#PrEP HIV infection
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
"A large clinical trial in South Africa and Uganda has shown that a twice-yearly injection of a new pre-exposure prophylaxis drug gives young women total protection from HIV infection.
The trial tested whether the six-month injection of lenacapavir would provide better protection against HIV infection than two other drugs, both daily pills. All three medications are pre-exposure prophylaxis (or PrEP) drugs.
Physician-scientist Linda-Gail Bekker, principal investigator for the South African part of the study, tells Nadine Dreyer what makes this breakthough so significant and what to expect next.
Tell us about the trial and what it set out to achieve
The Purpose 1 trial with 5,000 participants took place at three sites in Uganda and 25 sites in South Africa to test the efficacy of lenacapavir and two other drugs.
Lenacapavir (Len LA) is a fusion capside inhibitor. It interferes with the HIV capsid, a protein shell that protects HIV’s genetic material and enzymes needed for replication. It is administered just under the skin, once every six months.
The randomised controlled trial, sponsored by the drug developers Gilead Sciences, tested several things.
The first was whether a six-monthly injection of lenacapavir was safe and would provide better protection against HIV infection as PrEP for women between the ages of 16 and 25 years than Truvada F/TDF, a daily PrEP pill in wide use that has been available for more than a decade.
Secondly, the trial also tested whether Descovy F/TAF, a newer daily pill, was as effective as F/TDF...
The trial had three arms. Young women were randomly assigned to one of the arms in a 2:2:1 ratio (Len LA: F/TAF oral: F/TDF oral) in a double blinded fashion. This means neither the participants nor the researchers knew which treatment participants were receiving until the clinical trial was over.
In eastern and southern Africa, young women are the population who bear the brunt of new HIV infections. They also find a daily PrEP regimen challenging to maintain, for a number of social and structural reasons.
During the randomised phase of the trial none of the 2,134 women who received lenacapavir contracted HIV. There was 100 percent efficiency.
By comparison, 16 of the 1,068 women (or 1.5%) who took Truvada (F/TDF) and 39 of 2,136 (1.8%) who received Descovy (F/TAF) contracted the HIV virus...
What is the significance of these trials?
This breakthrough gives great hope that we have a proven, highly effective prevention tool to protect people from HIV.
There were 1.3 million new HIV infections globally in the past year. Although that’s fewer than the 2 million infections seen in 2010, it is clear that at this rate we are not going to meet the HIV new infection target that UNAIDS set for 2025 (fewer than 500,000 globally) or potentially even the goal to end Aids by 2030...
For young people, the daily decision to take a pill or use a condom or take a pill at the time of sexual intercourse can be very challenging.
HIV scientists and activists hope that young people may find that having to make this “prevention decision” only twice a year may reduce unpredictability and barriers.
For a young woman who struggles to get to an appointment at a clinic in a town or who can’t keep pills without facing stigma or violence, an injection just twice a year is the option that could keep her free of HIV.
What happens now?
The plan is that the Purpose 1 trial will go on but now in an “open label” phase. This means that study participants will be “unblinded”: they will be told whether they have been in the “injectable” or oral TDF or oral TAF groups.
They will be offered the choice of PrEP they would prefer as the trial continues.
A sister trial is also under way: Purpose 2 is being conducted in a number of regions including some sites in Africa among cisgender men, and transgender and nonbinary people who have sex with men.
It’s important to conduct trials among different groups because we have seen differences in effectiveness. Whether the sex is anal or vaginal is important and may have an impact on effectiveness.
How long until the drug is rolled out?
We have read in a Gilead Sciences press statement that within the next couple of months [from July 2024] the company will submit the dossier with all the results to a number of country regulators, particularly the Ugandan and South African regulators.
The World Health Organization will also review the data and may issue recommendations.
We hope then that this new drug will be adopted into WHO and country guidelines.
We also hope we may begin to see the drug being tested in more studies to understand better how to incorporate it into real world settings.
Price is a critical factor to ensure access and distribution in the public sector where it is badly needed.
Gilead Sciences has said it will offer licences to companies that make generic drugs, which is another critical way to get prices down.
In an ideal world, governments will be able to purchase this affordably and it will be offered to all who want it and need protection against HIV."
-via The Conversation, July 3, 2024
#HOLY FUCKING SHIT#100% EFFECTIVE AGAINST HIV INFECTION#AND JUST TWO SHOTS PER YEAR HOLY FUCKING SHIT#THIS IS UNBELIEVABLY GAME-CHANGING#hiv#hiv aids#hiv awareness#lgbtq news#medical news#drug trials#hiv prevention#prep#uganda#south africa#aids#aids crisis#good news#hope
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Brittney McNamara (December 5, 2016). "What to Do If You've Been Exposed to HIV." Teen Vogue.
The more people who know about what to do in that situation, the better.
#HIV#emergency preparedness#PrEP and PEP#sexually transmitted infections#safer sex#sex education#Teen Vogue#community safety#PrEP#HIV AIDS#PEP#queue#rated PG-13
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
Call : +917997101303 | Whatsapp : https://wa.me/917997101505 | Website : https://fidicus.com
ఎక్కువ మందితో ప్రొటెక్షన్ లేకుండా కలుస్తున్నారా? Unprotected Sex | HIV AIDS PrEp Treatment Cure
Stay protected from HIV infection even when engaging in sex with multiple unknown partners by using PrEP (Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis) treatment. This YouTube video explains how PrEP effectively reduces the risk of HIV transmission when taken consistently. Learn about the importance of regular medical consultations, proper condom use, and adherence to the medication. Stay informed and safeguard your health with these essential prevention strategies.
