#Online Trademark Assignment Agreement in India
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Trademark Assignment is a legally registered document created to perform the transaction between the assignor and assignee. Check the Best Online Process only at Eazystartups.
#Trademark Assignment Agreement in India#Online Trademark Assignment Agreement in India#Eazy Startups#India
0 notes
Text
A Guide To Registration Of Limited Liability Partnerships (LLPs) in India
As The Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) has announced that LLP incorporation has moved to the web, just like SPICE+, as a result of the second amendment to the Limited Liability Partnership (Second Amendment) Rules, 2022. The incorporation document must be electronically filed with the Registrar in the form FiLLiP (Form for incorporation of Limited Liability Partnership) with the Registrar with jurisdiction over the registered office.
How Do You Form A Limited Liability Partnership (LLP)
LLPs combine the features of a corporation and a partnership in one business structure. They are a combination of corporations and partnerships. A small business in India often chooses an LLP Incorporation because of its low registration fees and easy maintenance.
Overview Of The Limited Liability Partnership (Second Amendment) Rules, 2022
A The LLP (Second Amendment) Rules, 2022 have undergone a few changes since they were announced on the 04th March 2022. These changes are as follows:
The number of designated partners at incorporation can be as many as five (without DIN numbers).
A PAN and TAN will be assigned as part of the LLP incorporation or registration process.
Incorporating an LLP through the web is similar to SPICE+.
It is also recommended to disclose contingent liabilities on Form 8 (Statement of Solvency) and Annual Return.
As a result, all LLP forms, including Form 9 - Consent of Partners, will be web-based, requiring all Designated Partners to sign digitally.
Incorporating A Limited Liability Company: Step-By-Step Guide
Name Reservation:
To incorporate an LLP, the first step involves reserving the name of the partnership. The applicant must fill out E-Form 1, which confirms availability.
Forming a Limited Liability Partnership (LLP):
If you wish to incorporate a Limited Liability Partnership (LLP), you must file FiLLiP after reserving a name. FiLLiP contains information about the LLP being formed, the partners/designated partners, and their consent to act as partners/ designated partners.
Agreement for Limited Liability Partnership:
A Within 30 days of LLP incorporation, the LLP Agreement must be executed and filed in E-Form 3. In LLP, mutual rights and duties are governed by an agreement between the partners or between the partners and the LLP, depending on the case. However, the LLP is still liable for its other obligations.
LLPs are incorporated using a Web-Based Process, which is as follows:
The LLP Incorporation (FiLLiP Form) is now available online as a result of the Limited Liability Partnership (Second Amendment) Rules, 2022. An DIN or DPIN applications are required along with name reservations, LLP incorporations, and/or new LLP incorporations under FiLLiP.
The eForm must include all supporting documentation, such as the names of designated partners and partners, etc. Once processed and found complete, an LLPIN is assigned.
A DIN/DPIN must also be issued to proposed designated partners/nominees of body corporate designated partners without valid DINs/DPINs.
When incorporating an LLP using this integrated form, the DIN/DPIN can be allocated to no more than five designated partners.
Document Requirements:
Documents required for the FiLLiP Form include:
It is required to submit the resolution on the letterhead of the body corporate being appointed a partner.
On the letterhead of that body corporate, an authorization/resolution naming the nominee/designated partner nominated to represent the company.
Document proving the address of a Limited Liability Partnership's Registered Office.
Subscriber consent form.
Regulatory authorities must approve the proposed name in principle before the attachment can be submitted.
Provide detail about the partnership/designated partnership(s) and/or company(s) in which the partner/designated partner is a director/ partner.
Owners or applicants of trademarks must approve trademark registration applications.
Any words or expressions in the proposed name that require approval from the Central Government.
The competent authority must approve collaboration and connection with a foreign country or place.
A copy of the Board Resolution of the existing company or the consent of the existing LLP is proof of no objection.
The advantages of LLP:
A Limited Liability Partnership is a type of business model that is
Based on an agreement, it is arranged and operated.
Provides flexibility without imposing detailed legal and procedural requirements.
Enables professional/technical expertise and initiative to interact with financial.
Thank you for giving your valuable time for reading this write-up, if still, you have any doubts regarding LLP Registration in India then please connect to our team at [email protected] or call us at 9988424211.
0 notes
Text
Trademark Assignment: All You Need to Know
This article on 'Assignment of Trademarks: All you need to know' was written by Shashanki Kaushik, an intern at Legal Upanishad.
Introduction
This article provides a comprehensive overview of the assignment of trademarks in India, focusing on the legal framework, relevant legislation, landmark judgements, and practical considerations. Understanding the nuances of trademark assignment is vital for businesses seeking to protect their intellectual property rights. In India, this process is governed by various laws, including the Trade Marks Act of 1999 and the Trade Marks Rules of 2017. This article explores the intricacies of trademark assignment, touching upon key aspects, legal provisions, and notable case law.
Assignment of Trademarks: Concept and Laws
Trade Marks Act, 1999, Section 2(1)(b): Definition of Assignment: The Act defines 'assignment' as the transfer of ownership, either with or without the goodwill of the business. Section 37: Requirements for Assignment: This section outlines the essential requirements for a valid trademark assignment, including the need for the assignment to be in writing and signed by both parties. Trade Marks Rules, 2017, Rule 68: Application for Assignment: Rule 68 specifies the procedure for filing an application for the assignment of trademarks, along with the prescribed form and fees.
Types of Trademark Assignment
- Complete Assignment- A complete assignment involves the transfer of both the trademark and the associated goodwill. - Partial Assignment- Partial assignment entails the transfer of the trademark without the goodwill of the business. - Assignment with Goodwill- Assignments that include goodwill are more common and ensure the new owner can benefit from the established reputation and customer base. - Assignment without Goodwill- Assigning a trademark without goodwill is less common and may occur when the assignor intends to retain the business's reputation.
Legal Procedures for Trademark Assignment
- Application to Registrar: The assignor and assignee must file a joint application with the Registrar of Trademarks for the assignment's approval. - Advertisement and Opposition: After acceptance, the Registrar will advertise the assignment application. Interested parties have the opportunity to oppose the assignment within the stipulated period. - Issuance of Certificate: Upon successful completion of the assignment process, the Registrar issues a certificate, signifying the new owner's rights over the trademark.
Landmark Judgments
- Ravi Kamal Bali v. Kala Tech and Entertainment (P) Ltd. This case reaffirmed that an assignment without goodwill does not affect the validity of the assignment. - Indian Performing Right Society Ltd. v. Dalia In this judgement, it was held that the assignee could enforce trademark rights against third parties, even without registering the assignment. Contact Us and avail the best assignment help for students available online!
Practical Considerations
- Due Diligence: Both parties should conduct thorough due diligence before entering into an assignment agreement, ensuring the trademark's validity and reputation. - Clear Agreement: The assignment agreement must be clear and comprehensive, specifying the terms, conditions, and considerations involved. - Record Keeping: Maintaining accurate records of the assignment is crucial for future reference and potential disputes. - Post-Assignment Compliance: The assignee must ensure compliance with ongoing trademark maintenance, including renewals and protection against infringement.
Tax Implications of Trademark Assignment
Trademark assignment can have significant tax implications for both parties involved. The consideration received or paid for the assignment may be subject to capital gains tax or other taxes, depending on the specific circumstances and applicable tax laws. It is crucial for both parties to seek professional tax advice to ensure compliance with tax regulations.
Licensing vs. Assignment
While trademark assignment involves the complete transfer of ownership, licensing allows the owner (licensor) to grant permission to another party (licensee) to use the trademark under specific terms and conditions. Licensing gives more control to the trademark owner and allows for greater flexibility in terms of use, territory, and duration. Assignment, on the other hand, transfers all rights and responsibilities to the assignee, including the duty to protect and enforce the trademark.
Franchising and Trademark Assignment
Franchising often involves the assignment of trademarks to franchisees. This allows franchisees to operate under a recognized brand, benefiting from the established reputation and marketing efforts of the franchisor. Franchise agreements typically include detailed provisions regarding trademark usage, quality control, and territorial rights. Careful consideration of trademark assignment is essential in the franchising context to maintain brand consistency and protect the trademark's value.
International Enforcement of Trademark Assignment
Enforcing trademark assignments across international borders can be challenging due to varying legal systems and regulations. Businesses engaging in cross-border trademark assignments should consider international treaties such as the Madrid Protocol and the Paris Convention, which provide mechanisms for protecting trademarks in multiple countries. Additionally, legal counsel with expertise in international trademark law is essential to navigate the complexities of enforcing trademark assignments globally. International Perspective Paris Convention for the Protection of Industrial Property (1883): India, as a signatory to the Paris Convention, recognizes the principle of national treatment for foreign trademark owners, providing a basis for international trademark assignment. TRIPS Agreement (1994): The Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) Agreement, part of the World Trade Organization (WTO), sets minimum standards for the protection of trademarks and includes provisions related to trademark assignment. International Trademark Assignment Madrid Protocol: Under the Madrid Protocol, businesses can efficiently protect their trademarks in multiple countries by filing a single international application. India became a member of the Madrid Protocol in 2013, facilitating international trademark assignments for Indian businesses. International Trademark Assignment Case Study: Coca-Cola: Coca-Cola's global presence is a prime example of an effective international trademark assignment. Through careful planning and legal strategies, the company has maintained consistent branding worldwide.
Conclusion
Trademark assignment is a vital aspect of intellectual property management in India. It provides opportunities for businesses to monetize their assets or expand their market presence. However, navigating the legal framework, complying with procedures, and safeguarding interests require careful consideration. As demonstrated through relevant legislation and case law, understanding the intricacies of trademark assignment is indispensable for both assignors and assignees in India.
List of References
- Mayashree Acharaya, 'Assignment of Trademark', CLear Tax, 22 February 2022, available at: https://cleartax.in/s/assignment-of-trademark - 'Assignment and Transmission of Rights', Selvam & Selvam, available at: https://selvams.com/kb/in/trademarks/assignment/ - 'Trademark Assignment', Corpbiz, available at: https://corpbiz.io/trademark-assignment Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Why need Promoting Energy Efficiency and Conservation
Energy is the future, and its conservation is crucial for creating a bright future. In today's world, where environmental concerns are at the forefront, it is essential for individuals and industries to prioritize energy conservation and embrace eco-friendly practices. We rely on energy in almost every aspect of our lives to live comfortably, be productive, and create a pleasant environment. Recognizing the significance of energy conservation, the Government of India implemented an innovative initiative on 1st March under the provisions of the Energy Conservation Act, 2001, known as the Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE). BEE plays a vital role in coordinating with designated customers, agencies, and organizations to identify, utilize, and improve existing resources and infrastructure for energy conservation. The Energy Conservation Act aims to regulate and promote energy conservation across the country.
One of the key aspects of BEE's initiatives is the issuance of BEE-rating certificates. These certificates raise awareness about energy efficiency and conservation by demonstrating a product's level of performance and electricity usage. But why does a product need a BEE-rating certificate?
The BEE-rating certificate ensures that specific energy efficiency standards are followed. It guarantees compliance with the Energy Conservation Act of 2001, ensuring that manufacturers and industries adhere to the law's requirements. By obtaining this certification, manufacturers and industries can secure their reputation for adhering to applicable standards and principles outlined in the Energy Conservation Act. It also helps maintain a certain level of efficiency, contributing to overall energy conservation efforts.
