#Managing high uric acid levels naturally
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
What Is Uric Acid and How It Affects Our Health
Although it is still debatable we have some clues to deal with this sneaky acid mainly hidden in junk foods Hyperuricemia In this short post, I will introduce you to uric acid because this sneaky acid something as small as a molecule could make or break our health. Uric acid is a tiny waste product that forms when our bodies break down purines , natural compounds in food some food. Sounds…
#allopurinol or febuxostat to lower production#Dealing with intense pain#Elevated Uric Acid#Emerging Concerns of Elevated Uric Acid on Obesit#Foods to avoid for lower uric acid levels#Gout prevention#How diet affects uric acid and gout risk#How uric acid impacts physical and mental health#Hyperuricemia#Hyperuricemia is increasing globally#Kidney stone prevention#Link between uric acid and mental health#Literature review by Dr Mehmet Yildiz#Managing high uric acid levels naturally#probenecid to enhance elimination#Signs of high uric acid and treatment options#Understanding gout symptoms and uric acid#Uric acid and kidney stones prevention tips#Uric acid levels and their hidden health impacts#Uric acid’s role in hypertension and heart health
0 notes
Text
Story at-a-glance
Alcohol consumption is linked to an increased risk of gout. A study found men who drink have a 69% higher risk compared to non-drinkers, while women showed no similar association
Gout occurs when your body produces uric acid faster than it’s able to eliminate it. Alcohol, especially beer, contributes significantly to elevated uric acid levels in the blood
Exercise, particularly at low- to moderate-intensity, helps manage uric acid levels. It produces anti-inflammatory effects that reduce responses caused by uric acid crystals and offers additional health benefits
Avoiding processed sugar, especially high-fructose corn syrup, is crucial in managing uric acid levels. Fructose stimulates pathways that produce uric acid from amino acid precursors
Natural remedies like applying citrates to affected joints and consuming quercetin can help relieve gout symptoms. Quercetin's antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties reduce uric acid production and increase excretion
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

Ayurvedic medicine for uric acid: High uric acid levels can lead to discomfort, swelling, and even severe joint pain. At WelnessCart, we provide effective Ayurvedic medicine for uric acid to help manage and control your uric acid levels naturally. These remedies are crafted with Ayurvedic principles, promoting a balanced and healthy lifestyle.
0 notes
Text
What Foods Are Bad for Kidney Stones? A Complete Guide to Avoid Painful Episodes
What Foods Are Bad for Kidney Stones?
Kidney stones are one of the most common urological conditions, affecting millions worldwide. These hard mineral and salt deposits can cause excruciating pain and discomfort, often leading to emergency medical visits. While various factors contribute to kidney stone formation, diet plays a pivotal role. Knowing which foods to avoid can significantly reduce your risk of developing kidney stones or prevent a recurrence.
In this article, we’ll explore the top foods you should steer clear of if you’re prone to kidney stones. We’ll address frequently asked questions and provide actionable tips to safeguard your kidney health. Let’s dive in!
What Foods Are Bad for Kidney Stones?
Certain foods contain high levels of substances that contribute to kidney stone formation. The primary culprits are oxalates, sodium, and animal proteins. Below, we’ll break down the foods to avoid:
1. Foods High in Oxalates
Oxalates are natural compounds found in many foods. When consumed in excess, they can bind with calcium in the kidneys, forming calcium oxalate stones—the most common type of kidney stones.
Examples: Spinach, rhubarb, beets, Swiss chard, sweet potatoes, nuts, and dark chocolate.
Why Avoid: These foods significantly increase the oxalate concentration in urine.
Pro Tip: Pairing oxalate-rich foods with calcium-rich foods can help reduce oxalate absorption in the gut.
2. Excess Sodium
A high-sodium diet causes your kidneys to excrete more calcium in the urine, raising the risk of stone formation.
Examples: Processed foods, canned soups, chips, salted snacks, and fast food.
Why Avoid: Sodium disrupts the delicate mineral balance in the kidneys, promoting stone development.
Actionable Tip: Keep daily sodium intake below 2,300 mg, or even lower if recommended by your doctor.
3. Animal Proteins
Diets high in animal protein can increase uric acid levels, a leading cause of uric acid stones. Additionally, animal protein reduces citrate levels, a natural stone inhibitor.
Examples: Red meat, poultry, eggs, and seafood.
Why Avoid: Excess protein intake creates an acidic environment in the urine, encouraging stone growth.
Alternative: Opt for plant-based proteins like lentils, beans, and quinoa.
4. Sugary Beverages and Foods
Sugars, especially fructose, can increase calcium, oxalate, and uric acid levels in the urine.
Examples: Soda, sweetened juices, candy, and desserts.
Why Avoid: Sugar-laden foods exacerbate dehydration, a significant factor in stone formation.
Solution: Choose water or unsweetened beverages to stay hydrated.
5. High-Purine Foods
Purines break down into uric acid, which can lead to uric acid stones.
Examples: Organ meats (liver, kidney), anchovies, sardines, mackerel, and beer.
Why Avoid: High purine intake elevates uric acid levels, heightening the risk of stones.
Recommendation: Limit purine-rich foods and drink plenty of water to flush out excess uric acid.
Conclusion
Understanding the connection between diet and kidney stones is crucial for prevention and management. Avoiding oxalate-rich foods, limiting sodium and animal proteins, and staying hydrated are practical steps to minimize your risk. By making informed dietary choices and consulting with your healthcare provider, you can take control of your kidney health.
If you or a loved one are struggling with kidney stones, our team at Rajeev Hospital in Madurai is here to help. Contact us today to learn more about personalized kidney care solutions.
FAQs About Foods and Kidney Stones
Q1: Can I still eat nuts if I’m prone to kidney stones? Nuts, especially almonds, are high in oxalates. If you have a history of calcium oxalate stones, it’s best to limit or avoid them. Opt for lower-oxalate alternatives like macadamia nuts.
Q2: Are all leafy greens bad for kidney stones? Not all leafy greens are problematic. While spinach and Swiss chard are high in oxalates, kale and arugula are low in oxalates and safe to consume.
Q3: Should I completely cut out dairy products? No, calcium from dairy products can bind with oxalates in the gut, reducing the risk of stone formation. However, moderation is key.
Q4: Is caffeine bad for kidney stones? Moderate caffeine intake from coffee or tea isn’t harmful and may even lower the risk of some stones. Avoid sugary coffee drinks and excessive caffeine consumption.
Q5: How much water should I drink to prevent kidney stones? Aim for at least 2-3 liters of water daily to dilute urine and reduce stone-forming substances.
[Kidney Stone Clinic Madurai]
#bestandrologyhospitalinmadurai#bestgeneralsurgeonsmadurai#besturologydoctorin madurai#besturologistinmadurai#besturologyhospitalinmadurai#bestpediatricurologistnearme#mostadvancedurologytreatments#uroflowmetrytestnearme
0 notes
Text
Managing Ammonia During Winter in Deep Litter Broiler Houses
Ammonia buildup in poultry houses, particularly during winter, poses a significant challenge for poultry farmers. Effective ammonia management is crucial for ensuring bird health and maintaining optimal productivity levels. Below, we explore how ammonia forms, its risks, and practical solutions, including poultry equipment for controlling ammonia in deep litter broiler houses during the colder months.
How Does Ammonia Form?
Ammonia (NH₃) primarily originates from manure that accumulates in deep litter systems. As litter moisture levels rise, they create an ideal environment for bacterial activity, which breaks down nitrogen compounds in the manure. One of the key byproducts of this breakdown is ammonia. High levels of ammonia can have detrimental effects on both poultry health and worker safety, especially during winter months when natural ventilation is limited.
Ideally, ammonia concentrations in poultry houses should remain below 25 ppm (parts per million). When levels exceed this threshold, it can negatively impact bird respiratory health, reduce productivity, and even increase mortality rates. During winter, outside temperatures are low, reducing the effectiveness of ventilation fans. This creates a situation where toxic gases, including ammonia, accumulate inside the house due to limited airflow, further exacerbating the problem.
In broiler poultry farms that rely on sidewall curtains and lack effective minimum ventilation systems, maintaining optimal temperatures becomes challenging. During the brooding stage, chicks require temperatures between 32°C and 36°C. However, due to the heat loss through side curtains and poor insulation farmers never achieve these temperature levels. Therefore, most farmers try to cover the house by covering the brooding area and providing additional covers on the side curtains. Consequently, these additional closures trap the air ventilation and contribute to the increase in toxic gases inside the house. When ventilation is inadequate, ammonia buildup becomes more pronounced, especially as warmer temperatures accelerate the breakdown of uric acid in the manure, leading to higher ammonia concentrations.
In such conditions, farmers often attempt to mitigate ammonia by opening side wall curtains halfway. While this allows for some gas exchange, it is not enough to maintain proper ventilation, resulting in a dangerous rise in ammonia levels. To combat this, some farmers use large fans to improve air circulation. However, these fans expel significant amounts of warm air, leading to increased heating costs and further temperature fluctuations.

