#Hakujaden
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
I’m going to be sick
25 notes
·
View notes
Text







HAKUJADEN (1958) dir. Taiji Yabushita
#mine#gifs#animanga#movies#filmedit#animationedit#dailyanime#anisource#anime#animeedit#fyanimegifs#dailyanimatedgifs#oldanimeedit#anime gifs#vintage anime#animation#animation gif#Panda and the Magic Serpent#Hakujaden#Toei Animation#Taiji Yabushita#白蛇伝
265 notes
·
View notes
Text

Hakujaden (1958)
88 notes
·
View notes
Text




Working on a post about Hakujaden for my Wordpress and it kills me how beautiful the backgrounds are and how lovely the color scheme is.
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
YOU FORGOT SAILOR MOON.
#tumblr poll#panda and the magic serpent#also known as#hakujaden#christ i'm old#oldtaku#i had it on vhs#and i adored it#i still do honestly#it was sailor moon after that#the original 1990s us broadcast
40K notes
·
View notes
Text


Hakujaden - Monster Strike
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Animation Night 188: Gisaburo Sugii and his cat films
Let me introduce you to a fellow.
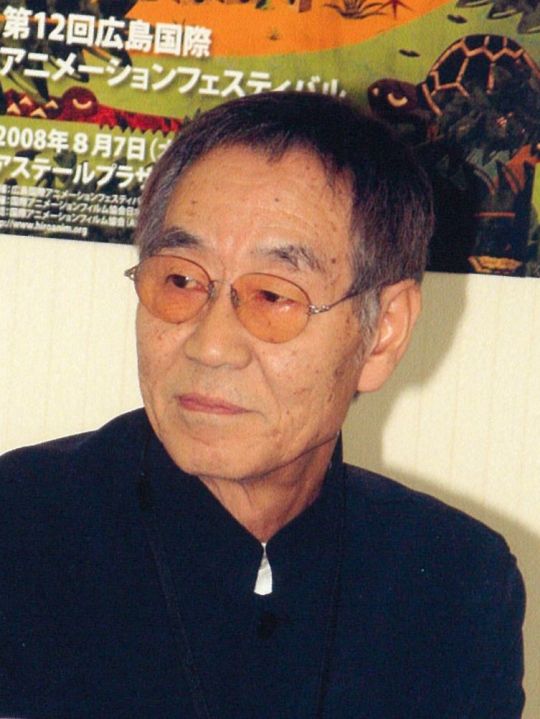

Gisaburō Sugii, born 1940, is one of the oldest school animators still working in the industry. His early filmography is something like a history of anime, or at least MushiPro: he started on Hakujaden [AN149] (where he did inbetweens), but he was one of the leaders of the Toei exodus over the rubbish working conditions and union busting (Sugii's close friend Rintarō was among the first to follow him), especially when Tezuka appeared on the animation scene with a place to land.
So from the earliest days of Astro Boy/Tetsuwan Atom, Sugii was a core Tezuka guy. (Thanks as ever to Matteo Watzky for presenting such detailed histories in English!) He helped clean up Tezuka's rough animations in an early form of the layout system, moving to his own satellite studio, worked on all sorts of projects. In fact, we saw a number of them when we watched Tezuka's short fims on Animation Night 83. For example, Sugii animated the moth in Tales of a Street Corner.
Before too long, Astro Boy was wrapping up, and the time came for Sugii to direct his own series: this was Goku no Daibōken and in the words of Matteo Watzky, it represented "a complete and unconditional rejection of everything Mushi - or rather Tezuka - had done so far" - gags over story, extremely limited animation. Adapting Tezuka's manga version of Journey to the West, the project had some rather grand ambitions:
It was rather in the writing and direction. Sugii was extremely ambitious: not only did he want to do a complete break with what Mushi had done before, he wanted to broaden the general “animation culture” in Japan [14]. He therefore focused entirely on the gags, trying to make them all as absurd as possible and breaking all sense of narrative continuity. This was the reason he had chosen Boku no Songoku in the first place: the road trip structure made it possible to completely change the setting each episode and make things different each time [15]. He refused to compromise on anything and was an extremely harsh director: he himself admitted how many conflicts he had with scriptwriters and storyboarders, whose work he kept rejecting until it had lost any semblance of sense or continuity [16].
Goku no Daibōken's story touches on another major figure of anime history: Osamu Dezaki (AN95) appears here as an episode director, though you'd likely not recognise his work - he closely followed his mentor Sugii's wacky style. Unfortunately, the show did not really do much to broaden anything, and was pretty roundly rejected by audiences, and even Tezuka himself publicly said it was too avant-garde and needed to change and the show ended up a sore memory for everyone involved.
But Sugii did not quit, and continued to work with the increasingly ailing Mushi Pro up through Belladonna of Sadness (AN69). This last-ditch effort was not enough to save the troubled studio (a story told elsewhere, check Watzky's articles for a very detailed version) and MushiPro went under. So, coming into the 70s, Sugii left the anime industry to go travelling.
But not forever.