Dr. Bharadwaz | HIV AIDS | Health & Fitness | Homeopathy, Medicine & Surgery | Clinical Research
#PrEP #HIVPrevention #SafeSex #SexualHealth #hivawareness
#DrBharadwaz #Helseform #Fidicus #Clingenious
#ClingeniousHealth #HelseformFitness #FidicusHomeopathy #ClingeniousResearch
#FidicusHIV #HIV #AIDS #HumanImmunodeficiencyViruses #AcquiredImmuneDeficiencySyndrome
#Treatment #Cure #Prevent #Relieve #Medicine #Vaccine
#AlternativeTherapy #AdjuvantTherapy #AlternativeMedicine #AlternativeSystem
Specialty Clinic Fidicus HIV highest success with homeopathy Improve Wellness | Increase Longevity | Addresses Questions
#hiv#hiv treatment#hiv prevention#treatment#treating hiv#hiv prep#how to prevent hiv#hiv infection#prep hiv#hiv status#ending hiv#hiv testing#treat hiv#hiv exposure#preventing hiv#hiv prevention method#prevention of hiv#hiv meaning#hiv prevention; undetectable; treatment as prevention; tasp#preventing hiv to aids#hiv cme#prevent contracting hiv#hiv medications#primary prevention of hiv#living with hiv#hiv cure news today#hiv transmission#Youtube
0 notes
Text
The Best News of Last Week
1. ‘We are just getting started’: the plastic-eating bacteria that could change the world

In 2016, Japanese scientists Oda and Hiraga published their discovery of Ideonella sakaiensis, a bacterium capable of breaking down PET plastic into basic nutrients. This finding marked a shift in microbiology's perception, recognizing the potential of microbes to solve pressing environmental issues.
France's Carbios has successfully applied bacterial enzyme technology to recycle PET plastic waste into new plastic products, aligning with the French government's goal of fully recycling plastic packaging by 2025.
2. HIV cases in Amsterdam drop to almost zero after PrEP scheme

According to Dutch AIDS Fund, there were only nine new cases of the virus in Amsterdam in 2022, down from 66 people diagnosed in 2021. The organisation claimed that 128 people were diagnosed with HIV in Amsterdam in 2019, and since 2010, the number of new infections in the Dutch capital has fallen by 95 per cent.
3. Cheap and drinkable water from desalination is finally a reality

In a groundbreaking endeavor, engineers from MIT and China have designed a passive solar desalination system aimed at converting seawater into drinkable water.
The concept, articulated in a study published in the journal Joule, harnesses the dual powers of the sun and the inherent properties of seawater, emulating the ocean’s “thermohaline” circulation on a smaller scale, to evaporate water and leave salt behind.
4. World’s 1st drug to regrow teeth enters clinical trials

The ability to regrow your own teeth could be just around the corner. A team of scientists, led by a Japanese pharmaceutical startup, are getting set to start human trials on a new drug that has successfully grown new teeth in animal test subjects.
Toregem Biopharma is slated to begin clinical trials in July of next year after it succeeded growing new teeth in mice five years ago, the Japan Times reports.
5. After Decades of Pressure, US Drugmaker J&J Gives Up Patent on Life-Saving TB Drug
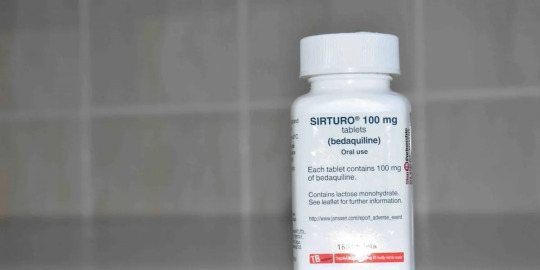
In what can be termed a huge development for drug-resistant TB (DR-TB) patients across large parts of the world, bedaquiline maker Johnson and Johnson said on September 30 (Saturday) that it would drop its patent over the drug in 134 low- and middle-income countries (LMICs).
6. Stranded dolphins rescued from shallow river in Massachusetts
youtube
7. ‘Staggering’ green growth gives hope for 1.5C, says global energy chief

The prospects of the world staying within the 1.5C limit on global heating have brightened owing to the “staggering” growth of renewable energy and green investment in the past two years, the chief of the world’s energy watchdog has said.
Fatih Birol, the executive director of the International Energy Agency, and the world’s foremost energy economist, said much more needed to be done but that the rapid uptake of solar power and electric vehicles were encouraging.
---
That's it for this week :)
This newsletter will always be free. If you liked this post you can support me with a small kofi donation here:
Buy me a coffee ❤️
Also don’t forget to reblog this post with your friends.
11K notes
·
View notes
Text


Senator Scott Wiener: Right wing extremists are trying to block access to PrEP, which all but eliminates HIV risk.
It’s part of their Make America Sick Again agenda.
PrEP can end HIV infections globally. These zealots don’t want that. They want to go back to the 1950s. They want people to get HIV as punishment for sin.
510 notes
·
View notes
Text
How is HIV spread?
"HIV is spread through 6 body fluids: blood, vaginal fluids, semen, pre-cum, rectal fluids, and breastmilk. To get HIV from one of these fluids, there are 4 things that need to happen.
HIV has to be present in the fluid. You can only get HIV from someone who is infected with HIV.
HIV needs to be present in a large enough quantity to cause an infection. HIV dies outside of the human body, so things like old, dried blood don’t spread HIV. Likewise, if someone is on treatment for their HIV and the amount of virus in their body is very low, they are unlikely to give you HIV.