Additionally, the lack of insulation in many poultry houses contributes to excessive heat loss, making it harder to maintain a stable indoor environment. This not only increases heating requirements but also complicates ammonia management.
Poultry Industry Equipment: Solutions for Managing Ammonia in Winter
Winter Ventilation Equipment:
Proper winter ventilation is essential for controlling ammonia levels. Minimum ventilation fans are key to removing toxic gases without causing excessive air drag. These fans are designed to exhaust just enough air to prevent ammonia buildup while maintaining stable temperatures. Proper side air inlets are also vital they ensure that cool air does not directly blow over the birds and help maintain even airflow throughout the house.

Tunnel inlets are effective at blocking drafts and preventing wind chill from affecting the birds. This helps create a stable and comfortable environment even in cold weather.
Insulated House Design:
One of the most effective ways to manage ammonia during winter is to ensure your poultry house is properly insulated. Insulated walls, roofs, and ceilings help retain heat, reducing the reliance on supplemental heating equipment. The recommended insulation levels for poultry houses are between R-19 and R-25. This insulation not only reduces energy costs but also helps maintain a consistent internal temperature, supporting bird health and well-being.

Insulation also aids in better ammonia control. By reducing the need for excessive heating, you can avoid overworking ventilation systems, which are crucial for managing both temperature and air quality. Proper insulation limits heat loss and makes it easier to maintain the required airflow and ammonia levels.
Reliable Climate Control Systems:
A well-maintained climate control system is essential for monitoring and regulating the poultry house environment. These systems control ventilation fans, inlets, heaters, and humidifiers, ensuring that all equipment works together efficiently. The use of accurate sensors for temperature, humidity, and static pressure allows for precise control, which is critical during winter when conditions can fluctuate rapidly.

By continuously monitoring and adjusting the environment, climate control systems help maintain the ideal temperature and humidity levels for poultry, improving both productivity and bird health. Additionally, this reduces the strain on heating systems and helps manage ammonia buildup more effectively.
Keep the Litter Dry:
Although this isn't a poultry equipment-specific solution, it plays a crucial role in efficient broiler feeding and broiler farming. Moisture in the litter is one of the primary contributors to ammonia production. To control ammonia levels, it's essential to keep the litter as dry as possible. Properly adjusted drinkers can help prevent water spillage, which is a common cause of wet litter. Regularly inspect the water system for leaks, and address any issues promptly.
If the litter becomes too wet, it is important to add dry bedding material to absorb excess moisture. This will help maintain the balance of the litter and reduce the likelihood of ammonia buildup. Additionally, periodic litter management practices such as turning the litter can help further reduce moisture and ammonia concentrations.
Looking for Poultry Industry Equipment?
Do you run a broiler poultry farm and struggling with managing ammonia levels during winter? Then, Gartech, one of the leading poultry equipment manufacturers, is here to help. We provide a range of poultry equipment, including cage broiler systems to help farmers maintain the right ventilation, optimal temperature levels, proper spacing, dry environment and more. Our equipment is trusted by thousands of poultry farmers worldwide. So, call us at +91 7447798692 to learn more about our broiler poultry farm equipment.
0 notes
Text
What is Uric Acid?
Why Does It Matter?
Uric acid is a waste product that can be produced in your body when it breaks down chemicals called **purines**, which are naturally occurring in some foods and beverages. Normally, uric acid is filtered out by the kidneys and then removed from your body in urine. However, excessive production of uric acid by your body, or an inability by your kidneys to remove it sufficiently from the body, can build it up in your blood, causing **uric acid crystals** to form in your joints, creating **gout**, a rather painful type of arthritis.
What is Gout?
Gout is caused by uric acid crystals building up inside the joints, causing sudden, severe pain, redness, and swelling. It's much more common in men, especially above 30 or 40 years of age. Gout most often strikes the big toe but can also occur in other parts of the body, including the knees, elbows, and fingers. The pain builds slowly - often at night - and can be extremely sharp.
Symptoms of High Uric Acid (Gout):
1. **Intense Severe Pain:** The joint may become very painful; often the big toe hurt, and most common at night. 2. **Swelling and Redness:** The appearance is of a swollen red joint that often feels warm. 3. **Tenderness:** The slightest rubbing or pressure on the affected joint can feel agonizing. 4. **Lumps or Bumps:** After some time, when uric acid crystals accumulate, they can become visible under the skin near the joints, called **tophi**.
What Are the Causes of High Uric Acid Levels?
The following are some of the factors that can cause uric acid to level up: - **Diet:** Foods high in purines—such as red meat, organ meats (liver), shellfish, and oily fish (such as sardines, mackerel, and anchovies)-are a common cause of uric acid buildup. Added sugars in liquids such as soda and alcoholic beverages, especially beer, are major contributors. - **Obesity:** A higher body weight increases your chance of developing gout because excess fat tissue produces more uric acid. - **Dehydration:** Not having enough water impairs your kidneys to remove uric acid. - **Genetics:** Having gout in the family means you tend to have higher uric acid levels.
How Do You Maintain Lowered Uric Acid Levels and Avoid Gout Attacks?
If you're dealing with high uric acid levels, or even want to prevent a future gout attack, making some simple lifestyle changes can make a big difference: 1. **Watch Your Diet:** - **Eat more fruits and vegetables:** These foods are low in purines and help keep your uric acid levels in check. - Limit high-purine foods: Reduce the intake of red meats, organ meats (such as liver), and some types of fish, such as sardines and mackerel. -Abstain from sugary drinks. Soda, fruit juice, and especially beer, may induce gout attack. 2. Exercise and Maintain Healthy Weight Exercise regularly as it helps in managing weight and overall health. - **Avoid crash diets** or rapid weight loss, as this can increase uric acid levels temporarily. 3. **Stay Hydrated:** Drink plenty of water—about 6–8 glasses a day. This will help flush out excess uric acid from your system. 4. **Consider Vitamin C:** - Vitamin C can help lower uric acid levels, so talk to your doctor about possibly taking a supplement. 5. **Take Medications if Needed:** - In some cases, your doctor might prescribe medication to help lower uric acid levels or reduce inflammation during a gout flare-up. 6. **Cut Back on Alcohol and Processed Foods:** - Abstaining from alcohol (in particular, beer) and processed foods can also reduce your risk for gout. Such foods can raise uric acid in your bloodstream. 7. **Annual Check-Ups:** - Monitor your uric acid levels, especially if you have a family history of gout or other predisposing factors. In fact, the earlier it is diagnosed, the better treatment can be managed.
In Summary
High levels of uric acid can cause painfully excruciating gout attacks, but appropriate management and, at times, prevention of flare-ups can be done. Dieting may not require extreme dieting, but being hydrated, having a healthy weight, and being very cautious with certain foods and habits can reduce the risk significantly. And, of course, if you are experiencing the mentioned symptoms or suspect to be in high uric acid, the best advice and treatment is from your doctor.
0 notes
Text
Gout: Symptoms & Natural Treatment

