#Heir Alexei Romanov
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
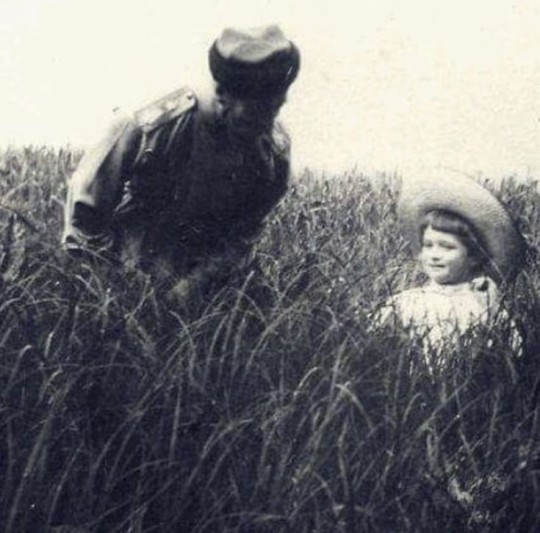

Tsar Nicholas II proudly looking at his smiling little son, Tsarevich Alexei, in fields, 1907. ✨❤
#🥺🥺🥺#proud father moment 🥴#tsar nicholas ii#nicholas alexandrovich#alexei nikolaevich#tsarevich alexei#romanov#romanovs#russian empire#tsardom of russia#1900s#1907#fields#dad and son#monarchs and their heirs
67 notes
·
View notes
Text
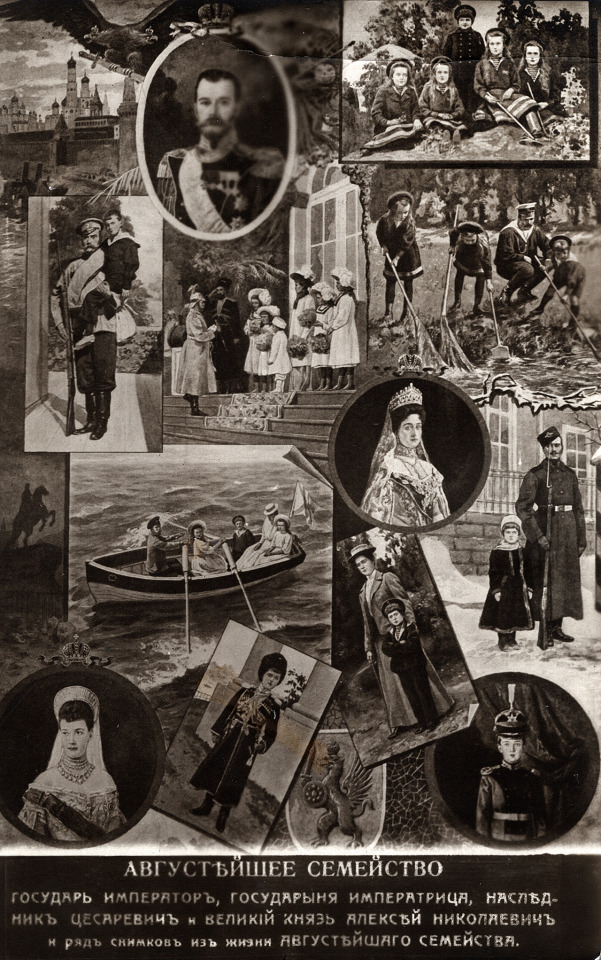

Illustrated postcard of the Russian Imperial Family.
Interestingly, the blurriness on that little portrait of Nicholas II is a fault of the card, not the scan. The card itself is blurry there for some reason.
#romanov#otma#nicholas ii#alexandra feodorovna#maria feodorovna#olga nikolaevna#tatiana nikolaevna#maria nikolaevna#anastasia nikolaevna#alexei nikolaevich#my collection#the text is like: the august family! the emperor! the empress! the heir! and . .. others
79 notes
·
View notes
Text
Fantasy Guide to Royal Children - Heirs and Spares

The lives of Princesses and Princes are of interest to most fantasy writers, it's where many of our heroes, side characters and antagonists hail from. But what is there life like? Is it always ballgrowns and servants? Or something more?
A Strict Order of Precedence

The first thing to know about royal children and siblings is that there's a very strict precedence of importance. Is it fair? No. But this is a system, it doesn't have to be fair. The heir comes first without argument. They are the most important child, they are always greeted first, they are the one to stand next to the monarch or their parents at occasions, they literally go first - and this doesn't change with age, if the heir is the youngest, they still have precedence over their siblings. After the heir, order of predence goes by age and the order effects the life of the children. For example, the older sister will marry begore any of her sisters. This order of deference will be so engrained in your character's life that they will believe it the norm and rarely question it, it probably won't spark any in-fighting.
Accommodation & Staff

Royal children are usually raised one of two ways. Either they are raised at court, in the same Palace as their parents or they are raised away from court under the care of trusted servants. Being raised away from their parents isn't a sign of remoteness or dislike or terrible parenting, it was a way of break a child into the constraints of royal life while giving them freedom of scrunity or danger. Usually these children are raised in the countryside for their health, as cities are usually cesspits for disease. Their parents would come to visit them or allow them to visit them at court. Children raised at court are raised with a higher level of scrunity and attention. They will be in the public eye.
Royal children will always be surrounded by staff. There will be nurses to wash and dress them, nannies to discipline and direct them, guards to protect them and usually, a guardian known as a governess to run their household and care for their needs. Staff are not allowed to hit royal children and must obey their commands. Some royal children were very close to their staff:
Kat Ashley and Elizabeth I
Baroness Lehzen and Queen Victoria
Klementy Grigorievich Nagorny and the Tsarevich Alexei Nikolaevich
Lala Bill and Prince John
However, some royal children faced neglect from their staff. George VI was abused by his nanny, who would pinch him during important occasions, openly favour his elder brother over him and deny him food, which many have been a cause of his speech impediment. After the Russian Revolution, another of the Tsarevich's nannies proved less loyal than the other. Andrei Yeremeyevich Derevenko abandoned his charge, but not before ordering the boy around and insulting him.
Day to Day Life

Royal children would be educated withing their home by tutors. They would usually take lessons all together (the heir may take other lessons). A royal child would recieve an education in languages, arithmetic, geography, etiquette, dancing, music, sports such as riding and literature. Sometimes they would even share lessons with the children of trusted nobles or their cousins. Only the heir will be taught statecraft and how to reign. There is no rhyme nor reason a spare would learn how to rule.
Some royal children are taught the value of their position. Many royal children will be raised strictly to adhere to their social standing and their place in it. Some children may be raised in isolation, kept from mingling and raised to think of themselves as higher than those around them. Some royal families preferred to raise their children as "normal" as possible. The last Romanov children slept in camp beds, with no pillows and we're expected to tidy their own rooms and help the servants. They didn't even use their proper titles, they were called by their names and given a tight monthly allowance to spend. Alexandra of Denmark and her sisters used to make their own clothes. Some royal children could even be encouraged to play with the children of servants and staff as well as nobility (Kolya Derevenko and Tsarevich Alexei Nikolaevich, Winifred Thomas and Prince John). Companionship was a great honour for noble and common child alike as sometimes, they would be invited to live or be educated alongside by the royal children.
Royal children will not undertake royal duties until they are of age. Younger children be be present for large scale events such as jubilees but would not be expected to partake in any duties themselves. When they are of age, they will usually be granted an annual allowance, be invited to social events, invited to be patrons of charities and participate in royal duties.
Heir Vs Spare

Heirs have more responsibility, all the prestige, more power but they have less freedom, less room to explore their own lives and be expected to always be the epitome of perfect. Heirs will be given responsibilities in government, sitting in on state meetings or undertaking state duties.
Spares have little in the way of real power but have the ability to live less regimental lives and gave more agency in their personal lives. Spares may act as ambassadors to other nations or undertake state visits on behalf of the monarchy or even take positions in the army. Spares are encouraged to find positions to support themselves outside the family, either in a marriage or undertaking some service to the country. Spares who stay in the country, tend to act as unofficial advisers to their sibling when they become monarch.
All Grown Up

When royal children grow up, there are usually certain expectations and limitations.
Heirs will be married quickly, the lineage must be secure. Heirs will usually marry either as part of a political alliance or marry somebody suitable - from a good family, the right background, and able to fit into a certain mould (i.e malleable, amiable and loyal). They will be expected to focus on the country, it's needs and support the monarch at all times. Their social circles will be scruntised, their every move will be noted and remarked upon. Heirs will never gave to worry about funding their lifestyle, the Crown is their job and it supports them.
Spares can marry or remain single if they choose, (but if the monarch instructs them go marry they must). Spares can travel, they can be idle, they can even persue amusements not permitted for the heir. Spares can win glory on the battlefield and mix with all sorts of people. That isn't to say spares are useless, spares often occupy very important spaces in society and government. Spares will usually take these positions not for just status but also for the pay. This is why spares are granted royal titles such as dukedoms (they can make money off the lands, be able to build a dynasty for themselves and their heirs and gain status).
#Fantasy Guide to heirs and Spares#Fantasy Guide to Royal Children#Fantasy Guide#write#writing#writeblr#writing resources#writing reference#writing advice#writers#writing advice writing resources#spilled ink#Writing reference writing resources#Writing resources writing reference#Writing advice writing reference#Writing advice writing resource#Royal children#Writing royal characters#Royalty#Writing royalty#Writing royals
3K notes
·
View notes
Note
Hi, it would be awesome if you could give us an idea about alexei's personality described by people in his close circle
Hello! Sorry for the late reply. Here are some quotes about Alexei from the people closest to him, and some extracts from his letters and diaries that show his personality.
Alexei's personality

