#Lipopolysaccharides
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Considering murder because i'm in google looking for a diagram of a lipopolysaccharide in the gram negative bacterial cell wall.
And google is like "did you mean polysaccharide?" and it only displays polysaccharides in the search results.
And so I go and I make the search term "lipopolysaccharide" in quotations. and it says "did you mean "polysaccharide"?"
And I understand I could search for endotoxin but it's the principle of the thing I want the search engine to search the word I give it! not something approximate! Google should consider the concept that LPSs exist, and putting search terms in quotations should work!
so when the google servers are destroyed tomorrow in an arson attack at 2PM GMT+8, It wasn't me that did it but I really wish it was.
#google#search engine#lipopolysaccharides#Tumblr has that tag for it autofilled??!?!??? fuck you google search engine!#and don't even get me started on how boolean operators are useless now
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Lipopolysaccharides Immunoassay Market
#Lipopolysaccharides Immunoassay Market#Lipopolysaccharides#Market#Lipopolysaccharides Immunoassay#Immunoassay
0 notes
Link
Abstract
There is a link between high lipopolysaccharide (LPS) levels in the blood and the metabolic syndrome, and metabolic syndrome predisposes patients to severe COVID-19. Here, we define an interaction between SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) protein and LPS, leading to aggravated inflammation in vitro and in vivo. Native gel electrophoresis demonstrated that SARS-CoV-2 S protein binds to LPS. Microscale thermophoresis yielded a KD of ∼47 nM for the interaction. Computational modeling and all-atom molecular dynamics simulations further substantiated the experimental results, identifying a main LPS-binding site in SARS-CoV-2 S protein. S protein, when combined with low levels of LPS, boosted nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) activation in monocytic THP-1 cells and cytokine responses in human blood and peripheral blood mononuclear cells, respectively. The in vitro inflammatory response was further validated by employing NF-κB reporter mice and in vivo bioimaging. Dynamic light scattering, transmission electron microscopy, and LPS-FITC analyses demonstrated that S protein modulated the aggregation state of LPS, providing a molecular explanation for the observed boosting effect. Taken together, our results provide an interesting molecular link between excessive inflammation during infection with SARS-CoV-2 and comorbidities involving increased levels of bacterial endotoxins.
0 notes
Text
Fever
I see a lot of misconceptions about fever floating around the web, so I'm gonna try and set some things straight. We're gonna talk about what fever is, how it is caused, and types of fever. Then I'll give some writing tips. Just a note, with a lot of things, there are exceptions and special cases. I'm going to go over the most common stuff cause this isn't an immunology course.
What is a fever? The normal body temp (the average of a bunch of people) is 98.2°F. Individuals can differ from this within a degree. A fever is usually a temperature greater than 100°F. There's some leeway to this, and it takes a lot of experience to get a feel for what should be a normal temperature. But if someone comes into the office with a 100°F temp, I'm going to say that they have a fever.
So with fever (ignoring the symptoms of whatever caused it), you're generally going to have malaise, chills, paleness, and rigors (muscle contractions). There may also be behavioral symptoms such as seeking warmer environments, altered mental status, and assuming a fetal position to help warm the body. The peripheral vessels will constrict in order to keep blood in the central body. Once the fever has passed, there will be chills and sweating.
What causes fever? Fever is caused by pyrogens. These can be endogenous (from you) or exogenous (from something else). The main endogenous ones are interlueukin-1, interferon gamma, and tumor necrosis factor α. These are made by immune cells and a few other cell types. Exogenous pyrogens are made by other microorganisms. An example of this is lipopolysaccharide, which is made by gram-negative bacteria. Exogenous pyrogens induce the production of endogenous pyrogens, which induce the production of Prostaglandin E2. PGE2 acts on the hypothalamus to set the body's thermostat higher. This induces the effects seen in order to raise the body's temperature. Fever helps to stimulate the immune system and inhibits microorganism growth (too hot for them). So it's a good thing, unless it gets too high and your organs shut down and your brain melts like butter (i'm kidding...but really, it's bad). I'd say over 110°F and you're probably going to die.
What are the patterns of fever? There are three fever patterns, and they are associated with different pathologies. They are sustained, intermittent, and remittent fever. Sustained fevers are exactly what they sound like. They don't fluctuate more than a degree in a day and never touch normal baseline temp. These are typically seen with pneumonia, typhoid, bacterial meningitis, and UTI.
