#Hydraulic Cylinder Maintenance
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
The Vital Significance of Regular Hydraulic Cylinder Maintenance

Introduction
In the realm of mechanical systems, hydraulic cylinders play an important role in powering heavy machinery and equipment. These robust and efficient devices convert hydraulic energy into mechanical force, driving a group of industrial processes. To confirm their optimal functionality and longevity, regular take care of hydraulic cylinders is of utmost importance. This article explores the essential importance of proactive maintenance in maximizing performance, preventing failures, and improving overall operational efficiency.
Enhancing Performance and Reliability
Hydraulic cylinders need routine maintenance to stay at the top of their game. Over time, deterioration, contamination, and fluid leaks may have a negative impact on their effectiveness. Potential problems can be found and fixed by regular inspections, cleaning, and lubrication, averting expensive breakdowns and cutting down on downtime. Businesses are able to continuously reach their production goals thanks to reliable operation and timely maintenance that protects against wear-related performance loss.
Preventing Costly Failures
Neglecting the maintenance of hydraulic cylinders can lead to serious problems, from modest setbacks to catastrophic breakdowns. Failed cylinders can disrupt production, put workers in danger, and seriously harm machinery. Following a detailed maintenance program enables specialists to spot and resolve early indications of wear, leaks, and other possible problems. This preventive method avoids key operations disruptions and serious breakdowns, while also drastically lowering repair costs.
Extended Equipment Lifespan
Hydraulic cylinders are frequently essential parts of pricey equipment and systems. Their lifespan is extended by routine maintenance, safeguarding the considerable investment made by corporations. The integrity of the cylinder is maintained through appropriate lubrication, seal replacements, and cleaning methods that reduce component wear, corrosion, and damage. Organizations may maximize their return on investment and avoid costly replacements by assuring the durability of hydraulic cylinders.
Operational Efficiency and Safety
Well-maintained hydraulic cylinders contribute to overall operational efficiency. They operate with minimal friction, reducing energy consumption and optimizing performance. Routine maintenance also ensures that cylinders operate within specified tolerances, maximizing system efficiency. Moreover, regular inspections and maintenance help identify potential safety hazards, allowing for timely repairs and the prevention of accidents in the workplace.
Environmental Sustainability
Proactive hydraulic cylinder maintenance promotes environmental sustainability. Leaks and fluid contamination can result in environmental pollution, leading to adverse effects on ecosystems. Regular maintenance reduces the risk of leaks, enhances the integrity of seals, and prevents fluid contamination. By minimizing hydraulic fluid consumption and preventing leaks, organizations can reduce their environmental footprint and demonstrate responsible stewardship.
Conclusion
Regular maintenance of hydraulic cylinders is an indispensable practice for businesses relying on these powerful devices. By prioritizing maintenance, companies can enhance performance, prevent costly failures, extend equipment lifespan, improve operational efficiency, ensure safety, and contribute to environmental sustainability. Investing in regular hydraulic cylinder maintenance not only protects the bottom line but also supports a seamless and productive industrial ecosystem.
0 notes
Text
If you work with hydraulic systems, you may be familiar with hydraulic cylinder honing, the process of smoothing and finishing the internal surface of a cylinder. Honing is an essential part of maintaining hydraulic systems, but many people have questions about the process. In this article, we'll answer the most common questions about hydraulic cylinder honing and provide you with expert tips to get the best results.
Learn more by clicking on the link
#caterpillar#jcb#heavyduty#heavy equipment maintenance#heavy maintenance#heavy equipment#heavy machinery#hydrauliccylinderrepair#hydraulics#cylinderhoning#hydraulic cylinder rebuild#excavator
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

0 notes
Text
Plunger pumps repair service
SK Hydraulic Engineers is a reputable company that specializes in providing plunger pump repair services. With a team of skilled technicians and extensive industry experience, they offer efficient and reliable solutions for repairing and maintaining plunger pumps. From diagnosing issues and conducting thorough inspections to replacing worn-out components and ensuring optimal performance, SK Hydraulic Engineers is committed to delivering top-notch service to their clients. Whether it's for industrial or commercial applications, customers can rely on their expertise to keep their plunger pumps operating smoothly and minimize downtime.