Gout results from the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints, causing severe pain and inflammation.
High uric acid levels are often linked to metabolic issues and excessive fructose consumption.
Fructose, not red meat, is a primary contributor to elevated uric acid and gout development.
Proper management of gout involves reducing sugar intake and optimizing nutrient balance.
Addressing underlying metabolic dysfunctions is essential for long-term gout relief.
Introduction

Gout is a form of arthritis characterized by sudden and severe pain, swelling, and redness in the joints, most often in the big toe.
It occurs when uric acid crystals accumulate in the joints, causing inflammation and pain.
Gout is closely related to high levels of uric acid in the blood, but several factors influence its development, including diet, metabolic health, and lifestyle.
Causes and Risk Factors
Uric Acid and Gout
Uric acid is a natural waste product formed when the body breaks down purines. Normally, uric acid is dissolved in the blood and eliminated through the kidneys.
However, when uric acid levels become too high, it can crystallize and settle in the joints, leading to gout.
The main drivers of elevated uric acid include metabolic issues, fructose consumption, and impaired kidney function.
The Role of Fructose in Gout

Fructose, found in sugary drinks and processed foods, is a major contributor to high uric acid levels.
Unlike glucose, fructose metabolism rapidly generates uric acid, particularly in the liver. Excessive fructose consumption has been linked to metabolic disorders such as insulin resistance, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and gout.
Reducing fructose intake is key to preventing gout flares and managing uric acid levels.
Common Triggers for Gout Attacks
Gout attacks can be triggered by various factors, including:
High consumption of fructose or sugar-laden foods
Alcohol intake, especially beer
Dehydration
Sudden increases in physical activity or stress
Certain medications that raise uric acid levels, like diuretics
Symptoms and Diagnosis

Common Symptoms
The most common symptom of gout is intense joint pain, often starting in the big toe, though other joints can be affected. Additional symptoms include:
Swelling and redness in the affected joint
Warmth and tenderness around the joint
Limited joint movement due to pain
Gout attacks, which can occur suddenly and last several days
Diagnosing Gout
Gout is typically diagnosed through physical examinations, blood tests to check uric acid levels, and imaging studies like ultrasounds or X-rays to detect uric acid crystals in the joints.
Joint fluid tests can also confirm the presence of uric acid crystals.
Treatment and Management

Dietary Adjustments
Managing gout involves making key dietary changes to reduce uric acid levels and prevent gout flares. Prioritizing nutrient-dense, low-sugar foods while reducing fructose intake is needed.
Contrary to popular belief, red meat is not a major cause of gout and provides essential nutrients like iron, zinc, and B vitamins.
Instead, eliminating sugary foods and drinks, especially those containing high-fructose corn syrup, is essential for reducing gout risk.
Medication Options
Medications are often prescribed to manage gout, especially during acute flare-ups. These include:
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Used to reduce pain and inflammation.
Colchicine: Helps reduce inflammation during a gout attack.
Allopurinol: Lowers uric acid levels by reducing its production in the body.
Probenecid: Increases uric acid excretion through the kidneys.
While medications are effective, long-term management should focus on lifestyle changes that address the underlying causes of high uric acid.
Long-Term Management Strategies
In addition to dietary changes and medications, managing gout involves other lifestyle adjustments:
Stay hydrated to support kidney function and uric acid excretion.
Maintain a healthy weight to reduce the metabolic stress associated with high uric acid levels.
Limit alcohol consumption, as it can interfere with uric acid excretion and trigger gout attacks.
Preventing Gout Flares

