#Mantinea
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Persefone
Persefone (alias Kore) era la dea greca dell’agricoltura e della vegetazione, in particolare del grano, e moglie di Ade , con la quale governa gli Inferi. Elemento importante dei Misteri Eleusini e della festa della Tesmoforia, la dea era venerata in tutto il mondo greco e appariva frequentemente in tutte le forme dell’arte greca. Kore – Persefone – Proserpina In molti culti antichi la dea,…
#Afrodite#Arte#Artista#Atene#ceramica attica#Convivio#Demetra#Dioniso#Esiodo#Kore#letteratura#Locri Epizefiri#Mantinea#Megalopoli#Misteri Eleusini#mitologia greca#mitologia. mito#Orfismo#Persefone#Proserpina#Sociologia#Sparta#Storia#Teogonia#Tesmoforia#Zeus
0 notes
Text

A beleza verdejante de uma Caria mantinea lampeto, família Riodinidae, Colômbia
#caria mantinea lampeto#riodinidae#entomology#animal#biologia#animals#animais#biology#invertebrates#invertebrados#butterfly#borboleta#inseto#insetos#insect#insects#insecta
78 notes
·
View notes
Text

Epaminondas defending Pelopidas by William Rainey
#epaminondas#pelopidas#art#william rainey#history#siege of mantinea#greek#ancient greek#greece#ancient greece#europe#european#antiquity#ancient#battle#war#thebes#theban
190 notes
·
View notes
Text

mmmmm, burger
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
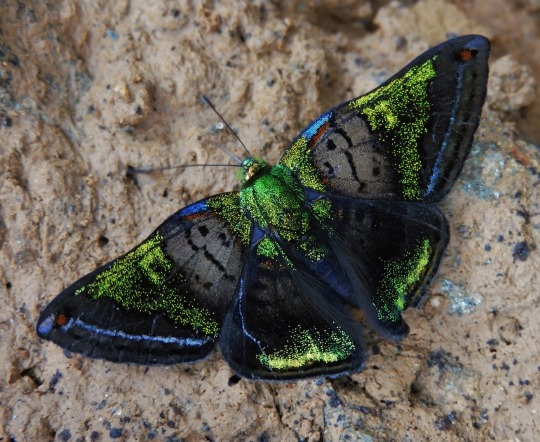

Green Mantle (Caria mantinea lampeto), family Riodinidae, Colombia
photograph by Jorge Eduardo Bernal Quintero
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
Despite Sparta’s reputation for superior fighting, Spartan armies were as likely to lose battles as to win them, especially against peer opponents such as other Greek city-states. Sparta defeated Athens in the Peloponnesian War—but only by accepting Persian money to do it, reopening the door to Persian influence in the Aegean, which Greek victories at Plataea and Salamis nearly a century early had closed. Famous Spartan victories at Plataea and Mantinea were matched by consequential defeats at Pylos, Arginusae, and ultimately Leuctra. That last defeat at Leuctra, delivered by Thebes a mere 33 years after Sparta’s triumph over Athens, broke the back of Spartan power permanently, reducing Sparta to the status of a second-class power from which it never recovered. Sparta was one of the largest Greek city-states in the classical period, yet it struggled to achieve meaningful political objectives; the result of Spartan arms abroad was mostly failure. Sparta was particularly poor at logistics; while Athens could maintain armies across the Eastern Mediterranean, Sparta repeatedly struggled to keep an army in the field even within Greece. Indeed, Sparta spent the entirety of the initial phase of the Peloponnesian War, the Archidamian War (431-421 B.C.), failing to solve the basic logistical problem of operating long term in Attica, less than 150 miles overland from Sparta and just a few days on foot from the nearest friendly major port and market, Corinth. The Spartans were at best tactically and strategically uncreative. Tactically, Sparta employed the phalanx, a close-order shield and spear formation. But while elements of the hoplite phalanx are often presented in popular culture as uniquely Spartan, the formation and its equipment were common among the Greeks from at least the early fifth century, if not earlier. And beyond the phalanx, the Spartans were not innovators, slow to experiment with new tactics, combined arms, and naval operations. Instead, Spartan leaders consistently tried to solve their military problems with pitched hoplite battles. Spartan efforts to compel friendship by hoplite battle were particularly unsuccessful, as with the failed Spartan efforts to compel Corinth to rejoin the Spartan-led Peloponnesian League by force during the Corinthian War. Sparta’s military mediocrity seems inexplicable given the city-state’s popular reputation as a highly militarized society, but modern scholarship has shown that this, too, is mostly a mirage. The agoge, Sparta’s rearing system for citizen boys, frequently represented in popular culture as akin to an intense military bootcamp, in fact included no arms training or military drills and was primarily designed to instill obedience and conformity rather than skill at arms or tactics. In order to instill that obedience, the older boys were encouraged to police the younger boys with violence, with the result that even in adulthood Spartan citizens were liable to settle disputes with their fists, a tendency that predictably made them poor diplomats. But while Sparta’s military performance was merely mediocre, no better or worse than its Greek neighbors, Spartan politics makes it an exceptionally bad example for citizens or soldiers in a modern free society. Modern scholars continue to debate the degree to which ancient Sparta exercised a unique tyranny of the state over the lives of individual Spartan citizens. However, the Spartan citizenry represented only a tiny minority of people in Sparta, likely never more than 15 percent, including women of citizen status (who could not vote or hold office). Instead, the vast majority of people in Sparta, between 65 and 85 percent, were enslaved helots. (The remainder of the population was confined to Sparta’s bewildering array of noncitizen underclasses.) The figure is staggering, far higher than any other ancient Mediterranean state or, for instance, the antebellum American South, rightly termed a slave society with a third of its people enslaved.
6K notes
·
View notes
Text
THIS DAY IN GAY HISTORY
based on: The White Crane Institute's 'Gay Wisdom', Gay Birthdays, Gay For Today, Famous GLBT, glbt-Gay Encylopedia, Today in Gay History, Wikipedia, and more … December 25






