#Thin Film Photovoltaic Cells
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Thin Film Photovoltaic Cells Market Forecast 2024 to 2032
Thin film photovoltaic cells, often referred to as thin film solar cells, are a type of solar cell technology that uses very thin layers of photovoltaic (PV) materials to convert sunlight into electricity. Unlike traditional crystalline silicon solar cells, which are typically rigid and thick, thin film solar cells are much thinner and can be produced using various deposition techniques on a variety of flexible or non-traditional substrates. This versatility in terms of substrate and manufacturing process allows for potential cost savings and new applications.
The Thin Film Photovoltaic Cells Market was valued at USD 1,736.85 Million in 2022 and is expected to register CAGR of 15.93% by 2032.
The Thin Film Photovoltaic Cells market is driven by key factors such as increasing demand for renewable energy sources, advancements in thin film technology, and increasing efficiency.
Get PDF Sample Report: https://www.xcellentinsights.com/enquiry/sample/1418
By Market Vendors:
Astronergy
AVANCIS
Eguana Technologies
First Solar
Hanergy Holding
Global Solar Energy
MiaSole
Solibro
Kaneka
Masdar
NexPower Technology
Sharp Solar Energy Solutions
Solar Frontier
SUNGEN International
Trony Solar Holdings
TSMC Solar
By Types:
Gallium Arsenide
Copper Indium Selenium
Cadmium Telluride
By Applications:
Business
Industrial
Residential
Get Full report + Tables + Graphs: https://www.xcellentinsights.com/reports/thin-film-photovoltaic-cells-market-1418
About Us:
Xcellent Insights is a market intelligence provider and consulting firm. We offer data-driven research services based on multiple analysis frameworks which helps businesses across the globe to understand current market scenario and align their strategic initiatives.
We offer syndicated research reports, customized research reports, consulting services and datasets which are mapped across multiple datapoints.
We provide research reports for all the industry sectors like Consumer Goods, Packaging, Chemicals and Materials, Healthcare, Pharmaceuticals, Medical Devices, Agriculture, Food and Beverages, Automobile and transportation, Electronics and Semiconductors, IT and Communication, Energy and Power, Machinery and Equipment.
Contact Us:
Name: Willie J
Phone: US: +1 4086277717
UK: +44 2086386439
Email: [email protected]
#Thin Film Photovoltaic Cells Market#Thin Film Photovoltaic Cells Market size#Thin Film Photovoltaic Cells Market share#Thin Film Photovoltaic Cells
0 notes
Text
Perovskite Solar Cell Market is Estimated to Witness High Growth Owing to Increasing Advent

Perovskite solar cells are a emerging photovoltaic technology that can convert sunlight into electricity. Perovskite material, a type of hybrid organic-inorganic lead or tin halide-based material, is used in the manufacture of perovskite solar photovoltaic cells. Key advantages of perovskite solar cells includes high power conversion efficiency, low manufacturing costs, flexibility and semitransparency. With governments across countries focusing on adopting renewable energy sources to meet increasing power demand as well as curb GHG emissions, the use of cost-effective solar technologies like perovskite solar cells is on the rise. Global Perovskite Solar Cell Market is estimated to be valued at USD 188.4 Mn in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 4,392.1 Mn by 2031, exhibiting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 56.8% from 2024 to 2031.
Key Takeaways Key players operating in the Perovskite Solar Cell market are Saule Technologies, FrontMaterials Co. Ltd., Xiamen Weihua Solar Co. Ltd., Fraunhofer ISE, Polyera Corporation, Solaronix SA, Dyesol, FlexLink Systems Inc., New Energy Technologies Inc, Oxford Photovoltaics, Hanwha Q CELLS, CubicPV, EneCoat Technologies, Microquanta Semiconductor, Greatcell Energy, Oxford PV, P3C, Perovskia Solar AG. The industry is witnessing lot of investments and research collaborations among key stakeholders to further improve efficiency and commercialization of perovskite solar cell technology. The key opportunities in the Perovskite Solar Cell Market Demand include the adoption of perovskite solar cells in building integrated photovoltaics owing to lightweight and semitransparency of the material. Rising photovoltaic installations worldwide is also driving research on more cost-effective solar technologies. Globally, the demand for perovskite solar cells is expected to significantly grow especially across Asia Pacific and European countries. Countries like China, India, Japan, UK, Germany are investing heavily to ramp up domestic production of perovskite solar panels to meet their renewable energy targets. Market drivers The increasing advent of cost-effective solar technologies is one of the key drivers propelling the demand for perovskite solar cells. With continuous research to improve efficiency and stability, the total cost of electricity from perovskite solar cells is declining rapidly making them more competitive than other commercial solar cell technologies. Growing focus on the use of renewable energy for both utility-scale projects as well as off-grid applications is further boosting the market growth.
PEST Analysis - Political: Solar energy policies in various countries are positively supporting perovskite solar cell market by providing subsidies and incentives. The governments are also mandating use of renewable energy sources including solar which is benefiting market growth. - Economic: Perovskite solar cells offer significant cost advantage over existing solar technologies which is attracting investments in R&D. The decreasing costs of manufacturing technology is making them commercially viable for mass adoption driving market revenues. - Social: Growing environmental concerns over climate change and depletion of conventional energy sources is increasing preference for clean and renewable solar energy among consumers and industries. This is positively impacting demand. - Technological: Significant research is being done to improve efficiency, stability and lifetime of perovskite solar cells. The new developments are making them more competitive against other solar technologies which will accelerate commercialization and market expansion. Perovskite solar cell market value is majorly concentrated in the Asia Pacific region, especially China, Japan and South Korea. This is due to presence of leading manufacturing companies, favorable government policies and growing demand for renewable energy in these countries. Europe is also emerging as a significant regional market driven by policy push for solar adoption and investments in solar innovation by companies. In terms of revenue growth, the market in Middle East and Africa region is projected to witness fastest expansion during the forecast period. This is attributed to increasing power demands, abundant solar resources and infrastructural development projects incorporating renewable energy in these regions. The initiatives to diversify energy sources away from oil and focus on solar will considerably support perovskite solar cell adoption and market revenues.
Get more insights on Perovskite Solar Cell Market
About Author:
Ravina Pandya, Content Writer, has a strong foothold in the market research industry. She specializes in writing well-researched articles from different industries, including food and beverages, information and technology, healthcare, chemical and materials, etc. (https://www.linkedin.com/in/ravina-pandya-1a3984191)
#Coherent Market Insights#Perovskite Solar Cell Market#Perovskite Solar Cell#Solar Energy#Photovoltaics#Renewable Energy#Thin-Film Solar Cells#Solar Technology#Energy Conversion
0 notes
Text
Thin-film Amorphous Silicon Solar Cell Market Research, Analysis, Demand, Overview and Regional Outlook Study 2017 – 2032
The market for solar photovoltaic (PV) cells based on thin layers of amorphous silicon, a non-crystalline type of silicon, is known as the thin-film amorphous silicon solar cell market. In comparison to conventional crystalline silicon sun cells, these thin-film solar cells provide benefits including flexibility, light weight, and low production costs. The demand for thin-film amorphous silicon solar cells is described in the following way:
Market Overview: In recent years, the thin-film amorphous silicon solar cell market has seen rapid expansion. The market has grown as a result of the rising demand for renewable energy, improvements in thin-film solar cell technology, and the requirement for affordable solar solutions. Applications for thin-film amorphous silicon solar cells include consumer electronics, off-grid solar systems, and building-integrated photovoltaics..
