#Thecostraca
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

A group of pelagic gooseneck barnacles (Lepas anatifera) on the shore of Morrow Bay, California, USA
by marlin harms
#pelagic gooseneck barnacle#barnacles#lepas anatifera#lepas#Lepadidae#Scalpellomorpha#Thecostraca#arthropoda#wildlife: california#wildlife: usa#wildlife: north america
106 notes
·
View notes
Text
Taxonomy Tournament: Crustaceans


Branchiopoda. This class is made up of fairy shrimp, clam shrimp, water fleas, and the shield shrimp. All members have gills on their apendages, including the mouthparts.
Thecostraca. This class is made up of barnacles, marine sessile filter feeders commonly found attached to boats, along with other genera that are parasites of echinoderms
#animals#biology#polls#poll tournament#zoology#fairy shrimp#arthropods#crustaceans#ecdytes#animal parasite#barnacles#Branchiopoda#Thecostraca#0xdv0x72
52 notes
·
View notes
Text

I was just there and got a video of these guys!
Let’s get cirri-ous: an acorn barnacle’s feathery phalanges are foolproof for filtering a feast from fast flows! These captivating crustaceans do a little headstand when they’re but wee plankton settling down, cementing their noggins to the seafloor before forming a shell around them. By flapping their feet in the current, those tiny toe hairs, called cirri, trap detritus and plankton as they pass by. Once a snack is secured, the barnacle pulls its legs inside, scrapes off its filtered fare and voila! Dinner is served!
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Round 2 Final Stats:
Previously I said any group to earn over 900 points will move on to Round 3, however, I’m going to make it the Top 10 just to make it even. Plus, what’s an extra two species?
For the final stats, I’ve made a little graphic with some doodles to remind y’all what each class is. (Couldn’t use emojis for everyone because, alas, there are not enough unique ones to represent all these animal groups!) The full list is typed out under the read more though, as well as the extra stats for this round!
The top classes (or phylogenetic equivalents) have been ranked thusly, listed here from highest ranking to lowest:

🦈 Chondrichthyes ~ 1,509
🐀 Mammalia ~ 1,437
🐍 Reptilia ~ 1,183
🐙 Cephalopoda ~ 1,175
🐸 Lissamphibia ~ 1,002
🐠 Actinopterygii ~ 983
🦀 Malacostraca ~ 954
🕷 Arachnida ~ 913
🐞 Insecta ~ 908
Actinistia ~ 853
🐌 Gastropoda ~ 796
🫁 Dipnoi ~ 598
🦪 Bivalvia ~ 507
Myxini ~ 492
Chilopoda ~ 479
Branchiopoda ~ 443
Polyplacophora ~ 427
Petromyzontida ~ 412
Pycnogonida ~ 405
Copepoda ~ 308
Ascidiacea ~ 394
Diplopoda ~ 393
Ostracoda ~ 278
Collembola ~ 272
Thecostraca ~ 253
Pauropoda ~ 246
Appendicularia ~ 229
Leptocardii ~ 222
Remipedia ~ 194
Symphyla ~ 166
Solenogastres ~ 164
Tergomya ~ 158
Scaphopoda ~ 142
Tantulocarida ~ 139
Cephalocarida ~ 134
Mystacocarida ~ 115
Caudofoveata ~ 110
Diplura ~ 94
Protura ~ 83
Ichthyostraca ~ 83
Our Top 10 Classes are Chondrichthyes, Mammalia, Reptilia, Cephalopoda, Lissamphibia, Actinopterygii, Malacostraca, Arachnida, Insecta, and Actinistia!
This means Chondrichthyes, Mammalia, Reptilia, Cephalopoda, Lissamphibia, Actinopterygii, Malacostraca, Arachnida, Insecta, and Actinistia will be moving on to Round 3, and broken up by Order (or some other phylogenetic equivalent).
Extra Stats:
Arthropod Class Pycnogonida (“sea spiders”)
~ was the first group of Round 2
~ was the first arthropod group of Round 2
~ had the highest amount of dislikes at 20
~ had the highest amount of hates at 5
Arthropod Class Symphyla (“garden centipedes”)
~ had the highest percentage of likes at 45%
Arthropod Class Ichthyostraca (“fish lice” and “tongue worms”)
~ had the highest percentage of dislikes at 9.1%
~ had the highest percentage of hates at 2.6%
Arthropod Class Mystacocarida (“mustache shrimp”)
~ had the lowest amount of loves at 13
~ had the lowest percentage of loves at 7.9%
~ had 0 hates
~ had the least reblogs at 8
~ had the least notes at 21
Arthropod Class Ostracoda (“seed shrimp”)
~ had 0 hates
~ received exactly 200 votes
Arthropod Class Copepoda (copepods)
~ had 0 hates
Arthropod Class Malacostraca (“crabs”, “lobsters”, “shrimp”, etc)
~ had the third most reblogs at 55
~ had the highest percentage of loves at 52.8%
~ had 0 dislikes and 0 hates
~ was the highest ranked Arthropod class
Arthropod Class Tantulocarida (tantulocarids)
~ had the highest amount of neutral votes at 91, along with Caudofoveata
Arthropod Class Cephalocarida (“horseshoe shrimp”)
~ had 0 hates
Arthropod Class Remipedia (remipedes)
~ had 0 hates
Arthropod Class Collembola (“springtails”)
~ had 0 hates
Arthropod Class/Order Protura (“coneheads”)
~ had the least votes at 125
~ had the lowest amount of favorites at 1
~ had the lowest percentage of favorites at 0.8%
~ had 0 hates
Arthropod Class Insecta (insects)
~ had 0 dislikes
Chordate Class Leptocardii (“lancelets”)
~ was the first Chordate group of Round 2
~ had 0 hates
Chordate Class Ascidiacea/Thaliacea (“sea squirts”, “salps”, “pyrosomes”, etc.)