The process for obtaining a BEE certificate involves several steps. The first step is product testing, which includes performance testing and safety testing. Performance testing evaluates the product's performance and assigns a star rating, while safety testing ensures that the product is consumer-friendly. These tests are crucial for determining a product's energy consumption and overall efficiency.
The next step is brand or company registration with BEE. This requires submitting the necessary documentation, such as a cover letter, registration fee payment receipt, online company registration form, agreement between BEE and the user of the label, certificate of trademarks, SSI certificate (if applicable), quality management system certificate (ISO 9001), authorized signatory letter, and BIS license. It is essential to ensure that all documents are properly filled out, signed, and stamped.
After brand registration, the next step is model registration. This involves submitting relevant documentation, including the test reports from the product testing phase and BEE Sample Label preparation, which helps consumers understand the product's energy-saving and cost-saving potential. The model registration process includes online and offline submission of the application, along with the required enclosures and a BEE Label Specimen. BEE officials scrutinize the application, test reports, and documents before granting approval.
Obtaining a BEE certificate has several advantages. It ensures adherence to energy efficiency standards, guarantees compliance with the law, secures the manufacturer's or industry's reputation, and helps maintain a certain level of efficiency.
In conclusion, BEE registration is an essential step in promoting energy efficiency and conservation. It not only benefits manufacturers and industries but also contributes to a sustainable and environmentally friendly future. By obtaining BEE certificates, businesses and individuals demonstrate their commitment to conserving energy and creating a better world for future generations. Let us all embrace energy conservation and work towards a brighter and more sustainable future.

#bee certificate price#bee certificate registration#bee certificate cost#bee certificate meaning#bee certification India
0 notes
Text
LLP Registration In Bangalore Tips by Kros Check
Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) is a form of business structure in India that combines the features of a partnership firm and a private limited company. It is a popular form of business structure for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and start-ups as it offers the benefits of limited liability protection to its partners while also allowing them to share profits and losses in a flexible manner, says Kros Chek, LLP Registration In Bangalore.
Here are some tips for LLP registration by Kros Check: Choose the right partners: Choose partners who complement each other in terms of skills, expertise, and resources. It is also important to have a clear understanding of each partner's roles and responsibilities in the LLP.
Choose a suitable name: The name of the LLP should be unique, catchy, and easy to remember. It should also not be similar to any existing company or trademark. The Registrar of Companies (ROC) has the power to reject a proposed name if it considers it to be inappropriate.
Obtain a Digital Signature Certificate (DSC): A DSC is mandatory for at least one of the partners for filing the LLP incorporation documents online. A DSC is a secure digital key that acts as a digital signature and helps in secure online communication.
Apply for a Director Identification Number (DIN): A DIN is a unique identification number assigned to the partners of an LLP. It is necessary for the partners to obtain a DIN before they can incorporate an LLP.
File the LLP incorporation documents: The incorporation documents include the LLP Agreement, Statement of Capital, and the Form for registering an LLP. These documents should be filed with the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) through the MCA21 portal.
Obtain the Certificate of Incorporation: After the MCA approves the LLP incorporation documents, a certificate of incorporation will be issued. This certificate serves as proof of the legal existence of the LLP.
Register for Goods and Services Tax (GST): All LLPs must register for GST if they are engaged in the supply of goods and services. GST registration is mandatory for LLPs with an annual turnover of more than 20 lakhs.
Open a current bank account: An LLP must open a current bank account in its name to carry out its business activities. The bank account must be opened in a bank that is authorized to deal with LLPs, says Kros Chek, llp company registration in bangalore.
Maintain proper books of accounts: LLPs must maintain proper books of accounts and records in accordance with the provisions of the Companies Act, 2013. These records should be maintained for at least 8 years from the date of their preparation.
File annual returns: LLPs must file an annual return with the ROC every financial year. The annual return must be filed within 60 days from the end of the financial year.In conclusion, LLP registration is a straightforward process that can be completed within a few weeks if all the necessary documents and procedures are followed correctly. It is important to choose the right partners, have a clear understanding of each partner's roles and responsibilities, and maintain proper books of accounts to ensure the smooth functioning of the LLP.Kros Check can assist with LLP registration by providing llp company registration services in Bangalore and support throughout the process.
365 Shared Space, 2nd Floor,
#153, Sector 5, 1st Block
Koramangala, HSR Layout,
Bengaluru,Karnataka 560102
Call:+91 9880706841
#llp company registration services in Bangalore#LLP Registration In Bangalore#llp company registration in bangalore
0 notes
Text
UGC NET Commerce Books, Question Paper, Free Study Material, MCQ
UGC NET Commerce Books, Question Paper, Free Study Material, MCQ The National Eligibility Test, also known as UGC NET or NTA-UGC-NET, is the test for determining the eligibility for the post of Assistant Professor and/or Junior Research Fellowship award in Indian universities and colleges. UGC NET is considered as one of the toughest exams in India, with success ratio of merely 6%. UGC NET Commerce Question Paper and MCQs Buy the question bank or online quiz of UGC NET Commerce Exam Going through the UGC NET Commerce Exam Question Bank is a must for aspirants to both understand the exam structure as well as be well prepared to attempt the exam. The first step towards both preparation as well as revision is to practice from UGC NET Commerce Exam with the help of Question Bank or Online quiz. We will provide you the questions with detailed answer. UGC NET Commerce Question Paper and MCQs : Available Now UGC NET Commerce Free Study Material : Click Here UGC NET Commerce Books : Click Here UGC NET Commerce Syllabus Unit 1 – Business Environment and International Business Concepts and elements of business environment: Economic environment- Economic systems, Economic policies(Monetary and fiscal policies); Political environment Role of government in business; Legal environment- Consumer Protection Act, FEMA; Socio-cultural factors and their influence on business; Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR), Scope and importance of international business; Globalization and its drivers; Modes of entry into international business, Theories of international trade; Government intervention in international trade; Tariff and non-tariff barriers; India’s foreign trade policy, Foreign direct investment (FDI) and Foreign portfolio investment (FPI); Types of FDI, Costs and benefits of FDI to home and host countries; Trends in FDI; India’s FDI policy, Balance of payments (BOP): Importance and components of BOP, Regional Economic Integration: Levels of Regional Economic Integration; Trade creation and diversion effects; Regional Trade Agreements: European Union (EU), ASEAN, SAARC, NAFTA International Economic institutions: IMF, World Bank, UNCTAD, World Trade Organisation (WTO): Functions and objectives of WTO; Agriculture Agreement; GATS; TRIPS; TRIMS Unit 2 – Accounting and Auditing Basic accounting principles; concepts and postulates, Partnership Accounts: Admission, Retirement, Death, Dissolution and Insolvency of partnership firms, Corporate Accounting: Issue, forfeiture and reissue of shares; Liquidation of companies; Acquisition, merger, amalgamation and reconstruction of companies, Holding company accounts, Cost and Management Accounting: Marginal costing and Break-even analysis; Standard costing; Budgetary control; Process costing; Activity Based Costing (ABC); Costing for decision-making; Life cycle costing, Target costing, Kaizen costing and JIT, Financial Statements Analysis: Ratio analysis; Funds flow Analysis; Cash flow analysis, Human Resources Accounting; Inflation Accounting; Environmental Accounting, Indian Accounting Standards and IFRS, Auditing: Independent financial audit; Vouching; Verification ad valuation of assets and liabilities; Audit of financial statements and audit report; Cost audit, Recent Trends in Auditing: Management audit; Energy audit; Environment audit; Systems audit; Safety audit Unit 3 – Business Economics Meaning and scope of business economics, Objectives of business firms, Demand analysis: Law of demand; Elasticity of demand and its measurement; Relationship between AR and MR, Consumer behavior: Utility analysis; Indifference curve analysis, Law of Variable Proportions: Law of Returns to Scale, Theory of cost: Short-run and long-run cost curves, Price determination under different market forms: Perfect competition; Monopolistic competition; Oligopoly- Price leadership model; Monopoly; Price discrimination, Pricing strategies: Price skimming; Price penetration; Peak load pricing Unit 4 – Business Finance Scope and sources of finance; Lease financing, Cost of capital and time value of money, Capital structure, Capital budgeting decisions: Conventional and scientific techniques of capital budgeting analysis, Working capital management; Dividend decision: Theories and policies, Risk and return analysis; Asset securitization, International monetary system, Foreign exchange market; Exchange rate risk and hedging techniques, International financial markets and instruments: Euro currency; GDRs; ADRs, International arbitrage; Multinational capital budgeting Unit 5 – Business Statistics and Research Methods Measures of central tendency, Measures of dispersion, Measures of skewness, Correlation and regression of two variables, Probability: Approaches to probability; Bayes’ theorem, Probability distributions: Binomial, poisson and normal distributions, Research: Concept and types; Research designs, Data: Collection and classification of data, Sampling and estimation: Concepts; Methods of sampling – probability and nonprobability methods; Sampling distribution; Central limit theorem; Standard error; Statistical estimation, Hypothesis testing: z-test; t-test; ANOVA; Chi–square test; Mann-Whitney test (Utest); Kruskal Wallis test (H-test); Rank correlation test, Report writing Unit 6 – Business Management and Human Resource Management Principles and functions of management, Organization structure: Formal and informal organizations; Span of control, Responsibility and authority: Delegation of authority and decentralization Motivation and leadership: Concept and theories, Corporate governance and business ethics, Human resource management: Concept, role and functions of HRM; Human resource planning; Recruitment and selection; Training and development; Succession planning, Compensation management: Job evaluation; Incentives and fringe benefits, Performance appraisal including 360 degree performance appraisal, Collective bargaining and workers’ participation in management, Personality: Perception; Attitudes; Emotions; Group dynamics; Power and politics; Conflict and negotiation; Stress management, Organizational Culture: Organizational development and organizational change Unit 7 – Banking and Financial Institutions Overview of Indian financial system, Types of banks: Commercial banks; Regional Rural Banks (RRBs); Foreign banks; Cooperative banks, Reserve Bank of India: Functions; Role and monetary policy management, Banking sector reforms in India: Basel norms; Risk management; NPA management, Financial markets: Money market; Capital market; Government securities market, Financial Institutions: Development Finance Institutions (DFIs); Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs); Mutual Funds; Pension Funds, Financial Regulators in India, Financial sector reforms including financial inclusion, Digitisation of banking and other financial services: Internet banking; mobile banking; Digital payments systems, Insurance: Types of insurance- Life and Non-life insurance; Risk classification and management; Factors limiting the insurability of risk; Re-insurance; Regulatory framework of insurance- IRDA and its role. Unit 