Strasbourg decided to send each of the two a civic crown, as revealed in a letter with 400 signatures published in number 231 of Mercure Universel (October 17 1791). On November 6 1791, Annales patriotiques et littéraires could reveal that the club of Saint-Laron ”has informed that of Paris of the tribute of homage which it has paid to Pétion to Robespierre, and of the annual festival which it established in their honor, to teach, it said, to children that a glance from the people is better than the caresses of kings,” on October 27 the club in l’Orient reported (in a letter published in number 123 of Révolutions de Paris) that ”the names of Robespierre and Péthion [sic] are in veneration among [its members],” and on October 18 the club of Lyon sent Pétion and Robespierre an open letter thanking the two for all their services.
Shortly after the closing of the National Assembly Pétion left for London, but not before he was able to hand a report written by him on patriotic societies to Robespierre, which the latter then read to the jacobins on October 5. When Robespierre too left the capital for Arras a few days later, Pétion’s shadow clearly accompanied him. In a letter to Maurice Duplay dated October 16 he could joyfully report the following:
At Arras itself, the people received me with demonstrations of affection which I cannot describe, and the thought of which still warms my heart. Every possible means was used to express it. A crowd of citizens had come out of town to meet me. They offered a civic crown, not only to me, but to Pétion as well, and in their cheers the name of my friend and companion in arms was often mingled with my own.
A month later, November 17, Robespierre writes to Maurice again:
…I think with sweet satisfaction about the fact that my dear Pétion may have been appointed mayor of Paris as I write. I will feel more keenly than anyone the joy that every citizen should be given by this triumph of patriotism and frank honesty over intrigue and tyranny.
Robespierre came back to Paris on November 28. One of the first things he did was go and dine at the house of Pétion (who he here goes so far as to call his family), as revealed by a letter to Antoine Buissart he wrote two days later:
With what joy we met again! With what delight we embraced! Pétion occupies the superb house inhabited by the Crosnes, the Lenoirs: but his soul is always simple and pure: the choice of him [as mayor] alone would suffice to prove the revolution. The burden with which he is charged is immense; but I have no doubt that the love of the people and its versus gives him the necessary means to carry it. I'm having dinner at his house tonight. These are the only times when we can see each other as a family, and talk freely.
Following Pétion’s election to mayor, his apperances in public become much fewer compared to his time as deputy of the National Assembly. Robespierre on the other hand could not get enough of praising his friend at the Jacobin club. On February 10 1792, he held a speech in which he cried out the following, apropos of suggesting holding a ceremony at the Champ-de-Mars and making a sacrifice on the altar of liberty:
O Pétion! You are worthy of this honor, worthy of deploying as much energy as wisdom in the dangers that menace the fatherland that we have defended together. Come, let us mingle our tears and weapons on the tombs of our brothers, remind ourselves of the pleasures of celestial virtue, and die tomorrow, if need be, from the blows of our common enemies.
Five days later, in his inaugural address as public prosecutor, Robespierre called Pétion ”the one of all my colleagues to whom I was most closely bound, by works, by principles, by common perils, as much as by the ties of the most tender of friendships,” and says it was due to Pétion’s advice that he was taken aback from proposing that National Assembly deputies not only be barred from serving on the Legislative Assembly, but also be excluded from any public offices at all following the start of said assembly. He then eulogized his friend once again: ”I swear that it is he who, up until this moment, has saved the capital and prevented the horrible plans of the enemies of our liberty; I swear that the courage and virtues of Pétion were necessary for the salvation of France.” A month after that, March 19, Pétion sent the Jacobins a letter disapproving of the recent usage of the so called ”bonnet rouge” among the club’s members. After the letter had been read out, Robespierre stood up and supported his motion, and together, the two succeded in getting the bonnet rouge depositioned from the Jacobin Club:
I respect, like the mayor of Paris, all that is the image of liberty, I will even add that I saw with a great pleasure this omen of the rebirth of liberty; however; enlightened by the reflections and by the same observations made by M. Pétion, I felt urged to present to society the reasons which have just been offered to you, but as I have only patriotism to fight with, I am charmed to be guided by M. Pétion, by a citizen whose civility and love for liberty is foolproof, by a citizen whose heart is ardent and whose head is cold and thoughtful, and who brings together all the advantages, talents and virtues necessary to serve the country, at a time when the most skillful and astute enemies can deal it disastrous blows.
And yet another month later, April 13 1792, Robespierre defended Pétion against attacks of unnamed enemies:
The mayor of Paris, they say, is ambitious; we are arsonists who slander the constituted authorities to elevate our ambition at the expense of others; well, prove it. Our goal has been to fight in the constituent assembly all the parties of tyranny, Pétion and I have done it, were it even the means Pétion would guarantee, far from foreseeing then that our principles would triumph over a cabal if strong, we believe that after the constituent assembly we would be immolated and that the principles of our ancestors would be adopted: I saw Pétion, at the time when he was brought to the position of Mayor of Paris, two months before his appointment, at a time when we can remember that the votes of the good citizens floated between him and me, I saw the mayor of Paris determined not to accept this place; he read the same feelings in my heart, and when he accepted it, I guarantee to the whole nation that he only did it because he had only considered it as a terrible pitfall for the citizen who would occupy it in such a stormy circumstance for the public good.
Despite Pétion’s massive new workload, he and Robespierre still found the time to see each other, albeit with work still being the main topic of discussion. In Réponse de Maximilien Robespierre à Jêrome Pétion (November 1792), Robespierre recalled that ”Last January to June, when the ministers were renewed, I saw you (Pétion) in the firm belief that it was you who had chosen them. As I asked you if this action of the court was not suspicious to you, you replied, with a very remarkable air of consent: “Oh! if only you knew what I know! If only you knew who nominated them!” I guessed you, and I said to you, laughing at your good faith: “it’s you, perhaps.” And then, rubbing your hands, you responded: “Hem, hem,” No matter how much you persisted in confirming this fact to me, I didn't want to believe it. I esteemed you too much to suppose that you would have the necessary credit with Louis XVI and his courtiers to give him ministers.” Somewhere after Robespierre was sworn in as public prosecutor, the two also co-authored the pamphlet Observations sur la nécessité de la reunion des hommes de bon foi contre les intrigues par Jérome Pétion, Maire de Paris; et Maximilien Robespierre, Accusateur Public du département de Paris.