Read more:- https://hydraulicpumpmotorrepairservices.business.blog/2023/07/28/the-essential-guide-to-maintaining-your-plunger-pump-tips-and-tricks/
#Hydraulic pump repair service#Hydraulic pump repair#Plunger pumps repair service#Vane hydraulic pump repair service#Tokimec hydraulic pump repair service#Hydraulic pump maintenance service#Vickers piston pump repair service#Vickers pumps repair service#Hydraulic motor repair service#Staffa hydraulic motor repair service#Danfoss hydraulic motor repair service#Danfoss hydraulic pump repair#Hydraulic motor repair#Hydro motor repair#Hydraulic cylinder repair service#Hydraulic valve repair service#Hydraulic pump valve repair service#Hydraulic Pump & Motor Repair Service#hydraulic repair service
0 notes
Text

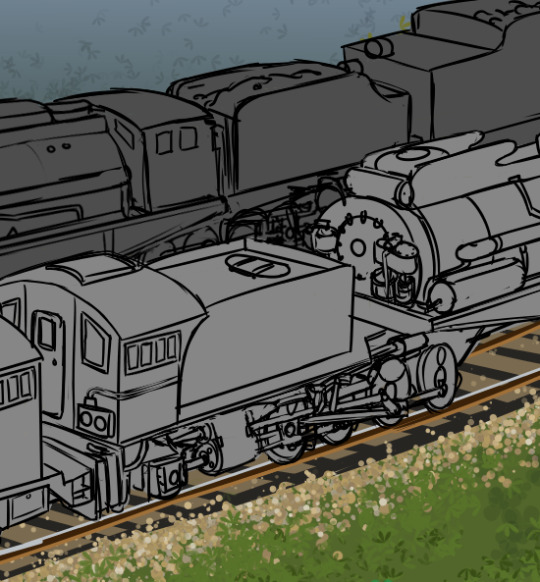
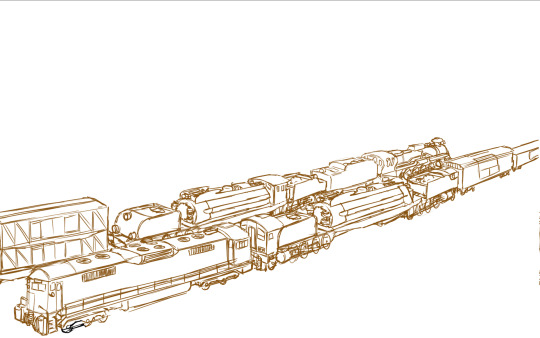
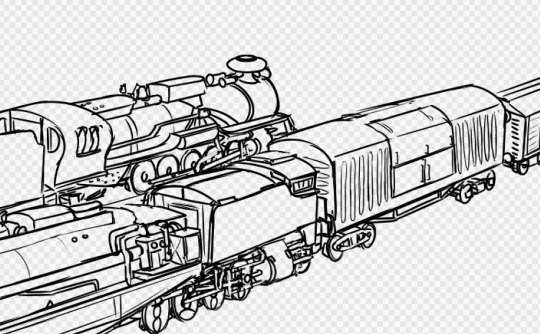
(zoom in!)
Two double-headers on the Trans-Gooiw Railroad passing each other in the hills, dragging long freight trains behind them, during the early days of the Pan-Mellanus Oil Crisis.
More mellanoid trains: Guz's Model Garratt | Museum-piece carrying rocket parts | Advanced Steam Tank Engine | Guz's bigger model Garratt | Tram and Coal Mine loco sketches.
The diesel-hydraulic at the front of the foreground consist, already somewhat old and tired by this point, dates back to around the time period that steam engines were originally retired on Mellanus. It's not very fuel efficient as it is, and with the oil rations, diesels can not handle the trains on their own any longer.
For a few years now the railroads have been taking their steam engines out of mothballs and museums, as coal was comparatively dirt-cheap. Still though, the various maintenance and operational complexities of running steam locomotives resulted in a lot of losses for the railroads.
Pictured here behind the diesel is an early attempt at the Advanced Steam Engine concept, modifying a member of a very prolific and successful 2-8-0+0-8-2 Garratt class with a gas producer combustion system, more modern cylinders and valve gear, and entirely replacing the cab with an electronic control system (with the more diesel-like control stands moved to separate cabs on the tenders). The electronic control scheme allows for the steam engine to be connected to a diesel engine to be run as a multiple unit, cutting down operational costs. However, as a modified prototype, this locomotive lacks some of the other features which exemplified the Advanced Steam era, such as modular ashpans, computerized control, and precision engineering.
On the other track, moving the opposite direction, we see a double header of two steam locomotives, another 2-8-0+0-8-2 loaned from the Slaibsgloth Coal Mine Railroad, and a 2-10-2 'easy' type non-articulated loco leads the train. In this case, there is no electronic connection, so a crew of four mellanoid slimes is necessary to operate the train.
The eagle-eyed railway fans will notice that there are radiators for a dynamic brake on the diesel, yet the diesel is an electric. Diesel-electric dynamic brakes switch the traction motors into generators, and dump the electricity out as waste heat--but there's no traction motors on a hydraulic. So why the radiator fins? There's still a dynamic engine brake on the diesel-hydraulic, so it still needs to be able to dissipate heat, especially on the mountain routes.
WIP images follow:




#Steam locomotive#steam engine#steam train#train#worldbuilding#mellanoid slime#railroad#diesel locomotive#road-switcher#diesel-hydraulic#locomotive#locomotive design#Garratt#Beyer-Garratt#articulated locomotive#Slime Trains#trains
90 notes
·
View notes
Text
Premium Chrome Rods by Shandong Baokun Metal Material Co., Ltd
For industries that demand durability, precision, and excellent surface finish, chrome rods are an ideal solution. Widely used in hydraulic systems, machinery components, and industrial applications, these rods are designed to deliver exceptional performance and longevity.
