#Marine/Freshwater
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Note
hi! do you have any fish pngs? I love your work! it's so high quality!!
thank you so much! I love fish so this was fun to make!
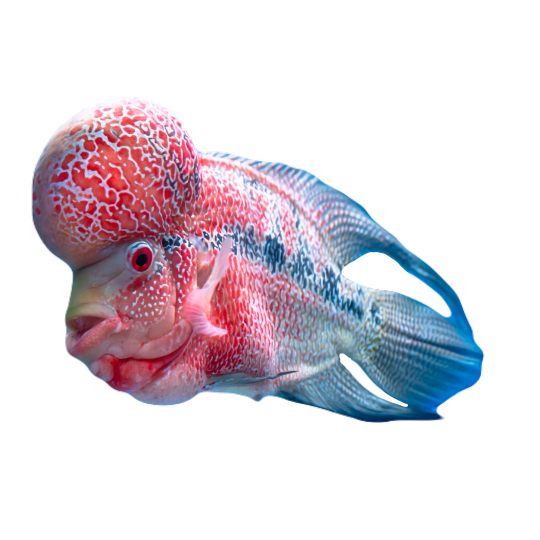
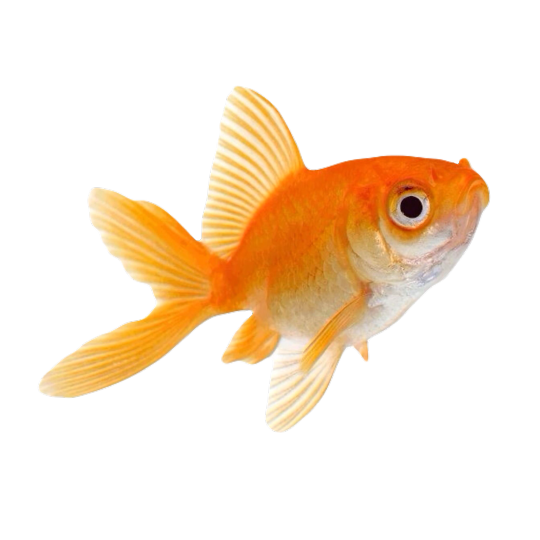