But all while this ”bromance” was playing out, so too was the debate on whether or not France ought to go to war. It’s most influential voices were Robespierre on the anti-war side, and Pétion’s childhood friend and freshly baked member of the Legislative Assembly Brissot on the pro-war side. Pétion himself would appear to have stayed neutral in the conflict, I have at least not been able to find any instance of him speaking his mind on the topic. But on April 25 1792, five days after France had declared war on Austria, he adressed the following letter to Robespierre, regretting the session at the Jacobins held the same day, during which Brissot’s ally Guadet had loudly denounced Robespierre, calling him an ”imperial speaker […] who constantly puts his pride before public affairs, the position to which he was called”, after which Robespierre had requested time to properly respond, something which he was granted. Pétion does however not attack Guadet for saying what he had said about Robespierre, instead confining himself to lamenting division in general in a time when external war has just been declared:
The session which took place yesterday [sic] at the Jacobins saddened me. Is it possible that we’re tearing ourselves apart like this with our own hands? I don't know what demon thus blows the fire of discord. What! It is when we are at war with the enemies without that we will stir up trouble within. The Society most useful to the progress of the public spirit and of liberty is on the point of being torn apart. We suspect each other, we insult each other, we slander each other, we accuse each other respectively of being traitors and corrupt. Perhaps if the men who present themselves thus were to see themselves in the open they would esteem each other. How hideous human passions are. What, we can't have the calm and energy of free men? We cannot judge objects in cold blood, we scream like children and are furious. I truly tremble when I consider who we are and always wonder if we will retain our freedom. I haven't rested all night, and have only dreamed of misfortunes. A grace, my friend, be aware of the split that is preparing itself. Caution and firmness. I see there men who seem to have the most fervent patriotism and whom I believe to be the most perverse and corrupt men. I see others who are only stunned and inconsequential but who do as much harm by levity as others by combination. Irritated self-esteem, deceived ambitions play the biggest game. When we reach port, must storms arise and the ship run the risk of crashing against the rock? Think about it seriously. Redouble your efforts to get us out of this mess. Be well. Your friend. Pétion.
On April 27 1792, Robespierre could deliver a speech by the name of Réponse de M. Robespierre, aux discours de MM. Brissot & Guadet du 25 avril 1792 in response to what Guadet had said about him two days earlier. In it, he stated among other things that the things the two reproached him for ”are precisely the same charges brought against me and against Péthion [sic] last July by Dandré, Barnave, Duport, La Fayette!” Something which the authors of the journal Chronique de Paris picked up on when recounting the speech:
…Before finishing, [Robespierre] had taken care to name M. Pétion, and to establish between them a community of ideas, a relation of feelings on the objects which divide the society. He knows very well that M. Pétion is far from approving his follies, or rather his fury, but he also knows that he could not disarm him without losing a large part of his popularity, so the goal was not missed, and Robespierre's party was swelled with all the worthy friends of the worthy Pétion.
Two days after that, April 29 1792, Pétion writes yet another letter to Robespierre:
My friend, I will go to the Jacobins tonight and ask to speak. I will not speak of people, but of things. I will set forth principles and I will come to conclusions suitable for restoring peace. The situation of this society is getting worse day by day. After having rendered such important services, when it can render still more important ones, it would be terrible if it gave the scandalous example of a split. The spirits are very irritated. One becomes the fable of all malicious people, the newspapers are tearing this Society apart, tearing its members apart, we must put an end to all writings. Your friend, Pétion.
Pétion did indeed show up to the Jacobins the very same day, where he, according to the minutes, ”made a long motion of order tending to maintain the union in the Society, and asked that all these quarrels be moved on from.” Right after the club had ordered the speech printed, Robespierre tried to take the floor but was refused by ”girondin” president Lasource. The next day, he once again attempted to speak against Brissot and Guadet, underlining that ”I want to keep to the limits fixed by M. Pétion,” but that his approach had been turned against them by ”libelists, directed against him, against me, against this society and against the people itself.” Robespierre again insists on a closeness between him and Pétion:
I know he is horrified of plots hatched against me: his heart has spilled over into mine; he cannot see without shuddering these horrible calumnies which assail me from all sides.
But his thoughts did not gain any approval from the jacobins this day either, and Robespierre instead opted to found a journal — Le Defenseur de la Constution — to attack his enemies from instead. When mayor Pétion and Procureur de la Commune Manuel got temporarily suspended from their duties on July 6 and arrested on July 7, for complicity in the demonstration of June 20, Robespierre used number 9 (July 14 1792) of said journal to defend them (in Réponse de Maximilien Robespierre à Jérôme Pétionhe confidently reminded him that ”no one more than me defended you in a more public and more loyal manner, against all the harassment [the court] brought upon you.”) On July 13, when the suspension of Pétion was lifted, ”M. Robespierre, while applauding [the decree], points out, however, that this should be less a cause for rejoicing as there are reasons for the true friends of liberty to grieve the fact that this decree was postponed for a fortnight.”
In Réponse de Maximilien Robespierre à Jérôme Pétion (November 30 1792), Robespierre reported about the following meeting (that Pétion also confirmed when later responding to him) the two had had, roughly a month after Pétion had been returned to duty, on the topic of popular insurrection:
On August 7, I saw the mayor of Paris enter my house; it was the first time that I received this honor, although I had been closely connected with you. I conclude that a great motive brings you; you talk to me for a whole hour about the dangers of insurrection. I had no particular influence on the events; but as I quite often frequented the Society of the Friends of the Constitution, where the members of the directory of the federates habitually went, you urged me earnestly to preach your doctrine in that society. You told me that it was necessary to defer resistance to oppression until the National Assembly had pronounced the deposition of the King; but that it was necessary at the same time to leave him the leisure to discuss this great question with all possible slowness. You could not, however, be sure that the court would adjourn the project of slitting our throats for as long as it pleased the National Assembly to adjourn the forfeiture; and everyone knew that the royalist party was then dominant in the Legislative Assembly; and your Brissot and his friends had delivered long speeches on this question, the sole object of which was to prove that it was necessary to retreat from it, and ceaselessly to postpone the decision. You even know what public disfavor their equivocal conduct had incurred; they saw in it only the project of frightening the court by the fear of an insurrection, in order to force it to take back ministers of their choice. I could have made these comparisons myself; but such was still my confidence in you, and, if it must be said, the feelings of friendship which your unexpected step aroused in my heart, that I believed you up to a certain point; but the people and the federals did not.
Two days later, the insurrection of August 10 took place. Pétion’s behavior during this night would become a big subject of quarrel between him and Robespierre in the months to come. Two days after the insurrection, August 12, Robespierre begun to serve at the so-called Insurrectional Commune. The power struggle between this body and the Legislative Assembly would it too serve as cause for conflict between the two. Already on Robespierre’s second day at the commune, August 13, Pétion and Manuel came there, having just escorted the royal family to their new prison in the Temple. Giving an account over this mission, the two stated that the place ”did not seem suitably arranged,” and that the king should be kept somewhere else instead. Later during the session, Robespierre claims (I can’t find this recorded in the session’s actual minutes) that Pétion presented a report from the Legislative Assembly to within 24 hours dissolve the commune and replace it by the old municipality, a proposal which got rejected. He would later reproach Pétion for both of these things.
According to J.M Thompson’s Robespierre (1935), on August 17 Robespierre was commissioned by the commune to interview Pétion to get him to co-operate (I can’t find this in the commune’s minutes either). The interview did however not go that well, resulting in the following letter from Pétion to Robespierre, written on August 20:
You know, my friend, what my feelings are for you, you know that I am not your rival, you know that I have always given you proofs of devotion and friendship. It would be useless to try to divide us, you would have to stop loving liberty in order for me to stop loving you. I have always found more fault with you to your face than behind your back. When I think you too ready to take offence, or when I believe, rightly or wrongly, that you are mistaken about a line of action, I tell you so. You also reproach me for being too trustful. You may be right; but you must not assume too readily that many of my acquaintances are your enemies. People can disagree on a number of unessential points without becoming enemies; and your heart is said to be in the right place. Besides, it is childish to take offence over the things people say against one. Imagine, my friend, the number of people who utter all lands of libels against the mayor of Paris! Imagine how many of them I know to have spread damaging reports about me! Yet it doesn’t worry me, I can assure you. If I am not totally indifferent to what others think about me, at least I value my own opinion more highly. No… you and I are never likely to take opposite sides: we shall always hold the same political faith. I need not assure you that it is impossible for me to join in any movement against you: my tastes, my character and my principles all forbid it. I don’t believe that you covet my position any more than I covet that of the king. But if, when my term of office comes to an end, the people were to offer you the mayoralty, I suppose that you would accept it; whereas in all good conscience I could never accept the crown. Look after yourself, let us march forward, we are in a situation threatening enough to force us to think only of the public good.
