#Plantation Economies
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
On May 28, 1914, the Institut für Schiffs-und Tropenkrankheiten (Institute for Maritime and Tropical Diseases, ISTK) in Hamburg began operations in a complex of new brick buildings on the bank of the Elb. The buildings were designed by Fritz Schumacher, who had become the Head of Hamburg’s building department (Leiter des Hochbauamtes) in 1909 after a “flood of architectural projects” accumulated following the industrialization of the harbor in the 1880s and the “new housing and working conditions” that followed. The ISTK was one of these projects, connected to the port by its [...] mission: to research and heal tropical illnesses; [...] to support the Hamburg Port [...]; and to support endeavors of the German Empire overseas.
First established in 1900 by Bernhard Nocht, chief of the Port Medical Service, the ISTK originally operated out of an existing building, but by 1909, when the Hamburg Colonial Institute became its parent organization (and Schumacher was hired by the Hamburg Senate), the operations of the ISTK had outgrown [...]. [I]ts commission by the city was an opportunity for Schumacher to show how he could contribute to guiding the city’s economic and architectural growth in tandem, and for Nocht, an opportunity to establish an unprecedented spatial paradigm for the field of Tropical Medicine that anchored the new frontier of science in the German Empire. [...]
[There was a] shared drive to contribute to the [...] wealth of Hamburg within the context of its expanding global network [...]. [E]ach discipline [...] architecture and medicine were participating in a shared [...] discursive operation. [...]
---
The brick used on the ISTK façades was key to Schumacher’s larger Städtebau plan for Hamburg, which envisioned the city as a vehicle for a “harmonious” synthesis between aesthetics and economy. [...] For Schumacher, brick [was significantly preferable] [...]. Used by [...] Hamburg architects [over the past few decades], who acquired their penchant for neo-gothic brickwork at the Hanover school, brick had both a historical presence and aesthetic pedigree in Hamburg [...]. [T]his material had already been used in Die Speicherstadt, a warehouse district in Hamburg where unequal social conditions had only grown more exacerbated [...]. Die Speicherstadt was constructed in three phases [beginning] in 1883 [...]. By serving the port, the warehouses facilitated the expansion and security of Hamburg’s wealth. [...] Yet the collective profits accrued to the city by these buildings [...] did not increase economic prosperity and social equity for all. [...] [A] residential area for harbor workers was demolished to make way for the warehouses. After the contract for the port expansion was negotiated in 1881, over 20,000 people were pushed out of their homes and into adjacent areas of the city, which soon became overcrowded [...]. In turn, these [...] areas of the city [...] were the worst hit by the Hamburg cholera epidemic of 1892, the most devastating in Europe that year. The 1892 cholera epidemic [...] articulated the growing inability of the Hamburg Senate, comprising the city’s elite, to manage class relationships [...] [in such] a city that was explicitly run by and for the merchant class [...].
In Hamburg, the response to such an ugly disease of the masses was the enforcement of quarantine methods that pushed the working class into the suburbs, isolated immigrants on an island, and separated the sick according to racial identity.
In partnership with the German Empire, Hamburg established new hygiene institutions in the city, including the Port Medical Service (a progenitor of the ISTK). [...] [T]he discourse of [creating the school for tropical medicine] centered around city building and nation building, brick by brick, mark by mark.
---
Just as the exterior condition of the building was, for Schumacher, part of a much larger plan for the city, the program of the building and its interior were part of the German Empire and Tropical Medicine’s much larger interest in controlling the health and wealth of its nation and colonies. [...]
Yet the establishment of the ISTK marked a critical shift in medical thinking [...]. And while the ISTK was not the only institution in Europe to form around the conception and perceived threat of tropical diseases, it was the first to build a facility specifically to support their “exploration and combat” in lockstep, as Nocht described it.
The field of Tropical Medicine had been established in Germany by the very same journal Nocht published his overview of the ISTK. The Archiv für Schiffs- und Tropen-Hygiene unter besonderer Berücksichtigung der Pathologie und Therapie was first published in 1897, the same year that the German Empire claimed Kiaochow (northeast China) and about two years after it claimed Southwest Africa (Namibia), Cameroon, Togo, East Africa (Tanzania, Burundi, Rwanda), New Guinea (today the northern part of Papua New Guinea), and the Marshall Islands; two years later, it would also claim the Caroline Islands, Palau, Mariana Islands (today Micronesia), and Samoa (today Western Samoa).
---
The inaugural journal [...] marked a paradigm shift [...]. In his opening letter, the editor stated that the aim of Tropical Medicine is to “provide the white race with a home in the tropics.” [...]
As part of the institute’s agenda to support the expansion of the Empire through teaching and development [...], members of the ISTK contributed to the Deutsches Kolonial Lexikon, a three-volume series completed in 1914 (in the same year as the new ISTK buildings) and published in 1920. The three volumes contained maps of the colonies coded to show the areas that were considered “healthy” for Europeans, along with recommended building guidelines for hospitals in the tropics. [...] "Natives" were given separate facilities [...]. The hospital at the ISTK was similarly divided according to identity. An essentializing belief in “intrinsic factors” determined by skin color, constitutive to Tropical Medicine, materialized in the building’s circulation. Potential patients were assessed in the main building to determine their next destination in the hospital. A room labeled “Farbige” (colored) - visible in both Nocht and Schumacher’s publications - shows that the hospital segregated people of color from whites. [...]