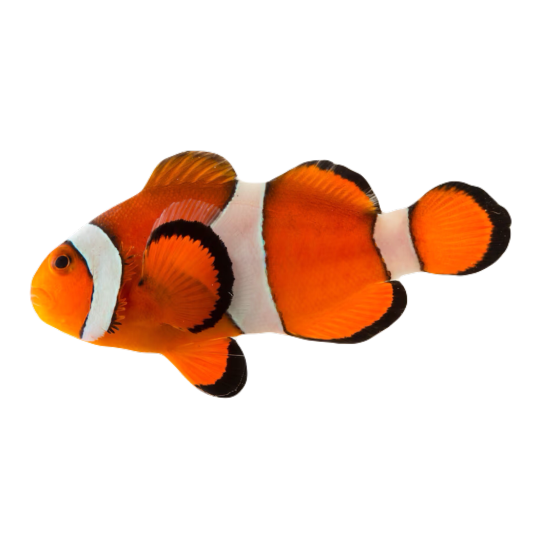
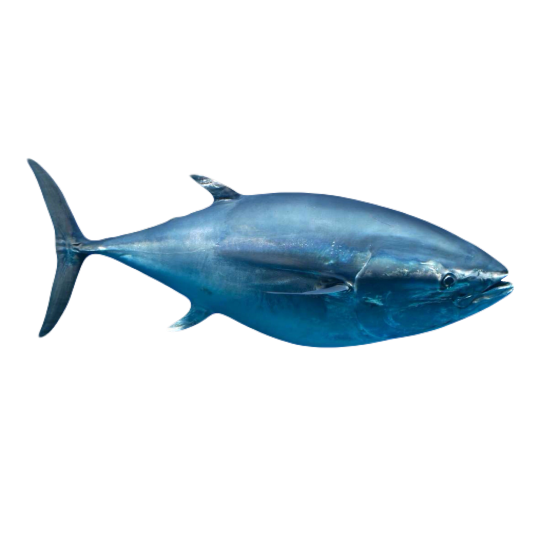
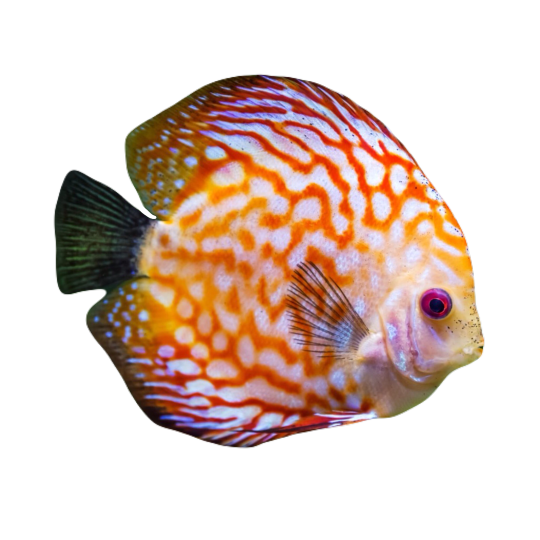
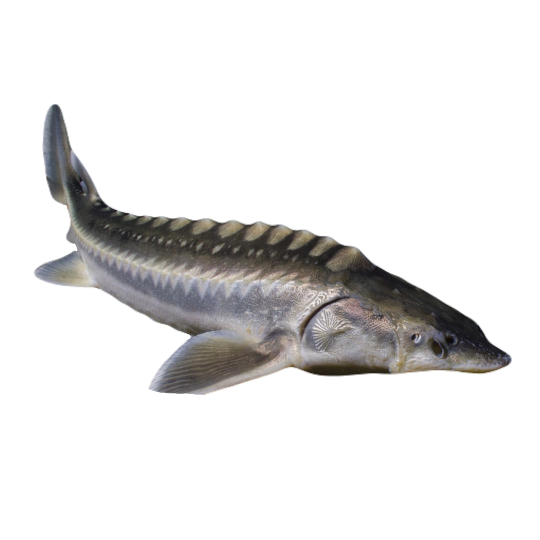
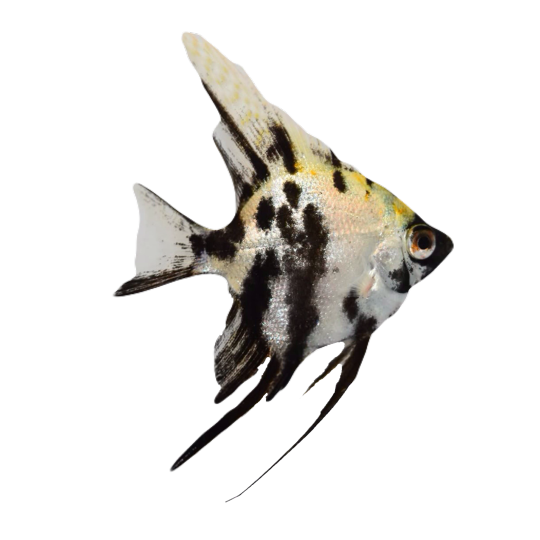
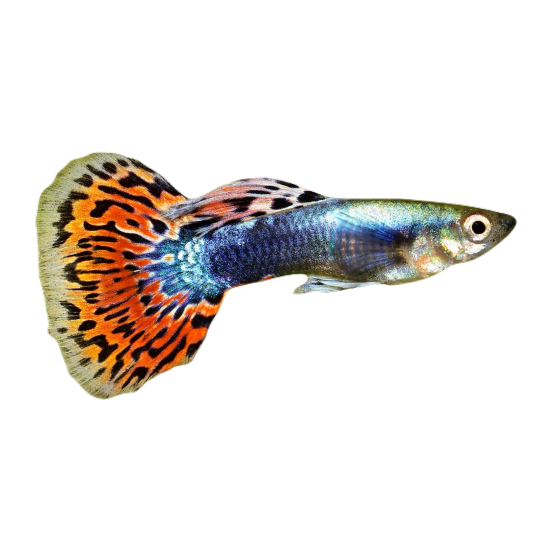
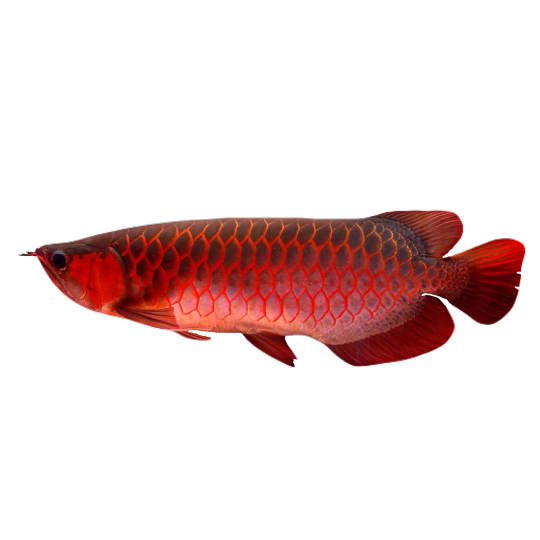