Shandong Baokun Metal Material Co., Ltd. is your trusted partner for high-quality chrome rods. With advanced manufacturing processes and strict quality control, we provide products that meet the highest standards, ensuring reliability and efficiency for your operations.
What Makes Chrome Rods Unique?
Chrome rods are steel rods coated with a layer of hard chrome, enhancing their surface hardness, corrosion resistance, and wear properties. This makes them perfect for heavy-duty applications where strength and precision are critical.
Key Benefits of Chrome Rods
Exceptional Durability: The chrome coating significantly enhances resistance to abrasion and corrosion, ensuring long-lasting performance.
High Precision: With a smooth and consistent finish, chrome rods are ideal for use in hydraulic cylinders and other precision machinery.
Versatile Applications: From construction to manufacturing, chrome rods are used in diverse industries for various functions.
Cost-Effective: The enhanced lifespan of chrome rods reduces maintenance and replacement costs over time.
Why Choose Shandong Baokun Metal Material Co., Ltd.?
As a leader in the steel industry, Shandong Baokun Metal Material Co., Ltd. offers an extensive range of chrome rods that are customized to meet your specific needs. Our rods are manufactured using high-grade materials and advanced technology to ensure superior quality and performance.
Whether you need standard sizes or custom dimensions, we have the expertise and capacity to deliver. Our commitment to excellent service, timely delivery, and competitive pricing makes us a preferred supplier for businesses worldwide.
Order Your Chrome Rods Today!
Upgrade your industrial projects with premium chrome rods from Shandong Baokun Metal Material Co., Ltd. Visit our website to explore our products or contact us for personalized solutions.
Experience unmatched quality and reliability with Shandong Baokun!
0 notes
Text
How to Rebuild a Hydraulic Cylinder: A Step-by-Step Guide

Hydraulic cylinders are essential for powering heavy machinery in various industries. Over time, they may wear out due to high usage, leaks, or contamination. Rebuilding a hydraulic cylinder restores its efficiency, saving you the cost of replacement. Follow this step-by-step guide to rebuilding your hydraulic cylinder effectively.
Step 1: Prepare the Workspace and Tools
Begin by setting up a clean and well-lit workspace. Gather essential tools such as wrenches, a soft-faced hammer, seal kits, snap ring pliers, and a cleaning solution. Refer to the hydraulic cylinder manual for specific instructions regarding the model.
Step 2: Disassemble the Hydraulic Cylinder
Release Hydraulic Pressure: Disconnect the hydraulic lines and release the pressure to avoid accidents.
Drain Hydraulic Fluid: Place a container underneath and fully drain the hydraulic fluid.
Remove the Cylinder: Detach the cylinder from the machinery carefully.
Open the Cylinder: Loosen and remove the gland nut or end cap using suitable tools. Slide the piston rod assembly out of the cylinder tube.
Step 3: Inspect and Clean Components
Inspect the piston, rod, seals, and other components for signs of wear, cracks, or damage.
Use a cleaning solution to remove debris, dirt, and contaminants. Dry all components thoroughly.
Step 4: Replace Damaged Parts
Examine the seals, O-rings, and bearings. Replace worn or damaged ones using the appropriate seal kit.
If the piston rod is bent or the cylinder tube is scratched, consider replacing or repairing them to ensure optimal performance.
Step 5: Reassemble the Hydraulic Cylinder
Lubricate the seals and reattach them to the piston and gland.
Reinsert the piston rod assembly into the cylinder tube.
Secure the gland nut or end cap tightly. Ensure all components are aligned correctly.
Step 6: Test the Rebuilt Cylinder
Reinstall the cylinder onto the machine and reconnect the hydraulic lines.
Refill the system with clean hydraulic fluid as per the manufacturer's specifications.
Test the cylinder under operating conditions to check for leaks and ensure smooth functionality.
Step 7: Regular Maintenance
Keep hydraulic fluid clean, inspect components periodically, and address minor issues promptly to avoid frequent rebuilds.
For a detailed guide, visit our blog: Guide to Rebuilding a Hydraulic Cylinder.
#how to rebuild a hydraulic cylinder#hydraulic cylinder rebuild#rebuilding a hydraulic cylinder#how to repair hydraulic cylinder#how to remove a hydraulic cylinder
0 notes
Text
Discover the Power of Hydraulic Hand Pump

Looking for a reliable solution to generate high pressure in various hydraulic applications? A Hydraulic Hand Pump is your go-to tool. It’s ideal for operating hydraulic cylinders, lifting heavy loads, and ensuring smooth operations. Lightweight, durable, and easy to use, it’s perfect for maintenance tasks in remote areas or workshops. Choose a Hydraulic Hand Pump to boost productivity with minimal effort. It’s time to take your hydraulic system to the next level!