Sol Invictus ("the Unconquered Sun") or, more fully, Deus Sol Invictus ("the Unconquered Sun God") was the late Roman state sun god. The cult was created by the emperor Aurelian in 274 and continued until the abolition of paganism under Theodosius I. The Romans held a festival on December 25 called Dies Natalis Solis Invicti, "the birthday of the unconquered sun."
The use of the title Sol Invictus allowed several solar deities to be worshipped collectively, including Elah-Gabal, a Syrian sun god; Sol, the patron god of Emperor Aurelian (270-274); and Mithras. Oh, and a Jewish upstart named Jesus.
December 25th was also considered to be the date of the winter solstice, which the Romans called bruma. It was therefore the day the Sun proved itself to be "unconquered" despite the shortening of daylight hours. (When Julius Caesar introduced the Julian Calendar in 45 B.C.E., December 25th was approximately the date of the solstice. In modern times, the solstice falls on December 21st or 22nd.)
The Sol Invictus festival has a "strong claim on the responsibility" for the date of Christmas, according to the Catholic Encyclopedia. Solar symbolism was popular with early Christian writers as Jesus was considered to be the "sun of righteousness."
The date for Christmas may also bear a relation to the sun worship. According to the scholiast on the Syriac bishop Jacob Bar-Salibi, writing in the twelfth century:
"It was a custom of the Pagans to celebrate on the same 25 December the birthday of the Sun, at which they kindled lights in token of festivity. In these solemnities and revelries the Christians also took part. Accordingly when the doctors of the Church perceived that the Christians had a leaning to this festival, they took counsel and resolved that the true Nativity should be solemnized on that day." (cited in "Christianity and Paganism in the Fourth to Eighth Centuries", Ramsay MacMullen).

The Death of Epaminondas
418 B.C. – Epaminondas,��Greek warrior and general, born (d: 362 B.C.). Considered to have been one of the great military geniuses of the ancient world, he is included here, on Christmas Day, not because of his victories in battle, but because he was revered for his moral character. He was revered, too, since he had risen from an impoverished family because of his goodness, strength and character.
Epaminondas was well educated; his musical teachers were among the best in their disciplines, as was his dance instructor. Most notably, his philosophy instructor Lysis of Tarentum (who had come to live with Polymnis in his exile) was one of the last major Pythagorean philosophers. Epaminondas was devoted to Lysis and was noted for his excellence in philosophical studies.
Not merely an academic, Epaminondas was noted for his physical prowess, and in his youth he devoted much time to strengthening and preparing himself for combat. In 385 B.C., in a skirmish near the city of Mantinea, Epaminondas, at great risk to his own life, saved the life of his future partner Pelopidas, an act thought to have cemented the life-long friendship between the two.
He was, like most Greek warriors, homosexual - but with a difference. He never married and did not produce an heir. His delight in boys was complete in itself for him. His two favorite boys, Asopichus and Leuctra, both fell in battle, as did Epaminondas. Both, by his order, are buried in his tomb.
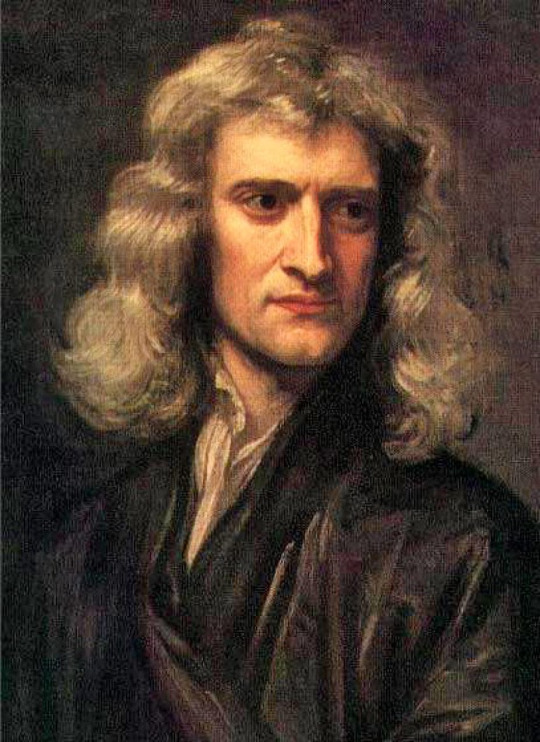