Demand Drivers:
Thin-film amorphous silicon solar cell demand would be influenced by a number of variables, such as government policies and incentives encouraging the use of solar energy, advances in thin-film technology, thin-film solar cells' cost competitiveness with other solar technologies, and the expansion of the solar energy market as a whole.
1. The switch to renewable energy: It sources has raised demand for solar photovoltaic (PV) technology due to environmental concerns and the need to minimise carbon emissions. Thin-film amorphous silicon solar cells have the ability to be produced on a big scale and at a low cost, helping to meet this need.
2. Flexible and Lightweight Design: Thin-film amorphous silicon solar cells have features that make them flexible and lightweight, making them appropriate for uses where conventional rigid solar panels are impractical. The potential applications of these cells are increased by their incorporation into curved surfaces, flexible substrates, and portable devices.
3. Cost-Effective Manufacturing: The production of thin-film amorphous silicon solar cells entails depositing amorphous silicon in thin layers on a variety of substrates, including flexible materials and glass. Thin-film technology is a cost-effective alternative since this production method enables higher throughput and cheaper material costs when compared to crystalline silicon solar cells.
4. Building-Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV): In BIPV, solar panels are integrated into building components like windows, facades, or roofing. Thin-film amorphous silicon solar cells are frequently utilised in BIPV. Solar energy production is made possible by this integration while yet keeping the beauty of the building.
5. Off-Grid and Portable Solar Systems: Thin-film amorphous silicon solar cells are suitable for off-grid and portable solar systems due to their flexibility and light weight. These cells can be deployed in rural and distant locations. These cells can be used in remote areas, rural electrification projects, camping equipment, and charging solutions for portable electronics.
In conclusion, the demand for building-integrated photovoltaics, off-grid and portable solar systems, flexibility and lightweight thin-film technology, and cost-effective manufacturing processes all contribute to the growth of the thin-film amorphous silicon solar cell market. Thin-film amorphous silicon solar cells are anticipated to play a vital role in satisfying the growing demand for clean and sustainable power generation as solar energy continues to gather momentum.
Here are some of the key benefits:
1. Cost-Effective Solar Technology: Low-cost components and production techniques can be used to create thin-film amorphous silicon solar cells.
Thin-film amorphous silicon solar cells: can be deposited on flexible substrates, making it possible to create lightweight and flexible solar panels.
3. Low-Light Performance: Amorphous silicon solar cells operate well in dimly lit regions, making them appropriate for locations with diffuse sunlight or light shade.
4. Rapid Energy Payback: When compared to other solar technologies, thin-film amorphous silicon solar cells have a comparatively quick energy payback time, which is the amount of time it takes to produce the same amount of energy that was used during manufacture.
Referrals to our Stringent datalytics company, trade journals, and websites that focus on market reports are encouraged. These sources frequently include thorough research, market trends, growth projections, competition analysis, and other insightful information about this market.
You can investigate the availability of particular reports linked to this market by going to our website or getting in touch with us directly. We offer thorough and in-depth information that might be helpful for firms, investors, and individuals interested in this industry, but these reports frequently need to be purchased or subscribed to.
“Remember to look for recent reports to ensure you have the most current and relevant information.”
Click Here, To Get Free Sample Report: https://stringentdatalytics.com/sample-request/thin-film-amorphous-silicon-solar-cell-market/10440/
Market Segmentations:
Global Thin-film Amorphous Silicon Solar Cell Market: By Company • Hanergy • Sharp Thin Film • Trony • Nexpower • GS Solar • Kaneka Solartech • Best Solar • QS Solar • T-Solar Global • Solar Frontier • Panasonic • Bosch Solar • United Solar • Kaneka • Schott Solar Global Thin-film Amorphous Silicon Solar Cell Market: By Type • Single Junction • Dual-junction • Multi-junction Global Thin-film Amorphous Silicon Solar Cell Market: By Application • Lamps • Chargers • Pest Controller • Power Stations • Curtain Wall Global Thin-film Amorphous Silicon Solar Cell Market: Regional Analysis The regional analysis of the global Thin-film Amorphous Silicon Solar Cell market provides insights into the market's performance across different regions of the world. The analysis is based on recent and future trends and includes market forecast for the prediction period. The countries covered in the regional analysis of the Thin-film Amorphous Silicon Solar Cell market report are as follows: North America: The North America region includes the U.S., Canada, and Mexico. The U.S. is the largest market for Thin-film Amorphous Silicon Solar Cell in this region, followed by Canada and Mexico. The market growth in this region is primarily driven by the presence of key market players and the increasing demand for the product. Europe: The Europe region includes Germany, France, U.K., Russia, Italy, Spain, Turkey, Netherlands, Switzerland, Belgium, and Rest of Europe. Germany is the largest market for Thin-film Amorphous Silicon Solar Cell in this region, followed by the U.K. and France. The market growth in this region is driven by the increasing demand for the product in the automotive and aerospace sectors. Asia-Pacific: The Asia-Pacific region includes Singapore, Malaysia, Australia, Thailand, Indonesia, Philippines, China, Japan, India, South Korea, and Rest of Asia-Pacific. China is the largest market for Thin-film Amorphous Silicon Solar Cell in this region, followed by Japan and India. The market growth in this region is driven by the increasing adoption of the product in various end-use industries, such as automotive, aerospace, and construction. Middle East and Africa: The Middle East and Africa region includes Saudi Arabia, U.A.E, South Africa, Egypt, Israel, and Rest of Middle East and Africa. The market growth in this region is driven by the increasing demand for the product in the aerospace and defense sectors. South America: The South America region includes Argentina, Brazil, and Rest of South America. Brazil is the largest market for Thin-film Amorphous Silicon Solar Cell in this region, followed by Argentina. The market growth in this region is primarily driven by the increasing demand for the product in the automotive sector.
Visit Report Page for More Details: https://stringentdatalytics.com/reports/thin-film-amorphous-silicon-solar-cell-market/10440/
Reasons to Purchase Thin-film Amorphous Silicon Solar Cell Market Report::
• To obtain insights into industry trends and dynamics, including market size, growth rates, and important factors and difficulties. This study offers insightful information on these topics.
• To identify important participants and rivals: This research studies can assist companies in identifying key participants and rivals in their sector, along with their market share, business plans, and strengths and weaknesses.
