#U.S World War II
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Two workers attaching a Pratt & Whitney R-2800 Double Wasp onto a F4U Corsair at the Chance-Vought factory in Stratford, Connecticut.
Date: March 1943
NARA: 179036630
#Vought F4U Corsair#Vought F4U#F4U Corsair#F4U#Corsair#Fighter#Aircraft#Airplane#United States Navy#U.S. Navy#US Navy#USN#Navy#World War II#World War 2#WWII#WW2#WWII History#History#Military History#Chance-Vought Factory#Factory#Stratford#Connecticut#March#1943#color photo#my post
488 notes
·
View notes
Text
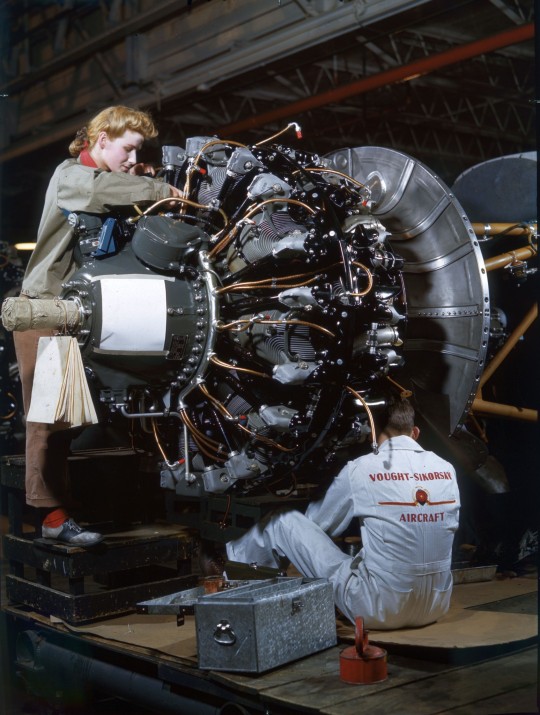
The WAVES of Change: Women's Valiant Service in World War II 🌊

When the tides of World War II swelled, an unprecedented wave of women stepped forward to serve their country, becoming an integral part of the U.S. Navy through the Women Accepted for Volunteer Emergency Service (WAVES) program. This initiative not only marked a pivotal moment in military history but also set the stage for the transformation of women's roles in the armed forces and society at large. The WAVES program, initiated in 1942, was a beacon of change, showcasing the strength, skill, and patriotism of American women during a time of global turmoil.
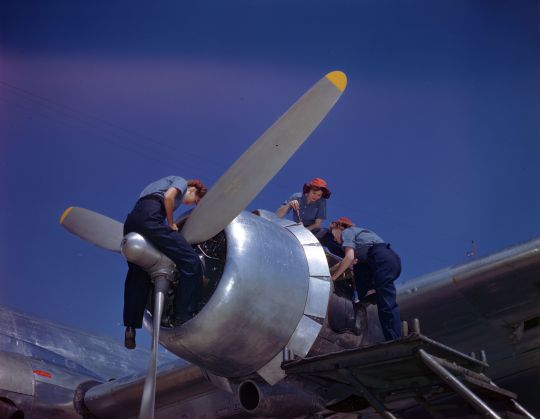

The inception of WAVES was a response to the urgent need for additional military personnel during World War II. With many American men deployed overseas, the United States faced a shortage of skilled workers to support naval operations on the home front. The WAVES program was spearheaded by figures such as Lieutenant Commander Mildred H. McAfee, the first woman commissioned as an officer in the U.S. Navy. Under her leadership, WAVES members were trained in various specialties, including communications, intelligence, supply, medicine, and logistics, proving that women could perform with as much competence and dedication as their male counterparts.

The impact of the WAVES program extended far beyond the war effort. Throughout their service, WAVES members faced and overcame significant societal and institutional challenges. At the time, the idea of women serving in the military was met with skepticism and resistance; however, the exemplary service of the WAVES shattered stereotypes and demonstrated the invaluable contributions women could make in traditionally male-dominated fields. Their work during the war not only contributed significantly to the Allies' victory but also laid the groundwork for the integration of women into the regular armed forces.