As can be seen, Pétion was still trying to salvage the relationship that had begun to deteriorate already in the spring, an effort that Robespierre seemed to share. If we’re to believe Buzot’s memoirs, written in 1793, Robespierre had suggested making ”a solemn declaration on the events which preceded the revolution of the 10th of August” to Pétion, who in his turn ”was willing to lend himself to it, for he had a kind of inexcusable weakness for Robespierre.” But when Robespierre came forward with the finished declaration that, according to Buzot, contained ”a lot of baseness and sweet talk [sic] for Louis XVI,”Pétion did however refuse to sign it, and Robespierre was forced to rework it. In an address from the representatives of the Paris commune to their fellow citizens dated September 1, Robespierre and his colleages also underlined that ”the principal artifice which our enemies employed to destroy us, was to oppose to the assembly of the representatives of the commune the names of Manuel and Pétion, and to claim that our existence is an attack against the authority in which these two magistrates were clothed.” But the relationship was well under way to break down, and the first days of September 1792 would be filled with conflicts between the two, in relation to the so called ”September massacres.” This time it would instead be Pétion who got appalled over Robespierre’s conduct.
Again on September 1, one day before the massacres, Robespierre held a speech to the same Paris Commune opposing the idea of opening the city’s barriers, that, in Pétion’s own words, ”saddened my soul.” […] [Robespierre] gave himself up to extremely animated declamations, to the lapses of a gloomy imagination; he perceived precipices under his feet, liberticidal plots; he pointed out pretended conspirators; he addressed himself to the people, excited the spirits, and occasioned, among those who heard him, the liveliest fermentation. I replied to this speech, to restore calm, to dissipate these black illusions, and to bring the discussion back to the only point which should occupy the assembly.”In Histoire générale et impartiale des erreurs, des fautes et des crimes commis pendant la Révolution française (1797), Louis Marie Prudhomme writes that, two days later, September 3 1792, Théophile Mandar went over to Danton’s place, where he saw ”all ministers, with the exception of Roland, Lacroix, president [of the Assembly], Pétion, mayor of Paris, Robespierre, Camille-Desmoulins, Fabre d’Églantine, Manuel and several members of the so-called Commune of August 10. The presidents and commanders from each of the 48 sections had come as well.” Half past seven in the evening everyone sat down in Danton’s salon to discuss the means to save Paris. Two hours later, Mandar, Pétion and Robespierre all retired to a different room, where Mandar laid out the idea of setting up a temporary dictatorship to stop the prison massacres for the two. Robespierre did however not respond positively, instead crying out: ”Be aware! Brissot would become dictator!” ”O Robespierre,” Mandar said to him, ”it is not the dictatorship that you fear, it is not the homeland that you love: it is Brissot that you hate.” ”I hate dictatorship and I hate Brissot!” Pétion meanwhile didn’t say a word.
The day after that, September 4, Pétion and Robespierre found themselves discussing Brissot (who Robespierre on September 2 had denounced as an accomplice of Brunswick at the Paris commune, leading to his house getting searched on the 3rd) once more, this time at the Hôtel de Ville, as revealed through the following part from Pétion’s Discours de Jérôme Pétion sur l’accusation intentée contre Maximilien Robespierre (November 5 1792):
The surveillance Committee launched an arrest warrant against Minister Roland; it was the 4th (September), and the massacres were still going on. Danton was informed of it, he came to the town hall, he was with Robespierre. […] I had an explanation with Robespierre, it was very lively. I still made him face the reproaches that friendship tempered in his absence, I told him: ”Robespierre, you are doing a lot of harm; your denunciations, your alarms, your hatreds, your suspicions, they agitate the people; explain yourself; do you have any facts? do you have proof? I fight with you; I only love the truth; I only want liberty.” ”You allow yourself to be surrounded,” [he replied], ”you allow yourself to be warned. You are disposed against me, you see my enemies every day; you see Brissot and his party.” ”You are mistaken, Robespierre; no one is more on guard than I against prejudices, and judges with more coolness, men and things. You’re right, I see Brissot, however rarely, but you don’t know him, and I know him since his childhood. I have seen him in those moments when the whole soul shows itself; where one abandons oneself without reservation to friendship, to trust: I know his disinterestedness; I know these principles, I assure you that they are pure; those who make him a party leader do not have the slightest idea of his character; he has lights and knowledge; but he has neither the reserve, nor the dissimulation, nor these catchy forms, nor this spirit of consistency which constitutes a party leader, and what will surprise you is that, far from leading others, he is very easy to abuse.” Robespierre insisted, but confined himself to generalities. ”Allow us to explain ourselves, I told him, tell me frankly what’s on your mind, what it is you know.” ”Well!” he replied, ”I believe that Brissot is with Brunswick.” ”What mistake is yours!” I exclaimed. ”It is truly madness; this is how your imagination leads you astray: wouldn't Brunswick be the first to cut his head off? Brissot is not mad enough to doubt it: which of us can seriously capitulate! which of us does not risk his life! Let us banish unjust mistrust.” Danton became entangled in the colloquy, saying that this was not the time for arguments; that it was necessary to have all these explanations after the expulsion of the enemies; that this decisive object alone should occupy all good citizens.
In her memoirs (1834), Charlotte Robespierre talks of yet another meeting between her brother and Pétion regarding the massacres, but in her version it is instead the former who accuses the latter of doing a lot of harm. Some historians have suggested this meeting is the same Pétion is describing above, though if that’s the case I wonder why he doesn’t mention Charlotte anywhere in his account (as well as why Robespierre would even bring his sister with him when going to discuss political matters in a city where a massacre is currently taking place…):
A few days after the events of 2 and 3 September, Pétion came to see my brother. Maximilien had disapproved of the prison massacres, and would have wanted each prisoner to be sent before judges elected by the people. Pétion and Robespierre conversed on these latest events. I was present at their interview, and I heard my brother reproach Pétion for not having interposed his authority to stop the deplorable excesses of the 2nd and 3rd. Pétion seemed piqued by this reproach, and replied dryly enough: All I can tell you is that no human power could have stopped them. He rose some moments later, left, and did not return. Any kind of relations ceased, from this day, between him and my brother. They did not see each other again until the Convention, where Pétion sat with the Girondins and my brother with the Mountain.