Reducing Fructose Intake
As fructose significantly contributes to elevated uric acid levels, cutting back on sugary drinks and processed foods is vital.
A diet rich in whole, low-carbohydrate foods supports metabolic health and prevents gout flares.
Optimizing Nutrient Intake
Eating a bioavailable nutrient-rich diet ensures the body gets essential nutrients like copper, which plays a key role in managing oxidative stress and iron regulation.
Proper nutrient balance helps the body manage uric acid more effectively.
Beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB)
Beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB) is one of the main ketone bodies produced by the liver during fat metabolism.
BHB is produced through a process called ketogenesis, where fats are broken down into ketones in the liver.
This occurs during times of carbohydrate restriction, fasting, or prolonged exercise. The body converts stored fat into ketones, with BHB being the primary ketone that circulates in the bloodstream and provides energy.
Beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB) has shown promising effects in reducing inflammation related to gout. Research indicates that BHB inhibits the NLRP3 inflammasome, a key driver in gout’s inflammatory response, particularly in neutrophils.
This inhibition reduces the production of IL-1β, a pro-inflammatory cytokine involved in gouty flares.
The anti-inflammatory properties of BHB offer a potential therapeutic avenue for treating gout, providing relief from the intense joint pain and inflammation associated with the condition.
Exercise and Weight Management
Regular physical activity and maintaining a healthy weight help improve insulin sensitivity, reduce inflammation, and lower the risk of metabolic conditions that contribute to gout.
However, sudden intense physical activity may trigger gout attacks, so exercise should be moderate and consistent.
Conclusion
Gout is a painful condition rooted in metabolic imbalances and high uric acid levels. While often misunderstood, the primary contributors to gout are fructose consumption and metabolic dysfunction, not red meat. Managing gout requires a combination of dietary changes, medication when needed, and long-term lifestyle adjustments that target the root causes of elevated uric acid. By focusing on reducing fructose intake and optimizing metabolic health, individuals can effectively manage and prevent gout flare-ups.
FAQs
What causes gout?
Gout is caused by the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints, often triggered by metabolic issues, fructose consumption, and impaired kidney function.
Is red meat a cause of gout?
No, red meat is not a primary cause of gout. The real culprit is excessive fructose consumption, which raises uric acid levels.
How can I prevent gout flare-ups?
Prevent gout flare-ups by reducing sugar and fructose intake, staying hydrated, maintaining a healthy weight, and following a nutrient-dense diet.
What is the role of fructose in gout?
Fructose is metabolized into uric acid, which contributes to gout development. Limiting sugary drinks and processed foods helps manage uric acid levels.
Can gout be cured?
While there is no cure for gout, it can be effectively managed through lifestyle changes, proper diet, and medications that reduce uric acid levels
Research
Ayoub-Charette S, Liu Q, Khan TA, Au-Yeung F, Blanco Mejia S, de Souza RJ, Wolever TM, Leiter LA, Kendall C, Sievenpiper JL. Important food sources of fructose-containing sugars and incident gout: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. BMJ Open. 2019 May 5;9(5):e024171. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-024171. PMID: 31061018; PMCID: PMC6502023.
Bai, L., Zhou, J.-B., Zhou, T., Newson, R.B. and Cardoso, M.A., 2021. Incident gout and weight change patterns: a retrospective cohort study of US adults. Arthritis Research & Therapy, [online] 23(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-021-02461-7.
Basaranoglu, M., Basaranoglu, G., & Bugianesi, E. (2015). Carbohydrate intake and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Fructose as a weapon of mass destruction. Hepatobiliary Surgery and Nutrition, 4(2), 109-116. https://doi.org/10.3978/j.issn.2304-3881.2014.11.05
Cristina, M. (2023). Insulin and the kidneys: A contemporary view on the molecular basis. Frontiers in Nephrology, 3, 1133352. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneph.2023.1133352
Ghio, A.J., Ford, E.S., Kennedy, T.P. and Hoidal, J.R., 2005. The association between serum ferritin and uric acid in humans. Free Radical Research, [online] 39(3), pp.337–342. https://doi.org/10.1080/10715760400026088.
Goldberg, E. L., Asher, J. L., Molony, R. D., Shaw, A. C., Zeiss, C. J., Wang, C., Morozova-Roche, L. A., Herzog, R. I., Iwasaki, A., & Dixit, V. D. (2017). β-hydroxybutyrate deactivates neutrophil NLRP3 inflammasome to relieve gout flares. Cell Reports, 18(9), 2077. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2017.02.004
Jamnik, J., Rehman, S., Blanco Mejia, S., de Souza, R.J., Khan, T.A., Leiter, L.A., Wolever, T.M.S., Kendall, C.W.C., Jenkins, D.J.A. and Sievenpiper, J.L., 2016. Fructose intake and risk of gout and hyperuricemia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. BMJ Open, [online] 6(10), p.e013191. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2016-013191.
Lanaspa, M.A., Sanchez-Lozada, L.G., Cicerchi, C., Li, N., Roncal-Jimenez, C.A., Ishimoto, T., Le, M., Garcia, G.E., Thomas, J.B., Rivard, C.J., Andres-Hernando, A., Hunter, B., Schreiner, G., Rodriguez-Iturbe, B., Sautin, Y.Y. and Johnson, R.J., 2012. Uric Acid Stimulates Fructokinase and Accelerates Fructose Metabolism in the Development of Fatty Liver. PLoS ONE, [online] 7(10), p.e47948. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0047948.
Lanaspa, M.A., Tapia, E., Soto, V., Sautin, Y. and Sánchez-Lozada, L.G., 2011. Uric Acid and Fructose: Potential Biological Mechanisms. Seminars in Nephrology, [online] 31(5), pp.426–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semnephrol.2011.08.006.
Maiuolo, J., Oppedisano, F., Gratteri, S., Muscoli, C. and Mollace, V., 2016. Regulation of uric acid metabolism and excretion. International Journal of Cardiology, [online] 213, pp.8–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2015.08.109.
Mainous, A.G., Knoll, M.E., Everett, C.J., Matheson, E.M., Hulihan, M.M. and Grant, A.M., 2011. Uric Acid as a Potential Cue to Screen for Iron Overload. The Journal of the American Board of Family Medicine, [online] 24(4), pp.415–421. https://doi.org/10.3122/jabfm.2011.04.110015.
Muscelli, E., 1996. Effect of insulin on renal sodium and uric acid handling in essential hypertension. American Journal of Hypertension, [online] 9(8), pp.746–752. https://doi.org/10.1016/0895-7061(96)00098-2.
Nakagawa, T., Lanaspa, M. A., & Johnson, R. J. (2019). The effects of fruit consumption in patients with hyperuricaemia or gout. Rheumatology, 58(7), 1133-1141. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kez128
Pina, A.F., Borges, D.O., Meneses, M.J., Branco, P., Birne, R., Vilasi, A. and Macedo, M.P., 2020. Insulin: Trigger and Target of Renal Functions. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology, [online] 8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2020.00519.
Rasool, M., Malik, A., Jabbar, U., Begum, I., Qazi, M.H., Asif, M., Naseer, M.I., Ansari, S.A., Jarullah, J., Haque, A. and Jamal, M.S., 2016. Effect of iron overload on renal functions and oxidative stress in beta thalassemia patients. Saudi Medical Journal, [online] 37(11), pp.1239–1242. https://doi.org/10.15537/smj.2016.11.16242.
Rho, Y.H., Zhu, Y. and Choi, H.K., 2011. The Epidemiology of Uric Acid and Fructose. Seminars in Nephrology, [online] 31(5), pp.410–419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semnephrol.2011.08.004.
Singh, J.A., Reddy, S.G. and Kundukulam, J., 2011. Risk factors for gout and prevention: a systematic review of the literature. Current Opinion in Rheumatology, [online] 23(2), pp.192–202. https://doi.org/10.1097/bor.0b013e3283438e13.
Skøtt, P., Hother-Nielsen, O., Bruun, N.E., Giese, J., Nielsen, M.D., Beck-Nielsen, H. and Parving, H.-H., 1989. Effects of insulin on kidney function and sodium excretion in healthy subjects. Diabetologia, [online] 32(9). https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00274259.
Wang, Y., Yang, Z., Wu, J., Xie, D., Yang, T., Li, H. and Xiong, Y., 2020. Associations of serum iron and ferritin with hyperuricemia and serum uric acid. Clinical Rheumatology, [online] 39(12), pp.3777–3785. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-020-05164-7.
Yamanaka H. [Alcohol ingestion and hyperuricemia]. Nihon Rinsho. 1996 Dec;54(12):3369-73. Japanese. PMID: 8976122.
0 notes
Text
Ayurvedic Remedies for Managing Uric Acid and Gout

