#Yttrium Metal News
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Yttrium Metal Prices 2025, Size, Trend, Graph, News and Forecast
Yttrium Metal Prices a rare earth element with the atomic number 39, has steadily gained attention in global markets due to its critical applications across high-tech industries. Its use in electronics, superconductors, and advanced materials has made it increasingly valuable. Over the past few years, yttrium metal prices have exhibited notable volatility driven by changes in global demand, supply chain dynamics, and geopolitical developments. As technological innovation surges forward, the strategic importance of yttrium has grown, creating fluctuations in market pricing and influencing investor sentiment. This metal’s market is particularly sensitive to the dynamics within the broader rare earth elements sector, as yttrium is often extracted as a byproduct of processing other rare earths such as dysprosium and terbium.
China dominates the global supply of yttrium metal, accounting for a significant share of production and refining. This market concentration gives China substantial influence over yttrium pricing trends. Any policy changes, export restrictions, or shifts in production quotas by Chinese authorities tend to have immediate and pronounced effects on global prices. In recent years, initiatives to curb illegal mining and promote sustainable extraction practices in China have led to reduced output, which in turn has caused price spikes. Conversely, any relaxation of these regulations or increases in output can lead to downward pressure on prices. Additionally, the Chinese government’s strategic stockpiling and export policies continue to play a crucial role in shaping international market dynamics.
Get Real time Prices for Yttrium Metal: https://www.chemanalyst.com/Pricing-data/yttrium-metal-1612
Demand for yttrium is primarily driven by its use in phosphors for LED displays and fluorescent lighting, as well as in the production of yttrium-aluminum-garnet (YAG) lasers and ceramics. With the rapid adoption of energy-efficient lighting and expanding use of lasers in industrial and medical applications, yttrium consumption has been rising steadily. The transition to electric vehicles and the expansion of 5G networks also support growth in the demand for yttrium-based components. Moreover, yttrium's role in military technology, including targeting systems and electronic warfare tools, enhances its strategic significance and bolsters market demand from defense sectors worldwide. These high-value applications make yttrium less susceptible to rapid demand declines, even in uncertain economic climates.
On the supply side, challenges persist due to the complex extraction and separation processes required to isolate yttrium from other rare earths. These processes are environmentally intensive and costly, often deterring new market entrants and limiting global production expansion. While there are efforts in regions like North America and Australia to develop alternative sources of yttrium and reduce dependency on Chinese supply, these initiatives are still in developmental stages and face considerable financial and regulatory hurdles. Recycling of rare earth materials, including yttrium, is gaining traction but remains a relatively small contributor to total supply due to technological and economic constraints. As such, the tight supply chain continues to exert upward pressure on prices when demand surges.
Yttrium metal prices are also influenced by macroeconomic factors such as currency fluctuations, trade policies, and global economic growth. For instance, a strong U.S. dollar can make dollar-denominated yttrium more expensive for buyers using other currencies, potentially dampening demand and softening prices. Likewise, tariffs and trade tensions—particularly between the United States and China—can disrupt supply chains and introduce price volatility. The COVID-19 pandemic underscored these vulnerabilities, as lockdowns and logistics disruptions caused temporary supply shortages and price increases in various critical materials, including yttrium. As the global economy continues to recover, demand for yttrium in industrial and technological applications is expected to increase, further influencing price trends.
Looking ahead, the yttrium metal market is likely to experience a gradual upward trend in pricing due to increasing technological integration and the strategic necessity of securing rare earth supply chains. Innovations in clean energy, smart manufacturing, and aerospace technologies are all expected to support long-term demand growth. At the same time, global efforts to diversify yttrium supply sources and invest in more sustainable mining practices could help stabilize the market in the medium to long term. Governments and corporations are increasingly recognizing the importance of rare earth independence, and investment in yttrium extraction outside China is beginning to gain momentum. However, until these alternative sources become commercially viable at scale, the market will remain heavily influenced by Chinese production trends and policy decisions.
In conclusion, the yttrium metal market is shaped by a complex interplay of supply constraints, technological advancements, geopolitical tensions, and economic trends. Prices are expected to remain dynamic, with potential for both short-term volatility and long-term growth. As global industries become more reliant on advanced materials, yttrium will continue to play a pivotal role, ensuring its position as a valuable and strategically important resource in the modern economy. Investors, manufacturers, and policymakers alike will need to closely monitor market developments to make informed decisions and manage risks in this evolving landscape. The outlook for yttrium remains promising, supported by robust demand fundamentals and increasing awareness of the need for supply chain resilience in critical mineral markets.
Get Real time Prices for Yttrium Metal: https://www.chemanalyst.com/Pricing-data/yttrium-metal-1612
Our Blog:
Nitrogen Based Fertilizer Prices: https://www.chemanalyst.com/Industry-data/nitrogen-based-fertilizer-17
Phosphorus Based Fertilizer Prices: https://www.chemanalyst.com/Industry-data/phosphorus-based-fertilizer-18
Contact Us:
ChemAnalyst
GmbH - S-01, 2.floor, Subbelrather Straße,
15a Cologne, 50823, Germany
Call: +49-221-6505-8833
Email: [email protected]
Website: https://www.chemanalyst.com
#Yttrium Metal Pricing#Yttrium Metal News#Yttrium Metal Price Monitor#India#united kingdom#united states#Germany#business#research#chemicals#Technology#Market Research#Canada#Japan#China
0 notes
Text
For most of the history of civilisation we’ve exploited a pretty small selection of metals, including copper and tin for bronze-age tools, iron for steel, and lead, gold and silver. Our repertoire has begun to diversify over the past century or so, with the widespread use of aluminium and other new metals. But in the past few decades the number of different metals we wield in our technological society has absolutely exploded. A modern smartphone contains more than 30 different elements. These include carbon and hydrogen in the plastic casing, silicon for the microchip wafers, and copper wiring and gold contacts. But there are also small amounts of a large number of other metals, each exploited for its own particular electronic properties, or for the tiny, powerful magnets used in the speaker and vibration motor. This means that if you own a smartphone, you have in your pocket a substantial fraction of all the stable elements of the periodic table. And it’s not just modern electronics that demand a huge diversity of different metals. So too do the high-performance alloys used in the turbines of a power station or aircraft jet engine, or the reaction-accelerating catalysts that we use in industrial chemistry for refining oil, producing plastics or synthesising modern medicinal drugs. Yet most of us have never even heard of many of these critical metals – elements with exotic names like tantalum, yttrium or dysprosium.
The concern is that unlike widespread resources like iron or nitrogen, several of these elements crucial to the modern world may become prohibitively scarce. These have become known as the endangered elements. In response to the Mendeleev anniversary, the European Chemical Society (EuChemS) has released a version of the periodic table (see above) to highlight the elements that are most at risk over the coming decades.