~ had 0 hates
Chordate Class Appendicularia (“larvaceans”)
~ had 0 hates
Chordate Class Chondrichthyes (“cartilaginous fish”)
~ had the most votes at 415
~ had the highest amount of loves at 181
~ had 0 dislikes and 0 hates
~ had the most reblogs at 105
~ had the most notes at 235
~ was the highest ranked group of chordates
Chordate Class Actinistia (“coelacanths”)
~ had 0 dislikes and 0 hates
~ was the first single genus (Latimeria) to be ranked
Chordate Class Dipnoi (“lungfish”)
~ had the highest amount of likes at 104
~ had 0 dislikes and 0 hates
~ contained the first of my personal favorites (Australian Lungfish) to be eliminated 🥲
Chordate Class Lissamphibia (amphibians)
~ had the lowest amount of neutral votes at 1, along with Reptilia and Gastropoda
~ had the lowest percentage of neutral votes at 0.4%, along with Reptilia and Gastropoda
~ had 0 dislikes and 0 hates
Chordate Class Reptilia (reptiles)
~ had the lowest amount of neutral votes at 1, along with Lissamphibia and Gastropoda
~ had the lowest percentage of neutral votes at 0.4%, along with Lissamphibia and Gastropoda
~ had 0 dislikes and 0 hates
Chordate Class Mammalia (mammals)
~ had the highest amount of favorites at 258
~ had the highest percentage of favorites at 80.6%
~ had the lowest amount of likes at 4
~ had the lowest percentage of likes at 1.2%
Molluscan Class Polyplacophora (“chitons”)
~ was the first Mollusc group of Round 2
~ had 0 hates
Molluscan Class Solenogastres (solenogasters)
~ had 0 hates
Molluscan Class Caudofoveata (caudofoveatans)
~ had the highest amount of neutral votes at 91, along with Tantulocarida
~ had the highest percentage of neutral votes at 58%
Molluscan Subclass Tergomya (tergomyans)
~ had 0 hates
Molluscan Class Cephalopoda (cephalopods)
~ had the second most reblogs at 66
~ had 0 dislikes and 0 hates
~ was the only molluscan class to make it into the Top Ten
Molluscan Class Scaphopoda (“tusk shells”)
~ had 0 hates
Molluscan Class Gastropoda (“snails” and kin)
~ had 0 dislikes and 0 hates
~ had the lowest amount of neutral votes at 1, along with Lissamphibia and Reptilia
~ had the lowest percentage of neutral votes at 0.4%, along with Lissamphibia and Reptilia
Molluscan Class Bivalvia (bivalves)
~ had 0 dislikes
#Thanks for voting!#Statistics#extras#poll results#round 2#I’ve made my peace with most of these but#i’m still grumpy about the millipedes tho#like really#y’all put copepods higher than them#also what happened to all the people who got arthropoda to win the first round#where’d you go#to be clear though I AM happy for the ones who did move forward#i am very proud to still have arachnids with us#and I’m excited to vote on all the different birds and insects#we can’t just do all of them or I’d be here all day lol
61 notes
·
View notes
Text
Fwd: Postdoc: GeorgeWashingtonU.BranacleSystematics