HIV needs to get into your body. This can happen if fluids from someone with HIV get into your blood – like through a needlestick, cut, or open sore – or if fluids come into contact with the inside of your rectum, urethra, or vagina. You cannot get HIV from touching things like blood or semen with unbroken skin.
You need to be susceptible to HIV infection. Some things, like taking PrEP to prevent HIV infection, make you less susceptible. Other things, like having an untreated STI, make you more susceptible."
(From Positively Informed: An HIV/AIDS Roundup)
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
If you are sexually active, please discuss PrEP with your doctor. And everyone should discuss it with all of their friends. Programs like Ryan White are incredibly important to reducing the spread of HIV/AIDS https://ryanwhite.hrsa.gov/about/four-years-hiv-success. These programs provide both HIV antiretrovirals(ARV) and PrEP to low income people and are the reason HIV isn’t ravaging the LGBTQ community like in the 80s. With funding cut, it will be significantly harder for low income people to get access to these medications and will cause HIV to spread through those communities.
ARVs can get people living with HIV to undetectable levels. And undetectable HIV is untransmittable https://www.cdc.gov/global-hiv-tb/php/our-approach/undetectable-untransmittable.html. When people lose access to these medications, they can transmit HIV to their sexual partners. PrEP is 99% effective in reducing the spread of HIV https://www.hiv.gov/hiv-basics/hiv-prevention/using-hiv-medication-to-reduce-risk/pre-exposure-prophylaxis. Not everyone will be able to access PrEP if these programs are cut, but everyone who can should get on it to reduce the spread as much as possible.
We already see health disparities of racial minorities in HIV infection rates https://www.cdc.gov/hiv/data-research/facts-stats/race-ethnicity.html. Black and Latine people will be the first to be affected by these cuts, but like much of our culture it will spread from those communities. It most likely will not reach the level of the 80s, but it will devastate the most vulnerable people in our communities. The wealthiest among us will still be able to afford medication, but for the rest of us, we need to do everything we can to stop the spread.
WE HAVE THE KNOWLEDGE
WE HAVE THE TOOLS
WE CANNOT ALLOW THESE MONSTERS TO KILL US AGAIN
225 notes
·
View notes
Note
wait, what's the difference between hpv and hiv and aids? i thought hiv was just aids and hpv was like. another term for hiv please 😭

okay. before I do this. I do want to remind everyone that this kind of info is incredibly easy to seek for yourself, with the help of simple search times like "what is hpv" or "hiv wikipedia," and I do really encourage doing that! learning how to seek out information is an important skill!
but god I am going to do this anyway, here we go.
HPV is human papillomavirus, an extremely common viral infection that virtually every sexually active person will contract at some point in their life. there are nearly 200 stains of HPV, nearly all of which are harmless, but there are 2 that can (but don't always) cause genital warts and 13 that can (but don't always) cause cancers of the cervix, anus, vagina, vulva, penis, and throat. roughly 90% of cases of HPV clear up and go away on their own within two years of contraction without ever causing any health problems; the majority of people who have it will be asymptomatic the entire time and may never know they have it.
HIV is human immunodeficiency virus, a virus that attacks and drastically weakens the immune system when untreated. it is considered an STI but is not spread exclusively through sexual contact, as it can also be transmitted via unclean syringes shared between people as well as from parents to children via childbirth or breastfeeding. while HIV can be fatal, usually when it develops into AIDS, as I posted about earlier tonight proper medicine and management can allow people with HIV can live full, healthy lives and even completely negate their risk of transmitting HIV.
it's also important to discuss PrEP (pre-exposure prophylaxis), which can be taken by people who do not have HIV to drastically reduce their risk of contracting it, and PEP (post-exposure prophylaxis) which can be taken for 28 days starting up to 72 hours after potential exposure to HIV to greatly reduce the risk of the virus taking hold.
AIDS is acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. AIDS develops when HIV is left untreated and progresses over years, when the immune system has been severely depleted. at this point people are very prone to what are known as "opportunistic" infections and cancers, further health complications that their immune system is unable to fight off as it ordinarily would. people with AIDS often deal with a state of constant fatigue, fever, chills, weakness, inflammation, and weight loss.
so, you know. slightly different things!
204 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Since it was first identified in 1983, HIV has infected more than 85 million people and caused some 40 million deaths worldwide.
While medication known as pre-exposure prophylaxis, or PrEP, can significantly reduce the risk of getting HIV, it has to be taken every day to be effective. A vaccine to provide lasting protection has eluded researchers for decades. Now, there may finally be a viable strategy for making one.
An experimental vaccine developed at Duke University triggered an elusive type of broadly neutralizing antibody in a small group of people enrolled in a 2019 clinical trial. The findings were published today [May 17, 2024] in the scientific journal Cell.
“This is one of the most pivotal studies in the HIV vaccine field to date,” says Glenda Gray, an HIV expert and the president and CEO of the South African Medical Research Council, who was not involved in the study.
A few years ago, a team from Scripps Research and the International AIDS Vaccine Initiative (IAVI) showed that it was possible to stimulate the precursor cells needed to make these rare antibodies in people. The Duke study goes a step further to generate these antibodies, albeit at low levels.
“This is a scientific feat and gives the field great hope that one can construct an HIV vaccine regimen that directs the immune response along a path that is required for protection,” Gray says.
-via WIRED, May 17, 2024. Article continues below.
