#Vascular Trauma Treatment
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
7 Ways to Protect Your Legs from Varicose Veins at Work
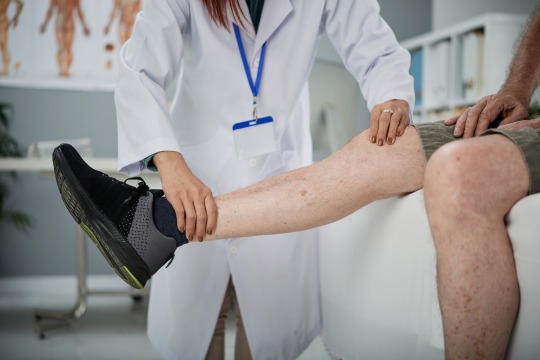
Discover effective strategies to combat varicose veins for individuals who work long hours standing up. Learn how to protect your health and well-being. Should you experience discomfort or seek treatment options, seeking professional medical advice is paramount. Dr. Sumit Kapadia, a distinguished vascular surgeon in Vadodara, specializing in varicose vein treatments, offers tailored solutions and expert guidance to address varicose vein concerns effectively.
#Glue Treatment Of Varicose Veins#Vascular Trauma Treatment#Fistula Operation For Dialysis#Endovascular Surgery#Vascular Trauma#Vascular Treatment#Laser Varicose Veins Treatment#Varicose Veins Best Doctor#Best Vascular Surgeon In India#Varicose Veins Best Treatment#Leg Bypass Surgery#Best Treatment For Varicose Veins#Varicose Veins Pregnancy#Av Fistula Surgery
1 note
·
View note
Text
⚕️Severe Trauma Protocol for Gallifreyans
For use on Gallifreyans and Time Lords only. Always seek your human advice from human health providers.
📖 Understanding Severe Trauma in Gallifreyans
Gallifreyan resilience is remarkable, but severe trauma remains a critical emergency. Due to their unique skeletal, circulatory, and nervous system structures, injuries can escalate rapidly if not addressed correctly. The Severe Trauma Protocol (STP) ensures structured assessment, stabilisation, and intervention while minimising complications unique to Gallifreyan physiology.
Key Considerations:
✔️ Higher risk of compartment syndrome due to denser circulatory & nerve networks.
✔️ Medullary 'motorway' injuries can cause rapid internal bleeding and respiratory complications.
✔️ Regeneration is NOT a first-line treatment—attempting to regenerate under unstable conditions can worsen injuries or lead to catastrophic failure.
✔️ Certain pain management techniques are unique to Gallifreyans, requiring a tailored approach.
✔️ Neurological injuries pose additional risks due to psionic function interplay—telepathic overload can complicate neurological assessments.
💥Pain Management in Severe Trauma
Gallifreyans possess unique methods of pain regulation, including nerve manipulation and endorphin control, but these techniques are limited for severe trauma. While minor injuries can be self-regulated, major trauma requires external analgesics and medical intervention.
📌 Pain Management Protocol:
Mild Pain: Paracetamol (2g every 4-6 hours).
Moderate Pain: Codeine (60-120mg every 4-6 hours) or tramadol (100-200mg every 6 hours).
Severe Pain: Morphine (10-20mg every 4 hours) or controlled healing coma.
Aspirin is NEVER to be used—severe anaphylaxis risk.
Emergency nerve block techniques may be considered for limb trauma and extreme pain cases.
🛑 Types of Severe Trauma & Immediate Management
1️⃣ Blunt Force Trauma
💥 Includes: Falls from height, vehicle impacts, physical combat. ⚠️ Risks: Internal bleeding, compartment syndrome, rib fractures, head trauma. 📌 Management:
Stabilise the spine and monitor for hidden fractures—Gallifreyan skin absorbs impact well, masking underlying skeletal damage.
Check for medullary bleeding—dark, thickened blood suggests severe internal trauma.
Administer fluids cautiously to avoid vascular overload.
Check for signs of latent telepathic shock—high-impact trauma can disrupt psionic pathways.
2️⃣ Penetrating Trauma
💥 Includes: Stab wounds, impalements, projectile injuries. ⚠️ Risks: Organ damage, haemorrhage, high infection risk. 📌 Management:
DO NOT remove deeply embedded objects—stabilise the object to prevent worsening of bleeding. It will work its way out on its own.
Use biological sealants for deep tissue damage—Gallifreyan wound healing can be accelerated with proper treatment.
Monitor for asynchronous heart activity—penetrating trauma may affect cardiac function.
Consider nerve suppression techniques to reduce excessive pain response.
3️⃣ Skeletal Trauma & Fractures
💥 Includes: Long bone fractures, spinal trauma, cranial injuries. ⚠️ Risks: Disrupted nerve function, prolonged healing, structural instability. 📌 Management:
Immobilise fractures immediately—Gallifreyan bones heal quickly but improperly if not set correctly.
Monitor for nerve damage—fractures near the shoulder nerve cluster can cause severe pain and paralysis.
Apply regenerative stabilisation techniques cautiously—improper healing may result in malformations.
Assess psionic coherence in cases of cranial trauma—brain injuries may induce temporary psionic instability.
4️⃣ Severe Burns & Radiation Exposure
💥 Includes: Plasma burns, time-radiation exposure, chemical burns. ⚠️ Risks: Tissue necrosis, hyperartronosis, systemic failure. 📌 Management:
Flush with sterile solution—time-energy burns require specialised decontamination.
Monitor for artron overload symptoms—increased energy absorption can trigger metabolic instability.
Assess psionic damage—radiation burns may disrupt telepathic function.
Consider metabolic stabilisation agents to counteract time-energy exposure.
5️⃣ Neurological Trauma & Psionic Overload
💥 Includes: Head trauma, telepathic shock, spinal cord injury. ⚠️ Risks: Psionic shutdown, memory fragmentation, neural instability. 📌 Management:
Assess consciousness WITHOUT relying on psionic input—young Gallifreyans may give false AVPTU results.
Monitor for telepathic seizures—spinal damage can cause neurological and psionic disruption.
Immobilise suspected spinal injuries—movement can cause irreversible psionic dysfunction.
Use psionic dampeners where needed to reduce neural overload.
📌 Key Points to Remember
Monitor metabolic changes post-stabilisation—Gallifreyan trauma can cause delayed systemic responses.
Use regeneration as a LAST RESORT—only if the patient is fully stabilised to prevent worsening injuries.
Assess psionic faculties in cases of prolonged unconsciousness—cognitive dysfunction may not always be physiological.
Medical Guides These are all practical guides to assessing and treating a Gallifreyan in an emergency or medical setting.
⚕️💕Gallifreyan CPR
⚕️👽Gallifreyan Assessment Scoring System (GASS)
⚕️👽ABCDE Assessment
⚕️⚠️Sepsis Emergency Response (SER)
⚕️⚠️Severe Trauma Protocol
⚕️🌡️Gallifreyan Thermoregulation and Emergency Response
⚕️🔮Psionic Emergency Pathways
⚕️✨Post-Regeneration Management
⚕️💤Gallifreyan Healing Coma Management
⚕️🩸Interpreting Gallifreyan Bloodwork
⚕️👶Gallifreyan Paediatric Emergencies
Any orange text is educated guesswork or theoretical. More content ... →📫Got a question? | 📚Complete list of Q+A and factoids →📢Announcements |🩻Biology |🗨️Language |🕰️Throwbacks |🤓Facts → Features:⭐Guest Posts | 🍜Chomp Chomp with Myishu →🫀Gallifreyan Anatomy and Physiology Guide (pending) →⚕️Gallifreyan Emergency Medicine Guides →📝Source list (WIP) →📜Masterpost If you're finding your happy place in this part of the internet, feel free to buy a coffee to help keep our exhausted human conscious. She works full-time in medicine and is so very tired 😴
#doctor who#dr who#dw eu#gallifreyans#gallifrey institute for learning#Time Lord biology#GAP Quick Guides#whoniverse#GIL: Biology#gallifreyan biology#GIL: Species/Gallifreyans#GIL#GIL: Biology/Medical
36 notes
·
View notes
Text
Sudden Death Due to Neurological Conditions: Understanding the Risks and Prevention
Sudden deaths are often attributed to cardiac causes, but neurological conditions can also lead to sudden fatalities. These causes include massive brain bleeds due to hypertension, ruptured arterial wall outpouching, vascular malformations, brain strokes from clots, seizures, brain injuries, and infections such as meningitis and brain abscess. Understanding these conditions and their prevention can save lives.
Sudden deaths due to Central nervous system (CNS) causes account for 15% of all cases of non-cardiac deaths. Many sudden neurological deaths are misclassified as cardiac deaths, with an estimated 10,000-25,000 such cases in the United States. There is an increased risk in Asians and Hispanics, especially women. Dr. Neeharika, Sr. Consultant Neurophysician of Star Hospital, the Top Neurophysician in Hyderabad gives an insight into SUDEP (Sudden unexpected death in epilepsy) in this article.
Neurological Causes of Sudden Death
Massive brain bleeds, primarily caused by hypertension, ruptured arterial outpouchings, and vascular malformations, can lead to rapid neurological deterioration and death due to the sudden increase in intracranial pressure. Brain strokes, often resulting from clots in brain blood vessels, can cause massive brain damage and lead to sudden death if not promptly treated. Seizures, particularly prolonged ones, can result in sudden unexpected death in epilepsy (SUDEP). Brain injuries from accidents that cause bleeding in or around the brain can be life-threatening. The bleeding can lead to dangerous pressure on the brain, fluid buildup (hydrocephalus), and even push parts of the brain out of place (herniation), all of which can be deadly, especially if unwitnessed and untreated.
Mechanisms of Death
Craniocerebral trauma and cerebrovascular deaths can result from direct mass effects, hydrocephalus, brain herniation, and neurocardiogenic pathways. Raised intracranial pressure in these conditions can cause severe autonomic disturbances, including cardiac arrhythmias, leading to sudden death. Similarly, sudden unexpected death in epilepsy (SUDEP) involves neurocardiogenic and neurorespiratory changes during seizures and cerebral shutdown after prolonged seizures. The risk factors for SUDEP include major neurological impairment, refractory seizures, seizures during nights, generalized tonic-clonic seizures, and noncompliance to anti-epileptic drug therapy. These mechanisms underline the importance of understanding and managing neurological conditions to prevent sudden fatalities.