Begin forwarded message: > From: [email protected] > Subject: Postdoc: GeorgeWashingtonU.BranacleSystematics > Date: 4 September 2024 at 06:49:21 BST > To: [email protected] > > > > Postdoc in Barnacle Molecular Systematics at George Washington University > (GWU) > > About the Project > The Computational Biology Institute, at the Milken Institute School of > Public Health’s Department of Biostatistics and Bioinformatics, GWU, > is offering a Postdoc position to develop a comprehensive phylogeny of > the barnacles (Crustacea: Thecostraca) and study the evolution of sexual > systems.Barnacles rank among the most biologically diverse, ubiquitous and > ecologically important marine metazoans. They exhibit a fascinating and > unique range of sexual systems, including hermaphroditism (both sexes), > dioecy (separate sexes) and androdioecy (hermaphrodites and males).We want > to apply exon probes for targeted capture sequencing to ~1,200 barnacle > species to build a robust phylogeny of the Thecostraca. Then coupling this > barnacle tree with fossil, morphological and ecological information in > a comparative analysis framework, we will test long-standing theoretical > predictions about the evolution of sexual systems and its diversification > across broad spatial, temporal and ecological scales. > > About the Postdoc > > The postdoc candidate will conduct research in phylogenomics and > evolutionary biology of barnacles and work together with the PI (Pérez- > Losada), collaborators and graduate students. Responsibilities: > + Compilation, generation and curation of genomic and other > (e.g., morphological and ecological) trait data for selected > barnacle species. > + Bioinformatic analysis of genomic data to infer phylogenies and > perform comparative analyses on traits to test hypotheses. > + Preparation and submission of manuscripts to scientific journals. > + Availability to travel to other institutions and work abroad for short > periods of time. > + Training of graduate and undergraduate students in the lab on the above- > mentioned duties. > + Delivering guest lectures or short workshops for relevant courses and > related topics offered at GW in the disciplines involved in the > research program. > > Qualifications > > PhD and expertise in molecular systematics, bioinformatics, comparative > phylogenetic methods, genomics and ideally barnacle taxonomy. > > Hiring Range > 61,008 - 65,000 > > Expected duration of appointment > Up to 3 years renewable every year upon performance > > Starting date > October 1, 2024 > > Healthcare Benefits > GWU offers a comprehensive benefit package for Postdoc Associates and > Scholars that includes medical, dental, vision, life & disability > insurance, time off & leave, well-being and various voluntary > benefits. Postdoc Scholars may also be eligible for retirement savings > and tuition programs. For program details and eligibility, please visit > https://ift.tt/gBUfdQr. > > Applicant Documents to Submit > Cover Letter > Curriculum Vitae > Statement of Research Interest > Two Letters of Recommendation > > Online Application > > All candidates must apply online via the following GWU link > https://ift.tt/WlhZPdC > > Contact > If you have further questions regarding this position you can email > Marcos Perez-Losada at [email protected] > > Marcos Perez-Losada, PhD > > Marcos Perez-Losada
0 notes
Text
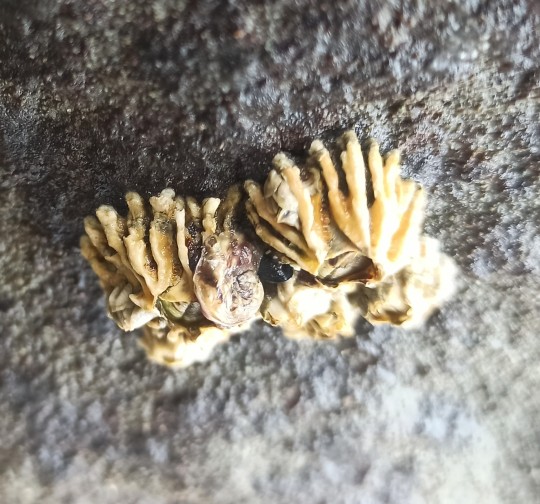
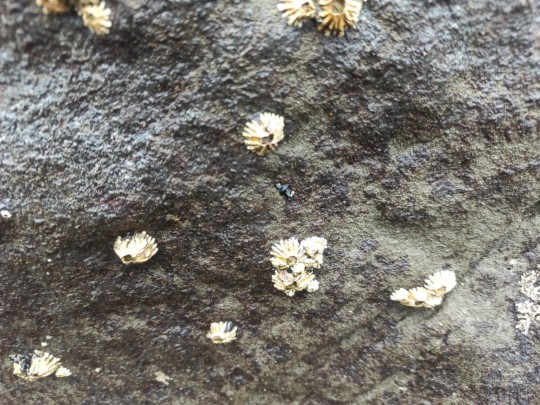
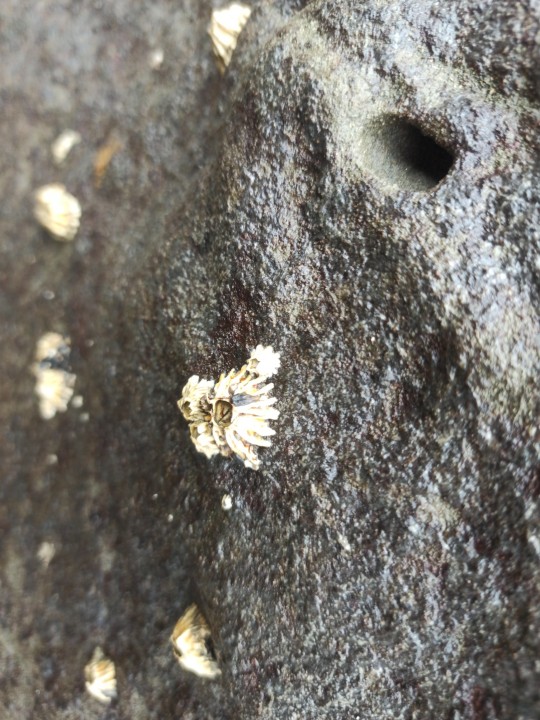
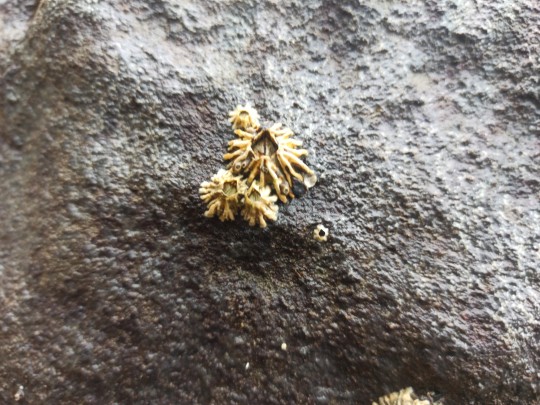








Epopella plicata is a species of symmetrical sessile barnacle in the family Tetraclitidae. It is found in New Zealand. On mid-tidal rocks.