Helium, for example is considered to be under serious threat in the next 100 years. It is the second most abundant element in the universe, but preciously rare on Earth because it is light enough to simply escape from the top of our atmosphere. The helium we do use is effectively mined from deep underground, usually along with natural gas, as it is produced as radiation particles from the decay of elements like uranium. Helium is very useful – as a cooling liquid for the superconducting magnets in hospital MRI scanners, for example, or as an extremely light gas for weather balloons and airships. But once it leaks into the air it is lost for ever, and there are concerns over meeting supply in the future. With this perspective, its frivolous use in party balloons seems almost painfully wasteful.
Many of these endangered elements are the sort of exotic metals used in modern electronics, and indeed the supply of 17 elements needed for smartphones may give cause for concern in years to come. Particularly worrying is the fact that many of those facing potential scarcity are exactly the elements we need for the green technologies to replace our reliance on fossil fuels – those used in rechargeable batteries, solar panels, and the powerful magnets within the motors of electric cars or generators in wind turbines. Gallium, for example, is needed for integrated circuits, solar panels, blue LEDs and laser diodes for Blu-ray Discs. Indium is used in everything from TVs to laptops, and in particular the touch-sensitive screens of modern smartphones and tablets. It is estimated that at current usage rates, available indium will be used up in 50 years and will become very expensive to collect and purify.
Except for helium, the problem isn’t that these scarce elements actually become lost to the planet, but that they become too expensive to mine or too dispersed to recycle effectively. “Rare earth elements”, such as yttrium, dysprosium, neodymium and scandium, are actually relatively plentiful in the Earth’s crust but aren’t geologically concentrated into rich ores. This means that they can’t be extracted economically in many areas of the world. And once they have been manufactured as tiny components within an electronic device, they can be even harder to reclaim and recycle. EuChemS calculates that 10m smartphones are discarded or replaced every month in the EU alone, and so serious action is needed to tackle these challenges of elemental scarcity.
#current events#environmentalism#capitalism#manufacturing#science#chemistry#mining#tantalum#yttrium#dysprosium#helium#indium#neodymium#scandium#dmitri mendeleev#periodic table
6 notes
·
View notes
Text

China has imposed new trade restrictions on samarium, gadolinium, terbium, dysprosium, lutetium, scandium, and yttrium.
These metals are critical to American big tech.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Russia: A Key Player in Scandium Production
According to a recent research, Industry revenue for Scandium Iodide is expected to rise to $1132.7 million by 2035 from $511.3 million of 2024. U.S., China, Japan, Germany and South Korea are the top 5 markets and combinely holds substantial demand share. The revenue growth of market players in these countries is expected to range between 4.9% and 7.2% annually for period 2025 to 2035.
Industry transition including shift towards eco-friendly lighting solutions and increased demand from the aerospace industry, are transforming the supply chain of Scandium Iodide market. The lighting sector aims to swap out mercury vapour lamps for environmentally friendly options which could lead to a major shift in the Scandium Iodide market landscape as it is a key component in mercury vapour lamps for generating intense discharge lighting sources. As the call for eco choices grows stronger in the industry there could be a drop in the demand for scandium iodide reflecting this transition pushing manufacturers to investigate alternative uses, for this material.
Potential Application Areas
Metal-Halide Lamps: The compound is also important in metal halide lamps as it helps to enhance the quality by filling in gaps in the spectral output of the lamps. This is particularly useful for industries like horticulture, cinemas and sports stadiums that require lighting. GE Lighting is a player, in this field and they create lamps that benefit from the consistent spectral properties of Scandium Iodide.
Laser Crystal Component: Scandium iodide plays a role in the scientific field as an additive in yttrium aluminum garnet lasers used widely in research facilities and industrial applications such as metalworking. Its incorporation in these lasers results, in enhanced energy efficiency and beam stability. This advancement has been attributed to Coherent Inc.
Industry Leadership and Strategies
The Scandium Iodide market is characterized by intense competition, with a number of leading players such as Stanford Materials Corporation, American Elements, Materion Corporation, Thermo Fisher Scientific, ABSCO Limited, Santoku Corporation, Sigma-Aldrich Co. LLC, Strem Chemicals Inc., LTS Research Laboratories Inc., Evans Chemetics LP, Alfa Aesar and Noah Technologies Corporation. These players are pushing the boundaries of innovation & technological advancements and forging strategic partnerships to expand the existing reach of the market. Below table briefs about adopted market strategies by leading players.
Access detailed report insights here - https://datastringconsulting.com/industry-analysis/scandium-iodide-market-research-report
About DataString Consulting
DataString Consulting assist companies in strategy formulations & roadmap creation including TAM expansion, revenue diversification strategies and venturing into new markets; by offering in depth insights into developing trends and competitor landscapes as well as customer demographics. Our customized & direct strategies, filters industry noises into new opportunities; and reduces the effective connect time between products and its market niche.
DataString Consulting is a professional market research company which aims at providing all the market & business research solutions under one roof. Get the right insights for your goals with our unique approach to market research and precisely tailored solutions. We offer services in strategy consulting, comprehensive opportunity assessment across various sectors, and solution-oriented approaches to solve business problems.
0 notes
Text
North America Medical Laser Systems Market Trends, Size, Segment and Growth by Forecast to 2030
Solid State Lasers Segment to Lead North America Medical Laser Systems Market from 2021 to 2028
A recent market research report titled “North America Medical Laser Systems Market to 2028 – COVID-19 Impact and Regional Analysis by Product Type, Application, End User, and Country” forecasts that the market will grow from US 919.72 million in 2021 to US 919.72 million in 2021 to US 2,257.13 million by 2028, achieving a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 13.7% during the forecast period. The primary driver of this growth is the significant increase in the elderly population, which is boosting demand for advanced medical laser systems. However, stringent safety regulations may pose challenges to market expansion. The report highlights key trends, drivers, and restraints influencing the North America medical laser systems market. 𝐃𝐨𝐰𝐧𝐥𝐨𝐚𝐝 𝐏𝐃𝐅 𝐁𝐫𝐨𝐜𝐡𝐮𝐫𝐞 - https://www.businessmarketinsights.com/sample/TIPRE00027259
Market Segmentation and Key Insights
The North America medical laser systems market is segmented by product type, application, end user, and country.
By Product Type:
Diode Lasers
Solid State Lasers
Sub-segments:
Holmium Yttrium Aluminum Garnet (Ho:YAG) Lasers
Erbium Yttrium Aluminum Garnet (Er:YAG) Lasers
Neodymium Yttrium Aluminum Garnet (Nd:YAG) Lasers
Thulium:Yttrium-Aluminum-Garnet Laser (Tm:YAG)
Potassium Titanyl Phosphate (KTP)
Alexandrite Lasers
Ruby Lasers
In 2020, the Erbium Yttrium Aluminum Garnet (Er:YAG) Lasers segment dominated the market.
Gas Lasers
Sub-segments:
CO2 Lasers
Argon Lasers
Krypton Lasers
Metal Vapor Lasers
Helium Neon Lasers
Excimer Lasers
In 2020, the CO2 Lasers segment held the largest market share.