0 notes
Text
#Hydraulic#heavy maintenance#JCB#heavy equipment#Hydraulic Cylinder Repair#hemsltd#caterpillar#Cylinder#filtration#hems#excavator#heavy machinery#honing
1 note
·
View note
Text

0 notes
Text


Image 1: a typical modern electric slime tram, with adorable "streamlining" and an Advanced Steam commuter train.
The steam engine is an Advanced steam engine with the gas generator boiler fired automatically using microcontrollers, with compound cylinders, steam super heaters, etc. The driver controls the locomotive electronically from a cab at either end of the train. Advanced steam engines were developed due to skyrocketing oil prices which drove up the price of electricity and made diesel hydraulics much less cost effective to operate. Old style steam locomotives would not have been considered up to snuff and the maintenance facilities for them had dwindled, but Advanced Steam sought to solve the maintenance and servicing problems. Most advanced steam was utilized for very large scale applications like freight hauls and migration trains, but the concepts could also be employed on smaller scales.
Image 2: Locomotives of the Slaibgloth Coal Mine. These comprise about 30 2-8-0+0-8-2 Garrats, 5 Shays, and 5 "easy" (non-articulated) locomotives utilizing spare engine sets from the Garrats and spare boilers from the Shays.
The Garrats were built in 2346 A.D. and retired in 2379 A.D. (two years ago) for service bringing coal carriages from the coal pits up to the interchange at the Glooiw & North Eastern. It is unusual for a coal burning steam engine to remain in revenue service--the majority that remained in use after the development of Diesel-Hydraulics were decommissioned with railway electrification and the ones that remained were mostly converted to oil burning. The Slaibsgloth steam engines meanwhile persisted right up until the closure of the coal mine. Glooiw & North Eastern has acquired the 40 locomotives. Their fates are uncertain but railway preservation groups remain optimistic.
#Mellanoid Slime Worldbuilding#Train#Steam train#steam engine#tram#trolley#railway#railroad#steam locomotive#steam train#Mellanoid slime worm#Slime Trains
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Advantages of Exlar Electric Cylinders Over Hydraulic Cylinders
The Advantages of Exlar Electric Cylinders Over Hydraulic Cylinders
Energy Efficiency
Higher Efficiency
Hydraulic systems operate at about 50% efficiency, whereas electric servo systems achieve 80% efficiency. This difference leads to up to 60% energy savings. These savings can even fund the retrofit of a hydraulic system to an electric one. (αλλαγη κλειδαριασ ασφαλειασ)
Idle Power Savings
In electric servo systems, configurations are possible that use no power when not in motion. By contrast, hydraulic systems are constantly using pressure and therefore power to hold position.
Greener
No Hazardous Waste
Electric actuators eliminate managing and disposing of hazardous hydraulic fluids.
Cost-Effective
Hydraulic fluids are expensive and often need to be replaced fairly frequently, which is avoided with electric solutions.
Safety, Reliability, and Maintenance
Less Maintenance
Requires remarkably less maintenance than hydraulic systems, which generally consist of high-pressure hoses, seals, or other devices.
No Chance of Oil Spills
Eliminates the chances of a hydraulic oil spill happening that is under high pressure.
Fire Safety
Electric drive systems avoid fire hazards working with flammable hydraulic oils—especially in high-temperature, atmospheric conditions of power plants.
Compact Design
Electric systems are compact since they do not have large hydraulic valves and oil tanks.
Noise Reduction
Electric actuators operate at noise levels about 30% lower than hydraulic systems, thus helping to meet workplace noise reduction requirements.
Installation and Usability Ease
Easy Installation
Electric systems are installed more quickly and easily than the intricate plumbing needed for hydraulic systems.
Lower Installation Costs
The installation time and costs are greatly reduced.
Easy Synchronization
Electric systems can easily synchronize axes, such as in press applications, without the added complication.
Additional Advantages
Higher Load Control
Better accuracy minimizes the stress that machine parts undergo, resulting in increased tool life compared to hydraulic systems.
Higher Cycle Rates
Electric systems achieve higher cycle rates due to better response time and acceleration capability.
Temperature Stability
Electric actuators perform efficiently through a wide temperature range and avoid the performance problems of hydraulic systems that are related to changes in oil viscosity.
Longer Service Life
Exlar roller screw actuators have a much longer service life compared to ball screw actuators, thus providing a more durable and cost-effective alternative.
Conclusion
Exlar electric cylinders outperform hydraulic systems in terms of energy efficiency, environmental sustainability, safety, ease of use, and long-term reliability. With better control, lower maintenance, and longer life, they are the perfect choice for advanced motion control applications.