In the 1960 article Charlotte Robespierre et ”ses mémoires,” Gabriel Pioro and Pierre Labracherie wanted to dismiss Charlotte’s story, finding it unlikely for her to have been in Paris by early September 1792, almost a whole month before her younger brother was elected to the National Convention and the two went to the capital for that reason. Though I suppose it’s not impossible for Charlotte to have gone to visit Maximilien beforehand, or that she’s simply very generous with what she describes as ”a few days.”
If Charlotte’s friend Armand Joseph Guffroy, who him to moved from Arras to Paris after getting elected to the National Convention, is to be believed, her claim that Pétion and Robespierre stopped seeing each other following the events of September gets muddied as well. In his Les secrets de Joseph Lebon et de ses complices… (1795) Guffroy writes: ”At Pétion’s house, the only time Robespierre took me there; I saw the latter eating a pot of fine jams, which were very expensive at the time.”
Regardless of any jam dinners, it’s clear the relationship was breaking down for real. On October 29 1792, Jean-Baptiste Louvet read his Accusation contre Maximilien Robespierre to the Convention, accusing him of turning himself into ”the idol of the people,” slandering ”the best patriots,” instigating the September massacres and tyrannizing the parisian electoral assembly, all with the goal of setting himself up as a dictator. A week later, November 7, Chabot told the jacobins that Pétion’s wife Suzanne had ”applauded everything Louvet said against Robespierre.”
Both Robespierre and Pétion picked up their pens to write a response speech to Louvet. Robespierre pronounced his to the Convention on November 5, which then passed onto the order of the day, preventing Pétion from holding his. The very same day, Collot d’Herbois exclaimed to the jacobins: ”I agree with Manuel on the comparison that he made in saying that Pétion and Robespierre were the twins of liberty; he meant that they were stars like Castor and Pollux; that they would appear in turn, but I ask that Robespierre be the summer star, and Pétion the winter star.” Pétion did however still wish to get his speech out, so shortly thereafter he published Discours de Jérôme Pétion, sur l’accusation intentée contre Maximilien Robespierre as a pamphlet instead. This is what would truly mark the beginning of the end for the relationship.
Pétion begins by writing that “I had promised myself to keep the most absolute silence on the events that have happened since August 10,” but that, after having heard so many things said about him and being asked for his opinion on the matters so many times, “I will say frankly what I know about some men, what I think about things.” After explaining to which groups he thinks the insurrection of August 10 was due and to which ones it wasn’t, and deploring of the September massacres, saying that ”I cannot bring myself to confuse glory with infamy, and to defile August 10 with the excesses of September 2” (thereby seperating himself from Robespierre, who his response to Louvet instead argued that the massacres had been the inevitable sequel to the insurrection, and that to condemn one would therefore be to condemn the other), Pétion turns to Robespierre. Having regretted the speech held by him on September 1, through which he, if unintentionally, ”led the commune into inconsiderate moves, into extreme parties,” and reported about their interview on September 4, Pétion brings up Louvet’s accusation that his friend had been aiming at dictatorship. Just like with Brissot, Pétion dismisses these accusations, but this through pointing out the flaws in the designated one’s personality:
Robespierre's character explains what he did: Robespierre is extremely touchy and defiant; everywhere he sees conspiracies, betrayals, precipices. His bilious temperament, his atrabilious imagination present all objects to him in dark colours; imperious in his opinion, listening only to himself, not supporting contrariety, never forgiving those who have hurt his self-esteem, and never recognizing his faults; denouncing lightly, and being irritated by the slightest suspicion; always believing that someone is occupying himself with him in order to persecute him; boasting of his services and speaking of himself with little reserve; not knowing the proprieties, and thereby harming the causes he defends; desiring above all the favors of the people, paying court to them unceasingly, and ringing out their applause with affectation; it is this, it is above all this last weakness, which, piercing through the acts of his public life, has been able to make people believe that Robespierre breathed high destinies, and that he wished to usurp the dictatorial power. As for me, I cannot persuade myself that this chimera seriously occupied his thoughts, that it was the object of his desires, and the goal of his anticipation.
At the very end of the pamphlet, Pétion publishes an open letter to the jacobins, a place where he, ”since some time have been attacked more or less openly.” Pétion reminds the society of the great services he has rendered it and even that he had saved it during the big Feuillant split one year earlier. He also recalled that Robespierre, unlike him, had been very afraid following this split — ”I saw Robespierre trembling, Robespierre wanting to flee, Robespierre not daring to go up to the assembly… ask him if I trembled. I saved Robespierre himself from persecution, by attaching myself to his fate, when everyone despised him.”
Robespierre answered Pétion in Réponse de Maximilien Robespierre à Jérome Pétion, a text that made up all of number 7 of his Lettres de Maximilien Robespierre à ses commettans (November 30 1792). Robespierre started by regretting having to write what he did in the first place:
What is, my dear Pétion, the instability of human affairs, since you, once my brother in arms and at the same time the most peaceful of all men, suddenly declare yourself the most ardent of my accusers? Don't think that I want to occupy myself here either with you or with me. We are both two atoms lost in the immensity of the moral and political world. It is not your accusations that I want to answer; I am accused of having already shown too much condescension in this way; it is up to your current political doctrine. It would already be a little late, perhaps, to refute your speech: but there is always time to defend truth and principles. Our quarrels are of a day: the principles are of all times. It is only on this condition, my dear Pétion, that I can consent to pick up the gauntlet you threw at me. You will even recognize, in my way of fighting, either the friendship, or the old weakness that I showed for you. If, in this completely philanthropic kind of fencing, you were exposed to some slight injury, it only affects your self-esteem; and you reassured me in advance on that point, by protesting yourself that it was null. Moreover, the right of censorship is reciprocal; it is the safeguard of freedom; and you love principles so much that you will find more pleasure, I am sure, in being the object of them yourself, than you felt in exercising them against me.
Robespierre then goes on to accuse Pétion of in his pamphlet not having treated the Insurrection of August 10th with the respect it deserves, depriving the people and sections of Paris — ”the destroyers of tyranny” — who carried it out of the merit of their service, and to even have done everything in his power to stop the insurrection by continuously telling the sections to remain calm. Then he hadn’t showed up to the Paris Commune until three days after the siege of of the Tuileries, and then to report that the assembly wanted to close the commune and call the old municipality back (”You constantly sighed for the return of your semi-aristocratic municipality. […] The spirit that animated the defenders of liberty frightened you!”) and to ”prove that it was not necessary to lock Louis XVI in the Temple, and that if he did not stay in a magnificent hotel the whole of France would rise up against the commune.”Pétion had even on his own initiative gone to the king two weeks before the insurrection — ”no one knows if it was to convert him or to justify yourself.” Robespierre asks why Pétion seemingly shows more indulgence for the court than for the people behind the insurrection, noting that ”I always believed I saw in you less condescension for the warmth of patriotism than for the excesses of the aristocracy.”
