#Grammar
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Writing Tips
Punctuating Dialogue
✧
➸ “This is a sentence.”
➸ “This is a sentence with a dialogue tag at the end,” she said.
➸ “This,” he said, “is a sentence split by a dialogue tag.”
➸ “This is a sentence,” she said. “This is a new sentence. New sentences are capitalized.”
➸ “This is a sentence followed by an action.” He stood. “They are separate sentences because he did not speak by standing.”
➸ She said, “Use a comma to introduce dialogue. The quote is capitalized when the dialogue tag is at the beginning.”
➸ “Use a comma when a dialogue tag follows a quote,” he said.
“Unless there is a question mark?” she asked.
“Or an exclamation point!” he answered. “The dialogue tag still remains uncapitalized because it’s not truly the end of the sentence.”
➸ “Periods and commas should be inside closing quotations.”
➸ “Hey!” she shouted. “Sometimes exclamation points are inside quotations.”
However, if it’s not dialogue exclamation points can also be “outside”!
➸ “Does this apply to question marks too?” he asked.
If it’s not dialogue, can question marks be “outside”? (Yes, they can.)
➸ “This applies to dashes too. Inside quotations dashes typically express—“
“Interruption” — but there are situations dashes may be outside.
➸ “You’ll notice that exclamation marks, question marks, and dashes do not have a comma after them. Ellipses don’t have a comma after them either…” she said.
➸ “My teacher said, ‘Use single quotation marks when quoting within dialogue.’”
➸ “Use paragraph breaks to indicate a new speaker,” he said.
“The readers will know it’s someone else speaking.”
➸ “If it’s the same speaker but different paragraph, keep the closing quotation off.
“This shows it’s the same character continuing to speak.”
#writing#writing tips#story ideas#reference#knowledge#writing reference#writerslife#writer things#writeblr#english#grammar#commas#dialogue#punctuation#american english
124K notes
·
View notes
Text
a few more commonly confused words
Afflict - to cause suffering or unhappiness (something a disease does) Inflict - to force pain or suffering (like if you smack someone) (Both cause pain)
Allude - to refer to something in an indirect manner Elude - to evade
Alone - no other person is with you Lonely - you are alone, and sad as a result
Amicable - a friendliness or goodwill between people or groups Amiable - friendly disposition
Arise - happen or occur Rise - to go up
Assent - refers to agreement Ascent - a climb
Aver - to affirm Avow - to openly declare
Correlation - a relationship Corollary - more like a consequence
Disassemble - to take something apart Dissemble - to hide your true self
Discreet - under the radar, careful Discrete - individual or detached
Disinterested - unbiased; out of the loop Uninterested - don't give a hoot; bored
Disperse - to scatter Disburse - to pay
Eminent - famous Imminent - refers to something about to happen Immanent - inherent
Exalt - to glorify or elevate something Exult - to rejoice
Expedient - something helpful Expeditious - speedy
Extant - still here Extent - the range of something
Faze - to disturb, bother, or embarrass Phase - a stage or step
Fictional - literary Fictive - specific Fictitious - just plain fake
Imply - to hint at something Infer - to make an educated guess
Ingenious - smart and clever Ingenuous - innocent and naive
Insidious - something that lies in wait to get you Invidious - something offensive or defamatory
Loath - unwilling or reluctant Loathe - to hate
Morbid - describes something gruesome Moribund - the act of dying
Paradox - a logical puzzle that seems to contradict itself Oxymoron - a figure of speech—words that seem to cancel each other out (e.g., instant classic)
Parameter - a limit that affects how something can be done Perimeter - the outline of a physical area
Practical - sensible Practicable - possible
Pragmatic - you're practical Dogmatic - you follow the rules
Premiere - the first public performance of something Premier - the very best
Prescribe - to recommend Proscribe - to forbid
Rebut - to try to prove something isn’t true Refute - to actually prove it isn’t
Reluctant - resisting or unwilling Reticent - quiet, restrained, or unwilling to communicate
Sources: 1 2 ⚜ More: Writing Basics ⚜ Writing Resources PDFs ⚜ Part 1
#writing basics#grammar#writing reference#writeblr#literature#dark academia#writers on tumblr#spilled ink#writing prompt#creative writing#light academia#writing refresher#words#langblr#linguistics#writing resources
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Struggling with descriptors? Here are some synonyms to make your scene more interesting!
=========
Afraid
=========
Apprehensive
Dread
Foreboding
Frightened
Mistrustful
Panicked
Petrified
Scared
Suspicious
Terrified
Wary
Worried
=========
Annoyed
=========
Aggravated
Dismayed
Disgruntled
Displeased
Exasperated
Frustrated
Impatient
Irritated
Irked
=========
Angry
=========
Enraged
Furious
Incensed
Indignant
Irate
Livid
Outraged
Resentful
=========
Aversion
=========
Animosity
Appalled
Contempt
Disgusted
Dislike
Hate
Horrified
Hostile
Repulsed
=========
Confused
=========
Ambivalent
Baffled
Bewildered
Dazed
Hesitant
Lost
Mystified
Perplexed
Puzzled
Torn
=========
Disconnected
=========
Alienated
Aloof
Apathetic
Bored
Cold
Detached
Distant
Distracted
Indifferent
Numb
Removed
Uninterested
Withdrawn
=========
Disquiet
=========
Agitated
Alarmed
Discombobulated
Disconcerted
Disturbed
Perturbed
Rattled
Restless
Shocked
Startled
Surprised
Troubled
Turbulent
Turmoil
Uncomfortable
Uneasy
Unnerved
Unsettled
Upset
=========
Embarrassed
=========
Ashamed
Chagrined
Flustered
Guilty
Mortified
Self-conscious
=========
Fatigue
=========
Beat
Burnt out
Depleted
Exhausted
Lethargic
Listless
Sleepy
Tired
Weary
Worn out
=========
Pain
=========
Agony
Anguished
Bereaved
Devastated
Grief
Heartbroken
Hurt
Lonely
Miserable
Regretful
Remorseful
=========
Sad
=========
Depressed
Dejected
Despair
Despondent
Disappointed
Discouraged
Disheartened
Forlorn
Gloomy
Heavy hearted
Hopeless
Melancholy
Unhappy
Wretched
=========
Tense
=========
Anxious
Cranky
Distressed
Distraught
Edgy
Fidgety
Frazzled
Irritable
Jittery
Nervous
Overwhelmed
Restless
Stressed out
=========
Vulnerable
=========
Fragile
Helpless
Insecure
Leery
Reserved
Sensitive
Shaky
=========
Yearning
=========
Envious
Jealous
Longing
Nostalgic
Pining
Wistful
=========
#writerscommunity#writing community#writers community#writing help#creative writing#story writing#fiction writing#writers on tumblr#writeblr#writing#vocabulary#writing tips#helping writers#references for writers#writing reference#writing advice#writing resources#writing tips and tricks#grammar#english language#english#synonyms#linguistics#fanfiction tips#creative writers#fanfic tips#character building#creative expression#motivation#creative inspiration
3K notes
·
View notes
Text