• To comprehend consumer behaviour: these research studies can offer insightful information about customer behaviour, including preferences, spending patterns, and demographics.
• To assess market opportunities: These research studies can aid companies in assessing market chances, such as prospective new goods or services, fresh markets, and new trends.
In general, market research studies offer companies and organisations useful data that can aid in making decisions and maintaining competitiveness in their industry. They can offer a strong basis for decision-making, strategy formulation, and company planning.
About US:
Stringent Datalytics offers both custom and syndicated market research reports. Custom market research reports are tailored to a specific client's needs and requirements. These reports provide unique insights into a particular industry or market segment and can help businesses make informed decisions about their strategies and operations.
Syndicated market research reports, on the other hand, are pre-existing reports that are available for purchase by multiple clients. These reports are often produced on a regular basis, such as annually or quarterly, and cover a broad range of industries and market segments. Syndicated reports provide clients with insights into industry trends, market sizes, and competitive landscapes. By offering both custom and syndicated reports, Stringent Datalytics can provide clients with a range of market research solutions that can be customized to their specific needs
Contact US:
Stringent Datalytics
Contact No - +1 346 666 6655
Email Id - [email protected]
Web - https://stringentdatalytics.com/
#Thin-film Amorphous Silicon Solar Cell#Solar Energy#Photovoltaics#Renewable Energy#Solar Cell Technology#Energy Efficiency#Thin-film Solar Panels#Amorphous Silicon Technology#Alternative Energy#Solar Power Generation#Sustainable Energy#Energy Conversion#Solar Panel Efficiency#Green Technology#Solar Energy Harvesting#Clean Energy#Solar Cell Manufacturing#Solar Energy Innovation#Photovoltaic Modules#Thin-film PV#Solar Electricity.#global market report#global market insights
0 notes
Text
Excerpt from this press release from the US Department of Energy:
As part of President Biden’s Investing in America agenda, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) today announced a $71 million investment, including $16 million from the President’s Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, in research, development, and demonstration projects to grow the network of domestic manufacturers across the U.S. solar energy supply chain. The selected projects will address gaps in the domestic solar manufacturing capacity for supply chain including equipment, silicon ingots and wafers, and both silicon and thin-film solar cell manufacturing. The projects will also open new markets for solar technologies such as dual-use photovoltaic (PV) applications, including building-integrated PV and agrivoltaics.
These efforts complement and strengthen the Biden-Harris Administration’s goal to rapidly deploy clean energy to help achieve net-zero emissions by 2050. These efforts advance the Biden-Harris Administration’s Justice40 initiative, which set a goal that 40% of overall benefits from certain federal climate and clean energy investments flow to disadvantaged communities that are marginalized by underinvestment and overburdened by pollution.
31 notes
·
View notes
Text

Semiconductors: Copper Zinc Tin Sulfide (CZTS)
A quaternary compound, Cu2ZnSnS4 is most commonly known as copper zinc tin sulfide, or simply CZTS. Today, it is most of interest for thin film solar cells, such as the one depicted in the image above. First created in the late 1960s, the compound's photovoltaic properties started to generate interest (and further research) in the 1980s and 90s. It has a reported band gap of 1.4–1.5 eV and is said to take the form of greenish-black crystals in bulk.
Beyond it's properties, CZTS is of interest because of how it's elemental composition differs from other common solar cell materials: all four elements in the compound are considered common, relatively inexpensive, safe raw materials. Whereas other solar cells may use expensive indium or tellurium, or toxic cadmium, CZTS cells promise lower costs and higher safety.
Challenges with CZTS include the formation of secondary phases, such as CuS or ZnS, which have been shown to have detrimental results on the desirable solar cell properties. These phases can be difficult to detect, though there are processes that can remove certain impurities. Elements and compounds like Zn and SnS are also relatively volatile, which can lead to processing challenges.
Sources/Further Reading: (Image source - 2024 article) (2015 Book chapter) (Stanford University) (AZoM) (Wikipedia)
#Materials Science#Science#Semiconductors#MaterialsPosts#Copper#Zinc#Tin#Sulfides#Solar power#MyMSEPost
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Global Thin film Solar Cell Market Is Estimated To Witness High Growth Owing To Increasing Adoption of Renewable Energy Sources

The global Thin film Solar Cell Market is estimated to be valued at US$ 33.01 Bn in 2022 and is expected to exhibit a CAGR of 19.4% over the forecast period 2023-2030, as highlighted in a new report published by Coherent Market Insights. A) Market Overview: Thin film solar cells are made from semiconductor materials that convert sunlight into electrical energy. These solar cells offer various advantages such as flexibility, lightweight, and superior aesthetics compared to traditional solar panels. The need for clean and sustainable energy sources is driving the demand for thin film solar cells as they provide an efficient way to generate electricity from the sun. With the increasing focus on reducing carbon emissions and combating climate change, the demand for renewable energy sources like thin film solar cells is expected to witness significant growth. B) Market Key Trends: One key trend in the thin film solar cell market is the increasing investment in research and development activities to enhance the efficiency of these solar cells. Researchers and manufacturers are investing in developing new materials and technologies to improve the conversion efficiency of thin film solar cells. For example, Oxford Photovoltaics, one of the key players in the market, is developing perovskite-based solar cells that have shown promising results in terms of efficiency and cost-effectiveness. This trend is driving innovation in the market and is expected to lead to the commercialization of more efficient thin film solar cell products. C) PEST Analysis: Political: Governments around the world are implementing favorable policies and incentives to promote the adoption of renewable energy sources. This is creating a conducive environment for the growth of the thin film solar cell market. Economic: The declining cost of thin film solar cells, coupled with the increasing demand for clean energy, is driving the economic feasibility of these solar cells. This is attracting investments from both government and private entities. Social: The increasing awareness about the environmental impact of traditional energy sources is driving the social acceptance and demand for renewable energy solutions like thin film solar cells. Additionally, the aesthetics and design flexibility offered by these solar cells are appealing to consumers. Technological: Advances in thin film solar cell technologies are improving their efficiency and performance. New materials and manufacturing processes are being developed, leading to the commercialization of more efficient and cost-effective products. D) Key Takeaways: Paragraph 1: The Global Thin Film Solar Cell Market Demand is expected to witness high growth, exhibiting a CAGR of 19.4% over the forecast period, due to increasing adoption of renewable energy sources. The need for clean and sustainable energy solutions is driving the demand for thin film solar cells. Paragraph 2: The Asia Pacific region is expected to dominate the thin film solar cell market, with countries like China, India, and Japan leading the way in terms of installation and production capacity. The region's favorable government policies, abundant solar resources, and growing energy demand are contributing to its fast-paced growth in the market. Paragraph 3: Key players operating in the global thin film solar cell market are Ascent Solar Technologies, Inc., FIRST SOLAR, Kaneka Corporation, MiaSolé Hi-Tech Corp., and Oxford Photovoltaics. These companies are investing in research and development activities to improve the efficiency and performance of their thin film solar cell products. They are also focusing on strategic collaborations, partnerships, and mergers and acquisitions to expand their market presence.