---
Despite belonging to two different disciplines [medicine and architecture], both Nocht and Schumacher’s publications articulate an understanding of health [...] that is linked to concepts of identity separating white upper-class German Europeans from others. [In] Hamburg [...] recent growth of the shipping industry and overt engagement of the German Empire in colonialism brought even more distant global connections to its port. For Schumacher, Hamburg’s presence in a global network meant it needed to strengthen its local identity and economy [by purposefully seeking to showcase "traditional" northern German neo-gothic brickwork while elevating local brick industry] lest it grow too far from its roots. In the case of Tropical Medicine at the ISTK, the “tropics” seemed to act as a foil for the European identity - a constructed category through which the European identity could redescribe itself by exclusion [...].
What it meant to be sick or healthy was taken up by both medicine and architecture - [...] neither in a vacuum.
---
All text above by: Carrie Bly. "Mediums of Medicine: The Institute for Maritime and Tropical Diseases in Hamburg". Sick Architecture series published by e-flux Architecture. November 2020. [Bold emphasis and some paragraph breaks/contractions added by me. Text within brackets added by me for clarity. Presented here for commentary, teaching, criticism purposes.]
#abolition#ecology#sorry i know its long ive been looking at this in my drafts for a long long time trying to condense#but its such a rich comparison that i didnt wanna lessen the impact of blys work here#bly in 2022 did dissertation defense in architecture history and theory on political economy of steel in US in 20s and 30#add this to our conversations about brazilian eugenics in 1930s explicitly conflating hygiene modernist architecture and white supremacy#and british tropical medicine establishment in colonial india#and US sanitation and antimosquito campaigns in 1910s panama using jim crow laws and segregation and forcibly testing local women#see chakrabartis work on tropical medicine and empire in south asia and fahim amirs cloudy swords#and greg mitmans work on connections between#US tropical medicine schools and fruit plantations in central america and US military occupation of philippines and rubber in west africa#multispecies#imperial#indigenous#colonial#landscape#temporal#see also us mosquito campaigns in panama and british urban planning in west africa and rohan deb roy work on india bengal entomology#ecologies#bugs#tidalectics#archipelagic thinking#plantations#intimacies of four continents#carceral geography#black methodologies#indigenous pedagogies
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
I saw this post yesterday and it’s been haunting me ever since. Pirates pretty much existed all over the world, so I’ll just be referring to English pirates since that’s what most people think of when they hear the word.
Pirates didn’t steal from peasants, but from merchants whose ships carried gold, silver, and other goods they were trading. They’d be going after people with large sums of wealth to get a big payday. Spanish galleons were good targets because they were huge ships with a ton of cargo, and were relatively slow compared to the smaller ships pirates used.
In fact, the working class often liked pirates because they’d sell their loot to them without the tariffs that would be imposed by the state. Plus, they’d spend all their plundered money at bars, blacksmiths, sailmakers, etc., boosting the local economy and retelling their adventures to people who wanted entertainment and excitement. So they were closer to Robin Hood than thieving rich guys.
Don’t get me wrong though, their actions weren’t altruistic- a man’s gotta make a living, and the navy sucked (and laid off a bunch of them)
(My source is Pirate Nests and the Rise of the British Empire, 1570-1740 by Mark G. Hanna if anyone was curious)
I don’t know where the idea that pirates stole from peasants came from. I suppose some of them did ransack the occasional coastal town, but most of the action happened at sea. So if there’s something I’m missing or haven’t heard of, I’d love to learn
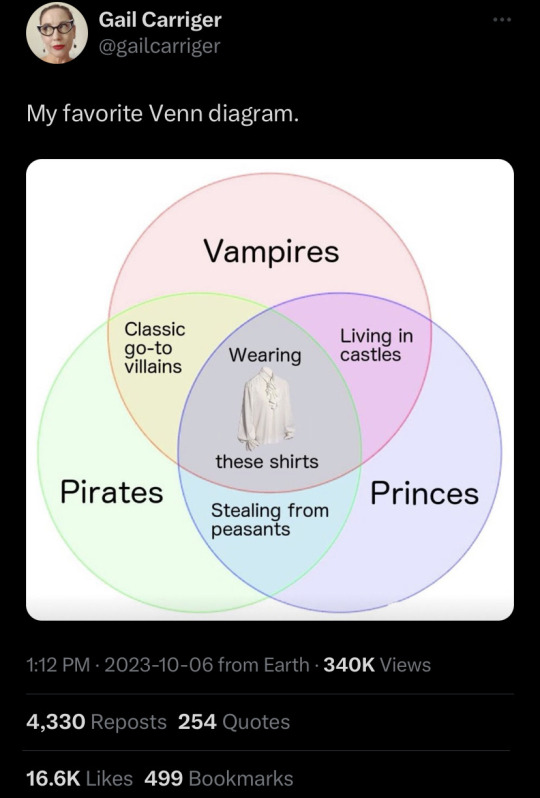
#yeah I didn’t just google that shit I read a whole book on it#it’s a fantastic book by the way#super long but very digestible#for a history book haha#also a lot of pirates started out as poor#and turned to piracy cause that’s WAYYY more lucrative than working on a plantation#it was one of the few ways men could break social class#I mean piracy was really dangerous and you’d be lowering your life spans by joining a crew! some of these guys were desperate#I mean some were fairly well off but were opportunistic etc.#plenty plenty of reasons to be a pirate#maybe it’s because modern media depicts pirates and looking for buried treasure or mythical objects (Pirates of the Caribbean)#so people don’t know the targets of actual historical pirates#anyways I love history I could keep talking about this#and I will#oftentimes local juries would deny the crimes of pirates#because they were so helpful to the local economies#and the courts couldn’t do anything about it which I think is funny
5K notes
·
View notes
Text
The Bridgerton Connection: Tracing the Links Between Jamaica and Regency-Era Real Estate
#Bridgerton#British aristocracy#colonial history#great houses#historical estates#Jamaica#luxury homes#Plantation Economy#Property Investment#Real Estate
0 notes
Text

Marpu Foundation’s partnership is a significant boost to corporate social responsibility (CSR) efforts and supports Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) through numerous impactful projects.