Vaccines work by training the immune system to recognize a virus or other pathogen. They introduce something that looks like the virus—a piece of it, for example, or a weakened version of it—and by doing so, spur the body’s B cells into producing protective antibodies against it. Those antibodies stick around so that when a person later encounters the real virus, the immune system remembers and is poised to attack.
While researchers were able to produce Covid-19 vaccines in a matter of months, creating a vaccine against HIV has proven much more challenging. The problem is the unique nature of the virus. HIV mutates rapidly, meaning it can quickly outmaneuver immune defenses. It also integrates into the human genome within a few days of exposure, hiding out from the immune system.
“Parts of the virus look like our own cells, and we don’t like to make antibodies against our own selves,” says Barton Haynes, director of the Duke Human Vaccine Institute and one of the authors on the paper.
The particular antibodies that researchers are interested in are known as broadly neutralizing antibodies, which can recognize and block different versions of the virus. Because of HIV’s shape-shifting nature, there are two main types of HIV and each has several strains. An effective vaccine will need to target many of them.
Some HIV-infected individuals generate broadly neutralizing antibodies, although it often takes years of living with HIV to do so, Haynes says. Even then, people don’t make enough of them to fight off the virus. These special antibodies are made by unusual B cells that are loaded with mutations they’ve acquired over time in reaction to the virus changing inside the body. “These are weird antibodies,” Haynes says. “The body doesn’t make them easily.”
Haynes and his colleagues aimed to speed up that process in healthy, HIV-negative people. Their vaccine uses synthetic molecules that mimic a part of HIV’s outer coat, or envelope, called the membrane proximal external region. This area remains stable even as the virus mutates. Antibodies against this region can block many circulating strains of HIV.
The trial enrolled 20 healthy participants who were HIV-negative. Of those, 15 people received two of four planned doses of the investigational vaccine, and five received three doses. The trial was halted when one participant experienced an allergic reaction that was not life-threatening. The team found that the reaction was likely due to an additive in the vaccine, which they plan to remove in future testing.
Still, they found that two doses of the vaccine were enough to induce low levels of broadly neutralizing antibodies within a few weeks. Notably, B cells seemed to remain in a state of development to allow them to continue acquiring mutations, so they could evolve along with the virus. Researchers tested the antibodies on HIV samples in the lab and found that they were able to neutralize between 15 and 35 percent of them.
Jeffrey Laurence, a scientific consultant at the Foundation for AIDS Research (amfAR) and a professor of medicine at Weill Cornell Medical College, says the findings represent a step forward, but that challenges remain. “It outlines a path for vaccine development, but there’s a lot of work that needs to be done,” he says.
For one, he says, a vaccine would need to generate antibody levels that are significantly higher and able to neutralize with greater efficacy. He also says a one-dose vaccine would be ideal. “If you’re ever going to have a vaccine that’s helpful to the world, you’re going to need one dose,” he says.
Targeting more regions of the virus envelope could produce a more robust response. Haynes says the next step is designing a vaccine with at least three components, all aimed at distinct regions of the virus. The goal is to guide the B cells to become much stronger neutralizers, Haynes says. “We’re going to move forward and build on what we have learned.”
-via WIRED, May 17, 2024
#hiv#aids#aids crisis#virology#immunology#viruses#vaccines#infectious diseases#vaccination#immune system#public health#medicine#healthcare#hiv aids#hiv prevention#good news#hope#medical news
922 notes
·
View notes
Text
It was the mid-1980s when Paul Toh came of age as a gay man, decades before smartphones and dating apps made sex a lot more accessible right at your fingertips. Toh has been diagnosed with HIV since 1989.
Now semi-retired with his own business distributing antiretroviral therapy medication and HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP), the 59-year-old said that in those days, cruising in public parks, toilets, and back alleys of dirty shophouses along pre-cleanup Singapore River for sex was par for the course.
Unsurprisingly, cruising in public made gay men easy targets for police officers. “They started going to these cruising grounds undercover, with the explicit intention of entrapping and arresting gay men,” Toh added.
Police raids in nightlife establishments with gay clientele also became common, with prominent gay discotheque Niche having its liquor license withdrawn by the police in 1989 and the Rascals incident of 30 May 1993, in which multiple patrons were arrested for not having their NRICs on them. This came to be remembered by veteran activists as Singapore’s Stonewall.
Fear about the spread of AIDS was part of the reason why police intensified their clamp down on queer spaces. In April 1987, Singapore experienced its first AIDS-related death. And one year later, the Director of Public Affairs of the Singapore Police Department said in a Straits Times article that “homosexual activities have been strongly linked to the dreaded AIDS disease,” making it an “added reason in the public interest for police to disallow homosexuals to convert places licensed for entertainment into places where they can congregate.”
Iris’ Work of Fighting Stigma
76-year-old health advisor Iris Verghese was among the first health workers to rise to the occasion when Singapore reported its first HIV/AIDS cases.
“I knew just as little about HIV/AIDS as everyone else,” said the retired nurse, who first joined Middle Road Hospital, a now-defunct treatment centre for sexually transmitted diseases, in 1974. As part of her job, Verghese was tasked with contact tracing people who had sexually transmitted infections.
The job brought Verghese to brothels and nightclubs in Geylang’s red-light district, which meant she was no stranger to serving society’s Others with kindness.
“A lot of it has to do with my faith.”
“I thought about my role models like Jesus and Mother Teresa—they didn’t care what illness you had. If they could hang out with people with leprosy, then who am I to refuse to care for those with HIV/AIDS?”