SUDEP Prevention:
· Patient education on medication compliance.
· Care plans for seizure clusters.
· Optimizing treatment for drug-resistant epilepsy.
· Prompt surgical evaluation for drug-resistant or lesional epilepsy.
· Epilepsy self-management programs.
· Lifestyle changes to avoid seizure triggers, including avoiding excessive alcohol and sleep deprivation.
· Use seizure monitoring devices like bed sensors, alarms, and heart rate monitors.
· Preventing airway obstruction with ventilated foam pillows and nocturnal supervision, especially for those with a habit of sleeping in a prone position.
Prevention of Brain Bleeds and Strokes:
· Regular monitoring of blood pressure.
· Lowering cholesterol levels.
· Maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
· Avoiding alcohol consumption and quitting smoking.
· Eating a balanced diet.
· Regular exercise.
· Regulating blood sugar levels in diabetics.
· Wearing helmets and ensuring children do the same.
· Buckling seat belts while driving.
Conclusion
Neurological conditions are significant contributors to sudden death, often under-recognized and misclassified as cardiac deaths. Awareness, early diagnosis, and prevention strategies are crucial in reducing these fatalities. Addressing immediate and long-term preventive measures is essential to safeguard those at risk.
STAR Institute of Neurosciences: A Trusted Leader in Neurological Care
The STAR Institute of Neurosciences stands among the top neurology hospitals in Hyderabad, providing advanced treatments and achieving exceptional outcomes for a broad range of neurological conditions, including Stroke, Epilepsy, Parkinson’s Disease, Neuropathies, and Myasthenia Gravis. With a team of leading neurologists and neurosurgeons supported by state-of-the-art technology, STAR Hospitals ensures comprehensive care while upholding its commitment to expertise, excellence, and empathy. Adopting a patient-first approach, STAR Hospitals continues to set new standards in neurology and neurosurgery in Hyderabad.
Please book your appointment with our leading neurologist in Hyderabad today at Star Hospital for expert consultations and personalized healthcare. Your health is our priority!
For more information: https://starhospitals.in/blogs/neurological-conditions-risks-and-prevention
top neurology hospitals, Neurological Conditions, Top Neurophysician in Hyderabad, top neurology hospitals in Hyderabad
#top dermatologist in hyderabad#best dermatology hospital in hyderabad#dermatologist in hyderabad#ent specialist near me#nephrology specialist in hyderabad#best ent hospital near me#ent hospital in hyderabad#top endocrinologist in hyderabad#best ent doctor near me#neurologist in banjara hills#neurosurgeon hyderabad#best neurosurgeon in hyderabad#neuro surgeon near me#neurologist near me#neuro hospital banjara hills#neurology hospital near me#best neurologist near me#famous neurologist in hyderabad#best neurology hospital in hyderabad#best neuro hospital in hyderabad#neurology hospital in hyderabad#neuro physician hyderabad#top neurologist in hyderabad#best neurologist in hyderabad#neurologist in hyderabad#best neuro physician in hyderabad#best neurology doctor in hyderabad#top neuro physician in hyderabad#top neurology hospitals#Neurological Conditions
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Long-term effects of Gaza war could quadruple Palestinian death toll, warn UK doctors
Surgeons who worked in Gaza fear disease, malnutrition and eradication of healthcare will reverberate for decades
Middle East crisis live: latest news updates
Mark Townsend Sat 22 Feb 2025 05.00 GMT
British doctors who worked in Gaza during the war have issued dire predictions over the long-term health of Palestinian civillians, warning that large numbers will continue to die.
The prevalence of infectious disease and multiple health problems linked to malnutrition, alongside the destruction of hospitals and killing of medical experts, meant mortality rates among Palestinians in Gaza would remain high after the cessation of Israeli shelling.
British-Palestinian reconstructive surgeon, Prof Ghassan Abu-Sittah, who worked in al-Shifa and al-Ahli Arab hospitals in Gaza City shortly after the war began, said levels of malnutrition there were so acute that many children would “never recover”.
Scientists have estimated that the total deaths from Israel’s war on Gaza could ultimately be as high as 186,000. The figure is almost four times higher than the 46,700 deaths that Gaza’s Hamas-run health ministry have reported.
Prof Nizam Mamode, a retired British transplant surgeon from Hampshire who last year worked at Nasser hospital in southern Gaza said the number of “non-trauma deaths” could ultimately be considerably higher than 186,000. One factor, he said, was the targeting of healthcare workers during the war.
He said that of six vascular surgeons who once covered the north of the strip, just one had remained. There were no cancer pathologists left alive.

View image in fullscreenDoctors said it was likely that irreversible damage had already been done to large numbers of children. Photograph: Anadolu/Getty Images
“Certain specialities have been eviscerated,” he said. “There are no more nephrologists [a doctor specialising in kidney care] left. They’ve all been killed. There are no more board-certified emergency medicine physicians.”
The 55-year-old plastic surgeon from London said the long-term health of people in Gaza depended on how quickly the territory and its infrastructure were rebuilt.
Last week, thousands of Palestinians began returning to northern Gaza to scenes of utter destruction after the withdrawal of Israeli troops from a strategic corridor that divides the north and south of Gaza.
“But to get doctors to move back to the north, you need to house them. Where are they going to live? Where are their families going to live?” said Abu-Sittah.
He said irreversible damage had already been done to large numbers of children.
“Studies on people who survived the second world war showed they are more likely to get NCDs [non-communicable diseases] if they had malnutrition as children. They’re also more likely to become diabetics, more likely to have hypertension, more likely to have diabetes in old age. You don’t recover.”
Last month, the UN estimated that more than 60,000 children in Gaza would need treatment for acute malnutrition in 2025. Some had already died, said the organisation.
Another concern is the spread of disease, helped by the destruction of infrastructure such as sewage facilities.
Abu-Sittahhas provided evidence to Scotland Yard and the international criminal court over what he witnessed working in Gaza. He described the prevalence of disease there as a catastrophe.
“Hepatitis, diarrhoeal disease, respiratory disease, polio that re-emerged in the war, will all continue because there’s still no sewerage and clean drinking water, still no housing, no primary-care clinics. You’re not going to be able to stop, or even stem, infectious diseases.”

View image in fullscreenThe dialysis unit at al-Shifa hospital in Gaza on 3 April 2024, two days after the Israeli military withdrew from the hospital complex. Photograph: AFP/Getty Images
He warned of the proliferation of drug-resistant bacteria, recounting an instance when six out of seven consecutive patients he saw had “multiple drug-resistant bacteria”.
In addition to the long-term impacts, he said 13,000 Gazans required immediate surgical interventions from war wounds. “The sheer number of complex injuries that need treatment means that it’s going to consume the health system for a generation,” he said.
Both doctors said the brutality and number of injuries they witnessed while working in Gaza was hard to overstate. Mamode, who gave evidence to MPs on the British parliament’s international development select committee inquiry into Gaza’s healthcare, said up to 70% of those he operated on were children.
“You’d have a three-year-old in intensive care for a week and we’d be told, ‘The parents are killed, the siblings are killed. Wait and see whether anyone is going to turn up for them.’ That was quite common.”
Abu-Sittah said that half of his patients were children and that despite working in numerous conflict zones including Iraq, Lebanon, Syria and Yemen, he had never performed as many amputations each day as he had in Gaza.
Mamode, a former clinical lead of transplant surgery at Guy’s and St Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust in London, warned that another vital long-term health issue was the psychological scarring on a population after 15 months of fighting.
“In the coming months, those issues will start to come to the fore, because people have just been focusing on day-to-day survival. When that pressure comes off [the psychological impacts] are going to manifest themselves in all sorts of ways.”
A spokesperson for the Israeli Defence Force (IDF) said it had been “well documented that Hamas uses hospitals and medical centres for its terror activities”.
They added: “If not stopped, under certain conditions, this illegal military use can make the hospital lose its protection from attack.”
#health#health and wellness#mental health#gaza#genocide#healing#healthylifestyle#palestine#egypt#health & fitness
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
My Hero Academia but it’s Hospital/Medical AU, these are the “roles”:
Izuku: General Surgical resident. (Special interest in trauma) (Struggling to pay debts from med school.)
Bakugo: General Surgical resident. (He’s giving a much more likable version of Dr. Romano from ER. Also has special interest in vascular and trauma)
Todoroki: Surgical resident…His dad owns the hospital/is a head surgeon or some 💩 (special interest in trauma)
Kaminari: 💯 a peds nurse. (Approved by my friend, actual peds nurse. He will be a pediatrician in the future.)
Uraraka: (If not an EMT) ER nurse? 👀 (maybe even in peds because, well, Yamada.)
Iida: Everyone’s worst nightmare… legal/risk management.
Hitoshi: Neuro surgery or psychiatric residency.
Kirishima: Surgical assistant (or EMT) 🚑
Ojiro: Tbh he’s giving Physical therapist vibes.
Mina: Emergency Medicine or anesthesiology💊
Tokoyami: Trauma Surgical residency OR Orthopedic.
Tsu: EMT or current ENT residency.
Ayoama: Aspiring to be a plastic surgeon to make people beautiful again but for now he’s an MS working part time in the office/desk.
Mineta: wanted to be an OBGYN but he ends up transferred in two days for obvious reasons… 🫠 is now a nurse.
Sero: EMT or honestly the burn unit 🤷♀️
Koda: Emergency medicine 💯 no doubt
Sato: Dietary or… hear me out… OBGYN 🙌🩺
Hagakure: Social services or labour and delivery 👶🏼
Teachers————
Aizawa: Attending surgical physician (Takes a lot of hits for his residents, mostly Izuku and Bakugo, but also is the reason Izuku takes up a hospital bed so often bc he’s a universal blood donor and that shit is liquid gold he intends to use for how many times he’s saved that idiots life.)