Education and Skill Development (SDG 4: Quality Education):
Marpu Foundation has demonstrated its commitment to quality education in the establishment of learning centers in neglected areas. By partnering with Marpu, corporations could aid more such schools being established; hence ensuring that children as well as adults access quality education and skill acquisition programs. This aligns with SDG 4, which targets inclusive and equitable quality education for all as well as promoting lifelong learning opportunities.
Health and Well-being (SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being):
Maternal-child health camps, nutrition awareness campaigns and disease prevention are some of the outreach activities done by Marpu foundation. In this regard, joining hands with Marpu can expand these health facilities thereby advancing community welfare. To illustrate, a firm can sponsor various health camps to offer basic medical services in remote areas thus supporting SDG 3 that aims at ensuring healthy lives and promoting well-being for all ages.
Clean Water and Sanitation (SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation):
Every human being has a right to clean water and sanitation, which Marpu Foundation has undertaken projects with aims to improve the quality of water supplies and sanitation facilities. Such initiatives could be scaled up with the help of corporate partners so that more communities can access adequate drinking water as well as sanitary facilities. This conforms with SDG 6 that aims at ensuring availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all.
Environmental Sustainability (SDG 13: Climate Action):
Marpu Foundation’s environmental programmes like tree planting campaigns and waste disposal efforts are directly linked to climate change response strategies. Supporting such schemes by firms will enhance their CSR policies in relation to SDG 13, which mainly emphasizes taking immediate action on global warming in order that is causing climate change effects. For example, sponsoring a large-scale tree plantation drive can significantly offset carbon footprints, fostering a greener environment.
Economic Growth and Employment (SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth):
Our company contributes toward economic growth through enabling local entrepreneurship development while offering vocational training courses leading to job creation by Marpu Foundation. Partnering with Marpu enables businesses to invest in these schemes, elevate their CSR standings and support SDG 8 that seeks to “promote sustained inclusive and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment and decent work for all” among others.
Marpu’s Projects examples:
1. Project Shiksha-It is focused on providing educational resources as well as training to less privileged children. Developmental centers for education and scholarship programs could be some of the areas corporate partners might consider supporting through financial aid.
2. Health on Wheels– A mobile clinic which takes medical services closer to the people especially those living in hard-to-reach areas. Companies can help increase its outreach by sponsoring more such facilities hence ensuring easy healthcare access.
3. Green Earth Campaign: Marpu's environmental program involves the plantation of trees, with an added element of spreading awareness for waste management. Businesses can participate by sponsoring tree plantations and waste recycling programs.
The Marpu Foundation further supports companies in the impact of their CSR and aligns with global efforts working towards the realization of the Sustainable Development Goals. This, therefore, contributes to a collaborative mindset when trying to help solve some of the world's dulling issues further improving the social, environmental, and economic welfare of people.
#ngo#csr#children#plantation#education#business#environmental#environment#healthcare#heath and wellness#article#content writing#finance#economy#creative writing
1 note
·
View note
Text
Bay Leaf Farming In Kenya: A Complete Cultivation Guide
Bay leaf, scientifically known as Laurus nobilis, is a fragrant and versatile herb widely used in culinary applications and traditional medicine. It’s an evergreen shrub or tree that can grow up to 30 feet in height. Its glossy leaves are the primary product of interest, possessing a distinctive aromatic flavor. In recent years, bay leaf farming has gained popularity in Kenya due to its economic…

View On WordPress
#Agribusiness#agricultural economy#agricultural extension#agro-processing#Agroecology#agroforestry#agroindustry#aromatic herb#bay leaf consumption#bay leaf diseases#bay leaf drying#bay leaf export#bay leaf extraction#bay leaf farming#bay leaf local market#bay leaf market#bay leaf oil#bay leaf pests#bay leaf plantation#bay leaf revenue#bay leaf storage#bay leaf value chain.#bay leaf varieties#bay leaf yield#crop rotation#culinary herbs#culinary use#cultivation#diversified farming#drip irrigation
0 notes
Note
I'm asking this genuinely, as a 19 yo with no education in economics and a pretty surface level understanding of socialism: can you explain the whole Bananas discourse in a way someone like me might understand? In my understanding it's just "This is just a product we can give up to create better worker conditions and that's fine" but apparently that's not the full picture?