8 – Marketing Management Marketing: Concept and approaches; Marketing channels; Marketing mix; Strategic marketing planning; Market segmentation, targeting and positioning, Product decisions: Concept; Product line; Product mix decisions; Product life cycle; New product development, Pricing decisions: Factors affecting price determination; Pricing policies and strategies, Promotion decisions: Role of promotion in marketing; Promotion methods – Advertising; Personal selling; Publicity; Sales promotion tools and techniques; Promotion mix, Distribution decisions: Channels of distribution; Channel management, Consumer Behaviour; Consumer buying process; factors influencing consumer buying decisions, Service marketing, Trends in marketing: Social marketing; Online marketing; Green marketing; Direct marketing; Rural marketing; CRM, Logistics management. Unit 9: Legal Aspects of Business Indian Contract Act, 1872: Elements of a valid contract; Capacity of parties; Free consent; Discharge of a contract; Breach of contract and remedies against breach; Quasi contracts, Special contracts: Contracts of indemnity and guarantee; contracts of bailment and pledge; Contracts of agency, Sale of Goods Act, 1930: Sale and agreement to sell; Doctrine of Caveat Emptor; Rights of unpaid seller and rights of buyer, Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881: Types of negotiable instruments; Negotiation and assignment; Dishonour and discharge of negotiable instruments, The Companies Act, 2013: Nature and kinds of companies; Company formation; Management, meetings and winding up of a joint stock company, Limited Liability Partnership: Structure and procedure of formation of LLP in India, The Competition Act, 2002: Objectives and main provisions, The Information Technology Act, 2000: Objectives and main provisions; Cyber crimes and penalties, The RTI Act, 2005: Objectives and main provisions, Intellectual Property Rights (IPRs) : Patents, trademarks and copyrights; Emerging issues in intellectual property, Goods and Services Tax (GST): Objectives and main provisions; Benefits of GST; Implementation mechanism; Working of dual GST. Unit 10: Income-tax and Corporate Tax Planning Income-tax: Basic concepts; Residential status and tax incidence; Exempted incomes; Agricultural income; Computation of taxable income under various heads; Deductions from Gross total income; Assessment of Individuals; Clubbing of incomes, International Taxation: Double taxation and its avoidance mechanism; Transfer pricing, Corporate Tax Planning: Concepts and significance of corporate tax planning; Tax avoidance versus tax evasion; Techniques of corporate tax planning; Tax considerations in specific business situations: Make or buy decisions; Own or lease an asset; Retain; Renewal or replacement of asset; Shut down or continue operations, Deduction and collection of tax at source; Advance payment of tax; E-filing of income-tax returns. NTA UGC NET Commerce Exam Pattern 2020 1. Paper I : It consists of 50 questions from UGC NET teaching & research aptitude exam (general paper), which you have to attempt in 1 hour. 2. Paper II : The UGC Commerce exam (paper 2) will have 100 questions and the total duration will be two hours. Each question carries 2 marks, so the exam will be worth 200 marks. Read below to know the pattern of NET Commerce examination (part II). Exam HighlightsDetails Test Duration120 minutes Total Questions100 Marks per question2 Total Marks200 Negative MarkingN/A Free Mock Test UGC NET Commerce : Click Here Online Test Series UGC NET Commerce : Click Here #UGCNETCommerce #UGCNETCommerce2020 #UGCNETCommerceExam #FreeTestSeries #QuestionsBank #UGCNETCommerceSyllabus #OnlineTestSeries #OnlineMockTest #ImportantQuestionPaper #ImportantQuestion
1 note
·
View note
Text
Disclaimer
Bluntbobhaircut.tumblr.com Web Site Agreement
The bluntbobhaircut.tumblr.com Web Site (the “Site”) is an online information service provided by Bluntbobhaircut.tumblr.com (“bluntbobhaircut.tumblr.com “), subject to your compliance with the terms and conditions set forth below. PLEASE READ THIS DOCUMENT CAREFULLY BEFORE ACCESSING OR USING THE SITE. BY ACCESSING OR USING THE SITE, YOU AGREE TO BE BOUND BY THE TERMS AND CONDITIONS SET FORTH BELOW. IF YOU DO NOT WISH TO BE BOUND BY THESE TERMS AND CONDITIONS, YOU MAY NOT ACCESS OR USE THE SITE. bluntbobhaircut.tumblr.com MAY MODIFY THIS AGREEMENT AT ANY TIME, AND SUCH MODIFICATIONS SHALL BE EFFECTIVE IMMEDIATELY UPON POSTING OF THE MODIFIED AGREEMENT ON THE SITE. YOU AGREE TO REVIEW THE AGREEMENT PERIODICALLY TO BE AWARE OF SUCH MODIFICATIONS AND YOUR CONTINUED ACCESS OR USE OF THE SITE SHALL BE DEEMED YOUR CONCLUSIVE ACCEPTANCE OF THE MODIFIED AGREEMENT. 1. Copyright, Licenses and Idea Submissions. The entire contents of the Site are protected by international copyright and trademark laws. The owner of the copyrights and trademarks are bluntbobhaircut.tumblr.com, its affiliates or other third party licensors. YOU MAY NOT MODIFY, COPY, REPRODUCE, REPUBLISH, UPLOAD, POST, TRANSMIT, OR DISTRIBUTE, IN ANY MANNER, THE MATERIAL ON THE SITE, INCLUDING TEXT, GRAPHICS, CODE AND/OR SOFTWARE. You may print and download portions of material from the different areas of the Site solely for your own non-commercial use provided that you agree not to change or delete any copyright or proprietary notices from the materials. You agree to grant to bluntbobhaircut.tumblr.com a non-exclusive, royalty-free, worldwide, perpetual license, with the right to sub-license, to reproduce, distribute, transmit, create derivative works of, publicly display and publicly perform any materials and other information (including, without limitation, ideas contained therein for new or improved products and services) you submit to any public areas of the Site (such as bulletin boards, forums and newsgroups) or by e-mail to bluntbobhaircut.tumblr.com by all means and in any media now known or hereafter developed. You also grant to bluntbobhaircut.tumblr.com the right to use your name in connection with the submitted materials and other information as well as in connection with all advertising, marketing and promotional material related thereto. You agree that you shall have no recourse against bluntbobhaircut.tumblr.com for any alleged or actual infringement or misappropriation of any proprietary right in your communications to bluntbobhaircut.tumblr.com. TRADEMARKS. Publications, products, content or services referenced herein or on the Site are the exclusive trademarks or servicemarks of bluntbobhaircut.tumblr.com. Other product and company names mentioned in the Site may be the trademarks of their respective owners. 2. Use of the Site. You understand that, except for information, products or services clearly identified as being supplied by bluntbobhaircut.tumblr.com, bluntbobhaircut.tumblr.comdoes not operate, control or endorse any information, products or services on the Internet in any way. Except for bluntbobhaircut.tumblr.com- identified information, products or services, all information, products and services offered through the Site or on the Internet generally are offered by third parties, that are not affiliated with bluntbobhaircut.tumblr.com a. You also understand that bluntbobhaircut.tumblr.com cannot and does not guarantee or warrant that files available for downloading through the Site will be free of infection or viruses, worms, Trojan horses or other code that manifest contaminating or destructive properties. You are responsible for implementing sufficient procedures and checkpoints to satisfy your particular requirements for accuracy of data input and output, and for maintaining a means external to the Site for the reconstruction of any lost data.YOU ASSUME TOTAL RESPONSIBILITY AND RISK FOR YOUR USE OF THE SITE AND THE INTERNET. bluntbobhaircut.tumblr.com PROVIDES THE SITE AND RELATED INFORMATION “AS IS” AND DOES NOT MAKE ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, REPRESENTATIONS OR ENDORSEMENTS WHATSOEVER (INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION WARRANTIES OF TITLE OR NONINFRINGEMENT, OR THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE) WITH REGARD TO THE SERVICE, ANY MERCHANDISE INFORMATION OR SERVICE PROVIDED THROUGH THE SERVICE OR ON THE INTERNET GENERALLY, AND bluntbobhaircut.tumblr.com SHALL NOT BE LIABLE FOR ANY COST OR DAMAGE ARISING EITHER DIRECTLY OR INDIRECTLY FROM ANY SUCH TRANSACTION. IT IS SOLELY YOUR RESPONSIBILITY TO EVALUATE THE ACCURACY, COMPLETENESS AND USEFULNESS OF ALL OPINIONS, ADVICE, SERVICES, MERCHANDISE AND OTHER INFORMATION PROVIDED THROUGH THE SERVICE OR ON THE INTERNET GENERALLY. bluntbobhaircut.tumblr.com DOES NOT WARRANT THAT THE SERVICE WILL BE UNINTERRUPTED OR ERROR-FREE OR THAT DEFECTS IN THE SERVICE WILL BE CORRECTED. YOU UNDERSTAND FURTHER THAT THE PURE NATURE OF THE INTERNET CONTAINS UNEDITED MATERIALS SOME OF WHICH ARE SEXUALLY EXPLICIT OR MAY BE OFFENSIVE TO YOU. YOUR ACCESS TO SUCH MATERIALS IS AT YOUR RISK. bluntbobhaircut.tumblr.com HAS NO CONTROL OVER AND ACCEPTS NO RESPONSIBILITY WHATSOEVER FOR SUCH MATERIALS. LIMITATION OF LIABILITY
IN NO EVENT WILL bluntbobhaircut.tumblr.com BE LIABLE FOR (I) ANY INCIDENTAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR INDIRECT DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, DAMAGES FOR LOSS OF PROFITS, BUSINESS INTERRUPTION, LOSS OF PROGRAMS OR INFORMATION, AND THE LIKE) ARISING OUT OF THE USE OF OR INABILITY TO USE THE SERVICE, OR ANY INFORMATION, OR TRANSACTIONS PROVIDED ON THE SERVICE, OR DOWNLOADED FROM THE SERVICE, OR ANY DELAY OF SUCH INFORMATION OR SERVICE. EVEN IF bluntbobhaircut.tumblr.com OR ITS AUTHORIZED REPRESENTATIVES HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES, OR (II) ANY CLAIM ATTRIBUTABLE TO ERRORS, OMISSIONS, OR OTHER INACCURACIES IN THE SERVICE AND/OR MATERIALS OR INFORMATION DOWNLOADED THROUGH THE SERVICE. BECAUSE SOME STATES DO NOT ALLOW THE EXCLUSION OR LIMITATION OF LIABILITY FOR CONSEQUENTIAL OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, THE ABOVE LIMITATION MAY NOT APPLY TO YOU. IN SUCH STATES, bluntbobhaircut.tumblr.com LIABILITY IS LIMITED TO THE GREATEST EXTENT PERMITTED BY LAW.bluntbobhaircut.tumblr.com makes no representations whatsoever about any other web site which you may access through this one or which may link to this Site. When you access a non-bluntbobhaircut.tumblr.com web site, please understand that it is independent from bluntbobhaircut.tumblr.com, and that bluntbobhaircut.tumblr.com has no control over the content on that web site. In addition, a link to a bluntbobhaircut.tumblr.com web site does not mean that bluntbobhaircut.tumblr.com endorses or accepts any responsibility for the content, or the use, of such web site. 3. Indemnification. You agree to indemnify, defend and hold harmless bluntbobhaircut.tumblr.com, its officers, directors, employees, agents, licensors, suppliers and any third party information providers to the Service from and against all losses, expenses, damages and costs, including reasonable attorneys’ fees, resulting from any violation of this Agreement (including negligent or wrongful conduct) by you or any other person accessing the Service. 4. Third Party Rights. The provisions of paragraphs 2 (Use of the Service), and 3 (Indemnification) are for the benefit of bluntbobhaircut.tumblr.com and its officers, directors, employees, agents, licensors, suppliers, and any third party information providers to the Service. Each of these individuals or entities shall have the right to assert and enforce those provisions directly against you on its own behalf. 5.Term; Termination. This Agreement may be terminated by either party without notice at any time for any reason. The provisions of paragraphs 1 (Copyright, Licenses and Idea Submissions), 2 (Use of the Service), 3 (Indemnification), 4 (Third Party Rights) and 6 (Miscellaneous) shall survive any termination of this Agreement. 6.Miscellaneous. This Agreement shall all be governed and construed in accordance with the laws of India applicable to agreements made and to be performed in India. You agree that any legal action or proceeding between bluntbobhaircut.tumblr.com and you for any purpose concerning this Agreement or the parties’ obligations hereunder shall be brought exclusively in a federal or state court of competent jurisdiction sitting in India . Any cause of action or claim you may have with respect to the Service must be commenced within one (1) year after the claim or cause of action arises or such claim or cause of action is barred. bluntbobhaircut.tumblr.com’s failure to insist upon or enforce strict performance of any provision of this Agreement shall not be construed as a waiver of any provision or right. Neither the course of conduct between the parties nor trade practice shall act to modify any provision of this Agreement. bluntbobhaircut.tumblr.com may assign its rights and duties under this Agreement to any party at any time without notice to you. Any rights not expressly granted herein are reserved. ________________________________________ COPYRIGHT NOTICE.© 2020 for: bluntbobhaircut.tumblr.com ,All rights reserved.