#funny#haha#memes#funnymemes#commas#grammar#medicalmemes#medicalhumor#chronicillnesshumor#diarrhea memes#chronic illness memes#grammar memes
27 notes
·
View notes
Text
I miss the interrobang. Now I have to use TWO separate marks for it?! Schade.
I love you dead punctuation marks.
118K notes
·
View notes
Text

My latest cartoon for New Scientist
22K notes
·
View notes
Text

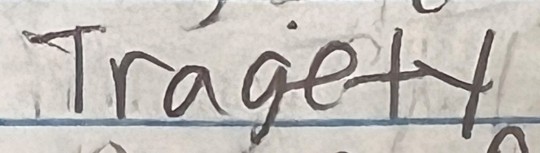

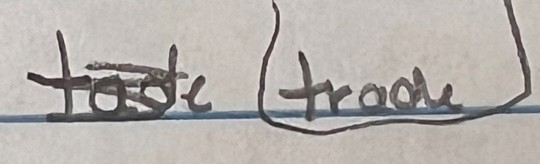
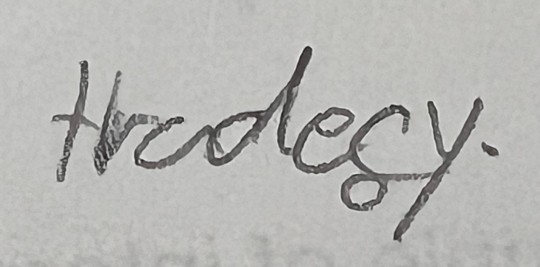
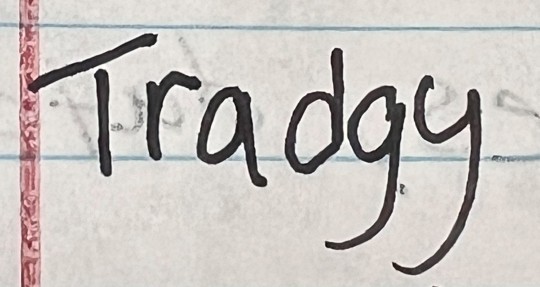
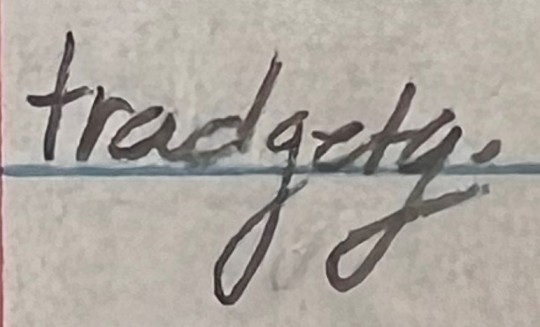
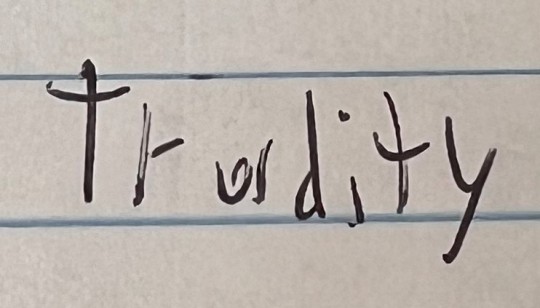
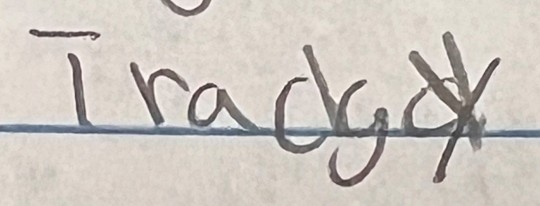
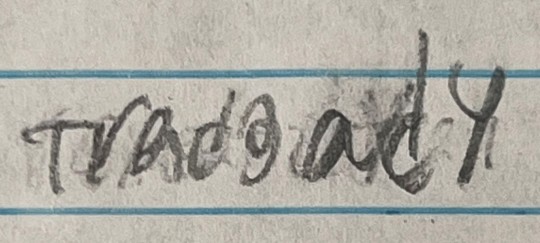