"The Heir ran along the shore and loudly expressed his joy with every surge of water. In general, how much noise and fun there was! I still remember this time with pleasure. Water splashed, flushed and cheerful children returned home." - Sofia Ivanovna Tyutcheva, nurse/nanny, A Few Years Before the Catastrophe
"Alexei, the only son of the Emperor and Empress, a more tragic child than the last Dauphin of France, indeed one of the most tragic figures in history, was, apart from his terrible affliction, the loveliest and most attractive of the whole family. Because of his delicate health Alexei began life as a rather spoiled child." - Anna Vyrubova, close family friend, Memories of the Russian Court
"The more the boy opened his heart to me the better I realised the treasures of his nature, and I gradually began to feel certain that with so many precious gifts it would be unjust to give up hope. Alexis Nicolaievitch was then nine and a half, and rather tall for his age. He had a long, finely-chiselled face, delicate features, auburn hair with a coppery glint in it, and large blue-grey eyes like his mother's. He thoroughly enjoyed life — when it let him — and was a happy, romping boy. Very simple in his tastes, he extracted no false satisfaction from the fact that he was the Heir — there was nothing he thought about less — and his greatest delight was to play with the two sons of his sailor Derevenko, both of them a little younger than he. He had very quick wits and a keen and penetrating mind. He sometimes surprised me with questions beyond his years which bore witness to a delicate and intuitive spirit. I had no difficulty in believing that those who were not forced, as I was, to teach him habits of discipline, but could unreservedly enjoy his charm, easily fell under its spell. Under the capricious little creature I had known at first I discovered a child of a naturally affectionate disposition, sensitive to suffering in others just because he had already suffered so much himself." - Pierre Gilliard, Alexei's tutor, Thirteen Years at the Russian Court
"Spring 1915 …Yesterday he [Alexei] gorged on black crackers and in the evening, he was sent directly to [Dr.] Derevenko." - Letter from Maria to Nicholas II, Maria Romanov: Third Daughter of the Last Tsar, Diaries and Letters
"18 March [1912] - Pavlovsk… Recently, on the 14th, my wife had lunch with their Majesties, and was embarrassed by the behaviour with the Heir, who is almost two years older than Vera. He wouldn’t sit up, ate badly, licked his plate and teased the others. The Emperor turned away, perhaps to avoid having to say anything, while the Empress rebuked her elder daughter Olga, who was next to her brother, for not restraining him. But Olga cannot deal with him." - 1912 Diary of Grand Duke Konstantin Konstantinovich
"In appearance he resembled his sister Tatiana : he had the same fine features, and her beautiful blue eyes ; he loved his sisters, and they adored him, and patiently submitted to his teasing. The Tsarevitch was a lively, amusing boy, with a wonderful ear for music, and he played well on the balalika : like Tatiana he was shy, but, once he knew and liked anyone, this shyness vanished. The Empress insisted upon her son being brought up, like his sisters, in a perfectly natural way. There was no ceremonial in the daily life of the Tsarevitch : he was merely a son, and a brother to his family, although it was sometimes quaint to see him assume '' grown up " airs. One day, when he was indulging in a romp with the Grand Duchesses, he was told that some officers of his regiment had arrived at the Palace and begged permission to be received by him. The Tsarevitch instantly ceased his game, and, calling his sisters, he said very gravely : *' Now, girls, run away. I am busy. Someone has just called to see me on business." - Lili Dehn, close family friend, The Real Tsaritsa
"Sunday 13th August 1906 …we were all invited to have tea with Their Majesties. All four daughters came to the dinging room, and also, the the great joy of our children, the two-year-old Tsesarevich. He went around the tea table and after greeting everyone, climbed onto his mother’s lap. Igor was sitting beside her, and the little Heir happily moved onto his lap and called him “New” as he was someone unfamiliar. After that, my boys and the Tsar’s girls played with him merrily on the floor…We were all delighted." - Diary of Grand Duke Konstantin Konstantinovich
The following are all from the diary of Sidney Gibbes, English tutor:
"25 January: [Alexei is] On sofa: foot tied up. Talked about the dog and then showed him new picture-book. Afterwards made a paper hat each, which turned out badly, and then began paper boxes; I showed him one complete. He spoke more English in making the box and asked the questions relative to it in English."
"3 February: We drew things on the blackboard with eyes shut. Added tails to pigs, and his manner lost much of its shyness."
"8 February: During this lesson we played on the floor, and I made him flags out of paper by drawing it and colouring. He coloured one and I the other. Flagstaff was also rolled out of paper and tied with wire."
"3 March …Began the story of ‘The Fisherman of York’. He understood very little. A[nastasia] N[ikolaevna] came in from Music [lesson] and explained in Russian." - Printed in Tutor to the Tsarevich
"The Tsarevich lay all day, while we tried to amuse him as best we could. The poor little man longed for Monsieur Gilliard's company. He knew so well how to entertain him and make him forget how ill and weak he still felt" - Sophie Buxhoeveden recalling Alexei's attachment to tutor Pierre Gilliard during imprisonment, Left Behind: Fourteen Months in Siberia During the Revolution
"If the Tsarevitch had any peculiarities, I think the most striking was a decided penchant for hoarding. Many descendants of the Coburgs have been unusually thrifty, and perhaps the Tsarevitch inherited this trait. While thrifty he was really a most generous child, although he hoarded his things to such an extent that the Emperor often teased him unmercifully. During the sugar shortage he saved his allowance of sugar, which he gravely distributed among his friends." - Lili Dehn, close family friend, The Real Tsaritsa
"This unusual and exciting night seemed to fill the Czar’s young son with mischief. As I sat in the room near the Emperor’s study, giving the final orders and' awaiting news of the arrival of the train, I could hear the youngster running about noisily, trying to get across the corridor to where I was, to see what was going on there" - Alexander Kerensky, head of the Provisional Government describing the night the Romanov's waited to be moved from the Alexander Palace, The Catastrophe
"Suffering and self-denial had their effect on the character of Alexei. Knowing what pain and sacrifice meant, he was extraordinarily sympathetic towards other sick people. His thoughtfulness of others was shown in his beautiful courtesy to women and girls and to his elders, and in his interest in the troubles of servants and dependents." - Anna Vyrubova, close family friend, Memories of the Russian Court
Alexei was "elegant, intelligent, and had unusual presence of mind. He possessed, moreover, other winning qualities: a warm, happy disposition, and a generous nature which made him eager to be of help and enabled him quickly to establish rapport with others." - General Count Alexander Grabbe, Major-General of the Tsar's convoy, The Private World of the last Tsar
"in the periods of what may be called his good health, he had all the spirits and mischief of any ordinary boy of his age… As time went on and his first shyness wore off, he treated us as friends and… had always some fun with us. With me it was to make sure that each button on my coat was properly buttoned, a habit which naturally made me take great care to have one or two unbuttoned, in which case he used at once to stop and tell me I was 'untidy again'" - General Sir John Hanbury-Williams, British ambassador in Mogilev, The Emperor Nicholas II, as I Knew Him
""He had a kind heart and was very fond of animals. He could be influenced only by his feelings, and would not yield to authority. He submitted only to the emperor. He was a clever boy but was not fond of books. His mother loved him passionately. She tried, but could not be strict with him, and most of his desires were obtained through his mother. Disagreeable things he bore silently and without grumbling. He was kind-hearted and during the last period of his life he was the only one who liked to give things away. In Tobolsk he had some odd fancies -- for example, he liked collecting old nails, saying: "They may be useful."" - Testimony of Sidney Gibbes to the Sokolov Report, The Last Days of the Romanovs (1920)
"Alexis Nicholaevitch, being a very playful and mischievous boy, on one occasion peeped through the fence. After this was learned by Nikolsky [deputy guard at Tobolsk] he came and made a huge fuss about it. He reprimanded the soldier who was on duty and spoke in a very sharp tone to the czarevitch. The boy got offended and protested to me that Nikolsky was shouting at him." - Testimony of Evgeny Kobylinsky to the Sokolov Report, The Last Days of the Romanovs (1920). To find more about Kobylinsky's unique relationship to the family, see this post.
Alexei's relationship with his sisters