These treatments help to reduce uric acid levels, relieve joint pain, and improve immunity in a natural way. Hyperuricemia, or high uric acid, develops when the crystals formed from the acid accumulate in the joints, resulting in inflammation, pain, and potentially serious consequences. When the kidneys fail to efficiently get rid of uric acid, which is a product of purine from food, the uric acid gets stored in the joints, chiefly the big toe, midfoot, ankle, and knees.
The ancient Indian healing system of Ayurveda focuses on balancing the body’s doshas (Vata, Pitta, and Kapha) with food, lifestyle, and herbal medicines. Vata imbalance is mainly responsible for the increase in uric acid and it occurs due to wrong dietary habits and sedentary lifestyle. Ayurveda brings the doshas back to balance with the use of herbal remedies and changes in lifestyle to treat the root causes of gout and uric acid buildup.
The Essential Ayurvedic Treatments for Uric Acid and Gout
Triphala
Triphala is a combination of three fruits—amla, bibhitaki, and haritaki—that is commonly considered useful for digestion and detoxification. Triphala is an ancient ayurvedic remedy revered for its ability to balance the doshas, so it may be able to lower inflammation associated with gout. Although some animal studies have shown anti-inflammatory effects, more research is needed to confirm its safety and efficacy in humans.
Giloy
Giloy is a powerful herb known as one of the natural remedies in Ayurveda that neutralizes high uric acid levels. Animal studies have shown that it has anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving properties, which may help relieve discomfort from gout. However, more human studies are warranted to confirm its effectiveness in regulating uric acid.
Neem
Yet another herb from Ayurveda—Neem—is effective in reducing inflammation as well. It is frequently utilized to relieve gout attacks, and neem paste can be applied to the afflicted area to alleviate pain. Indeed, science has backed neem's anti-inflammatory properties, although there is little direct evidence connecting neem to lowered uric acid.
Bitter Gourd
Bitter gourd, an ancient plant used in Ayurveda to balance Vata, is occasionally used in treating gout. Although bitter gourd has a long history of use, there is currently no scientific evidence to show that it works to lower uric acid or treat symptoms of gout.
Turmeric
Turmeric, known for its anti-inflammatory ingredient curcumin, is a potent Ayurvedic remedy for joint health. Research has found that curcumin is beneficial for arthritis and can reduce symptoms associated with it, including gout. While turmeric helps reduce inflammation, it does not lower uric acid levels. It is an easy enough spice to add to dishes, or many people drink it in the form of “golden milk” or haldi doodh.
As a complete approach to gout, the Ayurvedic philosophy heals through dietary changes, lifestyle modifications, and consistent herbal support. By correcting the Vata imbalance that leads to increased uric acid levels, these treatments work to relieve symptoms and bring long-term health.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Uric Acid 101: 10 Common Questions and Brief Answers
What it is, why should we care, and what can we do In my community seminars one of the frequently asked questions by seniors is about painful gout. Some of them heard about uric acid on TV shows or YouTube videos and want to learn what it is, how can they balance it, and how they deal with effectively. In this short post I will provide a summary of my answers in simple words hoping it can…
#Foods to Avoid for High Uric Acid#Gout Pain Relief Tips#How to Reduce Uric Acid Naturally#Kidney Stones and Uric Acid#Lifestyle Changes to Lower Uric Acid#Mental Health and Uric Acid Levels#Signs of High Uric Acid Levels#Uric Acid and Health#Uric Acid and Heart Health#Uric Acid Management Guide
1 note
·
View note
Text
Foods to Avoid for Controlling Uric Acid Levels
Uric acid is a natural by-product of digesting purine-rich foods. Normally, kidneys filter and remove uric acid from the body. However, when uric acid levels become too high, conditions like hyperuricemia and gout can develop. Managing these conditions starts with understanding which foods to avoid. ROLE OF URIC ACID IN THE BODY Uric acid is created when the body breaks down purines, found in…
0 notes
Text
Foods to Avoid for Controlling Uric Acid Levels
Uric acid is a natural by-product of digesting purine-rich foods. Normally, kidneys filter and remove uric acid from the body. However, when uric acid levels become too high, conditions like hyperuricemia and gout can develop. Managing these conditions starts with understanding which foods to avoid. ROLE OF URIC ACID IN THE BODY Uric acid is created when the body breaks down purines, found in…
0 notes
Text
Best Kidney Stone Treatment in Kota
Kidney stones are a common health issue that can cause severe pain and discomfort if left untreated. Kota, a vibrant city in Rajasthan, offers a range of high-quality medical facilities and experienced professionals for kidney stone treatment. Choosing the best treatment option involves understanding the types of kidney stones, the severity of the condition, and the available medical solutions tailored to each patient. Here, we’ll explore the most effective treatments for kidney stones in Kota, focusing on the latest advancements and highly recommended medical facilities.