1 note
·
View note
Text
What is Provisional Patent Application?
The patent is an elite legitimate right of the patentee that awards him the lawful power to restrict others from making or utilizing a protected innovation. A temporary application is a concise summary revealing the pith and the idea of the creation. The fundamental application can be recorded prior to documenting the total determination. It clarifies the patent in a word yet not totally. Documenting a temporary patent is exceptionally valuable for creators as it locks the need date and gets the development so no other person can guarantee authority over it. Patent Filing in Jaipur
Documents for filing a Permanent Patent
Description of the Invention
Detailed description of the invention and details about what the patentee wants to claim out of the invention.
Technical aspects of the invention
Technical details about the invention and drawings along with copy of Provisional patent (if filed).
Applicants Information
Name, address, contact details and nationality of each applicant for the patent.

Benefits of Provisional Patent
Filing a provisional patent is very useful for inventors as it locks the priority date and secures the invention so that no one else can claim authority over it.
Establishes Priority Rights
Filing a provisional patent enables the applicant to secure a priority date for his patent and thus refraining any other individual from filing such a similar patent. Patent Company
Gauge the Worth of Invention
Filing a provisional application is a simpler and affordable step for initial patent protection. The inventor gets 12 months’ time before filing the complete specification which is referred to as complete patent in the common parlance.
Buys Time to make required changes
A provisional patent gives the inventor time to work on the invention and brush up on its utility, novelty, and the inventive factor until it is finalized as per the established standards. A period of 12 months is given to file the final patent draft called a complete specification.
Monetary Returns
The patent is a great asset and can extract way bigger monetary benefits than any other intellectual property if managed intelligently. The owner can license, assign, or sell its patent whenever needed. Many pharmaceutical companies have made great profits through their patented products through licensing, assigning, etc. Patent Company in Jaipur
Process for Permanent Patent
Follow Quick Process
Spare less than 10 minutes to fill our online Questionnaire
Upload all the required Documents to proceed with permanent patent filing
Make quick payment through our secured gateways
Experts at LW are here to help
Assigned Relationship Manager
Consultation regarding the permanent patent application
Drafting of Documents and Agreements
Preparation & Filing of Application
Your Assignment Agreement is ready
All it takes is 25 working days*
Revisions
Suppose the application mentions registering the design in more than one class, then each class of Registration must have a separate application. Patent Registration Services
Presentation
A disclaimer or novelty statement should be attached to each representation concerning the mechanical processes, trademark number, letters.
Delivery & Support
The applicant or authorized person must endorse and duly sign each representation.
Visit More:- Patent Registration in Jaipur
Contact Us:
Address: Jamuna Nagar, Sodala, Jaipur, India, 302006
Phone: 982 938 8100
Email: [email protected]
0 notes
Text
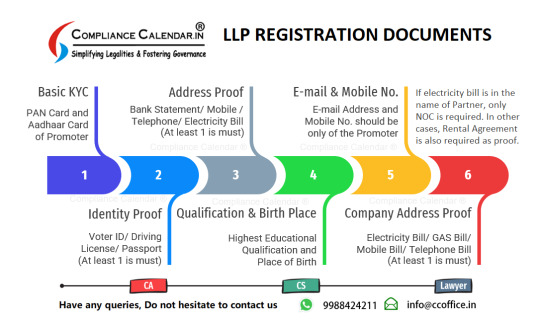
Six Steps of Limited Liability Partnership Registration
What is a Limited Liability Partnership?
This type of business entity, Limited Liability Partnership (Limited Liability Partnership), was introduced in India in 2008 with the enactment of the Limited Liability Partnership Act, 2008. This
hybrid firm has characteristics of both a partnership firm and a limited liability company. Here, two or more individuals invest their money in a particular business to earn a high profit. The mutual privileges and obligations of the partners are standardized by the partnership agreement.
Requirements for the formation of a Limited Liability Partnership
Minimum of two partners, two designated partners, and office location within Indian territory. There is no specific minimum authorised share capital requirement to form an LLP.
Documents Required for LLP Registration
Documents are required from Partners
Aadhar Card of the partners
PAN Card of the partners
Photo of the partners
Residential Proof
Bank statement not old before two months
Documents for registering a Limited Liability Partnership Company
Rental Agreement
EB Receipt
NOC
Six Simple Steps for Limited Liability Partnership Registration in India
The Registering authority for Limited Liability Partnership is the Registrar of Companies. The procedure is explained in this article in simple six steps.
Step 1: Name Approval
The primary step for Limited Liability Partnership Registration is to apply for name approval before the ROC Registration Authority by submitting the objects and the Limited Liability Partnership Name. But before that, the company name can be checked by ourselves for availability using the ROC Portal and Trademark Registration Website.
If the name is distinct enough, the registrar of Companies shall allot the name. RUN-Limited Liability Partnership is a simple and easy-to-use web service for reserving a name for a new Limited Liability Partnership.
Step 2: Obtain a Digital Signature
The next step to registering a Limited Liability Partnership is to get digital signatures for all partners. A digital signature is used to sign all online application forms and government regulatory processes such as ROC registration, GST return, IE code application and more.
This digital signature is mandatory for all partners in Limited Liability Partnership.
Step 3: Apply for DPIN
Once you get the digital signature, you can apply for a Designated Partner Identification Number (DPIN) by submitting the necessary documents before the Registrar of Companies. Documents required to obtain a DIN Number are Aadhaar Card, PAN Card, Passport Size Photograph and Residence Proof.
After verifying the same, the Registrar of Companies shall assign a unique number known as the DPIN Number. Form DIR-3 is required to get the Designated Partner Identification Number
Step 4: Incorporation Certificate
By submitting the Form for Incorporation of Limited Liability Partnership the Registrar of Companies shall issue the Incorporation certificate for the Limited Liability Partnership.
Step 5: Submission of Limited Liability Partnership Agreement
This Limited Liability Partnership Agreement governs the mutual relationship, rights, responsibilities and duties of the partners. The necessary form for submitting the Limited Liability Partnership Agreement before the registrar of companies is Form 3.
The agreement should be submitted within 30 days from the date of Incorporation of the Limited Liability Partnership.
Step 6: Obtain a PAN Card
The final step in the formation of a Limited Liability Partnership is to apply for an online PAN Number in the name of the Company. Once you obtain the PAN Card, you can open a Current Account in the name of the Limited Liability Partnership.
Advantages of LLP / Limited Liability Partnership Registration
Easy to incorporate
No minimum share capital required
No limit for maximum partners
Protection against liability
Separate legal entity
Property can be bought in the company name
Can be extended after the death of partners
Partners may retire or resign
Fewer compliances
0 notes
Text
How to incorporate a Pvt. Ltd. company?
The private limited company is a private firm, where all the shares are sold to the shareholders. This type of company is difficult to dissolve. In India, about 93% of the companies are enlisted under the Private Limited Company as it is a modest and popular form of business. The private limited companies are legislated by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs.
If you are looking to establish a private limited company, you are at the right place. Read on to know more about the incorporation procedure in detail.
What are the boons of the private limited company registration?
By transferring the shares, it is easy to collect funds.
Before the minimum number of the share capital was Rs 1 lakh. But now, there is no minimum capital required.
No pressure of fund requirements.
No risk to personal properties.
It is a separate legal force.
The members are given a limited liability.
The company is very difficult to dissolve.
The transfer is clear as distinguished to the transfer of a dividend in a company race as a proprietary responsibility or a treaty.
What are the necessities for the private limited company?
The shareholders need to be a natural individual or an artificial legitimate force.
The two shareholders are required in a private limited company.
Minimum requirement of two directors.
The directors of the company must be a citizen of India.
There must be 200 members maximum.

How to incorporate a private limited company registration?
The first step is to register to a private limited company and obtain the DSC (Digital Signature Certificate) of the Directors and Subscribers to MOA.
The e-form is documented with the Ministry after attaching the DSC of the Authorised Signatory for Company Incorporation. It is also required for the petition of the DIN of the directors.
The DSC of the subscriber is required to document MOA (Memorandum of Association) and AOA (Articles of Association).
The Director Identification Number (DIN) allotment is maintained by the Ministry to the individual who is a director of the company.
DIN is as important as PAN.
Then, for the reservation of the name an application needs to be filled.
The application is to be made in Form INC-1, where one can assign a maximum of six names in order of choice (the names applied are not similar or nearly matching any surviving Company or LLP or Registered Trademark).
After the approval of the name, the applicant is stored for 60 days, in the remaining time one has to apply for the Incorporation of the Company, non-compliance of which leads to isolation of the name approved by the Ministry.
After the reservation of the name, one shall continue preparing an Application of Certificate of Incorporation in SPICe form supported by SPICe MOA and SPICe AOA.
The application is delivered by paying the requisite Stamp Duty as acceptable in the lawsuit of the worrying state on the portal.
Once the application is accepted, the form for application of PAN and TAN of the company is developed online, which shall be accepted after connecting the DSC with MCA.
After the confirmation of the application and statements provided, the concerned RoC may grant the Certificate of Incorporation (COI).
COI is conclusive proof of the validity of the company.
Whereas, the Date of Incorporation, Company Identification Number (CIN), and Permanent Account Number (PAN) is referred to with the signature and stamp of the Registrar.
After the Certificate of Incorporation is approved, the company may start up the Business workout as the incorporation procedure is finished.
What are the documents required for incorporation?
NOC from the property owner.
If the Director does not have a DIN, then address proof and identity proof must be attached.
According to the Trade Mark Act, it is mandatory to attach the trademark registration certificate or trademark application document.
Affidavit on a Stamp Paper is to be given by all the members of the Company to state their eagerness to serve as the shareholders of the Company.
Address proof.
Rental agreement.
Utility bills paper.
Central Governments approval copy.
Conclusion:
Because of the stability provided in a private limited company, it is one of the top preferences of a majority of people and by following the procedure of registration with accuracy, you can get started with your own Pvt. Ltd. Company smoothly!
Contact Us: +91 8929218091 Please Visit: https://www.taxlegit.com/
#Private limited company registration#LLP company Registration#One person Company Registration#Startup india registration
0 notes
Text
Trademark Assignment is a legally registered document created to perform the transaction between the assignor and assignee. Check the Best Online Process only at Eazystartups.
#Online Trademark Assignment Agreement in India#Business Registration Online#Online Company Registration#Online Income Tax Filing#Online Income Tax Registration
0 notes
Text
The Fight for Martha Graham's Copyrights and Trademarks in Technique, Style, Choreography, Sets, Jewellery, Costumes and Music.