Phylum: Arthropoda
Subphylum: Crustacea
Class: Thecostraca
Subclass: Cirripedia
Order: Balanomorpha
Family: Tetraclitidae
Genus: Epopella
Browns Bay, Auckland 0630
7QQ2+MPF Auckland
-36.7108220, 174.7518110
0 notes
Text
don't fucking challenge me i know every beast
NON-BEASTLY BEASTS:
Non-ParaHoxozoa:
Calcarea (Calcareous Sponges)
Hexacinellida (Glass Sponges)
Demospongiae (Demosponges)
Tentaculata (Tentacled Ctenophores)
Beroida (Non-Tentacled Ctenophores)
ParaHoxozoa, Non-Nephrozoa:
Placozoa
Anthozoa (Corals, Sea Pens, and Tube-Dwelling Anenomes)
Medusozoa (Jellyfish and Hydrozoans)
Myxozoa
Xenacoelomorpha
MINIBEASTS:
Spiralia, Non-Lophotrochozoa:
Gnathifera (Rotifers and Jaw Worms)
Mesozoa
Rouphozoa (Flatworms and Gastrotrichs)
Lophotrochozoa, Non-Mollusca:
Cycliophora
Annelida (Segmented Worms)
Nemertea (Ribbon Worms)
Bryozoa
Entoprocta
Phorodina (Horseshoe Worms)
Brachiopoda
Mollusca:
Solenogastres
Caudofoveata
Polyplacophora (Chitons)
Bivalvia (Clams, Scallops, Mussels, Oysters, Cockles, and others)
Monoplacophora
Scaphopoda (Tusk Shells)
Gastropoda (Snails, Slugs, Sea Snails, Sea Slugs, and others)
Cephalopoda (Nautiloids, Cuttlefish, Squid, and Octopi)
Ecdysozoa, Non-Arthropoda:
Loricifera
Priapulida (Penis Worms [sic])
Kinorhyncha (Mud Dragons)
Nematoda (Roundworms)
Nematomorpha (Horsehair Worms)
Tardigrada (Tardigrades)
Onchyophora (Velvet Worms)
Arthropoda, Non-Mandibulata:
Pycnogonida (Sea Spiders)
Xiphosura (Horseshoe Crabs)
Acariformes (Cheese Mites, Scabies Mites, Eyelash Mites, House Mites, and others)
Opiliones (Harvestmen)
Ricinulei (Hooded Tickspiders)
Solifugae (Camel Spiders)
Parisitiformes (Ticks, Varroa Mites, and others)
Pseudoscorpiones (Pseudoscorpions)
Scorpiones (Scorpions)
Araneae (Spiders)
Amblypigi (Whip Spiders)
Urgopygi (Whip Scorpions)
Mandibulata, Non-Insecta:
Chilopoda (Centipedes)
Symphyla (Pseudocentipedes)
Pauropoda
Diplopoda (Millipedes)
Ostracoda (Seed Shrimp)
Mystacocarida
Branchiura (Fish Lice)
Pentastomida (Tongue Worms)
Copepoda (Copepods)
Tantulocarida
Thecostraca (Barnacles and others)
Malacostraca (Crabs, Lobsters, Shrimp, Isopods, Amphipods, and others)
Cephalocarida (Horseshoe Shrimp)
Branchiopoda (Fairy Shrimp, Tadpole Shrimp, Water Fleas, and others)
Remipedia
Collembola (Springtails)
Protura
Diplura (Two-Pronged Bristletails)
Insecta, Non-Neoptera:
Archaeognatha (Jumping Bristletails)
Zygentoma (Silverfish, Firebrats, and others)
Odonatoptera (Dragonflies and Damselflies)
Ephemeroptera (Mayflies)
Neoptera, Non-Holometabola:
Zoraptera (Angel Insects)
Dermaptera (Earwigs)
Plecoptera (Stoneflies)
Orthoptera (Grasshoppers, Crickets, and others)
Mantodea (Mantises)
Blattodea (Cockroaches and Termites)
Notoptera (Ice Crawlers and Rock Crawlers)
Phasmatodea (Stick Insects and Leaf Insects)
Embioptera (Webspinners)
Psocodea (Lice)
Hemiptera (Shield Bugs, Aphids, Scale Insects, Cicadas, Planthoppers, Assassin Bugs, Water Boatmen, Pond Skaters, and others)
Thysanoptera (Thrips)
Holometabola
Hymenoptera (Sawflies, Bees, Wasps, and Ants)
Strepsiptera
Coleoptera (Beetles)
Raphidioptera (Snakeflies)
Neuroptera (Lacewings, Antlions, and others)
Megaloptera (Dobsonflies and others)
Lepidoptera (Butterflies and Moths)
Trichoptera (Caddisflies)
Diptera (Flies, Mosquitoes, Gnats, Midges, Hoverflies, and others)
Mecopteroidea (Scorpionflies, Hangingflies, and Fleas)
SLIGHTLY MORE BEASTLY BEASTS:
Ambulacraria:
Echinodermata (Starfish, Sea Urchins, Brittle Stars, Feather Stars, and others)
Hemichordata (Acorn Worms and others)
Chordata (Non-Vertebrata):
Leptocardii (Lancelets)
Tunicata (Sea Squirts, Salps, Pyrosomes, and others)
Vertebrata (Non-Eutelostomi):
Myxini (Hagfish)
Hyperoartia (Lampreys)
Elasmobranchii (Sharks, Rays, and Skates)
Holocephali (Chimaeras)