The legacy of the WAVES program is a testament to the courage and determination of the women who served. Their contributions went largely unrecognized for many years, but the program's impact on military and gender norms has been profound. The WAVES paved the way for future generations of women in the military, demonstrating that service and sacrifice know no gender. Today, women serve in all branches of the U.S. military, in roles ranging from combat positions to high-ranking officers, thanks in no small part to the trail blazed by the WAVES.
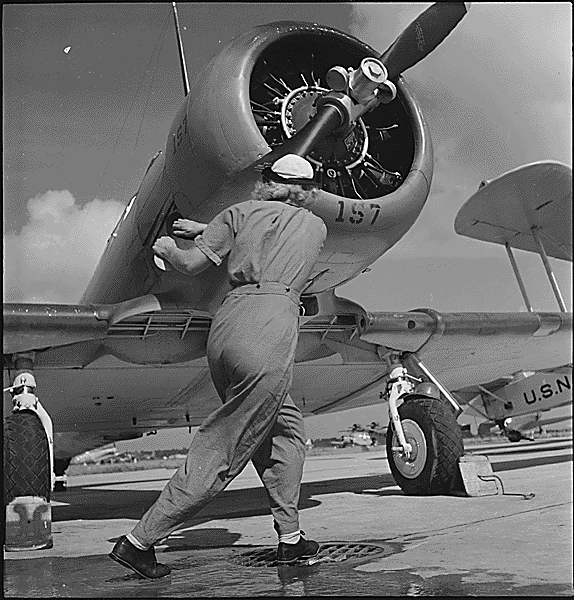
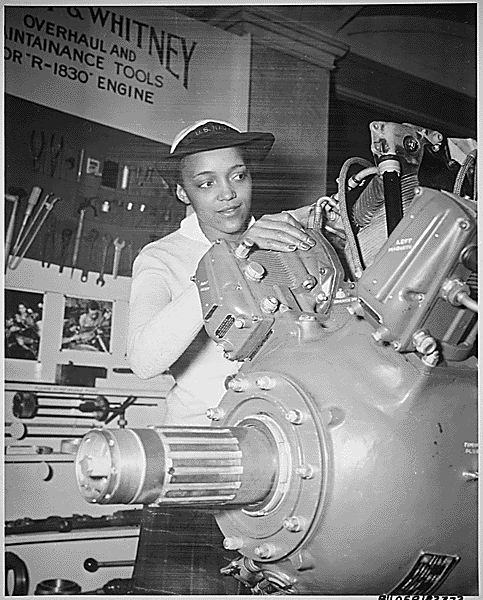
The WAVES program was more than just a wartime necessity; it was a watershed moment in the history of women's rights and military service. The women of WAVES not only supported the United States during a critical period but also propelled forward the conversation about gender equality in the armed forces and beyond. Their legacy is a reminder of the strength and resilience of women who rise to the challenge, breaking barriers and making waves in pursuit of a better world.
Read more: https://prologue.blogs.archives.gov/2023/11/06/historic-staff-spotlight-eunice-whyte-navy-veteran-of-both-world-wars/
212 notes
·
View notes
Text
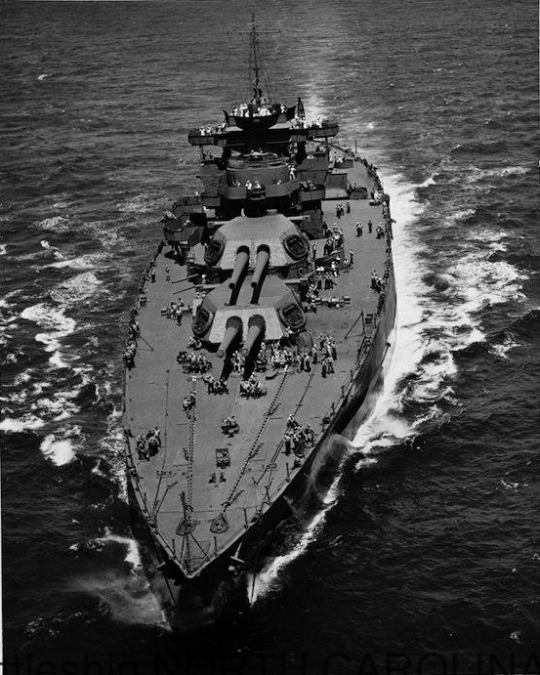
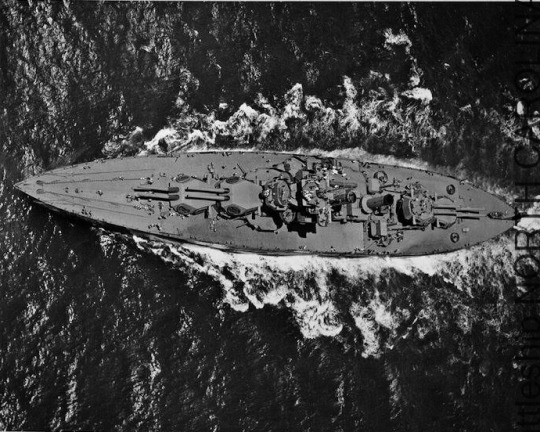
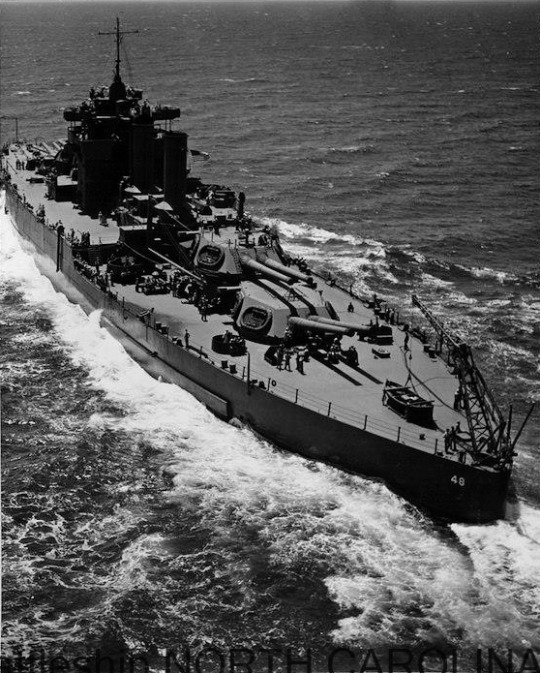