alright so some pretty important background to all this is that we're all talking about the fact that bananas, grown in the global south, are available year-round at extremely low prices all around europe and the USA. it's not really about bananas per so--the banana in this discourse is a synechdoche for all the economic benefits of imperialism.
so how are cheap bananas a result of imperialism? first of all i want to tackle a common and v. silly counterargument: 'oh, these ridiculous communists think it's imperialist for produce to be shipped internationally'. nah. believing that this is the communist objection requires believing in a deeply naive view of international traide. this view goes something like 'well, if honduras has lots of bananas, and people in the usa want bananas and are willing to pay for them, surely everyone wins when the usa buys bananas!'.
there are of course two key errors here and they are both packed into 'honduras has lots of bananas'. for a start, although the bananas are grown in honduras, honduras doesn't really 'have' them, because the plantations are mostly owned by chiquita (formerly known as united fruit) dole, del monte, and other multinationals--when they're not, those multinationals will usually purchase the bananas from honduran growers and conduct the export themselves. and wouldn't you know it, it's those intervening middleman steps--export, import, and retail, where the vast majority of money is made off bananas! so in the process of a banana making its way from honduras to a 7/11, usamerican multinationals make money selling the bananas to usamerican importers who make money selling them to usamerican retailers who make money selling them to usamerican customers.
when chiquita sells a banana to be sold in walmart, a magic trick is being performed: a banana is disappearing from honduras, and yet somehow an american company is paying a second american company for it! this is economic imperialism, the usamerican multinational extracting resources from a nation while simultaneously pocketing the value of those resources.
why does the honduran government allow this? if selling bananas is such a bad deal for the nation, why do they continue to export millions of dollars of banans a year? well, obviously, there's the fact that if they didn't, they would face a coup. the united states is more than willing to intervene and cause mass death and war to protect the profits of its multinationals. but the second, more subtle thing keeping honduras bound to this ridiculously unbalanced relationship is the need for dollars. because the US dollar is the global reserve currency, and the de facto currency of international trade, exporting to the USA is a basic necessity for nations like honduras, guatemala, &c. why is the dollar the global reserve currency? because of usamerican military and economic hegemony, of course. imperialism built upon imperialism!
this is unequal exchange, the neoimperialist terms of international trade that make the 'global economy' a tool of siphoning value and resources from the global south to the imperial core. & this is the second flaw to unravel in 'honduras has a lot of bananas' -- honduras only 'has a lot of bananas' because this global economic hegemony has led to vast unsustainable monoculture banana plantations to dominate the agriculture of honduras. it's long-attested how monoculture growth is unsustainable because it destroys soil and leads to easily-wiped-out-by-infection plants.
so, bananas in the USA are cheap because:
the workers that grow them are barely paid, mistreated, prevented from unionizing, and sometimes murdered
the nations in which the bananas are grown accept brutally unfair trade and tariff terms with the USA because they desperately need a supply of US dollars and so have little position to negotiate
shipping is also much cheaper than it should be because sailors are chronically underpaid and often not paid at all or forced to pay to work (!)
bananas are cheap, in conclusion, because they're produced by underpaid and brutalized workers and then imported on extortionate and unfair terms.
so what, should we all give up bananas? no, and it's a sign of total lack of understanding of socialism as a global movement that all the pearl-clutching usamericans have latched onto the scary communists telling them to stop buying bananas. communism does not care about you as a consumer. individual consumptive choices are not a meaningful arena of political action. the socialist position is not "if there was a socialist reovlution in the usa, we would all stop eating bananas like good little boys", but rather, "if there's a socialist revolution in the countries where bananas are grown, then the availability of bananas in the usa is going to drop, and if you want to be an anti-imperialist in the imperial core you have to accept that".
(this is where the second argument i see about this, 'oh what are you catholic you want me to eat dirt like a monk?' reveals itself as a silly fucking solipsistic misunderstanding)
and again, let's note that the case of the banana can very easily be generalised out to coffee, chocolate, sugar, etc, and that it's not about individual consumptive habits, but about global economic systems. if you are donkey fucking kong and you eat 100 bananas a day i don't care and neither does anyone else. it's about trying to illustrate just one tiny mundane way in which economic imperialism makes the lives of people in the global north more convenient and simpler and so of course there is enormous pushback from people who attach moral value to this and therefore feel like the mean commies are personally calling them evil for eating a nutella or whatever which is frankly pretty tiring. Sad!
tldr: it is not imperialism when produce go on boat but it is imperialism when produce grown for dirt cheap by underpaid workers in a country with a devalued currency is then bought and exported and sold by usamerican companies creating huge amounts of economic value of which the nation in which the banana was grown, let alone the people who actually fucking grew it, don't see a cent -- and this is the engine behind the cheap, available-every-day-all-year-everywhere presence of bananas in the usa (and other places!)
15K notes
·
View notes
Text
The local population in countries that export bananas typically eat different varieties grown primarily by small farmers. The ones for the Americans and the Europeans, Cavendish variety bananas, are grown in huge, monoculture plantations that are susceptible to disease. The banana industry consumes more agrichemicals than any other in the world, asides from cotton. Most plantations will spend more on pesticides than on wages. Pesticides are sprayed by plane, 85% of which does not land on the bananas and instead lands on the homes of workers in the surrounding area and seeps into the groundwater. The results are cancers, stillbirths, and dead rivers.
