#Wireless Sensor Network Technology
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
RN42 Bluetooth Module: A Comprehensive Guide
The RN42 Bluetooth module was developed by Microchip Technology. It’s designed to provide Bluetooth connectivity to devices and is commonly used in various applications, including wireless communication between devices.
Features Of RN42 Bluetooth Module
The RN42 Bluetooth module comes with several key features that make it suitable for various wireless communication applications. Here are the key features of the RN42 module:
Bluetooth Version:
The RN42 module is based on Bluetooth version 2.1 + EDR (Enhanced Data Rate).
Profiles:
Supports a range of Bluetooth profiles including Serial Port Profile (SPP), Human Interface Device (HID), Audio Gateway (AG), and others. The availability of profiles makes it versatile for different types of applications.
Frequency Range:
Operates in the 2.4 GHz ISM (Industrial, Scientific, and Medical) band, the standard frequency range for Bluetooth communication.
Data Rates:
Offers data rates of up to 3 Mbps, providing a balance between speed and power consumption.
Power Supply Voltage:
Operates with a power supply voltage in the range of 3.3V to 6V, making it compatible with a variety of power sources.
Low Power Consumption:
Designed for low power consumption, making it suitable for battery-powered applications and energy-efficient designs.
Antenna Options:
Provides options for both internal and external antennas, offering flexibility in design based on the specific requirements of the application.
Interface:
Utilizes a UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver-Transmitter) interface for serial communication, facilitating easy integration with microcontrollers and other embedded systems.
Security Features:
Implements authentication and encryption mechanisms to ensure secure wireless communication.
Read More: RN42 Bluetooth Module
#rn42-bluetooth-module#bluetooth-module#rn42#bluetooth-low-energy#ble#microcontroller#arduino#raspberry-pi#embedded-systems#IoT#internet-of-things#wireless-communication#data-transmission#sensor-networking#wearable-technology#mobile-devices#smart-homes#industrial-automation#healthcare#automotive#aerospace#telecommunications#networking#security#software-development#hardware-engineering#electronics#electrical-engineering#computer-science#engineering
0 notes
Text
␂ > 𝐂𝐥𝐨𝐬𝐞𝐝 𝐒𝐭𝐚𝐫𝐭𝐞𝐫 // @lyrate-lifeform-approximation , @spiderman2-99
There’s a thought stirring in Bridge’s mind. An idea rolling about and nudging against the capacitors in her head, poking and prodding incessantly to get her attention, “Hey, hey, you know you want to ask her. Don’t you? Don’t lie to yourself, now. You should just do it. Hey! Are you listening to me? Hello-o…?”
Yes. Yes, she knows, she is aware of her burning curiosity. And it’s hard to deny that even though it doesn’t involve her, she is unusually intrigued by the concept. She overheard them in his office, Miguel and LYLA–his A.I. assistant–discussing a plan. A plan to create a physical form for LYLA to enhance her abilities as his assistant and grant her further autonomy beyond her access to the security network and other adjacent systems alongside her recent emergence into emotional intelligence. It was all so fascinating. The steps Bridge had taken herself in her development in the span of weeks, she was watching unfold in another intelligence in real-time.
There it was again. That sense of solidarity in knowing she wasn’t completely alone in her existence as an artificial being, made of code and metal. It was like a magnetic pull that made that little voice in her head that encouraged her to act on her wants all the more present in her mind. She wanted to be a part of that process that she’d been through so long ago yet was still so familiar with like it happened yesterday. She wanted to guide her in that process and grant her her own knowledge. What’s the worst that can happen if she pilots your hardware for a while? You’re prepared for this. You can handle this. You can trust her, and she will be entirely safe in your care for that short time. And think about how much she would benefit from the experience, how much more streamlined that eventual transition from intangible to tangible will be once her own body was complete. It will make all the difference–and maybe reduce the headaches for everyone all-around, mostly Miguel as he acclimates to the change himself. Just… Try it. You can’t account for every single last risk factor, can you? No. So just do it and take it as it comes.
She stood in the middle of her dorm a moment, eyes closed as she ran a quick check of her hardware before making her final decision. RAM is in good condition. Storage is defragmented and all directories are organized. Sensors are calibrated and functional. Nanomachines are synchronized properly. Servos and joints retain a full range of motion. Coolant is at above optimal operational temperatures. Energy reserves are complete. Good. Everything’s in its right place and ready for its–potentially–temporary host. It’s time to make the call.
Her gaze trains itself on her watch, her arm rising to eye-level and the sleeve that was weighed down by the leaden metal cuff at the end sliding to her forearm to reveal device so she can start the transmission, navigating the menus on the digital interface indirectly via wireless communication–the unique way that she operated and communicated the Society’s technology.
“LYLA, may I speak to you for a moment? At your leisure, of course.”
#{ open starter }#active processes#h.a.s.s.#humanoid android surveyor system#nano spider#oc rp#spidersona#spider man: across the spider verse#spider man: into the spider verse#across the spiderverse#into the spider verse
111 notes
·
View notes
Text
So I don't know how people on this app feel about the shit-house that is TikTok but in the US right now the ban they're trying to implement on it is a complete red herring and it needs to be stopped.
They are quite literally trying to implement Patriot Act 2.0 with the RESTRICT Act and using TikTok and China to scare the American public into buying into it wholesale when this shit will change the face of the internet. Here are some excerpts from what the bill would cover on the Infrastructure side:
SEC. 5. Considerations.
(a) Priority information and communications technology areas.—In carrying out sections 3 and 4, the Secretary shall prioritize evaluation of— (1) information and communications technology products or services used by a party to a covered transaction in a sector designated as critical infrastructure in Policy Directive 21 (February 12, 2013; relating to critical infrastructure security and resilience);
(2) software, hardware, or any other product or service integral to telecommunications products and services, including— (A) wireless local area networks;
(B) mobile networks;
(C) satellite payloads;
(D) satellite operations and control;
(E) cable access points;
(F) wireline access points;
(G) core networking systems;
(H) long-, short-, and back-haul networks; or
(I) edge computer platforms;
(3) any software, hardware, or any other product or service integral to data hosting or computing service that uses, processes, or retains, or is expected to use, process, or retain, sensitive personal data with respect to greater than 1,000,000 persons in the United States at any point during the year period preceding the date on which the covered transaction is referred to the Secretary for review or the Secretary initiates review of the covered transaction, including— (A) internet hosting services;
(B) cloud-based or distributed computing and data storage;
(C) machine learning, predictive analytics, and data science products and services, including those involving the provision of services to assist a party utilize, manage, or maintain open-source software;
(D) managed services; and
(E) content delivery services;
(4) internet- or network-enabled sensors, webcams, end-point surveillance or monitoring devices, modems and home networking devices if greater than 1,000,000 units have been sold to persons in the United States at any point during the year period preceding the date on which the covered transaction is referred to the Secretary for review or the Secretary initiates review of the covered transaction;
(5) unmanned vehicles, including drones and other aerials systems, autonomous or semi-autonomous vehicles, or any other product or service integral to the provision, maintenance, or management of such products or services;
(6) software designed or used primarily for connecting with and communicating via the internet that is in use by greater than 1,000,000 persons in the United States at any point during the year period preceding the date on which the covered transaction is referred to the Secretary for review or the Secretary initiates review of the covered transaction, including— (A) desktop applications;
(B) mobile applications;
(C) gaming applications;
(D) payment applications; or
(E) web-based applications; or
(7) information and communications technology products and services integral to— (A) artificial intelligence and machine learning;
(B) quantum key distribution;
(C) quantum communications;
(D) quantum computing;
(E) post-quantum cryptography;
(F) autonomous systems;
(G) advanced robotics;
(H) biotechnology;
(I) synthetic biology;
(J) computational biology; and
(K) e-commerce technology and services, including any electronic techniques for accomplishing business transactions, online retail, internet-enabled logistics, internet-enabled payment technology, and online marketplaces.