Actinopterygii (Non-Acanthomorpha):
Cladistia (Bichirs and Reedfish)
Acnipenseriformes (Paddlefish and Sturgeons)
Halecomorphi (Bowfins)
Ginglymodi (Gars)
Elopocephalai (Eels, Ladyfish, Halosaurs, and others)
Osteoglossocephala (Arapaima, Goldeye, and others)
Clupei (Herrings and Anchovies)
Apelocephali (Slickheads and others)
Anotophysa (Milkfish, Beaked Salmon, and others)
Cypriniformes (Carp, Goldfish, Loaches, Minnows, and others)
Characiformes (Characins, Pacu, Pirahnas, Tetras, and others)
Gymnotiformes (Knifefish and Electric Eels)
Siluriformes (Catfish)
Lepidogalaxii (Salamanderfish)
Protacanthopterygii (Salmon, Pike, Trout, Barreleye, and others)
Stomiati (Smelts, Marine Hatchetfish, and others)
Ateleopodia (Jellynose Fish)
Aulopa (Bombay Duck and Lancetfish)
Myctophata (Lanternfish)
Acanthomorpha:
Lampridacea (Oarfish, Opah and others)
Paracanthomorphacea (Cods, Dories, Cavefish, and others)
Polymixiacea (Beardfish)
Berycimorphaceae (Fangtooths, Pineconefishes, and others)
Holocentrimorphaceae (Soldierfish)
Ophidiiformes (Pearlfish)
Batrachoidimophara (Toadfish)
Gobiomorpharia (Seahorses, Pipefish, Tunas, Flying Gurnards, and others)
Anabantaria (Gouramis, Swamp Eels, and others)
Carangaria (Swordfish, Flatfish, Remoras, and others)
Ovalentaria (Blennies, Cichlids, Flying Fish, Mullets, and others)
Eupercaria (Anglerfish, Pufferfish, Wrasses, Sunfish, Sticklebacks, Lumpsuckers, Lionfish, Angelfish, Perches, Archerfish, Triggerfish, Bass, and others)
Sarcopterygii:
Actinistia (Coelocanths)
Dipnoi (Lungfish)
BEASTS PROPER:
Lissamphibia
Salientia (Frogs and Toads)
Caudata (Salamanders and Newts)
Gymnophiona (Caecilians)
Reptilia (Non-Aves)
Rhynchocephalia (Tuatara)
Dibamidae (Blind Skinks)
Gekkota (Geckos and Flap-Footed Lizards)
Scinciformata (Skinks and others)
Laterata (Tegus and Worm Lizards)
Anguimorpha (Slow Worms, Monitors, Gila Monster, and others)
Iguania (Anoles, Iguanas, Chameleons, and others)
Serpentes (Snakes)
Testudines (Turtles and Tortoises)
Crocodilia (Crocodiles, Gharials, Alligators, and Caiman)
Aves (Non-Passeriformes):
Palaeognathae (Ostriches, Kiwis, and others)
Galloanserae (Chickens, Ducks, and others)
Mirandornithes (Flamingos and Grebes)
Columbimorphae (Doves and others)
Otidimorphae (Cuckoos, Turacos, and Bustards)
Gruimorphae (Gulls, Cranes, Auks, and others)
Ophistocomidae (Hoatzins)
Strisores (Hummingbirds, Nightjars, Potoos, and others)
Phaethoquornithes (Boobies, Loons, Ibises, Penguins, Albatrosses, Tropicbirds, and others)
Acciptirimorphae (Vultures, Hawks, Eagles, and others)
Strigiformes (Owls)
Coraciimorphae (Kingfishers, Woodpeckers, Quetzals, and others)
Cariamiformes (Seriemas)
Falconiformes (Falcons)
Psittaciformes (Parrots)
Passeriformes:
Acanthisitti (New Zealand Wrens)
Tyranni (Overnbirds, Spadebills, Gnateaters, and others)
Menurida (Lyrebirds and others)
Climacterida (Bowerbirds and others)
Meliphagida (Honeyeaters, Bristlebirds, and others)
Orthonychida (Logrunners and others)
Corvides (Crows, Jays, Boatbills, Shriketits, Sittellas, Birds-Of-Paradise and others)
Passerides (Satinbirds, Sparrows, Larks, Tits, Oxpeckers, Thrushes, Wrens, Finches, Tanagers, Nuthatchers, and others)
Mammalia (Non-Laurasiatheria):
Monotremata (Platypus and Echidnas)
Marsupialia (Kangaroos, Opossums, Wombats, and others)
Xenarthra (Anteaters, Sloths, and others)
Athrotheria (Elephants, Manatees, Aardvarks, and others)
Lagomorpha (Rabbits, Hares and others)
Rodentia (Mice, Rats, Cavies, Beavers, Squirrels, and others)
Scandentia (Treeshrews)
Dermoptera (Colugos)
Primates (Lemurs, Marmosets, Baboons, Gibbons, Chimpanzees, and others)
Lauasiatheria (Non-Carnivora):
Eulipotyphla (Shrews, Moles, Hedgehogs, and others)
Chiroptera (Bats)
Artiodactyla (Girrafes, Deer, Whales, Pigs, Camels, and others)