Yagi: Trauma Surgeon/Attending.
Yamada: Pediatrician 💯👶🏼🩺 (Or ENT)
Nezu: He runs this bitch. Duh.
Snipe: Surgeon/attending.
Kurose: Trauma Surgeon/Attending. (Poss. EMT)
Ectoplasm: Urologist.
Midnight: Anesthesiologist without a doubt. (Takes Mina under her wing a lot)

Vlad King: Colorectal or dietary. 
Hawks: Trauma Surgeon.
Endeavor: Chief of surgery. Owns hospital.
Villains/Patients————
AFO: Trauma surgeon from a different hospital. He hates Yagi and anyone affiliated with him passionately because he made a surgical “mistake” that resulted in the death of his brother, which he blames both Toshonori and the hospital for.
Dabi: Endeavor springs him out of trouble often by trying to keep his burn victims alive. He’s the local arsonist, but they don’t know it yet. He’s single handedly filled the burn unit. But he needs therapy more than a jail cell, according to his sister.
Toga: A young, homeless girl who needs psychiatric help but refuses to seek it if she can’t be around her current obsession(s)— Uraraka and Izuku, who she stalks and later abducts.
Shigaraki: Stalks Izuku Midoriya. Not because he wants him— but because he wants to become him as part of his disorder (DID). He believes Izuku Midoriya is his “brother” who stole his life. He also believes that his mentor/attending, AFO, wants what is best for him- but in reality he just needs someone to pin the blame on for any surgical mishaps in the future, or better yet, a future surgeon able to compete with Yagi’s new favorite.
Kurogiri: An EMT who doesn’t trust UA hospital after a surgical procedure gone wrong, he is often in trouble for directing patients anywhere but UA hospital when possible. He has also taken Tomura under his wing in terms of living together and caring for him as if his own son.
Moonfish: Cannibal/serial killer under Hitoshi’s (if psychiatrists) watch, who one day escapes the hospital and attempts to kill/eat Kaminari (who matches his VP).
Mr. Compress: A pediatrician who plants mistrust in his patients with UA hospital, an issue brought to light when a woman panics and refuses medical treatment for her nephew because of rumors he has planted.
Magne: An abusive asshole who you somehow kill off in the end, just make sure someone has the ability to save him but chooses not to in Greys Anatomy stick elevator scene.
Twice: Multi personality disorder patient who is often a good time to be around, walks around aimlessly, talks with the kiddos. He’s not really a “villain” in this universe but more of a man lost in his own mind, per usual.
Lady Nagant: A woman with PTSD who snaps. Former patient of AFO, who tried to convince her to seek care at his hospital, but she is unsure where to go. Eventually she learns to trust Izuku Midoriya after a drunken night at the bar leads to her getting shot, which he must save her life.
#my hero academia#mha imagines#anime#bnha imagines#bakugou katsuki#izuku mydoria#deku#shoto torodoki#mha endeavor#uraraka ochacho#kaminari denki/shinsou hitoshi#greys anatomy#surgery#hospital#alternate universe#hospital au
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Understanding Tinnitus: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Tinnitus, often described as a ringing, buzzing, or humming sound in the ears, affects millions worldwide. While it’s not a condition itself, it’s typically a symptom of an underlying issue.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the causes, symptoms, and available treatments for tinnitus, helping you better understand this common auditory phenomenon.
What is Tinnitus?
Tinnitus refers to the perception of sound without an external source. It can manifest in one or both ears, and the noise may be constant or intermittent. People describe it as ringing, buzzing, hissing, clicking, or even roaring sounds.
Types of Tinnitus
Subjective Tinnitus: Only the individual hears the sound. It’s the most common type and is often linked to ear problems or nerve damage.
Objective Tinnitus: A rare form where others, such as a doctor, can also detect the noise. This type is often associated with vascular or muscular issues.
Common Causes of Tinnitus
Tinnitus can result from various factors, including:
Hearing Loss: Age-related hearing loss (presbycusis) and exposure to loud noises can damage the auditory nerve.
Ear Infections or Blockages: Wax build-up, infections, or foreign objects can cause temporary tinnitus.
Medications: Certain drugs, such as aspirin, antibiotics, or diuretics, can induce tinnitus as a side effect.
Health Conditions: Issues like high blood pressure, cardiovascular diseases, or temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders can contribute to tinnitus.
Injuries: Head or neck trauma may affect auditory nerves or brain function, leading to tinnitus.
Recognizing Symptoms of Tinnitus
The primary symptom is hearing a sound without an external source. However, it may also accompany:
Sensitivity to sound (hyperacusis)
Difficulty concentrating
Stress or anxiety
Sleep disturbances
Diagnosing Tinnitus
Consulting an audiologist or otolaryngologist is essential for an accurate diagnosis. A detailed medical history, physical examination, and hearing tests are usually conducted to determine the cause.
Treatment Options for Tinnitus
While there’s no universal cure for tinnitus, various treatments can help manage symptoms:
1. Sound Therapy
Using white noise machines, hearing aids, or nature sounds can mask tinnitus and provide relief.
2. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT helps patients manage emotional responses to tinnitus, reducing its impact on daily life.
3. Medications
Although no specific drug cures tinnitus, some medications, like antidepressants or anti-anxiety drugs, can alleviate associated stress.
4. Lifestyle Modifications
Avoid Loud Noises: Use ear protection in noisy environments.
Stress Management: Yoga, meditation, or relaxation techniques can reduce tinnitus severity.
Healthy Diet: Reducing caffeine and alcohol intake may help.
5. Tinnitus Retraining Therapy (TRT)
This combines counseling with sound therapy to retrain the brain and minimize tinnitus perception.
Preventing Tinnitus
Prevention is key to avoiding tinnitus or preventing it from worsening. Here are some tips:
Protect Your Ears: Use earplugs in loud environments.
Limit Loud Music Exposure: Keep volume levels safe when using headphones.
Maintain Overall Health: Regular exercise and a balanced diet support auditory health.
Seek Prompt Treatment: Address ear infections or injuries immediately.
Final Thoughts
Tinnitus can significantly impact one’s quality of life, but understanding its causes and available treatments is the first step toward effective management. If you’re experiencing persistent tinnitus, consult a healthcare professional for a personalized treatment plan.
Need Expert Advice?
If you're struggling with tinnitus, don’t hesitate to seek help. Early intervention can prevent further complications and improve your quality of life.
For more insights into ear health and related topics, stay tuned to our blog!
youtube
#lando norris#viral#dc comics#bruce wayne#fitness#dnp#medicine#phan#health#trending#tinnitus#Youtube
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Retinal and choroidal vascular drop out in a case of severe phenotype of Flammer Syndrome. Rescue of the ischemic-preconditioning mimicking action of endogenous Erythropoietin (EPO) by off-label intra vitreal injection of recombinant human EPO (rhEPO) by Claude Boscher in Journal of Clinical Case Reports Medical Images and Health Sciences
Abstract
Background: Erythropoietin (EPO) is a pleiotropic anti-apoptotic, neurotrophic, anti-inflammatory, and pro-angiogenic endogenous agent, in addition to its effect on erythropoiesis. Exogenous EPO is currently used notably in human spinal cord trauma, and pilot studies in ocular diseases have been reported. Its action has been shown in all (neurons, glia, retinal pigment epithelium, and endothelial) retinal cells. Patients affected by the Flammer Syndrome (FS) (secondary to Endothelin (ET)-related endothelial dysfunction) are exposed to ischemic accidents in the microcirculation, notably the retina and optic nerve.
Case Presentation: A 54 years old female patient with a diagnosis of venous occlusion OR since three weeks presented on March 3, 2019. A severe Flammer phenotype and underlying non arteritic ischemic optic neuropathy; retinal and choroidal drop-out were obviated. Investigation and follow-up were performed for 36 months with Retinal Multimodal Imaging (Visual field, SD-OCT, OCT- Angiography, Indo Cyanin Green Cine-Video Angiography). Recombinant human EPO (rhEPO)(EPREX®)(2000 units, 0.05 cc) off-label intravitreal injection was performed twice at one month interval. Visual acuity rapidly improved from 20/200 to 20/63 with disparition of the initial altitudinal scotoma after the first rhEPO injection, to 20/40 after the second injection, and gradually up to 20/32, by month 5 to month 36. Secondary cystoid macular edema developed ten days after the first injection, that was not treated via anti-VEGF therapy, and resolved after the second rhEPO injection. PR1 layer integrity, as well as protective macular gliosis were fully restored. Some level of ischemia persisted in the deep capillary plexus and at the optic disc.
Conclusion: Patients with FS are submitted to chronic ischemia and paroxystic ischemia/reperfusion injury that drive survival physiological adaptations via the hypoxic-preconditioning mimicking effect of endogenous EPO, that becomes overwhelmed in case of acute hypoxic stress threshold above resilience limits. Intra vitreal exogenous rhEPO injection restores retinal hypoxic-preconditioning adaptation capacity, provided it is timely administrated. Intra vitreal rhEPO might be beneficial in other retinal diseases of ischemic and inflammatory nature.
Key words : Erythropoietin, retinal vein occlusion, anterior ischemic optic neuropathy, Flammer syndrome, Primary Vascular Dysfunction, anti-VEGF therapy, Endothelin, microcirculation, off-label therapy.