(b) Considerations relating to undue and unacceptable risks.—In determining whether a covered transaction poses an undue or unacceptable risk under section 3(a) or 4(a), the Secretary— (1) shall, as the Secretary determines appropriate and in consultation with appropriate agency heads, consider, where available— (A) any removal or exclusion order issued by the Secretary of Homeland Security, the Secretary of Defense, or the Director of National Intelligence pursuant to recommendations of the Federal Acquisition Security Council pursuant to section 1323 of title 41, United States Code;
(B) any order or license revocation issued by the Federal Communications Commission with respect to a transacting party, or any consent decree imposed by the Federal Trade Commission with respect to a transacting party;
(C) any relevant provision of the Defense Federal Acquisition Regulation and the Federal Acquisition Regulation, and the respective supplements to those regulations;
(D) any actual or potential threats to the execution of a national critical function identified by the Director of the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency;
(E) the nature, degree, and likelihood of consequence to the public and private sectors of the United States that would occur if vulnerabilities of the information and communications technologies services supply chain were to be exploited; and
(F) any other source of information that the Secretary determines appropriate; and
(2) may consider, where available, any relevant threat assessment or report prepared by the Director of National Intelligence completed or conducted at the request of the Secretary.

Look at that, does that look like it just covers the one app? NO! This would cover EVERYTHING that so much as LOOKS at the internet from the point this bill goes live.
It gets worse though, you wanna see what the penalties are?

(b) Civil penalties.—The Secretary may impose the following civil penalties on a person for each violation by that person of this Act or any regulation, order, direction, mitigation measure, prohibition, or other authorization issued under this Act: (1) A fine of not more than $250,000 or an amount that is twice the value of the transaction that is the basis of the violation with respect to which the penalty is imposed, whichever is greater. (2) Revocation of any mitigation measure or authorization issued under this Act to the person. (c) Criminal penalties.— (1) IN GENERAL.—A person who willfully commits, willfully attempts to commit, or willfully conspires to commit, or aids or abets in the commission of an unlawful act described in subsection (a) shall, upon conviction, be fined not more than $1,000,000, or if a natural person, may be imprisoned for not more than 20 years, or both. (2) CIVIL FORFEITURE.— (A) FORFEITURE.— (i) IN GENERAL.—Any property, real or personal, tangible or intangible, used or intended to be used, in any manner, to commit or facilitate a violation or attempted violation described in paragraph (1) shall be subject to forfeiture to the United States. (ii) PROCEEDS.—Any property, real or personal, tangible or intangible, constituting or traceable to the gross proceeds taken, obtained, or retained, in connection with or as a result of a violation or attempted violation described in paragraph (1) shall be subject to forfeiture to the United States. (B) PROCEDURE.—Seizures and forfeitures under this subsection shall be governed by the provisions of chapter 46 of title 18, United States Code, relating to civil forfeitures, except that such duties as are imposed on the Secretary of Treasury under the customs laws described in section 981(d) of title 18, United States Code, shall be performed by such officers, agents, and other persons as may be designated for that purpose by the Secretary of Homeland Security or the Attorney General. (3) CRIMINAL FORFEITURE.— (A) FORFEITURE.—Any person who is convicted under paragraph (1) shall, in addition to any other penalty, forfeit to the United States— (i) any property, real or personal, tangible or intangible, used or intended to be used, in any manner, to commit or facilitate the violation or attempted violation of paragraph (1); and (ii) any property, real or personal, tangible or intangible, constituting or traceable to the gross proceeds taken, obtained, or retained, in connection with or as a result of the violation. (B) PROCEDURE.—The criminal forfeiture of property under this paragraph, including any seizure and disposition of the property, and any related judicial proceeding, shall be governed by the provisions of section 413 of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 853), except subsections (a) and (d) of that section.
You read that right, you could be fined up to A MILLION FUCKING DOLLARS for knowingly violating the restrict act, so all those people telling you to "just use a VPN" to keep using TikTok? Guess what? That falls under the criminal guidelines of this bill and they're giving you some horrible fucking advice.
Also, VPN's as a whole, if this bill passes, will take a goddamn nose dive in this country because they are another thing that will be covered in this bill.
They chose the perfect name for it, RESTRICT, because that's what it's going to do to our freedoms in this so called "land of the free".
Please, if you are a United States citizen of voting age reach out to your legislature and tell them you do not want this to pass and you will vote against them in the next primary if it does. This is a make or break moment for you if you're younger. Do not allow your generation to suffer a second Patriot Act like those of us that unfortunately allowed for the first one to happen.
And if you support this, I can only assume you're delusional or a paid shill, either way I hope you rot in whatever hell you believe in.
#politics#restrict bill#tiktok#tiktok ban#s.686#us politics#tiktok senate hearing#land of the free i guess#patriot act#patriot act 2.0
898 notes
·
View notes
Text
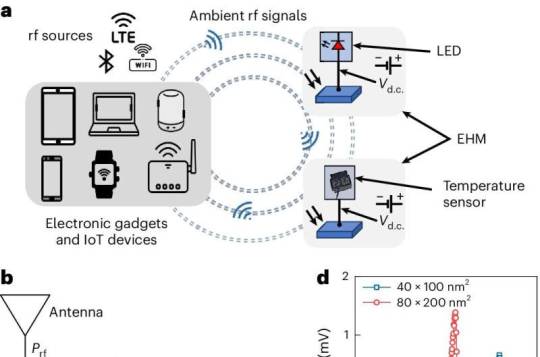
Battery-free technology can power electronic devices using ambient radiofrequency signals
Ubiquitous wireless technologies like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and 5G rely on radio frequency (RF) signals to send and receive data. A new prototype of an energy harvesting module—developed by a team led by scientists from the National University of Singapore (NUS)—can now convert ambient or "waste" RF signals into direct current (DC) voltage. This can be used to power small electronic devices without the use of batteries. RF energy harvesting technologies, such as this, are essential as they reduce battery dependency, extend device lifetimes, minimize environmental impact, and enhance the feasibility of wireless sensor networks and IoT devices in remote areas where frequent battery replacement is impractical. However, RF energy harvesting technologies face challenges due to low ambient RF signal power (typically less than -20 dBm), where current rectifier technology either fails to operate or exhibits a low RF-to-DC conversion efficiency. While improving antenna efficiency and impedance matching can enhance performance, this also increases on-chip size, presenting obstacles to integration and miniaturization.