#Thin Film Solar Cell Market#Thin Film Solar Cell Market Demand#Solar Cells#Thin Film Solar Cell Market GRowth#Thin Film Solar Cell Market Trends#Coherent Market Insights
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Thin Film Solar Cell Market
Thin Film Solar Cell Market Size, Share, Trends: First Solar, Inc. Leads
Integration of Thin Film Solar Cells in Consumer Electronics
Market Overview:
The thin film solar cell market is expected to develop at a CAGR of 12.5% from 2024 to 2031. The market value is predicted to rise from USD XX billion in 2024 to USD YY billion in 2031. Asia-Pacific dominates the market, accounting for the vast majority of worldwide sales. Key metrics include increased use of renewable energy sources, rising demand for building-integrated photovoltaics, and technological breakthroughs in thin-film solar cell efficiency. The market is expanding rapidly due to the global push for clean energy, lower manufacturing costs, and the adaptability of thin-film solar cells in a variety of applications. The industry is transitioning to more efficient and adaptable solar cell technologies, particularly in emerging markets and specialist applications.
DOWNLOAD FREE SAMPLE
Market Trends:
The thin-film solar cell business is expanding rapidly as these cells become more integrated into consumer products. The increased need for portable, self-powered devices, as well as the necessity for sustainable energy solutions in everyday products, are driving this trend. For example, the use of thin-film solar cells in smartphones has resulted in an estimated 15% increase in battery life for outdoor applications. Furthermore, the market for solar-powered wearables, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, has increased by 30% over the last year, with thin-film solar cells playing a critical role in increasing device autonomy. Thin film solar cells' flexibility and lightweight nature make them perfect for integration into a wide range of consumer devices, creating new market opportunities and driving product design innovation.
Market Segmentation:
The Cadmium Telluride (CdTe) segment dominates the thin film solar cell market, accounting for the largest market share. Cadmium telluride (CdTe) has emerged as the dominant force in the thin film solar cell market, owing to its low cost, high efficiency, and well-established manufacturing techniques. This segment's popularity stems from the technology's ability to provide competitive performance at cheaper costs when compared to other thin film technologies and classic crystalline silicon cells. According to industry experts, CdTe thin film solar cells have attained a record efficiency of 22.1% in laboratory settings, while commercial modules typically achieve efficiencies of 18-19%.
Market Key Players:
The thin film solar cell market is highly competitive, with major players focusing on technological innovation and strategic alliances. Key companies such as First Solar, Inc., Solar Frontier K.K., Hanergy Thin Film Power Group Limited, Ascent Solar Technologies, Inc., Kaneka Corporation, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, Sharp Corporation, Suntech Power Holdings Co., Ltd., United Solar Ovonic LLC, and Trony Solar Holdings Co., Ltd. dominate the market.
Contact Us:
Name: Hari Krishna
Email us: [email protected]
Website: https://aurorawaveintellects.com/
0 notes
Text
Two-Dimensional Materials Market: Growth, Trends and Opportunities Through 2024-2031
The Two-Dimensional Materials Market is creating waves across multiple industries, from electronics and energy to healthcare and automotive. Characterized by ultra-thin structures just one atom thick, materials such as graphene, molybdenum disulfide, and hexagonal boron nitride offer exceptional electrical, thermal, and mechanical properties. These qualities have led to widespread interest and investment in the 2D Materials Market, which promises to reshape sectors dependent on lightweight, durable, and conductive materials.
According to BIS Research, the Two-Dimensional Materials Market is set to grow from $526.1 million in 2022 to $4 billion by 2031, with a CAGR of 25.3% over the forecast period.
Market Growth and Trends
Driven by breakthroughs in nanotechnology, the Two-Dimensional Materials Market is expected to expand rapidly in the coming years. Electronics and energy storage are two of the fastest-growing applications, where 2D materials enhance efficiency and sustainability. The market is further propelled by demand for flexible and miniaturized electronics, particularly in the semiconductor and photovoltaic industries, making these materials an attractive choice for next-generation applications.
Request a Free Sample Report on the Two-Dimensional Materials Market
Key Technologies Shaping the Market
Several notable 2D materials are leading the transformation in this sector:
· Graphene: Known for its incredible strength and conductivity, graphene is ideal for high-performance sensors, batteries, and flexible electronic devices.
· Molybdenum Disulfide (MoS₂): Frequently used in transistors and photodetectors, MoS₂ is popular for its stability and flexibility in nanoelectronics.
· Hexagonal Boron Nitride: This material acts as an excellent insulator and is widely used in high-performance thermal management systems.
Demand Drivers
Key drivers shaping the Two-Dimensional Materials Market include:
· Rising Demand for Miniaturized Electronics: As industries shift towards compact and lightweight electronic devices, 2D materials offer a sustainable solution without compromising performance.
· Sustainability Goals in Energy: The demand for energy-efficient materials in solar cells, fuel cells, and batteries fuels the growth of 2D materials.
· Medical and Biotechnology Applications: With exceptional biocompatibility and electrical conductivity, 2D materials support the development of advanced medical devices and sensors. Download Complete TOC of the Two-Dimensional Materials Market Report
On-Field to Lead the Two-Dimensional Materials Market
On-field applications of 2D materials are expected to lead the market, especially in sectors like flexible electronics and wearable technologies, where adaptability and durability are critical. These materials’ unique attributes facilitate the development of cutting-edge products, from transparent conductive films to biocompatible implants, opening avenues for real-world, on-field applications across industries.
Key Players
Company Type 1 (by Material Type): Graphene
· NanoXplore Inc.
· Cabot Corporation
And many others
Company Type 2 (by Material Type): Black Phosphorus
Smart-elements GmbH
Ossila Ltd.
Company Type 3 (by Material Type): Mxene
· Ossila Ltd.
· ACS Material LLC
And many others
Company Type 4 (by Material Type): TMDCs
Ossila Ltd
6 Carbon Technology
PlanarTECH LLC
And many others
Get More Market Insights on Advanced-materials-chemicals
Conclusion
The Two-Dimensional Materials Market is on an upward trajectory as demand for advanced materials grows across diverse applications. With their superior physical properties and versatility, 2D materials are set to redefine the future of electronics, energy storage, and biomedical applications. BIS Research, recognized as a best market research company, provides premium market intelligence reports on deep technologies poised to cause significant market disruption in the coming years.