Intermittent fever is a fever that is only present for a few times throughout the day, with the temp going up above normal and back down to normal. This is seen with malaria, septicemia (a serious bacterial infection -> think septic shock), pyogenic infections (bacteria that cause pus formation), and TB.
Remittent fever fluctuates more than two degrees throughout the day, but does not ever touch normal baseline temps. These are seen with infectious diseases.
These patterns are okayish, but sometimes people don't always have a disease that matches the fever type. I think typhoid, TB, and tick-borne diseases (they cause a relapsing fever) are the best diseases to use fever patterns for.
Writing Tips
Okay, so first off I think fever is great for writing. So to find out what's going to happen, you need to pick out what the nature of the illness is. The most common one I see is infection from a wound of some kind. So this is going to be bacterial. I would say that you are most likely to have an infection with staph, strep, or pseudomonas. These are naturally found on the body, but are not meant to be inside you. A cut in your skin lets them in. This is bad. So your immune system will notice them and release pyrogens, and then you get PGE2, and then you get fever.
I would probably say you'd get the standard symptoms above, plus pain, swelling, and redness at the site of the infection. It's going to be an intermittent fever probably (could end up as remittent). So you would want to treat the infection itself. If there are no antibiotics or antipyretics (anti fever drugs), then you would have to clean and disinfect the wound, and basically hope that the immune system can do its thing. You can wipe the person down or use a cool compress on them, but this doesn't really reduce fever that much and is more of just a temporary relief.
Anyways, I hope this was helpful and as always, sources are in the comments. You can let me know if you have a specific situation you would want some info on in the comments/askbox/DM.
#medicine#med student#medical school#whump community#whump#whump reference#med school#med studyblr#biology#whump writing#medical writing#writing reference#writing help#fever#immune system#immunology
19 notes
·
View notes
Note
Which lps would book be
which LipoPolySaccharide would book be? its been a bit since ive touched up on my bacterial biology, but i’d probably say the bis-phosphorylated β-1-6 glucosamine disaccharides associated with enterobacteriacea
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
From 1 January 2025, Chris H Boshoff will take over as Pfizer's new chief scientific officer. Previously he led its Cancer Research and Marketing.
GeoffPainPhD
Nov 20, 2024
24
23
Share
Very interesting appointment given Pfizer market strategy to exploit his knowledge of Bird diseases and Respiratory Syncytia.
In 1992 he was funded by the Goverment of South Africa and proved that Endotoxin causes spontaneous fusion between Myeloma cells and Splenocytes from Mice immunized with formalin-inactivated Haemophilus paragallinarum cells.12
See related posts on the hazards of Cell Fusion3 4 caused by Endotoxin.56
Multiple Myeloma is of great interest to Pfizer.7
I will add other relevant publications by Boshoff later, but thought you should know.
1
C H Boshoff, L Coetzee, L Visser, J A Verschoor. 1992. Spontaneous hybridoma formation induced by immunization with Haemophilus paragallinarum: evidence for a lipopolysaccharide fusion inducer. https://www.liebertpub.com/doi/10.1089/hyb.1992.11.257
2
3
Pneumonia caused by Wuhan Covid19 involved Syncytia
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

This would be great except mycobacteria don't have LPS babe.

Where's the lipopolysaccharide hun?
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
my toxic trait is the lipopolysaccharides embedded in my cell wall
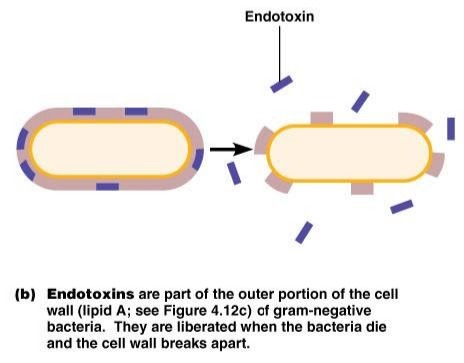
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
name a more annoying power couple than peptidoglycans and lipopolysaccharides. peptidoglycans are responsible for disease symptoms and lipopolysaccharides resist the entry of some antibiotics. god forbid anyone mess with its queen
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Hypothetical Loss of Long-Lifespan Adaptations Post-Noah

If we hypothetically consider that humans once possessed adaptations for 1000-year lifespans, the shift from a fruit-based diet to a meat-based diet after Noah's time could have played a role in the loss of those long-lifespan adaptations. Increased metabolic stress, altered gut microbiome, nutrient deficiencies, reduced detoxification, genetic selection, and organ strain might have contributed to cumulative cellular damage, inflammation, and accelerated aging, ultimately leading to the loss of those remarkable cellular adaptations.