0 notes
Text
Restoring Dump Trailers After a Collision
Restoring dump trailers after a collision can be a challenging yet necessary task to ensure that the trailer continues to function safely and efficiently. The restoration process involves assessing the damage, repairing or replacing parts, and performing maintenance checks. Here’s a comprehensive guide to restoring dump trailers after a collision:
1. Assess the Damage
Visual Inspection: Start by carefully inspecting the dump trailer for any visible damage, including dents, cracks, bent frames, or broken components. Pay attention to the body of the trailer, axles, suspension system, and the dump mechanism.
Check the Dump Mechanism: Ensure that the hydraulic system, including the lift cylinders, pump, and control valve, is intact. A collision can damage these components, affecting the trailer’s ability to lift and unload.
Frame and Chassis Inspection: Check the integrity of the frame and chassis, as damage to these parts can compromise the trailer’s overall structure. Look for signs of bending or twisting.
Wheels and Tires: Inspect the tires and wheels for any damage caused by impact. Flat or damaged tires may need to be replaced, and bent wheels may require realignment or replacement.
Axles and Suspension: Examine the axles and suspension system for any cracks or signs of misalignment. A bent axle or damaged suspension can affect the trailer’s ability to handle loads safely.
2. Assess the Hydraulic System
Hydraulic Lines and Cylinder Inspection: Look for any leaks or damage to hydraulic hoses, lines, and cylinders. Leaking hydraulic fluid can lead to loss of power and make the trailer unusable. Replace any damaged lines and test the hydraulic lift system to ensure it’s functioning properly.
Pump and Control Valve Check: If the hydraulic pump or control valve was damaged in the collision, it may need to be repaired or replaced. Test the pump to ensure it’s pumping fluid correctly and the control valve responds properly to inputs.
3. Repair or Replace Damaged Components
Frame and Body: If the trailer’s frame is bent or damaged, it may need to be realigned or replaced. For minor body damage, such as dents or scratches, you may be able to perform some cosmetic repairs, including sanding, welding, or applying a new coat of paint.
Replace Worn Parts: Replace any damaged parts that can no longer be repaired. This includes broken axles, bent suspension parts, or worn-out tires. If the trailer has a damaged dump bed or hinge, it may need to be replaced as well.
Welding and Metal Work: If the trailer’s frame has been bent, cracked, or deformed during the collision, it may require professional welding to restore its strength. Ensure that all welds are completed by a certified welder to ensure the structural integrity of the trailer.
4. Address Electrical and Lighting Issues
Inspect Electrical Wiring: The electrical system, including wiring for the lights and any other electronics, should be checked for damage. Collisions can cause wiring to short out or become loose, so replace or repair any faulty wiring.
Lighting and Indicators: Ensure all lights (brake lights, tail lights, turn signals, etc.) are functional and replace any broken bulbs or damaged light fixtures. Proper lighting is crucial for safety, especially when the trailer is being towed.
5. Test the Trailer’s Functionality
Hydraulic System Test: After repairs, test the hydraulic lift system to ensure it can lift and lower the bed properly. Check for smooth operation and ensure there are no leaks in the system.
Weight Distribution and Load Tests: Before using the trailer for hauling loads, test the weight distribution and ensure the trailer can handle the expected load without issues. A fully loaded test run will help confirm that the repairs are solid and the trailer is safe to use.
Brake Functionality Check: Check the braking system to ensure that it is functioning correctly, especially after repairs. Test the trailer’s brakes and make sure they respond appropriately to inputs.
6. Repainting and Finishing Touches
Paint and Rust Protection: After all structural and mechanical repairs, consider repainting the trailer to protect it from rust and corrosion. A fresh coat of high-quality automotive paint will not only improve the trailer’s appearance but also extend its lifespan.
Apply Protective Coatings: After painting, applying a protective coating to vulnerable areas like the chassis and undercarriage can help prevent future rust and corrosion from road salt, moisture, and other environmental factors.
7. Regular Maintenance After Repair
Ongoing Inspections: After restoring the dump trailer, establish a regular inspection schedule to catch any issues early. Regular checks for wear, rust, and mechanical issues will help maintain the trailer’s reliability and safety.
Lubrication: Regularly lubricate moving parts, especially those in the hydraulic system and suspension, to ensure smooth operation and to prevent premature wear.
Conclusion
Restoring a dump trailer after a collision requires a systematic approach to assess the damage, repair or replace damaged parts, and ensure the trailer is fully functional and safe. By addressing both structural and mechanical components, as well as performing regular maintenance, you can extend the life of the trailer and ensure it’s ready for heavy-duty use. If the damage is extensive, consulting a professional for repairs may be necessary to ensure the safety and reliability of the trailer.
Read more: Looking For Car Shipping Overseas Shipper
0 notes
Text
High-Pressure Hydraulic Filters: Importance, Types, and Signs of a Clogged Filter
Hydraulic systems are the backbone of countless industries, from manufacturing to construction. They rely on clean hydraulic fluid to operate efficiently. A high pressure filter plays a vital role in ensuring the longevity and performance of these systems by trapping contaminants that could otherwise cause wear and tear. In this blog, we’ll explore the importance of high-pressure filters, hydraulic filter housings, and common symptoms of clogged hydraulic filters.