"We all kissed the Empress' hand and that of the Grand Duchesses. That year, we kissed the Tsarevitch's little hand, too; but afterwards, that custom was stopped, since the Tsarevitch didn't miss his chance to boast about it and give himself airs in front of his sisters." - General Alexander Spiridovich, Chief of Security, Last Years at Tsarskoe Selo, Volume 1
"10 January. Aleksei and Anastasia are both moving their beds into the playroom, where they lie next to each other all day. During the day we all have tea up there." - Extract from Tatiana's 1917 diary, Tatiana Romanov, Daughter of the Last Tsar: Diaries and Letters
"Aleksei, my little soul, darling little one. It is so boring here without you and Papa… I was just at the Grand Palace with Maria and Shvybz [Anastasia]… I squeeze you in my mind and love you very very much." - undated letter from Tatiana to Alexei, circa 1916, Russia’s Last Romanovs: In Their Own Words
"As for poor Alexei Nikolaevich, he was as if rooted to the armchair the whole time [unwell]. It was touching to see his sister, Tatiana Nicholaievna, lavishing attention on him before the luncheon." - General Alexander Spiridovich, Chief of Security, Last Years at Tsarskoe Selo, Volume 2
"Sweet Piggy! Sleep well and wake up in the morning with a belly full of milk! Alexei 1914" - letter from Alexei to Anastasia, Alexei: Russia's Last Tsesarevich - Letters, diaries and writings (Volume 1)
"...Don’t tease Maria" - Letter from Alexandra to Alexei, 1 December 1914, Alexei: Russia's Last Tsesarevich - Letters, diaries and writings (Volume 1)
"28 January Tuesday …Too lazy to write this by himself, so Olga is writing it!" - Alexei's 1916 diary, Alexei: Russia's Last Tsesarevich - Letters, diaries and writings (Volume 2)
Alexei's haemophilia

"Everything possible, everything known to medical science, was done for the child Alexei. The Empress nursed him herself, as indeed, with the assistance of professional women, she had nursed all her children. Three trained Russian nurses were in attendance, with the Empress always superintending. She bathed the babe herself, and was with him so much that the Court, ever censorious of her, complained that she was more of a nurse than an Empress." - Anna Vyrubova, close family friend, Memories of the Russian Court
"Livadia. 30 August 1913 …Alexei is well. He has already had 4 mud baths. I took a photo of him when he was being treated in the mud and will glue in an album for you. Alexei’s leg stretched 175 degrees and the leg is almost straight" - letter from Maria to former nanny/nurse Maria Ivanovna Vishnyakova. Maria Ivanovna Vishnyakova was Alexei’s nanny, though was dismissed by Alexandra following disagreements and allegations against Rasputin. I find it intriguing that the girls stayed in touch with her and kept her informed of Alexei's health.
I have slightly less information/quotes on Alexei saved as my research is largely about his sisters, but I hope that this was insightful nonetheless. Thank you for your question!
#q#ask#answered#Alexei Nikolaevich#Alexei Romanov#Tsarevich Alexei#Romanov family#Russian history#Imperial Russia#quotes#sources#letters#diaries#Sidney Gibbes#Sydney Gibbes#Pierre Gilliard#Alexander Grabbe#John Hanbury-Williams#Sofia Ivanovna Tyutcheva#Sophie Buxhoeveden#Isa Buxhoeveden#Lili Dehn#Alexander Spiridovich#Anna Vyrubova#Evgeny Kobylinsky
54 notes
·
View notes
Note
do you know where the first few of the romanovs resided before all of the palaces were built and if so, are any of them remaining? do we know what they look like?
I'm afraid very little from the earliest days of the Romanov dynasty had survived the ravages of time. By the time of Nicholas II, many early residences had already been either destroyed or replaced by the modern and elegant palaces we see today. Here's a few that survived.
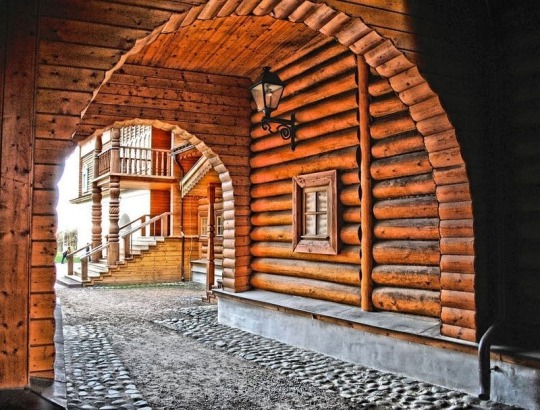
The Cabin of Peter the Great May 1703
Built during the founding of the city of Saint Petersburg, the log cabin was the first St. Petersburg "palace" of Tsar Peter the Great. The small wooden house was constructed in just three days, by soldiers of the Semyonovskiy Regiment.
At that time, the new St. Petersburg was described as "a heap of villages linked together, like some plantation in the West Indies".
The Cabin was boarded up and camouflaged during the Second World War. It was the first St. Petersburg museum to reopen in September 1944, after the end of the Siege of Leningrad.
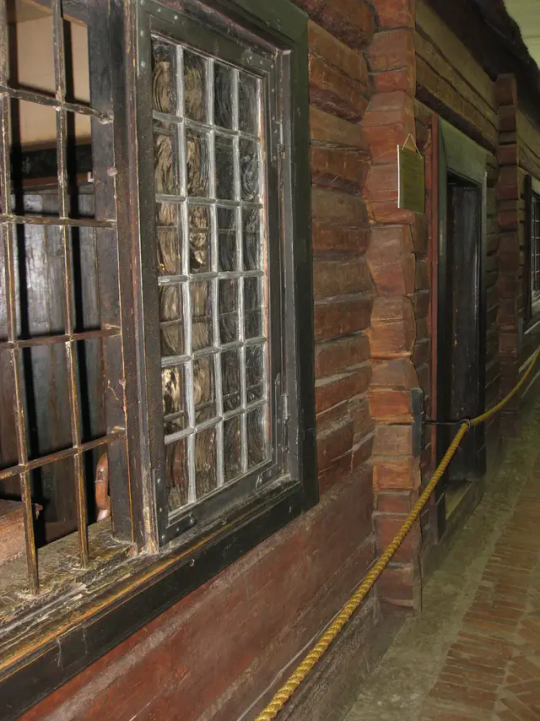



This cabin must have appeared as a huge downgrade after the wooden palace of Tsar Alexei!
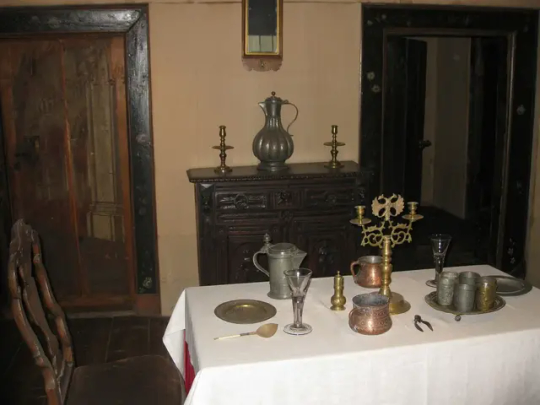
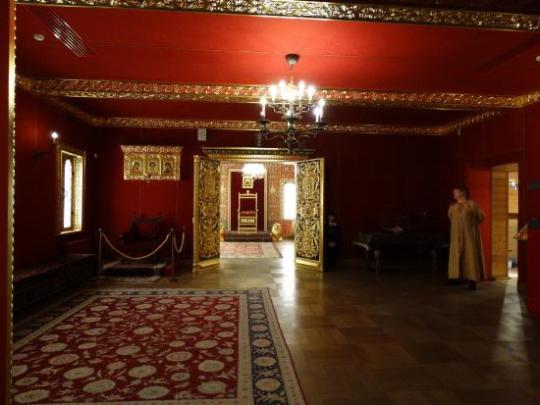
The Wooden Palace of Tsar Alexei Romanov 1667
The recreation of an authentic mid-17th century Romanov residence was built recently in 2010. The Palace of Tsar Alexei Mikhailovich, also known as the Wooden Palace of Tsar Alexei, is a large wooden palace in Kolomenskoye, near Moscow, Russia.
The original was built in 1667 without using any fasten materials, nails or hooks. The wooden palace, famed for its fanciful, fairytale roofs, was a summer residence for Russian tsars before St. Petersburg was constructed.
The palace was divided into male and female halves, with the Tsar and Tsarevitches towers and chambers in the male half and the Tsarina's towers in the female half.
The palace's interior featured rich decorations, including carving, painting, gilding, and ceramic tiles, as well as rectangular and round stoves, weathercocks, and windows and porches.
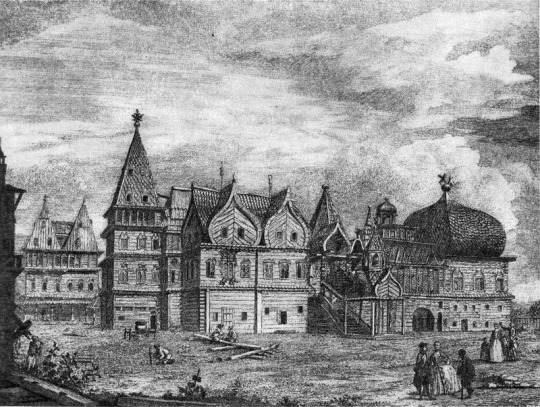



Foreigners referred to this huge maze of intricate corridors and 250 rooms, as 'an Eighth Wonder of the World'. Although basically only a summer palace, it was the favorite residence of Tsar Alexei I.
The future Empress Elizabeth Petrovna was born in the palace in 1709, and Tsar Peter the Great spent part of his youth here.
Upon the departure of the court for the swamps of St. Petersburg, the palace fell into disrepair, so that Catherine the Great refused to make it her Moscow residence. On her orders the wooden palace was demolished in 1768, but thankfully, the detailed plans of the palace had survived.