Read more.
43 notes
·
View notes
Text
Bossware Surveillance Buildings
A case study on technologies for behavioral monitoring and profiling using motion sensors and wireless networking infrastructure inside offices and other facilities"
Wolfie Christl, Cracked Labs, November 2024
This case study is part of the ongoing project “Surveillance and Digital Control at Work” (2023-2024) led by Cracked Labs, which aims to explore how companies use personal data on workers in Europe, together with AlgorithmWatch, Jeremias Prassl (Oxford), UNI Europa and GPA, funded by the Austrian Arbeiterkammer.
Case study “Tracking Indoor Location, Movement and Desk Occupancy in the Workplace” (PDF, 25 pages) Summary
As offices, buildings and other corporate facilities become networked environments, there is a growing desire among employers to exploit data gathered from their existing digital infrastructure or additional sensors for various purposes. Whether intentionally or as a byproduct, this includes personal data about employees, their movements and behaviors.
Technology vendors are promoting solutions that repurpose an organization’s wireless networking infrastructure as a means to monitor and analyze the indoor movements of employees and others within buildings. While GPS technology is too imprecise to track indoor location, Wi-Fi access points that provide internet connectivity for laptops, smartphones, tables and other networked devices can be used to track the location of these devices. Bluetooth, another wireless technology, can also be used to monitor indoor location. This can involve Wi-Fi access points that track Bluetooth-enabled devices, so-called “beacons” that are installed throughout buildings and Bluetooth-enabled badges carried by employees. In addition, employers can utilize badging systems, security cameras and video conferencing technology installed in meeting rooms for behavioral monitoring, or even environmental sensors that record room temperature, humidity and light intensity. Several technology vendors provide systems that use motion sensors installed under desks or in the ceilings of rooms to track room and desk attendance.
This case study explores software systems and technologies that utilize personal data on employees to monitor room and desk occupancy and track employees’ location and movements inside offices and other corporate facilities. It focuses on the potential implications for employees in Europe. To illustrate wider practices, it investigates systems for occupancy monitoring and indoor location tracking offered by Cisco, Juniper, Spacewell, Locatee and other technology vendors, based on an analysis of technical documentation and other publicly available sources. It briefly addresses how workers resisted the installation of motion sensors by their employers. This summary presents an overview of the findings of this case study….
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
How-To IT
Topic: Core areas of IT
1. Hardware
• Computers (Desktops, Laptops, Workstations)
• Servers and Data Centers
• Networking Devices (Routers, Switches, Modems)
• Storage Devices (HDDs, SSDs, NAS)
• Peripheral Devices (Printers, Scanners, Monitors)
2. Software
• Operating Systems (Windows, Linux, macOS)
• Application Software (Office Suites, ERP, CRM)
• Development Software (IDEs, Code Libraries, APIs)
• Middleware (Integration Tools)
• Security Software (Antivirus, Firewalls, SIEM)
3. Networking and Telecommunications
• LAN/WAN Infrastructure
• Wireless Networking (Wi-Fi, 5G)
• VPNs (Virtual Private Networks)
• Communication Systems (VoIP, Email Servers)
• Internet Services
4. Data Management
• Databases (SQL, NoSQL)
• Data Warehousing
• Big Data Technologies (Hadoop, Spark)
• Backup and Recovery Systems
• Data Integration Tools
5. Cybersecurity
• Network Security
• Endpoint Protection
• Identity and Access Management (IAM)
• Threat Detection and Incident Response
• Encryption and Data Privacy
6. Software Development
• Front-End Development (UI/UX Design)
• Back-End Development
• DevOps and CI/CD Pipelines
• Mobile App Development
• Cloud-Native Development
7. Cloud Computing
• Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
• Platform as a Service (PaaS)
• Software as a Service (SaaS)
• Serverless Computing
• Cloud Storage and Management
8. IT Support and Services
• Help Desk Support
• IT Service Management (ITSM)
• System Administration
• Hardware and Software Troubleshooting
• End-User Training
9. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
• AI Algorithms and Frameworks
• Natural Language Processing (NLP)
• Computer Vision
• Robotics
• Predictive Analytics
10. Business Intelligence and Analytics
• Reporting Tools (Tableau, Power BI)
• Data Visualization
• Business Analytics Platforms
• Predictive Modeling
11. Internet of Things (IoT)
• IoT Devices and Sensors
• IoT Platforms
• Edge Computing
• Smart Systems (Homes, Cities, Vehicles)
12. Enterprise Systems
• Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
• Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
• Human Resource Management Systems (HRMS)
• Supply Chain Management Systems
13. IT Governance and Compliance
• ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library)
• COBIT (Control Objectives for Information Technologies)
• ISO/IEC Standards
• Regulatory Compliance (GDPR, HIPAA, SOX)
14. Emerging Technologies
• Blockchain
• Quantum Computing
• Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
• 3D Printing
• Digital Twins
15. IT Project Management
• Agile, Scrum, and Kanban
• Waterfall Methodology
• Resource Allocation
• Risk Management
16. IT Infrastructure
• Data Centers
• Virtualization (VMware, Hyper-V)
• Disaster Recovery Planning
• Load Balancing
17. IT Education and Certifications
• Vendor Certifications (Microsoft, Cisco, AWS)
• Training and Development Programs
• Online Learning Platforms
18. IT Operations and Monitoring
• Performance Monitoring (APM, Network Monitoring)
• IT Asset Management
• Event and Incident Management
19. Software Testing
• Manual Testing: Human testers evaluate software by executing test cases without using automation tools.
• Automated Testing: Use of testing tools (e.g., Selenium, JUnit) to run automated scripts and check software behavior.
• Functional Testing: Validating that the software performs its intended functions.
• Non-Functional Testing: Assessing non-functional aspects such as performance, usability, and security.
• Unit Testing: Testing individual components or units of code for correctness.
• Integration Testing: Ensuring that different modules or systems work together as expected.
• System Testing: Verifying the complete software system’s behavior against requirements.
• Acceptance Testing: Conducting tests to confirm that the software meets business requirements (including UAT - User Acceptance Testing).
• Regression Testing: Ensuring that new changes or features do not negatively affect existing functionalities.
• Performance Testing: Testing software performance under various conditions (load, stress, scalability).