USS WEST VIRGINIA (BB-48) en route to the Puget Sound Navy Yard, Washington, for permanent repairs and reconstruction.
Date: April 30, 1943
National Archives via Battleship North Carolina Archives: P2016.026
#USS West Virginia (BB-48)#USS West Virginia#Colorado Class#Dreadnought#Battleship#Warship#Ship#World War II#World War 2#WWII#WW2#WWII History#History#United States Navy#U.S. Navy#US Navy#USN#Navy#Pacific Ocean#April#1943#my post
100 notes
·
View notes
Text
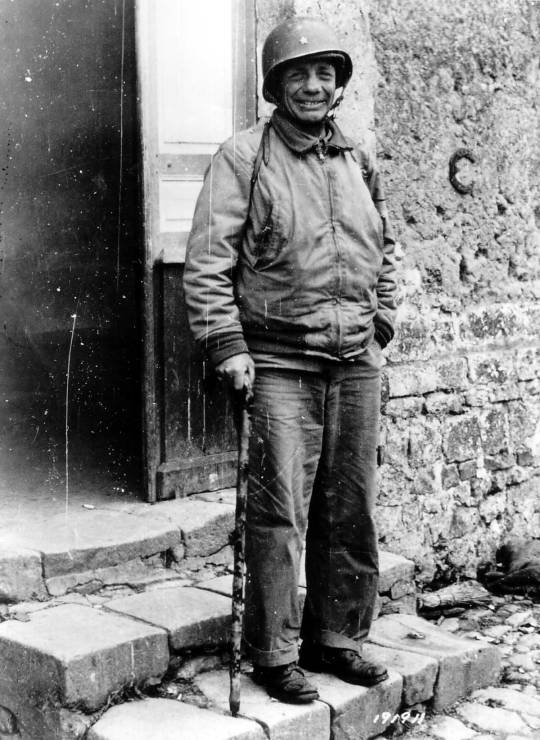