Summer Palace of Peter the Great
1714
One of the earliest imperial residences I can think of that still exists today is the modest Summer Palace of Peter the Great, which is located on an island near the Peter and Paul Fortress, the burial place of the Romanovs.
The palace was built between 1710 and 1714, a few years before the proclamation of the Russian Empire. By the time of Tsar Nicholas II's reign at the end of the 19th century, it became vacant.
During the Second World War, both the Summer Palace and Summer Gardens were badly damaged by a German bombing raid. The building was repaired, however, and the layout remains unchanged from the original.
Above: The palace as depicted in 1809. Below: The residence today.



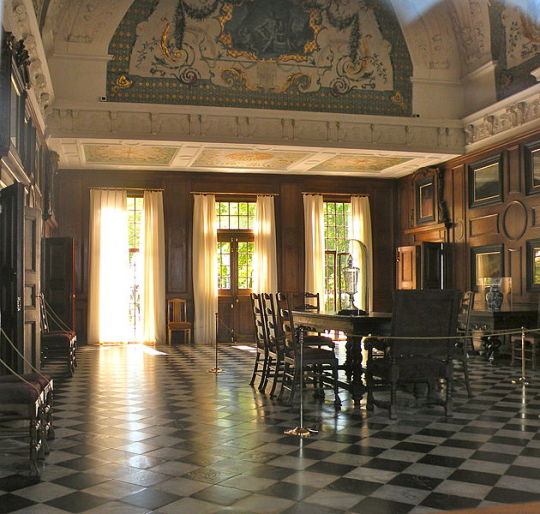
Monplaisir Palace in Peterhof 1714-1716
There is another residence owned by Peter the Great that is still standing today. And that is the Monplaisir Palace in Peterhof.
The following painting depicts the formidable Tsar and his son and heir Tsarevich Alexei Petrovich, who has been accused of preparing to seize power, in the interior of the Monplaisir Palace. Before pronouncing sentence, Peter I gazes into his son's eyes, still hoping to discern signs of remorse.


Above: The Parade Hall of Monplaisir Palace today.




#romanov#romanovs#palace#palaces#history#russian culture#russian history#royal history#imperial russia#moscow#saint petersburg#peterhof#russian imperial family#ask
41 notes
·
View notes
Text



Three photos of The Romanov Family with Grigory Rasputin
Photo 1: Top Row: Olga, Middle Row: Anastasia, Alexei, Rasputin, Alexandra Feodorovna, Bottom Row: Maria, Tatiana, Maria Vishnyakova, 1909
Photo 2: Tatiana (obscured), Maria, Anastasia, Rasputin, Alexandra Feodorovna, Olga, 1907
Photo 3: Unkown Woman (if anyone knows who she is please tell me!), Maria Vishnyakova, Alexei, Rasputin, Maria (on the floor), Anastasia, Tatiana (above Anastasia), 1910
The Romanov family’s relationship with Rasputin is unlike the stereotypical “seducing madman” version that you might first hear. Alexei, the only son and heir to the Russian throne, was a hemophiliac (a disease where the blood cannot clot resulting in any minor bump or bruise could lead to severe hemorrhaging and even death) and had many accidents resulting in major pain for not just him, but for his entire family, especially his mother, Empress Alexandra Feodorovna. The Tsar and Tsarina (Nicky and Alix) were desperate to relieve their son’s pain and heard about Rasputin, a renound mystic healer, from some distant relatives and invited him to court to try to relieve Alexei’s pain. He came to court in 1906 and immediately calmed the boy who prior to this point would not stop crying, and managed to soothe both him and his worried family. Eventually the hemorrhaging stopped Alexei eventually made a full recovery. This “miracle” made Rasputin an immediate source of comfort for the family and became a new important friend. He visited the family often and Alexei and his sisters always looked forward to his visits, even Anastasia who was as young as 7 years old was writing to her mother saying:
“Mama darling! I really want to see Him. I wish him and his children all the best, and send Him my best regards, and all his family. I saw him last night, and I was very happy, tell] him please, my dear Mama…To my Mama from Anastasia”
“Thank you, Mama darling. Tell Anya that I send him my regards. Mama, what is his name? I don't Know My Friend's name is, and I love him so much more than can tell you. Anastasia”
Their relationship with Rasputin remained close throughout his life, various visits and letters, Alexei getting hurt and Rasputin writing or saying calming words and sharing aspects of religion. He remained very close to the family until his death, committed by Romanov hands, and they always remembered him as a close friend and confidant.
There was no love or romance between Rasputin and the “Russian Queen” as the tales tell. He was a friend and a tool to help soothe Alexei, her youngest child. A theory historians have, one that I agree with, is that Rasputin didn’t miraculously heal Alexei, his presence deeply calmed and set Alexandra at peace and because of that, Alexei got calmer because seeing a parental figure stressed while you are in pain doesn’t help you get better does it?
#otma#Romanovs#Romanov#Rasputin#grigori Rasputin#grigory rasputin#naotmaa#otmaa#tsarina alexandra feodorovna#Alexandra feodorovna#Alix of hesse#Tsarevich Alexei#alexei nikolaevich#alexei romanov#olga nikolaevna#maria nikolaevna#tatiana nikolaevna#anastasia nikolaevna#russian imperial family#russian history#1908#Maria Vishnyakova#grand duchess anastasia nikolaevna of russia#grand duchess olga nikolaevna#grand duchess maria nikolaevna#grand duchess anastasia nikolaevna#grand duchess Tatiana nikolaevna#quotes#letters and diaries#informational post
24 notes
·
View notes
Text