At BIS Research, we focus exclusively on technologies related to precision medicine, medical devices, diagnostics, life sciences, artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), Internet of Things (IoT), big data analysis, blockchain technology, 3D printing, advanced materials and chemicals, agriculture and FoodTech, mobility, robotics and UAVs, and aerospace and defense, among others
0 notes
Text
6 Solar Energy Careers and Their Roles in the Industry
The Newcastle solar energy industry has grown rapidly over the past decade, creating a wide range of career opportunities in various sectors. From research and development to installation and maintenance, solar-related jobs are essential to powering the future. If you aim to land a career in the solar industry, here are some careers you might want to consider and their roles:
Solar Panel Installer
A solar panel installer is a professional responsible for setting up solar photovoltaic (PV) systems that convert sunlight into electricity. Their job encompasses a variety of tasks to ensure the safe, efficient, and effective installation of solar panels. Some of what they do is perform site assessments. It is when they evaluate the installation site to determine the system's feasibility. They inspect roofs, grounds, or other areas to ensure they can support solar panels. They also work with designers and engineers to plan the layout of the solar panel system and determine the angle, positioning, and orientation of panels for optimal sunlight exposure.
Project Manager
A project manager in the solar industry oversees and coordinates the planning, implementation, and completion of solar energy projects, ensuring they meet quality, budget, and timeline objectives. Their responsibilities span multiple stages of a solar project, from conception to commissioning. When it comes to project planning, they define the project scope, objectives, and deliverables. They also develop detailed project timelines and schedules. Regarding the budget, they prepare and manage budgets for solar projects. Part of their job is monitoring costs and ensuring everything stays within budget.
Solar Engineer
A solar engineer plays a critical role in designing and maintaining solar energy systems. Their work focuses on the technical and scientific aspects of harnessing solar power to produce electricity or heat. In system design and planning, they calculate energy output based on solar radiation levels, location, and orientation of panels. They also create technical drawings and layouts using software like AutoCAD, PVsyst, or similar tools. Some of their skills include proficiency in renewable energy systems and solar technologies, strong analytical and mathematical skills, and familiarity with software for simulation and design.
Sales Representative
A sales representative connects potential customers with solar energy solutions. Their primary responsibility is to educate clients about the benefits of solar energy and assist them in selecting the best solar products and services to meet their needs. Some of what they do is identify and contact potential customers through various channels such as phone calls, online inquiries, and in-person visits. They also attend trade shows, community events, or seminars to promote solar products and services. Another side of their job includes educating clients. They explain the benefits of solar energy, including cost savings, environmental impact, and government incentives, and provide clear information about solar system types, warranties, and maintenance requirements.
Research Scientist
A solar research scientist conducts advanced studies and experiments to improve solar energy technologies, optimise efficiency, and develop innovative applications for solar power. Their work is critical in advancing the field of renewable energy. To do all this, they study and develop new materials for solar panels, such as thin films, perovskites, or other advanced photovoltaic materials, and explore innovative designs to enhance solar cell efficiency and durability. With what they do, there is a reduction in the cost of solar energy, an increase in the adoption of sustainable energy sources, address global energy challenges, and contribute to climate change mitigation.
Marketing Manager
A solar marketing manager promotes solar energy products and services, driving customer awareness, and enhancing the company's market presence. Their primary responsibilities include strategic planning, branding, and customer engagement within the solar energy industry. They research competitors, pricing trends, and customer behaviour. Identifying emerging markets and opportunities for solar energy solutions is also part of the job. Their skills and qualifications revolve around marketing expertise, communication skills, analytical skills, creativity, and knowledge of solar technology.
The solar energy sector offers a broad range of job opportunities, each critical to the growth and development of renewable energy solutions. Whether you are interested in hands-on technical work, sales, project management, or policy advocacy, the solar industry provides a variety of rewarding career paths that contribute to a sustainable future.
0 notes
Text
Solar Power System for Homes: A Sustainable Energy Solution

In today's world, where climate change and environmental concerns are becoming increasingly prominent, finding alternative energy sources is essential. Among the most popular and effective solutions is solar power. Solar power systems for homes are a sustainable, cost-effective, and eco-friendly way to meet a household's energy needs. This article will explore the benefits, components, installation process, and costs associated with solar power systems for residential use.
What is a Solar Power System?
A solar power system is a setup that converts sunlight into electricity through solar panels. These panels are made up of photovoltaic (PV) cells, which capture sunlight and convert it into electricity. The system consists of several key components: solar panels, an inverter, batteries (optional), and a monitoring system. The energy produced can be used to power everything from lights and appliances to heating and air conditioning in your home.
How Does a Solar Power System Work?
Solar Panels: Solar panels are the most prominent component of a solar power system. When sunlight hits the panels, the photovoltaic cells inside generate a flow of electricity.
Inverter: Solar panels produce direct current (DC) electricity. However, most household appliances use alternating current (AC). The inverter converts the DC electricity into AC electricity, making it usable for everyday purposes.
Batteries (optional): Some homeowners choose to install batteries to store excess energy generated by the solar panels. This allows them to use solar power even when the sun isn't shining, like during nighttime or cloudy days.
Monitoring System: A monitoring system tracks the performance of the solar power system, helping homeowners see how much energy is being produced, consumed, and stored.
Grid Connection: In many cases, homes with solar systems are connected to the electrical grid. If the solar panels produce more energy than the household needs, the excess power is fed back into the grid. Some regions offer net metering, where homeowners get credit for the excess energy they supply.
Benefits of Solar Power Systems for Homes
Cost Savings: One of the biggest advantages of solar power is the potential for long-term cost savings. Once the system is installed, the electricity generated is essentially free. While the initial investment can be significant, tax incentives and rebates can reduce the upfront cost. Over time, homeowners can see a substantial reduction in their electricity bills.
Environmentally Friendly: Solar energy is a clean, renewable resource. By choosing solar power, homeowners reduce their reliance on fossil fuels, decrease their carbon footprint, and contribute to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. This is an essential step in combating climate change and preserving the environment.
Energy Independence: With a solar power system, homeowners can reduce or eliminate their dependence on the electrical grid. This can be particularly beneficial in areas where electricity prices are high or where power outages are frequent. Solar power systems give homeowners control over their energy production.
Increased Property Value: Homes with solar power systems tend to have higher property values. Buyers are often attracted to homes with solar panels due to the potential for lower energy costs and sustainability.
Government Incentives: Many governments offer incentives to encourage the adoption of solar energy. These incentives can include tax credits, rebates, grants, and net metering programs. These financial incentives can significantly offset the installation cost.
Components of a Solar Power System
Solar Panels: The heart of the system, solar panels are made up of photovoltaic cells that convert sunlight into electricity. They come in various types, including monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film, each offering different efficiencies and costs.
Inverter: The inverter is crucial for converting DC electricity from the panels into AC electricity that can be used in your home. There are two main types of inverters: string inverters and microinverters. String inverters are typically used in large systems, while microinverters are ideal for homes with shading issues or roofs with multiple orientations.
Batteries: Batteries are not always necessary, but they can be helpful for storing excess solar energy. This stored energy can be used when sunlight is not available, such as at night or on cloudy days. Lithium-ion batteries are commonly used for solar power storage.
Mounting and Racking System: The panels need to be securely mounted on your roof or ground area. The mounting system ensures the panels are at the right angle for maximum sun exposure.