What Is a High-Pressure Hydraulic Filter?
A high pressure hydraulic filter is designed to remove impurities from hydraulic fluid in systems that operate at pressures exceeding 3,000 psi. These filters protect critical components like pumps, valves, and cylinders from debris, ensuring uninterrupted operation even in the most demanding environments.
High-pressure filters are ideal for applications where the hydraulic system is subjected to extreme operating conditions, such as heavy machinery, mining equipment, and industrial presses.
Key Features of a High-Pressure Hydraulic Filter Housing
A high pressure hydraulic filter housing is the enclosure that holds the filter element. This housing is built to withstand high-pressure fluid flows and ensure reliable filtration without leaks or structural damage.
Key characteristics of a hydraulic filter housing include:
Robust Construction: Made from durable materials like stainless steel or aluminum to handle extreme pressures.
Sealing Mechanisms: Designed with advanced sealing systems to prevent fluid bypass or contamination.
Ease of Maintenance: Equipped with features for quick filter element replacement without downtime.
Symptoms of a Clogged Hydraulic Filter
Over time, hydraulic filters can become clogged with debris, leading to a range of performance issues. Recognizing these symptoms early can help you prevent costly repairs.
Reduced System Efficiency: A clogged filter can restrict fluid flow, leading to sluggish or unresponsive machinery.
Increased Operating Temperatures: Blocked filters force the hydraulic system to work harder, resulting in overheating.
Unusual Noises: Whining or knocking sounds may indicate a problem with fluid circulation caused by a clogged filter.
Pressure Drops: Sudden or unexplained drops in system pressure often point to filter blockages.
Dirty Fluid: Visible contaminants in the hydraulic fluid reservoir may signal filter failure.
Regular maintenance and timely replacement of clogged filters can mitigate these risks and extend the lifespan of your equipment.
Benefits of Using High-Pressure Hydraulic Filters
Investing in quality high-pressure filters and housings provides numerous advantages:
Enhanced Equipment Reliability: Prevents damage to hydraulic components.
Extended Lifespan: Reduces wear and tear, improving the durability of the entire system.
Cost Savings: Minimizes downtime and repair costs caused by component failures.
Conclusion
A high pressure hydraulic filter is an indispensable component of any hydraulic system, particularly those operating under extreme conditions. Paired with a durable high-pressure hydraulic filter housing, these filters ensure optimal system performance by removing contaminants and protecting sensitive components. However, staying vigilant about the symptoms of a clogged hydraulic filter is equally important to maintain efficiency and avoid downtime.
For the best results, invest in premium filters and adhere to a regular maintenance schedule tailored to your system’s needs. This proactive approach ensures smooth operations and reduces the risk of costly breakdowns.
Read More Blogs:
When and How to Change Hydraulic Filters
Replacement Hydraulic Filter Elements
Exploring the Small Hydraulic System Parts and Maintenance
Complete Guide to Hydraulic Oil Filters
#high pressure Hydraulic filter#high pressure hydraulic filter housing#clogged hydraulic filter symptoms#high pressure filter#Harvard Filter
0 notes
Text
Common Brake System Problems: Causes, Symptoms, and Expert Solutions

The brake system is one of the most critical safety features in any vehicle. When functioning properly, it ensures safe stopping power, preventing accidents and maintaining optimal control of your car. However, like any other system, brakes are subject to wear and tear, and issues can arise over time. Understanding the common problems, their causes, symptoms, and solutions can help you maintain your brakes and drive safely.
Common Brake System Problems
1. Worn Brake Pads
Cause:
Brake pads wear down over time due to friction against the rotors when you apply the brakes.
Symptoms:
Squealing or screeching noises when braking.
Reduced braking efficiency.
Visible thinning of the brake pads (less than ¼ inch).
Solution:
Replace brake pads with high-quality replacements to restore braking performance. Regular inspections can prevent excessive wear and rotor damage.
2. Warped Rotors
Cause:
Excessive heat generated during braking can warp the rotors, especially during aggressive driving or frequent braking in heavy traffic.
Symptoms:
Vibrations or pulsations in the brake pedal when braking.
Uneven stopping power.
Grooves or scoring visible on the rotor surface.
Solution:
Resurface or replace the rotors, depending on the extent of the damage. Pair with new brake pads to ensure even wear.
3. Leaking Brake Fluid
Cause:
Damaged brake lines, master cylinder seals, or caliper seals can result in fluid leaks, compromising hydraulic pressure.
Symptoms:
Spongy or soft brake pedal.
Brake fluid warning light on the dashboard.
Puddles of fluid under the vehicle near the wheels.
Solution:
Identify and repair the source of the leak, followed by refilling and bleeding the brake system to remove air and restore proper pressure.
4. Sticking Brake Calipers
Cause:
Dirt, rust, or debris can cause the calipers to stick, preventing the pads from releasing fully after braking.
Symptoms:
Car pulling to one side while driving.