Perissodactyla (Horses, Tapir, and Rhinoceros)
Pholidota (Pangolins)
Carnivora:
Viverroidea (Hyenas, Mongooses, Civets, and others)
Feloidea (Lions, Tigers, Caracals, Wildcats, Leopards, and others)
Nandiniidae (African Palm Civet)
Caninae (Wolves, Foxes, and others)
Ursidae (Bears)
Musteloidea (Skunks, Weasels, Otters, Raccoons, and others)
Pinnipedia (Seals, Sea Lions, and Walruses)
Interview questions for gym leaders
4K notes
·
View notes
Photo
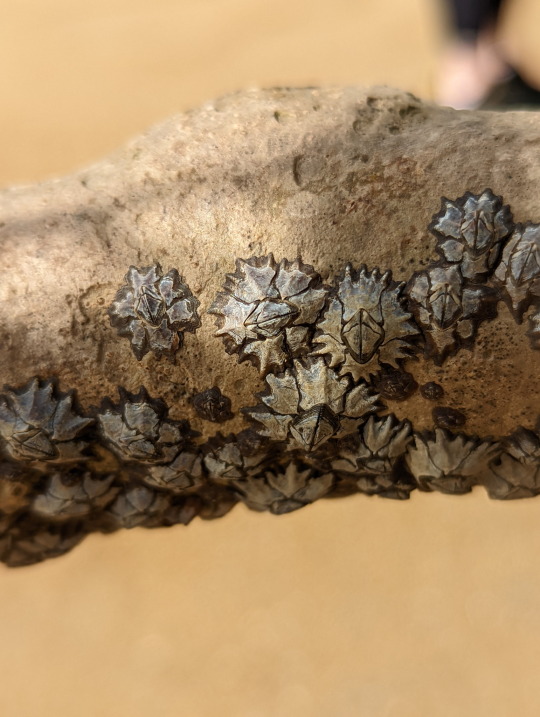
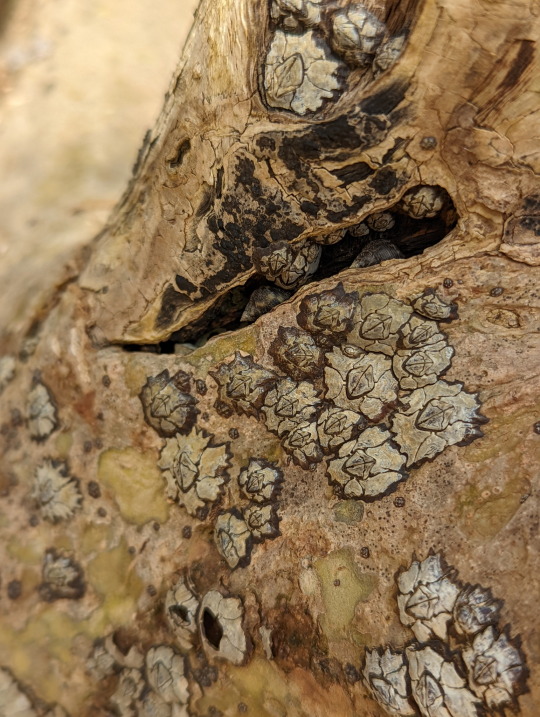




Barnacles at home on a Mangrove tree
many people don’t seem to realize that barnacles are a kind of crustacean. Well, you do now.
Why they’ve called a Mangrove tree home, is because they simply look for any sturdy surface to latch onto. Permanently. That’s why they’re often found on man-made structures.
Unidentified, Family Chthamalidae
15/06/22
#Chthamalidae#Barnacles#Chthamaloidea#Balanomorpha#Thoracicalcarea#Thoracica#Normal Barnacles#Cirripedia#Thecostraca#Hexanauplia#Multicrustacea#Crustacea#crustaceans#tidepooling#outside entomology
38 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Red thatched barnacle (Tetraclita rubescens)
Photo by Marlin Harms
#red thatched barnacle#barnacle#tetraclita rubescens#tetraclita#tetraclitinae#tetraclitidae#tetraclitoidea#balanomorpha#sessilia#thoracica#cirripedia#thecostraca#hexanauplia#crustacea#pancrustacea#arthropoda#panarthropoda#ecdysozoa
27 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Barnacle (by me)
#barnacle#Cirripedia#Thecostraca#Maxillopoda#Crustacea#Arthropoda#crustacean#marine life#beach#coast#autumn#Raritan Bay Waterfront Park#South Amboy#Middlesex County#New Jersey#mine
30 notes
·
View notes
Text
Oh man, yeah there's a bunch of parasitic barnacles that infect decapods too that are just like...well you can't tell they're a barnacle from looking. They start out as your standard crustacean naupilus and moult into a barnacle cyprid lava like a normal barnacle, but then, when a female Sacculina finds an uninfected crab she moults into a kinda living hypodermic needle and then moults again in a way that kinda just...injects part of herself into the crab, abandoning the rest of her body like organs etc. This grows roots through its body and an external sack which the crab treats like its own eggs (regardless of the sex of the crab btw).
The blobby bit under the crab? That's the external part of a parasitic barnacle. The internal bit spreads through the whole rest of the crab but they're so fine there's not really any good images online.

And the weird thing is that they're only somewhat related to Dendrogaster, like they're both in the Thecostraca but Sacculina and its relatives are nested within the larger grouping of barnacles so like, they've evolved "weird, blobby internal parasites" at least twice.

Dendrogaster (a crustacean that parasitizes starfish)
54K notes
·
View notes
Text
Taxonomy Tournament: Crustaceans


Thecostraca. This class is made up of barnacles, marine sessile filter feeders commonly found attached to boats, along with other genera that are parasites of echinoderms
Tantulocarida. This class is made up of minute external parasites that infect other crustaceans
#animals#biology#polls#poll tournament#zoology#barnacles#arthropods#crustaceans#ecdytes#Animal parasite#Thecostraca#Tantulocarida#0x72v0x8d#animal tournament#Animal Tournament Round 1
26 notes
·
View notes
Text
Round 2 - Arthropoda - Thecostraca




(Sources - 1, 2, 3, 4)
Thecostraca is is a class of crustaceans, many of which have planktonic larvae which become sessile or parasitic as adults. The most well-known group are the Barnacles (subclass Cirripedia), but Thecostraca also includes the parasitic Ascothoracida, and the mysterious Facetotecta.