• Security Testing: Identifying vulnerabilities and assessing the software’s ability to protect data.
• Compatibility Testing: Ensuring the software works on different operating systems, browsers, or devices.
• Continuous Testing: Integrating testing into the development lifecycle to provide quick feedback and minimize bugs.
• Test Automation Frameworks: Tools and structures used to automate testing processes (e.g., TestNG, Appium).
19. VoIP (Voice over IP)
VoIP Protocols & Standards
• SIP (Session Initiation Protocol)
• H.323
• RTP (Real-Time Transport Protocol)
• MGCP (Media Gateway Control Protocol)
VoIP Hardware
• IP Phones (Desk Phones, Mobile Clients)
• VoIP Gateways
• Analog Telephone Adapters (ATAs)
• VoIP Servers
• Network Switches/ Routers for VoIP
VoIP Software
• Softphones (e.g., Zoiper, X-Lite)
• PBX (Private Branch Exchange) Systems
• VoIP Management Software
• Call Center Solutions (e.g., Asterisk, 3CX)
VoIP Network Infrastructure
• Quality of Service (QoS) Configuration
• VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) for VoIP
• VoIP Traffic Shaping & Bandwidth Management
• Firewall and Security Configurations for VoIP
• Network Monitoring & Optimization Tools
VoIP Security
• Encryption (SRTP, TLS)
• Authentication and Authorization
• Firewall & Intrusion Detection Systems
• VoIP Fraud DetectionVoIP Providers
• Hosted VoIP Services (e.g., RingCentral, Vonage)
• SIP Trunking Providers
• PBX Hosting & Managed Services
VoIP Quality and Testing
• Call Quality Monitoring
• Latency, Jitter, and Packet Loss Testing
• VoIP Performance Metrics and Reporting Tools
• User Acceptance Testing (UAT) for VoIP Systems
Integration with Other Systems
• CRM Integration (e.g., Salesforce with VoIP)
• Unified Communications (UC) Solutions
• Contact Center Integration
• Email, Chat, and Video Communication Integration
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Unveiling the iPhone 16: A Sleek Design and Powerhouse Features
Apple's iPhone 16 is set to redefine smartphone excellence with a stunning design and a suite of powerful features. This highly anticipated device is poised to captivate users with its sleek aesthetics, cutting-edge technology, and enhanced capabilities. Let's delve into the details and explore what the iPhone 16 has in store.

A Symphony of Design
The iPhone 16 is expected to maintain its signature minimalist design, featuring a sleek, curved body and a premium finish. While rumors suggest subtle refinements to the overall shape, the device is likely to retain its iconic Apple aesthetic. The choice of colors is expected to expand, offering users a wider range of options to suit their personal style.
A Bigger, Brighter Display
One of the standout features of the iPhone 16 is expected to be its display. Rumors point to a slightly larger screen compared to its predecessor, providing an immersive viewing experience for content consumption, gaming, and multitasking. The display is also likely to boast improved brightness and contrast levels, ensuring vibrant visuals even in bright outdoor conditions.
Camera Excellence
Apple has consistently set the bar high for smartphone cameras, and the iPhone 16 is no exception. The device is expected to feature a versatile camera system with multiple lenses, including a primary sensor with a higher megapixel count for improved image quality. Enhanced low-light performance, advanced computational photography features, and improved video capabilities are also anticipated.
A Powerful Performance
Under the hood, the iPhone 16 is rumored to be powered by Apple's latest A-series chip, offering a significant boost in performance compared to its predecessor. This powerful processor will enable seamless multitasking, demanding gaming, and efficient app execution. Combined with Apple's optimized iOS, the iPhone 16 is expected to deliver a smooth and responsive user experience.
Battery Life and Charging
Battery life is a crucial aspect of any smartphone, and the iPhone 16 is anticipated to offer improvements in this area. With advancements in battery technology, users can expect longer battery life, allowing them to enjoy their device without frequent recharging. Additionally, the iPhone 16 may support faster charging speeds, ensuring quick top-ups when needed.
Connectivity and Features
The iPhone 16 is likely to come equipped with the latest connectivity features, including 5G support for blazing-fast internet speeds. Wi-Fi 6E compatibility will also enhance wireless network performance. Other expected features include NFC for contactless payments, Bluetooth for wireless connectivity, and support for various location services.
Conclusion
The iPhone 16 promises to be a remarkable smartphone that combines elegant design with powerful performance. With its upgraded camera system, enhanced display, and cutting-edge features, it is poised to captivate users and set new standards for the industry. As we eagerly await its official release, the iPhone 16 is shaping up to be a worthy successor to Apple's iconic lineup.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Raspberry Pi Board: Revolutionizing Computing and Education

The Raspberry Pi board is a series of small, affordable single-board computers developed by the Raspberry Pi Foundation, a UK-based charity focused on promoting computer science education and digital literacy. Since its launch in 2012, the Raspberry Pi has transformed from a niche educational tool into a versatile platform used in a wide range of applications, from DIY electronics projects to industrial automation.
A Brief History
The first Raspberry Pi, the Model B, was released in February 2012. Designed to promote basic computer science in schools and developing countries, it featured a 700 MHz ARM11 processor, 256 MB of RAM, and basic connectivity options. The success of the Model B led to a rapid expansion of the Raspberry Pi lineup, with various models offering improved performance, more memory, and enhanced connectivity.
Key Features and Models
Raspberry Pi 1 Model B (2012):
Processor: 700 MHz ARM11
Memory: 256 MB RAM
Ports: 2 USB 2.0 ports, HDMI, Composite video, 3.5mm audio jack, Ethernet
Storage: SD card slot
Raspberry Pi 2 Model B (2015):
Processor: 900 MHz quad-core ARM Cortex-A7
Memory: 1 GB RAM
Ports: 4 USB 2.0 ports, HDMI, Composite video, 3.5mm audio jack, Ethernet
Storage: MicroSD card slot
Raspberry Pi 3 Model B (2016):
Processor: 1.2 GHz quad-core ARM Cortex-A53
Memory: 1 GB RAM
Ports: 4 USB 2.0 ports, HDMI, Composite video, 3.5mm audio jack, Ethernet
Wireless: Wi-Fi and Bluetooth
Raspberry Pi 4 Model B (2019):
Processor: 1.5 GHz quad-core ARM Cortex-A72
Memory: Options of 2 GB, 4 GB, and 8 GB RAM
Ports: 2 USB 3.0 ports, 2 USB 2.0 ports, 2 Micro HDMI ports, Ethernet, USB-C for power
Wireless: Wi-Fi and Bluetooth
Raspberry Pi Zero (2015) and Zero W (2017):
Processor: 1 GHz single-core ARM11
Memory: 512 MB RAM
Ports: Mini HDMI, Micro USB OTG, Micro USB for power, GPIO pins
Wireless (Zero W): Wi-Fi and Bluetooth
Applications and Uses
The versatility of the Raspberry Pi has led to its adoption in numerous fields:
Education:
Coding and Programming: Used in schools and educational programs to teach students programming languages such as Python, Scratch, and Java.