1642 – Sir Isaac Newton (d.1726/27) was an English mathematician, astronomer, theologian and physicist (described in his own day as a "natural philosopher") who is widely recognised as one of the most influential scientists of all time and a key figure in the scientific revolution. His book Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica ("Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy"), first published in 1687, laid the foundations of classical mechanics. Newton also made pathbreaking contributions to optics, and he shares credit with Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz for developing the infinitesimal calculus.
Isaac Newton was born (according to the Julian calendar, in use in England at the time) on Christmas Day, 25 December 1642 (NS 4 January 1643) "an hour or two after midnight", at Woolsthorpe Manor in Woolsthorpe-by-Colsterworth, a hamlet in the county of Lincolnshire.
From the age of about twelve until he was seventeen, Newton was educated at The King's School, Grantham, which taught Latin and Greek and probably imparted a significant foundation of mathematics. He was removed from school, and by October 1659, he was to be found at Woolsthorpe-by-Colsterworth, where his mother, widowed for a second time, attempted to make a farmer of him. Newton hated farming. Henry Stokes, master at the King's School, persuaded his mother to send him back to school so that he might complete his education. Motivated partly by a desire for revenge against a schoolyard bully, he became the top-ranked student, distinguishing himself mainly by building sundials and models of windmills.
Newton's Principia formulated the laws of motion and universal gravitation that dominated scientists' view of the physical universe for the next three centuries. By deriving Kepler's laws of planetary motion from his mathematical description of gravity, and using the same principles to account for the trajectories of comets, the tides, the precession of the equinoxes, and other phenomena, Newton removed the last doubts about the validity of the heliocentric model of the Solar System and demonstrated that the motion of objects on Earth and of celestial bodies could be accounted for by the same principles. Newton's theoretical prediction that the Earth is shaped as an oblate spheroid was later vindicated by the geodetic measurements of others, thus convincing most Continental European scientists of the superiority of Newtonian mechanics over the earlier system of Descartes.
Newton also built the first practical reflecting telescope and developed a sophisticated theory of colour based on the observation that a prism decomposes white light into the colours of the visible spectrum. Newton's work on light was collected in his highly influential book Opticks, first published in 1704. He also formulated an empirical law of cooling, made the first theoretical calculation of the speed of sound, and introduced the notion of a Newtonian fluid.
Newton was a fellow of Trinity College and the second Lucasian Professor of Mathematics at the University of Cambridge. He was a devout but unorthodox Christian, who privately rejected the doctrine of the Trinity and who, unusually for a member of the Cambridge faculty of the day, refused to take holy orders in the Church of England.
Beyond his work on the mathematical sciences, Newton dedicated much of his time to the study of alchemy and biblical chronology, but most of his work in those areas remained unpublished until long after his death. Politically and personally tied to the Whig party, Newton served two brief terms as Member of Parliament for the University of Cambridge, in 1689–90 and 1701–02. He was knighted by Queen Anne in 1705 and he spent the last three decades of his life in London, serving as Warden (1696–1700) and Master (1700–1727) of the Royal Mint, as well as president of the Royal Society (1703–1727).Although it was claimed that he was once engaged, Newton never married. The French writer and philosopher Voltaire, who was in London at the time of Newton's funeral, said that he
"was never sensible to any passion, was not subject to the common frailties of mankind, nor had any commerce with women—a circumstance which was assured me by the physician and surgeon who attended him in his last moments".
The widespread belief that he died a virgin has been commented on by writers such as mathematician Charles Hutton, economist John Maynard Keynes, and physicist Carl Sagan.
Newton did have a close friendship with the Swiss mathematician Nicolas Fatio de Duillier, whom he met in London around 1689. Their intense relationship came to an abrupt and unexplained end in 1693, and at the same time Newton suffered a nervous breakdown. Some of their correspondence has survived.
In September of that year, Newton had a breakdown which included sending wild accusatory letters to his friends Samuel Pepys and John Locke. His note to the latter included the charge that Locke "endeavoured to embroil me with woemen". Items like these have led some historians to speculate that Newton was homosexual.