Besides this main charge, Robespierre also reproaches Pétion of not having done enough to stop the demonstration of June 20, which, unlike the insurrection, was driven by ”the intriguers who surrounded you [who] wanted […] to regain possession of the ministry,” of being jealous of him for getting elected first deputy of Paris, which he claims is what caused him to stand for election in Eure-et-Loir instead (”you were unable to hide your sorrow at the very moment; and rather than suffer the affront of priority given to another citizen, you preferred to be chosen third in Chartres, than second in Paris”), making a big deal of having reached the conclusions presented in the pamphlet by shutting himself alone (”Is an author obliged to prove that he himself went into secrecy to compose his works? And aren’t such singular oratorical precautions suspect?”) and interpretating La Fayette favorably even after the massacre on Champ-de-Mars, having guaranteed Robespierre ”a hundred times” of his innocence since he was at the head of the armies. Robespierre claims that it was this friendly attitude that caused Pétion to be elected to escort the king back from Varennes. He fights back against Pétion’s description of his personality — ”I am as easygoing, as good-natured in private life, as you find me touchy in public affairs; although you have long experienced it, and my friendship for you has long survived the processes which most offended my principles” — giving an equally unflattering one in return: ”I guarantee that, far from being sullen, defiant, melancholic, you are the man whose blood circulates most gently, whose heart is least agitated by the spectacle of human perfidies, whose philosophy most patiently supports the misery of others.” He also takes offence over Pétion’s claim that he was afraid during the splitting of the jacobin club and that Pétion saved him from persecution. Robespierre claims that he was persecuted no more than Pétion during this period, and besides, ”why are you more attached to me than to the homeland, or at least to your own honor? And how did you imagine that you were for me a more powerful protector than the public interest, and the sanctity of the cause that I defended?”
Robespierre does however seek to exempt Pétion somewhat. He concludes his pamphlet and recent conduct is the result of him having let praise go to his head as mayor (forgetting that the true heros of history were martyrs) due to being misled by intriguers (the girondins). On August 11 or 12, Guadet and Brissot would even have come over to his place, the latter openly reprimanding him for ”the ease with which you had complied with the popular wish,” accusing him of cowardice and summoning him to stop ”the chariot of the revolution.” This, according to Robespierre, is what caused Pétion to show up to the commune the following day to announce the assembly’s plan to dismantle it and bring the old municipality back.
Pétion wrote back in Observations de Jérôme Pétion sur la lettre de Maximilien Robespierre, released somewhere in December 1792, the majority of which was spent debunking all of Robespierre’s reproaches. No, he did everything he could to stop the demonstration of June 20, and ”I defy anyone to say I brought it about or rejoiced over it.” No, he has only ever spoken about the Insurrection of August 10 ”with admiration and enthusiam,” he will however never conflate it with ”the horrible day of September 2.” No, he did not try to stop the insurrection, he only put an end to a badly organized movement on July 26 that wouldn’t have led to any good, and during the night when it happened he only wrote a circular to the sections (he was kept from going out), recommending them to maintain order and tranquility in general, a circular which the sections appreciated. No, he has indeed rendered justice to the people of Paris for their role in the insurrection, he even wrote outright: it is due to the people. No, he has given the sections the credit they deserve as well, he just said the insurrection would have taken place even without the support from the commissioners sent by some of them. The sections have in fact showered him with proofs of their confidence, and he has kept up a ”fraternal correspondence” with them. No, he didn’t appear at the commune until three days after ”the day of the Tuileries,” he was there already the day after it, speaking of their victory, and when he came there on the thirteenth it was not to put forward a report dismantling the commune. No, it is a lie that Guadet and Brissot came over on August 11 or 12 and scolded him for not having put a stop to the insurrection, they did on the other hand come over the night before and exclaim: the homeland is saved! No, he absolutely did not visit the king in order to convert him or justify himself two weeks before the insurrection (”I couldn’t believe my eyes! […] You know me, and these words come out of your mouth. You read my compte rendu to my fellow citizens, and these words come out of your mouth!”). The king had in fact requested him in several secrets meetings that he refused, he only ever went to see him on official invitations and for business. No, he is not attacking the Jacobins in his letter, he’s protecting them against fights and intrigues which could dishonor them.
Pétion is certain Robespierre knew full well non of these charges were founded, claiming he made them in order to ”indispose the public against me, and make it favorable to you by declaring yourself its avenger. If this is clever, it is neither fair nor just.” He then directs some denounciations against him in turn, starting by regretting the humorous tone used by Robespierre in his response — ”you say of me what you do not think; you say it with bitterness, with passion; you allow yourself sarcasm, irony, mind games beyond all propriety” — and especially that he refers to him by his firstname like that’s supposed to be funny. Where Robespierre accused him of being blinded by ”intriguers,” Pétion reproaches Robespierre of being the ”courtier” of the people, placing himself at the head of whatever opinion that for the moment happens to be popular, in order to remain so himself. That is why he has never gone to a public riot to try to stop ”the excesses of the malicious”, out of fear of making them his enemies, and why he today carasses the sections, even though both he and his friends spoke ill or them during the electoral assembly. It is also the reason Pétion always defended him against the charge that he had had the ambition to become mayor — ”not only would he find himself overwhelmed by often minute details, and above all without glory, but, as one must sometimes know how to resist the aberrations of public opinion, how one must know how to momentarily incur the disgrace of the people, he would never have the strength to tell them that he is in the wrong: he would believe his reputation or popularity lost.” While denying that him standing for election in Eure-et-Loir had anything to do with him being jealous of Robespierre (if the people of Paris didn’t give him the most votes, it was because they found him more useful as mayor), Pétion also critiques the electoral assembly of Paris, which he claims ”was influenced, was dominated by a small number of men,” lifting the fact Robespierre’s brother got elected as a deputy of Paris as an example. Pétion also comes back to his critique of Robespierre’s actions during the September massacres again, seemingly endorsing the idea that he on September 2 had tried to use them to rid himself of his political opponents:
I said that on this occasion you gave yourself over to the excesses of a disordered and dark imagination; that you allowed yourself odious denunciations; that you had gone so far as to denounce as traitors, men that were friends of liberty, whose talents were in your eyes the real crimes, against which you had not the slightest proof, and that this was then to indicate the victims. I now add that in the fury of your declamations, you announced that it was necessary to purge the soil of liberty of the conspirators who infected it; but with a tone, a gesture which was so well understood, that the spectators responded with trembling, and shouted: Yes... Yes, let’s do it.
Nevertheless, he reveals to Robespierre that when one of the many citizens outraged by this wanted to denounce and testify against him, Pétion had stopped him from doing so. Like how Robespierre underlined how he for a long time had defended Pétion and believed his intentions to be good, Pétion too reminds him that ”when I was told that you were my enemy, that you were eaten up with jealousy against me, that you would never forgive me the favor I enjoyed, I defended you with all my soul, I took your side against all odds.” Today, he must however announce that ”I am forced to believe in the baseness and wickedness of your heart,” and he reveals that ”what caused the blindfold to fall off my eyes” was a speech Robespierre held at the Jacobins on October 28, where he says that, the day after the massacre on Champ de Mars, ”I saw Pétion, who then also fought against the intriguers.” Pétion reacts strongly on this choice of wording:
You only uttered one word, and it was more treacherous than a whole speech. You seemed to throw it away accidentally: you said, going back to the time of the Constituent Assembly, that then I was fighting intriguers, and that I embraced the good party, as if I had never ceased to pursue both traitors and enemies of liberty. Don't worry, I won't let them rest. I was well aware of the system of calumny and persecution directed against me; but I thought, I confess, that it would be without result, and I deigned to do so. I believed above all that you were not immersed in this intrigue.