The supermarkets dominate the banana trade and force the price of bananas down. Plantations resolve this issue by intensifying and degrading working conditions. Banana workers will work for up to 14 hours a day in tropical heat, without overtime pay, for 6 days a week. Their wages will not cover their cost of housing, food, and education for their children. On most plantations independent trade unions are, of course, suppressed. Contracts are insecure, or workers are hired through intermediaries, and troublemakers are not invited back.
Who benefits most from this arrangement? The export value of bananas is worth $8bn - the retail value of these bananas is worth $25bn. Here's a breakdown of who gets what from the sale of banana in the EU.
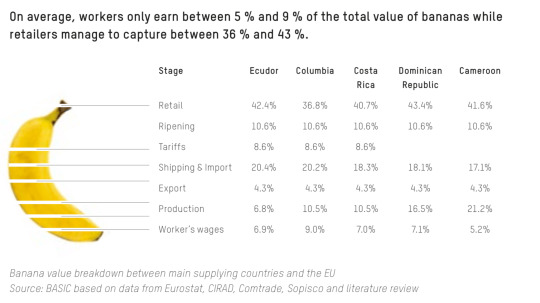
On average, the banana workers get between 5 and 9% of the total value, while the retailers capture between 36 to 43% of the value. So if you got a bunch of bananas at Tesco (the majority of UK bananas come from Costa Rica) for 95p, 6.65p would go to the banana workers, and 38p would go to Tesco.
Furthermore, when it comes to calculating a country's GDP (the total sum of the value of economic activity going on in a country, which is used to measure how rich or poor a country is, how fast its economy is 'growing' and therefore how valuable their currency is on the world market, how valuable its government bonds, its claim on resources internationally…etc), the worker wages, production, export numbers count towards the country producing the banana, while retail, ripening, tariffs, and shipping & import will count towards the importing country. A country like Costa Rica will participate has to participate in this arrangement as it needs ‘hard’ (i.e. Western) currencies in order to import essential commodities on the world market.
So for the example above of a bunch of Costa Rican bananas sold in a UK supermarket, 20.7p will be added to Costa Rica’s GDP while 74.3p will be added to the UK’s GDP. Therefore, the consumption of a banana in the UK will add more to the UK’s wealth than growing it will to Costa Rica’s. The same holds for Bangladeshi t-shirts, iPhones assembled in China, chocolate made with cocoa from Ghana…it’s the heart of how the capitalism of the ‘developed’ economy functions. Never ending consumption to fuel the appearance of wealth, fuelled by the exploitation of both land and people in the global south.
7K notes
·
View notes
Text
“This system of severity of exploitation of poor people of color at the bottom of global supply chains goes back centuries. Few people sitting for breakfast in England in the 1700s knew that their tea was sweetened by sugar harvested under brutal conditions by African slaves toiling in the West Indies. The slaves remained far removed from the British breakfast table until a band of abolitionists placed the true picture of slavery directly in front of the English people. Stakeholders fought to maintain the system. They told the British public not to trust what they were told. They espoused the great humanity of the slave trade—Africans were not suffering, they were being “saved” from the savagery of the dark continent. They argued that Africans worked in pleasing conditions on the islands. When those arguments failed, the slavers claimed they made changes that remedied the offenses taking place on the plantations. After all, who was going to go all the way to the West Indies and prove otherwise, and even if they did, who would believe them?
The truth, however, was this—but for the demand for sugar and the immense profits accrued through the sale of it, the entire slavery-for-sugar economy would not have existed. Furthermore, the inevitable outcome of stripping humans of their dignity, security, wages, and freedom can only be a system that results in the complete dehumanization of the people exploited at the bottom of the chain.
Today’s tech barons will tell you a similar tale about cobalt. They will tell you that they uphold international human rights norms and that their particular supply chains are clean. They will also assure you that conditions are not as bad as they seem and that they are bringing commerce, wages, education, and development to the poorest people of Africa (“saving” them). They will also assure you that they have implemented changes to remedy the problems on the ground, at least at the mines from which they say they buy cobalt. After all, who is going to go all the way to the Congo and prove otherwise, and even if they did, who would believe them?
The truth, however, is this—but for their demand for cobalt and the immense profits they accrue through the sale of smartphones, tablets, laptops, and electric vehicles, the entire blood-for-cobalt economy would not exist. Furthermore, the inevitable outcome of a lawless scramble for cobalt in an impoverished and war-torn country can only be the complete dehumanization of the people exploited at the bottom of the chain.
So much time has passed; so little has changed.”
— from Cobalt Red, Siddharth Kara
#perhaps cynically I would add it isn’t just ‘who would believe it if they knew’ but also ‘would they care’#cobalt red#resource extraction#colonialism#cobalt#slavery#skravler
473 notes
·
View notes
Text
A Fascinating Book I'm Reading

One of the best non-fiction reads I've read in a while, it's not a military history book, but details specifically the Confederate government, culture, society, the legal system, and economy.