New Post has been published on https://www.bananaip.com/ip-news-center/the-fight-for-martha-grahams-copyrights-and-trademarks-in-technique-style-choreography-sets-jewellery-costumes-and-music/
The Fight for Martha Graham's Copyrights and Trademarks in Technique, Style, Choreography, Sets, Jewellery, Costumes and Music.

Martha Graham is well known for her modern dance technique, choreography, sets, costumes, jewellery and other creative work, and she is today a legend in dance circles. Her unique technique and style is referred to as Martha Graham Technique or Graham’s Technique after her name. Martha Graham was quite protective of her creative work, and allowed very few dance companies to perform her choreographies during her life time. In her effort to finance her creative work and promote/disseminate her technique/style, Martha Graham formed Martha Graham Center of Contemporary Dance (“Centre”) and Martha Graham School of Contemporary Dance (“School”). Both of them had the same set of directors, and the Center along with other non-profit organisations funded her work.
Martha Graham’s Employment
In 1956, Martha Graham entered into a part time employment agreement with the School as program director. The contract required her to dedicate one third of her time to the School for a period of ten years. Her responsibilities included teaching dance and overseeing educational programs of the School. When the contract expired in 1966, Martha Graham was appointed as the Artistic Director of the Center and School, and was required under the contract to create dance work and monitor/manage performances. She continued in this position until her death in 1991.
Martha Graham’s Will
Martha Graham developed a close relationship with Ronald Portas, a photographer, to whom she decided to bequeath her rights and interests in her dance works, musical scores, scenery sets, personal papers and her name. Towards this end, she executed a will in his favour. After Martha Graham’s death, Portas was appointed the Artistic Director of the School. In 1998, Portas set up the Martha Graham’s Trust (“Trust”) and later Martha Graham School and Dance Foundation (“Foundation”). He vested all copyrights in Martha Graham’s works acquired through the will in the Trust. He granted an exclusive license to the Center to teach Martha Graham’s Technique along with a non-exclusive license for live performances of her works.
Dispute over Martha Graham’s Works
Ronald Portas served as the Artistic Director of the Center after Martha Graham, and when he wanted to leave, a dispute arose about who should be appointed next. That led to a conflict, and both the Center and the Trust obtained copyright registrations for the same dance works of Martha Graham. Ronald Portas filed a suit before the Court of Southern District of New York asking the Court to enjoin the Center and the School from using Martha Graham’s trademark, teaching her technique, and performing her choreographies. He also sought a declaration from the Court that the Trust owned all rights over Martha Graham’s dances, sets, jewellery, costumes, etc. The Center contested the Trust’s ownership, and claimed that it owned the works.
Martha Graham’s Copyright and Trademark Ownership
After reviewing the facts, the Court held that the Center owned copyrights over choreographies with respect to 45 of Martha Graham’s dances as they were made during her employment tenure with the Center and the School. Applying the work for hire doctrine, the Court concluded that all copyrights in the dance works created by Martha Graham during her course of employment belonged to the Center and not the Trust as claimed by Portas. It stated that only one work belonged to Portas and the Trust by virtue of Martha Graham’s will. The Court further held that ten of Martha Graham’s works were in the public domain, nine were not published with appropriate notices, and copyrights were not reserved with respect to five works. The Court also held that the Center held rights with respect to use of Martha Graham’s name and trademarks.
On Appeal, the Court of Appeals for the Second Circuit (“Second Circuit”) affirmed a majority of District Court’s findings. However, with respect to works created during Martha Graham’s employment as a part time employee and a couple of other works, the Court remanded the case to the District Court to determine ownership once again in line with its directions. The Second Circuit also held that Acrobats of God dance copyright vested with Ronald Portas and the Trust.
Following the remand, the District Court of the Southern District of New York came to the conclusion that the Center owned the copyrights with respect to Martha Graham’s copyrights during her employment as part-time employee as well as common law copyrights assigned by Martha Graham after she established the Center. On appeal, the Second Circuit affirmed this judgment of the District Court. The Supreme Court refused to hear the case, putting an end to this IP ownership battle. As it stands today, the Center and School set up Martha Graham own IP over most of her works.
Conclusion
Different facets of dance, ranging from the dancer’s name and technique/style to her choreography, sets, costumes and jewellery can be protected under different forms of IP. The protection will not only provide a dancer the much needed recognition of her work, but will also provide a dancer the opportunity to control the use of her work and gain commercial benefits. However, if ownership of dance work, transfer of rights and licenses are not clearly laid out, the dancer may not be able to take advantage of her IP rights. In today’s dance culture, where most dance work and performance works on word of mouth, dancers may not find themselves in the most suitable position to own and assert their IP rights and gain financial benefits from their creative work and performances. Like in the Martha Graham’s case, dancers may not hold IP rights they think they hold and may not be able to control/commercialise them as they wish.
Reference
Martha Graham School and Dance Foundation, Inc., and Ronald Protas, Individually and As Trustee of the Martha Graham Trust, Plaintiffs-counter-defendants-appellants, v. Martha Graham Center of Contemporary Dance, Inc., and Martha Graham School of Contemporary Dance, Inc., Defendants-counterclaimants-appellees, US Court of Appeals for the Second Circuit – 455 F.3d 125 (2d Cir. 2006) if they do not appropriate steps to protect and manage IP rights in their dance works.
INTELLEPEDIA IP SEMINARS
Dancing with Intellectual Property
From dance choreography and settings to dance music and costumes, various aspects of dance can be protected as intellectual property. Protecting dance sequences and moves, videos and music, sets and costumes, personality attributes and names, and social media presence can help dancers commercialise their creative work and prevent its misuse.
Aimed at dancers, this specially designed session helps dancers understand how to protect their creativity and movement art. It provides insights into how their work can be commercialised, and what steps can be taken to prevent infringement of their work online and offline.
Faculty
Dr. Kalyan C. Kankanala
The session will be led by Dr. Kalyan C. Kankanala, a reputed entertainment law attorney in India. He has over the years provided IP consultation and advisory services for several performers, artists, authors and musicians.
Register here – https://www.townscript.com/e/dancing-with-intellectual-property-222404
0 notes
Text
Career Opportunities in IPR for Lawyers
This article is written by Krishnendra Joshi, Research Associate, LawSikho.
We are a PUBG crazy generation. Did you ever wonder what protection should a game developer attain, copyright or trademark to protect his intellectual property in the game? Can there be PUBG shirts and merchandise that sell in hundreds of thousands? How will the game producers benefit from the same?
What makes Apple the richest company in the world? According to research, a 32GB iPhone 7 that retails for $649 costs Apple only $219.80 in components, with manufacturing adding just $5 to the price. Have you ever wondered how does it earn the rest of the money? It’s on account of the intellectual property of course. What makes Apple Inc. the biggest brand in the world?
China is far bigger in manufacturing. India has more engineers. There are more resources in Africa. Russia has more natural gas and oil. However, U.S.A is richer, and a superpower, because it has more intellectual property than any other country.
Every time we buy a mobile phone, watch movies or search online, entities from the U.S.A earn money thanks to intellectual property.
Intellectual Property is a valuable asset class in itself.
India and the entire world is now waking up to the potential of intellectual property. And intellectual property lawyers are now very sought after.
I assume that you are reading this article because you are interested in intellectual property law as a career at some level. Let me give you a detailed picture which may help you to decide for or against, or to simply assess the opportunities.
Click Here
IPR is a recession proof career
Experts expect a global recession to hit us soon. You need to be very careful now about the career choices you make. Is IP a good career choice in the current global or country-specific economic environment?
Innovation and inventions are part of human development, and therefore intellectual property lawyers will always be needed to protect ideas and ownership of inventions. Even if some law practices are affected by the recession, such as investment law, property law or capital market, the field of intellectual property law will continue to grow.
Economies like India can grow now significantly only on the back of intellectual property development. Apart from that, enforcement of intellectual property within the country, which has become a major market, is also critical and generates a massive amount of work for lawyers.
Also, as India has been shifting from informal to the formal economy over the last decade and the trend is expected to continue over the next decade, businesses will be registering and enforcing trademark, copyright and even develop patents.
Communities have begun to wake up to the potential of geographical indications and other sui generis protections for community intellectual properties and indeed there are some amazing activities in terms of IP related legal work.
The major clients of IP lawyers
While every industry requires a lot of IP related support, there are three that run up the biggest bills. They are the biggest clients of IP lawyers. The top one is the Media and Entertainment industry. The second in the technology industry. And finally, biotechnology is also a major industry that depends a lot on IP lawyers.
Apart from these three, fashion, sports and pharma are the next three big clients of IP lawyers.
What kind of work do IP lawyers do?
Contracts Negotiation and Management
IP lawyers advice on exploiting your IPR commercially. Qualcomm collects the majority of its revenue of around 11 billion US dollars from selling licenses of its mobile processing chips. An army of lawyers have to work on not only those licensing agreements but enforcing patents, engage in patent wars with major telecom manufacturers and even on monitoring services across the world.
Law schools will teach you the difference between an assignment and license but that’s not enough. What happens when the copyright is assigned on a perpetual basis and the assignee fails to exercise his rights? Or how do you stop unlicensed players across the world from stealing your IPR? Once they are cornered by your enforcement lawyers, what kind of settlement agreements do you enter into?
Whether it be franchising a new outlet for McDonald’s or getting into a character merchandising agreement for selling merchandise and toys of your favorite Marvel movie, transferring IPR through commercial arrangements forms the basis of exploitation of IPR for value creation.
Do you know what kind of non-standardised clauses are specific in IPR agreements? How will you negotiate a limitation of liability clause? How do you determine the level of diligence required for negotiating a disclaimer clause?
The most common agreements you must learn if you are working as an IP lawyer would be assignment agreement and licensing agreement. These are like bread and butter for most IP lawyers. There are of course many other complicated IP contracts.
Non-contractual drafting
Apart from contracts, there would be a bunch of other drafting too. Lawyers have to learn how to draft even emails. Ask the lawyers who screwed up by writing a mail in the wrong language.
Issuing cease and desist notices, takedown notices are pre-litigation enforcement mechanisms which IPR lawyers must know. They may also have to draft litigation documentation as well as applications for registration of IPR that must be done very carefully.
I hope you are realizing the gap between theory and practice coupled with the huge learning and training opportunity available to law grads and young IP professionals alike.
Registration of IPR
The market for IP registration has become extremely competitive making profit margins thinner. Only patent registration can still be considered premium work. Registration of copyright or trademark is not so profitable anymore.
There are online service providers charging from Rs. 2000 – Rs. 5000 for a single class trademark registration application excluding regulatory fees. However, there can be more money making opportunities in objections, oppositions and other procedures when these applications run into trouble, often because they were drafted by less competent people.
While registration of IP has become a volume game with very low margin, licensing, assignments, objections, oppositions, litigation and related work have massively increased in volume over the years too, turning IP law into an ever more lucrative profession.
That’s the deep end of the pool, however, and highly skilled lawyers who can deliver results tend to do better in IP law.
Brand management
You all get fascinated by the JK Rowling rags to riches story. Harry Potter is a great success story of a brand built around a character and a story later made into movies. IPR attorneys play an important role in creating strategies to bring your brand to the marketplace and figure out new ways to generate revenues from the brand. They also help to put in place agreements and commercial arrangements and enforce IPR so that a brand’s value is not diluted.