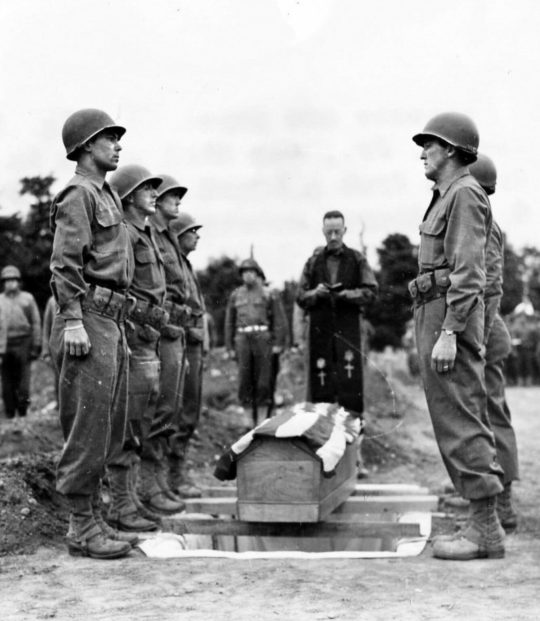
Brigadier General Theodore Roosevelt Jr. -- the eldest son of the 26th President of the United States -- was the only Allied general to land on the beaches of Normandy with the first wave of soldiers during the D-Day invasion on June 6, 1944.
Crippled by arthritis, hobbled by old combat wounds from the First World War, and forced to use a cane as he landed on Utah Beach with the U.S. Army's 4th Infantry Division on D-Day, General Roosevelt was the oldest man to take part in the opening stage of the invasion. He had made three requests to personally lead the assault on Utah Beach before finally being given command despite concerns about his health. During the confusion and chaos of the largest seaborne assault in human history, Roosevelt realized that tidal currents had carried nearly two dozen of the initial landing craft to the wrong location and was said to have announced, "We'll start the war from right here!"
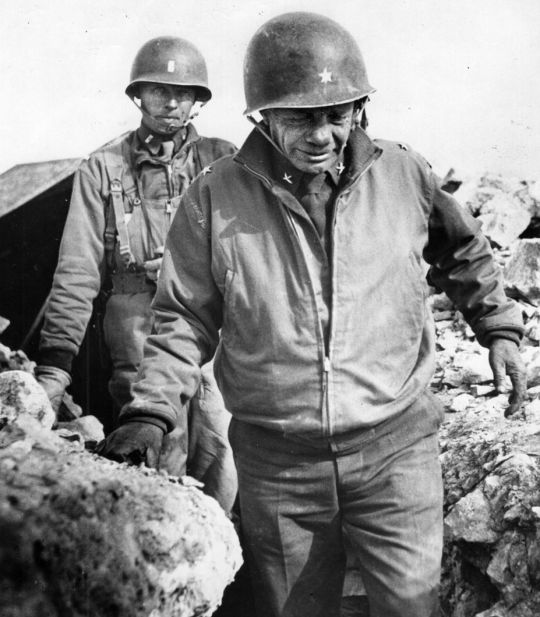


For his actions on D-Day, General Roosevelt would be awarded the country's highest military decoration, the Congressional Medal of Honor, on September 21, 1944:
For gallantry and intrepidity at the risk of his life above and beyond the call of duty of 6 June 1944, in France. After two verbal requests to accompany the leading assault elements in the Normandy invasion had been denied, Brig. Gen. Roosevelt's written request for this mission was approved and he landed with the first wave of the forces assaulting the enemy-held beaches. He repeatedly led groups from the beach, over the seawall and established them inland. His valor, courage, and presence in the very front of the attack and his complete unconcern at being under heavy fire inspired the troops to heights of enthusiasm and self-sacrifice. Although the enemy had the beach under constant direct fire, Brig. Gen. Roosevelt moved from one locality to another, rallying men around him, directed and personally led them against the enemy. Under his seasoned, precise, calm, and unfaltering leadership, assault troops reduced beach strong points and rapidly moved inland with minimum casualties. He thus contributed substantially to the successful establishment of the beachhead in France.
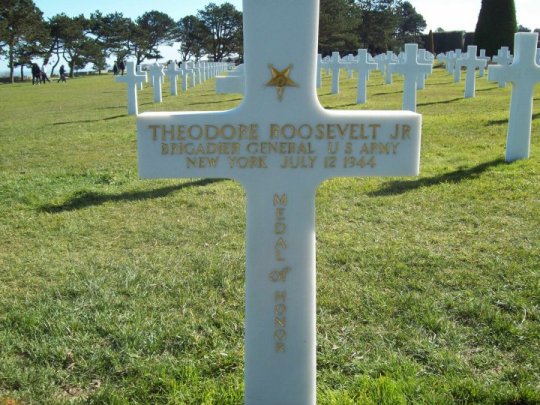
However, the Medal of Honor would be awarded to Theodore Roosevelt Jr. posthumously. On July 12, 1944, thirty-six days after landing in Normandy on D-Day, General Roosevelt died in his sleep at the age of 56 after suffering a heart attack. In a letter to his wife, General George S. Patton would write, "Teddy R[oosevelt] died in his sleep last night. He had made three landings with the leading wave -- such is fate...He was one of the bravest men I ever knew." General Patton would join General Omar Bradley and numerous other generals as honorary pallbearers at Roosevelt's funeral. Roosevelt was buried at the Normandy American Cemetery and Memorial along with thousands of his fellow American soldiers who died in Europe during World War II. He is buried next to his youngest brother, Quentin Roosevelt, who was killed in action in 1918 after being shot down over France during World War I.