"In 1913, the Romanovs celebrated the tercentenary of the dynasty's rise to power. As expected, the planned festivities were glorious. The previous years had been one of prosperity, the industrialization continued to evolve and this economic flourishing made it possible to celebrate the family's success grandly. Politicians and aristocracy hoped that the memory of great figures of the past could strengthen the unity of the nation around the Tsar. The Imperial family left Tsarskoye Selo for the Winter Palace in St. Petersburg for celebrations that began on March 6 with a te-déum in Kazan Cathedral. The following days were full of ceremonies and festivities for the Tsars, whether receiving delegations from all parts of Russia in typical costumes, or going to balls. Alexandra attended in a court dress and wearing the Kokoshnik, the traditional head arrangement of Russian women. The daughters wore white dresses with the ribbon of the Order of St. Catherine, and all the Grand Dukes were present. Olga and Tatiana, "the big pair", already attended parties as adults and could wear beautiful long dresses. Even the Faberge egg that Nicholas gave to Alexandra that year honored the dynasty. Decorated with images of all the Romanov Tsars, it had inside as a surprise two maps of Russia, one from 1613 and the other from 1913. In May, the family boarded a ship to Kostroma in order to repeat the steps of Michael, the first Tsar of the family, from the Ipatiev monastery, where he lived, to the throne. Everywhere, peasants greeted the procession effusively, even entering the water of the Volga River to get a closer look at them or throwing themselves to the ground to kiss Nicholas's shadow. The best part of the celebration took place in Moscow, when Nicholas crossed Red Square alone and entered the Kremlin with the sound of the prayers of the priests lined up along his way. According to protocol, both the Empress and the heir were to walk behind the Tsar, but Alexei, again ill, had to be carried by one of his sailors. The success of the celebrations strengthened the belief, especially for Nicholas and Alexandra, that the autocracy remained strong and had support from the people. On the other hand, the Duma Liberals still insisted on reforms, not finding ears in the Tsar and his ministers. And behind all this, opponents of the regime continued to act, even in exile."
The Last Tsars | Paulo Rezzutti
(loose translation)
#facts#tsar nicholas ii#tsarina alexandra#grand duchess olga#grand duchess maria#alexei nikolaevich#tatiana nikolaevna#grand duchess anastasia#otma#otmaa#naotmaa#tercentenary#my own#tsar#tsarina#romanovs#grand duchess#tsarevich#the romanovs#alix of hesse#nicholas romanov#russian history#xx century#grand duchess tatiana#tsarevich alexei
48 notes
·
View notes
Text
Finished Anastasia by Sophie Lark! Random thoughts with full spoilers below:
-you can definitely tell the author likes the 1997 animated Anastasia movie, there are some elements that feel inspired by/paying homage to that film (Damien/Dimitri similar sounding names, him calling Anastasia “Anya”, the music box, Rasputin’s greenish hue at times, and my favorite the white bat called Bat (Bartok!)). Even the illustrations bring that movie to mind.
-this is not a historical retelling by absolutely any means whatsoever (it is about as accurate as My Lady Jane - which is actually a good comparison cause that show also creates a magic filled alternate reality and the main premise is a doomed historical figure survives), but there are obviously real places and people mentioned which sent me down the Wikipedia and YouTube documentaries rabbit hole. So despite this being a complete fantasy novel, I actually learned a bit by looking up the real world history on my own! I’m embarrassed at how long it took me to realize that Felix was a real person (and it was his Wikipedia entry that made me suspicious about the novel’s ending)
-I never was crazy about Damien himself (though his death touch was nice and angsty and added a whole new layer of obstacle to their romance) but I liked him and Anastasia’s relationship (even more post Revolution) I just wish had a few more moments and interactions when they were growing up together in a show don’t tell way. But I was so so looking forward to the complete grief stricken angst and breakdown as regret when he found out about Anastasia’s “death”; and it happens in the time skip! I love that trope, and was so annoyed it happened off screen.
-Anastasia’s relationship and interactions with her family was well-done. It really showed that even though her family was extremely flawed and in the wrong, they all desperately loved and protected each other (which I think is part of the tragedy of the last Romanovs, that they were well known to be a close and loving family but absolutely terrible autocratic rulers. They would’ve been happier not being the imperial family).
-the big spoiler: time travel solves (mostly) all. I suspected this was gonna happen when historical figures that are known to survive the Revolution were all killed off in the first timeline. In all honesty, I didn’t mind it. This was a fantasy story, the time manipulation element has been part of the plot from the beginning so didn’t come out of left field, and the foreword directly stated Anastasia was going to have her happily ever after. And as mentioned above, the more I read the more I realized in order for her to have a happily ever after, she needed both Damien and her family. I actually had more trouble accepting that Anastasia became Tsarina. I mean, it was a big thing that the girls could not inherit the throne, that was why Alexei having hemophilia and being sickly and likely to die was SO MAJOR politically, cause her dad just couldn’t “decide” to give the throne instead to one of the daughters….except that is exactly what happened. And not even Olga, the eldest child, but the youngest daughter! That part (weirdly enough out of all lol) broke my suspension of disbelief for a bit, but after some time I realized that it was the best ending for the AU to give the throne to the person that had lived the terrible alternate future and could lead Rusya to peace and prosperity for all (since no Revolution happened in the new timeline). I just had to headcanon it that it got passed through the Duma due to Anastasia’s time walking capabilities (which the heir was always supposed to have but she was the only one of her siblings to inherit). And I did like the symmetry of Damien (who was supposed to Attaman) leaving to become the Rusyan consort, while Alexei (who was supposed to be Tsar) instead becoming a Cossack. And you know what, it is still bittersweet that Anastasia lost the version of Damien that she first married, and all the moments and understanding and memories they had built together.
-so, this book felt like a fanfic, and I mean that in the best possible way. There were illustrations (which were gorgeous) and a soundtrack (with tracks interspersed throughout the novel so you know what part each song corresponds with). It does not replace the Anastasia 1997 movie in my heart of hearts (which will probably always be my favorite Anastasia retelling) and did not ignite a new obsession (which was kinda hoping it would). But this was very obviously a passion project, and I enjoyed reading it, and have already lent my copy out to someone else. In a couple years will definitely re-read it again.
Edited to add: I forgot to mention that Rasputin being a vampire was a twist that completely took me by surprise but I thought was a very clever fantastical take on Alexei’s dependence on his “healing” powers
#Anastasia by Sophie lark#Anastasia#Damien kaledin#Anastasia/Damien#Anastasia retelling#Anastasia book#anastasia 1997#sophie lark#romanovs#Russian Revolutions fantasy AU
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Tsar Alexei II, The Beloved
June 7th, 1989
St. Petersburg, Empire of Russia

I was awoken by the sounds of sirens and vehicles passing by my tenement on Millionnaya Street around 2:44 a.m. I thought nothing of it until I was jolted from my slumber by the Palace Church whose bell had been struck and rang out loudly but only once. A minute later another solitary strike of the bell and I knew... a knell for the sovereign.

I hurried to get dressed and rushed out the door to the Palace Park. As I arrived, I noticed something erected in front of the main gate to the Winter Palace.

A wreath lay upon a black satin pillow and was flanked by lilies, the traditional flowers for mourning. A plaque lay before the wreath with the words etched into the cast iron that read,
Обращение к народу Императорской России
С сожалением сообщаем Вам о кончине нашего Царя, вошедшего в царство бессмертия.
"A Proclamation to the People of Imperial Russia
We regret to inform you of the passing of the Tsar who has entered the realm of immortality."

I hurried to the Neva side, there were several vehicles from the Imperial Household Security Services, I hurried to ask the photographer if he had any information about what has happened. He told me that the Tsar had died peacefully in his sleep. The Prime Minister was rushed to the scene to witness and sign the order of Ascent for the Heir Ivan Alexievich Romanov. He said I could get a better look from the park across the river.

I couldn't believe I got to witness this scene in history, the body was being loaded into an ambulance to be taken to the hospital for autopsy to ensure the causes were indeed natural and not nefarious.
7 notes
·
View notes
Text

Emperor Nicholas I (1796 - 1855) and Empress Alexandra Feodorovna (1798 -1860 - nee Princess Friederike Luise Charlotte Wilhelmine of Prussia
Nicholas I, the Iron Tzar, and his sons
This couple was the first “Nicholas and Alexandra” in the Romanov Dynasty. They were Nicholas II's great grant-parents.
It was said that he was the best-looking man in Europe. She was tall and fair and enjoyed jewels, gowns, and balls. They loved each other, and their union was not unhappy, but he did not remain faithful to her (after he died, his last mistress was employed as Alexandra’s lectrice, and they became friends.) Nicholas and Alexandra had seven children, four sons, and three daughters. Those four sons would ensure that the generation of Romanovs following them would not want for male heirs. As a matter of fact, there would be too many Grand Dukes, making it necessary for his grandson, Alexander III, to change the Pauline laws, re-defining who would be considered a Grand Duke or Duchess, among other things (only grandsons/grandaughters of a Tzar would be Grand Duke/Duchesses; great-grandsons and so on would be Princes and Princesses of the blood).