Pétion ends with yet another unflattering description:
I do not think, and I do you this justice, that you are a man to ever allow yourself to be influenced by the lure of riches; but let Pon know how to skilfully caress your vanity; let the most salutary project be presented to you like an intrigue woven by your enemies, like a conspiracy, like a betrayal, your imagination immediately catches fire, you lose yourself in an abyss of conjectures, and you give in to the first panel held out to you. I will show you twenty of your opinions which are absolutely in the same direction as that of the court and of the counter-revolutionaries. If these opinions had been held by anyone other than you, his reputation would be lost, and he would be regarded as a traitor to his country. I saw men of good faith, without any interest who were not your enemies, who said to me: is it possible that Robespierre is sold, I always told them not to worry, but that you had a bad head, and that you lead to the delirium of your imagination. I have always added at the same time that you would sacrifice everything for a quarter of an hour of popular favour.
Robespierre responded in Deuxième lettre de Maximilien Robespierre en réponse au second discours de Jérôme Petion, that made up all of number 10 of Lettres à ses comettras… He started by telling Pétion that his complaints that he used irony, ridicule and tried to caluminate him seem unjust to him, and that he won’t change his tone for this second reply. Besides, he adds, the friends of the homeland find such few occasions to laugh these days. As for calling Pétion by his firstname, he reminds him that he never did so without adding his lastname as well, and what’s so bad about the name Jérôme anyways?
Turning to countering Pétion’s arguments, Robespierre writes that, even if Pétion does view the insurrection of August 10 as something positive, his conduct during it was still way too moderate. Pétion admits to in the conversation they had on August 7 have wanted to postpone the insurrection until the moment when the legislative assembly would have pronounced on the king's forfeiture, ”that is to say, until the end of the centuries.” He confesses to in the days before August 10 have tried to keep the calm ”and all the reasons that you give to explain your conduct on one of these occasions may well prove that you were a brave man, but not that you were a determined revolutionary, nor a clever politician.” He might not have visited the king on his own initiative, but that’s nevertheless how it came across for all patriots (besides, I didn’t write you had the shame (honte) to visit the king, I wrote goodness (bonté)! Robespierre even argues that the reason Pétion stayed at home during the insurrection was because ”you felt so inclined to oppose the insurrection of the people against the tyranny armed to slaughter them, that you knew of no other way of resisting this temptation than to be kept at home.” Pétion’s debunking of the anecdote Brissot and Guadet scolding him for not having stopped the insurrection, Robespierre counters with the fact it was an ”irreproachable citizen” that gave him the story, one whose word he chooses to believe over that of Pétion’s.
As for Pétion’s debunking of the claim he was indifferent to stop the demonstration of June 20, Robespierre simply doesn’t believe it — ”nothing is easier or better proven.” He ridicules Pétion’s suggestion that he was trying to make him look bad in the eyes of the jacobins, ”as if it was me who had composed the diatribe printed at the end of your speech against me,” and when Pétion himself has barely showed up at the club in the last year — ”Jérôme Pétion is therefore a very high power, since he thus places his sole authority in opposition to the services of an immortal society of friends of freedom; since he dares to present it as a stupid herd led by intriguers, at the head of whom he places me.” Pétion’s anger over the fact Robespierre in a speech held two months earlier is recorded to have said Pétion served the revolution well during the National Assembly (implying he doesn’t anymore), he dismisses since, in the version of the speech given in number 3 of Lettres à ses comettras, no such words can be found. Robespierre likewise dismisses Pétion’s claim that he wasn’t jealous at him for getting more votes to the Convention, reminding him that ”the pain did not even allow you to fulfill the commitment you had made with a very well-known man in the republic, to meet that day, at his home, to dine, with me, for an object which essentially concerned public harmony,” as well as Pétion’s suggestion that the electoral assembly was influenced by nepotism since he could only cite his brother as an example, who, he assures, was elected only due to his own merits. The idea that Robespierre would have spoken ill of the sections or denounced men at the commune just to have them ”exposed to the knife” during the September massacres he too dismisses as simply slander. It is this last charge that breaks the camel’s back for Robespierre:
Pétion, this excess of atrocity exempts me from all the consideration that I persisted in maintaining with you; and from now on you will only owe my moderation to my contempt. I abandon you to that of all the citizens who have seen me, heard me like this, and who deny you. I abandon you to that of all judicious men, who, in your expressions, as vague as they are artificial, perceive at the same time the hatred, the lie, the implausibility, the contradiction, the insult made at the same time to the public, to the patriotic magistrates, as much as to myself. Pétion, yes, you are now worthy of your masters; you are worthy of cooperating with them in this vast plan of slander and persecution, directed against patriotism and against equality. But no; I am wrong to get angry with you, whatever your intentions; because you take care to ward off all the blows you want to deal yourselves; and following a stroke of wickedness, I see a hundred ridiculous things happen, which you indulge in on purpose for my small pleasures.
In the last couple of pages, Robespierre jokingly accuses Pétion of during his time as mayor have gotten into his head the idea that France wanted to crown him king and that he, like Caesar, would have to fight this off. ”Good god! We would then have gotten us a king by the name of Jérôme the first! […] If you felt some regrets, who knows if we might not enjoy this one day. You have good friends, who lack neither power nor resources. It is not without reason that they do not want to let us make laws or a constitution, that there has not even been a question of the declaration of rights yet; that they work, with marvelous skill, to kindle civil war, and to plunge us into anarchy; who knows if France will not be obliged to come back to your knees and ask you to dictate laws to it?” He then addresses Pétion as you would a king throughout the rest of the letter, calling him ”sire” and ”your majesty.”
This was truly the final nail in the coffin for the relationship. In number 1 of the second series of his Lettres à ses commettans (January 1 1793), Robespierre regretted the earlier constant tying together of him and Pétion, now viewing it as an attempt of his enemies to undermine him:
In the past, I still remember, Brissot and a few others had entered into I don't know what conspiracy to make my name almost synonymous with that of Jérôme Pétion; they took so much trouble to put them together. I don't know if it was for love of me or of Pétion: but they seemed to have plotted to send me to immortality, in company with the great Jérôme. I have been ungrateful; and, to punish me, they said: since you don't want to be Pétion, you will be Marat. Well, I declare to you, monsieurs, that I want to be neither.
The trial of Louis XVI, which had been ongoing at the same time as Pétion and Robespierre’s breakup exchange, provided yet another moment for the two to oppose each other, with Pétion suggesting the Convention first discuss whether or not the king should be judged, a question deemed quite unneccessary for Robespierre, who instead wanted to see the king executed right away, without any trial. In a speech to the Convention held December 3 he lamented the direction Pétion had led them in:
Today Louis shares the mandataries of the people; we speak for and we speak against him. Who would have suspected two months ago that it would be a question here, whether he was inviolable? But since a member of the National Convention (citizen Pétion) presented the question, whether the King could be judged, as the object of serious deliberation, preliminary to any other question, the inviolability of which the conspirators of the Constituent Assembly covered up his first perjuries, was invoked, to protect his latest attacks. O crime! O shame!