#History#Theodore Roosevelt Jr.#General Theodore Roosevelt#Ted Roosevelt#Brigadier General Theodore Roosevelt Jr.#D-Day#D-Day 80#D-Day + 80 Years#World War II#WWII#Second World War#Military History#U.S. Army#Generals#Normandy Landings#Battle of Normandy#D-Day Invasion#Operation Overlord#Normandy#4th Infantry Division#Allied Generals#Theodore Roosevelt#General Ted Roosevelt#President Roosevelt#Roosevelt Family#Quentin Roosevelt#Allied Invasion of France#Utah Beach#Medal of Honor#Congressional Medal of Honor
92 notes
·
View notes
Text
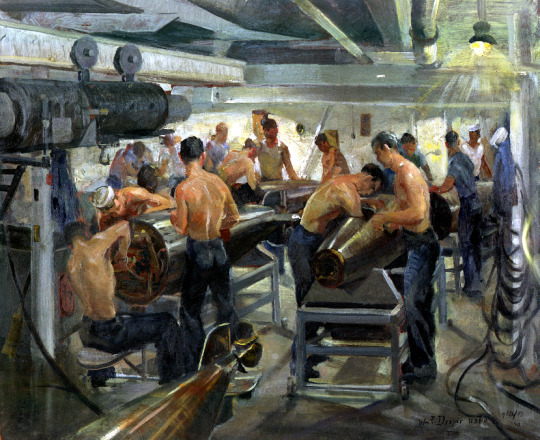

“Preparing Tin Fish,” by U.S. Naval Reserve combat artist William Franklin Draper, September 12, 1943.
Record Group 330: Records of the Office of the Secretary of Defense Series: Combined Military Service Digital Photographic Files
Image description: Painting of sailors in a small room, working on torpedoes. Some reach inside torpedoes via a side panel, some work on the head of the torpedoes, and some hold the torpedoes steady.
#archivesgov#September 12#1943#1940s#World War II#WWII#U.S. Navy#USN#sailors#torpedo#munitions#painting#art#combat art
269 notes
·
View notes
Text

World War II Propaganda (U.S. Government Printing Office, 1943)
"This is the Enemy," Barbara J. Marks Artwork.
Remember when we were fighting them, instead of electing them?
#This is the Enemy#Barbara J. Marks#World War II Propaganda#poster#art#vintage#WWII#U.S. Government Printing Office
45 notes
·
View notes
Text

Members of the Army Signal Corps come home, August 1945.
Photo: U.S. Army via the Rijksmusuem
#vintage New York#1940s#World War II#soldiers return#homecoming#U.S. Army#1940s New York#vintage NYC
44 notes
·
View notes
Text

They packed the attack... Douglas Aircraft Company ad - 1944.
#vintage illustration#vintage advertising#american industry#life during wartime#ww2#wwii#wwii era#ww2 era#the 40s#the 1940s#war production#military industrial complex#war supplies#world war ii#world war two#world war 2#u.s. military#military aircraft#douglas aircraft company#douglas aircraft#douglas sbd dauntless#douglas a-20 havoc#douglas a-20#douglas c-47 skytrain#douglas c-47
33 notes
·
View notes
Text