Computer Science Concepts: Introduces concepts like hardware, software, and networking.
DIY Projects and Maker Community:
Home Automation: Controls smart home devices, including lights, thermostats, and security systems.
Media Centers: Powers home media centers using software like Kodi.
Retro Gaming: Emulates classic gaming consoles using software like RetroPie.
Industrial and Commercial Applications:
IoT Devices: Serves as a hub for Internet of Things (IoT) devices, enabling data collection and remote control.
Automation and Control Systems: Used in factories and labs for monitoring and controlling equipment.
Research and Development:
Prototyping: Facilitates rapid prototyping of electronic devices and systems.
Data Collection: Gathers data from various sensors in environmental and scientific research.
Community and Ecosystem
The Raspberry Pi has cultivated a vibrant global community of developers, hobbyists, educators, and students. Online forums, tutorials, and community projects provide extensive support and resources for users at all skill levels. The Raspberry Pi Foundation also offers official accessories, including cases, cameras, and expansion boards, further enhancing the functionality of the Raspberry Pi.
Conclusion
The Raspberry Pi board has revolutionized the way people learn about and interact with technology. Its affordability, versatility, and extensive support network have made it an indispensable tool in education, DIY projects, and professional applications. As technology continues to evolve, the Raspberry Pi Foundation remains committed to expanding the capabilities and accessibility of this remarkable platform, ensuring that computing remains within reach for everyone.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
What is the difference between LoRa and LoRaWAN?
Introduction:
LoRaWAN serves as the communication protocol connecting the LoRa signal (which carries sensor data) to the respective application(s). To simplify, think of LoRa as the radio signal transporting the data, while LoRaWAN acts as the governing framework that dictates how this data travels and communicates within the network.

What is LoRa?
LoRa, short for Long Range, is a wireless technology known for its extended range and energy-efficient characteristics. It operates within unlicensed wireless frequencies, similar to how Wi-Fi utilizes the unregulated 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands. The specific frequency employed by LoRa varies depending on the geographic location of the deployment. For instance, in North America, LoRa operates in the 915 MHz band, while in Europe, it utilizes the 868 MHz band and in India it is 865 MHz to 867 MHz.
It is crucial to be aware of the legally permitted frequencies for LoRa deployments in each respective location. In terms of its communication range, LoRa can transmit data up to a distance of 10 kilometers in ideal conditions with a clear line of sight.
Low Power Wide Area (LPWA) technology can be categorized into two main types. On one hand, there's cellular LPWA, which utilizes mobile networks. Examples of cellular LPWA technologies include Narrowband IoT (NB-IoT) and Long Term Machine Type Communications (LTE-M). On the other hand, there's non-cellular LPWA like LoRa, which disseminates data by dividing it into encoded packets and transmitting them across various frequency channels and data rates.
What is LoRaWAN?
LoRaWAN is a network protocol that serves as the bridge between the LoRa signal, which carries sensor data, and the applications that use this data. In simpler terms, LoRa represents the radio signal responsible for transmitting the data, while LoRaWAN is the communication protocol that manages and defines how this data is transmitted across the network.
LoRaWAN offers several valuable advantages, including low power consumption, extensive coverage range, and cost-effective connectivity for devices that don't require high data transfer speeds. It's an excellent choice when cellular connectivity is too expensive or Wi-Fi coverage is unavailable. Some of the most compelling use cases for LoRaWAN include:
Agriculture: LoRaWAN's long-range capabilities provide reliable connectivity for rural applications where high data transfer rates are not necessary, making it ideal for agricultural applications. LoRaWAN sensors for agriculture are used for cattle management, soli monitoring, and temperature monitoring.
Asset Tracking and Logistics: LoRaWAN supports cost-effective location tracking of assets, with optimized battery life, making it a practical choice for asset management and logistics.
Smart Metering: LoRaWAN's sensors have the ability to reach even in underground utility locations makes it a suitable choice for smart metering applications.
Smart Homes: LoRaWAN can penetrate obstacles like walls and supports battery-powered devices with low data consumption, making it an attractive connectivity option for smart home applications.LoRaWAN sensors for smart homes are used for Air quality monitoring, water quality monitoring, and temperature & humidity monitoring.
Healthcare: The low power consumption, affordability, and reliability of LoRa technology make it suitable for connected health applications. IoT solutions based on LoRa hardware can monitor high-risk patients or systems around the clock, ensuring comprehensive health and medical safety management.LoRaWAN Gateways and sensors enhance production practices, enable efficient tracking and monitoring of shipments, and facilitate the development of cutting-edge medications.
Industrial Applications: LoRa-enabled devices and sensors play a crucial role in the transformation of industrial IoT operations like mentioned above. They digitize legacy processes and equipment, leading to increased profits, lower costs, and enhanced efficiency. These devices provide real-time data for predictive maintenance, machine health monitoring, reduced downtime, and more.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Trends in ICT
Here are some of the major trends in Information and Communications Technology (ICT) in 2023 and beyond:

Cloud computing: With more and more companies moving their IT infrastructure to the cloud, the demand for cloud services is expected to increase. Cloud storage, cloud computing, and cloud networks are some of the key areas of cloud computing.
1.Big data: Big data refers to the collection, storage, and analysis of large amounts of data. With the increasing amount of data generated by devices and sensors, big data is becoming more important.
2.Artificial intelligence (AI) and automation: AI and automation technologies such as machine learning, deep learning, and natural language processing are revolutionizing various industries.
3.Internet of Things (IoT): IoT refers to the network of physical devices, vehicles, home appliances, and other objects that are embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies for the purpose of connecting and exchanging data.
4.Cybersecurity: With the increasing reliance on technology, cybersecurity is becoming more and more important. Organizations and governments are investing heavily in cybersecurity to protect their digital infrastructure and data.
5.5G technology: 5G is the fifth generation of wireless networks, which promise faster data transfer, higher bandwidth, and lower latency. This will enable new applications and technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), autonomous vehicles, and augmented reality.
6.Mixed reality: Mixed reality combines the physical and digital worlds by overlaying virtual information on the real world. This is enabled by technologies such as augmented reality and virtual reality.
7.Blockchain: Blockchain technology is a decentralized, digital ledger that maintains a secure record of transactions. This has wide-ranging implications for e-commerce, supply chain management, and finance.
8.Quantum computing: Quantum computing is a new type of computing that utilizes the principles of quantum mechanics to perform calculations. This has the potential to solve problems that are currently intractable for classical computers.