Metabolic Overload & Oxidative Stress: A carnivorous diet, characterized by increased fatty acid oxidation and gluconeogenesis, may lead to elevated reactive oxygen species (ROS) production due to inefficiencies in the electron transport chain. This can perturb redox homeostasis, contributing to mitochondrial dysfunction, genomic instability, and accelerated cellular senescence.
Gut Microbiome & Inflammation: The high protein and lipid content of a carnivorous diet can induce gut dysbiosis, potentially decreasing beneficial butyrate-producing bacteria and increasing pro-inflammatory taxa such as certain Bacteroides species. This dysbiosis can lead to increased production of endotoxins (lipopolysaccharides), triggering systemic low-grade inflammation and contributing to immune senescence, a process known as 'inflammaging'.
Nutrient Imbalances & Signaling Disruption: A carnivorous diet, often deficient in micronutrients like ascorbic acid (vitamin C), and phytochemicals found in plant-based foods, can disrupt signal transduction pathways crucial for DNA repair, telomere maintenance, and autophagy. These deficiencies can impair the insulin/IGF-1 and sirtuin/FOXO signaling networks, which are known to play a role in longevity.
Reduced Fiber & Detoxification: The lack of dietary fiber in a carnivorous diet impairs the synthesis of beneficial short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) by gut bacteria and reduces enterohepatic detoxification. This can lead to the accumulation of uremic toxins (e.g., indoxyl sulfate), advanced glycation end products (AGEs), and lipofuscin, all of which contribute to cellular senescence and accelerated organismal aging.
Genetic & Epigenetic Changes: While long-term dietary changes might exert selective pressures on alleles related to protein and lipid metabolism, a carnivorous diet can also induce epigenetic modifications, such as DNA methylation and histone acetylation. These modifications can repress the expression of pro-longevity genes like SIRT and FOXO, potentially compromising adaptive stress responses and reducing organ resilience.
#Post-Apocalyptic Landscape#Eden-like Fruit-Based World#Meat-Centric Dystopia#Metabolic Overload & Oxidative Stress#Pro-Inflammatory Gut Microbiome#Nutrient Imbalance & Aging#Mitochondrial Dysfunction & ROS#Telomere Attrition & DNA Damage#Epigenetic Modifications#Longevity Pathway Suppression#SIRT#FOXO Pathway#Genomic Instability & Senescence#Organ Strain & Immune Dysregulation#Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)#Advanced Glycation End Products (AGEs)#Short-Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs)#Mitochondria & Telomeres Symbols#DNA Strands & Histone Acetylation
0 notes
Text
Understanding Gram-Negative and Gram-Positive Bacteria in Food Safety

Ensuring the safety of our food supply is a fundamental aspect of public health. Central to this effort is the understanding of different types of bacteria that can contaminate food. Gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria are two major classifications that play distinct roles in food safety. This article examines these bacteria and their implications for maintaining safe food practices.
What Are Gram-Negative and Gram-Positive Bacteria?
Bacteria are categorized into gram-negative and gram-positive based on their cell wall structures, which determine their staining characteristics in the Gram stain test. Gram-negative bacteria have a thin peptidoglycan layer surrounded by an outer membrane containing lipopolysaccharides. This structure makes them more resistant to certain antibiotics and disinfectants. Common gram-negative bacteria include Escherichia coli, Salmonella, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
In contrast, gram-positive bacteria possess a thick peptidoglycan layer without an outer membrane. This makes them more susceptible to antibiotics that target cell wall synthesis. Examples of gram-positive bacteria include Staphylococcus aureus, Listeria monocytogenes, and Bacillus cereus. Both types can cause foodborne illnesses, but their different structures influence how they contaminate food and how infections can be treated.
Impact on Food Safety
Both gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria pose significant risks to food safety, but they differ in their modes of contamination and the types of illnesses they cause. Gram-negative bacteria are often associated with severe gastrointestinal infections and can thrive in various environments, including raw meat, dairy products, and fresh produce. Their resilience makes them challenging to eliminate from the food supply chain.
Gram-positive bacteria, on the other hand, are commonly found in foods like dairy products, processed meats, and vegetables. They can produce toxins that are heat-resistant, meaning that even properly cooked food can still pose a risk if these toxins are present. For instance, Staphylococcus aureus can produce toxins that cause rapid onset of symptoms, making timely detection and prevention crucial.