Nicholas I with his four sons: Tsarevich Alexander Nikolayevich (1818 - 1881 - future Alexander II), Grand Duke Konstantin Nikolayevich (1827 - 1882), Grand Duke Nikolay Nikolayevich (1831 - 1891), and Grand Duke Mikhail Nikolayevich (1832- 1909.)
According to the literature, Nicholas raised his two elder sons very strictly but had more of a paternal relationship with the younger two. His priority was to bring them up so that they were true soldiers and so that when Alexander inherited the throne, the other three would help and support him. And they did. Nicholas I adored his daughters and was devastated when his youngest daughter Alexandra (better known as Adini), died. (His daughters would be discussed in another post.)
Below are the sons of Nicholas I and their spouses:
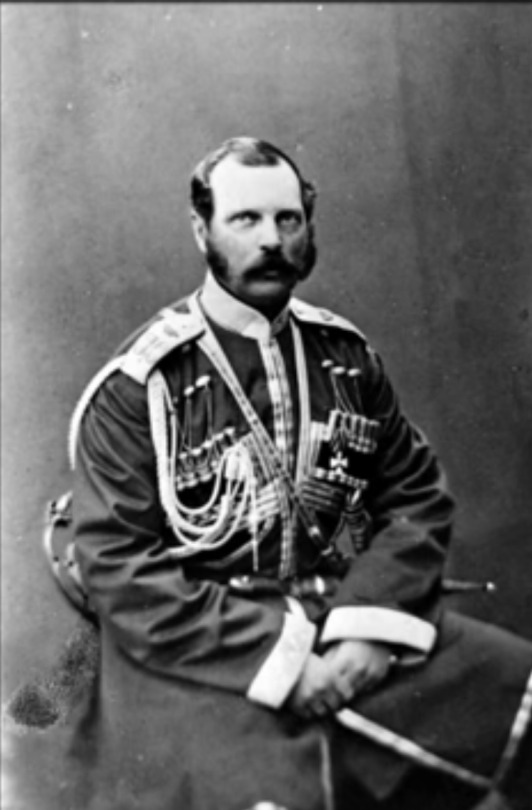
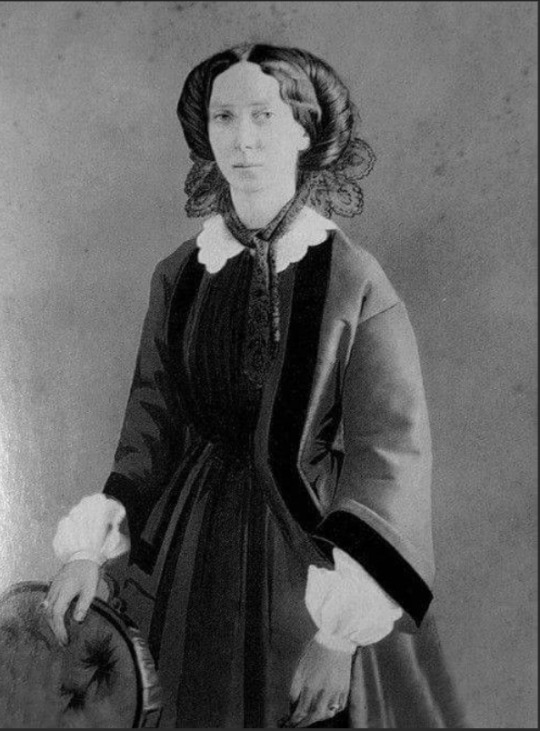
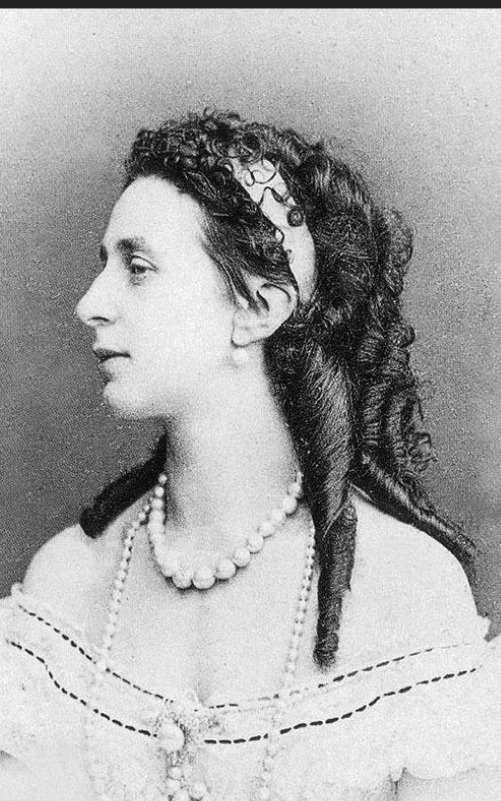
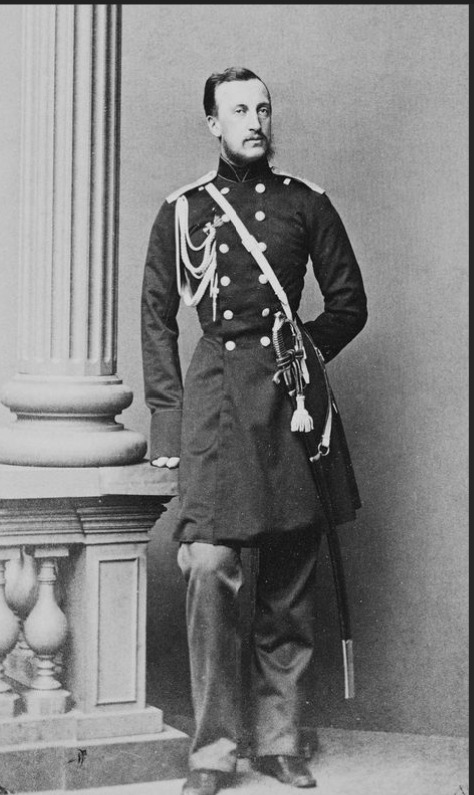
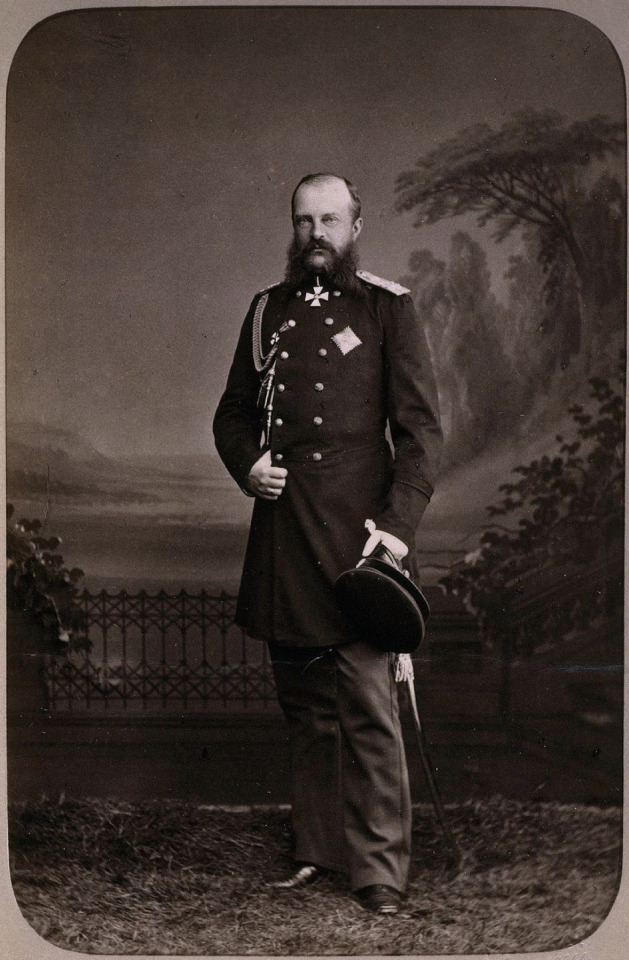








1. Emperor Alexander II and his first wife Empress Maria Alexandrovna (born Princess Wilhemine Marie of Hesse); Issue listed below (Only legitimate issue surviving to adulthood listed; not in birth order)
Grand Duchess Marie
Grand Duke Nicholas Alexandrovich
Alexander III
Grand Duke Vladimir
Grand Duke Alexei
Grand Duke Sergei
Grand Duke Pavel
2. Grand Duke Konstantin Nikolayevich and Grand Duchess Alexandra Iosifovna (Princess Alexandra of Saxe Altenburg); Issue listed below (Only legitimate issue surviving to adulthood listed; not in birth order) - They would be known as the "Konstantinovichi"
Grand Duke Nicholas
Grand Duke Konstantin
Grand Duke Dmitry
Grand Duke Vyacheslav
Grand Duchess Olga
Grand Duchess Vera
3. Grand Duke Nikolay Nikolayevich (the Elder) and Grand Duchess Alexandra Petrovna of Russia, born Duchess Alexandra Frederica Wilhelmina of Oldenburg. Issue listed below (Only legitimate issue surviving to adulthood listed; not in birth order); Known as the "Nikolayvichi”
Grand Duke Nicholas Nikolayevich
Grand Duke Peter Nikolayevich
4. Grand Duke Mikhail Nikolayevich and Grand Duchess Olga Feodorovna (nee Princess Cecilie of Baden) Issue listed below (Only legitimate issue surviving to adulthood listed; not in birth order) They were known as the "Mikhailovichi" (although they preferred to be called the "Michels;" the family called them the "Wild Caucasians" because they grew up in the Caucus and had strong opinions that they voiced loudly)
Grand Duchess Anastasia Mikhailovna
Grand Duke Nicholas Mikhailovich
Grand Duke Mikhail
Grand Duke George
Grand Duke Alexander
Grand Duke Sergei
Grand Duke Alexei
The children and grandchildren of these couples would be directly involved in one way or the other in the Great War, the Russian Revolution, the Civil War in Russia, and the overthrow of the monarchy and the Romanov Dynasty. Some would lose their lives, others would lose children, brothers, and spouses, and all would lose their country, status, and privileges.
#russian history#romanov dynasty#imperial russia#Emperor Nicholas I#Emperor Alexander II#Grand Duke Konstantin Nikolayevich#Grand Duchess Alexandra Iosifovna#Grand Duke Nikolay Nikolayevich#Grand Duchess Alexandra Petrovna of Russia#Grand Duke Mikhail Nikolaevich#Grand Duchess Olga Feodorovna#vintage photography
93 notes
·
View notes
Text

Emperor Nicholas II holding his son and heir Tsarevich Alexei Nikolaevich Romanov, on the deck of the Imperial yacht 'Polar Star', 1905.
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
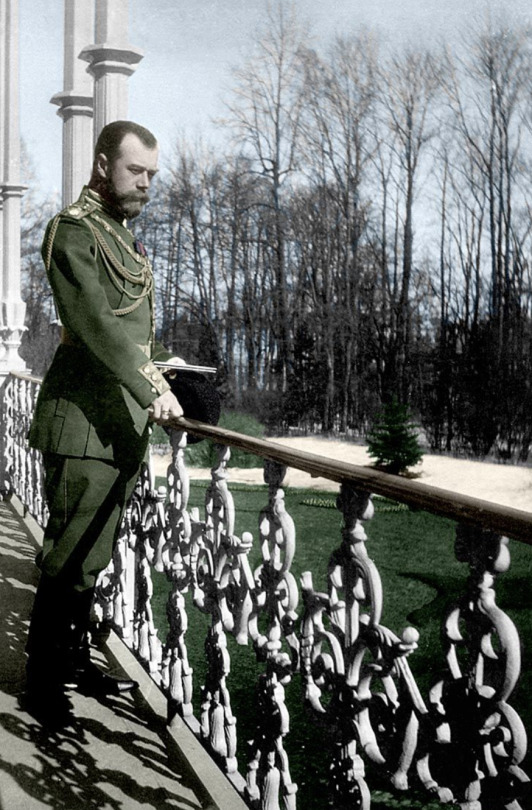