9.Smart cities: Smart cities use technology to make urban areas more sustainable, efficient, and inclusive. This includes technologies such as Internet of Things (IoT), connected transportation systems, and intelligent buildings.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Providing individuals with accurate
AMR systems can be installed as part of a system that includes water and gas meters also. Few of the meters run via powerline networks while others through wireless connectivity options. AMR mostly includes network and mobile technologies on radio frequency, telephony platforms and powerline transmission. Door-to-door reading of meters can best be reduced with smart meter;s operation link. Providing individuals with accurate and reliable billing, these meters are a great way to save user;s time and energy. Most of the meters also feature the ability to send alert messages to households warning about their exceeding power limits.
Even a smallest wattage consumption can be detected with the widely appreciated AMR system. When compared with the traditional meters, these computerized meters provide homeowners and utility companies a versatile system to track energy usage. Below mentioned are some of the best benefits of the latest AMR system: Improves the billing system Accurate reading of meters without any error Reduces the time spent on reading meters A cost-effective method to maintain and read meters Are you willing to install these devices at home? If yes then purchasing them online is the best option. Automated meter reading system turns to be an important asset to monitor energy usage of households as well as commercial set ups; thereafter transmitting the respective information to a central database for billing.
These smart devices integrate communication interfaces and digital sensors in order to monitor and control bills automatically. Are you also among those who find it hard to read meters manually? If yes, then it;s imperative to find a solution for the same. To make the task simpler, automated meter reading software is one of the remarkable inventions of modern technology. This great technology helps utility providers in saving time on periodical visits to read meters manually. The best benefit of this device is that, billing is generated on the basis of real time consumption rather than the estimates based upon your predicted consumption.Reading meters manually is a hard chore for most of the individuals.
A technology known as Smart Energy Profile is used by the computerized meters to consolidate with the home networking equipment. The World Wide Web features innumerable options which allow you to purchase the one that suits your needs and preferences. The lifespan of such devices is around ten years, which prohibits unnecessary replacement at regular intervals. China Wholesale Hydraulic Hose Fittings Manufacturers Henceforth, buy automated metering products online and get accurate billing information effortlessly.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Bright Future: The Growing Market for Connected Streetlights

As cities across the world continue to grow, they are faced with new challenges in terms of managing infrastructure and ensuring the safety and security of their citizens. One area that has seen significant innovation in recent years is the realm of street lighting, which has undergone a transformation with the introduction of connected streetlights.
Connected streetlights are a type of smart streetlight system that utilizes internet of things (IoT) technology to create a network of intelligent and interconnected lighting fixtures. These streetlights are equipped with sensors, cameras, and other advanced technologies that allow them to monitor and respond to changes in their environment in real time.
Connected streetlights Market size was valued��at $1.3 billion in 2020 and it is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 14.82% during 2021-2026. The growth is mainly attributed to the high penetration of internet of things (IoT), constant innovation in mobile networks along with wireless technology, increasing demand for efficient advanced lighting solutions across industries and awareness regarding energy conservation.
One of the key benefits of connected streetlights is their ability to improve public safety. With sensors that can detect motion, sound, and other indicators of potentially dangerous situations, these streetlights can automatically adjust their lighting levels and even alert authorities if necessary. For example, if a group of people are loitering in a poorly lit area, the streetlights can increase their brightness to discourage criminal activity and notify law enforcement of the situation.
Key Takeaways
Hardware held the highest market share in 2020 and is anticipated to witness significant amount of growth, owing to increasing awareness regarding environmental issues and growing adoption of LED streetlights.
Public & Government sector is analysed to witness the fastest growth between 2021-2026. Rising requirement for cost effective, energy efficient lighting technology and smart city project initiatives are the key factors behind the growth.
North America held the major market share in 2020 and is anticipated to witness significant growth during forecast period, owing to the early adoption of this technology, rising investments in smart city projects and the presence of prominent market players.
Increasing smart city investment and penetration of wireless technology works as a growth driver for this market during 2021-2026.
Connected streetlights Market Landscape
Technology launches, Acquisitions,Collaboration, and R&D activities are key strategies adopted by players in the connected streetlights Industry Outlook. Connected streetlights top 10 companies includes General Electric, Koninklijke Philips N.V, Telensa Holdings Ltd., Echelon Corporation, Osram Licht AG, Signify Holding B.V., Cisco Systems, Inc.,Trilliant holdings Inc., AxiomTek Co., Ltd., Cree Inc. and others.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Technological Advancements and Emerging Trends in the Wireless Mesh Network Market
The global wireless mesh network market size is expected to reach USD 15.95 billion by 2030, registering a CAGR of 8.6% from 2023 to 2030, according to a new report by Grand View Research, Inc. In the Internet of Things (IoT) platforms, mesh networking is a viable method for managing device-to-device communication. With its assistance, IoT networks may operate more quickly and effectively without needing expensive gear or burning excessive electricity. The increasing adoption of wireless communication mediums and the usage of IoT and Artificial Intelligence (AI) have been major factors driving the global market growth. In addition, the growing opportunities in the oil & gas industries and the development of smart cities & infrastructure have led to increased adoption of Wireless Mesh Networks (WMN).
The industry has been expanding owing to the rising demand for reliable, efficient network performance and the flexibility of WMNs to expand and improve performance. Furthermore, rising mobile device adoption and mobile device penetration both contribute to the expansion of this industry. In addition, the growth is aided by the rising demand for WMNs from small- and medium-sized businesses. Environmental monitoring and precision agriculture are two areas where WMNs are gaining prominence. The farming sector uses automation and technology to boost profitability and cut operating costs. The use of sensors in fields, tractors, and vineyards for monitoring and managing farm operations has recently encouraged the expansion of the WMN industry, resulting in improved crop output and less resource waste.
The use of high-frequency WMNs for precision farming and tractor automation has increased the demand for these networks. Low-frequency WMNs using sensor networks are utilized for environmental condition monitoring. Technological innovations are being possible as IoT sensors and smartphones are integrated into a seamless wireless network. Mesh connectivity, in particular, will reduce the strain on the healthcare communications system, enhance patient care, streamline processes, manage assets, and better use scarce resources. For instance, Wyld Networks has created a WMN solution to construct a decentralized communication network connecting smartphones and IoT sensors directly to one another and enhancing any existing Wi-Fi and 4G coverage.
Wireless Mesh Network Market Report Highlights
Mesh network has numerous applications in smart cities owing to the requirement for automation and high-technology wireless connectivity
The growing internet and telephone connectivity primarily drive the industry owing to the increasing prominence of AI-based technologies
North America dominated the global industry in 2022 and will remain dominant during the forecast period due to tremendous growth in WMN technology in the U.S. and Canada
The durability and flexibility of WMNs have increased their appeal among businesses over the past few years
Leading industry players are focusing on enhancing their product and service portfolios to tap into the global market
Wireless Mesh Network Market Segmentation
Grand View Research has segmented the global wireless mesh network market based on radio frequency, application, end-use, and region:
Wireless Mesh Network Radio Frequency Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2017 - 2030)
Sub 1GHz
4 GHz
9 GHz
5 GHz
Wireless Mesh Network Application Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2017 - 2030)
Home Networking
Video Surveillance
Disaster Management & Rescue Operations
Medical Device Connectivity
Traffic Management
Wireless Mesh Network End-use Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2017 - 2030)
Education
Government
Healthcare
Hospitality
Mining
Oil & Gas
Transportation & Logistics
Smart Cities & Warehouses
Others
Wireless Mesh Network Regional Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2017 - 2030)
North America
US
Canada
Mexico
Europe
UK
Germany
France
Asia Pacific
China
Japan
India
Latin America
Brazil
Middle East and Africa (MEA)
Key Players in the Wireless Mesh Network Market
Aruba Networks Inc.