Now, let me introduce you to a book.
Night on the Galactic Railroad (銀河鉄道の夜, Ginga Tetsudō no Yoru) - written in 1927, and published posthumously in 1934 - is a classic Japanese fantasy novel by Kenji Miyazawa in which two boys go on a strange journey across the galaxy. It soon becomes apparent that the train that the boys ride on is kind of a psychopomp train. It has that fascinating blend of early science and odd religious overtones you often get in novels from the early 20th Century, with such themes as the difference between Buddhist and Christian ideas of heaven, as well as all sorts of odd adventures.
It does not star anthropomorphic cats. But then again, it doesn't say anywhere that its characters aren't anthropomorphic cats, right? If you're Gisaburō Sugii, that's enough!

In the early 80s, Sugii returned to Group TAC, a studio largely consisting of former MushiPro staff, full of memories of travel. He started out directing adaptations of the baseball manga Nine, but soon he ended up directing an cataptation of Night on the Galactic Railroad, which came out in 1985.
Jokes aside, the book is deliberately ambiguous about what its characters look like, so Sugii came up with the cat thing as a way to preserve Miyazawa's intent. His approach to direction heavily emphasises the landscape, embedding the characters in dark spaces that reflect their feelings and build the generally omnious mood as they journey into death. And it works! The result is a film widely regarded as a classic by those who've seen it.
One notable feature is the film's fascination with the constructed language Esperanto, among the earliest aspiring universal languages. The film features all kinds of Esperanto text and an esperanto subtitle track, and even has an alternative Esperanto title, Nokto de la Galaksia Fervojo. This was a fascination of Miyazawa's, though I don't believe it features in the novel particularly prominently, but Sugii evidently wanted that to be part of the tribute...

In the wake of that, Sugii... went back to directing sports anime, this time the series Touch about Tennis, as well as a number of other projects including a Street Fighter film in 1994. He didn't abandon literary subjects though, adapting the Genji Monogatari, a foundational work of Japanese lit, in 1987 - though I can find little more about this adaptation. He even directed a Lupin III film! But none of those films are about cats, so we're gonna skip right over them.
In 2012, Sugii - now 72! - returned to books and cats with The Life of Budori Gusuko, adapting another novel by Miyazawa - this time at MushiPro successor Tezuka Productions. The animation is certainly more elaborate...

The film follows abandoned child Budori Gusuko in a world frozen by strange storms. Left to fend for himself, Budori's problems mulitply as his sister his kidnapped, leading him on a journey into dreams as he tries to get to the bottom of all of it.
The story is notable for anticipating the idea of the greenhouse effect, albeit in a way that rings rather odd in the context of present climate change. It generally doesn't seem to be viewed quite as favourably as Galactic Railroad but it's too good a thematic pairing not to do, so tonight the plan is to watch both films! Elaborate old weird anime, we're so back. And not a boob in sight, so twitch should chill out.
All being well, Animation Night 188 will be starting at 22:00 UK time, which is about two hours from this post - we're back on twitch.tv/canmom, thankfully they didn't ban me for long. Hope to see you there!
25 notes
·
View notes
Text