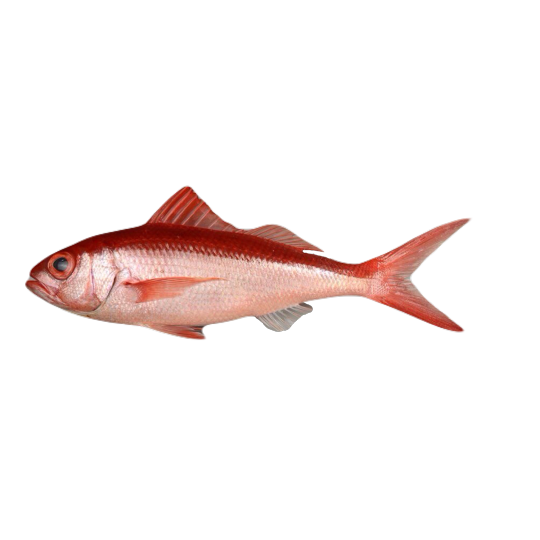
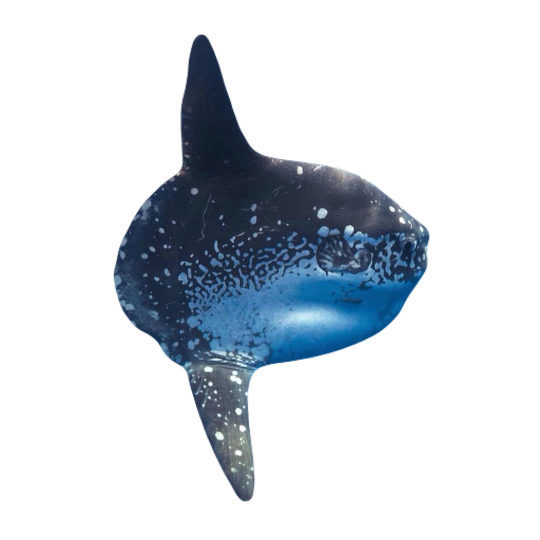
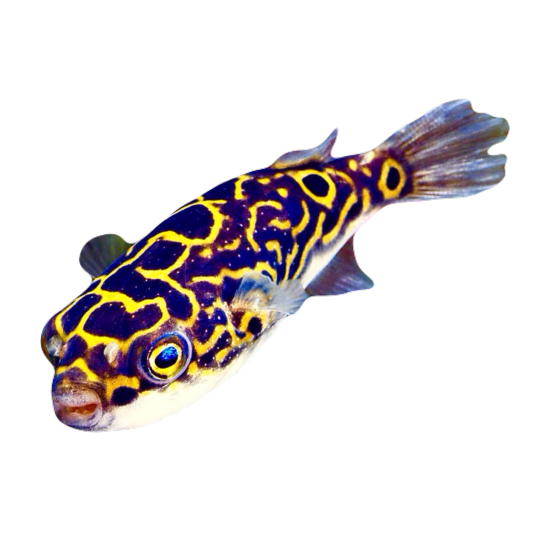
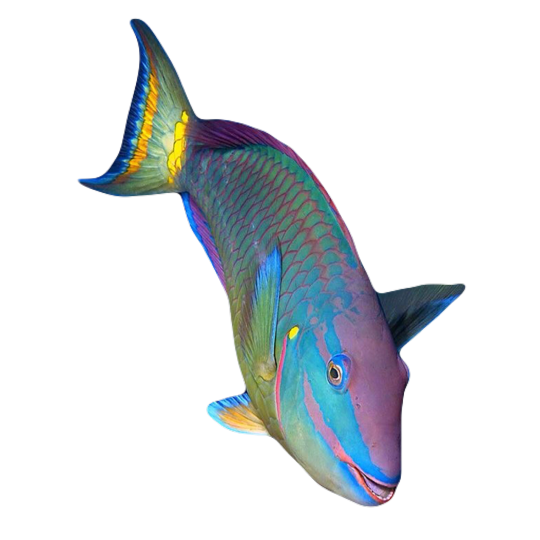
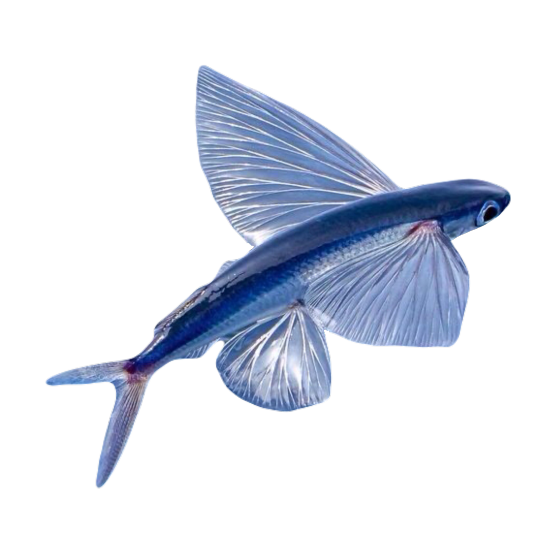
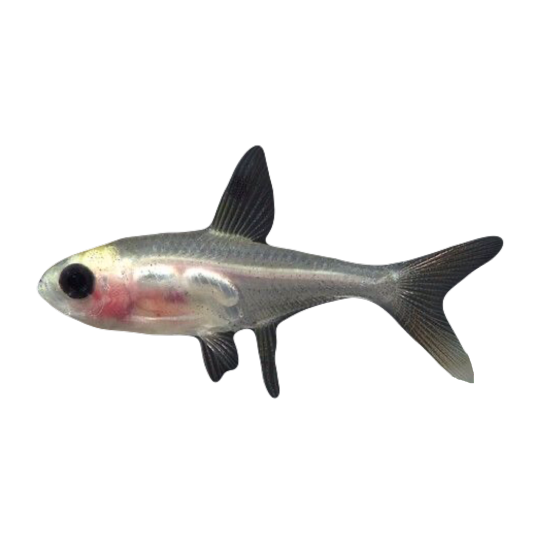






