"Artist and Model" - John Minton
1917 – John Minton (d.1957) was a painter of landscapes, town scenes, and figure subjects in oil and watercolor, as well as an acclaimed illustrator. Minton's homosexuality was an important influence on his work. One of his main themes was the young male figure in emotionally charged settings.
Like many middle class gay men of his generation, Minton was drawn to men who fulfilled a manly ideal, and this attraction manifested itself in much of his work, where he portrayed his handsome working class lovers and other ideals of masculinity such as Guardsmen and matadors.

Two Bullfighters
Minton's early work focused on the urban landscape he discovered during nocturnal jaunts around London, where he also discovered an active sexual underground. Visits to Spain in 1949 and Jamaica in 1950 offered Minton a fresh repertoire of subjects and enriched his palette of colors.
Although Minton was dedicated to painting, his reputation developed as a result of his skill as an illustrator for a wide range of books, as well as for magazines such as The Listener and The Radio Times.
Between 1950 and 1952 Minton lived openly with his lover Ricky Stride, a bodybuilding ex-sailor, often his model. Theirs was a volatile relationship and ended as a result of almost constant fighting, which often resulted in violence on Stride's part.
On January 12, 1950, The Listener published a letter Minton wrote in response to a review of a new biography of Oscar Wilde which discussed Wilde's sexuality and relationship with Lord Alfred Douglas in a denigrating fashion. Outraged, Minton pointed out the enormous contribution made to society by homosexuals and highlighted the fact that "the same vicious law which imprisoned Wilde still operates" and pleaded for a "saner and more comprehensive attitude towards the homosexual in society."
Minton's character revealed some great contradictions—his wild gaiety and love of wit and banter disguised and competed with an inner melancholy that verged on depression. Towards the end of his life, Minton began to express an obsession with death, and he was particularly moved by the death of film star and symbol of disaffected youth James Dean.
Minton's output was considerable. Between 1945 and 1956 he had seven solo exhibitions at the Lefevre Gallery, notwithstanding his work as tutor to the painting school of the Royal College of Art in 1949, a post that he held until the year before his death. Minton's appearance in this period is shown in a 1952 portrait by Lucian Freud, as well as in self-portraits. In the 1940s Minton, Freud and fellow artist Adrian Ryan had been in a love triangle.
Minton's last painting, which remained unfinished, was initially based upon a car crash that he had witnessed in Spain; but it also, he told his friend Ruskin Spear, represented "James Dean and all that." As a result the painting was posthumously titled Composition: The Death of James Dean in September 1955.
On January 20, 1957 John Minton committed suicide by taking an overdose of Tuinal.

1950 – Time magazine ran its first article on homosexuality. It said that homosexuals should not work in government jobs because they are a security risk.

1950 – Yehuda Poliker is an Israeli singer, songwriter, musician, and painter. Poliker first became known in the 1980s as the lead vocalist for the band Benzene. In 1985, after the band was dismantled, he began a varied solo career that included motifs from rock, pop and traditional Greek music. He is openly gay.
Yehuda Poliker (birth name: Leonidas Polikaris) was born in Kiryat Haim, a suburb of Haifa, Israel. His parents were Greek Jews and Holocaust survivors who were deported to Auschwitz from Thessaloniki.
In 1981, Poliker began his career-long collaboration with writer and producer Yaakov Gilad. Poliker's band, Benzene, released two albums: 24 Sha'ot (24 Hours) and Mishmeret Layla (Night Watch), which included hit singles such as "Hofshi Ze Legamrei Levad" ("Free Is Totally Alone"), "Geshem" ("Rain") and "Yom Shishi" (Friday). After Benzene broke up, Poliker began a solo career. In 1985, he released his first solo album, Einaim Shely (These Eyes of Mine). All of the tracks on the album were well-known Greek songs literally translated into Hebrew. In 1986, Poliker released his second solo album, Kholem Behakitz (Daydreamer). His third album, Efer VeAvak (Dust and Ashes), released in 1988, dealt mostly with the children of Holocaust survivors. It sold more than 70,000 copies, and in 2005, was rated by Ynet as number one of the top 100 best albums ever recorded in Israel.
Poliker's father, Jacko, told the story of his escape from Auschwitz in the 1988 film Because of That War (Hebrew: B'Glal Hamilhamah Hahi), which featured music by his son. The film included interviews with Yehuda Poliker and Yaakov Gilad, whose parents, Polish Jews, also survived Auschwitz.

1978 – Dylan Vox is an American actor and producer who has worked in television, film and theatre.
Vox was born in Marietta, Georgia, and was adopted one month after birth by Donna Blount. At an early age, he began riding horses and showed Western Pleasure placing in both regional and national competitions. After high school graduation, Vox received bachelor's degrees in Political Science and Journalism from the Georgia Southern University before moving to Denver, Colorado and training with Olympic Ice Dancer Carol Fox where he had some success on the national level with his partner Erin Bales. Vox retired from skating, and attended and graduated from law school.
Vox starred in the Los Angeles premiere of Debbie Does Dallas: The Musical and the world premiere of the hip-hopera "City Kid" earning a LA Stage Alliance Ovation Award nomination and a NAACP theatre award nomination.. He also was an original cast member of Hunky Dory, an original musical interpretation of the 1971 David Bowie album.
Vox appeared as himself on the reality television series Fight for Fame, Open Call, and the Spike detective series Murder. Vox has appeared in the here! cable station's gothic horror series Dante's Cove as Colin and as a series regular in here!'s vampire series The Lair also playing a character named Colin (although they are different characters).