Charge Controller (optional): In systems with batteries, a charge controller ensures the batteries are charged correctly and prevents overcharging.
Monitoring System: A solar monitoring system tracks your system’s performance and energy production. It can be accessed via an app or web portal and allows homeowners to optimize energy usage and ensure the system is functioning efficiently.
Steps to Install a Solar Power System
Assess Your Home's Energy Needs: Before installing a solar power system, evaluate your household's energy consumption. This helps determine how many solar panels you need and the system's size.
Get a Professional Assessment: A solar installer can assess your roof's condition, the amount of sunlight it receives, and other factors that influence energy generation. They will provide a proposal with system size, costs, and expected savings.
Obtain Permits and Approvals: Most regions require permits for solar installations. Your installer will handle the necessary paperwork, including permissions from local authorities and utility companies.
Installation: The installer will mount the solar panels, set up the inverter, and connect the system to the grid (if applicable). This process typically takes a few days to complete.
Inspection and Activation: After installation, a final inspection by a licensed professional ensures the system is working correctly. Once approved, the system is activated, and you can start producing your own electricity.
Costs of Solar Power Systems
The cost of installing a solar power system can vary depending on several factors, such as the size of the system, the type of panels, and the complexity of installation. On average, the cost can range from $10,000 to $30,000 before incentives. However, government incentives can reduce the overall cost by up to 30%.
Despite the initial cost, the return on investment (ROI) for solar power is impressive. Homeowners can expect to see a reduction in their electricity bills, and many systems pay for themselves in 5 to 10 years. After that, the energy generated is essentially free.
Conclusion A solar power system for your home offers numerous benefits, including lower electricity bills, environmental sustainability, and energy independence. While the initial cost may seem high, the long-term savings and potential government incentives make it a smart investment for homeowners looking to reduce their carbon footprint and embrace renewable energy. As technology advances and installation costs continue to decrease, solar power will become an increasingly accessible and popular option for homeowners worldwide.
More info - +1(818) 650 1464 or [email protected]
1 note
·
View note
Text
#Global AR Photovoltaic Glass Market Size#Share#Trends#Growth#Industry Analysis By Type(3.2mm#4mm)#By Application(Thin Film Solar Cell Module#Others) Key Players#Revenue#Future Development & Forecast 2023-2032
0 notes
Text
Residential solar panels are photovoltaic (PV) panels installed on homes to harness energy from the sun and convert it into electricity. These panels are typically placed on the roof, although they can also be installed on the ground in areas with limited roof space or other specific needs visit their website
Here’s a breakdown of how residential solar panels work and what they entail:
How They Work:
Solar Cells: The panels consist of many solar cells made from semiconductor materials (usually silicon) that absorb sunlight.
Photovoltaic Effect: When sunlight hits the solar cells, it excites the electrons in the semiconductor material, generating an electric current.
Inverter: The electricity produced by the solar panels is direct current (DC). Since most homes use alternating current (AC), an inverter is used to convert the DC electricity into AC electricity for use in the home.
Electrical Distribution: The electricity is then distributed throughout the home to power appliances, lights, and other systems.
Grid Connection (optional): Many residential solar systems are connected to the electrical grid. This allows homeowners to send excess energy back to the grid (in exchange for credits or compensation) or draw from the grid when the solar panels aren’t generating enough power (e.g., at night or on cloudy days).
Types of Solar Panels:
Monocrystalline Solar Panels: Made from a single crystal structure, they are highly efficient and have a longer lifespan, but they are more expensive.
Polycrystalline Solar Panels: Made from silicon crystals that are melted together, these are less efficient but more affordable.
Thin-Film Solar Panels: These panels are made from layers of photovoltaic material. They are lightweight and flexible but are typically less efficient than crystalline panels.
Benefits of Residential Solar Panels:
Lower Electricity Bills: Solar panels can significantly reduce a home’s electricity bills by providing free, renewable energy from the sun.
Sustainability: Solar energy is clean and reduces the carbon footprint of a household, contributing to environmental conservation.
Energy Independence: Homeowners become less dependent on utility companies, and they can produce their own energy.
Increased Property Value: Homes with solar installations tend to have higher resale values due to the long-term savings and environmental benefits.
Considerations:
Initial Cost: The upfront cost of installing solar panels can be high, though there are financial incentives, rebates, and tax credits available in many regions.
Roof Space: Solar panels need enough space to be installed, and the roof must have good sun exposure for the panels to be effective.
Maintenance: Solar panels require minimal maintenance, but it’s important to keep them clean and check for any damage or shading that could impact performance.
In conclusion, residential solar panels offer a sustainable way for homeowners to generate their own electricity, reduce energy bills, and lessen their environmental impact, though the initial investment and proper installation are key to their success.

0 notes
Text
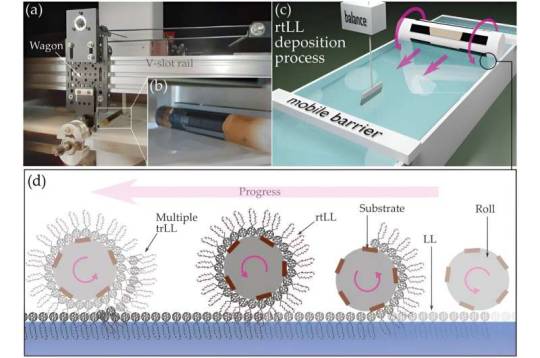
Researchers develop new method for manufacturing tailor-made semiconductor thin films
Organic semiconductor materials are promising key technologies for the development of state-of-the-art optoelectronic components and are used in photovoltaics as well as in sensor technology and microelectronics. In order to produce thin organic semiconductor films automatically and with well-defined properties, researchers—led by Leibniz IPHT in Jena, Germany—have developed a new technological approach for depositing thin films with high molecular precision. The method for manufacturing thin films with tailor-made electronic properties is presented in the journal Advanced Materials. Organic semiconductors, which usually consist of carbon-based molecular materials or polymers, are part of a variety of today's applications: For example, ultra-thin, mechanically flexible and lightweight semiconductor thin films are used in modern transistors, sensitive sensors, or organic solar cells. Their energy conversion potential and thus their functionality is determined by the electronic energy levels of the organic thin films, which depend on the molecules as well as their arrangement and the interactions between neighboring molecules within the thin films.
Read more.
#Materials Science#Science#Thin films#Semiconductors#Manufacturing#Materials processing#Organic materials
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
Solar Panels for Sale: Unlock Your Path to Affordable Renewable Energy
The environmental effects of using fossil fuels have never been more apparent, and energy prices are rising. Keeping up with monthly electricity bills may be a difficult task for both homes and businesses. Furthermore, conventional energy sources exacerbate climate change by making a significant contribution to carbon emissions.
The challenge then becomes: how can we lower energy costs while making the world cleaner and greener?