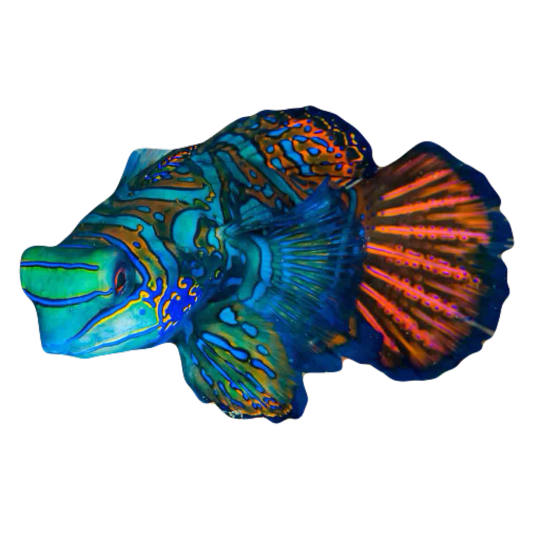







#requested#png#transparent#random pngs#fish#marine biology#animals#underwater#fishblr#nature#naturecore#curators on tumblr#sea#ocean#sea critters#sea creatures#aquarium#aquatic#aquatics#freshwater#river
4K notes
·
View notes
Text

Drawing rainbow trout in my diary <3
9K notes
·
View notes
Text

Front facing pike Tuesday
#pike#musky#fish#my photo#marine biology#not marine animal#zoology#fishblr#front facing#fishes#animals#aquarium#freshwater fish
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Close encounters!
My beautiful koi betta Bisby has had a jumping spider neighbor taking advantage of her tank light to hunt bugs under for some time, and recently they met face to face! Very happy to capture each of them acknowledging the other - and Bisby's quick look back at me as if to say "you're seeing this too right?!" 🧡
Edit ✨️ For all those concerned, yes, she does have a lid! I'd just cleaned and was hanging out right there where I filmed from at my office desk. If you are new to fish keeping, please invest in a good lid or when picking setups, favor tank kits that include one!
#bettablr#betta fish#aquaria#freshwater aquarium#marine bio#marine biology studyblr#marine bio studyblr#biology#jumping spider#fish keeping#aquarist#betta#marine biology
9K notes
·
View notes
Text