Verghese’s work is well-documented, and everyone has given her the accolades she deserves—from President Halimah Yacob to the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Singapore to the Straits Times, which named her an everyday hero in 2019.
Plague, a 15-minute short film by Singaporean filmmaker Boo Junfeng, captures the emotional gravity of the care work performed by Verghese and health workers like herself.
The emotionally-stirring film is inspired by Verghese’s work with HIV/AIDS patients in the ’80s and offers a look into the life of Jamie, a patient who stopped coming to the clinic for treatment and counselling.
In the film’s climax, set in the patient’s HDB flat, Verghese tries to dissuade Jamie from inflicting internalised stigma. Jamie insists on using disposable plastic cups and utensils and cleaning every surface he touches for fear of passing the virus to his loved ones.
Wanting to prove that HIV/AIDS is not transmissible through saliva, Verghese takes Jamie’s plastic cup and drinks from it. She then hands him a regular glass, beckoning for him to drink from it, only for him to swipe it away, breaking the glass and cutting himself in the process.
Thus comes the true test of Verghese’s dedication to her profession as she steels herself to the drastically heightened risk. Now that her patient is bleeding, she is dealing no longer just with saliva, but with blood carrying the virus.
In our interview, Verghese recalled many incidents like these. One that stuck with me was her counselling session with Singapore’s first HIV patient, a young gay professional, in 1985. “As I listened to him and gave him a hug, he broke down and cried,” she said. “He said he felt so good afterwards.”
Safe Sex Outreach in the 80s
“Things were very different in the ’80s and ’90s,” said Professor Roy Chan, Founding President of Action for AIDS Singapore (AfA). AfA is a non-government organisation founded in 1988 to fight HIV/AIDS infection in Singapore.
“There was no internet then. When we set up AfA, we had to rely on word of mouth, phone calls, faxes, pagers, and so on. Mobilisation was not as easy then, but we overcame the obstacles we faced. It was very much more hands-on in those days,” Chan recalled.
Chan set up AfA as a non-governmental organisation in 1988 to respond to the needs of people living with HIV/AIDS, regardless of their sexual orientation or gender identity, as well as to advocate for greater action and awareness around HIV/AIDS.
AfA was also one of the first community groups in Singapore that served the needs of LGBTQ+ individuals—namely men who have sex with men—disproportionately affected by HIV/AIDS.
“Back then, people didn’t have as much access to the internet as we do today, meaning that accurate information on HIV/AIDS was much harder to come by, making education efforts vital,” Chan recalled. “On the flip side, no internet meant the gay nightlife scene was more vibrant than what it is today.”
Since the gay community in the 1980s and 1990s did not have the internet and mobile phone apps to meet other people online, they had to go to physical spaces to fulfil their need for connection, whether it was nightlife establishments or cruising grounds.
Gay clubs were hence crucial in AfA’s outreach programs on safe sex practices back in the ’80s—even if it meant risking the possibility of police raids.
Back then, there were very few places in Singapore where gay men felt safe enough to gather in abundance, making gay clubs a viable hub for outreach and education.
AfA’s outreach efforts endure today in the form of the Mobile Testing Van initiative on weekends. The van, parked outside popular gay nightlife spots in Singapore, aims to bring HIV testing closer to the public, bridging the fear and stigma of walking into a stand-alone clinic to get tested.
The Consequence of Outreach
The people brave enough to put themselves out there to serve a larger cause were but a small minority, especially given the cultural milieu of the time.
“There was so much that was unknown about HIV/AIDS even among the medical community, much less the general public,” said Verghese.
“Even at Middle Road Hospital, two doctors resigned, and twenty-five nurses asked to be transferred out.”
AfA’s awareness campaigns and fundraiser drives drew a lot of publicity—and no doubt some backlash.
Still, beneath all the headlines and the star power lent by high-profile celebrity allies was the silence surrounding individual HIV/AIDS cases.
“It was all very hush-hush. People didn’t want to talk about it. No one wanted to know who died of AIDS,” Verghese shared when I asked if the atmosphere in the 90s was similar to that depicted in films and drama series such as The Normal Heart and Pose.
The shows portrayed the HIV/AIDS crisis in the disease’s epicentre in New York as being a time of deaths and countless funerals attended by surviving gay men.
One exception to this veil of silence was Paddy Chew, the first Singaporean person to come out publicly as being a person living with HIV/AIDS.
Chew—well-known for his one-man autobiographical play Completely With/Out Character—told Verghese and her husband that he wanted no crying at his funeral.
“He asked me to arrange his funeral such that his ashes will be thrown into the sea from a Singapore Armed Forces boat,” said Verghese. She and Chew’s close friends were instructed to be dressed in their party best, with helium balloons that were to be released out at sea.
“There was one helium balloon that drifted away from the other balloons. To me, that felt like it was Paddy’s soul saying goodbye to us one last time.”
A Tale of Two HIV Diagnoses
Perhaps by coincidence—or not, since Verghese was one of the very few nurses dedicated to caring for HIV/AIDS patients at the time—Toh’s then-partner was also one of Verghese’s patients.
“My then-partner Freddie and I handled our HIV diagnoses very differently, but of course, we also came from very different backgrounds and life experiences,” said Toh.
“I found out about my status because an ex-lover of mine had come down with pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP). I flew to Sydney for a diagnosis so that I wouldn’t be registered in the local system here if I was found to be positive.”
On the other hand, Freddie found out about his HIV-positive status because he was a regular blood donor. Not only was his diagnosis inevitably recorded in the national registry, but Freddie also ran into legal trouble. He was charged in court for false disclosure of his sexual activity.