Burning smell near the affected wheel.
Increased fuel consumption due to drag.
Solution:
Clean or replace the affected caliper. Lubricate the caliper slides and pins to ensure smooth operation.
5. Brake Fade
Cause:
Overheating of brake components due to continuous heavy braking can reduce braking power.
Symptoms:
Increased stopping distance.
Brake pedal feels normal but lacks stopping power.
A burning smell from the brakes.
Solution:
Allow the brakes to cool down and avoid prolonged heavy braking. Use performance-grade brake pads and rotors if driving conditions often involve high stress on brakes.
6. Anti-lock Brake System (ABS) Issues
Cause:
Faulty sensors, wiring issues, or problems with the ABS module can hinder the system’s functionality.
Symptoms:
ABS warning light on the dashboard.
Pulsating brake pedal under normal braking conditions.
Reduced control in slippery conditions.
Solution:
Diagnose the ABS system using specialized tools and address faulty components. Professional repair is recommended for complex electronic issues.
Preventive Maintenance Tips for Brake Systems
Regular Inspections: Check brake pads, rotors, and fluid levels during routine maintenance.
Replace Components Promptly: Don’t delay replacing worn brake pads, rotors, or fluid.
Avoid Overloading: Excessive vehicle weight can strain the brake system.
Mind Your Driving Habits: Reduce aggressive braking and allow sufficient stopping distance.
Flush Brake Fluid: Replace brake fluid every 2-3 years or as recommended by the manufacturer to prevent contamination and corrosion.
When to Seek Professional Help
While some brake issues can be addressed with basic tools and knowledge, others require expert diagnosis and repair. Professional technicians have the skills and equipment to handle complex brake problems, ensuring safety and reliability. If you notice persistent symptoms or warning lights, consult a trusted mechanic immediately.
Final Thoughts
Maintaining your vehicle’s brake system is essential for safety and peace of mind. By staying proactive with inspections, understanding common issues, and addressing them promptly, you can ensure optimal braking performance. Remember, when it comes to brakes, it’s always better to be safe than sorry.
0 notes
Text
Common Issues with Used Wheel Loaders and How to Fix Them
Used wheel loaders are vital machines for construction, mining, and other heavy-duty tasks. They are often sought after due to their lower price tag compared to new models. However, buying a used wheel loader comes with certain risks, including potential mechanical issues. While these machines are built to withstand heavy use, wear and tear over time can lead to problems that may affect their performance and longevity. This blog post will discuss some common issues with used wheel loaders and provide insights on how to address them.
1. Engine Problems
Common Issues: The engine is the heart of any wheel loader. If the engine is in poor condition, the entire machine will suffer. Common engine issues include:
Hard starting or no start: A used wheel loader might have difficulty starting, particularly in cold weather. This could be due to a weak battery, faulty starter motor, or clogged fuel filters.
Loss of power: If the engine loses power during operation, this could be due to issues like fuel system problems, air intake blockages, or worn-out components such as the turbocharger or fuel injectors.
Excessive smoke or overheating: Excessive smoke (black, white, or blue) from the exhaust could indicate internal engine problems like worn piston rings, head gasket failure, or a clogged exhaust system. Overheating could also be a result of cooling system failure.
How to Fix It:
Regular Maintenance: To prevent engine problems, ensure that the wheel loader undergoes regular oil changes, air filter replacements, and fuel filter replacements. These tasks are critical for the engine’s performance and longevity.
Battery Check: Make sure that the battery is in good condition, fully charged, and that terminals are clean and free from corrosion.
Inspect the Fuel System: Clean fuel injectors, replace clogged fuel filters, and check for leaks in the fuel lines.
Address Overheating: Inspect the radiator and cooling system for leaks, blockages, or damaged hoses. Ensure the thermostat and water pump are functioning properly.
2. Transmission Problems
Common Issues: Transmission issues are another common problem with used wheel loaders. The transmission is responsible for controlling the machine's movement and ensuring smooth shifting between gears. Some typical transmission problems include:
Slipping gears: If the loader's gears slip or fail to engage, it could be a sign of low transmission fluid, worn-out clutches, or a failing transmission pump.
Delayed shifting or rough shifting: If the loader hesitates or experiences jerky movements when shifting gears, it could indicate a malfunctioning valve body or problems with the clutch packs.
Leaks: Transmission fluid leaks are a sign that the seals or gaskets are worn, which can lead to fluid loss and, ultimately, transmission failure.
How to Fix It:
Check Fluid Levels: Always maintain the proper fluid levels for the transmission. Low fluid levels can lead to slipping gears and rough shifting. Top up with the recommended transmission fluid.
Replace the Fluid and Filters: Old, contaminated transmission fluid can cause poor performance. Change the fluid regularly and replace the filters to keep the system clean and running smoothly.
Inspect for Leaks: Inspect the transmission for any leaks around seals and gaskets. If you find any, replace the damaged seals or gaskets immediately to prevent further fluid loss.