My fish, The Gooch. She’s an elephant Nosed fish, Marcusenius schilthuisiae. She is scared of metal tongs and objects because elephant fish produce electrical pulses, kind of like a sixth sense, and the way it bounces off the metal is very noticeable to them


Her irl
#aquariumblr#freshwater aquarium#aquariums#aquablr#elephant nosed fish#my art#artists on tumblr#marine biology#icthyology#fish#fishblr
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Fish of the Day
Today's fish of the day is the necklace carpetshark!

The necklace carpetshark, also known by the name varied carpetshark, and scientific name Parascyllium variolatum, is one of the best known carpet sharks in the genus Parascyllium. The scientific name draws from the latin word for spotted, referring to the white spots surrounding the body. Other than the Latin scientific name, this shark is known by many English names other than the two previously listed. In Australia, it is often referred to as: ring-neck catshark, or southern catshark. Despite sharing many features with catsharks, or ground sharks as they are sometimes referred, the Parascyllium genus nor the Parascylliidae family it resides in is considered catsharks, and this is why these names are often not used in classification.

Regardless of the naming structure, let's get into the location of this fish! Found around the coasts of Australia from 37 degrees South to 41 degrees South, around inshore waters. These sharks are known for their demersal lifestyle, living along the seabed. Living at a depth of 180 meters or higher the necklace carpetshark spends its nights over rocky coral reefs, kelp or seagrass beds, or sandy floors. During the day however, this shark shelters primarily in caves, although it can be found in camouflage along the seabed on rare occasions. This has led to these sharks being rarely seen by those not actively looking for them.

Necklace carpet sharks, like many of their relatives, possess a slender elongated body. With a maximum length of 91cm with most adults ranging 60cm-91, these sharks can be differentiated from their family members by the broad black markings that cover the gills, small spiracles, and smaller mouth than most. Their mouths possess 28 teeth along the top jaw, and 32 teeth along the lower. Their prey is primarily made up of shellfish along the seabed, which is caught as these sharks lunge at them from behind. These sharks are little predated on in adulthood, but on the rare occurrences, it is done by larger fish, sharks, or marine mammals in the area. Although, other than this eggs cases are often fed on by certain seasnails.

The reproduction of the necklace carpetshark is similar to that of its family. As an oviparous shark, eggs are laid outside of the mother, where they are then left to fend for their own to hatch, and then throughout its youth. Inside the mother, embryos feed on the yolk of its egg sack. Outside the mother, 2-3 eggs will be laid at a time with eggs being covered in 2-3 tendrils, which will anchor them to the sea bed, often during the summer months. After being laid, eggs will hatch within 12-39 days, with many of the juveniles being predated on per season. Eventually, once these sharks have gotten larger than 60cm, they are considered adults and develop sex characteristics, eventually going on to breed and lay their own offspring. Currently there are no known threats to the necklace carpet shark populations.

That's the necklace carpetshark! I hope everyone had a wonderful time reading about them!
#fish#fish of the day#fishblr#fishposting#aquatic biology#marine biology#freshwater#freshwater fish#animal facts#animal#animals#fishes#informative#education#aquatic#aquatic life#nature#river#ocean#Parascyllium variolatum#shark#carpet shark#carpetshark#sharks#necklace carpet shark#varied carpet shark#cat shark
592 notes
·
View notes
Text