Introduction
Retinal Venous Occlusion (RVO) treatment still carries insufficiencies and contradictions (1) due to the incomplete deciphering of the pathophysiology and of its complex multifactorial nature, with overlooking of factors other than VEGF up-regulation, notably the roles of retinal venous tone and Endothelin-1 (ET) (2-5), and of endothelial caspase-9 activation (6). Flammer Syndrome (FS)( (Primary Vascular Dysfunction) is related to a non atherosclerotic ET-related endothelial dysfunction in a context of frequent hypotension and increased oxidative stress (OS), that alienates organs perfusion, with notably changeable functional altered regulation of blood flow (7-9), but the pathophysiology remains uncompletely elucidated (8). FS is more frequent in females, and does not seem to be expressed among outdoors workers, implying an influence of sex hormons and light (7)(9). ET is the most potent pro-proliferative, pro-fibrotic, pro-oxidative and pro-inflammatory vasoconstrictor, currently considered involved in many diseases other than cardio-vascular ones, and is notably an inducer of neuronal apoptosis (10). It is produced by endothelial (EC), smooth vascular muscles (SVMC) and kidney medullar cells, and binds the surface Receptors ET-A on SVMC and ET-B on EC, in an autocrine and paracrine fashion. Schematically, binding on SVMC Receptors (i.e. through local diffusion in fenestrated capillaries or dysfunctioning EC) and on EC ones (i.e. by circulating ET) induce respectively arterial and venous vasoconstriction, and vasodilation, the latter via Nitrite oxide (NO) synthesis. ET production is stimulated notably by Angiotensin 2, insulin, cortisol, hypoxia, and antagonized by endothelial gaseous NO, itself induced by flow shear stress. Schematically but not exclusively, vascular tone is maintained by a complex regulation of ET-NO balance (8) (10-11). Both decrease of NO and increase of ET production are both a cause and consequence of inflammation, OS and endothelial dysfunction, that accordingly favour vasoconstriction; in addition ET competes for L-arginine substrate with NO synthase, thereby reducing NO bioavailability, a mechanism obviated notably in carotid plaques and amaurosis fugax (reviewed in 11).
Severe FS phenotypes are rare. Within the eye, circulating ET reaches retinal VSMC in case of Blood-Retinal-Barrier (BRB) rupture and diffuses freely via the fenestrated choroidal circulation, notably around the optic nerve (ON) head behind the lamina cribrosa, and may induce all pathologies related to acute ocular blood flow decrease (2-3)(5)(7-9). We previously reported two severe cases with rapid onset of monocular cecity and low vision, of respectively RVO in altitude and non arteritic ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION) (Boscher et al, Société Francaise d'Ophtalmologie and Retina Society, 2015 annual meetings).
Exogenous Recombinant human EPO (rhEPO) has been shown effective in humans for spinal cord injury (12), neurodegenerative and chronic kidney diseases (CKD) (reviewed in 13). Endogenous EPO is released physiologically in the circulation by the kidney and liver; it may be secreted in addition by all cells in response to hypoxic stress, and it is the prevailing pathway induced via genes up-regulation by the transcription factor Hypoxia Inducible Factor 1 alpha, among angiogenesis (VEGF pathway), vasomotor regulation (inducible NO synthase), antioxidation, and energy metabolism (14). EPO Receptor signaling induces cell proliferation, survival and differentiation (reviewed in 13), and targets multiple non hematopoietic pathways as well as the long-known effect on erythropoiesis (reviewed in 15). Of particular interest here, are its synergistic anti-inflammatory, neural antiapoptotic (16) pro-survival and pro-regenerative (17) actions upon hypoxic injury, that were long-suggested to be also indirect, via blockade of ET release by astrocytes, and assimilated to ET-A blockers action (18). Quite interestingly, endogenous EPO’s pleiotropic effects were long-summarized (back to 2002), as “mimicking hypoxic-preconditioning” by Dawson (19), a concept applied to the retina (20). EPO Receptors are present in all retinal cells and their rescue activation targets all retinal cells, i.e. retinal EC, neurons (photoreceptors (PR), ganglion (RGG) and bipolar cells), retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) osmotic function through restoration of the BRB, and glial cells (reviewed in 21), and the optic nerve (reviewed in 22). RhEPO has been tested experimentally in animal models of glaucoma, retinal ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) and light phototoxicity, via multiple routes (systemic, subconjunctival, retrobulbar and intravitreal injection (IVI) (reviewed in 23), and used successfully via IVI in human pilot studies, notably first in diabetic macular edema (24) (reviewed in 25 and 26). It failed to improve neuroprotection in association to corticosteroids in optic neuritis, likely for bias reasons (reviewed in 22). Of specific relation to the current case, it has been reported in NAION (27) (reviewed in 28) and traumatic ON injury (29 Rashad), and in one case of acute severe central RVO (CRVO) (Luscan and Roche, Société Francaise d’Ophtalmologie 2017 annual meeting). In addition EPO RPE gene therapy was recently suggested to prevent retinal degeneration induced by OS in a rodent model of dry Age Macular Degeneration (AMD) (30).
Case Report Presentation
This 54 years female patient was first visited on March 2019 4th, seeking for second opinion for ongoing vision deterioration OR on a daily basis, since around 3 weeks. Sub-central RVO (CRVO) OR had been diagnosed on February 27th; available SD-OCT macular volume was increased with epiretinal marked hyperreflectivity, one available Fluorescein angiography picture showed a non-filled superior CRVO, and a vast central ischemia involving the macular and paraoptic territories. Of note there was ON edema with a para-papillary hemorrage nasal to the disc on the available colour fundus picture.
At presentation on March 4, Best Corrected Visual Acuity (BCVA) was reduced at 20/100 OR (20/25 OS). The patient described periods of acutely excruciating retro-orbital pain in the OR. Intraocular pressure was normal, at 12 OR and 18 OS (pachymetry was at 490 microns in both eyes). The dilated fundus examination was similar to the previous color picture and did not disclose peripheral hemorrages recalling extended peripheral retinal ischemia. Humphrey Visual Field disclosed an altitudinal inferior scotoma and a peripheral inferior scotoma OR and was in the normal range OS, i.e. did not recall normal tension glaucoma OS . There were no papillary drusen on the autofluorescence picture, ON volume was increased (11.77 mm3 OR versus 5.75 OS) on SD-OCT (Heidelberg Engineering®) OR, Retinal Nerve Fiber (RNFL) and RGC layers thicknesses were normal Marked epimacular hypereflectivity OR with foveolar depression inversion, moderately increased total volume and central foveolar thickness (CFT) (428 microns versus 328 OS), and a whitish aspect of the supero-temporal internal retinal layers recalling ischemic edema, were present . EDI CFT was incresead at 315 microns (versus 273 microns OS), with focal pachyvessels on the video mapping . OCT-Angiography disclosed focal perfusion defects in both the retinal and chorio-capillaris circulations , and central alterations of the PR1 layer on en-face OCT
Altogether the clinical picture evoked a NAION with venous sub-occlusion, recalling Fraenkel’s et al early hypothesis of an ET interstitial diffusion-related venous vasoconstriction behind the lamina cribrosa (2), as much as a rupture of the BRB was present in the optic nerve area (hemorrage along the optic disc). Choroidal vascular drop-out was suggested by the severity and rapidity of the VF impairment (31). The extremely rapid development of a significant “epiretinal membrane”, that we interpreted as a reactive - and protective, in absence of cystoid macular edema (CME) - ET 2-induced astrocytic proliferation (reviewed in 32), was as an additional sign of severe ischemia.
The mention of the retro-orbital pain evoking a “ciliary angor”, the absence of any inflammatory syndrome and of the usual metabolic syndrome in the emergency blood test, oriented the etiology towards a FS. And indeed anamnesis collected many features of the FS, i.e. hypotension (“non dipper” profile with one symptomatic nocturnal episode of hypotension on the MAPA), migrains, hypersensitivity to cold, stress, noise, smells, and medicines, history of a spontaneously resolutive hydrops six months earlier, and of paroxystic episods of vertigo (which had driven a prior negative brain RMI investigation for Multiple Sclerosis, a frequent record among FS patients (33) and of paroxystic visual field alterations (7)(9), that were actually recorded several times along the follow-up.
The diagnosis of FS was eventually confirmed in the Ophthalmology Department in Basel University on April 10th, with elevated retinal venous pressure (20 to 25mmHg versus 10-15 OS) (4)(7)(9), reduced perfusion in the central retinal artery and veins on ocular Doppler (respectively 8.3 cm/second OR velocity versus 14.1 mmHg OS, and 3.1/second OR versus 5.9 cm OS), and impaired vasodilation upon flicker light-dependant shear stress on the Dynamic Vessel Analyser testing (7-9). In addition atherosclerotic plaques were absent on carotid Doppler.
On March 4th, the patient was at length informed about the FS, a possible off label rhEPO IVI, and a related written informed consent on the ratio risk-benefits was delivered.
By March 7th, she returned on an emergency basis because of vision worsening OR. VA was unchanged, intraocular pressure was at 13, but Visual Field showed a worsening of the central and inferior scotomas with a decreased foveolar threshold, from 33 to 29 decibels. SD-OCT showed a 10% increase in the CFT volume.
On the very same day, an off label rhEPO IVI OR (EPREX® 2000 units, 0,05 cc in a pre-filled syringe) was performed in the operating theater, i.e. the dose reported by Modarres et al (27), and twenty times inferior to the usual weekly intravenous dose for treatment of chronic anemia secondary to CKD. Intra venous acetazolamide (500 milligrams) was performed prior to the injection, to prevent any increase in intra-ocular pressure. The patient was discharged with a prescription of chlorydrate betaxolol (Betoptic® 0.5 %) two drops a day, and high dose daily magnesium supplementation (600 mgr).
Incidentally the patient developed bradycardia the day after, after altogether instillation of 4 drops of betaxolol only, that was replaced by acetazolamide drops, i.e. a typical hypersensitivity reaction to medications in the FS (7)(9).
Subjective vision improvement was recorded as early as D1 after injection. By March 18 th, eleven days post rhEPO IVI, BCVA was improved at 20/63, the altitudinal scotoma had resolved (Fig. 5), Posterior Vitreous Detachment had developed with a disturbing marked Weiss ring, optic disc swelling had decreased; vasculogenesis within the retinal plexi and some regression of PR1 alterations were visible on OCT-en face. Indeed by 11 days post EPO significant functional, neuronal and vascular rescue were observed, while the natural evolution had been seriously vision threatening.