3. Hydraulic System Failures
Common Issues: The hydraulic system is integral to the loader's performance, controlling the bucket, lift arms, and steering. Common hydraulic issues include:
Leaking hydraulic fluid: Leaks in the hydraulic hoses, cylinders, or connections can lead to a loss of hydraulic power, causing poor lifting performance or complete failure.
Slow or jerky movement: If the loader's hydraulic functions move slowly or erratically, it could be due to air in the hydraulic system, low fluid levels, or a failing hydraulic pump.
Overheating: Hydraulic fluid can overheat due to excessive use, inadequate cooling, or low fluid levels, leading to performance issues and potential system failure.
How to Fix It:
Inspect for Leaks: Regularly inspect hydraulic hoses, cylinders, and connections for signs of leaks. Replace any damaged hoses or seals promptly.
Check Fluid Levels: Make sure that hydraulic fluid levels are topped up and that the fluid is clean. If the fluid looks contaminated or dirty, replace it.
Replace Worn Components: If the hydraulic pump, motor, or valve has worn out, replacing them is necessary to restore full functionality.
Bleed the System: If air has entered the hydraulic system, it may need to be bled to restore proper operation.
4. Steering Issues
Common Issues: The steering system of a wheel loader ensures smooth maneuvering, which is especially important in tight spaces. Common steering problems include:
Hard or unresponsive steering: This can happen if the hydraulic steering pump or steering cylinder is malfunctioning or if there is a fluid leak.
Excessive play in the steering wheel: This could indicate worn-out steering linkages or bushings.
Steering drift: If the loader pulls to one side or drifts, there could be an issue with the hydraulic steering control valve or an imbalance in tire pressure.
How to Fix It:
Inspect Hydraulic System: Check the hydraulic pump and fluid for proper function. Replace any damaged or worn components.
Check Steering Linkages: Inspect steering linkages, joints, and bushings for wear. Replace any worn-out parts to restore precise control.
Align Tires: Check tire pressures and ensure they are properly aligned to prevent steering drift.
5. Brake System Failures
Common Issues: The braking system is critical for the safety of the loader and its operator. Some common brake issues include:
Weak or spongy brakes: This could be due to air in the brake lines, low brake fluid, or worn brake pads.
Overheating brakes: Overheating can occur if the brakes are constantly overused, leading to reduced braking performance.
Brake fluid leaks: Leaks in the brake system can cause a loss of pressure, leading to brake failure.
How to Fix It:
Check Brake Fluid: Ensure that the brake fluid is topped up and free from contaminants. Replace it if necessary.
Inspect Brake Pads: If the brake pads are worn down, replace them to restore braking efficiency.
Bleed the Brakes: If air has entered the brake lines, bleed the system to remove air bubbles and restore full braking power.
Check for Leaks: Inspect the brake lines, master cylinder, and brake calipers for leaks. Replace any damaged parts to prevent further fluid loss.
6. Tire Wear and Damage
Common Issues: Tires are one of the most important components of a wheel loader since they provide traction and stability. Tire issues can range from uneven wear to blowouts. Common problems include:
Uneven wear patterns: This can result from improper tire inflation, misalignment, or unbalanced tires.
Punctures or cuts: Tires may become damaged by sharp objects or excessive wear over time.
Low tread depth: Worn-out tires with low tread depth can significantly reduce traction, especially on slippery surfaces.
How to Fix It:
Regular Tire Inspections: Regularly inspect tires for wear, punctures, and damage. Replace tires that are excessively worn or damaged.
Check Tire Inflation: Maintain the correct tire pressure according to the manufacturer's recommendations. Overinflated or underinflated tires can cause uneven wear and reduce performance.
Rotate Tires: Regularly rotate the tires to ensure even wear. This will help extend the life of the tires and improve the loader’s handling.
7. Electrical System Failures
Common Issues: Electrical system issues can prevent the loader from starting or cause intermittent performance problems. Common electrical issues include:
Dead battery: A dead or dying battery can cause starting issues, especially in cold weather.
Faulty alternator: If the alternator fails, the battery won’t charge properly, leading to electrical malfunctions.
Blown fuses or bad wiring: Faulty fuses or damaged wiring can lead to problems with lights, indicators, and other electrical components.
How to Fix It:
Check the Battery: Inspect the battery’s voltage and condition. If the battery is old or damaged, replace it.
Test the Alternator: Ensure the alternator is charging the battery properly. If the alternator is faulty, it will need to be replaced.
Inspect Wiring and Fuses: Check the wiring for any visible damage or corrosion. Replace blown fuses and repair any damaged wiring to restore proper function.
Conclusion
Used wheel loaders can offer significant value for those looking to save on equipment costs, but they come with the risk of mechanical issues. Regular inspection and preventative maintenance can help identify and fix common problems before they lead to costly repairs. By staying on top of engine maintenance, hydraulic system care, brake checks, and other key components, you can extend the lifespan of your used wheel loader and keep it running efficiently.
0 notes