“Because of how the entire trial turned out, Freddie was sentenced to imprisonment for twice the expected duration. It affected his entire outlook in life, feeling like he was being framed by a bigger power with an agenda, with the whole world against him,” said Toh, who cared for Freddie until he passed in 2008.
Toh, on the other hand, took his diagnosis as an opportunity to re-evaluate his life and make the most of the eight years that the doctor told him back in 1989 he had left to live.
“When I received my diagnosis, the only thing in my mind was this: it is the quality of life that matters, not the quantity.” And so, the two spent the next few years of their lives travelling the world, making their remaining years as meaningful as they could be.
Anything for a Chance at Life
Maximising his remaining years did not stop at travel for Toh. Having managed to get his hands on antiretroviral therapy in Sydney in the form of azidothymidine (AZT), he went on to look for more effective forms of medication while the technology was being developed in real-time. Toh wanted to help other HIV patients like himself.
In 1994, Toh joined the Asia Pacific Network of People with HIV/AIDS (APN+), a regional network advocating for the improvement of the lives of people with HIV/AIDS in the Asia-Pacific region, later becoming a Board member and secretariat.
“North America and Europe were progressing swiftly in their battle against HIV/AIDS thanks to the work of activists there putting pressure on their governments and the medical community to channel funding towards the research and development of suitable treatment for HIV/AIDS,” said Toh.
“In Asia, however, it’s a different story. We had to be street smart in our advocacy while also looking elsewhere for allies.”
This meant looking to donors in the West who could be persuaded to recognise the importance of HIV/AIDS advocacy in Asia.
“I was very lucky to have the opportunity to be one of the first few Asians who had access to HAART, said Toh.
HAART (Highly active antiretroviral therapy) is a triple-combination of antiretroviral drugs discovered in 1996 by Professor David Ho. Toh had been invited to attend the 11th International Conference on AIDS in Vancouver, Canada, where the discovery of this triple cocktail was announced.
Within three months of beginning HAART treatment in 1996, Toh saw his health improving tremendously, with his CD4 count—a measure for the immune system of PLHIV—increasing exponentially and his viral load becoming undetectable within the fourth month.
Although Toh already had a supply of free antiretroviral medication from his healthcare provider in Sydney, he continued to look elsewhere for alternative sources for patients who were unable to afford the patented medication.
“Unlike Taiwan, Hong Kong, and South Korea, where medication for HIV/AIDS was provided to patients for free, Singapore was the only Asian Tiger which did not do so,” said Toh.
“Meanwhile, pharmaceutical companies in developing countries like Brazil, India, and Thailand were manufacturing their own generic antiretroviral medication in spite of patent laws, making it more affordable.”
While still not free, MOH announced in 2020 that HIV medication would become subsidised.
Singapore’s Very Own ‘Buyers Club’
With patented HIV/AIDS medication in the ’80s continuing to be inaccessible to many who needed it, buyers clubs—similar to the one featured in the 2013 film Dallas Buyers Club—would soon emerge worldwide, including Singapore.
“The funny thing was that Australia had easy access to HIV/AIDS medication, so there was a lot of stock available in Sydney,” said Verghese. A family vacation down under in 1987 turned into an informal research trip for her to network and gather the information that she needed to perform her job optimally.
During her trip, she met HIV researcher Dr David Cooper, who brought her to Albion Street Centre (now known as The Albion Centre), which specialises in HIV/AIDS management.
Through her newfound contacts, Verghese managed to get her hands on some of the unused stocks of medication in Sydney back to Singapore for her support group.
“We even got the help of the Singapore Airlines flight attendants to pool together their unused baggage allowance to bring this medication back,” she recounted with a laugh.
Antiretroviral medication was not the only asset that Verghese brought back. She learned a lot about the virus from the professionals she met in Sydney, allowing her to move faster than the national response and gather the information needed to tend to her patients.
A Ground Up Initiative
“George Yeo was actually very impressed with what we were doing,” recounted Verghese. “He wanted to meet with the community to learn more about our efforts and arranged a closed-door meeting with us.”
The meeting was the culmination of months of sending letters to Yeo, the Minister of Health at the time. The dialogue session was held to discuss the government’s rule that mandated the bodies of AIDS sufferers to be buried or cremated within twenty-four hours of dying.
This rule was finally lifted in December 2000, after four years of advocacy by AfA.
They argued that the policy was outdated, having been implemented in the mid-1980s when hardly anything was known about HIV/AIDS.
“I think we’ve certainly had to prove ourselves as an organisation over the years,” Chan said. “There might have been concerns among some who thought of us as a gay rights organisation, or misconceptions that AfA worked solely on issues that concern gay people.”
“But we’ve proven ourselves over the years to be a serious and effective organisation tackling HIV/AIDS and sexual health with clear metrics of success, and the results and continued support from the government speak for themselves,” added Prof Chan.
Toh, who served as AfA’s Executive Director from 2007-2009, concurs.
“Actually, not many people know this, but MOH has been quite supportive of AfA over the years. Even during my term, they would hold closed-door discussions with us, intently wanting to work with us on eliminating HIV/AIDS,” said Toh. He reckoned that MOH did not want to be publicly seen as supporting something considered by society as ‘morally corrupt’ no matter how beneficial it is to wider society.
The Fruits of Our Predecessors’ Labour Are Not Handed on a Silver Plate
The history of HIV/AIDS and its role in fomenting community-building among the LGBTQ+ community has always been a topic of fascination for me.