What I find most fascinating about the book was just how fucked up the Confederacy became even from the early outset. Especially in terms of law and order. Due to the incredible manpower demands most men of military age either enlisted or were later conscripted into the army. This resulted in severe manpower shortages at home. When this happened, the system of slavery the Confederates were fighting for became a grave liability as there was no one left to control the millions of slaves that populated the south. As a result, whole plantations of slaves would run away and form free communities in the wilderness, surviving by pillaging plantations and farms, or robbing travelers on highways. In Louisiana there was a slave town hidden deep in the swamps that housed 2,000 people! At the same time thousands of Confederate soldiers were deserting as the war started going bad. Many soldiers found that their homestead and family was falling apart in their absence, so they deserted. These deserters were declared outlaws, and as a result many banded together, formed groups, and made a living as bandits and marauders.
At the same time many officers in the Confederate army who were garrisoned in specific places became de facto military dictators and warlords over the territory they controlled. They often disobeyed the law and refused to carry out orders issued by the Confederate government, but due to manpower shortages and the disorganization of the government there was little that could be done to reign them in. Often, these warlord Confederates acted as bandits, pillaging the territory they controlled not just for food and necessary supplies but for valuables as well. In many cases, whole towns and even counties rebelled against Confederate military authorities as they were sick of being pillaged by warlord Confederates. A good example was Jones County, Mississippi which actually seceded from the Confederacy as a result. Often, these rebel towns and counties survived by banditry and became marauders themselves just to make a get by.
According to the author, by 1863 much of the rural south was in a state of lawlessness and anarchy with the countryside controlled by bandits, marauders, independent towns or counties, pro-Union enclaves, and military warlords. Like bruh, this would be a good setting for an open world RPG game, perhaps something set in the Red Dead Redemption Universe.
Anyway if you are a Civil War buff I highly recommend this book.
675 notes
·
View notes
Text
"The transformation of ancestral lands into intensive monoculture plantations has led to the destruction of Guatemala’s native forests and traditional practices, as well as loss of livelihoods and damage to local health and the environment.
A network of more than 40 Indigenous and local communities and farmer associations are developing agroecology schools across the country to promote the recovery of ancestral practices, educate communities on agroecology and teach them how to build their own local economies.
Based on the traditional “campesino a campesino” (from farmer to farmer) method, the organization says it has improved the livelihoods of 33,000 families who use only organic farming techniques and collectively protect 74,000 hectares (182,858 acres) of forest across Guatemala.
Every Friday at 7:30 a.m., María Isabel Aguilar sells her organic produce in an artisanal market in Totonicapán, a city located in the western highlands of Guatemala. Presented on a handwoven multicolor blanket, her broccoli, cabbage, potatoes and fruits are neatly organized into handmade baskets.
Aguilar is in a cohort of campesinos, or small-scale farmers, who took part in farmer-led agroecology schools in her community. As a way out of the cycle of hunger and poverty, she learned ecological principles of sowing, soil conservation, seed storage, propagation and other agroecological practices that have provided her with greater autonomy, self-sufficiency and improved health.
“We learned how to develop insecticides to fend off pests,” she said. The process, she explained, involves a purely organic cocktail of garlic, chile, horsetail and other weeds and leaves, depending on what type of insecticide is needed. “You want to put this all together and let it settle for several days before applying it, and then the pests won’t come.”
“We also learned how to prepare fertilizer that helps improve the health of our plants,” she added. “Using leaves from trees or medicinal plants we have in our gardens, we apply this to our crops and trees so they give us good fruit.”
The expansion of large-scale agriculture has transformed Guatemala’s ancestral lands into intensive monoculture plantations, leading to the destruction of forests and traditional practices. The use of harmful chemical fertilizers, including glyphosate, which is prohibited in many countries, has destroyed some livelihoods and resulted in serious health and environmental damage.
To combat these trends, organizations across the country have been building a practice called campesino a campesino (from farmer to farmer) to revive the ancient traditions of peasant families in Guatemala. Through the implementation of agroecology schools in communities, they have helped Indigenous and local communities tackle modern-day rural development issues by exchanging wisdom, experiences and resources with other farmers participating in the program.
Keeping ancestral traditions alive
The agroecology schools are organized by a network of more than 40 Indigenous and local communities and farmer associations operating under the Utz Che’ Community Forestry Association. Since 2006, they have spread across several departments, including Totonicapán, Quiché, Quetzaltenango, Sololá and Huehuetenango, representing about 200,000 people — 90% of them Indigenous.
“An important part of this process is the economic autonomy and productive capacity installed in the communities,” said Ilse De León Gramajo, project coordinator at Utz Che’. “How we generate this capacity and knowledge is through the schools and the exchange of experiences that are facilitated by the network.”
Utz Che’, which means “good tree” in the K’iche’ Mayan language, identifies communities in need of support and sends a representative to set up the schools. Around 30-35 people participate in each school, including women and men of all ages. The aim is to facilitate co-learning rather than invite an “expert” to lead the classes.
The purpose of these schools is to help farmers identify problems and opportunities, propose possible solutions and receive technical support that can later be shared with other farmers.
The participants decide what they want to learn. Together, they exchange knowledge and experiment with different solutions to thorny problems. If no one in the class knows how to deal with a certain issue, Utz Che’ will invite someone from another community to come in and teach...