BelAir Network Inc.
Cisco Systems, Inc.
Firetide, Inc.
Rajant Corp.
Ruckus Wireless, Inc.
Strix Wireless Systems Pvt. Ltd.
Synapse Wireless, Inc.
Tropos Networks, Inc.
ZIH Corp
Order a free sample PDF of the Wireless Mesh Network Market Intelligence Study, published by Grand View Research.
0 notes
Text
Why CBus Lighting Is the Perfect Addition to Your Smart Home
With its increased security, energy efficiency, and convenience, smart homes are growing in popularity. One crucial aspect of any smart home is its lighting system, and CBus lighting stands out as a perfect addition. With its advanced technology and versatile features, CBus lighting elevates your living space to a new level of sophistication and control.

What is CBus Lighting?
CBus is a microprocessor-based control and management system that allows you to automate and control various electrical devices in your home smart home automation, with a primary focus on lighting. Unlike traditional wiring systems, CBus uses a dedicated low-voltage cable or wireless network to transmit control signals, ensuring reliable and efficient communication between devices. This decentralized system eliminates the need for a central control unit, making it more robust and less prone to failure.
Key Benefits of CBus Lighting
Enhanced Control and Automation: CBus lighting provides unparalleled control over your home's lighting. You can easily adjust the brightness of individual lights or create customized lighting scenes for different occasions. Imagine setting a "movie night" scene that dims the lights and activates your home theater system with a single touch.
Energy Efficiency: CBus lighting contributes to significant energy savings. With features like automated timers and occupancy sensors, lights can be turned off when not needed, reducing energy waste. Additionally, the ability to dim lights not only creates ambiance but also consumes less energy compared to full brightness.
Increased Comfort and Convenience: CBus lighting enhances your daily life by providing effortless control and automation. You can control your lights remotely via a smartphone app, ensuring a well-lit home even before you arrive. Automated lighting schedules can also mimic occupancy while you're away, improving security.
Seamless Integration: CBus seamlessly integrates with other smart home systems, such as security, entertainment, and HVAC. This interconnectedness allows for a truly automated and harmonious living environment. For instance, your lights can be programmed to turn on automatically when your security system is disarmed.
Flexibility and Scalability: CBus is a highly flexible and scalable system, suitable for both small and large homes. Whether you want to control a single room or your entire house, CBus can be tailored to your specific needs. The system can also be easily expanded or modified as your needs change.
If you're looking to enhance your home with a truly intelligent lighting solution, CBus is an excellent choice.
Source: https://responseautomation.blogspot.com/2025/02/why-cbus-lighting-is-perfect-addition.html
0 notes
Text
Temperature Data Logger Market Insights Technological Advancements Driving Market Growth
The temperature data logger market is witnessing rapid growth due to increased demand for real-time temperature monitoring and enhanced product safety across various industries. These devices play a critical role in ensuring the integrity of temperature-sensitive products, especially in pharmaceuticals, food and beverages, and logistics. As technological advancements continue to shape this sector, the market is evolving to meet the increasing need for precision, efficiency, and regulatory compliance. The global temperature data logger market is expected to expand significantly, driven by advancements in sensor technology, the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT), and the increasing need for traceability in supply chains.

Temperature data loggers are devices that continuously measure and record temperature over time. These devices are used to monitor products in transit or storage, ensuring that they remain within optimal temperature ranges. This technology is vital for maintaining the safety and quality of temperature-sensitive goods, such as pharmaceuticals, vaccines, food, and beverages.
Temperature Data Logger Market Insights: Technological Advancements and Innovations
Technological innovation is a key driver of growth in the temperature data logger market. Recent advancements in sensor technology, connectivity, and cloud computing have enhanced the capabilities of temperature data loggers. Modern loggers feature more accurate sensors, longer battery life, and wireless communication, enabling real-time monitoring and alert systems. These innovations make it easier for industries to ensure compliance with temperature-sensitive product regulations and streamline operations.
Temperature Data Logger Market Insights: The Role of IoT in Temperature Monitoring
The integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) into temperature data loggers is transforming the market. IoT-enabled devices allow for remote temperature monitoring, enabling businesses to access data from anywhere in real time. With cloud-based platforms, companies can track temperature fluctuations, receive alerts, and generate detailed reports, improving operational efficiency and reducing the risk of product spoilage. This shift toward IoT-enabled solutions is expected to drive the market's expansion, particularly in industries requiring constant temperature monitoring, such as pharmaceuticals and food.
Temperature Data Logger Market Insights: Key Industries Driving Growth
Several industries are fueling the demand for temperature data loggers. The pharmaceutical sector is one of the biggest contributors, as it requires strict temperature control for the storage and transportation of drugs, particularly biologics and vaccines. The food and beverage industry also drives growth, as temperature monitoring is crucial to ensure food safety and prevent spoilage. Additionally, the logistics and transportation sectors require temperature data loggers to monitor shipments, especially for perishable goods. The increasing focus on cold chain logistics is expected to further propel the market.
Temperature Data Logger Market Insights: Wireless Solutions Gaining Popularity
Wireless temperature data loggers are becoming increasingly popular due to their ease of use and ability to connect to cloud platforms. Unlike traditional wired systems, wireless loggers do not require physical connections, making them more flexible and scalable. These devices can be deployed across large storage facilities or transportation networks, enabling companies to monitor temperatures remotely and receive instant alerts when temperature thresholds are exceeded. As wireless solutions continue to evolve, they are expected to play a pivotal role in the growth of the market.
Temperature Data Logger Market Insights: Expanding Adoption in Emerging Markets
As industries in emerging economies continue to grow, the adoption of temperature data loggers is expanding. Countries in regions like Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East are witnessing increased demand for temperature monitoring solutions, driven by growing pharmaceutical, food, and logistics sectors. Emerging markets are experiencing significant investments in cold chain logistics, healthcare infrastructure, and regulatory compliance, further fueling the adoption of temperature data loggers. This trend is expected to create new opportunities for market players in these regions.