Understanding Kidney Stones and Their Types
Kidney stones are solid deposits made up of minerals and salts that form in the kidneys. They vary in size, composition, and symptoms, and can sometimes pass naturally through the urinary tract. However, in cases where stones are too large or cause intense pain, medical intervention becomes necessary. There are four primary types of kidney stones:
Calcium Stones: The most common type, often formed due to high calcium intake or oxalate levels.
Struvite Stones: Linked to urinary tract infections, these stones can grow rapidly.
Uric Acid Stones: Common in individuals with high protein intake or dehydration issues.
Cystine Stones: Rare, often resulting from genetic disorders affecting amino acid levels.
In Kota, doctors first evaluate the type and size of the kidney stone before recommending a treatment plan that may include non-invasive methods, advanced surgical options, or lifestyle changes to prevent recurrence.
Top Treatments for Kidney Stones in Kota
Medication and Lifestyle Adjustments: For smaller kidney stones, doctors in Kota often start with conservative treatments. Patients may be advised to increase water intake, change their diet, and take prescribed medications that help dissolve stones or ease their passage through the urinary tract. Pain relief medication is also prescribed to manage discomfort. Urologists may suggest lifestyle adjustments to reduce recurrence, like minimizing salt intake and avoiding foods high in oxalates.
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL): ESWL is a popular, non-invasive procedure for breaking down small-to-medium-sized kidney stones using shock waves. This treatment is generally recommended for stones that are unlikely to pass naturally. During the procedure, high-energy waves are directed toward the kidney stone, fragmenting it into smaller pieces that can be passed in urine. Many hospitals in Kota offer ESWL as a safe, outpatient procedure, allowing patients to resume daily activities quickly.
Ureteroscopy (URS): For medium-sized stones lodged in the ureter, ureteroscopy is often recommended. In this minimally invasive procedure, a small, flexible tube (ureteroscope) is inserted through the urethra to locate and remove the stone. The procedure is effective and typically requires only a short hospital stay. Kota’s leading urology centers offer ureteroscopy with advanced laser technology, ensuring minimal discomfort and high success rates.
Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL): PCNL is a more invasive option for treating large or complex kidney stones. This procedure involves creating a small incision in the back to access and remove the stone. It’s typically recommended for patients with larger stones that cannot be treated with ESWL or ureteroscopy. Kota’s specialized urology hospitals employ skilled surgeons for PCNL, using state-of-the-art equipment to minimize risks and promote faster recovery.
Laser Lithotripsy: For patients with smaller stones, laser lithotripsy is a precise and effective solution. Using a laser fiber, doctors can break the stone into smaller fragments, making it easier for the body to eliminate. This advanced procedure is becoming increasingly popular in Kota’s top hospitals due to its accuracy, minimal discomfort, and faster recovery.
Why Kota is an Excellent Choice for Kidney Stone Treatment
Kota has made significant advancements in healthcare over recent years, especially in urology and kidney treatments. The city hosts several well-equipped hospitals and clinics, staffed by qualified urologists and equipped with cutting-edge technology for kidney stone treatment. Facilities such as Sudha Hospital, Amar Medical Centre, and SR Kalla Memorial Hospital offer a range of specialized services, personalized care, and a patient-centered approach. Our services in Best Kidney Stone Treatment in Kota.
Conclusion
Kidney stone treatment in Kota encompasses a wide array of options, from medication and dietary modifications to advanced, minimally invasive procedures. By consulting with a skilled urologist and choosing a reputable medical facility, patients can access the best treatment tailored to their needs and lifestyle, ensuring quicker recovery and reduced recurrence.
0 notes
Text
Conquer Kidney Stones: Your Comprehensive Guide to Urology Treatment
Kidney stones are not just a health inconvenience; they can be incredibly painful and, if left untreated, lead to serious complications. Urology treatment for kidney stones has evolved significantly over the years, offering patients a range of options to manage and eliminate these hard deposits effectively. Understanding the various types of kidney stones, their causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for anyone looking to conquer this ailment.
Kidney stones form when minerals and salts in the urine crystallize and harden. The causes can vary widely, including dietary factors, dehydration, and metabolic issues. While some stones may pass naturally, others may require medical intervention. The experience of suffering from kidney stones can range from mild discomfort to excruciating pain, often manifesting in the lower back, abdomen, or groin.
This comprehensive guide will explore the intricacies of urology treatment for kidney stones, aiming to arm you with the knowledge necessary to make informed decisions regarding your health. From preventive measures and lifestyle changes to advanced surgical options, we will cover it all. Whether you’re dealing with your first kidney stone or are a recurrent sufferer, understanding urology treatment can help you take control of your condition and improve your quality of life.
Quick Data Point
Type of Kidney Stone CompositionPrevalence (%)SymptomsCalcium OxalateCalcium and Oxalate80%Severe pain, hematuria, nauseaUric AcidUric Acid5-10%Painful urination, swellingStruviteMagnesium Ammonium Phosphate10-15%Fever, chills, flank painCystineCystine<1%Frequent urination, abdominal pain
Urology Treatment for Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are a common urological issue, and urology treatment offers various methods to alleviate symptoms and prevent recurrence. Understanding these treatments can help you choose the best path for your specific needs.
Understanding Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are hard deposits made of minerals and salts that form inside your kidneys. They can vary in size from a grain of sand to a golf ball. Here's a deeper dive into the types of kidney stones and their unique characteristics.
Types of Kidney Stones
Calcium Oxalate Stones
Formation: These stones form when calcium in the urine combines with oxalate, a substance found in various foods.
Causes: Often linked to dietary factors such as high intake of oxalate-rich foods (spinach, nuts) or insufficient calcium intake.
Uric Acid Stones
Formation: These occur when urine is too acidic.
Causes: High protein diets, dehydration, and conditions that increase uric acid levels (like gout).
Struvite Stones
Formation: Form as a response to urinary tract infections.
Causes: Bacterial infections that raise urine pH, leading to the crystallization of struvite.
Cystine Stones
Formation: These are rare and occur due to a genetic disorder that causes the kidneys to excrete too much cystine.
Causes: Genetic factors that lead to high levels of cystine in the urine.
Symptoms of Kidney Stones
Recognizing the symptoms of kidney stones early can lead to more effective urology treatment. Symptoms may include:
Severe Pain: Often described as the worst pain ever experienced, typically starting in the back and radiating to the lower abdomen and groin.
Hematuria: Blood in the urine, which may appear pink, red, or brown.
Frequent Urination: A feeling of urgency or the need to urinate more often than usual.
Nausea and Vomiting: Commonly occurs due to pain or as a reaction to kidney issues.
Infections: Symptoms like fever and chills can indicate a urinary tract infection.
Diagnosis of Kidney Stones
Effective urology treatment begins with accurate diagnosis. The following methods are commonly used to diagnose kidney stones:
Medical History and Physical Exam
Doctors assess symptoms and medical history, focusing on dietary habits and family history of kidney stones.
Imaging Tests
CT Scans: Highly effective for detecting kidney stones.
Ultrasound: Useful for those who wish to avoid radiation exposure.
X-rays: May identify larger stones but are less effective for smaller ones.
Urine Tests
A 24-hour urine collection can help identify the type of stones and any risk factors present.
Blood Tests
These tests measure kidney function and check for excess calcium, uric acid, or other substances that may contribute to stone formation.
Urology Treatment Options for Kidney Stones
Once diagnosed, various urology treatment options can be employed based on the size, type, and location of the kidney stone.
1. Conservative Management
For small kidney stones, conservative management may be the best course of action. This includes:
Hydration: Increasing fluid intake helps flush out the stones.
Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can alleviate discomfort.
Monitoring: Regular follow-ups to monitor the stone's progression.
2. Medications
Certain medications can facilitate the passage of stones or prevent their formation:
Alpha-blockers: These relax the muscles in the ureter, helping stones pass more easily.
Thiazide diuretics: Can help prevent calcium stones in those with high calcium levels in urine.
3. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL)
This non-invasive procedure uses sound waves to break stones into smaller pieces that can be passed naturally. Key points include:
Indications: Best suited for stones smaller than 2 cm.
Recovery: Generally minimal downtime, allowing patients to return to normal activities quickly.
4. Ureteroscopy
This technique involves inserting a thin tube through the urethra and bladder into the ureter to remove or break up the stone.
Advantages: Effective for larger stones or those lodged in the ureter.
Considerations: May require anesthesia and a short recovery period.
5. Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL)
This minimally invasive surgery is performed for large or complex stones, typically over 2 cm.
Procedure: A small incision is made in the back, and instruments are used to remove the stone.
Recovery: Longer recovery time compared to other methods, with potential for complications.
6. Dietary and Lifestyle Changes
Preventive measures are crucial for reducing the risk of kidney stones. Consider the following:
Hydration: Aim for at least 2-3 liters of water daily.
Dietary Adjustments: Reduce sodium, animal protein, and oxalate-rich foods; increase fruits and vegetables.
Regular Exercise: Helps maintain a healthy weight and reduce the risk of stones.
Complications of Kidney Stones
While kidney stones can often be treated effectively, complications may arise if left untreated, including:
Infections: Urinary tract infections can occur due to obstruction.
Kidney Damage: Prolonged blockage can lead to kidney impairment.
Recurrence: Without lifestyle changes, kidney stones are likely to recur.
When to Seek Medical Attention
It's essential to seek urology treatment when experiencing symptoms such as:
Severe Pain: Unrelenting pain that doesn’t subside.
Signs of Infection: Fever, chills, or persistent nausea and vomiting.
Difficulty Passing Urine: Inability to urinate or significant changes in urination patterns.
Living with Kidney Stones
Managing kidney stones is not just about treatment; it also involves making lifestyle adjustments to prevent recurrence. Here are some strategies:
1. Regular Check-ups
Regular visits to a urologist can help monitor kidney health and detect issues early.
2. Staying Hydrated
Maintain proper hydration levels, especially in hot weather or during physical activity.
3. Balanced Diet
Focus on a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, while avoiding excessive salt and sugar.
4. Educating Yourself
Understanding your condition and potential triggers can empower you to make informed choices about your health.
Conclusion
Urology treatment for kidney stones is a multifaceted approach that combines immediate management, ongoing care, and lifestyle modifications. Whether you're experiencing your first stone or have been dealing with recurrent issues, a proactive approach can significantly improve your quality of life. By understanding the types of kidney stones, symptoms, and available treatment options, you can take charge of your health.