Unrealized Potential in Solar Energy Even though there are renewable energy options available, many businesses and homeowners are reluctant to switch. People are frequently held back by worries about up-front expenses, ignorance, or skepticism regarding the dependability of solar energy. But delaying solar energy investment for too long could result in years of needless costs and a higher carbon impact.
The worst part is that solar panels have already been deployed and are benefiting millions of people worldwide. In reality, with more than 70 GW of installed solar capacity as of 2023, India has become a leader in the use of renewable energy. However, there is still a vast amount of unrealized potential.
If you continue to only use conventional energy sources, you're losing out on significant cost savings as well as the opportunity to future-proof your energy needs.
Sale of Inexpensive and Effective Solar Panels Purchasing solar panels is now a wise, essential move towards both financial and environmental sustainability rather than a luxury. Here, we'll go over the essentials of buying solar panels, discuss why this is the ideal time to take action, and present interesting case studies of actual solar panel users.
Solar Panels: What Are They? Photovoltaic (PV) cells are used in solar panels, which are devices that use sunlight to generate electricity. These panels come in a variety of forms, including thin-film, polycrystalline, and monocrystalline, and are often composed of silicon. Their primary benefit is their capacity to capture the sun's plentiful energy and lessen reliance on fossil fuels.
Why Purchasing Solar Panels for Sale Is the Best Option Right Now Reduction in Costs: Over the past decade, the cost of solar panels has plummeted by nearly 80%, making it more accessible than ever. Depending on the manufacturer and technology, the typical cost of a solar panel system for residential installations in India as of 2024 ranges from ₹50,000 to ₹70,000 per kW.
Government Incentives and Subsidies: Depending on your state and the type of installation, initiatives such as the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) subsidies can lower upfront expenses by 20% to 40%. This implies that your initial investment can be much reduced.
Return on Investment (ROI): With a lifespan of more than 25 years, solar panels provide decades of essentially free electricity and usually pay for themselves in 5 to 7 years. In a commercial setting, for instance, a 5 kW system can save companies up to ₹1.2 lakh a year.
Energy Independence: Having solar panels reduces your dependency on the erratic electricity prices of the grid. You will even have electricity during blackouts if you install a battery storage system.
Solar Panel Types Available for Purchase:
Monocrystalline Panels
High effectiveness (18%–22%) Ideal for small roof spaces
Long-lasting but marginally more costly polycrystalline panels:
mediocre effectiveness (15–17%) Economical Perfect for bigger areas
Panels with thin films:
Flexible and lightweight Cheaper but less effective Ideal for setups that are not traditional
A Residential Success Story
Location: Maharashtra's Pune System: ₹1,80,000 (after subsidy) for a 3 kW rooftop solar panel system Savings on electricity bills: ₹24,000 per year
A Pune family made the decision to upgrade their house with solar panels in 2021. They chose a 3 kW monocrystalline system after considering a number of alternatives. Their electricity bill decreased by almost 90% in the first month after the installation, which only took three days.
They had already saved ₹48,000 by 2023 because to the installation, demonstrating the dependability and profitability of solar panels as an investment.
How to Choose the Right Solar Panels for Sale
Determine Your Energy Requirements: To begin, figure out how much electricity you use each month. About 250 kWh are used monthly by the average Indian family, necessitating a 2 kW system.
Assess Roof Space and Orientation: South-facing roofs with less shade are ideal for solar panel installation. Make sure there is adequate room for the necessary capacity.
Examine the warranty and panel efficiency. While more efficiency panels may be more expensive initially, they will perform better over time. Choose panels that come with a minimum warranty of 10 to 25 years.
Verify Certification: To ensure quality and safety, make sure the panels fulfil international standards, such as IEC and BIS certifications in India.
Commercial Solar Panels: Revolutionizing the Business Landscape Because of economies of scale, solar energy may help businesses even more. Small and medium-sized businesses (SMEs) can save up to ₹2.5 lakh a year with a 10 kW solar panel installation. Commercial setups can also benefit from tax advantages like accelerated depreciation, which can cut the effective cost by about 40%.
Gujarati Industrial Solar Setup Case Study
Business: Manufacturer of Textiles System: 50 kW of solar energy Price: ₹25,000,000 (after subsidies) Electricity savings: ₹7,50,000 per year Within four years of the solar system's installation in 2020, the business recouped its initial expenditure. They now save enough money each year to put back into new company ventures.
Dispelling Frequently Held Myths Regarding Solar Panels for Sale Solar Panels Are Too Expensive : Fact: Solar panels are now more inexpensive than ever thanks to financing choices and incentives.
They Don’t Work on Cloudy Days: The truth is that solar panels can still produce power in the presence of diffuse sunlight, but to a lesser extent.
Maintenance Is a Hassle: The truth is that solar panels just need to be cleaned and inspected occasionally.
0 notes
Text
Energy Harvesting Technology Market: Growth, Trends, and Future Outlook
The energy harvesting technology market is experiencing rapid growth as businesses and industries seek sustainable solutions to meet the increasing demand for power. Energy harvesting, also known as power scavenging, refers to the process of capturing and storing ambient energy from the environment, such as light, heat, motion, and vibrations, and converting it into usable electrical power. This technology is finding applications across various sectors, from consumer electronics to industrial machinery, automotive, and healthcare.
The global energy harvesting technology market size was valued at USD 0.6 billion in 2023 and is estimated to reach USD 0.9 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 10.0% during the forecast period 2023-2028
The growth of the market is driven by rising environmental concerns, miniaturization and flexibility requirements, and integration of IoT devices in energy harvesting systems for building and home automation.
Download PDF Brochure @ https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/pdfdownloadNew.asp?id=734
Key Trends in the Energy Harvesting Technology Market
1. Growing Demand for Renewable Energy Sources
The global push for clean and sustainable energy has significantly boosted the adoption of energy harvesting technologies. As governments and corporations aim to reduce carbon footprints, energy harvesting offers an eco-friendly solution to power low-energy devices.
2. Integration with IoT Devices
The rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) is one of the most significant drivers of the energy harvesting technology market. With numerous IoT devices requiring continuous energy to operate, energy harvesting provides an efficient solution, especially for remote and wireless devices.
3. Advancements in Energy Storage Technologies
Innovations in energy storage, such as improved capacitors and batteries, are enhancing the efficiency of energy harvesting systems. These advancements enable devices to store energy more effectively, making them more practical for long-term use.
4. Miniaturization of Energy Harvesting Systems
As consumer electronics get smaller, energy harvesting systems are also becoming more compact. This miniaturization is helping to expand their use in applications like wearables, sensors, and wireless communication systems.
Types of Energy Harvesting Technologies
Energy harvesting technologies can be classified based on the type of energy they capture. Some of the most commonly used types include:
Solar Energy Harvesting: This involves capturing solar radiation and converting it into electrical power. Solar cells, whether photovoltaic or thin-film, are frequently used in solar-powered energy harvesting systems.
Thermal Energy Harvesting: Thermal harvesters utilize temperature differences to generate energy. This can involve using thermoelectric materials that convert heat into electrical energy.