However cystoid ME (CME) had developed . Indo Cyanin Green-Cine Video Angiography (ICG-CVA) OR, performed on March 23, i.e. 16 days after the rhEPO IVI, showed a persistent drop in ocular perfusion: ciliary and central retinal artery perfusion timings were dramatically delayed at respectively 21 and 25 seconds, central retinal vein perfusion initiated by 35 seconds, was pulsatile, and completed by 50 seconds only (video 3). Choroidal pachyveins matching the ones on SD-OCT video mapping were present in the temporal superior and inferior fields, and crossed the macula; capillary exclusion territories were present in the macula and around the optic disc.
By April 1, 23 days after the rhEPO injection, VA was unchanged, but CME and perfusion voids in the superficial deep capillary plexi and choriocapillaris were worsened, and optic disc swelling had recurred back to baseline, in a context of repeated episodes of systemic hypotension; and actually Nifepidin-Ratiopharm® oral drops (34), that had been delivered via a Temporary Use Authorization from the central Pharmacology Department in Assistance Publique Hopitaux de Paris, had had to be stopped because of hypersensitivity.
A second off label rhEPO IVI was performed in the same conditions on April 3, i.e. approximately one month after the first one.
Evolution was favourable as early as the day after EPO injection 2: VA was improved at 20/40, CME was reduced, and perfusion improved in the superficial retinal plexus as well as in the choriocapillaris. By week 4 after EPO injection 2, CME was much decreased, i.e. without anti VEGF injection. On august 19th, by week 18 after EPO 2, perfusion on ICG-CVA was greatly improved , with ciliary timing at 18 seconds, central retinal artery at 20 seconds and venous return from 23 to 36 seconds, still pulsatile. Capillary exclusion territories were visible in the macula and temporal to the macula after the capillary flood time that went on by 20.5 until 22.5 seconds (video 4); they were no longer persistent at intermediate and late timings.
Last complete follow-up was recorded on January 7, 2021, at 22 months from EPO injection 2. BCVA was at 20/40, ON volume had dropped at 7.46 mm3, a sequaelar superior deficit was present in the RNFL with some corresponding residual defects on the inferior para central Visual Field , CFT was at 384 mm3 with an epimacular hyperreflectivity without ME, EDI CFT was dropped at 230 microns. Perfusion on ICG-CVA was not normalized, but even more improved, with ciliary timing at 15 seconds, central retinal artery at 16 seconds and venous return from 22 to 31 seconds, still pulsatile , indicating that VP was still above IOP. OCT-A showed persisting perfusion voids, especially at the optic disc and within the deep retinal capillary plexus. The latter were present at some degree in the OS as well . Choriocapillaris and PR1 layer were dramatically improved.
Last recorded BCVA was at 20/32 by February 14, 2022, at 34 months from EPO 2. SD-OCT showed stable gliosis hypertrophy and mild alterations of the external layers .
Discussion
What was striking in the initial clinical phenotype of CRVO was the contrast between the moderate venous dilation, and the intensity of ischemia, that were illustrating the pioneer hypothesis of Professor Flammer‘s team regarding the pivotal role of ET in VO (2), recently confirmed (3)(35), i.e. the local venous constriction backwards the lamina cribrosa, induced by diffusion of ET-1 within the vascular interstitium, in reaction to hypoxia. NAION was actually the primary and prevailing alteration, and ocular hypoperfusion was confirmed via ICG-CVA, as well as by the ocular Doppler performed in Basel. ICG-CVA confirmed the choroidal drop-out suggested by the severity of the VF impairment (31) and by OCT-A in the choriocapillaris. Venous pressure measurement, which instrumentation is now available (8), should become part of routine eye examination in case of RVO, as it is key to guide cases analysis and personalized therapeutical options.
Indeed, the endogenous EPO pathway is the dominant one activated by hypoxia and is synergetic with the VEGF pathway, and coherently it is expressed along to VEGF in the vitreous in human RVO (36). Diseases develop when the individual limiting stress threshold for efficient adaptative reactive capacity gets overwhelmed. In this case by Week 3 after symtoms onset, neuronal and vascular resilience mechanisms were no longer operative, but the BRB, compromised at the ON, was still maintained in the retina.
As mentioned in the introduction, the scientific rationale for the use of EPO was well demonstrated by that time, as well as the capacities of exogenous EPO to mimic endogenous EPO vasculogenesis, neurogenesis and synaptogenesis, restoration of the balance between ET-1 and NO. Improvement of chorioretinal blood flow was actually illustrated by the evolution of the choriocapillaris perfusion on repeated OCT-A and ICG-CVA. The anti-apoptotic effect of EPO (16) seems as much appropriate in case of RVO as the caspase-9 activation is possibly another overlooked co-factor (6).
All the conditions for translation into off label clinical use were present: severe vision loss with daily worsening and unlikely spontaneous favourable evolution, absence of toxicity in the human pilot studies, of contradictory comorbidities and co-medications, and of context of intraocular neovascularization that might be exacerbated by EPO (37).
Why didn’t we treat the onset of CME by March 18th, i.e. eleven days after EPO IVI 1, by anti-VEGF therapy, the “standard-of-care” in CME for RVO ?
In addition to the context of functional, neuronal and vascular improvements obviated by rhEPO IVI by that timing in the present case, actually anti VEGF therapy does not address the underlying causative pathology. Coherently, anti-VEGF IVI : 1) may not be efficient in improving vision in RVO, despite its efficiency in resolving/improving CME (usually requiring repeated injections), as shown in the Retain study (56% of eyes with resolved ME continued to loose vision)(quoted in (1) 2) eventually may be followed by serum ET-1 levels increase and VA reduction (in 25% of cases in a series of twenty eyes with BRVO) (38) and by increased areas of non perfusion in OCT-A (39). Rather did we perform a second hrEPO IVI, and actually we consider open the question whether the perfusion improvement, that was progressive, might have been accelerated/improved via repeated rhEPO IVI, on a three to four weeks basis.
The development of CME itself, involving a breakdown of the BRB, i.e. of part of the complex retinal armentorium resilience to hypoxia, was somewhat paradoxical in the context of improvement after the first EPO injection, as EPO restores the BRB (24), and as much as it was suggested that EPO inhibits glial osmotic swelling, one cause of ME, via VEGF induction (40). Possible explanations were: 1) the vascular hyperpermeability induced by the up-regulation of VEGF gene expression via EPO (41) 2) the ongoing causative disease, of chronic nature, that was obviated by the ICG-CVA and the Basel investigation, responsible for overwhelming the gliosis-dependant capacity of resilience to hypoxia 3) a combination of both. I/R seemed excluded: EPO precisely mimics hypoxic reconditioning as shown in over ten years publications, including in the retina (20), and as EPO therapy is part of the current strategy for stabilization of the endothelial glycocalix against I/R injury (42-43). An additional and not exclusive possible explanation was the potential antagonist action of EPO on GFAP astrocytes proliferation, as mentioned in the introduction (18), that might have counteracted the reactive protective hypertrophic gliosis, still fully operative prior to EPO injection, and that was eventually restored during the follow-up, where epiretinal hyperreflectivity without ME and ongoing chronic ischemia do coincide (Fig. 6 and video 6), as much as it is unlikely that EPO’s effect would exceed one month (cf infra). Inhibition of gliosis by EPO IVI might have been also part of the mechanism of rescue of RGG, compromised by gliosis in hypoxic conditions (44). Whatever the complex balance initially reached, then overwhelmed after EPO IVI 1, the challenge was rapidly overcome by the second EPO IVI without anti-VEGF injection, likely because the former was powerful enough to restore the threshold limit for resilience to hypoxia, that seemed no longer reached again during the relapse-free follow-up. Of note, this “epiretinal membrane “, which association to good vision is a proof of concept of its protective effect, must not be removed surgically, as it would suppress one of the mecanisms of resilience to hypoxia.
To our best knowledge, ICG-CVA was never reported in FS; it allows real time evaluation of the ocular perfusion and illustration of the universal rheological laws that control choroidal blood flow as well. Pachyveins recall a “reverse” veno-arteriolar reflex in the choroidal circulation, that is NO and autonomous nervous system-dependant, and that we suggested to be an adaptative choroidal microcirculation process to hypoxia (45). Their persistence during follow-up accounts for a persisting state of chronic ischemia.
The optimal timing for reperfusion via rhEPO in a non resolved issue:
in the case reported by Luscan and Roche, rhEPO IVI was performed on the very same day of disease onset, where it induced complete recovery from VA reduced at counting fingers at 1 meter, within 48 hours. This clinical human finding is on line with a recent rodent stroke study that established the timings for non lethal versus lethal ischemia of the neural and vascular lineages, and the optimized ones for beneficial reperfusion: the acute phase - from Day 1 where endothelial and neural cells are still preserved, to Day 7 where proliferation of pericytes and Progenitor Stem Cells are obtainable - and the chronic stage, up to Day 56, where vasculogenesis, neurogenesis and functional recovery are still possible, but with uncertain efficiency (46). In our particular case, PR rescue after rhEPO IVI 1 indicated that Week 3 was still timely. RhEPO IVI efficacy was shown to last between one (restoration of the BRB) and four weeks (antiapoptotic effect) in diabetic rats (24). The relapse after Week 3 post IVI 1 might indicate that it might be approximately the interval to be followed, should repeated injections be necessary.
The bilateral chronic perfusion defects on OCT-A at last follow-up indicate that both eyes remain in a condition of chronic ischemia and I/R, where endogenous EPO provides efficient ischemic pre-conditioning, but is potentially susceptible to be challenged during episodes of acute hypoxia that overwhelm the resilience threshold.
Conclusion
The present case advocates for individualized medicine with careful recording of the medical history, investigation of the systemic context, and exploiting of the available retinal multimodal imaging for accurate analytical interpretation of retinal diseases and their complex pathophysiology. The Flammer Syndrome is unfortunately overlooked in case of RVO; it should be suspected clinically in case of absence of the usual vascular and metabolic context, and in case of elevated RVP. RhEPO therapy is able to restore the beneficial endogenous EPO ischemic pre-conditioning in eyes submitted to challenging acute hypoxia episodes in addition to chronic ischemic stress, as in the Flammer Syndrome and fluctuating ocular blood flow, when it becomes compromised by the overwhelming of the hypoxic stress resilience threshold. The latter physiopathological explanation illuminates the cases of RVO where anti-VEGF therapy proved functionally inefficient, and/or worsened retinal ischemia. RhEPO therapy might be applied to other chronic ischemia and I/R conditions, as non neo-vascular Age Macular Degeneration (AMD), and actually EPO was listed in 2020 among the nineteen promising molecules in AMD in a pooling of four thousands (47).