When Robespierre a few weeks later, on December 28, defended himself against the charge of having belonged to ”the cabal of Lafayette” (just your typical convention workday) he nevertheless exclaimed: ”I attest to my former colleagues, Pétion, Rabaud, and many others, if I had any connections with this faction!” When the time had arrived to finally decide the former king’s fate, Pétion voted for an appeal to the people, and for death with the so called Mailhe amendment, calling for a postponement of the execution, while Robespierre voted against an appeal to the people and for immediate execution.
On January 27, six days after the execution of the king, Pétion was struck from the Jacobin club’s list of members, on the suggestion of Monestier. Two months later, March 26, Pétion and Robespierre were both elected for the so called Commission of Public Safety, alongside 23 others. The commission, which consisted of both fervent montagnards and fervent girondins, was however off to a rocky start, and already on April 6 it was put to death and replaced by the Committee of Public Safety.
Four days after that, April 10, Robespierre spoke for long at the Convention, denouncing the girondins as ”a powerful faction conspiring with the tyrants of Europe to give us a king, with a sort of aristocratic constitution” led by Brissot. The girondins were the successors of Lafayette, accomplices of Dumouriez, Miranda and d’Orléans, and supported by William Pitt, who had dishonored the Insurrection of August 10 and wanted to flee Paris with the king, tried to cause civil war by calling for an appeal to the people during the trial of said king, as well as having ”depressed the energetic patriots, protected the hypocritical moderates, successively corrupted the defenders of the people, attached to their Cause those who had some talent, and persecuted those whom they could not seduce.” Robespierre ended with asking that the Revolutionary Tribunal be charged with setting up a trial for ”Dumouriez and his accomplices” as well as for the Orléans family, Sillery and Madame de Genlis. Pétion’s name got mentioned outright four times in the speech, Robespierre accusing him of being the friend and defender of the general Francisco de Miranda, arrested since February 1793 after a failed siege of the city Maastricht and later denounced as an accomplice of Dumouriez.
Two days later, April 12, a stormy exchange played out between the two former friends at the Convention, after Pétion had asked that François-Martin Poultier be censored for making a personal suggestion when meant to speak in the name of his committee of war. Several variants of this exchange can be found throughout the different journals. Here is the one given in the Moniteur:
Robespierre: I demand the censure of those who protect the traitors. (Pétion rushes to the tribune, some murmurs rise) Robespierre: And their accomplices. Pétion: Yes, their accomplices, and you yourself. It is finally time for all these infamies to end, it is time at last for all this infamy to end; it is time for traitors and slanderers to lay their heads on the scaffold; and I pledge here to pursue them to death. Robespierre: Answer the facts. Pétion: It’s you I will be pursuing. Yes, Robespierre will have to be branded at last, as the slanderers used to be.
The Mercure universel:
Pétion: I ask that the rapporteur be censored; instead of the committee's opinion, he allows himself to report his own to mislead the public. We must punish the conspirators. Robespierre: That’s you. (applauds from the tribunes, cries of indignation in the assembly) Pétion (runs to the tribune; unrest): It is finally time for all these infamies to end, it is time for the convention to be respected: I will pursue the slanderers, the traitors! Robespierre: Where are they? Pétion: You!
Journal de Paris:
Pétion asks that this member be censored, for having expressed an opinion that the Committee of War had not directed to him. Here Robespierre interrupts Pétion, and the interpellation he made, which we did not hear, was undoubtedly very lively, because Pétion flew to the tribune, and in a voice more vehement than he ever used in the two Assemblies of which he was a member, he complained of this system of slander adroitly directed against the true friends of liberty, by these people who thus believe they are hiding, at the moment that they will be discovered, the plots that they themselves have formed. He thunders against these informers who, without proof, pile denunciations on top of each other, without ever proving any of them. Pétion concluded that all denunciations should be signed, under penalty of being subjected to the same contempt as their authors.
Le Logotachigraphe:
Pétion: I demand censure against the rapporteur who allowed himself to overstep the powers he had received from the committee. Marat: I ask that we pursue the traitors. (noise) Pétion (flies to the tribune): I will indeed ask that the traitors and conspirators be punished (interrupted by boos from the stands. Part of the assembly stands up and shows its indignation: the president is summoned to remind the stands of respect.) The president: I have called the tribunes to order several times, and I call them again at this moment, to the execution of the law which prohibits any sign of disapproval and approval, and I conjure them, in the name of public safety, to remember that all is lost if the National Convention does not retain its liberty. Pétion: It is impossible (murmurs) to tolerate this infamy any longer. It is impossible for an honest man to restrain his indignation when he sees that men who should keep the most profound silence; that men who are marked with the most infamy dare to insult him with this audacity. Yes, I intend to pursue the traitors; I intend to pursue the slanderers, and I tell all of France that Robespierre must either be punished or branded with hot iron on the forehead as a slanderer.
Le Thermomètre du Jour:
Pétion calls for censure against Poultier for having expressed an opinion tending to mislead the public. It is necessary to underline, said Robespierre, that one is trying to save the traitors. Immediately Pétion, going up to the podium, said: ”It is impossible for an honest man to tolerate any longer the system of slander and disorganization that I see followed with a constancy that only great interest can give. Yes, I will fight against traitors and slanderers. In the end, either I must be punished or Robespierre must be branded with the hot iron with which ancient peoples branded slanderers. Even before the existence of the convention, people had already formed the wish to slander it, to outrage it, to degrade it, and some people have continued to follow this system. I ask what more our enemies would have done? Aren't these the real enemies of the republic? I will never compromise with despots, and if the enemy were at the gates of Paris, we would see which are the brave false ones, and which ones are the courageous republicans!
Pétion then went on a long rant about the need to punish the traitors, before denouncing Marat. Robespierre responded that ”I will be permitted to respond to your calumnies,” to which Pétion, according to Le Logotachigraphe, replied the following way:
I would like a written struggle to begin here, because words are elusive; I would like the indictments to be recorded in writing and the answers that each person submitted to put their head to be heard in writing, and I would then ask that whoever is found guilty loses it. I do not claim to be constantly engaged in a struggle, neither with lungs nor with screams, nor with insults and insults; all this means nothing: this is not how free men justify themselves: free men act with perfect integrity. I am not asking here for imprecation or approval; but I ask for peace and quiet; I ask above all that we do not allow ourselves these indecent accusations, a thousand times more atrocious than facts. We have already fought in writing with Robespierre; he knows that I know him, and certainly, I am doing him a kind of justice here. At the constituent assembly, for example, Robespierre behaved well, and I admit that I have never been convinced why he changed. (Long uproar.)
Later the same session, Guadet used Robespierre’s former friendship with Pétion as a weapon against him apropos of getting accused of being an accomplice of Dumouriez: ”Can’t I say to Robespierre: You have had liaisons with Pétion, but you accuse Pétion of betraying the public sake.” […] Well! Since you have had liaisons with Pétion, I can therefore conclude you have been in on his projects. Why then do you start by suppose me to have liaisons with Dumouriez, which is false, and conclude that since Dumouriez has turned traitor I must be considered one as well?” In the defense he wrote a few months later, the girondin Gensonné similarily stated: ”in 1791 and 1792, Robespierre had the most intimate liasons with Pétion, Buzot and Roland, how can he accuse them today without accusing himself?”