Under the name Brad Benton, Vox performed in many hard and soft gay pornographic films, including Big Timber, Blades, BuckleRoos, Desperate Husbands, Devil Inside, and Longhorns. and was nominated for over 12 GayVN Awards and 15 Grabby Awards, winning Best Supporting Actor at the GayVN Awards in 2004 and 2005 and nine Grabby awards over all.
Vox has written for a number of LGBT-themed websites and writes a blog entitled "21st - Century Vox." He currently serves as the Sports Editor and as a featured columnist for GayWired.com.
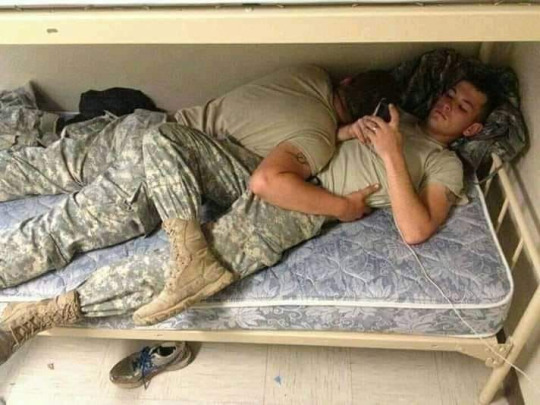

1982 – Two married US Army men are found, fully clothed, in bed together and are accused of sex. They say they only fell on the bed while drunk, but accept honorable discharges rather than fight the charges and possibly receive dishonorable discharges.


25 notes
·
View notes
Text
I. Enamorarse y desenamorarse.
«La naturaleza del amor implica —tal como lo observó Lucano dos milenios atrás y lo repitió Francis Bacon muchos siglos más tarde— ser un rehén del destino.
En el Simposio de Platón, Diótima de Mantinea le señaló a Sócrates, con el asentimiento absoluto de este, que «el amor no se dirige a lo bello, como crees», «sino a concebir y nacer en lo bello». Amar es desear «concebir y procrear», y por eso el amante «busca y se esfuerza por encontrar la cosa bella en la cual pueda concebir». En otras palabras, el amor no encuentra su sentido en el ansia de cosas ya hechas, completas y terminadas, sino en el impulso a participar en la construcción de esas cosas.
El amor está muy cercano a la trascendencia; es tan sólo otro nombre del impulso creativo y, por lo tanto, está cargado de riesgos, ya que toda creación ignora siempre cuál será su producto final.
En todo amor hay por lo menos dos seres, y cada uno de ellos es la gran incógnita de la ecuación del otro. Eso es lo que hace que el amor parezca un capricho del destino, ese inquietante y misterioso futuro, imposible de prever, de prevenir o conjurar, de apresurar o detener. Amar significa abrirle la puerta a ese destino, a la más sublime de las condiciones humanas en la que el miedo se funde con el gozo en una aleación indisoluble, cuyos elementos ya no pueden separarse. Abrirse a ese destino significa, en última instancia, dar libertad al ser: esa libertad que está encarnada en el otro, el compañero en el amor. Como lo expresa Erich Fromm: «En el amor individual no se encuentra satisfacción […] sin verdadera humildad, coraje, fe y disciplina»; y luego agrega inmediatamente, con tristeza, que en «una cultura en la que esas cualidades son raras, la conquista de la capacidad de amar será necesariamente un raro logro».
Amor líquido,
Zygmunt Bauman
37 notes
·
View notes
Text

Caria mantinea lampeto
(https://pamsbutterflies.com/butterfly/3298/caria-mantinea-lampeto),
Green Mantle. The Bolivian sub-species...
Caranavi, Bolivia.
May 2019
138 notes
·
View notes
Text