Fiber Lasers
Sub-segments:
Thulium Fiber Lasers
Erbium Fiber Lasers
Ytterbium Fiber Lasers
In 2020, the Thulium Fiber Lasers segment led the market.
Dye Lasers
By Application:
Dermatology
Ophthalmology
Gynecology
Dentistry
Cardiology
Urology
Others In 2020, the dermatology segment accounted for the largest market share.
By End User:
Hospitals
Specialty Clinics
Ambulatory Surgery Centers
Others In 2020, specialty clinics held the largest share of the market.
By Country:
United States
Canada
Mexico In 2020, the United States contributed the most significant share to the market.
Competitive Landscape
Key players in the North America medical laser systems market include Alcon Inc., Artivion, Inc., Bausch Health Companies Inc., BIOLASE, Inc., Boston Scientific Corporation, Candela Medical, Ellex, Iridex Corporation, Koninklijke Philips N.V., and Lumenis Be Ltd. These companies are focusing on organic growth strategies such as product launches and expansions to strengthen their market position.
For example, in 2022, CryoLife, Inc. rebranded itself as Artivion, Inc., reflecting its strategic shift toward providing innovative technologies for aortic disease treatment. The company also changed its NYSE ticker symbol to "AORT" from "CRY" to align with its new focus.
Market Drivers and Restraints
Drivers:
Aging Population: The growing elderly population in North America is driving demand for medical laser systems, particularly in applications like dermatology, ophthalmology, and urology.
Technological Advancements: Continuous innovations in laser technology, such as improved precision and reduced recovery times, are enhancing adoption rates.
Restraints:
Stringent Safety Regulations: Compliance with rigorous safety standards and regulatory requirements may slow down market growth.
High Costs: The high cost of medical laser systems and procedures could limit accessibility for some end users.
Future Outlook
The North America Medical Laser Systems Market is poised for robust growth, driven by the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, rising demand for minimally invasive procedures, and advancements in laser technology. The solid state lasers segment, particularly Er:YAG lasers, is expected to maintain its dominance due to its wide range of medical applications and superior performance characteristics. Additionally, the dermatology and specialty clinics segments are anticipated to remain key contributors to market revenue.
As companies continue to innovate and expand their product portfolios, the market is likely to witness further consolidation and strategic partnerships, ensuring sustained growth over the forecast period.
About Us:
Business Market Insights is a market research platform that provides subscription service for industry and company reports. Our research team has extensive professional expertise in domains such as Electronics & Semiconductor; Aerospace & Défense; Automotive & Transportation; Energy & Power; Healthcare; Manufacturing & Construction; Food & Beverages; Chemicals & Materials; and Technology, Media, & Telecommunications Author’s Bio: Akshay Senior Market Research Expert at Business Market Insights
0 notes
Text
Interaction between rare earth metals and other elements

Rare earth metals have typical metal properties. They have strong chemical activity and can form a variety of compounds, including hydrides, chlorides, silicides, carbides, organic / inorganic salts and complexes. This is the basis for the rare earth metal in the metallurgical industry as a purification, impurity removal and refinement modifier.
Rare earth metals are unstable in air, and their stability increases with increasing atomic number; in other words, the rare earth metals with larger atomic radius have weaker oxidation resistance; light rare earth metals can be easier oxidized than heavy rare earth metals, and lanthanum is the most active. Lutetium and Scandium are the most resistant to air oxidation.
Rare earth metals are widely used as reducing agents, which can reduce oxides of iron, cobalt, nickel, chromium, vanadium, niobium, tantalum, zirconium, titanium, silicon and other elements into metals. Due to the difference in the reducing ability of rare earth metals, and the vapor pressure of the lanthanum is much smaller than that of Samarium, Europium, Ytterbium and Thulium, Lanthanum (cerium) can be used to reduce europium, europium, europium, europium metal from its oxides. However, the activity of rare earth metals is lower than that of alkali metals and alkaline earth metals, so lithium and calcium are commonly used as reducing agents to reduce rare earth metals from their halides.
Interactions between rare earth metals occur. If the two rare earth metals have the same crystal structure at the corresponding temperature, they can form a continuous solid solution; if the two rare earth metals have different crystal structures, they can only form a finite solid solution; Only two rare earth metals belonging to different subgroups (cerium and yttrium) can form intermetallic compounds.
The behavior of Yttrium and scandium in alloys is similar to that of heavy rare earth metals; the behavior of Ytterbium in magnesium alloys is similar to that of light rare earths. The melting point and elastic modulus of Europium and Ytterbium are similar to those of light rare earth lanthanum and cerium.
Rare earth metals and transition metals (iron, manganese, nickel, gold, silver, copper, zinc) and magnesium, aluminum, gallium, indium, thallium can form many alloys. Moreover, many intermetallic compounds are formed in their binary and multicomponent alloys.
Some of these compounds have high melting points, high hardness, high thermal stability, and are dispersed in the non-ferrous alloy matrix or grain boundaries. They play an important role in resisting high temperature, creep resistance, and improving the strength of the alloy. Many of these rare earth intermetallic compounds have been widely used in high and new technology with special functions. It is expected that more new intermetallic compounds will be developed in succession.
Only tantalum / niobium and tungsten / molybdenum and their alloys have little interaction with rare earth metals. Tantalum and molybdenum have almost no interaction with rare earth metals and their halides. Under vacuum or inert gas, tantalum can be used at 1700 °C, molybdenum can be used at 1400 °C, and it is used as the electrode for molten salt electrolysis and the carrying crucible for rare earth metals and rare earth alloys.
0 notes
Text
Ukraine Business Roundup — Trump wants Ukraine's 'rare earths'

The following is the Feb. 4, 2025 edition of our Ukraine Business Roundup weekly newsletter. To get the biggest news in business and tech from Ukraine directly in your inbox, subscribe here.
President Donald Trump came out on Feb. 3 saying he wanted to make a deal with Ukraine by giving the war-torn country weapons and aid in return for its “rare earths and other things.��
“We’re looking to do a deal with Ukraine, where they’re going to secure what we’re giving them with their rare earths and other things,” Trump told reporters in the Oval Office.
“I want to have security of rare earths. We’re putting in hundreds of billions of dollars. They have great rare earths. And I want security of the rare earths, and they’re willing to do it,” he said.
It’s not quite clear what exactly Trump meant by “rare earths and other things.” Ukraine is home to all sorts of highly sought-after raw materials from critical minerals to rare earth elements.
What’s more clear is why Trump wants them. China controls 70% of global rare earth mining capacity and 90% of processing capacity. Having easy access to these materials could boost the U.S.’s competitiveness — something at the top of the new president’s “America First” agenda.
For Kyiv’s part, President Volodymyr Zelensky has positioned Ukraine’s natural materials as part of a peace plan. Reports late last year said Zelensky’s team had even delayed a deal on critical materials with former President Joe Biden’s team so it could offer it to Trump in case he won the elections.
So what critical resources does Ukraine actually have and how viable are they, really? Ukraine has 20 of the world’s critical minerals and metals like titanium used in the aerospace and defense industries and lithium, an essential component of electric vehicle batteries.