Pétion made good on his promise to start ”a written struggle,” as he soon thereafter released yet another pamphlet, this time by the name of Réponse très-succinte de Jérome Petion, au long libelle de Maximilien Robespierre (1793), a 14 page long work where he answered Robespierre’s attack from the 10th. Robespierre didn’t respond to it thank god.
On May 17, Desmoulins presented his 84 pages long Histoire des Brissotins, ou, Fragment de l'histoire secrète de la révolution, et des six premiers mois de la République to the Jacobin club, a pamphlet we know Robespierre had had a hand in through a note inserted in one of Desmoulins’ later publications. In total, Pétion’s name got mentioned a total of 22 times in the damning work that painted him and the other ”girondins” as royalists, accomplices of Dumouriez and in the pay of foreigners. They had been leading an anglo-prussian committee working for the military failure of France, which they wanted to divide into 20-30 federalist republics, or to overturn the republican government altogether, and to set up the Duke of Orléans as monarch. For Pétion’s part, Desmoulins threw suspicion on the fact that he, during his trip to London after the closing of the National Assembly, had been accompanied by Madame de Genlis (the cousin of the duke of Orléans), her niece Rose-Henriette Peronne de Sercey and daughter Pamela, ”that we can call the three graces, and who pressed his virtuous and fortunately incorruptible knee; and wasn’t it upon his return that he was appointed mayor of Paris?” Desmoulins also picked up Robespierre’s criticism of Pétion’s attitude towards the insurrection of August 10, but this time he got accused of not only not having wanted the event to take place, but also to have signed the order for the Swiss guard to fire on the people. He was also claimed to have received 30 000 francs per month from Dumouriez in order to ”throw away the foundations of the republic” during his time as mayor.
Desmoulins concluded that the establishment of a democratic republic wouldn’t happen before ”the vomiting of the Brissotins from the bosom of the Convention,” and on May 26, a week after the pamphlet’s publication, Robespierre had reached the same conclusion, telling the jacobins that ”the people must rise up. This moment has arrived.” Three days later he repeated himself — “I say that, if the people do not stand up as a whole, liberty is lost, and that only a detestable empiricist can tell them that there remains another doctor than themselves” — and two days after that, the insurrection of May 31 took place, which ended with the Convention on June 2 issuing arrest warrants against 29 of its deputies and two ministers. One of these 31 men was of course Pétion, who was placed under house arrest like the others. It was however a very loose one, and many of the proscribed managed to get away. On June 24, Jeanbon Saint-André could report to the Convention that Pétion had escaped, after which he suggested bringing those still remaining under house arrest to actual prisons, a proposal which Robespierre supported.
Having gone underground (while his wife, child and father all got arrested and his mother-in-law executed), Pétion occupied himself with writing, both his memoirs as well as Observations de Pétion, a constructive criticism of the poem Charlotte Corday, tragédie en 5 actes et en vers, that his fellow runaway Jean-Baptiste Salle had penned down. ”Barère and Robespierre,” Pétion wrote in these, ”are known for being the greatest cowards on earth. In my view, the trick is Barère's distinctive character. Robespierre is no less perfidious; but what distinguishes him is that in danger he loses his head, he discovers in spite of himself the fear which torments him, he speaks only of assassinations, only of lost liberty, he sees the entire Republic destroyed in his person, whereas Barère, more dissimulated, without being less cowardly, is always coldly atrocious and preserves until the end the hope of succeeding.” Buzot, who was hiding out alongside Pétion, did on the other hand recall the latter’s former fondness of Robespierre in the memoirs he at the same time was working on: ”there was this great difference between Pétion and me — he had a particular deference for Robespierre, and I had an invincible aversion for this man who had the face of a cat.”
Robespierre for his part had no nice things to say about Pétion. On March 21 1794 he reminded the Jacobins how Lafayette, Pétion and Dumouriez had all conceived ”the terrible project of starving and enslaving [the people]” but that luckily these ”monsters” had now fallen. A few days later, April 1 1794, he shut down a proposal that the recently arrested Danton be allowed to come and defend himself before the Convention by pointing out that this was not the first time a former ”patriot” turned out to be a traitor — ”And I too was a friend of Pétion; as soon as he unmasked himself, I abandoned him; I also had liaisons with Roland; he betrayed, and I denounced him. Danton wants to take their place, and in my eyes he is nothing more than an enemy of the homeland.” Finally, on June 27 1794 he talked about yet another conspiracy, and regretted that it would be hard to make ”so many horrors” perceptible to the people that once ”were seduced by the Lameths, the d'Orléans, the Brissots, the Pétions, the Héberts.”
On June 17 1794, Pétion, Buzot and Barbaroux left the garret in Saint-Émilion where they since five months back had been hiding out, after the people taking care of them had gotten arrested, and set out into the countryside. When in the next day some people approached, Pétion and Buzot took flight once more while Barbaroux unsuccessfully tried to blow his brains out and was captured. Eventually his friends decided to take the same way out. It is unclear when exactly this double suicide took place, tradition placing it on June 18 and Michel Biard, in the book La liberté ou la mort: mourir en député 1792-1795 (2015) instead dating it to June 24, having consulted two doctors with expertise in the field. Regardless, on July 8 1794, the Moniteur published the following letter from the Popular Society of Castillon that had been read at the Convention the day right before:
Citizen Representatives, our search has not been in vain. When we annonced to you that the scroundel Barbaroux had been taken, we assured you that his accomplices Pétion and Buzot would soon be under our control. We’ve got them now, Citizen Representatives, or rather they are no more. The end which the law prescribes was too good for such traitors; divine justice reserved for them a fate more fitting to their crimes. We found their bodies, hidden and disfigured, half eaten by worms; their scattered limbs had been devoured by dogs, their bloody hearts eaten by ferocious beasts. Such was the horrible end of their still more horrible lives. People! Contemplate this awful spectacle, the terrible monument to your vengeance! Traitors! May this ignominious death, may this abhorred memory make you recoil with horror and shudder with terror! Such is the terrible fate which sooner or later will be reserved for you. Signed The Sans-Culottes of the Popular and Republican Society of Castillon.
By the time the letter reached Paris, Robespierre had already stopped showing up at both the Convention and the Committee of Public Safety. But he probably still found out about what had happened, if not through the letter to the Convention, then through another one written to him on June 30 by Marc Antoine Jullien, representative on mission in Bordeaux, asking ”to raze to the ground the houses where Guadet, Salle, Pétion, Buzot and Barbaroux were [hiding], [and] transfer the military commission to Saint-Emilion, to there judge and make perish on the spot the authors or accomplices guilty of hiding the conspirators.” While we lack the sources to say anything really substantial about Robespierre’s psyche, it is nevertheless interesting to speculate if the news of his former friend’s horrible fate (as can be seen from the letter to the Convention, it isn’t even explained that Pétion and Buzot had committed suicide before getting mauled by the animals) was a contributing factor to Robespierre’s growing isolation from public life and deteriorating mental health during his last month alive…
85 notes
·
View notes
Text
https://www.joinjeremy.org/about-3 Jeremy Busby is a wrongfully convicted incarcerated journalist who has faced near constant retaliation from TDCJ officials. Please take action to demand #SafetyForJeremy and #JoinJeremy.
0 notes