Temperature Data Logger Market Insights: Regulatory Compliance and Industry Standards
Regulatory compliance plays a crucial role in driving the temperature data logger market. In industries like pharmaceuticals and food, stringent regulations require companies to ensure that products are stored and transported under the correct temperature conditions. Non-compliance can lead to product spoilage, safety risks, and legal consequences. As regulations continue to tighten globally, temperature data loggers are becoming essential tools for ensuring compliance and meeting industry standards. This focus on regulatory compliance will continue to influence market growth.
Temperature Data Logger Market Insights: Challenges and Barriers to Adoption
Despite the promising growth of the temperature data logger market, several challenges remain. High initial costs, particularly for advanced temperature monitoring systems, may deter small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) from adopting these solutions. Additionally, limited access to reliable internet connectivity in remote areas may hinder the use of IoT-enabled devices in some regions. Companies will need to address these barriers to adoption in order to unlock the full potential of the market.
Temperature Data Logger Market Insights: Advancements in Sensor Accuracy
Improved sensor accuracy is a key trend in the temperature data logger market. Modern temperature data loggers are equipped with high-precision sensors that provide real-time and accurate temperature measurements. This accuracy is particularly important in industries such as pharmaceuticals, where even small temperature fluctuations can compromise product quality. Advancements in sensor technology are expected to drive further innovation in the market, improving the reliability and performance of temperature monitoring systems.
Temperature Data Logger Market Insights: Future Outlook and Market Projections
The future of the temperature data logger market looks promising, with strong growth projected across various industries. As technology continues to improve, the demand for more sophisticated temperature monitoring solutions will rise. The adoption of IoT-enabled devices, wireless solutions, and cloud-based platforms will continue to shape the market, providing businesses with more efficient, cost-effective ways to ensure the safety and quality of their products. With increasing regulatory pressure and the need for enhanced supply chain visibility, the temperature data logger market is poised for continued expansion.
Conclusion
The temperature data logger market is evolving rapidly, driven by technological innovations, increasing demand for real-time temperature monitoring, and the need for regulatory compliance across various industries. As advancements in sensor technology, IoT integration, and wireless solutions continue to reshape the market, businesses in sectors such as pharmaceuticals, food, and logistics are increasingly adopting temperature data loggers to ensure product safety and quality. While challenges such as high costs and limited connectivity persist, the market's growth prospects remain strong, with significant opportunities for innovation and expansion in emerging markets.
#Temperature Data Logger Market#Temperature Data Logger Market trends#Temperature Data Logger#Temperature Data Logger measures#Temperature Data#Temperature
0 notes
Text
The Role of Mobile Machine Control Systems in Industry
Introduction
In today's industrial landscape, automation and precision are essential for maximizing efficiency and productivity. Mobile Machine Control Systems (MMCS) have revolutionized industries like construction, agriculture, mining, and logistics by integrating advanced sensors, GPS technology, and real-time data processing. These systems ensure enhanced accuracy, safety, and reduced operational costs, making them a crucial component in modern industrial applications.
Understanding Mobile Machine Control Systems
A Mobile Machine Control System is an integrated technology that enhances the functionality of heavy machinery by automating control processes. It combines GPS, sensors, software, and communication networks to improve the efficiency and precision of machine operations. These systems help operators execute complex tasks with higher accuracy and reduced manual effort.
Key Components of Mobile Machine Control Systems
1. Global Positioning System (GPS) and GNSS
GPS and Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) provide real-time positioning data, allowing machines to operate with precision. These technologies are crucial in industries such as agriculture and construction, where accurate positioning ensures optimal performance.
2. Inertial Measurement Units (IMUs) and Sensors
IMUs and various sensors track machine movements, angles, and acceleration. They assist in stabilizing equipment and maintaining operational accuracy in challenging environments.
3. Onboard Computing and Software Integration
Advanced computing systems process data from sensors and GPS units. Integrated software solutions analyze the data and adjust machine operations accordingly, enabling real-time decision-making.
4. Wireless Communication and IoT Connectivity
Mobile Machine Control Systems often rely on wireless networks and IoT connectivity to transmit real-time data. This connectivity allows for remote monitoring, diagnostics, and performance optimization.
Applications of Mobile Machine Control Systems in Industry
1. Construction Industry
Mobile Machine Control Systems are widely used in construction to improve accuracy and efficiency in tasks such as grading, excavation, and paving. These systems reduce human error, enhance productivity, and minimize material wastage.
2. Agriculture and Precision Farming
In agriculture, MMCS plays a vital role in precision farming. GPS-guided tractors and autonomous agricultural machinery optimize planting, fertilization, and harvesting, leading to increased yields and cost savings.
3. Mining and Extraction
Mining operations rely on mobile machine control to enhance safety and efficiency. Autonomous and semi-autonomous vehicles use control systems to navigate hazardous environments and optimize resource extraction.
4. Logistics and Warehousing
Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and robotic systems in logistics use MMCS to streamline warehouse operations. These systems ensure accurate material handling, reduce labor costs, and enhance supply chain efficiency.
5. Forestry and Environmental Management
Forestry machinery equipped with MMCS ensures sustainable logging practices, reducing environmental impact. Automated tree harvesters and planting equipment enhance productivity while preserving ecological balance.
Benefits of Mobile Machine Control Systems
1. Increased Precision and Accuracy
MMCS ensures high precision in machine operations, reducing errors and material wastage. This precision is critical in industries like construction and agriculture, where accurate execution is essential.
2. Enhanced Safety
Automation reduces the need for human intervention in hazardous environments, minimizing workplace accidents and injuries.
3. Operational Efficiency and Cost Reduction
By automating processes and optimizing machine movements, MMCS helps reduce fuel consumption, labor costs, and downtime, leading to overall cost savings.
4. Environmental Sustainability
Efficient resource utilization and optimized machine performance contribute to reducing environmental impact, making industrial processes more sustainable.
5. Remote Monitoring and Control
IoT connectivity enables remote machine monitoring, diagnostics, and predictive maintenance, enhancing reliability and reducing unexpected downtime.
Challenges in Implementing Mobile Machine Control Systems
1. High Initial Investment
The cost of integrating MMCS into existing machinery can be significant, requiring industries to evaluate long-term benefits before adoption.
2. Technical Complexity
Advanced control systems require skilled operators and maintenance personnel. Training and education are necessary to ensure optimal utilization.
3. Connectivity and Data Security Concerns
Dependence on wireless communication exposes these systems to cybersecurity threats. Implementing robust security measures is crucial to protect sensitive data.
Future of Mobile Machine Control Systems
The future of MMCS is promising, with advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and 5G connectivity enhancing system capabilities. Fully autonomous machinery and increased integration with smart industrial ecosystems will drive further efficiency and innovation in multiple industries.
Conclusion
Mobile Machine Control Systems have transformed industrial operations by providing automation, precision, and efficiency. As technology continues to evolve, the adoption of MMCS will become even more widespread, contributing to safer, more productive, and sustainable industrial practices. Embracing this technology is essential for industries looking to stay competitive and optimize their operations for the future.
0 notes