Vibration Energy Harvesting: This technology captures mechanical energy from vibrations or motion and converts it into electrical power. It is often used in industrial applications where machinery generates constant vibrations.
Radio Frequency (RF) Energy Harvesting: RF harvesters capture energy from radio waves transmitted by wirelesscommunication devices like Wi-Fi routers and mobile networks.
Drivers of the Energy Harvesting Technology Market
Several factors are contributing to the growth of the energy harvesting technology market:
Sustainability and Environmental Concerns: With increasing concerns over environmental sustainability, businesses are investing in energy-efficient technologies like energy harvesting to reduce reliance on traditional power sources.
Cost Reduction in Energy Harvesting Devices: Over the years, the cost of manufacturing energy harvesting devices has decreased, making them more accessible and affordable for consumers and industries.
Government Regulations and Incentives: Governments worldwide are introducing policies that promote the use of renewable energy technologies. Energy harvesting fits into these initiatives by offering green and efficient solutions.
Challenges Facing the Energy Harvesting Technology Market
Despite its potential, the energy harvesting technology market faces several challenges:
Limited Power Output: Many energy harvesting technologies are limited by their power generation capabilities, making them suitable only for low-energy applications.
High Initial Investment: While the operational costs of energy harvesting devices are low, the initial investment can be significant, especially for large-scale implementations in industries like automotive and manufacturing.
Technical Barriers: The complexity of integrating energy harvesting systems with existing technologies, such as sensors and communication devices, presents a challenge in terms of design and implementation.
Market Outlook and Future Trends
The future of the energy harvesting technology market looks promising. Key developments include:
Widespread Adoption of IoT: As the IoT ecosystem grows, the demand for energy harvesting solutions will continue to rise. Energy harvesting will play a crucial role in powering IoT devices that are deployed in remote or difficult-to-reach locations.
Smart Cities and Infrastructure: Energy harvesting will be integral to powering smart infrastructure, such as sensors and surveillance systems used in smart cities. These systems require reliable, low-maintenance power sources, making energy harvesting a natural fit.
Innovation in Hybrid Energy Harvesting: Future energy harvesting systems may combine different energy sources (solar, thermal, and mechanical) to create more efficient and reliable power generation solutions.
The energy harvesting technology market is rapidly evolving, driven by the increasing demand for sustainable, efficient, and cost-effective energy solutions. As advancements continue in areas such as miniaturization, storage, and hybrid systems, energy harvesting is poised to become a critical technology in powering IoT devices, smart cities, and industrial systems. While challenges remain, the long-term outlook for energy harvesting technology remains positive, with continuous innovation paving the way for a greener, more energy-efficient future.
FAQs on Energy Harvesting Technology Market
1. What is energy harvesting technology?
Energy harvesting technology refers to the process of capturing and converting ambient energy (such as light, heat, motion, or vibrations) into electrical power. This energy can be used to power small electronic devices or stored for later use.
2. What are the main types of energy harvesting technologies?
The main types of energy harvesting technologies are solar, thermal, vibration, and radio frequency (RF) energy harvesting.
3. How does energy harvesting benefit the environment?
Energy harvesting helps reduce reliance on traditional power grids, which are often powered by non-renewable resources. By utilizing ambient energy, it promotes sustainability and reduces environmental impact.
4. What industries are adopting energy harvesting technologies?
Industries such as consumer electronics, automotive, healthcare, industrial manufacturing, and IoT are all adopting energy harvesting technologies to power low-energy devices and systems.
5. What are the challenges in the energy harvesting technology market? Challenges include limited power output, high initial investment costs, and technical barriers in integrating energy harvesting devices with existing systems.
0 notes
Text
The Future of Clean Energy: Exploring Solar Power Generation
What is Solar Power Generation?
Solar power generation uses sunlight as a clean, renewable energy source to produce electricity. It involves the conversion of sunlight into usable energy through photovoltaic (PV) panels or solar thermal systems. As the demand for sustainable and eco-friendly energy solutions grows, solar power has emerged as a reliable alternative to fossil fuels, offering numerous environmental and economic benefits.
Why Solar Power Generation is Essential Today
With concerns over climate change and depleting fossil fuel reserves, solar energy provides a promising solution for reducing carbon emissions and reliance on non-renewable resources. Solar power generation is increasingly adopted worldwide, and it plays a crucial role in the transition to a more sustainable and resilient energy future.
Key Benefits of Solar Power Generation:
Clean Energy: Reduces greenhouse gas emissions.
Cost-Effective: Reduces electricity bills over time.
Low Maintenance: Solar panels require minimal upkeep.
Job Creation: Solar installations boost local employment.
Types of Solar Power Generation Systems
Photovoltaic (PV) Systems PV systems are the most common type of solar technology, where solar panels capture sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity. Inverter systems then convert this DC power into alternating current (AC) for residential or commercial use.
Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) CSP systems use mirrors to concentrate sunlight onto a central receiver that generates heat. This thermal energy is then converted into electricity through steam-driven turbines.
Solar Thermal Systems Solar thermal technology uses sunlight to heat fluids for residential or industrial applications, such as water heating or space heating.
Solar Power Installation Process
Site Assessment: Identifying a suitable location for maximum sun exposure.
System Design: Choosing system size and components based on energy needs.
Permitting and Financing: Securing necessary permits and exploring financing options.
Installation: Installing solar panels, inverters, and other necessary equipment.
Grid Connection: Connecting to the grid for seamless electricity flow and storage options.
Advances in Solar Technology
Bifacial Solar Panels These panels capture sunlight on both sides, increasing energy production.
Thin-Film Solar Cells Flexible and lightweight, these cells can be used on various surfaces.
Floating Solar Panels Installed on water bodies, these panels help save land space and improve efficiency.
Smart Inverters and Battery Storage Allowing solar systems to store excess energy for later use, improving resilience.
Solar Power’s Role in Energy Independence and Grid Stability
Solar energy offers energy independence, especially for communities in remote areas. By reducing dependency on centralized power sources, solar power enhances resilience and ensures consistent energy supply.
Financial Incentives and Policies Supporting Solar Adoption
Governments worldwide support solar adoption through tax incentives, grants, and rebate programs, making it easier for homeowners and businesses to transition to solar.
Conclusion: Embracing Solar Power for a Sustainable Future
Solar power generation is a game-changer in achieving sustainable energy goals. By embracing solar power, individuals and businesses contribute to a greener planet, reduce costs, and help future generations enjoy a cleaner, healthier environment.
#Top Plant Engineering & Consulting Services#Mechanical Engineering Services#Advanced Plant Engineering Solutions#BIM Services in Pune India#Top Civil & Structural Engineering Consultants#Plant Design & MEP Services#Top MEP Design Consultants & Engineering Consultancy#HVAC Design & Engineering Services#MEP Design Consultants for Plumbing & Fire Protection Services In Pune#solar energy production#solar electric power generation
0 notes