Facetotecta, comprising only the genus Hansenocaris, are known only from their larvae (image 3) and adults have yet to be recognized, though some scientists believe they may actually be larval tantulocaridans.
Ascothoracidans are parasites of echinoderms and cnidarians. Most genera are meso and endoparasitic (living inside the host) while some are ectoparasitic (living on the outside of the host). They are similar in anatomy to copepods, with six pairs of legs, an abdomen with four segments, a telson, and a bivalved carapace. They feed on their host via piercing and sucking mouthparts, and some more advanced species also absorb nutrients through the carapace. They are sexually dimorphic, in many cases so much so that the smaller males will live inside the larger female’s mantle cavity.
Barnacles (subclass Cirripedia) are more well-known than other Thecostracans. Adult barnacles are sessile filter feeders, except for the infraclass Rhizocephala, which are parasites of other crustaceans. Barnacles attach themselves to a surface as adults, be that a rock, the shell of a mollusc, a ship, or a large animal such as a whale. They come in two common forms: acorn barnacles which grow their shells directly on a surface (image 4) and goose barnacles which attach themselves via a stalk (image 1). Barnacles have a carapace made of six calcareous plates, with a lid made of four more plates. They attach themselves to the substrate by means of a cement gland at the base of their antennae. Eight pairs of thoracic limbs, called cirri, extend from the carapace to filter plankton from the water and bring it towards the mouth. The hairs on these limbs are very sensitive to touch, and help the barnacle sense the world around them. They also have three simple eyes (ocelli) which can sense changes in light, allowing them to close their plates quickly if a shadow is detected.
Thecostracans have nauplius larvae, characterised by a head with antennules, antennae, mandables, and a single eye, three pairs of limbs, a carapace, and a telson. Barnacle larvae are brooded by the parent until their first moult, after which they are released to swim freely using setae.
The oldest known thecostracan fossil is dated from the Middle Cambrian. Traces of the parasitic forms have been dated from the Cretaceous.

Propaganda under the cut:
Barnacles have the longest penis (relative to body size) of any living animal. You can see it in action in the above gif and in this video.
Most barnacles are not parasitic (other than hitching a ride) and usually do no harm to the large animals they attach to. An overload of barnacles tends to be a symptom of an underlying issue, such as the animal being unable to shed its skin. Non-professionals scraping or pulling barnacles off of whales and turtles often does more harm than good for the affected animal!
12th-18th Century Europeans thought that Brants and Barnacle Geese emerged, fully formed, from Goose Barnacles. Gerald of Wales claimed to have seen the birds hanging down from pieces of timber, William Turner accepted the theory, and John Gerard claimed to have seen the birds emerging from their shells. In County Kerry, until relatively recently, Catholics abstaining from meat during Lent could still eat this bird because it was considered a fish.
As filter-feeders, barnacles play an important role in the ecosystem: not only for transferring nutrients up the food chain, but also for keeping the water clean.
When a barnacle chooses its home, it produces a biological glue made of six different proteins. While the glue hardens, it accumulates limestone salts, turning into a concrete-like shell. Barnacle glue is six times stronger than any manmade glue. Scientists are trying to replicate this glue for use in the fields of engineering, construction and medicine, where it can be used as a biological sealant during or post-surgery.
#i could add SO MUCH more but I am trying to make these descriptions shorter both for your sake and for mine#looking forward to narrowing these down to smaller groups in later rounds where I won’t have to write So Dang Much#anyway crabs are coming in the next one#round 2#animal polls#arthropoda
36 notes
·
View notes
Text
Fwd: Postdoc: GeorgeWashingtonU.MolecularSystematics
Begin forwarded message: > From: [email protected] > Subject: Postdoc: GeorgeWashingtonU.MolecularSystematics > Date: 10 August 2024 at 05:11:52 BST > To: [email protected] > > > > Postdoc in Barnacle Molecular Systematics at George Washington University > (GWU) > > About the Project > The Computational Biology Institute, at the Milken Institute School of > Public Health’s Department of Biostatistics and Bioinformatics, GWU, > is offering a Postdoc position to develop a comprehensive phylogeny of > the barnacles (Crustacea: Thecostraca) and study the evolution of sexual > systems.Barnacles rank among the most biologically diverse, ubiquitous and > ecologically important marine metazoans. They exhibit a fascinating and > unique range of sexual systems, including hermaphroditism (both sexes), > dioecy (separate sexes) and androdioecy (hermaphrodites and males).We want > to apply exon probes for targeted capture sequencing to ~1,200 barnacle > species to build a robust phylogeny of the Thecostraca. Then coupling this > barnacle tree with fossil, morphological and ecological information in > a comparative analysis framework, we will test long-standing theoretical > predictions about the evolution of sexual systems and its diversification > across broad spatial, temporal and ecological scales. > > About the Postdoc > > The postdoc candidate will conduct research in phylogenomics and > evolutionary biology of barnacles and work together with the PI (Pérez- > Losada), collaborators and graduate students. Responsibilities: > - Compilation, generation and curation of genomic and other > (e.g., morphological and ecological) trait data for selected > barnacle species. > - Bioinformatic analysis of genomic data to infer phylogenies and > perform comparative analyses on traits to test hypotheses. > - Preparation and submission of manuscripts to scientific journals. > - Availability to travel to other institutions and work abroad for short > periods of time. > - Training of graduate and undergraduate students in the lab on the above- > mentioned duties. > - Delivering guest lectures or short workshops for relevant courses and > related topics offered at GW in the disciplines involved in the > research program. > > Qualifications > > PhD and expertise in molecular systematics, bioinformatics, comparative > phylogenetic methods, genomics and ideally barnacle taxonomy. > > Hiring Range > 61,008 - 65,000 > > Expected duration of appointment > Up to 3 years renewable every year upon performance > > Starting date > 01/09/2024 > > Healthcare Benefits > GWU offers a comprehensive benefit package for Postdoc Associates and > Scholars that includes medical, dental, vision, life & disability > insurance, time off & leave, well-being and various voluntary > benefits. Postdoc Scholars may also be eligible for retirement savings > and tuition programs. For program details and eligibility, please visit > https://ift.tt/HF9oVA7. > > Applicant Documents to Submit > Cover Letter > Curriculum Vitae > Statement of Research Interest > Two Letters of Recommendation > > Online Application > > All candidates must apply online via the following GWU link > https://ift.tt/ypOdzxc > > Contact > If you have further questions regarding this position you can email > Marcos Perez-Losada at [email protected] > > Marcos Perez-Losada, PhD > > > Marcos Perez-Losada
0 notes
Photo


1 note
·
View note
Text
Taxonomy Tournament: Results of Round 1
Long post, many stats.