#off-label therapy#JCRMHS#anti-VEGF therapy#Erythropoietin#Journal of Clinical Case Reports Medical Images and Health Sciences impact factor.#Primary Vascular Dysfunction
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
I’ve worked in a trauma center long enough to have seen someone get stabbed directly in the heart and still survive because of how quickly they were treated. Even if an artery is cut, tourniquets and a vascular surgeon can work wonders. There’s literally like four or five places on the body that could result in an injury serious enough to kill someone (assuming they had prompt access to first aide and got treatment for the wound in a reasonable timeframe.) A portion of people who are stabbed in those vulnerable places do end up with life altering physical damage, but they still survive.
Writers who are looking to make their stories realistic should be aware of this, but it’s not common knowledge outside of the medical field.
one of my greatest pet peeves in fiction, and it is truly stupid I know, is that no one seems to understand how genuinely hard it is to kill someone via stabbing. stab wounds have a mortality rate of like 5%. especially abdominal stabbing. tv shows and movies show dudes getting stabbed one time in the lower abdomen with a tiny knife and then they fall over. like what did he die of precisely. that man died of Small Knife
#so true#it often just goes into muscle#or into the peritoneal cavity#if you hit an artery that’s different#but surviving that is definitely possible#if you apply a torniquet and get them to a vascular surgeon#they’ll probably make it#plus your really essential organs are well protected
72K notes
·
View notes
Text
Fistula Needle Manufacturers in India – Why SurgiKart is the Trusted Leader
In the ever-evolving landscape of medical device manufacturing, India has emerged as a global powerhouse. Among the many players in this competitive market, SurgiKart stands out as one of the most trusted and innovative fistula needle manufacturers in India. Known for its commitment to excellence, product safety, and international quality standards, SurgiKart has earned the confidence of healthcare professionals not only in India but across more than 50 countries worldwide.
With a focus on delivering high-performance dialysis products, SurgiKart’s fistula needles are carefully engineered to ensure safe and efficient vascular access during hemodialysis procedures. As chronic kidney diseases rise globally, the demand for reliable and top-quality fistula needles continues to grow — and SurgiKart has positioned itself as a frontrunner in meeting this critical need.
What Makes SurgiKart a Leading Choice for Fistula Needles?
When it comes to fistula needle manufacturers in India, several factors distinguish SurgiKart from its competitors. The company operates from a state-of-the-art facility in New Delhi that includes a Class 10,000 clean room, a cutting-edge ETO Gas Sterilization Plant, and precision-controlled molding areas. This enables the brand to maintain stringent quality control at every stage of the manufacturing process.
Moreover, SurgiKart is ISO 13485:2003 certified and many of its products, including fistula needles, are CE marked and US FDA 510(k) approved, reflecting its global-standard quality. The company’s commitment to safety, innovation, and patient comfort is evident in the meticulous design of each needle — ensuring minimal trauma, reduced pain, and seamless blood flow during dialysis.
The Importance of High-Quality Fistula Needles in Dialysis
Fistula needles play a critical role in the dialysis process, providing a direct connection to the bloodstream via an arteriovenous fistula. The precision and design of these needles significantly influence the comfort of the patient and the effectiveness of treatment. Poorly designed needles can lead to complications such as hematomas, infections, and clotting, compromising both patient health and treatment outcomes.
As one of the foremost fistula needle manufacturers in India, SurgiKart places paramount importance on quality assurance and patient safety. The company's fistula needles are manufactured using biocompatible materials, sharp triple-beveled tips for painless insertion, and flexible wings for better grip and control. Each product undergoes rigorous testing to ensure sterility, durability, and reliability under clinical conditions.
SurgiKart’s Global Reach and Manufacturing Excellence
SurgiKart has built a global reputation not just as a local manufacturer, but as an international exporter of medical devices. The company serves over 52 countries, supported by a network of 300+ overseas distributors, making its products accessible in both developed and emerging healthcare markets. Its robust manufacturing infrastructure and professional team of over 300 experts ensure that every fistula needle adheres to global regulatory standards while remaining cost-effective.
This level of professionalism and scale has made SurgiKart a preferred OEM/contract manufacturer for many leading healthcare brands worldwide. The company’s ability to customize products, deliver large volumes on time, and maintain quality consistency has earned it a loyal customer base spanning continents.
Why Healthcare Providers Trust SurgiKart
Medical professionals and healthcare institutions trust SurgiKart not only because of its superior product quality but also because of its commitment to customer service and ethical manufacturing. The company’s Director, Mr. Sachin Chawla, brings over 20 years of experience in the medical device industry, guiding the company with vision, integrity, and a customer-first approach.
In addition to fistula needles, SurgiKart manufactures a comprehensive range of medical devices used in:
Infusion therapy
Transfusion therapy
Dialysis
Urology
Gastroenterology
Anesthesia
Cardiac surgery
General surgical disposables
This extensive portfolio allows healthcare providers to source multiple critical products from a single trusted supplier — an advantage that few fistula needle manufacturers in India can offer.
Customization and Innovation at Its Core
Another factor that sets SurgiKart apart is its emphasis on innovation and customization. Recognizing that healthcare needs vary by region and patient type, the company offers customized design and packaging options to meet specific client requirements. Whether it’s a variation in needle gauge, length, hub color coding, or wing flexibility, SurgiKart works closely with clients to deliver personalized solutions that enhance clinical efficiency and patient comfort.
The company continually invests in R&D to stay ahead of the curve. By incorporating feedback from medical professionals and dialysis experts, SurgiKart ensures that its fistula needle designs reflect the latest advancements in medical technology and clinical practices.
Made in India, Trusted Worldwide
Being one of the top fistula needle manufacturers in India, SurgiKart takes immense pride in contributing to the “Make in India” initiative. With its world-class infrastructure and global certifications, the company proves that India can produce medical devices that match — and often exceed — international standards.
The “Made in India” label, when backed by SurgiKart’s reputation, signifies trust, affordability, and uncompromised quality. This combination is what makes SurgiKart’s fistula needles a preferred choice not just in India, but across hospitals and clinics around the world.
Final Thoughts
In the medical field, where patient safety and procedural precision are non-negotiable, the importance of choosing the right partner for medical supplies cannot be overstated. Among the numerous fistula needle manufacturers in India, SurgiKart has proven time and again that it is a company driven by quality, innovation, and global impact.
With a legacy of trust, a robust international presence, and a focus on continuous improvement, SurgiKart is not just manufacturing medical devices — it is shaping the future of healthcare. Whether you are a healthcare professional, distributor, or procurement officer, choosing SurgiKart means choosing reliability, safety, and world-class performance.
If you're looking for fistula needle manufacturers in India who truly understand the needs of patients and practitioners alike, SurgiKart is the name to trust.
0 notes
Text
Healing from the Ground Up: Managing Diabetic Foot and Ankle Wounds with Expert Care
Living with diabetes presents numerous health challenges, one of the most critical being foot health. When high blood sugar levels impair circulation and nerve function, even minor foot issues can evolve into serious complications. That’s why consulting a Diabetic Foot Doctor is vital for individuals with diabetes. These specialists are trained to monitor, treat, and prevent foot problems that may otherwise go unnoticed until they become dangerous.
One of the most common reasons diabetic patients seek a Diabetic Foot Doctor is for wounds that don’t heal properly. In diabetics, the body’s ability to fight infection and repair skin tissue is significantly reduced. A simple blister or callus can progress to a chronic ulcer if not treated promptly. Left unattended, these wounds could lead to infections, abscesses, or even amputations. Regular visits to a Diabetic Foot Doctor ensure these issues are caught early and managed with the proper care.
Just as important as the feet are the ankles, which also face risks due to decreased sensation and compromised healing ability in diabetic individuals. Ankle Wound Treatment must be handled delicately and efficiently, given how easily these injuries can worsen. Whether the wound is caused by trauma, pressure, or footwear-related friction, timely Ankle Wound Treatment can prevent complications such as cellulitis or osteomyelitis—serious infections that threaten both mobility and overall health.
Modern podiatry clinics now offer advanced wound care solutions tailored for diabetic patients. Treatments may include debridement (the removal of dead tissue), specialized dressings that promote faster healing, and the use of biologics or skin substitutes. Offloading devices, which reduce pressure on the affected area, are often incorporated into the healing process. A skilled Diabetic Foot Doctor will not only treat the wound but also work with patients on lifestyle adjustments that can enhance healing—like blood sugar control, smoking cessation, and proper footwear.
A particularly challenging aspect of diabetic wound care is the development of peripheral neuropathy, which can make patients unaware of injuries until they become severe. This is where routine checkups and screenings come in. By scheduling regular visits, patients can catch potential problems before they escalate. Preventive care, guided by a knowledgeable Diabetic Foot Doctor, remains one of the strongest defenses against diabetic foot complications.
When it comes to ankle injuries in diabetic individuals, specialized Ankle Wound Treatment protocols must be followed. Ankle wounds are prone to swelling due to gravity, and in the diabetic population, this swelling can exacerbate tissue breakdown. Compression therapy, wound irrigation, and infection management are just a few of the strategies a podiatrist may use. Addressing the root cause—be it ill-fitting shoes, poor gait, or vascular issues—is also a crucial part of the recovery plan.
For those searching for trusted care, thrivefootandankle.com provides access to professionals who understand the intricacies of diabetic foot and ankle care. With an emphasis on early detection, patient education, and comprehensive treatment strategies, they help patients maintain mobility and avoid complications.
In addition to clinical treatments, self-care at home plays a critical role. Patients are often guided on how to properly inspect their feet and ankles, moisturize safely without causing maceration, and identify early warning signs like redness, temperature changes, or drainage. Empowering patients with knowledge and tools is just as important as the care provided in the office.