The last Kiss before the Battle
In ancient Greece, homosexuality was not taboo. In fact, it was sometimes even encouraged. The Greeks believed that male love made warriors stronger and more determined.
The Sacred Band of Thebes, also known as the Theban Sacred Band, was a notable military unit in the 4th century BC. This elite unit consisted of 150 warriors, all of whom were members of the noble class. Under the leadership of Epaminondas, a brilliant Theban general, the Sacred Band was trained to be a formidable fighting force. It was also known for its openness towards homosexuality.
Its fame is primarily based on its outstanding performance in the Battle of Leuctra in 371 BC. In this historic conflict, they managed to defeat the then-powerful Spartans. Epaminondas encouraged his men in this decisive battle with inspiring words: "We will either defeat the Spartans today or die in battle." These words are testament to the determination and courage that characterized the Sacred Band.
Another significant moment in its history took place in the Battle of Mantinea in 362 BC. Here, Pelopidas, who was leading the Sacred Band at the time, is said to have encouraged his men with the words: "We are the best warriors in Greece, and we will fight for our freedom today." This commitment to freedom and self-belief helped to solidify the unit's legendary reputation.
At the time of the Sacred Band and the Battles of Leuctra and Mantinea, homosexuality was viewed differently in Greek society than it is today. In fact, it was sometimes even encouraged, especially among the Spartans, who believed that love between men enhanced their fighting prowess. In ancient times, Greek culture was known for its acceptance and openness towards same-sex relationships. This cultural aspect allowed such love relationships, like the one between the two lovers, to be lived in a certain way freely, without the social stigmas that arose later in history.
#gayart#gaycomic#ancient#romanbaths#ancientrome#ancientart#lgbt#loveandfriendship#gayhistory#AncientGreece#HistoricalLove#LGBTQHistory#WarriorsOfThebes#LoveAndWar#SacredBand
88 notes
·
View notes
Note
What, in your personal opinion, would you say are the main mistakes made by Athens during the Pelopennesian War? What could they have done to win?
This is not my area of expertise at all (I would recommend @warsofasoiaf or Bret Devereaux) so I'm going to be going back to the couple of classes I took on ancient Greece in my undergrad days.
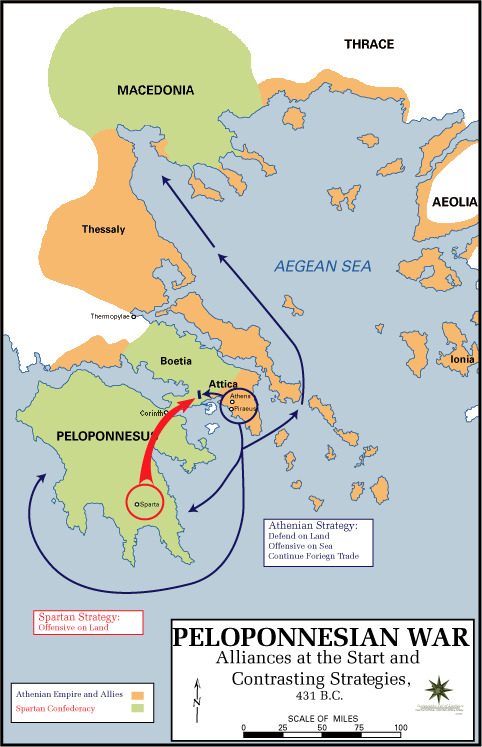
I would argue that the Athenians' initial defensive strategy under Pericles and then its more aggressive successor under Cleon and Demosthenes was in general quite successful against the Spartans. The Battle of Amphipolis was very much a close-run thing that still resulted in Athens being able to challenge Spartan hegemony on the Peloponnese for the first time.
However, I think Alcibiades was the most significant factor in the Athenian defeat. Having squandered Athens' opportunity to crack Spartan land power at Mantinea, Alcibiades went all-in on his Sicilian expedition - and then promptly defected to the Spartans, fracturing Athenian political unity. The Sicilian expedition all but destroyed Athens' naval hegemony, and even after they were able to somewhat recover, the mounting losses and internal conflict meant that Athens could not fight both Sparta and the Persians at the same time.
37 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Athenian historian Thucydides once remarked that Sparta was so lacking in impressive temples or monuments that future generations who found the place deserted would struggle to believe it had ever been a great power. But even without physical monuments, the memory of Sparta is very much alive in the modern United States. In popular culture, Spartans star in film and feature as the protagonists of several of the largest video game franchises. The Spartan brand is used to promote obstacle races, fitness equipment, and firearms. Sparta has also become a political rallying cry, including by members of the extreme right who stormed the U.S. Capitol on Jan. 6, 2021. Sparta is gone, but the glorification of Sparta—Spartaganda, as it were—is alive and well.
Even more concerning is the U.S. military’s love of all things Spartan. The U.S. Army, of course, has a Spartan Brigade (Motto: “Sparta Lives”) as well as a Task Force Spartan and Spartan Warrior exercises, while the Marine Corps conducts Spartan Trident littoral exercises—an odd choice given that the Spartans were famously very poor at littoral operations. Beyond this sort of official nomenclature, unofficial media regularly invites comparisons between U.S. service personnel and the Spartans as well.
Much of this tendency to imagine U.S. soldiers as Spartan warriors comes from Steven Pressfield’s historical fiction novel Gates of Fire, still regularly assigned in military reading lists. The book presents the Spartans as superior warriors from an ultra-militarized society bravely defending freedom (against an ethnically foreign “other,” a feature drawn out more explicitly in the comic and later film 300). Sparta in this vision is a radically egalitarian society predicated on the cultivation of manly martial virtues. Yet this image of Sparta is almost entirely wrong. Spartan society was singularly unworthy of emulation or praise, especially in a democratic society.
To start with, the Spartan reputation for military excellence turns out to be, on closer inspection, mostly a mirage. Despite Sparta’s reputation for superior fighting, Spartan armies were as likely to lose battles as to win them, especially against peer opponents such as other Greek city-states. Sparta defeated Athens in the Peloponnesian War—but only by accepting Persian money to do it, reopening the door to Persian influence in the Aegean, which Greek victories at Plataea and Salamis nearly a century early had closed. Famous Spartan victories at Plataea and Mantinea were matched by consequential defeats at Pylos, Arginusae, and ultimately Leuctra. That last defeat at Leuctra, delivered by Thebes a mere 33 years after Sparta’s triumph over Athens, broke the back of Spartan power permanently, reducing Sparta to the status of a second-class power from which it never recovered.
Sparta was one of the largest Greek city-states in the classical period, yet it struggled to achieve meaningful political objectives; the result of Spartan arms abroad was mostly failure. Sparta was particularly poor at logistics; while Athens could maintain armies across the Eastern Mediterranean, Sparta repeatedly struggled to keep an army in the field even within Greece. Indeed, Sparta spent the entirety of the initial phase of the Peloponnesian War, the Archidamian War (431-421 B.C.), failing to solve the basic logistical problem of operating long term in Attica, less than 150 miles overland from Sparta and just a few days on foot from the nearest friendly major port and market, Corinth.