sneak peek of some new charms hitting the shop this weekend! unsure about the date yet but I’ll keep you all posted <3
3 cherry shrimp + one sexy shrimp, all super tiny and perfect for multitasking as a zipper pull 🦐
450 notes
·
View notes
Text
Fun facts.
Jellyfish are the oldest animals with organs
Thre are some freshwater jellyfish
Some Upside Down jellyfish sleep, being the first discovered case of of animals without a central nervous system to do so
A species of Upside Down Jellyfish, the Cassiopea Xamachena, releases jelly with cells for moving and cells for stinging, around it. That's why swimmners feel stung just from getting close
Some Box Jellyfish have excellent sight, for obstacle avoidance and hunting
Jellyfish can be considered top predators. When ecosystems get disrupted, they can take over, and by then it's rather difficult to restore the original state
Human damage to ecosystems and climate has in fact led to an increase in jellyfish blooms, impacting multiple industries
126 notes
·
View notes
Text
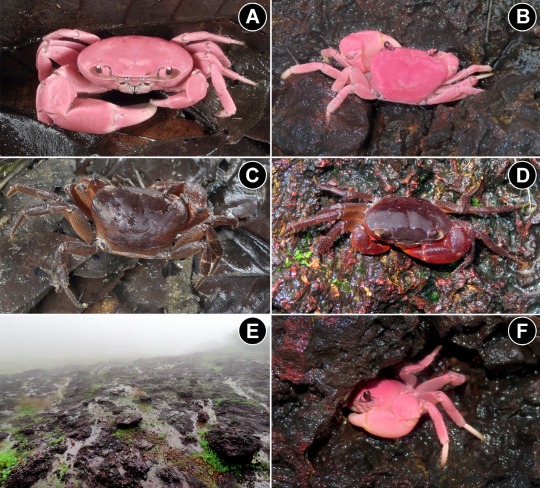

I think tumblr would be into the bright pink freshwater crab that was just discovered
#ghat crab#freshwater crab#new species#crab#crabs#Ghatiana dvirupa#biology#marine biology#not really its#freshwater biology#arthropod#beasts
472 notes
·
View notes
Text

Brook Lamprey
Bachneunauge
(Foto: B. Stemmer)
114 notes
·
View notes
Text

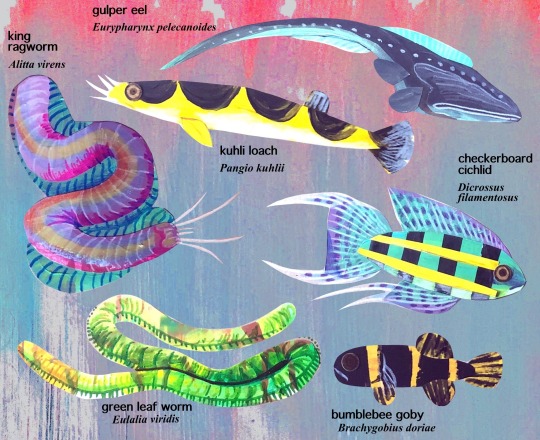
aquatic animal illustrations for friends
#art#artists on tumblr#mixed media#collage#acrylic painting#colored pencil#traditional art#fish#fishblr#fish art#polychaete#marine biology#freshwater fish#marine fish#marine invertebrates#wormart
963 notes
·
View notes
Text