Ankle and foot health cannot be taken lightly, especially for those managing diabetes. Early intervention through Ankle Wound Treatment and consistent evaluations by a Diabetic Foot Doctor are key to preventing complications. By integrating expert care with personal diligence, patients can confidently walk the path to healing.
For more info:-
Facebook
0 notes
Text

What can you do for bleeding varicose veins?
Say goodbye to the unsightly pain and discomfort of bleeding varicose veins with our advanced treatment options. From minimally invasive procedures to customized care plans, we are here to help you achieve healthier, happier legs. Contact us today for a consultation and take the first step towards smoother, happy legs.
#Cost of Spider Vein Removal#Vascular and Endovascular Surgery#Vascular Surgeon#Chemoport Insertion#Chemoport Insertion Procedure#Chemoport Placement#Glue Treatment of Varicose Veins#Vascular Trauma Treatment#Endovascular Surgery#Best Hospital for Varicose Veins Treatment in India#Best Vascular Surgeon in Surat#Vascular Trauma#Doppler Test for Varicose Veins
0 notes
Text
Perlove Medical Interventional C-arm Machine: Performance and Applicable Departments

Compared to traditional DSA, interventional C-arm machines offer the following advantages:
Enhanced Image Quality: High-power X-rays penetrate deeper tissues to obtain clearer and more accurate images, critical for detailed observations.
Increased Contrast: High-power X-rays induce stronger ionization effects, enhancing contrast in images and aiding more precise disease diagnoses.
Wide Applicability: High-power interventional C-arm machines are suitable for imaging high-density tissues in obese patients, facilitating procedures ranging from major to minor surgeries.
Which departments can Perlove Medical’s interventional C-arm machines be applied in?

Comprehensive Intervention: Mainly for tumor intervention and non-vascular disease interventions, such as Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization (TACE) and percutaneous biopsy.
Obstetrics and Gynecology Intervention: For procedures like tubal recanalization and Uterine Artery Embolization (UAE) for treating uterine fibroids.
Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP): Primarily used for procedures like ERCP and Percutaneous Transhepatic Cholangiography (PTC).
Vascular Surgery: Including procedures such as lower limb stent placement, lower limb arterial thrombolysis, carotid artery embolization, and diffuse hemorrhage embolization.
Urology: Used for procedures like urography and treatment of urinary tract strictures.
Orthopedic Surgery: Handling common orthopedic procedures such as bone setting, realignment, and nailing to enhance surgical efficiency and safety.
Trauma Surgery: Assisting precise screw implantation to improve surgical success rates and reduce postoperative complications.
Spine and Joint Surgery: Applicable for procedures like vertebral augmentation, elbow joint replacement, hip joint replacement, knee joint replacement, and anatomical realignment.

Perlove Medical’s interventional C-arm machine utilizes a rotating anode tube with high thermal capacity, complemented by intelligent thermal management and advanced cooling technologies. This significantly enhances overall heat dissipation efficiency, thereby greatly increasing equipment durability and supporting continuous operation for multiple interventional surgeries.
0 notes
Text
What Toenail Colors Reveal About Your Health
Most of us rarely give our toenails a second thought—until something looks or feels off. But changes in toenail color aren’t just cosmetic. They can reveal a great deal about your health. From simple infections to underlying conditions, your toenails may be sending signals that shouldn’t be ignored.
At Grandville Foot and Ankle, we understand that healthy feet begin with strong, well-maintained toenails. Whether you're experiencing discoloration, thickening, or brittleness, our foot specialists take these changes seriously. We’re here to explain what different toenail colors might mean and how we can help.

What Healthy Toenails Should Look Like
Healthy toenails are typically:
Pale pink near the cuticle
White at the free edge
Smooth, without ridges or dents
Even in thickness and free of spots
Any deviation from this could be a red flag. Let’s explore the most common toenail color changes and what they might indicate.
Common Toenail Colors and What They Could Mean
Yellow Toenails
Yellowing is one of the most frequent toenail complaints. While sometimes caused by frequent nail polish use, especially darker shades, persistent yellow nails often point to something more serious:
Fungal infections (onychomycosis)
Psoriasis or eczema
Respiratory disorders such as bronchitis
Diabetes
Poor circulation or lymphedema
At Grandville Foot and Ankle, we provide comprehensive fungal infection treatments, including topical and oral antifungal medications. We also offer laser therapy to target tough infections painlessly.
White or Pale Toenails
Noticing white spots or full discoloration? These may result from:
Minor trauma to the nail
Zinc or calcium deficiency
Fungal infections
Liver or kidney issues (in more serious cases)
If your toenail is white all over or doesn’t improve, it’s time for a podiatric assessment. At our clinic, we determine whether it’s surface-level damage or something deeper.
Blue or Purple Toenails
A bluish or purplish hue in your toenail may signal:
Circulatory problems
Poor oxygen levels in the blood
Raynaud’s disease (reduced blood flow in extremities)
Bruising after trauma
Cold weather exposure
These changes can come and go with temperature shifts. However, if your toenails frequently look purple without a known cause, it may point to an underlying vascular or cardiac issue.
Green Toenails
Greenish toenails are usually caused by:
Bacterial infections, particularly Pseudomonas
Prolonged moisture exposure
Nail bed separation from the plate
Our team uses topical treatments and debridement to clear these infections and helps you prevent recurrence by keeping feet dry and clean.
Black or Brown Toenails
These can look alarming—and for good reason. Black or brown discoloration may be caused by:
Bruising from injury (subungual hematoma)
Fungal infections
Blood clotting disorders
Melanonychia (pigmented streaks)
In rare cases, subungual melanoma (a form of skin cancer)
If you haven’t injured your toe recently and the discoloration doesn’t go away, don’t ignore it. At Grandville Foot and Ankle, we use clinical tools and may recommend a biopsy if there's any sign of melanoma.
Medical Conditions That Affect Toenail Color
Sometimes, toenail color changes are a symptom of deeper systemic issues. These may include:
Diabetes: increases risk of fungal infections and poor circulation.
Liver disease: may cause white or “Terry’s” nails.
Kidney disease: can lead to half-and-half nails (white and brown).
Heart and lung disease: reduce oxygen, leading to bluish nails.
Nutrient deficiencies: especially iron, zinc, and biotin.
If your nails are changing and you already live with one of these conditions, we’ll help manage the foot-specific symptoms and coordinate care with your medical team if needed.
When You Should See a Podiatrist
It’s time to schedule an appointment if:
Your toenail color changes suddenly or worsens over time
Nails thicken, crack, or pull away from the nail bed
You notice vertical dark streaks or black spots
You experience discomfort, swelling, or infection around the nails
Over-the-counter treatments haven’t worked
At Grandville Foot and Ankle, we specialize in advanced diagnostics. Our podiatrists assess nail health thoroughly, and if needed, can perform lab testing, biopsies, or recommend antifungal treatments tailored to your condition.
Trusted Products for Restoring Toenail Health
To support our patients’ recovery and help maintain healthy nail appearance, we recommend a few standout products available at Grandville Foot and Ankle:
Tolcylen™ Antifungal & Nail Renewal Solution
Combines antifungal agents with moisturizers and nail brighteners
Targets discoloration and thickening
Easy brush-on application for daily use
Formula 3® Antifungal Solution
Deep-penetrating and effective against onychomycosis
Doctor-trusted, fast-drying, and easy to use
Ideal for early-stage nail fungus
KeryFlex® Nail Restoration System
Restores natural appearance of damaged or discolored nails
Durable, flexible resin used by professionals
Ideal for patients needing cosmetic improvement alongside treatment
These solutions not only help fight infection but also improve nail texture, clarity, and strength.
In-Depth Questions About Toenail Color and Health
What should I do if my toenail suddenly turns dark?
Sudden dark discoloration can stem from trauma, causing blood to collect under the nail (a subungual hematoma). However, if there's no memory of injury, a dark spot might indicate something more serious like melanoma or melanonychia.
If you see a black or dark brown streak running vertically or the discoloration expands, see a podiatrist immediately. At Grandville Foot and Ankle, we’ll examine the nail and determine whether further testing is needed.
Can nail polish permanently stain toenails?
Regular nail polish, especially in darker colors, can leave yellowish stains if you skip a base coat. These stains are generally harmless and will grow out.
However, persistent discoloration after removing polish may suggest a fungal infection. It’s always best to give your nails a break from polish occasionally and monitor their natural color. We also offer assessments to confirm whether discoloration is cosmetic or medical.
How can I tell if a fungal infection is causing my nail color to change?
Fungal toenails often look:
Yellow, white, or green
Thick and brittle
Crumbly at the edges
Lifting from the nail bed
The longer a fungal infection is left untreated, the harder it becomes to eliminate. At Grandville Foot and Ankle, we offer quick, accurate diagnoses and multiple treatment options, including topical and oral medications.
When is a streak in the toenail a cause for concern?
Vertical stripes (melanonychia) can be benign, particularly in people with darker skin. However, if the streak appears suddenly, widens, or darkens over time, it may be a sign of skin cancer under the nail.
This type of melanoma is rare but serious. If caught early, it’s treatable. We’ll evaluate the nail and may recommend a biopsy to rule out malignancy.
Simple Ways to Keep Your Toenails Healthy
You can reduce the risk of discoloration and infection by following these steps:
Wash and dry feet thoroughly, especially between the toes
Keep toenails trimmed straight across
Avoid digging into the sides of the nail
Use clean, disinfected nail tools
Wear moisture-wicking socks and breathable shoes
Change socks daily and rotate shoes
Avoid walking barefoot in public spaces
And remember: toenail changes are easiest to treat when caught early.
Why Grandville Foot and Ankle Is Your Best Choice
At Grandville Foot and Ankle, we take pride in offering expert foot and nail care with a personal touch. Our board-certified specialists use advanced diagnostic tools to get to the bottom of your nail concerns. From minor discoloration to chronic fungal infections and trauma, we treat it all.
Our office also offers access to professional-grade products like Tolcylen™, Formula 3®, and KeryFlex®—so you don’t have to rely on guesswork or store-bought solutions. We guide you every step of the way toward healthier nails and happier feet.