Ukraine also possesses rare earth elements — under which titanium and lithium do not fall — such as cerium, yttrium, lanthanum, and neodymium. Demand for these materials has jumped in recent years as the world shifts to renewable forms of energy. Rare earth elements are crucial for making the powerful magnets used in wind turbine generators.
The issue, however, is geography. Raw materials are unevenly distributed across Ukraine and around $12 trillion has ended up in Russian-occupied territory, according to SecDev, a global digital risk and resilience firm.
And there’s the fact that a lot of these mineral deposits are underdeveloped, with the total value unknown, according to an analysis from the Kyiv School of Economics. Existing estimates put the value of Ukraine’s critical minerals anywhere between $3-$26 trillion.
Read reporter Dominic Culverwell’s full article here.

Ukrainian then-President Viktor Yanukovych in Kyiv, Ukraine, on May 17, 2010. (Sasha Mordovets/Getty Images)
Making millions off stolen Ukrainian resources
Speaking of critical resources. Oleksandr Yanukovych, the son of former Ukrainian President Viktor Yanukovych, has made billions selling coal from Russian-occupied Ukrainian territories to Turkey, independent Russian investigative outlet Important Stories reported on Feb. 4.
Viktor Yanukovych was Ukraine’s pro-Kremlin president from 2010 to 2014 before fleeing to Russia with his family in the wake of the EuroMaidan Revolution. In October 2024, reports emerged that Oleksandr Yanukovych had been granted Russian citizenship.
The company behind the coal exports, Energoresurs, is registered in Rostov-on-Don, Russia, and has exported nearly half a million tons of coal abroad between 2023 and 2024. Journalists linked Energoresurs to Oleksandr Yanukovych through his coal holdings and mining enterprises.
According to the investigation, the firm sources coal from suppliers in occupied Donbas and transports it to Turkey by rail and sea.
The coal is reportedly sold to an offshore company, Energy Union, registered in the British Virgin Islands. Energoresurs sells the coal at a significantly low price — an average of $60 per ton in 2024 — allowing the company to minimize export duties before reselling it at a higher price on international markets.

A Huless tethered drone system. (Brave1/LinkedIn)
Ukrainian drone maker attracts $1 million
Huless, a Ukrainian company developing tethered drone systems, secured over $1 million in private financing, loans, and a grant from Ukrainian Defense Tech cluster Brave1, the company said in a press release on Jan. 30.
Huless makes the Highline-T, a drone that can operate for up to four hours at heights up to 100 meters, even without GPS signals, the company says.
Unlike kamikaze or bomber drones that blow up Russian positions or vehicles, the Highline-T’s main function is to carry radio equipment that boosts the operational range of other drones and remote-controlled ground vehicles.
The tethered drone stays connected to the ground via a cable that provides constant power and data connection independent of interference from electronic warfare.
Huless plans to use the funding to expand its market presence and develop its tethered drone technology for military communications, the company said.

A bakery worker sifts flour to bake bread in Druzhkivka, Ukraine on Dec. 16, 2024. (Yelyzaveta Sekretarenko / The Kyiv Independent)
Front-line lifeline
One of the oddities of Russia’s war has been the parallel realities that coexist, almost seamlessly: on the one side are daily air raid sirens, Russian attacks, and casualties, on the other, people grabbing coffee, children going to school, businesses growing.
Nowhere are these two starkly divergent realities more clear than near the front lines.
Reporter Yelyzaveta Sekretarenko took a trip to the front-line town of Druzhkivka, located just 15 kilometers from the embattled city of Chasiv Yar to talk to the local entrepreneurs and businesses that remain despite the dangers.
In one scene in Sekretarenko’s article, taxi driver Serhiy Pohrebnyakov sits calmly behind the wheel of his car waiting for customers as explosions go off and people around begin running in different directions for cover.
Beyond the services or goods they provide — taxi rides, baked bread, and shampoo and razors for soldiers at roadside kiosks — these small businesses contribute to a semblance of normalcy in their community amid all the devastation wrought by Russia.
Read the full article here.
What else is happening
Ukraine’s inflation expected to peak by mid-2025, cool by year-end
Ukraine’s inflation rate is set to peak at 15% by mid-2025 before dropping to 8.4% by year’s end, Ukraine’s Central Bank said on Jan. 31. Poor harvests and higher wages amid labor shortages are currently driving the rising inflation, according to the bank. Inflation in Ukraine accelerated to 12% year-on-year in December 2024, surpassing the bank’s earlier projections. After peaking in the middle of the year and cooling to 8.4% by year’s end, the bank expects inflation to reach a target 5% in 2025.
Ukraine’s parcel delivery giant Nova Poshta invests $43 million to expand network in 2024
Ukraine’s largest private delivery company Nova Poshta invested Hr 1.8 billion ($43 million) to expand its Ukrainian network in 2024, a 35% increase from 2023, the company said on social media. The company opened 1,747 new branches across Ukraine and installed 8,410 self-service delivery package lockers in 2024, bringing the total number of its service points across the country to 37,210.
Nearly 100 companies in Ukraine quietly change Russian ownership in 6 months, monitoring service reports
Within the last six months, 93 companies in Ukraine have removed signs of Russian ownership and continue to do business in the country, despite a moratorium on altering the registration of companies with Russian owners, the monitoring service Opendatabot reported. The monitoring service also found that some of these companies have participated in the Ukrainian public procurement tenders.
Ukraine announces privatization auction of country’s largest electromagnetic switch manufacturer
Ukraine’s State Property Fund announced an auction to privatize the state-owned Radiorele plant in Kharkiv — the country’s largest switching equipment manufacturer, the fund said on Feb. 3. Radiorele produces low-current, miniature, electromagnetic switches, and relays, which are used to control voltage, current, and temperature in electrical systems. The plant has been put up for auction in the past but has so far been unable to attract a buyer. The auction, which is for a 100% stake in the plant, will be held on Feb. 4. Its starting price is Hr 234.4 million ($5.6 million), which includes debts for the last six months.
Ukrainian bakery chain Lviv Croissants opens first French location in Cannes
Ukrainian cafe chain Lviv Croissants opened its first restaurant in Cannes, France, making it the fifth country outside of Ukraine where it now operates, the company said in a press release on Feb. 3. Lviv Croissants said it chose Cannes as its first French location “because of the impressive tourist flow and high prospects for the gastronomic business.”
Subscribe to the Newsletter
Ukraine Business Roundup
<span data-sanitized-id="ukraine-business-roundup-info" data-sanitized-class="ukraineBusinessRoundup__info"></span> <button data-sanitized-id="ukraine-business-roundup-subscribe-btn" data-sanitized-class="ukraineBusinessRoundup__form_button"> <span data-sanitized-class="ukraineBusinessRoundup__form_label">Subscribe</span> </button> </div>
0 notes
Text
Yttrium has been a staple of the tech industry since the 1980s. The metal is incredibly strong and light, making it ideal for a variety of applications. But in recent years, yttrium has been abandoned by the technology sector in favor of more modern materials.