The Spartans were at best tactically and strategically uncreative. Tactically, Sparta employed the phalanx, a close-order shield and spear formation. But while elements of the hoplite phalanx are often presented in popular culture as uniquely Spartan, the formation and its equipment were common among the Greeks from at least the early fifth century, if not earlier. And beyond the phalanx, the Spartans were not innovators, slow to experiment with new tactics, combined arms, and naval operations. Instead, Spartan leaders consistently tried to solve their military problems with pitched hoplite battles. Spartan efforts to compel friendship by hoplite battle were particularly unsuccessful, as with the failed Spartan efforts to compel Corinth to rejoin the Spartan-led Peloponnesian League by force during the Corinthian War.
Sparta’s military mediocrity seems inexplicable given the city-state’s popular reputation as a highly militarized society, but modern scholarship has shown that this, too, is mostly a mirage. The agoge, Sparta’s rearing system for citizen boys, frequently represented in popular culture as akin to an intense military bootcamp, in fact included no arms training or military drills and was primarily designed to instill obedience and conformity rather than skill at arms or tactics. In order to instill that obedience, the older boys were encouraged to police the younger boys with violence, with the result that even in adulthood Spartan citizens were liable to settle disputes with their fists, a tendency that predictably made them poor diplomats.
But while Sparta’s military performance was merely mediocre, no better or worse than its Greek neighbors, Spartan politics makes it an exceptionally bad example for citizens or soldiers in a modern free society. Modern scholars continue to debate the degree to which ancient Sparta exercised a unique tyranny of the state over the lives of individual Spartan citizens. However, the Spartan citizenry represented only a tiny minority of people in Sparta, likely never more than 15 percent, including women of citizen status (who could not vote or hold office). Instead, the vast majority of people in Sparta, between 65 and 85 percent, were enslaved helots. (The remainder of the population was confined to Sparta’s bewildering array of noncitizen underclasses.) The figure is staggering, far higher than any other ancient Mediterranean state or, for instance, the antebellum American South, rightly termed a slave society with a third of its people enslaved.
The ancient sources are effectively unanimous that the helots were the worst treated slaves in all of Greece; helotry was an institution that shocked the conscience of Athenian slaveholders. Critias, an Athenian collaborator with Sparta, was said to have quipped that it was in Sparta that “the free were most free and the slaves most a slave,” a staggering statement about a society that was mostly enslaved (and about Critias as a person that he thought this was praise). Plutarch reports the various ways that the Spartans humiliated and degraded the helots, while the Athenian orator Isocrates argued that it was a crime to murder enslaved people everywhere in Greece, except Sparta. Sparta, with both the most slaves per capita and the worst treated slaves, was likely the least free society in the whole of the ancient world.
Nor were the Spartans particularly good stewards of Greek freedom. While their place in popular culture, motivated by films such as 300, puts the Spartans at the head of efforts to defend Greek freedom from the expanding Persian Empire, Sparta was not always so averse to Persia. Unable to deal with the Athenian fleet itself, Sparta accepted Persian money during the Peloponnesian War to build its own, selling the Ionian Greeks back into Persian rule in exchange for humbling Athens. That war won the Spartans a brief hegemony in Greece, which they quickly squandered, ending up at war with their former allies in Corinth.
Unable to win that war either, Sparta again turned to Persia to enforce a peace, called the “King’s Peace,” which sold yet more Greek city-states to the Persian king in exchange for making Sparta into Persia’s local enforcer in Greece, tasked with preventing the emergence of larger Greek alliances that could challenge Persia. Far from being the defender of Greek independence, when given the chance the Spartans opened not only the windows but also the doors to Persian rule. They also refused to join in Alexander the Great’s expedition against Persia, for which Alexander mocked them by dedicating the spoils of his first victories “from all of the Greeks, except the Spartans.”
Instead of a society of freedom-defending super-warriors, Sparta is better understood as a place where the wealthiest class of landholder, the Spartans themselves, had succeeded in reducing the great majority of their poor compatriots to slavery and excluded the rest, called the perioikoi, from political participation or citizenship. The tiny minority of Spartan citizens derived their entire income from the labor of slaves, being legally barred from doing any productive work or engaging in commerce.
And rather than spending their time in ascetic military training, they spent their ample leisure time doing the full suite of expensive, aristocratic Greek pastimes: hunting (a pastime for the wealthy rather than a means of subsistence in the ancient world), eating amply, accumulating money, funding Olympic teams, breeding horses, and so on. Greek authors such as Xenophon and Plutarch continually insist that the golden age of Spartan austerity and egalitarianism existed in the distant past, but each author pushes that golden age further and further into that past, and in any event, archaeology tells us it was never so.
And that lavish lifestyle was clearly very important to the Spartans because they were willing to sacrifice all of their other ambitions on the altar to it. Beginning in the early 400s, the population of Spartan citizens, defined by being rich enough in land to make the mess contributions that were a key part of military and social lfie, began to decline as Spartan families used inheritance and marriage to consolidate holdings and increase their wealth, from 8,000 Spartan citizens in 480 B.C. to 3,500 in 418 to 2,500 in 394 to just 1,500 in 371. The collapse in the number of Spartans who qualified for citizenship had disastrous effects on the manpower available for the Spartan army, causing Sparta’s strategic ambitions to all crumble, one by one. Yet efforts by Agis IV (245-241 B.C.) and Cleomenes III (235-222 B.C.) to arrest the decline were foiled precisely because the Spartan political system denied any political voice to any but the leisured rich, who had little incentive to change.
Sparta is no inspiration for the leaders of a free state. Sparta was a prison in the guise of a state and added little to the sum of the human experience except suffering. No American, much less any U.S. soldier, should aspire to be like a Spartan.
72 notes
·
View notes
Text