Patients choose us because we combine trusted experience with genuine care. We treat your feet like family.
Final Thoughts:
Your toenails can reveal more than just your grooming habits—they can reflect your internal health. Discoloration, thickening, and texture changes may be signs of something bigger. The good news? These conditions are manageable, especially when addressed early.
At Grandville Foot and Ankle, we specialize in comprehensive nail evaluations and effective treatments for all kinds of toenail issues. Whether you're dealing with fungal infections, bruising, streaks, or color changes, we’re here to help you restore confidence and comfort.
0 notes
Text
What Is Arterial Thoracic Syndrome? An Overview of Symptoms and Causes

Arterial thoracic syndrome is a rare condition in which blood vessels, specifically the arteries in the chest, become compressed or restricted. This compression can lead to reduced blood flow, causing various symptoms. Often associated with anatomical abnormalities, such as a cervical rib or other structural issues in the chest, this syndrome can significantly affect a person's cardiovascular health if left untreated. Understanding arterial thoracic syndrome's symptoms and underlying causes is vital for early detection and appropriate treatment.
Symptoms of Arterial Thoracic Syndrome
The arterial thoracic syndrome manifests in several distinct symptoms, many of which may be similar to other vascular disorders. Key signs include:
Arm pain or weakness
Coldness or numbness in the extremities
Fatigue or difficulty moving arms and hands
Pale or discolored skin in affected areas
Pain or tightness in the chest or shoulder
These symptoms result from a decrease in blood flow due to arterial compression.
Causes of Arterial Thoracic Syndrome
The primary cause of arterial thoracic syndrome is the subclavian artery compression, often caused by abnormal anatomical structures. These include:
Cervical rib: An extra rib in the neck can compress the artery.
Thoracic outlet syndrome: Narrowing the space between the collarbone and the first rib.
Trauma or injury: Damage to blood vessels can lead to narrowing.
Prompt medical evaluation is crucial to determine the cause and prevent long-term complications associated with the syndrome.
0 notes
Text
Trusted Wound Care Doctor with Expertise in Skin Regeneration 🩺✨

When it comes to healing wounds—whether from injury, surgery, or chronic illness—the role of a trusted wound care doctor is critical. But when that care is paired with expertise in skin regeneration, it opens the door to faster recovery, improved appearance, and long-term skin health. With today’s advances in medicine, patients now benefit from treatments that not only close wounds but also help regrow healthy, functional skin.
The Vital Role of a Wound Care Doctor 👨⚕️🩹
Wound care doctors are medical professionals trained in the diagnosis, treatment, and management of a variety of skin and tissue injuries. These specialists handle wounds that are not healing properly on their own, as well as complex or high-risk wounds caused by conditions such as diabetes, poor circulation, or pressure damage.
Types of Wounds Treated ⚠️
Acute wounds – surgical incisions, lacerations, abrasions, or burns
Chronic wounds – diabetic foot ulcers, venous ulcers, pressure sores
Post-surgical wounds – especially those with complications or slow healing
Traumatic wounds – resulting from accidents or blunt force trauma
By assessing the underlying causes, wound care doctors can provide not just symptom relief but a strategic path toward healing.
Why Trust Matters in Wound Care 🤝💯
Healing is a process that requires both technical skill and patient trust. Many wound care journeys are long and emotionally taxing. A trusted wound care doctor doesn’t just treat the wound—they provide reassurance, build confidence, and establish a caring relationship with the patient.
Building a Healing Partnership ❤️🩹
Patients often feel vulnerable, especially when wounds are visible, painful, or persistent. Trust is built when doctors:
Explain the treatment plan clearly and thoroughly 📋
Listen to concerns without judgment 🧏♀️
Make the patient feel seen and respected 🙌
Stay consistent and transparent with care decisions 🧠
This connection often leads to better adherence to treatment and faster results.
What Is Skin Regeneration? 🌱🧬
Skin regeneration refers to the body’s natural ability to repair and restore damaged tissue. In cases where this process is compromised or too slow, advanced wound care doctors step in with regenerative therapies to promote new skin growth and minimize scarring.
How Regeneration Works 🧪
The skin has multiple layers, and true regeneration involves restoring not only the surface but also the underlying structures like collagen, elastin, and vascular networks. Wound care experts may use:
Growth factors and stem cell therapies
Biologic dressings (such as amniotic membrane or extracellular matrix)
Skin grafting or engineered skin substitutes
Laser or microneedling therapy to stimulate tissue repair
These techniques rebuild skin integrity, improve function, and often reduce the need for invasive surgery.
Combining Wound Care with Regenerative Medicine ⚕️🧫
Today’s top wound care doctors blend traditional medical expertise with cutting-edge regenerative techniques. This approach doesn’t just heal the wound—it restores the skin’s health, appearance, and function more completely.
Benefits of Regenerative Wound Treatments 🌟
Faster healing time ⏱️
Reduced pain and inflammation 🌬️
Lower infection risk 🔒
Less scarring and better cosmetic results 💁♂️
Enhanced mobility and function 🤸
Patients who undergo regenerative treatment often report improved quality of life and more confidence in their recovery.
Who Can Benefit from a Regenerative Wound Care Doctor? 👩🦳🧑🦼
Certain individuals may benefit more from specialized regenerative wound care, such as:
People with diabetes or peripheral vascular disease
Elderly patients with thinning or fragile skin
Surgical patients with poor wound closure or infection risk
Athletes or active individuals seeking faster return to activity
Burn victims requiring advanced skin replacement techniques
Early referral to a specialist with skin regeneration knowledge can prevent complications and reduce recovery time.
The Patient Experience: What to Expect 👣📝
When you visit a trusted wound care doctor who specializes in regeneration, you can expect a personalized, hands-on approach to healing.
Step-by-Step Healing Journey 📈
Initial Consultation – a comprehensive wound and health assessment
Wound Measurement & Imaging – to track size, depth, and tissue quality
Customized Treatment Plan – combining traditional care and regenerative therapies
Regular Monitoring & Adjustments – tweaking the plan based on healing response
Education & Self-Care – guidance on how to protect the skin and avoid future wounds
Throughout the process, the doctor will focus on both short-term wound closure and long-term skin restoration.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Regenerative Wound Care 🔮🧠
As medical technology evolves, regenerative medicine will continue to revolutionize wound care. Innovations on the horizon include:
3D-bioprinted skin grafts
Nanotechnology for drug delivery
Gene therapy for skin regeneration
AI-driven wound tracking tools
These advances promise not only to speed up healing but also to improve how skin looks and feels post-recovery.
Conclusion: Expertise You Can Trust for Healing Skin and Restoring Confidence 💎
A trusted wound care doctor with expertise in skin regeneration is more than a medical provider—they are a partner in your healing journey. By combining scientific precision, innovative therapies, and compassionate care, they help patients heal faster, look better, and feel stronger.
If you or a loved one is facing a difficult wound, don’t settle for standard care. Seek out a specialist who understands how to treat the wound and restore the skin—naturally and effectively. Because healing isn’t just about closing a wound—it’s about rebuilding hope, confidence, and quality of life. 🌈
1 note
·
View note
Text
Best CT Scan Facility in Kandivali East: A Look Inside Shreejii Hospital & Research Centre
When it comes to advanced diagnostic imaging, few names in Kandivali East stand out like Shreejii Hospital & Research Centre. Known for its patient-centric care, modern infrastructure, and reliable diagnostic services, Shreejii Hospital has earned a reputation as one of the best CT scan facilities in the area. Whether you’re a patient seeking early diagnosis or a doctor looking for precise imaging support, this hospital delivers with a blend of expertise and technology.
Why Choose Shreejii Hospital & Research Centre for CT Scans?
CT (Computed Tomography) scans are a crucial part of modern diagnostics, helping detect everything from brain injuries to tumors, organ abnormalities, and vascular conditions. At Shreejii Hospital, CT scans are conducted using state-of-the-art machines that ensure high-resolution images with minimum radiation exposure. This means patients receive accurate results with an added layer of safety.
What sets Shreejii Hospital apart is not just the technology, but also the skilled radiology team behind the machines. With a team of experienced radiologists and trained technicians, every scan is handled with utmost precision and care. Reports are reviewed promptly, and patients are guided through the process with empathy and clarity.

Book Appointment
Quick, Comfortable & Affordable Scanning Experience
Time and comfort are two important factors for anyone undergoing a scan. At Shreejii Hospital, the appointment process is fast and hassle-free, with same-day or next-day scheduling often available. The scanning process itself is smooth, with support staff on hand to help patients feel at ease — especially important for first-time visitors or those who may feel anxious.
Affordability is another key strength. Despite offering top-tier services, Shreejii Hospital maintains competitive and transparent pricing, making quality CT scans accessible to a larger section of the community. The hospital also accepts various insurance and medical benefit schemes, which further reduces out-of-pocket costs.
Types of CT Scans Offered
Shreejii Hospital offers a wide range of CT scan services, including:
CT Brain (for stroke, trauma, or neurological conditions)
CT Chest (to detect lung infections, tumors, or blockages)
CT Abdomen & Pelvis (for gastrointestinal or kidney-related issues)
CT Angiography (for heart and blood vessel evaluation)
Each scan is tailored to the patient’s clinical needs, and the radiology team works closely with referring physicians to ensure clarity in diagnosis and treatment planning.
Trusted by Doctors, Preferred by Patients
Shreejii Hospital’s CT scan department is trusted by numerous local physicians, who refer their patients here for its reliable reports and quick turnaround. For patients, the combination of expert staff, compassionate care, and modern technology makes Shreejii the go-to destination for diagnostic imaging in Kandivali East.
Book Appointment
Book Your CT Scan Today
If you or your loved one needs a CT scan, don’t compromise on quality. Visit Shreejii Hospital & Research Centre in Kandivali East for a service experience that combines trust, technology, and thoughtful care.
📞 To book an appointment or for queries, call 9920660648
🌐 Visit www.shreejiihospitals.com to learn more.
0 notes