If you suspect you have kidney stones or are experiencing symptoms, don't hesitate to consult a healthcare professional. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and pave the way for a healthier future. For specialized care, consider visiting an urologist in Bahrain to explore your treatment options.
Through education, awareness, and the right medical guidance, you can conquer kidney stones and live a more comfortable life.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Kidney Stones: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment
What is Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are hard mineral and salt deposits that form in the kidneys, often resulting from high levels of certain substances in urine, such as calcium, oxalate, and uric acid. They can vary in size and may be as small as a grain of sand or as large as a golf ball. Kidney stones can cause significant pain, particularly when they move through the urinary tract, leading to symptoms like intense discomfort, blood in urine, nausea, and frequent urination. Treatment options include hydration, pain management, and sometimes surgical procedures to remove larger stones.
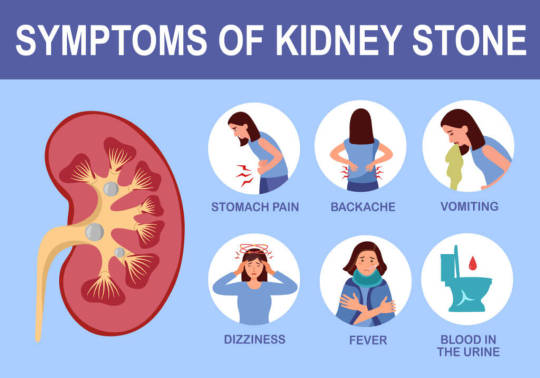
How common are kidney stones?
Kidney stones are relatively common, with an estimated occurrence in about 10-15% of people at some point in their lives. The prevalence can vary based on factors such as geographic location, diet, and genetics. They are more frequently found in men than women, and certain age groups, typically adults between 30 and 60 years old, are at higher risk. The recurrence rate is also notable, with many individuals experiencing multiple episodes over their lifetime.
What are the symptoms of kidney stones?
The symptoms of kidney stones can vary depending on the size and location of the stone, but common signs include severe pain in the lower back or side, which may radiate to the abdomen and groin; blood in the urine (hematuria); frequent urination; a strong urge to urinate; nausea or vomiting; and cloudy or foul-smelling urine. Some individuals may also experience discomfort during urination or a urinary tract infection. The pain often comes in waves and may change in intensity as the stone moves through the urinary tract.
Other kidney stone symptoms include:
Nausea and vomiting.
Bloody pee.
Pain when you pee.
Inability to pee.
Feeling the urge to pee a lot.
Fever or chills.
Cloudy or foul-smelling pee.
What causes kidney stones?
Kidney stones are formed when the urine becomes concentrated with certain substances, leading to the crystallization of minerals. Common causes include dehydration, which results in concentrated urine; dietary factors, such as high intake of oxalate (found in foods like spinach and chocolate) and sodium; metabolic disorders that affect the balance of minerals;
obesity; certain medical conditions like hyperparathyroidism; and a family history of kidney stones. Additionally, certain medications and supplements can contribute to stone formation.
Each type has different causes and may require different treatment approaches.
How are kidney stones diagnosed?
Treatment for kidney stones depends on their size, location, and the severity of symptoms. For small stones, drinking plenty of fluids may help in passing them naturally, along with pain management. Larger stones might require medical interventions such as extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL), which uses shock waves to break stones into smaller pieces, or ureteroscopy, where a thin tube is inserted to remove the stone. In some cases, particularly with very large stones, a procedure called percutaneous nephrolithotomy may be necessary, involving surgical removal through a small incision in the back. Preventive measures, including dietary changes and medications, may also be recommended to reduce the risk of recurrence.
RIRS, or Retrograde Intrarenal Surgery - is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat kidney stones that are located in the renal pelvis or calyces. During RIRS, a flexible ureteroscope is inserted through the urinary tract up to the kidney, allowing the surgeon to visualize and access the stones. Once located, stones can be broken up using laser energy or removed using small instruments. RIRS is particularly beneficial for patients with smaller stones or those who have not had success with other treatments, as it allows for effective stone removal with reduced recovery time and minimal complications.
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL): A non-invasive method that uses shock waves to break stones into smaller fragments that can be passed through urine.
Ureteroscopy: Involves the insertion of a thin, flexible tube through the urethra and bladder into the ureter to remove or break up stones, often using lasers.
Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL): A minimally invasive surgery where a small incision is made in the back to directly access and remove larger stones.
Cystoscopic Laser Lithotripsy (CLT) is a simple and gentle way to treat bladder stones. During the procedure, a thin, lighted tool called a cystoscope is inserted through the urethra into the bladder to see the stone. A laser is then used to break the stone into smaller pieces, making it easier to pass out during urination or to remove with a small basket. CLT is less invasive than traditional open surgery, causing less discomfort and allowing for a faster recovery.
It's essential to consult with a urologist surgeon for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan for your specific case of Stone. Type, Size and Location
Consult wellsun medicity discuss your risk factors and develop a personalized plan to reduce your risk.
Wellsun Medicity Multispecialty Hospital
www.wellsunmedicity.com
Dr. Neeraj Agarwal
MBBS (KGMU) MS General Surgeon
M.CH Urologist, Kidney Transplant Surgery
Call: +91-8810787432
#best hospital for heart surgery in lucknow#best cardiology hospital in lucknow#best mics surgeon in lucknow#best cardiac surgeon in lucknow#best open heart surgeory in lucknow#best hospital for respiratory diseases in gonda#best neuro hospital in lucknow#best cardiac hospital in lucknow#best angioplasty in lucknow#best cardiologist in lucknow
0 notes
Text
Expert Kidney Stone Specialist in Patna: Comprehensive Care for Lasting Relief
Kidney stones are a painful yet treatable condition that can disrupt your daily life. Ignoring the symptoms can lead to severe complications, such as infections or permanent kidney damage. If you are experiencing symptoms, consulting a kidney stone specialist in Patna ensures timely diagnosis, advanced treatments, and long-term relief. This blog will provide insights into causes, symptoms, treatments, and how to find the right specialist in Patna to meet your healthcare needs.
What Are Kidney Stones?
Kidney stones are solid deposits formed from minerals and salts that build up in the kidneys. Depending on their size, some stones pass naturally through the urinary tract, while others can block urine flow and cause significant pain. The guidance of a kidney stone specialist in Patna helps ensure that you receive personalised treatment and preventive care.
Types of Kidney Stones
A kidney stone specialist in Patna will determine the type of stone to tailor the treatment effectively. The main types include:
Calcium Stones: Formed from calcium oxalate or phosphate, these are the most common.
Uric Acid Stones: Often linked with high protein intake and dehydration.
Struvite Stones: Typically caused by urinary infections.
Cystine Stones: A rare genetic disorder causes these stones to form.
Understanding the type of stone is critical for long-term prevention, and your kidney stone specialist in Patna will guide you on managing the underlying causes.
Causes of Kidney Stones
Several factors increase the risk of developing kidney stones, including:
Dehydration: Not drinking enough water causes minerals to accumulate.
Diet: High salt, sugar, or oxalate-rich foods contribute to stone formation.
Obesity: Increased body weight can alter metabolic processes, leading to stone development.
Genetics: A family history of kidney stones raises your risk.
A kidney stone specialist in Patna will thoroughly assess these factors and recommend lifestyle changes to prevent recurrence.
Symptoms of Kidney Stones
Recognizing the symptoms early can prevent complications. Consult a kidney stone specialist in Patna if you experience:
Severe pain in the back or side (flank pain)
Pain while urinating or a burning sensation
Blood in urine (pink or reddish discoloration)
Nausea and vomiting
Frequent urge to urinate but little output
Fever and chills (if infection is present)
The pain associated with kidney stones can be intense and may fluctuate as the stone moves through the urinary tract. If you encounter any of these symptoms, seeking immediate help from a kidney stone specialist in Patna is crucial.
Diagnostic Techniques Used by Specialists
A kidney stone specialist in Patna will use several diagnostic methods to detect stones, including:
Urinalysis: Checks for infection, minerals, or crystals in urine.
Blood Tests: Measures calcium and uric acid levels.
Ultrasound: Non-invasive imaging to locate stones.
CT Scan: Provides detailed images of the urinary system.
X-Ray: Detects large stones in the kidneys or bladder.
These tests help the specialist decide on the best treatment approach for your condition.
Advanced Treatment Options in Patna
Treatment varies depending on the size and location of the stone. A kidney stone specialist in Patna offers several advanced procedures:
1. Medications
For small stones, doctors may prescribe pain relievers and muscle relaxants to help the stone pass naturally.
2. Shock Wave Lithotripsy (SWL)
This non-invasive treatment uses sound waves to break the stone into smaller fragments.
3. Ureteroscopy
A thin tube with a camera is inserted to locate and remove stones directly.
4. Laser Lithotripsy
Laser technology breaks down stones into tiny pieces for easier passage.
5. Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL)
For larger stones, this surgical method removes the stone through a small incision in the back.
A kidney stone specialist in Patna will recommend the most suitable treatment based on your condition.
Post-Treatment Recovery and Prevention
After treatment, it’s essential to follow your specialist's advice to prevent future occurrences. Here are some tips from a kidney stone specialist in Patna:
Stay Hydrated: Drink at least 2-3 liters of water daily.
Modify Your Diet: Avoid foods high in salt and oxalates.
Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity increases the risk of stones.
Regular Check-Ups: Periodic consultations with a kidney stone specialist in Patna will help monitor your health and detect potential recurrences early.
Choosing the Right Kidney Stone Specialist in Patna
Finding the best kidney stone specialist in Patna ensures you receive effective and timely care. Here are some tips to help you choose the right doctor:
Experience and Expertise: Look for a specialist with a proven track record in treating kidney stones.
Hospital Affiliation: Ensure the doctor is associated with reputable hospitals.
Patient Reviews: Check online reviews to gauge patient satisfaction.
Comprehensive Care: The best specialists offer personalized treatment plans and preventive care advice.
Leading Hospitals for Kidney Stone Treatment in Patna
Several top hospitals in Patna provide advanced kidney stone treatment. Some of the most renowned include:
Satyadev Superspeciality Hospital
Paras HMRI Hospital
Ruban Memorial Hospital
Medica Magadh Hospital
These hospitals are equipped with modern technology and staffed with experienced kidney stone specialists in Patna to ensure quality care.
Cost of Kidney Stone Treatment in Patna
The cost of treatment depends on the procedure and hospital. Here is an approximate range:
Shock Wave Lithotripsy (SWL): ₹40,000 - ₹60,000
Ureteroscopy: ₹60,000 - ₹80,000
Laser Lithotripsy: ₹70,000 - ₹90,000
Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL): ₹1,00,000 - ₹1,50,000
Most insurance plans cover kidney stone treatments. Consult with your insurer and your kidney stone specialist in Patna for more information.
Conclusion
Kidney stones can cause extreme discomfort, but effective treatment is available. Consulting a kidney stone specialist in Patna ensures that you receive the best possible care, from diagnosis to post-treatment guidance. With modern techniques like laser lithotripsy and SWL, specialists can relieve your pain and prevent future recurrences.Don’t wait for the symptoms to worsen—schedule an appointment with a kidney stone specialist in Patna today and take the first step towards a healthier, pain-free life.
0 notes
Text
🌿 Natural Treatment for Kidney Stones: A Comprehensive Guide to Relief and Prevention