The three biggest landslides were Opiliones (daddy longlegs) beating Parasitiformes (ticks) (87.89%, 334 to 46 votes), Terebellida (Pompeii worms) beating Scolecida (bamboo worms) (88.94%, 193 to 24 votes), and Hemiptera (true bugs) beating Phthiraptera (lice) (91.04%, 19 to 193 votes).
The three closest matches were Perissodactyla (horses and rhinos) beating Pholidota (pangolins) (50.6%, 747 to 765 votes), Caniformia (canines, bears, foxes...) beating Feliformia (felines, mongooses...) (50.28%, 538 to 532 votes), and Struthioniformes (ostriches) and Rheiformes (rheas) tying (50%, 144 to 144 votes).
To break the tie, I will discount my own vote (for Struthioniformes), so Rheiformes win.
Interesting that the top 3 landslides were all invertebrates (actually all top 7), while the 3 closest matches were all between Chordates (actually 4).
The average winning percent was 67.10% for all matches, and was 71.28% between non-chordates and 62.91% between chordates. So the chordate matches were closer in general.
As you may have guessed from the biggest landslides, parasites fared quite poorly. While the bracket started with 9 primarily parasitic clades, only 3 made it to this round (Hirudinea [leeches], Eucestoda [tapeworms], D. medinensis [nematode]) and all three were against other parasites.
The biggest landslide among Mammals was Didelphidae (possums) beating Hyracoidea (dassies) (80.26%)
The biggest landslide among Birds was Columbiformes (pigeons and doves) beating (flamingos) (72.34%)
The biggest landslide among Non-Avian Reptiles was Serpentes (snakes) beating Rhynchocephalia (tuatara) (60.60%). The closest match among Reptiles was Iguania (iguanas, chameleons...) beating Anguimorpha (Komodo dragon) (51.09%)
The biggest landslide among Cartilaginous Fish was Myliobatiformes (stingrays) beating Rajiformes (skates) (81.20%). The closest match was Rhinopristiformes (shovelnose ray, sawfish...) beating Torpediniformes (electric rays) (51.44%)
The biggest landslide among Bony Fish (and Chordates in general) was Osteoglossiformes (African Knifefish) beating Hiodontiformes (mooneyes) (84.71%). The closest match was Toxotidae (archerfish) beating Istiophoriformes (swordfish) (50.64%).
The biggest landslide among Echinoderms was Asteroids (starfish) beating Peripodida (sea daisies) (82.95%). The closest match was Echinacea (sea urchins) beating Gnathostomata (sand dollars) (55.38%).
The closest match among Annelids was Eunicida (eg. Bobbit worm) beating Phyllodocida (eg. Gossamer worm) (54.38%)
The biggest landslide among Gastropods was Neomphalida (volcano snails) beating Umbraculoidea (false limpets) (86.67%). The closest was Conidae (cone snails) beating Strombidae (conches) (51.39%)
The biggest landslide among Cephalopods was Sepiida (cuttlefish) beating Spirulida (Ram's horn squid) (77.53%). The closest match was Oegopsida (glass squid, giant squid...) beating Myopsida (European squid, reef squid...) (61.9%).
The biggest landslide among other molluscs was Polyplacophora (chitons) beating Scaphopoda (Tusk Shells) (84.35%). The closest was Heterodonta (edible clams) beating Palaeoheterodonta (freshwater mussels) (52.08%)
The closest match among Insects was Mantodea (mantises) beating Blattodea (roaches and termites) (72.9%). Interestingly still a pretty big landslide.
The biggest landslide among Crustaceans was Thecostraca (barnacles) beating Tantulocarida (parasites of crustaceans) (83.33%). The closest match was Branchiopoda (fairy shrimp) beating Copepods (56.54%)
The closest match among Invertibrates was Eucestoda (tapeworms) beating Amphilinidea (parasites of turtles) (50.65%).
Round 2 starts tomorrow!
#Animal Tournament#Animal Tournament Announcements#biology#taxonomy#animal biology#marine biology#evolution#zoology#tumblr polls#tournament poll#poll tournament#bracket tournament
41 notes
·
View notes