On the photograph: Nicolas (Nikolai Alexandrovich), the former Tsar of Russia, at the terrace in Alexandrovsky Palace.
'Rumours' of the 'murder' of Nicolas II as depicted by Siberian LIfe newspaper in July 1918:
‘Siberian Life’, No. 62, Thursday July 18, 1918: Was Nikolai Romanov really killed?
The newspaper ‘Power of the People’ published the following article on the matter of the murder of Nikolai Romanov:
'News of the murder of former Tsar Nikolai Romanov appeared in the local Siberian press. All this news was based entirely on rumours.
In the Moscow newspapers delivered to us yesterday, dated June 22, 23 and 25, we have found the following interesting data regarding rumors about the murder of Nikolai Romanov.
The newspaper ‘Bel. Rus.’ reported by telegraph from Petrograd on June 24:
‘New Life telegraphs from Tsaritsyn that, according to information received, the former Tsarina Alexandra Fedorovna and her two daughters, Olga and Tatyana, have been brought to Perm. The former Tsar Nikolai Romanov and the former heir are not there. Railway employees who accompanied the train with prisoners say that Nikolai Romanov was killed last week. The exact date of the murder is not indicated, but it is reported that news of the murder of Nikolai Romanov appeared only two days after the murder.
The former Tsar was allegedly shot by two guards guarding him. The railway workers did not receive any information regarding the former Heir.’
‘Our Century’ (formerly ‘Rech’) of June 23 cites a report in the press bureau of the Sov . adv. commissioners with the following content:
‘In recent days, a number of bourgeois press have reported rumors about the murder of the former Tsar Nikolai Romanov. We are told from official sources that daily communications take place between Moscow and Yekaterinburg via direct wire, and so far, no message has been received from Yekaterinburg about the murder of Nikolai Romanov. Thus, all rumors reported in the bourgeois press are complete fiction.’
Regarding the ‘death’ of the former heir Alexei, the same newspaper cites the following excerpt from the newspaper ‘New Life’:
‘New Life’ reports that, according to the stories of those who came from Yekaterinburg, the former Heir, Alexei, died two weeks ago. Since moving from Tobolsk, Alexey has not gotten out of bed .’
‘Freedom of Russia’ (formerly ‘Russian Vedomosti’)responds to rumors about the fate of Nikolai Romanov in issue No. 53 of June 23 :
‘In recent days, reports continue to appear in some Moscow newspapers regarding the fate of Nicholas II and his family, either confirming, based on information from various sources, the initial rumor about the murder of the former emperor, or refuting this rumor. Some messages contain various details of what happened in Yekaterinburg. Unfortunately, we are unable to verify these rumors through our correspondent in Yekaterinburg. In Moscow, at the German embassy, our employee, who went there yesterday to check the said message, was given a categorical answer that the embassy had no information either confirming or refuting rumors about the murder of Nicholas II or members of his family. A similar answer was given in Soviet circles. The Soviet authorities also do not have any information from Yekaterinburg concerning the fate of the former Emperor .’
The officialdom of the Soviet government ‘Izvestia V.Ts. Spanish com. owls slave . and arm . dep .’ in issue 129 of June 25, provides the following categorical denial - a telegram about the murder of Nikolai Romanov from the chairman of the Yekaterinburg Soviet of Deputies: ‘Ekaterinburg, June 24. The rumor about the murder of former Tsar Nikolai Romanov is yet another provocative lie.’ Comrade of the Chairman of the Executive Committee Zagvoskin. Secretary Korobolkin.
" What to believe?" – asks ‘The Will of the People’.



Images: left top: the cover of the newspaper Siberian Life dated 18 July 1918; top right: the article called 'Was Nikolai Romanov really killed?; bottom: the newspaper clip of the article 'Was Nikolai Romanov really killed?' that appeared in the Siberia lIfe on 18 July 1918.
#research#romanovs#investigation#nicolas ii#seraphima bogomolova#evidence#murder mystery#newspapers#rumours#July 1918
7 notes
·
View notes
Text






VERSES : Honor and Bloodshed (Medieval) Verse FC: Olivia Cooke
Her Majesty Natalia Alianovna, sole remaining heir to House Romanov. Following her family's death in a fire when she was an infant, leaving her in the care of Ivan Petrovich Bezukhov, Natalia reclaimed the throne at age fifteen. She was forced to marry, and wed a teenager named Nikolai, who was a year older than her. They expected a child not long after. Nikolai is later killed while aiding in war.
Unfortunately, following a long labor and strenuous birth, their infant daughter did not make it. Her name was Roza Nikolaevna. Natalia didn't remarry until the age of twenty-eight, to the arranged engagement of Alexei Andreovitch Shostakov.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Romanov myths part one: Alexei being injured by sledding down the stairs
Although Alexei was given more freedom than is assumed by many people, and certainly had a rambunctious personality, the long-standing story of him sledding down the stairs and then crashing, causing a haemophilia attack in Tobolsk is a myth.
Both Nicholas and Alexandra do not mention this in their diaries, and surviving letters from the Grand Duchesses also do not record Alexei’s rumoured ill-fated sledding adventure. This especially is unusual, as their letters from Tobolsk included a lot of detail about them having fun sledding and on the snow mountain they constructed, so this omission is telling. Alexei did, however, have a sled and a boat which he, his friend Kolya Derevenko, and sister Olga sometimes rode down the stairs and onto the pond (which appears to be mostly small pools of water with a lot of imagination) outside (Olga apparently lost her balance and then fell out once!)

From Alexei's diary (note how he does not mention crashing or having a haemophilia attack):
Sunday 25/7 March [1918]
At eight o'clock there was a religious service, Mama and the sisters sang because the choir was busy. Kolya came at two o'clock. We played in the garden in the afternoon. We shot at a target with bows and arrows [there is a photo of this - see below]. It's very interesting. After tea, we played hide and seek. I received a sleigh and a boat as a gift from a local trader, models of the sleds and boats of the region. Kolya and I played with them a lot and we went down the stairs in the boat. He left at nine o'clock.


Alexei’s sister Anastasia writes about the boat and ‘pond’ here:
4/17 April 1918
Thank you very much, dear Dalechka, for the letter. It took a long time to get here – since December! But it is good it arrived. How are you? We think of you often. It is more or less quiet here. The weather has been divine, but not very warm the last few days. We continue to chop and cut up firewood, and it turns out pretty good. We fixed up our swing, and started to use it again, but probably the ropes will break soon as it has been done poorly. Our garden is a mass of water and mud. My brother has a little boat in which we, so to say, take a ride (it is a big imagination.) There is still not enough water, so we push it of the tracks with sticks and of course get completely soaked. Well, it is a little bit of fun! And how do you pass the time? Well, we are off for a walk so I must finish. I wish all of you the very best. Big greetings to all! I kiss you firmly. Greetings to your Papa and Seryozha.
Anastasia.
In reality, Alexei injured himself after contracting a bad cough. This was most likely caught off one of the visiting children to the house who kept him company, probably Kolya. The repeated coughing unfortunately triggered internal bleeding, leading to a haemophilia attack which left him unable to walk.
It was this attack that meant Alexei, Olga, Tatiana, and Anastasia were not moved to Ekaterinburg with their parents and sister Maria, as the Heir was too ill to move across the country. However, he did make some sort of recovery, at least to the point of being able to be safely transported to Ekaterinburg, and he is photographed sat upright on the Rus steamer, although looking thin. Despite this slight recovery, he was still unable to walk for the rest of his life. The night of the execution he was given a chair to sit on due to being unable to stand independently for any length of time.


A staircase at Tobolsk
So - where did this myth of Alexei sledding down the stairs causing his last haemophilia attack come from?
Robert K. Massie’s 1967 book ‘Nicholas and Alexandra’ appears to be the origin of the story in popular history. On page 490, Massie wrote:
‘[Alexei] was devising new and reckless games which no one seemed able to inhibit. One of these — riding down the inside stairs on a boat with runners which he had used on the snow mountain — led to calamity. He fell and began to bleed into the groin.’
Whilst Massie’s book is a cornerstone in Romanov historical works, it was released 56 years ago, when there was still a fair amount of mystery and rumour surrounding the Romanovs and their final months. The 1971 film, also named ‘Nicholas and Alexandra’, adapted the book into a three-hour epic film dedicated a whole scene to re-enacting this myth, giving it more publicity.
VIDEO CREDIT: Nicholas and Alexandra, Franklin J. Schaffner, 1971, Columbia-Warner Distributors, Archive.org, uploaded by Olga Movie Man on December 26, 2019, https://archive.org/details/1971nicholasandalexandra. Alexei played by Roderic Noble. They make Tobolsk look a LOT rougher and barren than it actually was!!
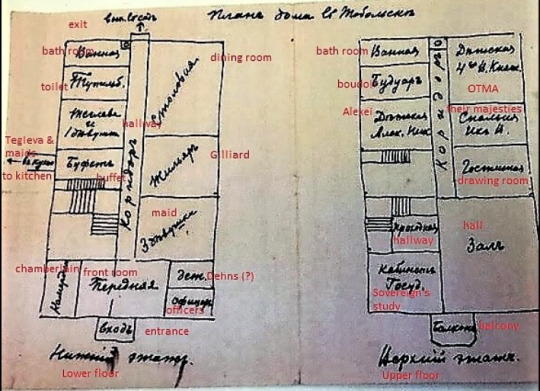
A floor plan of the Governor's Mansion, Tobolsk, drawn by Prince Vasily Dolgorukov. Translated in red by Helen Azar.
To summarise: although Alexei did have a boat and a sled whilst at Tobolsk and did ride them down the stairs, these games never caused a haemophilia attack and he never crashed them to the point of causing serious injury. Rather, he contracted a cough which caused internal bleeding. Robert K. Massie mistakenly put this in his book 'Nicholas and Alexandra', and the myth became more popular due to its inclusion in the 1971 film of the same name.
SOURCES:
Diary and letters quoted available here
Alexei: Russia's Last Tsesarevich - Letters, diaries and writings, by George Hawkins
Anastasia Romanov: The Tsar's Youngest Daughter Speaks Through Her Writings (1907 - 1918), by Helen Azar and George Hawkins
Nicholas and Alexandra - film, directed by Franklin J. Schaffner - free to watch here
Nicholas and Alexandra - Robert K. Massie - free to read here
Floorplan of Tobolsk - Helen Azar's website
Tour of Tobolsk in its current form as a museum - (Russian language!)
Photos: public domain, toptyumen
#Romanov#Romanov family#russian history#myths#myth busting#Alexei Nikolaevich#Alexei Romanov#Nicholas II#Tsar Nicholas#Alexandra Feodorovna#Tsarina Alexandra#OTMA#OTMAA#Nicholas and Alexandra#Nicholas and Alexandra 1971#Anastasia Nikolaevna#Anastasia Romanov#sources#dated#my own#Tobolsk#captivity#sledding#Olga Romanov#Tatiana Romanov#Maria Romanov#tsarist russia#romanov russia#romanov dynasty#romanov family
83 notes
·
View notes
Text