For example, an Indian counterpart Hari Puttar which tried to encash on the Harry Potter brand was quickly shut down by lawyers who were responsible for protecting the brand value of the Harry Potter franchise.
Brand management also involves anti-counterfeiting strategies. Lawyers convert legal concepts into enforceable rights and commercially valuable assets.
Portfolio management
Xerox is much more than a photocopier company. It had a huge portfolio of around 8000 patents to its credit but it often failed to take action against infringement by competitors. Big corporations tend to have massive intellectual property asset bases which require professional management which usually lawyer tend to offer. This includes global infringement monitoring services and identifying monetization opportunities.
GE is a company which also has a massive portfolio of exciting patents, but it is very serious about protecting and monetizing them. This has been attracting value investors towards GE stocks as they expect the amazing IP portfolio to give amazing results in near future.
Intellectual property lawyers look after legal-commercial strategies enabling planning regarding portfolio creation and management, licensing the technology
Enforcement of IP
Enforcement of agreements and IP rights through strategic litigation is the most lucrative practice for IP lawyers. It is also the area where more new and best-paid jobs are arising in the industry.
Work can range from coming up with strategies to bring an action against breach of confidential information, holding infringing parties to account, taking credible action against breach of trade secrets, defending claims of IP infringement, preventing misuse of IP rights by vendors, distributors are others who may get access to valuable IP etc.
Lawyers help in creating risk mitigation strategies
In the pharma sector, Johnson & Johnson recently not only called back its disputed batch of drugs but also redesigned its policies as well as the vision to ensure the highest form of integrity and quality. What role do you think lawyers played in this?
A team of IPR lawyers works with the top management to develop powerful strategies in such cases where the company is dealing with regulatory breaches or posing a threat to the company’s brand image. They have to come up with risk mitigation strategies to deal with the immediate situation as well as come up with prevention strategies for the future of the organization.
Fortune 500 companies are risk-averse in nature. Even if you ignore the expenses and time involved in litigation, there is negative publicity attached with opting for litigation. IPR lawyers advise on preparing pre-litigation and settlement strategies as well as aggressive litigation strategies where required.
Are you a lawyer with any science degree?
Well, you can work your way to becoming a patent agent after clearing the patent agent exam. Any science graduate can become a patent agent by clearing the exam, and one does not need a law degree for the same. However, for obvious reasons, lawyers have a significant advantage in building a patent law practice as they do not only do filing but can help with a much wider range of services.
Did you hear that Apple has filed a new patent application with USPTO last month on the concept of a foldable iPhone?
Well as a patent attorney, drafting and filing patent applications for inventors and scientists is your mojo. Managing and advising on patent portfolio also forms a key advisory area for patent attorneys.
Depending on your experience and expertise you might have to work with an international clientele for filing and prosecution in foreign offices.
However, as a lawyer, you are likely to go much beyond drafting and filing patent applications and work on patent litigations and prosecution cases.
Where should you work as an IP lawyer?
Law firms
The best IPR Law firms are mostly boutique law firms. They can have smaller teams in comparison with say a corporate transactions team of a tier 1 law firm. Big law firms also have IPR teams, but they are usually small and often gets paid far less than the corporate lawyers in the firm.
Companies
Most companies require IP lawyers, if not specialized ones then at least general in-house lawyers who also have to do IP work. In sectors like media and entertainment, technology, pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, sports and broadcasting, movies, music, publishing etc. IP lawyers are in great demand and these companies often require large IP law teams.
IPR thinktanks
There are large IPR, technology, competition law and internet related thinktanks that need to hire IPR lawyers in large number for research and policy-related work.
Litigators
IP litigation is steadily on the rise, especially when it comes to trademark-related disputes. Patents and copyright prosecutions and disputes are also on the rise. It is the best time in history to be IPR litigator, also because most IP lawyers are concentrated on other kinds of work.
IP Monitoring services
In recent times IP rights monitoring services have become very prominent and profitable. Large MNCs and IP owners appoint monitoring agencies all over the world whose job is to keep a check on who is misusing such intellectual property and taking legal action to recover any illegal profits and prevent further misuse of copyright, trademark or patent. They prevent counterfeit products, catch illegal copies, detect misuse of copyright and then take legal action as per pre-approved mandates. A large number of lawyers can get employment in such IP monitoring service providers.
How to approach IP law as a career if you are interested
You will see two kinds of aspiring IP lawyers in the job market. One breed of IP aspirants will be extremely focused about IPR. they will start building their CV around IPR during their law school itself. You will either find a lot of IP focused internships. Their experience will range from a trademark team of a law firm to the legal department of an FMCG company.
They would probably have industry-focused certifications, workshops, and conferences on their resume. Writing a few research papers and online legal blogs is appreciated when you sit for the interview. Basically, there are lawyers who have been interested in IPR for a while and can demonstrate the same based on the history of their activities which are worthy of being mentioned on one’s resume.
There is another class of IP lawyers who choose IP as their last resort. You may or may not find a couple of IP internships during their law schools in their CV, but they claim to be very interested in IP when they apply for IP jobs. This is very problematic. If you say you are interested in IP, there better be enough in your CV that proves the same.
The best way to do so is to write and publish at least a dozen high-quality articles on IP law and publish them on credible internet platforms where IP lawyers are likely to read them.
Also, start attending events related to IP lawyers and take up practical IP law-oriented courses which can speed up your growth and understanding of IP law work.
The placement scenario is changing for the Good
The salary you might command while starting out is subjective.
The reputation of your college matters but law firms have become a lot flexible in terms of hiring and retaining talent. Even our students from KIIT law school have bagged placements with tier 1 IPR firms through smart planning and focused internships during law schools.
Law firms like Wadia & co. have a system wherein they offer assessment internships for 3 months. You work and report under a senior associate or the partner during the period of internship. Your chances of bagging the job are based on your performance.
Tier 1 IP law firms may offer starting salaries around 50-70 k per month while smaller law firms may offer anything between 20k-50k per month. Law firms will pay better if you have previous IP litigation experience because that is the most in-demand skill right now.
Your focus must be on acquiring the right skills rather than the salary numbers in your formative years. The potential to earn astronomical sums is very much present provided you can deliver results to clients.
There is a lot of churning in terms of IP recruitment
There is a lot of turnover in the IPR job market. Bright law students join a law firm and switch in 1 to 1.5 years to another firm or another area of practice.
Law firms are aware of the churning going on in the market. Therefore, they offer attractive performance-based appraisals in the range of 25-30% after 1 year onwards.
Rewards lie ahead if you are willing to give your career the time it deserves
The first 4 years in the niche IPR practice area is extremely critical for anyone wanting to become an indispensable part of his law firm team but also the IPR industry. You progress to become a senior associate, work closely with law firm partners. You will also have enough opportunities to strike out on your own and establish your own practice. The prospects of making a name for yourself in the industry are quick as it is a close-knit community, provided you can deliver high quality work consistently.
Top sought after skills
Pay special attention to communication skills
Your communication skills play a key role especially in a field like IPR. What if you are seeking an injunction in a trademark prosecution trying to convince the appellate authority about the pre-existing reputation of your trademark? Your ability to convince lies purely on how succinctly you are able to communicate to the court about your legal position. The same applies to negotiation situations. Even within your own team, things will get tough if your communication skills are poor.
Don’t undervalue the importance of legal writing
Likewise, your drafting skills and written communication also plays a crucial part in your success in the legal profession, It’s a sad irony that legal writing is an undervalued and often ignored skill in law schools. Your success in drafting cease and desist notices, takedown notices, writing and negotiating balanced contracts depend upon how well you structure your written communication.
Law firms expect you to be conversant with the procedure
See, knowing the basics of IPR law is not rocket science. The Acts are easy to understand and smaller in volume too. Students and young law graduates often feel cheated when they realize the huge gap that exists between theory and practice.
Everyone is taught the theory of trademark registration. However, it’s very important to know about the procedure for registration. Whether to file a single class application or a multiclass application for your product is not something you dwell upon in law school.
Focus on practically learning the procedures during the internships and courses you undertake. You must know about the basic useful stuff like performing prior art searches, freedom to operate searches, trademark searches. You will be able to bring awesome value by the time you start working in a law firm.
Keep abreast with the latest developments, reading is crucial
Reading the latest judgments and constantly learning on the go is crucial. Keeping yourself up to date with regulatory and policy developments around IPR, writing blogs, Keeping abreast with the latest innovation are certain basic traits that you must imbibe in your day to day working as an IP professional.
You can check out the other courses you may find relevant:
Diploma
Diploma in Entrepreneurship Administration and Business Laws
Diploma in Advanced Contract Drafting, Negotiation and Dispute Resolution
Diploma in M&A, Institutional Finance and Investment Laws (PE and VC transactions)
Diploma in Companies Act, Corporate Governance and SEBI Regulations
Executive Certificate Course
Certificate Course in Advanced Civil Litigation: Practice, Procedure and Drafting
Certificate Course in Advanced Corporate Taxation
Certificate Course in Real Estate Laws
Certificate Course in Arbitration: Strategy, Procedure and Drafting
The post Career Opportunities in IPR for Lawyers appeared first on iPleaders.
Career Opportunities in IPR for Lawyers syndicated from https://namechangersmumbai.wordpress.com/
0 notes
Text
Career Opportunities in IPR for Lawyers
This article is written by Krishnendra Joshi, Research Associate, LawSikho.
We are a PUBG crazy generation. Did you ever wonder what protection should a game developer attain, copyright or trademark to protect his intellectual property in the game? Can there be PUBG shirts and merchandise that sell in hundreds of thousands? How will the game producers benefit from the same?
What makes Apple the richest company in the world? According to research, a 32GB iPhone 7 that retails for $649 costs Apple only $219.80 in components, with manufacturing adding just $5 to the price. Have you ever wondered how does it earn the rest of the money? It’s on account of the intellectual property of course. What makes Apple Inc. the biggest brand in the world?
China is far bigger in manufacturing. India has more engineers. There are more resources in Africa. Russia has more natural gas and oil. However, U.S.A is richer, and a superpower, because it has more intellectual property than any other country.
Every time we buy a mobile phone, watch movies or search online, entities from the U.S.A earn money thanks to intellectual property.
Intellectual Property is a valuable asset class in itself.
India and the entire world is now waking up to the potential of intellectual property. And intellectual property lawyers are now very sought after.
I assume that you are reading this article because you are interested in intellectual property law as a career at some level. Let me give you a detailed picture which may help you to decide for or against, or to simply assess the opportunities.
Click Here
IPR is a recession proof career
Experts expect a global recession to hit us soon. You need to be very careful now about the career choices you make. Is IP a good career choice in the current global or country-specific economic environment?
Innovation and inventions are part of human development, and therefore intellectual property lawyers will always be needed to protect ideas and ownership of inventions. Even if some law practices are affected by the recession, such as investment law, property law or capital market, the field of intellectual property law will continue to grow.
Economies like India can grow now significantly only on the back of intellectual property development. Apart from that, enforcement of intellectual property within the country, which has become a major market, is also critical and generates a massive amount of work for lawyers.
Also, as India has been shifting from informal to the formal economy over the last decade and the trend is expected to continue over the next decade, businesses will be registering and enforcing trademark, copyright and even develop patents.
Communities have begun to wake up to the potential of geographical indications and other sui generis protections for community intellectual properties and indeed there are some amazing activities in terms of IP related legal work.