World War II Propaganda (U.S. Government Printing Office, 1942)
Propaganda Poster "He's Watching You," Glenn Grohe Artwork
55 notes
·
View notes
Text
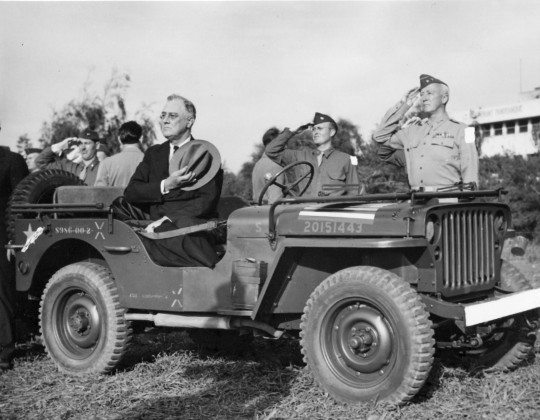

President Franklin D. Roosevelt Seated in Jeep with Hat over his Heart, Reviewing Troops with General George Patton, Casablanca.
Date: January 18, 1943
NARA: 6728535
#Jeep#Willys MB#Slat Grille#Willys#MB#Military Jeep#United States Army#U.S. Army#US Army#Army#World War II#World War 2#WWII#WW2#WWII History#History#January#1943#Casablanca#Africa#President Franklin D. Roosevelt#Franklin D. Roosevelt#President#my post
114 notes
·
View notes
Photo

United States Steel Corp, 1942
#USS#ad#1942#vintage#advertisement#illustration#wartime#homefront#WWII#appliances#kitchen#housewife#buy war bonds#U.S. Steel#advertising#World War II#home front
330 notes
·
View notes
Text
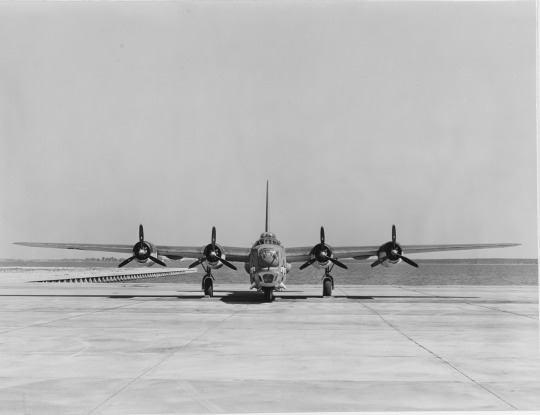
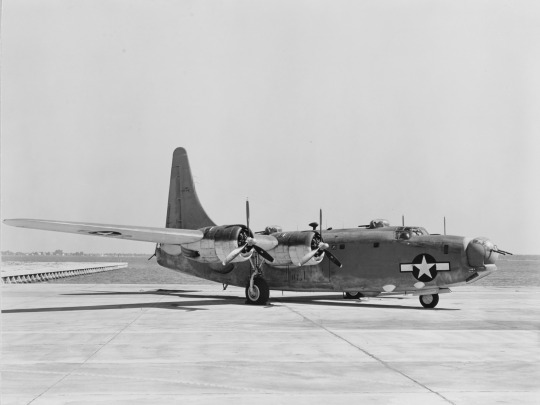
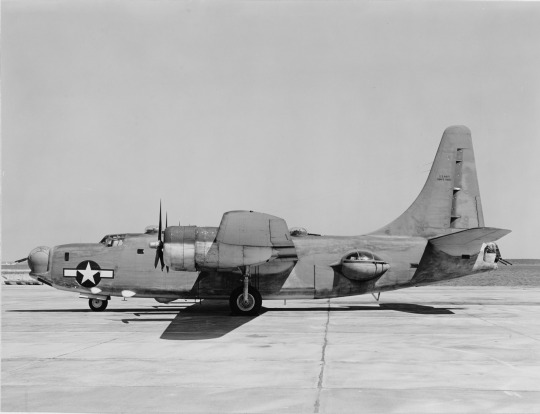
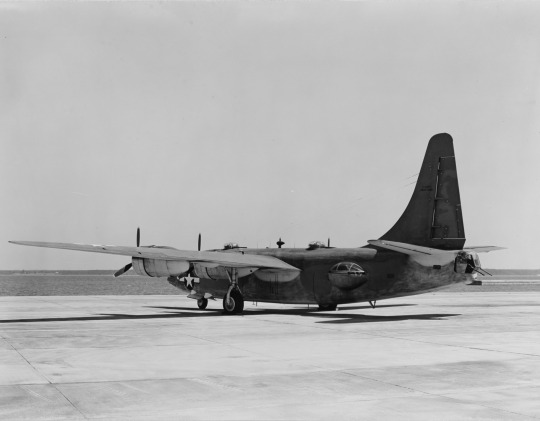