Epaminondas Defending Pelopidas at the Battle of Mantinea, illustration by William Rainey for Plutarch’s Lives for Boys and Girls by W.H. Weston (1900)
68 notes
·
View notes
Text
i've started reading d.m. smith's comparisons of the extant sources of the telegony just to inflict psychic damage on myself
[Pseudo-Apollodorus:] "But some say that Penelope was seduced by Antinous and sent away by Odysseus to her father Icarius, and that when she came to Mantinea in Arcadia she bore Pan to Hermes. However others say that she met her end at the hands of Odysseus himself on account of Amphinomus, for they allege that she was seduced by him.
like yeah yeah they love making penelope unfaithful with the lead suitors (and hermes)
[Servius:] "It is said that when [Odysseus] at last returned to Ithaca he discovered Pan in his home, who was born of Penelope and all of her suitors—as the very name “Pan” seems to assert."
ALL OF THEM??
ALL of the suitors. 108 of them
how did she find the ENERGY
#doesn't help that i'm insane and immediately thought like 'oh like how cats can be fertilized by several males within a seven day period'#which would make it a good SIXTEEN suitors per day. applaudable. what is her secret#this is like the stories that make diomedes' wife not just unfaithful but like TURBO-UNFAITHFUL#male insecurities central#the telegony#penelope of ithaca#odysseus#tagamemnon#first impressions tag
15 notes
·
View notes
Text

Green Mantle (Caria mantinea lampeto), family Riodinidae, Caranavi, Bolivia
photograph by Pamela Sai
662 notes
·
View notes
Text
At the Battle of Thermopylae, there were
300 Spartiates (plus helots who fought, but were never mentioned even in Herodotus; at least one per Spartan, but almost certainly more);
500 hoplites from Mantinea;
500 from Tegea;
120 from (Arkadian) Orchomenos;
1000 from ‘the rest of’ Arkadia;
400 from Korinth;
200 from Phlios;
80 from Mykenai;
the ‘full fighting force’ of Opous (in Lokris - no number given);
700 from Thespiai;
400 from Thebes;
1000 from Phokis.
[Herodotus, 7.202-3]
That’s ~ 5000 hoplites.
Not 300.
5000.
#ancient sparta#sparta#ancient greece#ancient history#spartan history#the battle of thermopylae#300#ancient propaganda
8 notes
·
View notes