Part of what Utz Che’ does is document ancestral practices to disseminate among schools. Over time, the group has compiled a list of basics that it considers to be fundamental to all the farming communities, most of which respond to the needs and requests that have surfaced in the schools.
Agroecology schools transform lives
Claudia Irene Calderón, based at the University of Wisconsin-Madison, is an expert in agroecology and sustainable food systems in Guatemala. She said she believes the co-creation of knowledge is “key to balance the decision-making power that corporations have, which focus on profit maximization and not on climate change mitigation and adaptation.”
“The recovery and, I would add, revalorization of ancestral practices is essential to diversify fields and diets and to enhance planetary health,” she said. “Recognizing the value of ancestral practices that are rooted in communality and that foster solidarity and mutual aid is instrumental to strengthen the social fabric of Indigenous and small-scale farmers in Guatemala.”
Through the implementation of agroecology schools across the country, Utz Che’ says it has improved the livelihoods of 33,000 families. In total, these farmers also report that they collectively protect 74,000 hectares (182,858 acres) of forest across Guatemala by fighting fires, monitoring illegal logging and practicing reforestation.
In 2022, Utz Che’ surveyed 32 women who had taken part in the agroecology school. All the women had become fully responsible for the production, distribution and commercialization of their products, which was taught to them in agroecology schools. Today, they sell their produce at the artisanal market in Totonicapán.
The findings, which highlight the many ways the schools helped them improve their knowledge, also demonstrate the power and potential of these schools to increase opportunities and strengthen the independence of women producers across the country...
The schools are centered around the idea that people are responsible for protecting their natural resources and, through the revitalization of ancestral practices, can help safeguard the environment and strengthen livelihoods."
-via Mongabay News, July 7, 2023
#a little older but still very good!#indigenous#farming#agriculture#sustainable agriculture#agroecology#land back#guatemala#latin america#north america#central america#indigenous knowledge#indigenous peoples#good news#hope
314 notes
·
View notes
Text
It's a consistent rule that media which conspicuously and deliberately refuses to engage with a social issue functionally supports the Status Quo. Sometimes this is an intentional strategy by someone who consciously holds this position but feels insecure with openly expressing it, but other times it's simply the natural outcome of presenting things in this way regardless of the creators intent. Like I've been reading a little about agricultural reform movements in the South Eastern USA before the US civil war, and the general refusal of the most popular agricultural journals to even mention slavery (i.e. the very bedrock of the Southern agricultural system) was clearly a way to support it without getting embroiled in the controversy around abolition that was raging among white settlers in the decades leading up to the war. This excerpt sums it up pretty well:
Considering the Southern Cultivator's resolution to "be exclusively devoted to Southern Agriculture" and its abundant references to planters and plantations, the journal remained remarkably silent about slavery in its first ten years. The editors had abundant reasons to ignore the subject. First, because agricultural journals relied on the exchange of information across multiple national and transatlantic networks, a preoccupation with slavery threatened to alienate critical partnerships. For this reason, agricultural publications both above and below the Mason-Dixon Line tempered their treatment of slavery. Like the Southern Cultivator, the Albany Cultivator, a northern journal with a large southern readership in the 1830s and 1840s, discussed plantations without often mentioning slaves. In both journals, "planters" and "plantations" served as euphemisms for slave owners and slave-labor landscapes Further, agricultural writers made a living by finding and addressing problems, and the editors of southern agricultural journals, even if so inclined, could not afford to suggest that slavery was a problem. Rather, the Southern Cultivator and similar publications mimicked mainstream agricultural philosophy by espousing the idea that the appearance and productivity of agrarian landscapes were an extension of the character and behavior of the landed proprietor. The Southern Cultivator thus bypassed questions of the utility and economy of slavery by focusing its critique on planters and their mismanagement of plantations. In 1849, in a rare direct engagement with national slavery debates, Daniel Lee declared to readers that "[t]he evils of defective system of husbandry—one that makes the soil poorer instead of richer—are mistakenly charged to the account of slave labor when they ought to be ascribed to the misdirection of such labor." The Southern Cultivator thus was a clearinghouse for the various ways planters could use agriculture, architecture, and horticulture to redirect slaves' labor into more culturally and economically productive channels. The journal was not a platform for critiquing or reforming the labor system itself
Philip Herrington (2012) Agricultural and Architectural Reform in the Antebellum South: Fruitland at Augusta, Georgia, The Journal of Southern History vol 78. No 4.
174 notes
·
View notes
Note
Why...why do you care about the homeless? I don't understand...
The homeless problem could easily be solved by either A. sending them to animal killing plantations & using the corpses for fertiliser. Or B. Sending them to a prison adjacent system where they'll partake in mandatory labour. It's also important to discourage homelessness by converting homeless shelters into something more productive, like police stations. Not only are these options beneficial in every aspect but they'll help the economy one way or another.
Now, before you call me inhumane or unhinged, let me tell you this: At the end of the day, being homeless is a choice. These "people" were born into our society & we offered them a chance to live comfortably. But instead of working an extra job or spending less money on something else to pay a bill, they spat at society's kindness & decided to be a burden, tell me, why should these "people" have the right to freedom if they reject everything we offer? Hell being homeless is incredibly easy to get out of too, jobs that require no skills are free, sure its an upwards hill that takes a ridiculous amount of effort but they should've thought of that when they decided to throw their future away, you reap what you sow, its only natural that being homeless is a struggle for class traitors.