I can only imagine what it must have been like to see everyone in your social circles and communities succumbing, one by one, to an unknown disease.
Covid-19 provided the closest representation of the tumultuous and uncertain time in the ’80s.
In the midst of writing this, however, the comparison became a much closer one. Monkeypox is now affecting men who have sex with men more than the rest of the general population.
“It’s not the same thing,” Chan said, cautioning against making blanket comparisons between monkeypox and HIV/AIDS.
“For starters,” he intoned, “monkeypox is not an unknown disease. We’ve known about monkeypox for decades, so it is nothing close to HIV back in the ’80s.”
Admittedly, life is easier for a gay man like me, who came of age at a time when HIV/AIDS is no longer considered a significant threat.
With common knowledge of medication as well as preventative measures like safer sex and pre and post-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP and PEP), it is easy for me and my peers to take for granted the freedoms that we now enjoy, thanks to decades of advocacy and destigmatisation.
But as Prof Chan said, “It is important not to be complacent. The freedoms and advancements we have today were not handed on a silver platter. Earlier generations had to fight very hard for all of these things.”
200 notes
·
View notes
Note
Is "safe sex" even real? Never done it so idk but you mentioned risk profiles once. I feel like demographically I've got a higher risk profile and the anxiety about that really prevents me from going and trying anything. Do you think that's overly anxious in a negative way?
"safe sex" is a really misleading and binary term. There is never any guarantee of safety in anything we do. Every choice we make comes with risks. Hell, choosing not to connect with other people sexually (if you have any desire to) does ITSELF come with its own risks and costs over time.
The chase after perfect, guranteed safety will only lead to us feeling powerless and afraid, because it is an impossibility. All that we can do is inform ourselves of the risks, mitigate the risks we are the most concerned about and that affect others, and then knowingly accept what risks we still face as the cost of leading a full, enjoyable life.
When we inform ourselves about risk mitigation, we learn there are certain steps that we should probably take to protect ourselves and others if we are engaging in behavior that carries risk. If you're having sex with a complete stranger, it's probably smart to use a condom. If you have sex regularly you might want an HPV vaccine or to be on PreP to prevent HIV transmission. When you meet up with people you should get tested for COVID. You should get vaccinated against COVID. If you want to get suspended in rope from the ceiling don't use a hardware store $3 carabeener, get the good shit from the rock-climbing supply store. Things like that.
But even if you use a condom, you might get herpes or HPV or crabs or a yeast infection. Even if you never have sex, you might already have herpes or HPV or crabs or a yeast infection. I've had several of those things, including some of the "scarier" sounding ones, and they're really not that big a deal. They're just a thing that happens in life. Most people have them. You pop a Valtrex when you have symptoms, you shove a suppostiory up your vulva when it itches, you sleep without underwear on, you communicate with partners, you move on with your life.
Sure, I do what I can to avoid the risks I am most concerned about. I take PreP right now because not getting HIV would be preferable to me. But I could still live if I got it. I am informed about the realities of living with HIV today, which makes that fear more manageable. It is easier for me to make carefully considered and yet realistic decisions surrounding my risk profile because I can confront the realities that scare me and learn more about them.
The body is not separable form its environment. We are connected to our surroundings and the people around us, and our bodies get sick, catch viruses, grow old, get messy, and die inevitably and return to the earth. With our one life, we each have to choose what is most important to us and what potential costs we can stand. But with each year that passes, a cost to our bodies is already incurred, and there's nothing we can do to prevent aging and death from coming our way.
So what would you like to do while you are around? Would you like to have sex with condoms? Go on PreP? Get the HPV vaccine? Take random loads in a glory hole? Make out and dry hump with a cutie at a party and catch her cold sore? Cross the street in the dark after looking both ways? Go out dancing so late that your sleep is disrupted for the whole week? Get your heart broken? Have a great all-consuming love? Have children? Endure a torn labia while giving birth? Try psychedelics? Go on a swinger's cruise? Get a UTI from spermicide? Roleplay online instead of meeting in person? Fuck people with a strap-on?
The choice is yours. And no choice you make will be perfect or come without risk. No life is safe. Accepting loss is one of the necessary tasks of leading a life. But you can educate yourself, reflect on what you most want out of life and what you fear, and then take steps to demystefy your worst fears and mitigate the risks that loom largest to you and the people you care about.
Whatever you decide, I hope you have some fun.