Hakujaden (Película)
#白蛇伝#PandaandtheMagicSerpent#TheWhiteSnakeEnchantress#TheGreatWhiteSnake#LegendoftheWhiteSerpent#LegendoftheWhiteSnake#animedescargas#anime
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Movie review: Hakujaden (1958)
A little history and context first. Also titled in English as "the legend of the white snake". is the first feature film (in color) and also of the theatrical type created by Toei Animation and released in 1958.
It is also important to mention that a restored version of this film was screened in April 2019 at the renowned Cannes Film Festival. So, it keeps being relevant and important for the culture.
Toei Animation Co., Ltd. is a Japanese animation studio that has produced numerous series, many of them world-renowned, such as Sally the Witch and Gegege no kitaro. Their most recent production is elemon (in case that you're looking something to watch).
So, the plot of the film in question tells the story of a boy who once had a pet snake in West Lake until his parents forced him to give it up. Years pass and during a violent storm, the snake magically transforms into the beautiful princess Bai-Niang. Bai-Niang finds Xu-Xian, but the lovers are separated by a local monk, Fa-Hai, who believes Bai-Niang is an evil spirit. Xu-Xian's two panda pets, Panda and Mimi, try to find Xu-Xian. In the end, Bai-Niang gives up his magical powers and remains in human form to prove that his love for Xu-Xian is genuine.
Now, at this point of the post it's important to mention that I've never been a fan of Oriental productions. To give you an idea, the only series I have seen on this subject was "Doraemon".
As a consequence of this, my knowledge is pretty basic, so, when it comes to describe or give an opinion on the film I would stay related to images, sketches, colours and the plot (especially the plot).
Of course that before this course I have never heard about the movie neither the producer, but, after watching it and doing some research on it, I find it important to emphasize on the historical aspect of this. I mean, a lot of people doesn't feel amazed by the plot or the characters (even tho they made characters that are not really evil, cause they tried to give an example for the kids) they aren't really that impresive. The thing is that is very well know for being the first feature film in color and especially, in being the first production on the area (even before the URSS).
I really liked the love story between the characters (yes I know it's weird to fall in love with someone who was a snake, but what can I say). Panda reminded me of Mushu (Mulan's dragon) and I really hated the priest or monk who tried to blame Bai-Niang and make her a liar. Still, I would have enjoyed it much more if the woman in the beginning was a butterfly or other animal, since I don't like her being understood as a snake or other analogies. Actually, I didn't really enjoy the dialogues (because they were out of sync) but as a child I watched movies with bad internet so it wasn't that annoying. If I had to choose between recommending it or not to a friend, I would, but only if, like me, he/she doesn't know much about this kind of productions and is looking for a first encounter.
In broad strokes, the film has everything, a love story with an antagonist, it has great historical merit, it is digestible and keeps you attentive, it is also beautiful and has good songs in my opinion. The characters are well constructed and consistent. So, thanks for the recommendation, I will continue to delve into this world :)
--- Francisca Tamayo Honores
0 notes
Text
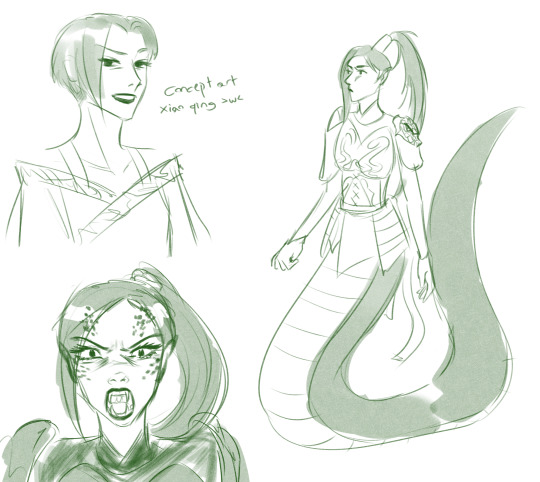