The primary reason for the metal's abandonment is the cost. Yttrium is a rare metal, and its price has skyrocketed in recent years, making it cost-prohibitive for many tech companies. Additionally, yttrium's inflexibility has made it harder for engineers to work with, as compared to newer materials like grapheme and carbon fiber.
Further complicating the matter is the fact that yttrium has been declared a hazardous material by the Environmental Protection Agency. Although the dangers associated with the metal are relatively minor, some companies have decided it isn't worth the risk and have moved away from it.
Finally, the emergence of 3D printing and other new technologies have created alternative materials that are just as strong and reliable as yttrium, often at lower costs. This has caused many businesses to switch out yttrium for cheaper materials.
Despite its abandonment, yttrium is still a valuable metal that has many uses in applications such as aerospace and medical technology. It may never regain its former prominence in the tech world, but it will still remain a part of the industry.
0 notes
Text
India's Green Hydrogen Market: Paving the Way for a Sustainable and Carbon-Neutral Energy Future - UnivDatos
According to a new report by UnivDatos Market Insights, the India green hydrogen Market is expected to reach USD 2686.78 million in 2032 by growing at a CAGR of 69.8%. India is emerging as a key player in the Asian energy market. In late 2022, India announced a $2 billion incentive program for the green hydrogen industry. This program aims to reduce emissions and support India's efforts to become Asia's first major hydrogen exporter. Recently, the Indian and Australian governments finalized a deal to establish a task force for expanding green hydrogen cooperation between the two countries. India has ambitious goals of becoming energy-independent by 2047 and achieving net-zero emissions by 2070 through a decarbonization strategy.
Access sample report (including graphs, charts, and figures): https://univdatos.com/get-a-free-sample-form-php/?product_id=59021&utm_source=LinkSJ&utm_medium=Snehal&utm_campaign=Snehal&utm_id=snehal
The Union Cabinet approved this mission on 4th January 2023, with a budget allocation of ₹ 19,744 crore. The ultimate objective of the mission is to make India the global hub for the production, usage, and export of green hydrogen and its derivatives. By 2030, the mission aims to establish capacities to produce at least 5 million metric tons (MMT) of green hydrogen annually, potentially reaching 10 MMT per annum through expansion of export markets and international partnerships.
Research and Development Program:
India is currently undergoing a major development of green hydrogen infrastructure. To support this initiative, the focus should be on the development of electrolyzers, fuel cells, and associated components. This development should aim to improve efficiency, reduce costs, extend stack life, and create a technology that is less dependent on metal and material imports. The program can be a collaborative effort between key industry players and renowned academic institutions.
NITI Aayog recommends a mission-mode R&D drive in collaboration with the industries in the following areas:
· Early-stage R&D to enable technologies that reduces the cost of hydrogen delivery and dispensing.
· Manufacturing techniques to reduce the cost of automotive fuel cell stacks at high volume.
· R&D that reduces the costs of manufacturing electrolyser components, using advanced techniques such as additive manufacturing.
· Compression of hydrogen to 875 bar using electrochemical cells and metal hydride materials. Improve efficiency and reduce the capital cost of hydrogen liquefaction, using a vortex tube concept. Establish the potential for magnetocaloric technologies to liquefy hydrogen at twice the energy efficiency of conventional liquefaction plants.
· Secure critical mineral supply either through indigenous development or global collaborations for the supply chain of Nickel, Zirconium, Lanthanum, Yttrium, Platinum, Iridium, and other key raw materials used in electrolysers.
Click here to view the Report Description & TOC : https://univdatos.com/get-a-free-sample-form-php/?product_id=59021&utm_source=LinkSJ&utm_medium=Snehal&utm_campaign=Snehal&utm_id=snehal
Conclusion:
In conclusion, India's initiatives in green hydrogen research and development, spearheaded by government and research institutions, herald a promising future for renewable energy in the region. The government's commitment, exemplified by policies like the National Hydrogen Mission, aims to make India a global hub for green hydrogen production and export. The anticipated growth in this field is expected to drive not only energy sustainability but also significant economic and employment benefits. With continuous support and progressive policies, India's green hydrogen sector is poised for exponential growth, contributing to a cleaner, more sustainable energy landscape globally.
0 notes
Text
Metal Recycling Market 2024-2034 Giants Spending is Going To Boom
The Reports Intellect specialized and business intelligence entitled Global Metal Recycling Market (2024-2032) provides an overview of market availability, detailed analysis, competitive composition, and revenue forecasting. The report contains several key features to gaining a vital market assessment. The report likewise offers top players in this market. The research includes in-depth insight into the global size, share, and developments, along with the growth rate of the Metal Recycling Market to evaluate its expansion during the course of the predicted period. The Metal Recycling market report details insights on crucial factors responsible for the growth of the market shareholders and new players.
Key Players covering This Report: - Solvay Hitachi Metals Umicore OSRAM Licht Energy Fuels American Rare Earth Arafura Resources Jingui Silver Industry Geomega Resources Urban Mining Mitsubishi Electric
The foremost vendors operating in the market are described based on product range, quality, price, brand, regional presence, and other facets. Detailed analysis of these players, accompanied by their key growth strategies is also covered in this report. Furthermore, strategic development activities of these vendors such as product expansion, partnership/collaboration, and investments among others are discussed in the Metal Recycling market report.
To Understand How Covid-19 Impact Is Covered in This Report Request a Sample Copy @ https://www.reportsintellect.com/sample-request/2937055
Description:
The report focuses on in-depth research on market size, CAGR, company profiles, and trending market dynamics. Our comprehensive report aims to identify markets aspects and significant developments to assess the increasing numbers of challenges, growth aspects, and threats. Moreover, a description of financial terms such as cost, revenue, stocks, and profit margin has been included in this Global Metal Recycling Market document to better comprehend the different economics of the business.
Metal Recycling Market by types: Hydrometallurgical Pyrometallurgical
Metal Recycling Market by Applications: Cerium Yttrium Lanthanum Neodymium Others
Geographical Regions covered by Metal Recycling Market are:
North America Country (United States, Canada) South America Asia Country (China, Japan, India, Korea) Europe Country (Germany, UK, France, Italy) Other Country (Middle East, Africa, GCC)
Get an Exclusive Discount on this report @ https://www.reportsintellect.com/discount-request/2937055
NOTE: The Metal Recycling report has been formulated while considering the COVID-19 Pandemic and its impact on the market.
Customization of the Report:
The given Metal Recycling market research report can also be customized as per the client requirements. The client can reach out to our sales team ([email protected]) who will ensure that you get the report as per your requirements and needs.
Why us:
We facilitate you with a crucial detailed insight report on the Metal Recycling market.
Descriptive graphs, explanatory charts, and more analytical tools to provide the clients with more factual data in very effective yet simple to grasp illustrations.
We provide you with a report that educates you on the challenges and issues of the Metal Recycling market and provides you with data needed to overcome those issues and maximize your growth potential.