Four culturally significant aquatic birds in Imperial Wardin- the skimmer gull, the albatross, the reed duck, and the hespaean.
The skimmer gull is a small seabird, distinguished by bright red beaks and a single, trailing tail plume. These are sacred and beloved animals with a long history of symbiosis with local fishers. They will intentionally attract the attention of fishermen, bringing them to shoals of fish that are too deep below the surface for the birds to reach. They then will snatch fish fleeing or caught in the nets, and will often be directly fed by their human assistants in an act of gratitude. They benefit tremendously from their sacred status and a taboo against killing or harming them, and can become absolute food-stealing menaces in seaside towns and cities.
The albatross is a seasonal visitor to the region, with this population migrating to small rocky islands in the White Sea to breed. The specific species occurring in this region is on the smaller side, and has a pale pink beak and soft orange legs. Albatrosses are common characters in regional animal folktales (usually as foolish, romantic types), and sometimes appear in tales as shapeshifters, usually turning into young women who have tumultuous affairs with lonely sailors.
Skimmer gulls and albatross are the most sacred animals of Pelennaumache, the face of God which looks upon the ocean, the winds, storms, maritime trade, fisheries, and broader concepts of luck and the infliction and deflection of curses. Killing either of these birds is considered to bring about disastrous bad luck (unless in the context of a proper sacrifice, most commonly in rites to bless ships and/or sailors with good winds and against ill fortune). The eggs of skimmer-gulls are free game and considered delicacies, while the preciousness of the albatross' single egg clutch is recognized and their consumption is generally discouraged (this isn't to say it doesn't happen).
Feathers of rightly sacrificed albatross and skimmer gulls are minor holy relics (ESPECIALLY gull tail plumes), and considered to be the ultimate good luck charm. The fortuitous find of a shed feather can also impart good luck and can be very valuable (the birds are sometimes poached for their feathers, though fears of the consequences are enough that this poaching is limited in scope). You will often see wealthier people wearing the feathers in hats and headdress, and any seafaring vessel worth its salt should have at least one aboard.
Both birds are evoked in the apotropaic Skimmer-Woman motif (in practice it generally has albatross characteristics, though is sometimes depicted with the tail plume of the gull).
The hespaean is a very unusual bird with two distinct species native to the region, one found exclusively in the western Black river system and its estuaries, and one found in the eastern Brilla and Kannethod river systems. They have very small pointed teeth in their bills, a trait virtually unknown outside of the flightless, beakless classes of birds (most prominently qilik). Their wings are vestigial and virtually nonexistent (with only two bony spurs remaining). These birds are almost exclusively aquatic and do not normally emerge onto land (they cannot walk upright at all, and must push themselves on their bellies). The legs of the Black river hespean develop blue pigmentation from their diet (the brighter the blue, the better fed and healthier the bird), which are waved above the surface during elaborate courtship displays. Both species are known for their haunting, warbling cries (very much like a loon, but more of a howling noise that develops into a shrill warble).
Hespaean build their nests in dense beds of reeds or small, vegetation-heavy river islands that provide some protection from predators. They raise their young during the height of the dry season (when more nesting surfaces are available and they can feed their young with more concentrated fish populations), which is an image of hope and resiliency during harsh dry times and the promise of the river's eventual bounty.
It is known that hespaean used to be caught as chicks and raised to help people catch fish (with ropes around their necks to prevent them from swallowing their catch). This practice is now very rare in the Imperial Wardi cultural sphere (mostly still practiced by the Wogan people along the Kannethod river, to whom these birds are also venerated animals) and has been largely replaced with the import of domesticated cormorants from the Lowlands to the southeast (which are more easily trained and can Usually be trusted not to attempt to swallow their catch).
These birds require large rivers that flow year round and have healthy, dense fish stocks. The population is in decline and they are now relatively rare, largely due to development and overfishing around rivers (and on a much larger timescale, the region becoming drier and water levels more irregular, and their competition with more versatile freshwater tiviit).
The reed duck is a migratory freshwater duck whose coming heralds the beginning of spring growth. They come to mate along rivers and wetlands during the early stages of the wet season, timing their eggs to hatch with the rise in water levels and growth of the vegetation and insects they feed on. They have striking red-brown and gray plumage and very little sexual dimorphism (though the male is somewhat brighter in color and the flesh around the bill turns bright red during the breeding season).
Reed ducks are not domesticated, but some populations are semi-tamed and encouraged to return to certain sites to breed (the riverside temple to Anaemache in Ephennos attracts a massive flock of the ducks every year, continually blessing it with their presence and coating its grounds in droppings), and these stocks are the primary source of sacrificial ducks and coveted shed feathers.
Hespaean and reed ducks are the most sacred animals of Anaemache, the Face of God which looks upon freshwater (particularly rivers), rains, seasonal flooding, fertile earth/seasonal fertility, and wild plant life.
The hespaean is representative of Anaemache as the River Itself and the river as a provider of fish. This association comes down to their all-seasons presence in the rivers, and their population density being a signal of a healthy, well-flowing river with good fish stocks. Lands adjacent to hespaean territory is often the most reliable and bountiful for human subsistence.
The reed duck in particular is the most venerated sacred animal of Anaemache, as representatives of Anaemache as a Face of seasonal fertility. Its coming announces the rains that the region's agriculture relies on, and their cycle of fertility closely matches the cycles of the rivers and that of the earth itself (with their new life emerging with rains, flooding, and new vegetation). There is no prohibition on hunting reed ducks (though proper rites and respect are expected for a sacred animal), and their meat and eggs is said to support female fertility and a healthy pregnancy.
#Hespaean are what I've been repeatedly misspelling as hespiornis up until now (got kind of lazy with the 'hespaean' name but the -an root#is established and makes sense). They're derived hesperornithes that have survived up to the present day but near exclusively as#smaller freshwater birds (their larger marine counterparts have been mostly displaced by tiviit and uhrwal)#Hespaean species exist outside of this region and have a worldwide (but highly fragmented and isolated) distribution#creatures
213 notes
·
View notes
Text