The major clients of IP lawyers
While every industry requires a lot of IP related support, there are three that run up the biggest bills. They are the biggest clients of IP lawyers. The top one is the Media and Entertainment industry. The second in the technology industry. And finally, biotechnology is also a major industry that depends a lot on IP lawyers.
Apart from these three, fashion, sports and pharma are the next three big clients of IP lawyers.
What kind of work do IP lawyers do?
Contracts Negotiation and Management
IP lawyers advice on exploiting your IPR commercially. Qualcomm collects the majority of its revenue of around 11 billion US dollars from selling licenses of its mobile processing chips. An army of lawyers have to work on not only those licensing agreements but enforcing patents, engage in patent wars with major telecom manufacturers and even on monitoring services across the world.
Law schools will teach you the difference between an assignment and license but that’s not enough. What happens when the copyright is assigned on a perpetual basis and the assignee fails to exercise his rights? Or how do you stop unlicensed players across the world from stealing your IPR? Once they are cornered by your enforcement lawyers, what kind of settlement agreements do you enter into?
Whether it be franchising a new outlet for McDonald’s or getting into a character merchandising agreement for selling merchandise and toys of your favorite Marvel movie, transferring IPR through commercial arrangements forms the basis of exploitation of IPR for value creation.
Do you know what kind of non-standardised clauses are specific in IPR agreements? How will you negotiate a limitation of liability clause? How do you determine the level of diligence required for negotiating a disclaimer clause?
The most common agreements you must learn if you are working as an IP lawyer would be assignment agreement and licensing agreement. These are like bread and butter for most IP lawyers. There are of course many other complicated IP contracts.
Non-contractual drafting
Apart from contracts, there would be a bunch of other drafting too. Lawyers have to learn how to draft even emails. Ask the lawyers who screwed up by writing a mail in the wrong language.
Issuing cease and desist notices, takedown notices are pre-litigation enforcement mechanisms which IPR lawyers must know. They may also have to draft litigation documentation as well as applications for registration of IPR that must be done very carefully.
I hope you are realizing the gap between theory and practice coupled with the huge learning and training opportunity available to law grads and young IP professionals alike.
Registration of IPR
The market for IP registration has become extremely competitive making profit margins thinner. Only patent registration can still be considered premium work. Registration of copyright or trademark is not so profitable anymore.
There are online service providers charging from Rs. 2000 – Rs. 5000 for a single class trademark registration application excluding regulatory fees. However, there can be more money making opportunities in objections, oppositions and other procedures when these applications run into trouble, often because they were drafted by less competent people.
While registration of IP has become a volume game with very low margin, licensing, assignments, objections, oppositions, litigation and related work have massively increased in volume over the years too, turning IP law into an ever more lucrative profession.
That’s the deep end of the pool, however, and highly skilled lawyers who can deliver results tend to do better in IP law.
Brand management
You all get fascinated by the JK Rowling rags to riches story. Harry Potter is a great success story of a brand built around a character and a story later made into movies. IPR attorneys play an important role in creating strategies to bring your brand to the marketplace and figure out new ways to generate revenues from the brand. They also help to put in place agreements and commercial arrangements and enforce IPR so that a brand’s value is not diluted.
For example, an Indian counterpart Hari Puttar which tried to encash on the Harry Potter brand was quickly shut down by lawyers who were responsible for protecting the brand value of the Harry Potter franchise.
Brand management also involves anti-counterfeiting strategies. Lawyers convert legal concepts into enforceable rights and commercially valuable assets.
Portfolio management
Xerox is much more than a photocopier company. It had a huge portfolio of around 8000 patents to its credit but it often failed to take action against infringement by competitors. Big corporations tend to have massive intellectual property asset bases which require professional management which usually lawyer tend to offer. This includes global infringement monitoring services and identifying monetization opportunities.
GE is a company which also has a massive portfolio of exciting patents, but it is very serious about protecting and monetizing them. This has been attracting value investors towards GE stocks as they expect the amazing IP portfolio to give amazing results in near future.
Intellectual property lawyers look after legal-commercial strategies enabling planning regarding portfolio creation and management, licensing the technology
Enforcement of IP
Enforcement of agreements and IP rights through strategic litigation is the most lucrative practice for IP lawyers. It is also the area where more new and best-paid jobs are arising in the industry.
Work can range from coming up with strategies to bring an action against breach of confidential information, holding infringing parties to account, taking credible action against breach of trade secrets, defending claims of IP infringement, preventing misuse of IP rights by vendors, distributors are others who may get access to valuable IP etc.
Lawyers help in creating risk mitigation strategies
In the pharma sector, Johnson & Johnson recently not only called back its disputed batch of drugs but also redesigned its policies as well as the vision to ensure the highest form of integrity and quality. What role do you think lawyers played in this?
A team of IPR lawyers works with the top management to develop powerful strategies in such cases where the company is dealing with regulatory breaches or posing a threat to the company’s brand image. They have to come up with risk mitigation strategies to deal with the immediate situation as well as come up with prevention strategies for the future of the organization.
Fortune 500 companies are risk-averse in nature. Even if you ignore the expenses and time involved in litigation, there is negative publicity attached with opting for litigation. IPR lawyers advise on preparing pre-litigation and settlement strategies as well as aggressive litigation strategies where required.
Are you a lawyer with any science degree?
Well, you can work your way to becoming a patent agent after clearing the patent agent exam. Any science graduate can become a patent agent by clearing the exam, and one does not need a law degree for the same. However, for obvious reasons, lawyers have a significant advantage in building a patent law practice as they do not only do filing but can help with a much wider range of services.
Did you hear that Apple has filed a new patent application with USPTO last month on the concept of a foldable iPhone?
Well as a patent attorney, drafting and filing patent applications for inventors and scientists is your mojo. Managing and advising on patent portfolio also forms a key advisory area for patent attorneys.
Depending on your experience and expertise you might have to work with an international clientele for filing and prosecution in foreign offices.
However, as a lawyer, you are likely to go much beyond drafting and filing patent applications and work on patent litigations and prosecution cases.
Where should you work as an IP lawyer?
Law firms
The best IPR Law firms are mostly boutique law firms. They can have smaller teams in comparison with say a corporate transactions team of a tier 1 law firm. Big law firms also have IPR teams, but they are usually small and often gets paid far less than the corporate lawyers in the firm.
Companies
Most companies require IP lawyers, if not specialized ones then at least general in-house lawyers who also have to do IP work. In sectors like media and entertainment, technology, pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, sports and broadcasting, movies, music, publishing etc. IP lawyers are in great demand and these companies often require large IP law teams.
IPR thinktanks
There are large IPR, technology, competition law and internet related thinktanks that need to hire IPR lawyers in large number for research and policy-related work.
Litigators
IP litigation is steadily on the rise, especially when it comes to trademark-related disputes. Patents and copyright prosecutions and disputes are also on the rise. It is the best time in history to be IPR litigator, also because most IP lawyers are concentrated on other kinds of work.
IP Monitoring services
In recent times IP rights monitoring services have become very prominent and profitable. Large MNCs and IP owners appoint monitoring agencies all over the world whose job is to keep a check on who is misusing such intellectual property and taking legal action to recover any illegal profits and prevent further misuse of copyright, trademark or patent. They prevent counterfeit products, catch illegal copies, detect misuse of copyright and then take legal action as per pre-approved mandates. A large number of lawyers can get employment in such IP monitoring service providers.
How to approach IP law as a career if you are interested
You will see two kinds of aspiring IP lawyers in the job market. One breed of IP aspirants will be extremely focused about IPR. they will start building their CV around IPR during their law school itself. You will either find a lot of IP focused internships. Their experience will range from a trademark team of a law firm to the legal department of an FMCG company.
They would probably have industry-focused certifications, workshops, and conferences on their resume. Writing a few research papers and online legal blogs is appreciated when you sit for the interview. Basically, there are lawyers who have been interested in IPR for a while and can demonstrate the same based on the history of their activities which are worthy of being mentioned on one’s resume.
There is another class of IP lawyers who choose IP as their last resort. You may or may not find a couple of IP internships during their law schools in their CV, but they claim to be very interested in IP when they apply for IP jobs. This is very problematic. If you say you are interested in IP, there better be enough in your CV that proves the same.
The best way to do so is to write and publish at least a dozen high-quality articles on IP law and publish them on credible internet platforms where IP lawyers are likely to read them.
Also, start attending events related to IP lawyers and take up practical IP law-oriented courses which can speed up your growth and understanding of IP law work.
The placement scenario is changing for the Good
The salary you might command while starting out is subjective.
The reputation of your college matters but law firms have become a lot flexible in terms of hiring and retaining talent. Even our students from KIIT law school have bagged placements with tier 1 IPR firms through smart planning and focused internships during law schools.
Law firms like Wadia & co. have a system wherein they offer assessment internships for 3 months. You work and report under a senior associate or the partner during the period of internship. Your chances of bagging the job are based on your performance.
Tier 1 IP law firms may offer starting salaries around 50-70 k per month while smaller law firms may offer anything between 20k-50k per month. Law firms will pay better if you have previous IP litigation experience because that is the most in-demand skill right now.
Your focus must be on acquiring the right skills rather than the salary numbers in your formative years. The potential to earn astronomical sums is very much present provided you can deliver results to clients.
There is a lot of churning in terms of IP recruitment
There is a lot of turnover in the IPR job market. Bright law students join a law firm and switch in 1 to 1.5 years to another firm or another area of practice.
Law firms are aware of the churning going on in the market. Therefore, they offer attractive performance-based appraisals in the range of 25-30% after 1 year onwards.
Rewards lie ahead if you are willing to give your career the time it deserves
The first 4 years in the niche IPR practice area is extremely critical for anyone wanting to become an indispensable part of his law firm team but also the IPR industry. You progress to become a senior associate, work closely with law firm partners. You will also have enough opportunities to strike out on your own and establish your own practice. The prospects of making a name for yourself in the industry are quick as it is a close-knit community, provided you can deliver high quality work consistently.
Top sought after skills
Pay special attention to communication skills
Your communication skills play a key role especially in a field like IPR. What if you are seeking an injunction in a trademark prosecution trying to convince the appellate authority about the pre-existing reputation of your trademark? Your ability to convince lies purely on how succinctly you are able to communicate to the court about your legal position. The same applies to negotiation situations. Even within your own team, things will get tough if your communication skills are poor.
Don’t undervalue the importance of legal writing
Likewise, your drafting skills and written communication also plays a crucial part in your success in the legal profession, It’s a sad irony that legal writing is an undervalued and often ignored skill in law schools. Your success in drafting cease and desist notices, takedown notices, writing and negotiating balanced contracts depend upon how well you structure your written communication.
Law firms expect you to be conversant with the procedure
See, knowing the basics of IPR law is not rocket science. The Acts are easy to understand and smaller in volume too. Students and young law graduates often feel cheated when they realize the huge gap that exists between theory and practice.
Everyone is taught the theory of trademark registration. However, it’s very important to know about the procedure for registration. Whether to file a single class application or a multiclass application for your product is not something you dwell upon in law school.
Focus on practically learning the procedures during the internships and courses you undertake. You must know about the basic useful stuff like performing prior art searches, freedom to operate searches, trademark searches. You will be able to bring awesome value by the time you start working in a law firm.