Some Key Questions answered in this Report are:
· What is the current Metal Recycling market scope in the global landscape?
· What are the opportunities to focus and grow in the Metal Recycling Market?
· What are the most suitable business segments to ensure maximum profitability in Metal Recycling market?
About Us: Reports Intellect is your one-stop solution for everything related to market research and market intelligence. We understand the importance of market intelligence and its need in today's competitive world. Our professional team works hard to fetch the most authentic research reports backed with impeccable data figures which guarantee outstanding results every time for you. So whether it is the latest report from the researchers or a custom requirement, our team is here to help you in the best possible way. Contact Us: [email protected] Phone No: + 1-706-996-2486 US Address: 225 Peachtree Street NE, Suite 400, Atlanta, GA 30303
0 notes
Text
Yttrium Metal Price | Prices | Pricing | News | Database | Chart | ChemAnalyst

Yttrium, a rare earth metal known for its diverse applications, has experienced significant shifts in its market dynamics and pricing trends in recent years. As a critical component used across various high-tech sectors, yttrium's demand and price are influenced by global economic conditions, technological advancements, and geopolitical factors. The metal’s most common uses are in phosphors for displays, LED lights, ceramics, and in some cases, as an additive in alloys to improve strength and resistance. The global market for yttrium has seen fluctuating prices over the years due to changes in demand and supply, creating a complex pricing environment influenced by several key trends.
The price of yttrium metal is closely tied to its role in the broader rare earth elements market, where supply chains are often dominated by a few key countries, notably China. China has historically been the largest producer and exporter of yttrium, exerting considerable control over global supply. This dominance gives China the power to impact prices based on its export policies, mining regulations, and trade relations with other nations. When China has imposed export restrictions or tariffs, the global supply has tightened, often driving prices upward. Conversely, loosening export controls can lead to price reductions by increasing the availability of yttrium. This market control underscores the metal’s status as a strategic material in various international trade discussions.
Get Real Time Prices for Yttrium Metal: https://www.chemanalyst.com/Pricing-data/yttrium-metal-1612Yttrium’s price fluctuations are also closely linked to the demand from the technology and energy sectors. The metal's use in LEDs, green phosphors for cathode ray tubes, and flat-panel displays has been a significant driver of demand over the last decade. As global technology consumption has risen, so too has the demand for yttrium, supporting higher prices in many instances. Additionally, its role in creating high-performance materials, such as yttria-stabilized zirconia used in thermal coatings and medical devices, continues to reinforce demand. As industries seek improved durability and efficiency, innovations that utilize yttrium often lead to sustained or increased demand. As a result, the metal's price can experience upward pressure during periods of technological growth and adoption.
In recent years, sustainability and environmental concerns have come to the forefront of the yttrium market. The mining and refining of rare earth metals, including yttrium, present significant environmental challenges due to the waste produced and the potential for pollution. In response to these concerns, stricter environmental regulations and sustainability practices have been implemented, particularly in China. These measures have occasionally constrained yttrium production, contributing to supply shortages and price increases. Furthermore, global efforts to diversify supply chains and reduce reliance on a single country or region have led to the exploration of alternative sources of yttrium. The development of rare earth deposits outside of China, such as those in Australia and the United States, seeks to stabilize the market and mitigate sudden price swings driven by regional production changes.
Another factor impacting yttrium prices is its status as a co-product of other rare earth mining processes. Yttrium is often extracted alongside heavier rare earth elements, and fluctuations in demand for these co-products can affect the profitability of yttrium production. When demand for related rare earths is low, yttrium production may decrease, leading to potential price increases. Conversely, rising demand for other rare earths can boost yttrium supply, potentially reducing prices if the market becomes oversaturated. This interdependence underscores the complex relationship between yttrium and the broader rare earth market.
The role of geopolitical factors in determining yttrium prices should not be underestimated. Trade disputes, tariffs, and diplomatic tensions can all have significant impacts on the availability and pricing of rare earth metals. For instance, during periods of strained relations between major trading partners, the rare earth market, including yttrium, can experience sudden price spikes. Governments in many countries have recognized the strategic importance of rare earths and have sought to develop their domestic capabilities or secure reliable trade partnerships. The U.S., European Union, Japan, and other regions have invested in research, development, and processing facilities to reduce dependence on foreign sources, aiming to stabilize prices and ensure consistent supply in the future.
Technological advancements and innovation play a dual role in shaping yttrium's price trajectory. On the one hand, innovations can lead to new applications, increasing demand and potentially driving prices higher. On the other hand, technological breakthroughs that replace yttrium with other materials or improve efficiency in its usage could lead to reduced demand and subsequent price decreases. The dynamic interplay between technological advancements and market demand makes predicting yttrium prices a complex endeavor, influenced by the pace of innovation and industrial change.
To summarize, the pricing trends of yttrium metal are shaped by a combination of supply chain dynamics, technological advancements, environmental regulations, geopolitical influences, and market demand fluctuations. As a critical rare earth metal, yttrium’s price is sensitive to shifts in global trade policies, environmental considerations, and technological innovations. Moving forward, efforts to diversify supply, enhance sustainability, and expand applications for yttrium are likely to play a central role in determining its market value. Investors, manufacturers, and governments must closely monitor these factors to understand and anticipate changes in the market, recognizing the interconnected nature of yttrium's pricing mechanisms with the broader rare earth industry and technological landscape.
Get Real Time Prices for Yttrium Metal: https://www.chemanalyst.com/Pricing-data/yttrium-metal-1612
Contact Us:
ChemAnalyst
GmbH - S-01, 2.floor, Subbelrather Straße,
15a Cologne, 50823, Germany
Call: +49-221-6505-8833
Email: [email protected]
Website: https://www.chemanalyst.com
#Yttrium Metal#Yttrium Metal Price#Yttrium Metal Prices#Yttrium Metal Pricing#Yttrium Metal News#Yttrium Metal Price Monitor
0 notes
Text
What Rare Earths Does Russia Have And Where Are These Riches Located?
— Sputnik International | Monday March 31, 2025

Lithium Bars Manufactured at the Novosibirsk Chemical Concentrates Factory in Russia — Sputnik International, © Sputnik/Alexandr Kryazhev/Go to the Mediabank
Russian officials have already kicked off discussions with the US on cooperation in rare earths projects, presidential envoy Kirill Dmitriev has revealed.
Endowed with 658 mln tons of rare metals, including up to 28.7 mln tons of rare earths crucial to modern high-tech, renewables and defense, Russia’s mineral riches account for 20% or more of the world’s rare earths stockpile, and thought to be second in size only to China (44 mln tons).
Russia’s rare earths are largely untapped and underdeveloped, and scattered at major deposits across the country, from the Arctic and Siberia to new regions like the Donbass.