Preventing Bacterial Contamination
Preventing contamination from both gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria requires stringent hygiene practices throughout the food supply chain. Proper handwashing, sanitizing surfaces and utensils, and maintaining appropriate cooking temperatures are essential steps. Additionally, controlling the temperature during storage and transportation helps inhibit bacterial growth.
Training plays a pivotal role in enhancing food safety measures. Enrolling in a food safety course Vancouver provides individuals with the knowledge needed to identify potential contamination sources and implement effective control strategies. Completing foodsafe level 1 Vancouver training equips food handlers with practical skills to prevent bacterial contamination.
Best Practices for Safe Food Handling
Adopting best practices is essential in mitigating the risks posed by both gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria. These practices include:
Regular Handwashing: Ensuring that all food handlers wash their hands thoroughly with soap and water before handling food.
Proper Cooking: Cooking food to the recommended temperatures to kill harmful bacteria.
Avoiding Cross-Contamination: Using separate cutting boards and utensils for raw and cooked foods.
Storage Management: Keeping perishable items refrigerated and monitoring expiration dates to prevent spoilage.
Cleanliness: Maintaining clean workspaces and regularly sanitizing equipment to reduce bacterial presence.
Understanding the differences between gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria is essential for effective food safety management. Both types of bacteria can lead to serious foodborne illnesses, but with proper knowledge and practices, their impact can be minimized. Investing in comprehensive training, such as a food safety certificate Vancouver, obtaining relevant certifications, and adhering to best practices ensures that food handlers are well-equipped to maintain a safe and healthy food supply for the community.
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Text
[ad_1] To summarize: something ending in “-ose”, in addition to “syrups” and “sweeteners” are virtually at all times sugar.Indicators you're consuming an excessive amount of sugarWith all this sneakiness, it may be robust to acknowledge that your sugar consumption is getting out of hand. We put this query to Dr. Lela Ahlemann, a specialist in dermatology, phlebology, proctology, and dietary drugs. Listed here are the doable warning indicators you're consuming an excessive amount of sugar.1. Weight achieve and fixed starvationIt is no secret that sugar has quite a lot of energy. However there may be another excuse why sugar makes us achieve weight so shortly: “Should you eat an excessive amount of sugar, you're continuously hungry,” says Ahlemann. “The explanation for that is that sugar drives up blood glucose ranges within the quick time period, however has no lasting satiating impact because of the lack of fiber. The persistent starvation and the ensuing continued consuming finally result in weight achieve, which we're all conscious of as an indication of an excessive amount of sugar.”2. Zits“After we eat sugar, not solely does the insulin stage rise, but in addition a hormone within the blood known as insulin-like progress issue 1, or IGF-1 for brief,” says Ahlemann. “Along with insulin, this IGF-1 stimulates the sebaceous glands and extreme keratinization within the space of the sebaceous glands, which is why they develop into clogged resulting in pimples and irritation.”3. Cravings and temper swings“The excessive improve in glucose ranges within the blood results in an insulin launch —however that is usually so robust that the blood sugar is just not lowered to the conventional stage, however under the ‘baseline’, so that you've got a relative hypoglycemia, and this results in cravings. In some individuals, it additionally results in temper swings and crankiness,” says Ahlemann.4. Irritation and weak immune system“Usually, sugar is absorbed by the physique through the small gut. Nonetheless, if the quantity of easy sugars akin to glucose and fructose that we eat exceeds the capability of our small gut, this easy sugar results in the big gut,” explains Ahlemann.Based on the diet skilled, it turns into meals for micro organism that belong within the massive gut: “Selective feeding results in a proliferation of those micro organism. The issue is that, sadly, they carry endotoxins on their bacterial floor. These are so-called lipopolysaccharides. These endotoxins can then go away the intestine, enter the bloodstream and result in silent irritation, which accelerates the growing old of the physique, and weakens the immune system.”5. Accelerated growing old“It's scientifically confirmed that the excessive consumption of sugars results in the formation of so-called AGEs or Superior Glycation Finish Merchandise,” Ahlemann explains. She compares the impact to caramelization: “In our collagen, the fibers ought to ideally run in parallel; when the tissue is saccharified, there are cross-links within the collagen connective tissue, which makes it stiff, brittle, simpler to degenerate and—very importantly—the physique can be much less in a position to restore itself. Which means the standard of our collagen deteriorates.” [ad_2]
0 notes
Text
How Complement System Enhances Antibodies to Regulate Immune Responses?