Convair PB4Y-2 Privateer (BU. no. 59351) parked at the Naval Air Station Patuxent River, Maryland.
Photographed on July 11, 1944.
U.S. Naval History and Heritage Command: NH 87982, NH 87983, NH 87984, NH 87985
#Consolidated PB4Y-2 Privateer#Consolidated PB4Y-2#PB4Y-2 Privateer#PB4Y-2#Privateer#Patrol Bomber#Bomber#United States Navy#U.S. Navy#US Navy#USN#Navy#World War II#World War 2#WWII#WW2#WWII History#History#Military History#Naval Air Station Patuxent River#Maryland#July#1943#my post
190 notes
·
View notes
Text
AP:
⭕️The US Navy is locked in combat with a shadowy, Iran-backed rebel group based in Yemen.
⭕️The US-led campaign against the Houthis has turned into the most intense running sea battle the Navy has faced since World War II.
⭕️Cmdr. Eric Blomberg with the USS Laboon: “I don’t think people really understand just kind of how deadly serious it is what we’re doing and how under threat the ships continue to be."
⭕️All signs suggest the warfare will intensify — putting US sailors, their allies and commercial vessels at more risk.
#us marines#us naval academy#us navy#u.s. navy#stand with iran#free iran#iranian#iran news#iran#free yemen#hands off yemen#stand with yemen#yemeni#yemen#houthis#world war ii#world war 2#world war two#warfare#waristerror#wariscapitalism#eat the rich#eat the fucking rich#war is coming#war is hell#war is real#war is a racket#class war#ausgov#politas
34 notes
·
View notes
Text

"Nerve systems for the Battle Wagons"
Artwork by Dwight Shepler
Posted on Flickr by James Vaughan: link
#USS NORTH CAROLINA (BB-55)#USS NORTH CAROLINA#USS WASHINGTON (BB-56)#USS Washington#North Carolina Class#Battleship#Warship#Ship#United States Navy#U.S. Navy#US Navy#USN#Navy#World War II#World War 2#WWII#WW2#WWII History#History#Military History#undated#1940s#my post
64 notes
·
View notes
Text

Gen. George S. Patton
#history#vintage#photography#portrait#black and white photography#george patton#george s patton#general#army#american army#u.s. army#us army#army histiry#veteran#us history#u.s. history#american history#20th century history#20th century#twentieth centrury#twentieth century history#world war ii#world war two#world war two history#world war ii history#war#war history
28 notes
·
View notes
Photo

“Air Surgeons recommendation that medicinal whiskey be made available all theatres of operation for the issue to Army Air Forces Combat crew members upon their return from serial combat missions or operations, is concurred in.” August 19, 1943.
Record Group 492: Records of Mediterranean Theater of Operations, United States Army
Series: Formerly Security Classified General Correspondence
File Unit: SECT 435, Coffee, Tea, Beverages, Drinks
Transcription:
Equals British Secret
Confidential
War Departement
Cmassified message center
AFHQ
Incoming message
War
filed 100233Z
AFSC N314/10
100732B
cjr
PRIORITY
FROM: AGWAR
TO: FREEDOM TO KIRK TO CARROLL, COX, KING, HAWLEY, SAMS,
TAMRAZ, MOORE, BLESSIE, MAXWELL
NO: 4590, August 1943
Air Surgeons recommendation that medicinal whiskey be made available all theatres of operation for the issue to Army Air Forces Combat crew members upon their return from serial combat missions or operations, is concurred in. Quantity required should be procured locally if possible, if not available locally, timely requisitions should be initiated if needs to be supplied from here. Forward immediately estimate of quantity required next 6 months.
ACTION: SURGEON
INFORMATION: SGS
NAAF
NAASC
DTC
RECORDS
MC IN 4536 10 AUG 43 1004B Ref No: 4590 jc
Equals British Secret
Confidential [crossed] Copy No. 12
The making of an exact copy of this message is forbidden
Regraded unclassified [stamp]
Order Sec Army by Tag per 60512 [stamp]
#archivesgov#August 19#1943#1940s#World War II#WWII#military#alcohol#coping mechanisms#U.S. Army#Army Air Force
190 notes
·
View notes