Besdies, do these "people" care that they're an eyesore? No, we shouldn't have sympathy for "people" who can't even help themselves. instead of working to redeem their privileges to live comfortably they'd rather beg to hard working civilians like leeches, use the money that children in their ignorance give them to buy drugs (while being a massive contributer to the black market) & just sit in alleyways doing nothing.
These are the true consequences of what happens when "people" decide to be lazy. They're a waste of the gift of life that had no right to be born. These "people" are a disease to our society & like any disease its only our natural response & duty to wipe it out.
**Besides

738 notes
·
View notes
Text
Parish Profile: St. Ann
Taino Heritage St. Ann, Jamaica, carries the echoes of a distant past, dating back to 600–650 A.D. It is believed to have been the first Taino/Arawak settlement on the island, a testament to the ancient roots deeply embedded in its soil. When Christopher Columbus embarked on his historic voyage in 1494, his ship found its way to the tranquil shores of Discovery Bay, St. Ann. Enchanted by the…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Liberia was created to be a new home for former slaves from the US and the Americo-Liberian population quickly became a ruling caste enriched by a plantation economy which relied upon the forced unpaid labor the people indigenous to the region. Which is to say, Liberia wound up mirroring the same oppression that it’s settlers were themselves freeing from. It’s not a stretch to say that with Israel we see a similar mirroring though rather than a plantation economy using slaves we see a mirroring of early 20th century European genocidal ethno-nationalism
I for one, think there may be something inherently broken in the premise of telling people that a bunch of land is now theirs and that they are now the masters of the people that were already living there
546 notes
·
View notes
Text
Indian tea production has been in severe crisis since the mid nineties largely due to neo-liberal structural adjustments in the Indian economy. The size of the tea industry, which is second only to China and accounts for 25 percent of global tea production, has made this a huge blow to the country’s agrarian economy. The industry employs 1.26 million people on tea plantations and two million additional people indirectly. As such, the economic crisis has had an enormous impact on the lives of local residents. In Kerala where I have been conducting research, there have been eight cases of suicide and twelve deaths due to starvation on tea plantations since 2001. Along with utter poverty and famine, tea plantation workers have faced increasingly unhygienic work environments, shattered social life/community relations, and withdrawal of the welfare measures previously enjoyed. The crisis punctured the isolated environments of the plantations and precipitated neoliberal reforms that closed down production in many areas either partially or completely. While many families remained on the plantations, large numbers of workers who had lived there for more than five generations were now compelled to seek work outside. Some went with their families to either their ancestral villages or regional industrial townships such as Coimbatore and Tirupur in Tamil Nadu. These plantation workers have now joined the ranks of the massive Dalit workforce powering India’s unorganised and informal sectors. In joining that pool of workers, Tamil Dalit labourers are exposed to aspects of a caste-ridden society from which they had previously been shielded. The situation of Saraswathi, a female retired worker in her early sixties, illustrates the dilemma and struggles of the workers who moved out the plantations.
— The hidden injuries of caste: south Indian tea workers and economic crisis by Jayaseelan Raj
#plantation tamils#kerala tea plantation#kerala#idukki#neocolonial india#neoliberalism#neoliberal india#plantation capitalism#plantation neoliberalism#tamil dalit workers#neoliberal casteism#jayseelan raj#tamil nadu#tamil labour migration
189 notes
·
View notes
Text
I'm not as well versed in the Philippines' history since I read this a long time ago, but the Philippines were taken from Spain as colonies after the US war with Spain in 1898. At the time, the Filipinos were already waging their own independence war against Spain. The Filipinos declared the First Philippine Republic in June 12 1899. However, the United States refused to accept it, which led to a bloody independence war that lasted decades, where the US military commited genocidal acts:
After World War II and the end of Japanese occupation, because of the obvious drag of holding a colonial possession of millions of people across the Pacific* during an era of decolonization, the US eventually "gave" the Philippines their independence in 1946 after World War II. The fact that they choose the 4th of July was not casual at all: they very much tried to imprint themselves, the former colonial power, as the gentle benefactors of a "daughter republic". There are INCREDIBLY racist cartoons of the US setting itself up as a "teacher" to its conquered nations, "preparing" them for self-determination.
This was a common practice by the US. I've read this in depth a long time ago and I'm sure you can find this in better detail elsewhere, but as the US was rising as an imperial power, it presented itself as an "Empire of Freedom", in suppossed contrast to the European powers, at the same time it did the same, if not worse (as shown in the Philipines) exploitation and crimes across the Pacific and Latin America. If they had could, they would have extended an entire plantation economy all around the Caribbean. Countless interventions testify this.
Of course the Philippines became independent, but it wasn't out of the benvolence of the United States. The US was perfectly willing and able to annex places on the Pacific. Of course you know about Hawai'i and Puerto Rico, which centuries after, still does not have self-determination. But how many Usamericans know about the "associated states" of Palau, Micronesia and the Marshall Islands, of the military bases at Guam? And let alone the countless genocides in the continental US in the name of manifest destiny.
Anyways. My point is, if you saw a post claiming the Philippines' independence was in the 4th of July, maybe you should have asked yourself why, exactly.
137 notes
·
View notes