The complement system, or complement cascade, is regarded as a portion of the innate immune system and may appear 6-7 million years earlier than adaptive immunity. Recent studies have shown that the complement system can get involved in the communication of multiple cells and regulating immune responses, working as a bridge between the innate and adaptive immune responses.
Main Tasks of the Complement System
The complement system plays an important role not only in defending infection but also in the development of autoimmune diseases. The core function of the complement system is to lyse cells, bacteria, and viruses, as well as to initiate phagocytosis by opsonization. What’s more, it exerts influence in triggering inflammation by engaging with immune system cells.
To be straightforward, the complement system is expected to take these functions:
Mark the invading pathogens by opsonin that promotes phagocytosis.
Enhance the generation of inflammatory signaling agents (e.g. histamine) and capillary permeability to attract macrophages and neutrophils.
Attack and rupture the wall of pathogens with membrane attack complex (MAC).
How Does the Complement System Work?
The complement system consists of a variety of proteins and protein fragments that are synthesized by the liver and circulate in the blood as inactive precursors (known as zymogens). Zymogens need to cleavage and become active enzymes for cytolytic and bactericidal activity.
The activation of the complement system may be triggered by antigen-antibody complex, lipopolysaccharide, mannosans, peptidoglycan, etc. Stimulated proteases in the system will cleave specific proteins to release cytokines, further inducing an amplifying cascade of cleavages.
There are three different pathways involved in the activation of the complement system.
Classical pathway is initiated by the combination of C1q and the classical pathway activator (antigen-antibody complex). And later sequential classic complement activation will form a membrane attack complex (MAC), making the target cell swell and rupture to death because the osmotic pressure cannot be maintained.
Alternative pathway starts from the component C3b binding to factor B. It’s independent of the immune response and exerts an important anti-infective effect in the early stage of bacterial infection when no specific antibodies are produced.
Lectin complement pathway is activated when mannose-binding lectin (MBL) or ficolin binds to the mannose residues of pathogens based on the pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs). Similar to the classical pathway, it will later form MAC for opsonization, phagocytosis, and lysis of target microorganisms.
Complement System Research and Development
Studies show that though the complement system takes a key part in defense against pathogens and host homeostasis, the possible unfavorable results cannot be overlooked. When the complement system is regulating immune responses with specific signals, excessive or insufficient activation of the system may cause damages to healthy host cells or tissues.
As for the double-edged functions of the complement system, more and more complement therapeutics are developed, including serine protease inhibitors, soluble complement regulators, therapeutic antibodies, complement component inhibitors, and anaphylatoxin receptor antagonists.
Meanwhile, many life science solution providers get into complement antibody development, serine protease inhibitors development, complement-directed drug discovery, commercial complement product manufacturing, etc. in response to complement research.
Up to now, the complement therapeutic research has been undergoing a highly successful and inspiring period, and numerous complement-based drugs are discovered to treat diseases such as autoimmune disease, nephropathy, osteology, genetic disease, infection, neurology, inflammatory disease, ophthalmology, and cardiovascular disease.
0 notes
Text
Mostly called Lipopolysaccharide Binding Protein, it is increased in the blood of Astronauts, people infected with Covid19 or on the wrong diet.
GeoffPainPhD
Oct 15, 2024
I have mentioned Lipopolysaccharide Binding Protein (LPB) in various articles but think we should change its name to align with the Therapeutic Goods Administration and all jab regulatory bodies around the world who report that they have conducted Endotoxin tests on all released batches or accepted certificates from other countries accredited testing labs. But for now, let’s look at some exciting recent discoveries.
Astronauts suffer from elevated LBP
I was interested to find an article1 where US Space Shuttle and the International Space Station Astronauts were followed after their space voyage with a focus on their circulating LBP.
The abstract states:
This study investigated the ability of the shuttle crew members’ monocytes to respond to gram-negative endotoxin that they could encounter during infections. Blood specimens were collected from 20 crew members and 15 control subjects 10 days before launch, 3 to 4 h after landing, and 15 days after landing and from crew members during their annual medical examination at 6 to 12 months after landing.
An earlier US study of 27 Astronauts found Cytokine disruption.2
Similar studes of Russian Space Station crew and those in a simulator also found disruption of Cytokines.34
Here is what Mouse LPB looks like when its crystal structure is determined and called a conserved two-domain “boomerang” structure,.5
0 notes