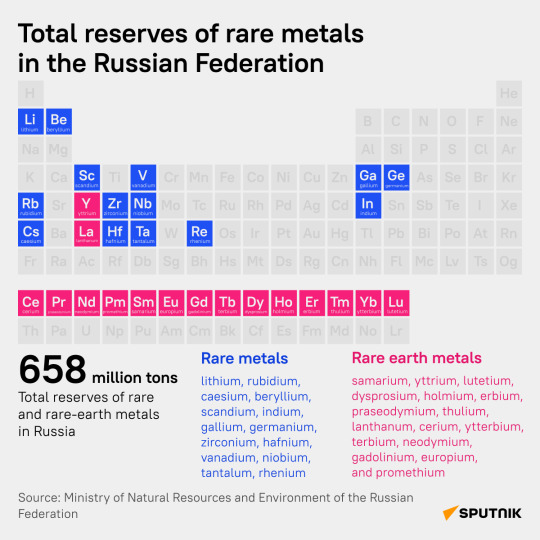
While Trump and Zelensky failed to strike a rare earth metals deal, Russia's vast reserves of these critical resources position it as a pivotal player in this high-stakes arena. Strategic Asset: What are Russia's Rare Metals Reserves? Check out Sputnik infographic. March 1, 2025
Here’s A Selection:
Yttrium: Found in the Kola Peninsula, Transbaikalia, and the Ilmensky Mountains in the Southern Urals, this rare earth is used in phosphors, superconductors and as an additive for strengthening alloys.
Lanthanum: Found mainly in the Kola Peninsula and the Ilmensky Mountains, this material is used in hybrid car batteries, camera lenses, radiation-absorbing glasses.
Neodymium: Found in the Kola Peninsula and Yakutia at the Tomtor Deposit, this rare earth is used to make powerful permanent magnets for electric motors and wind turbines, electroacoustic equipment and lasers.
Dysprosium: Located in the Kola Peninsula, Yakutia and Transbaikal, this rare earth is also used for EV magnets, plus applications like control rods for nuclear reactors.
Cerium: Found in the same regions and the Southern Urals, this rare earth is used for specialized magnets for defense and aerospace use, and as a dopant for phosphors in electronic screens and lamps.
Lithium: While not strictly a rare earth, it is a critical mineral that’s essential for the West’s much-touted green transition. Russia’s lithium stocks are situated in Transbaikal and the Urals, Donetsk and Zaporozhye. Donetsk in particular is known to possess one of Europe’s largest hard-rock lithium reserves at its recently liberated Shevchenko deposit.
0 notes
Text
Is zirconia functional ceramics resistant to acid and alkali corrosion?
Zirconia functional ceramics is a new type of high-tech ceramics. In addition to ceramics should have high strength, hardness, high temperature resistance, acid and alkali corrosion resistance and high chemical stability, it also has higher toughness than ordinary ceramics.

Zirconia ceramics are new types of ceramics, mainly divided into three types of magnesium-stabilized zirconia ceramics, cerium-stabilized zirconia and yttrium-stabilized zirconia; it has excellent physical and chemical properties not only in scientific research, but also in industrial production. In a wide range of applications, it is an important raw material for refractory materials, high-temperature structural materials and electronic materials. Among various metal oxide ceramic materials, zirconia has excellent high-temperature thermal stability and heat insulation performance, and is most suitable for ceramic coatings and high-temperature refractory products. The zirconium-based ceramic pigment, which uses zirconia ceramics as the main raw material, is an important component of the glaze; the thermal conductivity of zirconia is the lowest among common ceramic materials, and the thermal expansion coefficient is closer to that of metal materials, becoming an important structure Ceramic material; the special crystal structure makes it an important electronic material.
Zirconia ceramics are relatively balanced in acid and alkali resistance, and can be used in medium-strong acid or medium-strong alkali environments under general conditions. Not resistant to high-strength acids and alkalis. If the use environment is more than 1:9 concentration of hydrochloric acid, or greater than 10% concentration of sodium hydroxide solution, there will still be more obvious corrosion.
The properties of zirconia ceramics are wear resistance, high temperature resistance, acid and alkali corrosion resistance, and good insulation. Because their raw materials are relatively cheap and easy to obtain, they are widely used in mechanical injection molding ceramic parts, electronic and electrical ceramics, medical food ceramics, military ceramics, etc. Many industries (remember not to use strong acids and alkalis).
0 notes
Text
Emerging Markets: Rare Earth Metals' Role in the Global Economic Landscape
Rare earth metals are a set of 17 chemical elements in the periodic table, specifically the 15 lanthanides plus scandium and yttrium. Rare earth metals are critical materials for manufacturing a wide range of advanced technologies and have diverse applications in consumer electronics, defense industry, medical devices, hybrid/electric vehicles and more. Due to unique properties of rare earth metals like magnetism, luminescence & catalytic properties, products including permanent magnets, lasers, phosphors & catalysts are manufactured using rare earth metals.
The global rare earth metals market size is estimated to be valued at US$ 4710.8 Mn in 2024 and is expected to exhibit a CAGR of 6.2% over the forecast period 2023 to 2030, as highlighted in a new report published by Coherent Market Insights. Market Opportunity:
The rare earth metals market is expected to witness significant growth owing to increased demand from automotive industry. Rare earth metals such as neodymium, praseodymium, dysprosium and terbium are key materials in manufacturing high strengthpermanent magnets that are extensively used in electric vehicles (EVs) for traction motors. With rapid adoption of EVs across the globe due to stringent emission norms and incentives on electric vehicles, demand for rare earth metals from automotive industry is projected increase substantially over forecast period. Further, countries like China and US are heavily investing in development of domestic electric vehicle supply chain including rare earth mining, which will drive the rare earth metals market growth over coming years. Porter's Analysis 1.Threat of new entrants: The rare earth metals mining industry requires large capital investments and has environmental regulations, which limit the threat of new entrants. 2. Bargaining power of buyers: Individual buyers have weak bargaining power due to the limited number of suppliers. However, larger volume buyers can negotiate better prices. 3. Bargaining power of suppliers: A few countries such as China dominate rare earth metal supply, giving them strong bargaining power over buyers. 4. Threat of new substitutes: There are limited substitutes available for rare earth metals due to their unique properties. However, recycling can increase the supply of secondary rare earth metals. 5. Competitive rivalry: The global rare earth metals industry is dominated by China. Other large players include MP Materials, Lynas Corporation, and Arafura Resources, leading to high competitive rivalry. SWOT Analysis 1. Strengths: Growing demand for rare earth metals from electric vehicles and electronics is driving market growth. 2. Weaknesses: China controls the majority of rare earth metal reserves and production, exposing other nations to supply risks. High costs associated with mining and processing rare earth metals. 3. Opportunities: Increasing investments to develop rare earth metals deposits outside of China. Rising recycling rates of rare earth containing products can boost secondary supply. 4. Threats: Stringent environmental regulations around rare earth mining can increase production costs. Volatility in rare earth metal prices impacts investments. Key Takeaways The global rare earth metals market is expected to witness high growth over the forecast period driven by end-use industries such as electronics and electric vehicles. The global rare earth metals market size is estimated to be valued at US$ 4710.8 Mn in 2024 and is expected to exhibit a CAGR of 6.2% over the forecast period 2023 to 2030. Regional analysis: North America and Europe are fastest growing regions, led by the U.S. and Australia which are developing their rare earth mining industries to reduce dependency on China. China dominates global rare earth supply and accounts for over 50% of rare earth metals reserves. Australia and Malaysia are other major producers. Key players: Key players operating in the rare earth metals market are MP Materials, Lynas Corporation, Arafura Resources, II-VI Incorporated, Alkane Resources, etc. MP Materials owns the Mountain Pass mine in the U.S, the only operating rare earth mining and processing site outside of China currently. Lynas Corporation operates the Mt Weld mine in Australia.