405 notes
·
View notes
Text
#RWRBMovie: Designing the sex scenes
“We need to make sure that it is unambiguous to anyone watching this scene what precisely is happening,” he says. “We’re going to be accurate to the body positioning, to the breath, to the moment of insertion.” Working with intimacy coordinator Robbie Taylor Hunt, López thought through every possible detail about how two men have sex — and what about that process needed to make it into the scene: “We talked about, ‘Does the prince douche before they go in? Do we need to tell the audience that? Does the audience just assume that that’s going on?’” A great deal of time was spent on whether Prince Henry would be on PrEP, a medication taken to prevent HIV infection during sex. “Robbie and I decided together that the prince is probably not on PrEP, because it would be too dangerous for him to ask for prescription,” López says. “So the prince absolutely uses condoms. And because we couldn’t really effectively answer the PrEP question narratively, we wanted to also just tell the story that the prince engages in safe sex practices and takes his sexual health seriously.” Eagle-eyed viewers have indeed caught sight of condom wrappers near Henry and Alex’s bed during a couple of points in the film — alongside a bottle of lube. “Once we had passed a certain part in the story, I was like, OK, let’s empty out some of the lube,’” López says. “Robbie and I were looking at it, like, ‘How much would they use? Like, well, let’s take it down about this much. OK, that makes sense to me.’” It was also vitally important to López to block out every beat of the sex scene in Paris. “Days before we shot that scene, Robbie and I actually got into the bed together,” the director says through laughter. “There are videos that could, like, ruin both our careers. Because we were like, ‘Alright, we’re having sex. What are we going to do? Okay, this pillow goes here. The condom’s going to land here. I’m going to do this.’ We probably overdid it in terms of the preparation for the scene. But we also wanted to make sure that we got on to set and we had an answer for every conceivable question.” The opportunity to show two men having sex in what amounts to a major studio romantic comedy was not lost on López. “I’d be a liar if I told you there wasn’t strategy to the scene, that I didn’t want to cause a conversation about why they’ve never seen this scene in a studio film,” he says. But he was also keenly aware of what he was asking of his actors. “Look, I don’t know if I could do it,” he says. “I’m fully aware that I’m asking two actors to do something that I’m probably not willing to do. I better make sure that I’m not wasting their time, that I’m not making them feel exploited, and that they are included in every single decision, every step of the way. It’s the only responsible way to do it. We knew that if Taylor and Nick didn’t feel safe, we would never have gotten that scene out of them.”
604 notes
·
View notes
Text
Doctors and public health advocates were once able to imagine the end of the HIV epidemic in our lifetime. The last four decades of scientific advancements had delivered new treatments and preventive medications that significantly curbed the rates of transmission and impacts of the once deadly virus. The number of new infections has dropped from more than 130,000 in the mid- 1980s to 37,000 by 2022 — and mortality rates have steadily dropped.
Millions in federal funding — supported by Democratic and Republican leadership alike ― had helped buoy a swath of programs and research into new injectable drugs for HIV prevention and treatment, which are long-lasting and less burdensome than daily medication, and can be used to address HIV disparities across race, gender and sexual orientation both in the United States and internationally.
“With the advent of injectables and how successful they’ve been, I think for many of us, for the first time in a long time, we could actually see what looked like the beginning of the end,” said Tori Cooper, the director of strategic outreach and training at Human Rights Campaign.
But in March, that glimmer of hope began to fade as the Trump administration decimated the nation’s HIV prevention programs as part of Robert F. Kennedy Jr.’s drastic overhaul of the Department of Health and Human Services agency.
The Office of Infectious Diseases & HIV Policy, which oversees the federal strategy on HIV prevention, shuttered its doors. Ten thousand federal health employees were laid off, including staff at five branches of the HIV prevention division of the Centers for Disease Control, who are tasked with tracking new infections and conducting research on strategies to reduce infection risk.
Top staffers, including Jonathan Mermin, the director of the National Center for HIV, Viral Hepatitis, STD and Tuberculosis Prevention ― which lost a quarter of their staff ― were reassigned to the Indian Health Service.
A preliminary HHS budget, obtained by The Washington Post on Wednesday, offers a window into the Trump administration’s priorities, and paints a picture of an even slimmer and reorganized health agency. The proposed budget slashes one-third of the agency’s spending, and eliminates funding for HIV services, including the Minority AIDS Initiative, several Ryan White HIV/AIDS programs, the CDC’s HIV/AIDs prevention and surveillance activities, and preventive services for elderly people and people living with disabilities.
“It’s spelling out a situation where we’re going to see more people get HIV and die from AIDS in the U.S. and internationally,” said Jeremiah Johnson, the executive director of PrEP 4 All, an HIV advocacy organization pushing for a nationwide program to boost access to preventive medication to underinsured communities.
20 notes
·
View notes
Note
Since you're sex positive, what's your take on guys with HIV (undetectable)? Would you have sex with them? Would you consider unprotected sex? Do you expect them to tell you about their status, or you're just assuming that there's always a chance that your sexual partner might be positive?
Yes, and I have in the past. And I think it's always good to assume some kind of risk for your own safety. It just keeps everyone healthier and safer. If you are comfortable with using protection and PrEP, it should be fine. Just be smart about these situations, and make sure your partner is being completely honest with you. I think you should always be transparent about any infection, whether it's HIV, the flu, COVID, gonorrhea... doesn't matter. You owe it to your partner to be transparent.
Don't lie to them just to get sex.
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
Last week, the FDA accepted Gilead Science's New Drug Application for lenacapavir. The drug is now on the fast-track for review, with a target action date of June 19, 2025.
Lenacapavir is a twice-a-year injection that is designed to prevent HIV infection in individuals living at elevated risk of HIV, and has been shown to be effective in clinical trials. If approved, this new drug would be a game-changer, as current oral drugs designed to prevent HIV infection require strict adherence to a daily regiment - a feat that is often difficult due to regular forgetfulness, stigma around HIV, or unstable access to care.
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
Slut-shaming and stigmatizing PrEP, condoms, and safe-sex measures as exclusively for "degenerates" who want to "avoid the consequences of their actions" (ironically, the same line that gets used on people with uteruses who want birth control and abortion access) doesn't lower the rates of HIV and other STIs. It just leads to higher rates of infection, as well as people who refuse medical care out of fear they'll be shamed for having an STI.
Granted, the cruelty is the point to most sex-negative people; most enjoy the idea of 'sinners' and 'degenerates' being 'punished' for their promiscuity. But if there's any of you who actually DO think this will reduce rates of infection, if there are any of you who are just misguided: Please know that you are wrong.
66 notes
·
View notes