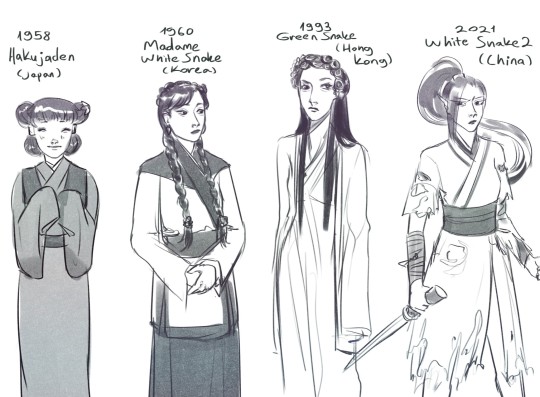


Xiao Qing doodles :>
#white snake#green snake#verta#blanca#xiao qing#xiao bai#madame white snake#the legend of the white snake#white snake 2#bai suzhen#hakujaden
101 notes
·
View notes
Text
Vintage Animated Ladies










#vintage cartoons#vintage animation#snow white#zebra centaur#princess glory#princess iron fan#panda and the white serpent#panda and the magic serpent#hakujaden#bai-niang#lois lane#queen grimhilde#blue fairy#pinnochio#vintage disney#fleischer studios#anime#vintage anime#toei animation
104 notes
·
View notes
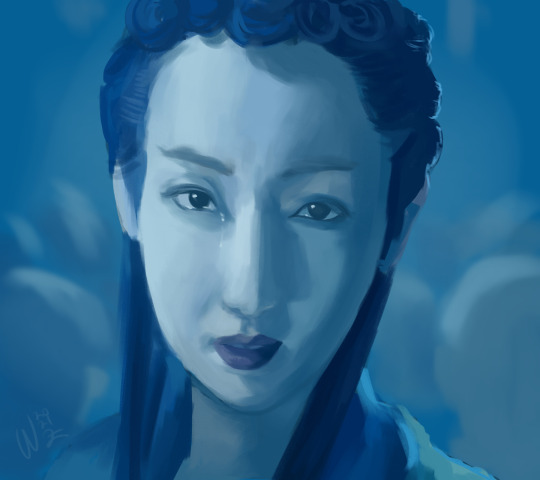
Photo

I just discovered that the old 1960s dub of Hakujaden, released in the US as Panda and the Magic Serpent, is on Amazon. I am torn. Because, on the one hand, my childhood. On the other hand, fucking Amazon.
Backstory: I had this movie on VHS. My grandfather gave it to me for my birthday, I think? I was probably 6 or 7 at the time and I adored it--and I still adore it.
And I think I do need to represent my old and abiding love for this movie (though I would shank a bitch to get a fully-restored, full-length, original Japanese version--hint hint, Criterion) by finally and officially drifting about a convention dressed as Bai Niang (above). I just need to do it. That’s all there is to it.
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
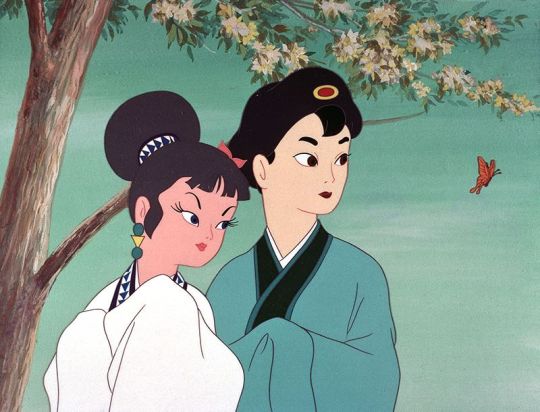

Hakujaden (1958)
139 notes
·
View notes
Photo


me with my childhood beanie babies
12 notes
·
View notes
Text



Hakujaden
26 notes
·
View notes
Photo


14 notes
·
View notes