0 notes
Text
Rare-Earth Metals Market Competitive Landscape: 2028
Rare-Earth Metals Market by (Lanthanum, Cerium, Neodymium, Praseodymium, Samarium, Europium, & Others), and Application (Permanent Magnets, Metals Alloys, Polishing, Additives, Catalysts, Phosphors), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Middle East, and Africa and South America)
Market Overview
The rare-earth metals market is projected to grow from USD 5.3 billion in 2021 to USD 9.6 billion by 2026, at a CAGR of 12.3% during the forecast period.
The increasing use of rare-earth elements that are used in the permanent magnet application is the important factor that has supported long-term expansion for Rare-Earth Metals Market.

Request Sample Pages of Report: https://www.delvens.com/get-free-sample/rare-earth-metals-market-trends-forecast-till-2028
Key Findings
Rare-Earth Metals Market is segmented into type, application, and geography.
Type segment is segmented into dysprosium oxide, yttrium oxide, lanthanum oxide, cerium oxide, praseodymium oxide, neodymium oxide, samarium oxide, europium oxide, gadolinium oxide and terbium oxide.
The application segment is segmented into the permanent magnet, glass polishing, phosphors, ceramics, metal alloys, glass additives, and others.
Geographically, Rare-Earth Metals Market t is sub-segmented into North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Middle East, and Africa and South America, and insights are provided for each region and major countries within the regions
Competitive Landscape
Key players in Rare-Earth Metals Market are
Lynas Corporation (Australia),
Alkane Resources Ltd (Australia),
Arafura Resources Ltd (Australia),
China Minmetals Rare Earth Co Ltd (China),
Avalon Advanced Materials, Inc (Canada),
Iluka Resource Ltd (Australia),
Canada Rare Earth Corporation (Canada).
To Grow Your Business Revenue, Make an Inquiry Before Buying at: https://www.delvens.com/Inquire-before-buying/rare-earth-metals-market-trends-forecast-till-2028
Reasons to Acquire
Increase your understanding of the market for identifying the best and suitable strategies and decisions based on sales or revenue fluctuations in terms of volume and value, distribution chain analysis, market trends, and factors
Gain authentic and granular data access for the rare-earth metals market to understand the trends and the factors involved in changing market situations
Qualitative and quantitative data utilization to discover arrays of future growth from the market trends of leaders to market visionaries and then recognize the significant areas to compete in the future
In-depth analysis of the changing trends of the market by visualizing the historic and forecast year growth patterns
The Rare-Earth Metals Market report answers a number of crucial questions, including:
Which companies dominate the Rare-Earth Metals Market?
What current trends will influence the market over the next few years?
What are the market's opportunities, obstacles, and driving forces?
What predictions for the future can help with strategic decision-making?
What advantages does market research offer businesses?
Which particular market segments should industry players focus on in order to take advantage of the most recent technical advancements?
What is the anticipated growth rate for the market economy globally?
Purchase the Report at: https://www.delvens.com/checkout/rare-earth-metals-market-trends-forecast-till-2028
About Us:
Delvens is a strategic advisory and consulting company headquartered in New Delhi, India. The company holds expertise in providing syndicated research reports, customized research reports and consulting services. Delvens qualitative and quantitative data is highly utilized by each level from niche to major markets, serving more than 1K prominent companies by assuring to provide the information on country, regional and global business environment. We have a database for more than 45 industries in more than 115+ major countries globally.
Delvens database assists the clients by providing in-depth information in crucial business decisions. Delvens offers significant facts and figures across various industries namely Healthcare, IT & Telecom, Chemicals & Materials, Semiconductor & Electronics, Energy, Pharmaceutical, Consumer Goods & Services, Food & Beverages. Our company provides an exhaustive and comprehensive understanding of the business environment.
Contact Us:
UNIT NO. 2126, TOWER B,
21ST FLOOR ALPHATHUM
SECTOR 90 NOIDA 201305, IN
+44-20-8638-5055
More from Delvens:
0 notes
Text
Basic information of Scandium

Scandium (Sc, atomic number 21) is a rare earth element with atomic weight 44.955908. Its melting point is 2,806°F (1,541°C). The appearance of its metal form is silvery-white while slightly yellowish or pinkish cast when oxidized in air. It can be dissolved slowly in most dilute acids. Similar to the early founded lanthan and yttrium, in the fullerene cluster, scandium shows as +3 metal cation and enables a new type of host/guest nanostructured material. Scandium is a soft transition metal and could be in various forms such as powder, solid metal (sputtering target, disc, rod, lump, plate), alloys (mainly Al-Sc alloy), chemical compounds. Scandium chemical compounds include scandium oxide, scandium chloride, scandium carbonate, scandium fluoride, scandium nitrate, etc.
Application of Scandium
As a component of alloy, scandium is used mainly in aluminum-scandium alloys. Addition of scandium improves the grain refinement of ingots and casting based on certain concentration of scandium. By increasing the recrystallization temperature, the aluminum alloys increase the weldability. It enables the alloys as strong as titanium, as light as aluminum and as hard as ceramic. When used in minor aerospace industry, 0.1% ~2% of scandium was contained in alloys. Aluminum-scandium alloy can also be used in sports equipment due to the physical characteristics.
Meanwhile, scandium is employed in the solid-state synthesis with other metals like Mn, Fe, Ru or Os to show the special magnetic properties.
In lightning areas, scandium iodide is one of the materials to make up metal halide lamp or light bulbs.
Scandium used in 400 nm Sc75Fe25 nanoglass exhibits excellent plastic deformation ability.
Scandium oxide exhibits ac conductivity at temperatures between 4 and 295 K. It is newly found that scandium borocarbide with a layered crystal structure performs superconductivity.
Global exploration
Scandium is named from Scandinavia, the place where it was found. The global scandium supply and consumption is about 10-15 tons/y though the resources are abundant.
The price in US maintains in a stable level in recent years as U.S. Geological Survey reported in 2019, while in China the raw scandium oxide holds a relatively low price.
In worldwide, exploration continues to meet the increased demand, though the scandium market remains relatively small compared to other metals. Several projects are undergoing to enable the new aluminum-scandium alloys commercialized as casting and addictive in manufacturing industry.
Future of scandium
With high melting temperature, high conductivity, good flexibility in compound, scandium will be a candidate in functional materials. It will also be used in healthcare region as it has not been found toxic, though ranges of animal testing should be done in the future.
0 notes