The Romanovs AU: Peter III(1728 - 1791) and Catherine II(1729 - 1792).
In 1745, the Prussian princess Sophia Augusta Frederica of Anhalt-Zerbst became the wife of the heir to the Russian throne, Peter, and converted to Orthodoxy. After adopting the Provo-Slavism, she ceased to be a Prussian princess and became the Russian Tsarevna Catherine Elekseevna. Peter did not love his wife, but after the birth of their eldest daughter he looked at her differently, and the birth of a son finally brought the couple closer together. In 1762 the Russian Empress Elisabeth died and Peter became Emperor. He reigned in the Russian Empire together with his wife. Almost 30 years they ruled in Russia, but in 1791 Peter died suddenly. For Catherine the death of her husband was a strong blow, she began to lead a reclusive life and did not want to see anyone except her eldest son, as he was similar to her late husband. A year later, Catherine herself died of a heart attack.
Children of Peter III and Catherine:
Elisabeth(1748 - 1815). First-born son of Peter III and Catherine II Alexeevna. Was named in honor of the Russian empress Elisabeth Petrovna. Elisabeth's parents did not like each other, but her birth brought them closer together. In 1764 she married Leopold II and became Empress of the Holy Roman Empire. The married life of Elizabeth and Leopold was a happy one. The marriage produced 12 children: Franz II, Alexander, Clementine, Karl, Mary, Louise, Ferdinand, Ludwig, Leopold, Caroline, Anna and Joseph.
Mary(1750 - 1825). Duchess of Hesse. In 1770 married Ludwig I of Hesse. She was loved not only by her husband and his relatives, but also by her subjects. Mother of 8 children: Ludwig II, Louise, George, Friedrich, Emil, Gustav, Charles, Henrietta.
Paul(1754 - 1822). Emperor of All Russia. The long-awaited heir to the Russian throne. After ascending the throne, Paul continued the work of his grandfather Peter I the Great. Under his rule the Russian Empire reached the peak of its power. Reforms beneficial to the state were adopted, and new and favorable treaties with other countries were concluded. Husband:
1)Augusta Hesse of Darmstadt(died in childbirth).
2)Sophia of Württemberg.
Father of 11 children: stillborn son, Alexander I, Constantine, Alexandra, Elena, Mary, Catherine, Olga, Anna, Nicholas I, Michael.
Anne(1757 - 1823). Queen of France, wife of Louis XVI and mother of 4 children: Louis, Mary, Charles, Sophia. She received her name in honor of her paternal grandmother. Was the favorite sister of Russian Emperor Paul. In 1789 the Great French Revolution began, and in 1791 Anne and her children fled to Russia. Two years later she learned of her husband's execution. Anne and her children never returned to France.
Alexey(1762 - 1812). The last child of Peter III and Catherine II Elekseevna. General Fieldzeichmeister. He was married to Louis XVI's sister Elizabeth. Father of 3 children: Mary, Catherine, Anton.
Романовы AU: Пётр III(1728 - 1791 ) и Екатерина II(1729 - 1792).
В 1745 году прусская принцесса София Августа Фредерика Ангальт-Цербстская стала женой наследника русского престола Петра и приняла провославие. После принятия провославия она перестала быть прусской принцессой и стала русской царевной Екатериной Елексеевной. Пётр не любил свою жену, но после рождения их старшей дочери он по другому посмотрел на нее, а рождение сына окончательно сблизило супругов. В 1762 году умерла российская императрица Елизавета Петровна и Пётр становится императором. Царствовал в российской империи совместно с женой. Почти 30 лет они правили Россией, но в 1791 году Пётр скоропостижно скончался. Для Екатерины смерть мужа стала сильным ударом, она начала вести затворнический образ жизни и никого не хотела видеть кроме старшего сына, так как он был похож на её покойного мужа. А через год не стало и самой Екатерины, она умерла от сердечного приступа.
Дети Петра III и Екатерины II:
Елизавета(1748 - 1815). Первенец Петра III и Екатерины II Алексеевны. Была названа в честь российской императрицы Елизаветы Петровны. Родители Елизаветы не любили друг друга, но её рождение их сблизило. В 1764 году вышла замуж за Леопольда II и стала императрицей Священной Римской империи. Супружеская жизнь Елизаветы и Леопольда была счастливой. В браке родилось 12 детей: Франц II, Александр, Клементина, Карл, Мария, Луиза Фердинанд, Людвиг, Леопольд, Каролина, Анна и Иосиф.
Мария(1750 - 1825). Герцогиня Гессенская. В 1770 вышла замуж за Людвиг I Гессенского. Её любил не только муж и его родственники, но и подданные. Мать 8 детей: Людвиг II, Луиза, Георг, Фридрих, Эмиль, Густав, Карл, Генриетта.
Павел(1754 - 1822). Император Всероссийский. Долгожданный наследник русского престола. После восшествия на престол Павел продолжил дело своего деда Петра I Великого. При его правлении российская империя достигла пика своей могущественности. Были приняты полезные для государства реформы, а также заключены новые выгодные договора с другими странами. Муж:
1)Августы Гессен Дармштадтской(умерла при родах).
2)Софии Вюртембергской.
Отец 11 детей: мертворожденный сын, Александр I, Константин, Александра, Елена, Мария, Екатерина, Ольга, Анна, Николай I, Михаил.
Анна(1757 - 1823). Королева Франции, жена Людовика XVI и мать 4 детей: Людовик, Мария, Шарль, София. Получила свое имя в честь бабушки по отцовской линии. Была любимой сестрой российского императора Павла. В 1789 году началась Великая французская революция, а в 1791 Анна с детьми сбежала в Россию. Через 2 года она узнала о казни мужа. Анна и её дети во Францию больше не вернулись.
Алексей(1762 - 1812). Последний ребёнок Петра III и Екатерины II Елексеевны. Генерал фельдцейхмейстер. Был женат на сестре Людовика XVI Елизавете. Отец 3 детей: Мария, Екатерина, Антон.
#history#history au#romanovs#russian#russian imperial family#royal family#royalty#russians#romanov family#18th century#19th century#17th century#russian history#russia#russian royalty#royals#royal#house of romanov#House of romanovs
6 notes
·
View notes
Note
Did Olga Nikolaevna have any extra privileges in terms of rank as the first born child?
I don't think she did legally or anything. The laws of succession at the time were such that a woman could only inherit if there were literally no eligible men left ahead of her. So technically OTMA were in line for the throne, but their father, brother, uncle, all their cousins, etc would have to die. Even after the revolution, if one of OTMA had theoretically survived, they still would have come after the Vladimirovichi, after Dmitri Pavlovich, after Nikolasha, after Uncle Sandro and all his sons, etc, Still plenty of male Romanovs ahead of them. They might have been a rallying point but they wouldn't have been seen as 'the rightful empress' or whatever.
But women did technically still have succession rights; that's why Tatiana Konstantinovna and Irina Alexandrovna had to sign them away when they married nobles instead of royals.
But articles at the time, especially before Alexei was born, do treat her like a possible 'future Empress.' Before the birth of Alexei there were rumors Nicholas would change the laws to allow Olga to inherit (or marry her to Dmitri Pavlovich and name them joint heirs or something), and after Alexei was born, there were enough rumors about his poor health that rumors still persisted that it might fall to Olga.
I don't think she had extra privileges exactly but that because she was the oldest she reached milestones that some of her siblings didn't. She came into her fortune, for example. She got to be out in society a little bit before the war, etc. Differences in dress and jewelry etc I think were more to do with age than special privileges as the eldest; the others would eventually have been the same.
24 notes
·
View notes