Brown trout, experimenting with just using colours right out the pot rather than mixing
#my art#sketchbook#for part of my dissertation im fully finishing a fresh sketchbook and its like pushing a boulder up a hill atm#need to experiment more#marine life#marine biology#sea creatures#fishblr#fish art#freshwater fish#trout
492 notes
·
View notes
Text

#dank memes#dark memes#best memes#lol#boop#haha#humor#funny memes#funny#memes#sea lion#seals#leopard seal#sea creatures#marine life#tegu#aquarium#fish tank#aquablr#freshwater aquarium#betta fish#planted aquarium
375 notes
·
View notes
Text



Settle In with the Sockeye Salmon
The sockeye salmon (Oncorhynchus nerka), also known as the red salmon, or the blueback salmon, is one of thirteen species of salmon endemic to the north Pacific Ocean. In their juvenile years they live in the open sea, but as fresh hatchlings and adults they can be found in freshwater rivers and streams. However, the subspecies known as the kokanee salmon are trapped in landlocked lakes and do not migrate as other sockeye salmon do. When migrating, the species can venture well inland to western North America and portions of eastern Asia, including Japan, Russia, and parts of Siberia.
Like most salmon, the sockeye is most famous for its lifecycle. It is an anadromous species, meaning that individuals migrate based on their life state. Newly hatched fry emerge from nests laid in the beds of freshwater systems, and spend their first 1-3 years before moving downstream to the ocean. There, they spend another 4-5 years in schools of up to several hundred, before they reach sexual maturity.
Beginning in July, mature adults begin the great migration back to the area in which they spawned. Once they reach their breeding grounds, males form into strict heirarchical groups and begin to court the available females. Meanwhile, each female digs a shallow nest in the riverbed and lays her eggs. Her chosen male partner-- or several-- lays a cloud of sperm over the eggs. A male may fertilize several nests before he dies; the female perishes soon after. The eggs, laid in clutches of up to 200, take approximately 40 days to hatch, at which point the cycle begins again.
As juveniles living in the ocean, red salmon are somewhat unremarkable. They have long, torpedo-shaped bodies that are generally silvery blue in color, sometimes with dark speckling. Individuals retain this coloring until well into their journy as adults, where males and females begin to significantly diverge. At their peak, adults may be anywhere from 60 to 84 cm (2 ft 0 in – 2 ft 9 in) in length and weigh from 2.3 to 7 kg (5–15 lb), with males being somewhat larger than females. Both males and females also change color; the head turns green, while the body turns bright red, although the color change is more striking in males. Finally, the shape of the male changes drastically, with the mouth becoming more hooked and the body growing a large hump.
Unlike other salmon, both adults and juvenile O. nerka feed throughout their lives. Fry and ocean-bound juveniles feed mainly on copepods and other zooplankton, while migrating adults also consume larger insects and invertebrates. Young blueback salmon are vulnerable to predation from larger fish such as lake trout, squawfish, and mountain whitefish, as well as larger invertebrates and frogs. Individuals living in the ocean are less predated upon, although they can still be caught by larger animals such as seals, sea lions, and sharks. Terminal-stage adults are large, easy targets and are consumed by a range of species; most namely bears and large birds such as gulls and eagles.
Conservation status: The IUCN considers the sockeye salmon to be of Least Concern. However, the species is listed on the United States Endangered Species Act. Populations have declined significantly throughout its range, largly due to overfishing, habitat degredation and the destruction of their breeding grounds.
Photos
NOAA Fisheries
Sergei Gorshkov
Roger Phillips
#sockeye salmon#Salmoniformes#Salmonidae#pacific salmon#salmon#salmonids#fish#freshwater fauna#freshwater fish#rivers#river fish#marine fauna#marine fish#open ocean#open ocean fish#Pacific ocean#north america#western north america#asia#east asia#north asia#animal facts#biology#zoology#ecology
78 notes
·
View notes
Text

Bunny pleco?
Its name is parsnip
#my art#pleco#plecostomus#plecos#aquariumblr#fish#creature design#monster design#artists on tumblr#fish art#bunnyblr#art#marine biology#freshwater aquarium#aquariums
87 notes
·
View notes