Keep abreast with the latest developments, reading is crucial
Reading the latest judgments and constantly learning on the go is crucial. Keeping yourself up to date with regulatory and policy developments around IPR, writing blogs, Keeping abreast with the latest innovation are certain basic traits that you must imbibe in your day to day working as an IP professional.
You can check out the other courses you may find relevant:
Diploma
Diploma in Entrepreneurship Administration and Business Laws
Diploma in Advanced Contract Drafting, Negotiation and Dispute Resolution
Diploma in M&A, Institutional Finance and Investment Laws (PE and VC transactions)
Diploma in Companies Act, Corporate Governance and SEBI Regulations
Executive Certificate Course
Certificate Course in Advanced Civil Litigation: Practice, Procedure and Drafting
Certificate Course in Advanced Corporate Taxation
Certificate Course in Real Estate Laws
Certificate Course in Arbitration: Strategy, Procedure and Drafting
The post Career Opportunities in IPR for Lawyers appeared first on iPleaders.
Career Opportunities in IPR for Lawyers published first on https://namechangers.tumblr.com/
0 notes
Text
Founders Equity Agreement Template India Online
If you do make a decision to acquire a co-founder on board indicator a contract to protect each party. Be certain you sign up to stay existing on the growth of the platform as well so you can utilize it once it will end up being available.Since running a firm is a long-term commitment, it's necessary to do adequate study and location in time to pick the kind of service. If you do choose to acquire a co-founder aboard indication an arrangement to safeguard each party. It is suggested to enter right into this kind of arrangement throughout the consolidation stage of the business. Whenever your app is wrapped up, it's time roll it out to the remainder of your organization.
In the occasion the agreement a part of the employee handbook or various other staff member standards, you should work with a legal representative to make specific it will certainly nevertheless be lawfully binding if the signature is on a different employment agreement file. A particular note if you're a founder of a start-up. While it's the case that equity has ended up being the most recommended settlement device in early-stage firms and therefore, it's undoubtedly needed for bring in skill as well as receiving future founders, furthermore it is just reasonable to ask for what one is entitled to. Truly believe concerning what IP the firm might have to market.Some allot even more equity to whoever established the idea.The War Versus Co Founder IP Assignement Ageement IndiaOwners face a wide range of decisions in managing their startups.

Some Updated Guidelines For Level-headed Products For Co Founders Agreement
Much like any kind of other contract, a couple of normal clauses have to be consisted of in the influencer promoting contract too. Make sure that it's extensive yet also basic to comprehend. With simply a trademark and also a checkbox on the FAST contract, entrepreneurs as well as consultants are currently able to concur in minutes on just how finest to function with each other, on what points to accomplish, and on the right quantity of equity damages. Your influencer promoting agreement needs to mention in which you want the material to be released.
The founder might choose to go with a different investor, or the owner may spend time working on modeling as well as reviewing the interest when they might have boosted the well worth of the company via various other quests! Frequently startup organisations have actually limited money resources and also would certainly such as to pay workers with equity or various other motivations rather of cash money.Starting a start-up is also challenging for a single individual. On top of that, if you're only simply beginning to coach other firms, focus on just a couple of to be specific that you offering each the overall quantity of time they need.Based on our co founder ip assignement ageement india very own experiences, and also so as to assist owners focus on the basics, we've dealt with to compile a list of important matters to take right into account when thinking about increasing your start-up into the united states. The main factor is they are like creators or they've been working as creators so that you need to make sure you maintain them throughout the life expectancy of your startup.
0 notes
Text
CCI’s Decision on Abuse of Dominant Position by Google
[Pallavi Panigrahi is a graduate of National Law School of India University, Bangalore and is currently working at a Corporate Law Firm in Mumbai.
Another post on the topic is available here]
The Competition Commission of India (“CCI”) last month imposed a fine of INR 135.86 crores on search engine giant Google (inclusive of Google LLC, Google India Private Limited and Google Ireland Limited) for abuse of dominant position under section 4 of the Competition Act, 2002 (“the Act”).
Facts
Information against Google was provided by Matrimony.Com Limited and Consumer Unity and Trust Society (CUTS) in two separate instances which were clubbed together as the allegations made were similar, viz, abuse of dominant position by Google in the markets for “online search” and “online search advertising” reflected in terms of search bias, manipulation of results, promotion of Google’s own vertical search sites by blending of its verticals’ results in the organic search results, etc.
Director General’s Investigation
Based on the information provided by the informants and the entire material on record, the CCI directed the Director General (“DG”) to investigate the allegations made against Google.
The DG, upon perusal of relevant information, determined that the primary service in question offered by Google was in the nature of “Online General Web Search Services” and that there could be no substitution between a general search service and a vertical search service or site-specific search service. Similarly, “Online Search Advertising” was significantly different from display advertising, social media advertising, e-mail based or mobile based advertising, etc., as it is linked to user-initiated queries that reflect the specific interests of the user in that instance relating to the subject matter of the query and thereby creates a very effective way of targeting potential consumers. The DG also found that “Online General Web Search Services” and “Online Search Advertising” were not substitutable but rather complementary and hence did not form the same relevant product market. Hence, the relevant markets determined by the DG were – “Market for Online General Web Search Services in India” and “Market for Online Search Advertising in India”.
After establishing the relevant market with the above-mentioned rationale, the DG went on to find that Google consistently maintained a high market share in the relevant markets from 2009 – 2013. Moreover, given that there were significant entry barriers owing to high cost, technology, requirements of scale, etc, Google enjoyed significant power owing to its resources, financial power and commercial advantages. The outcome of the aforementioned factors was that Google’s position of strength enabled it to function independent of competitive forces in the market, thereby rendering it a dominant player.
The DG went on to find that not only did Google enjoy a dominant position in the market, there was substantial cause to hold that there was abuse of the same, based on the following conduct:
– First, Google blended its vertical search services into the general search results in a manner that was not applicable to non-Google vertical search services such that its own specialised search services ranked higher than other vertical search services in the Search Engine Results Page (“SERP”). This affected users as they were not necessarily directed to the most relevant results for their queries. It also hampered competition in ancillary markets that lost out on significant audience. Taken together, this was found to be a violation of section 4 of the Act.
– Secondly, in spite of the presence of required technology, Google did not disclose quality scores to advertisers, even for historical data, and thereby rendered the entire process for placement of advertisements opaque and vulnerable to discriminatory practices thereby falling foul of section 4 of the Act.
– Thirdly, Google was not required to pay any consideration for its in-house ads, thereby giving it a substantial advantage over its competitors. Additionally, Google had access to scores of its competitors and therefore the ability to score its advertisements higher. Checks placed by Google to prevent the same were deemed ineffective and the same was considered to be an abuse of dominant position under section 4 of the Act.
– It was also found that Google placed unfair conditions upon trademark owners by allowing such trademarks to be bid on as keywords by competitors. This is because, as mentioned earlier, results that occupied higher positions on SERP were the ones for which higher bids were placed by concerned entities rather than the ones that were most relevant. This led to situations of use of trademarks of trademark owners by other entities due to higher bidding for such keywords.
– The DG also found that Google was using its dominant position in the relevant market to impose certain restrictive conditions in its agreements for advertising services ranging from prohibiting partners from using services of competitors to placing restrictions on the positioning of ads of competitors. These restrictions were instrumental in preventing competing service providers from achieving the required scale of functioning thereby preventing them from breaking through entry barriers in the market.
CCI’s Analysis
The CCI agreed with the determination of the relevant product market with the relevant geographical market being delineated as India, as the conditions for supply of “Online General Web Search Services” and “Online Advertising Search Services” in India were different from those in other locations, and the dominant position enjoyed by Google in the relevant product market was in India. It also agreed with the determination that Google does indeed occupy a dominant position in the above mentioned relevant markets.
Google’s Online Search Services are Free?
Before going into the details of abuse of dominance found by the DG, the CCI addressed a primary objection raised by Google – that for the application of section 4 of the Act, there had to be a sale of goods or services, but the online search services provided by Google were free and hence would not attract the provisions of section 4 at all.
The CCI categorically disagreed with this contention made by Google. It held that users provided indirect consideration to Google by contributing to the collection of “Big Data” every time they availed of its search services which enabled Google to attract advertisers. Moreover, each time users clicked on advertised links provided by Google, ad-based revenue was generated for the Company.
Hence, the services provided by Google were certainly not free and could attract investigation under section 4 of the Act.
Abuse of Dominant Position
The CCI found that, until 2010, Google followed a mechanism whereby universal search results were assigned pre-determined fixed positions and were not reflective of the most relevant results for the user’s queries. Thus, the CCI agreed with the DG to the extent that this practice of Google till 2010 was indeed a violation of its dominant position.
Moreover, with respect to leveraging of Google’s vertical search services, the CCI agreed with the DG to the extent that the display of Google’s commercial flight units at the top of search results relating to flights also was an instance of search bias as clicking on these prominently placed links directed users to Google’s own vertical sites and not to third party vertical sites.
The CCI also found that Google’s conduct with respect to the terms in the agreements for its negotiated intermediary search services that enabled publishers to display a Google search option for users on their pages demanded exclusivity as these agreements contained terms that prevented publishers from displaying search options from competing search engines. This was held to be violative of section 4 of the Act.
The CCI, however, did not find any abuse of dominant position by Google with respect to the imposition of unfair terms and conditions on advertisers, the use of unfair mechanism in bidding for keywords for the advertisers in the context of trademarks held by such advertisers and the imposition of unfair terms with relation to multihoming (use of advertising campaigns across different platforms) and interoperability of data across platforms.
Based on the above findings, the CCI went on to impose a fine of INR 135.86 Crores (that is, 5% of the average total revenue generated by Google in India across business segments from 2013-2015). It also directed that Google clarify that the commercial flight units displayed prominently in the search results for flights only lead to Google’s flight pages and not that of its competitors. Additionally, Google was directed to remove the clauses leading to exclusivity in its agreements for negotiated search intermediate services.
Analysis
In recent times, Google has been in the dock for violation of anti-trust regulations across the world with regulators coming down hard on the search giant for the manner in which it deals with its search functions. Not long ago, the European Union imposed a record fine of $2.7 billion on Google for anti-competitive behaviour. The finding in that case was a familiar one – Google privileged its vertical search services relating to online shopping in search results at the cost of competitors.
To that end, the finding of the CCI is in line with the global trend. However, it must be noted that the CCI’s finding of anti-trust behaviour on part of Google is a limited one, as the CCI has found in favour of Google on almost all counts barring three tightly circumscribed ones. Moreover, the fine imposed on Google is almost insignificant when compared to the mammoth amount of revenue that the search engine giant generates in India. The directions of the CCI with respect to unfair display of Google’s commercial flight units and unfair terms in its agreements for negotiated search intermediate services come across as mere lip service and do not seem likely to even count as a slap on the wrist for a corporation with the kind of resources and dominance Google has.
With the push for increased digitization in India, this case could have been a seminal one given the extremely dynamic character of Google that simultaneously acts as a provider of services to users and market place for advertisers. With more and more day to day transactions shifting to the digital space, CCI is likely to see numerous such cases in the future. However, whether the CCI’s stance in the instant case becomes something to go by or not remains to be seen.
– Pallavi Panigrahi
The post CCI’s Decision on Abuse of Dominant Position by Google appeared first on IndiaCorpLaw.
CCI’s Decision on Abuse of Dominant Position by Google published first on https://divorcelawyermumbai.tumblr.com/
0 notes