Kidney stones are incredibly painful and can disrupt your day-to-day life. If you're looking for alternatives to medical interventions, natural treatment for kidney stones , then you may visit https://moonstonenutrition.com/ which offers several effective options. These remedies can help relieve discomfort, prevent new stones from forming, and support kidney health overall.
Understanding Kidney Stones 🩺
Kidney stones form when minerals, like calcium or uric acid, crystallize in the kidneys and can block the urinary tract. Common symptoms include severe pain, nausea, and difficulty urinating. While medical treatment is often necessary for larger stones, smaller stones may pass with proper self-care and the use of natural remedies.
Hydration is Key 💧
One of the most important factors in preventing kidney stones is staying hydrated. Dehydration can cause minerals to crystallize, leading to stone formation. Here are some hydration tips:
Drink at least 8-10 glasses of water a day to flush out your kidneys and urinary tract.
Add lemon juice to your water. The citric acid can help break down small stones and prevent new ones from forming.
Consider coconut water for an added hydration boost. Coconut water is not only hydrating but can also help balance electrolyte levels, reducing the risk of stone formation.
Dietary Adjustments for Kidney Health 🥦

Your diet plays a significant role in both preventing and managing kidney stones. By making a few tweaks to your meals, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing stones. Here are some dietary recommendations:
Limit oxalate-rich foods, such as spinach, beets, nuts, and chocolate, as they can contribute to stone formation.
Increase calcium intake (through food, not supplements) to bind oxalate in the gut and prevent it from being absorbed into the bloodstream. Dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified plant-based alternatives are excellent sources of calcium.
Cut back on sodium to lower calcium levels in your urine. High salt levels in your diet can increase the chances of forming stones.
Include more foods rich in magnesium like bananas, avocados, and legumes to balance minerals and reduce stone risk.
Herbal Remedies for Kidney Stones 🌿
Several herbal remedies are believed to help with kidney stones by either reducing their formation or assisting in their breakdown. Here are a few that are commonly used:
Chanca Piedra ("stone breaker"): This Amazonian herb is widely known for its ability to help break down kidney stones and promote their passage through the urinary tract.
Dandelion root: A natural diuretic that can increase urine production and help flush out small stones.
Nettle leaf: Known for its anti-inflammatory properties, nettle leaf can promote healthy fluid flow through the kidneys and prevent new stones from forming.
Apple Cider Vinegar for Stone Dissolution 🍎
Apple cider vinegar (ACV) contains acetic acid, which can help soften and break down kidney stones. Here’s how to use it:
Mix 2 tablespoons of apple cider vinegar with water and drink it once or twice a day.
Add a dash of honey for taste if the vinegar is too strong.
ACV also has alkalizing effects, which can help prevent future stones from forming by balancing your body's pH levels.
The Power of Basil and Celery 🍃
Basil and celery are two plants that can help promote kidney health:
Basil juice: Drinking basil tea or juice may help dissolve kidney stones and reduce pain. Basil is rich in acetic acid, which is believed to help break down stones.
Celery juice: Known for its diuretic properties, celery juice may encourage the expulsion of kidney stones by increasing urine production.
Exercise and Movement 🏃♂️
Physical activity can also aid in the passage of small kidney stones. Moderate exercises like walking or light jogging can stimulate kidney function and help move stones through your system more quickly. However, avoid heavy exercise if you are in severe pain, as it may exacerbate your symptoms.
When to Seek Medical Attention 🚑
While natural treatments can help with smaller kidney stones or prevent new ones from forming, it's important to recognize when medical intervention is necessary. Seek medical help if you:
Experience intense pain that doesn’t improve with natural remedies.
Notice blood in your urine.
Have a fever or chills, which may indicate an infection.
In cases where stones are too large to pass naturally, medical treatments like shock wave therapy or surgery may be required.
Preventing Future Stones 🛡️
Prevention is always better than cure. To reduce your risk of developing kidney stones again:
Stay hydrated throughout the day.
Follow a balanced diet that includes low sodium and moderate calcium intake.
Avoid foods that are high in oxalates and incorporate citrus fruits into your meals.
For more comprehensive insights into alleviating kidney stone pain and natural remedies, explore this informative guide on natural treatment for kidney stones. It covers more holistic approaches and tips for maintaining kidney health!
Conclusion 💡

Kidney stones are undoubtedly painful, but the natural treatments listed here may provide relief and prevent future stones from forming. By staying hydrated, adjusting your diet, and incorporating herbal remedies and natural detoxifiers like apple cider vinegar, you can support your body in breaking down and passing stones naturally. Always remember to consult your healthcare provider if symptoms worsen or if stones are too large to pass on their own. Click here to know more about natural treatment for kidney stones.
0 notes