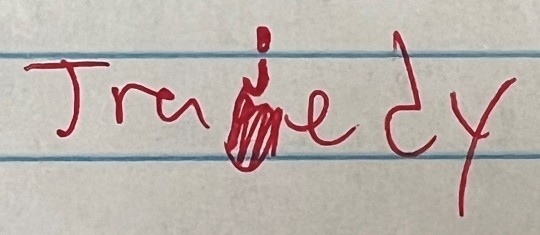





Another year, another group of my delightful ninth graders trying to spell the word "tragedy" for their Romeo and Juliet assignment.
Last year's collection
#i started questioning how to spell it myself#but again... at least they knew the right answer#i love them endlessly#teacherblr#teacher life#teaching#english class#english teacher#grammar#literature#romeo and juliet#shakespeare#william shakespeare#language#tragedy
67K notes
·
View notes
Text

Infinite Conjunction Junction
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
Chciken...?
☺
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
Grammar PSA
the expression you're looking for is reining in. it is NOT reigning in. it comes from horseback riding.
you REIN IN your horse when you pull on the rein to tell him to slow down.
similarly, you GIVE HIM FREE REIN when you loosen your grip on the reins and let him run as fast as he likes.
that's where the metaphor comes from. you can rein in your evil vizier when he proposes a little too much child murder, or you can give him free rein when you need your enemies obliterated and only underhanded treachery will do. but unless he actually pulls off that nefarious coup he's plotting, the only one reigning here is you.
#grammar#spelling#vocabulary#english language#idk what people tag these as I don't really see them much#but it's one of my biggest pet peeve homophones and I just saw it in a published news article#and I can rein myself in no longer
5K notes
·
View notes
Text
The worst thing about formal English is that it offers these wonderful suffixes, then only lets you use them in prescribed circumstances. I should be able to describe things as meatful or leftly or falsewise without departing from the formal register if I darn well please.
8K notes
·
View notes
Note
can you do a 3 papers to read on indigenous languages?
this is another huge topic so I'm gonna err on the side of "these are just three really cool papers" rather than "this is representative of the entire linguistic field"
Riestenberg, Freemond, Lillehaugen, Washington. Prioritizing Community Partners’ Goals in Projects to Support Indigenous Language Revitalization. In: Decolonizing Linguistics. Ed. Anne H. Charity Hudley, Christine Mallinson, and Mary Bucholtz, Oxford University Press. doi.org/10.1093/oso/9780197755259.003.0019, and the PDF is here.
Junker, M. O. (2018). Participatory action research for Indigenous linguistics in the digital age. Insights from practices in community-based research: From theory to practice around the globe, 164175. doi.org/10.1515/9783110527018-009, pdf on the author's website here.
Leonard, W. Y. (2021). Toward an anti‐racist linguistic anthropology: An Indigenous response to white supremacy. Journal of Linguistic Anthropology, 31(2), 218-237. pdf is here.
(TBH you could just sit down and read the entire Decolonizing Linguistics book, it's like 500 pages/20 chapters by a huge community of authors. It's open access!)
I realize that none of these links are actually describing the linguistic properties of indigenous languages directly, and are more about how and whether non-indigenous linguists should go about doing that. But all of the authors listed above also do linguistic description and analysis, so after you've read some of these pieces you can go look more into their other work.
943 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ye are all a bunch of weirdos.
NO ONE knows how to use thou/thee/thy/thine and i need to see that change if ur going to keep making “talking like a medieval peasant” jokes. /lh
They play the same roles as I/me/my/mine. In modern english, we use “you” for both the subject and the direct object/object of preposition/etc, so it’s difficult to compare “thou” to “you”.
So the trick is this: if you are trying to turn something Olde, first turn every “you” into first-person and then replace it like so:
“I” → “thou”
“Me” → “thee”
“My” → “thy”
“Mine” → “thine”
Let’s suppose we had the sentences “You have a cow. He gave it to you. It is your cow. The cow is yours”.
We could first imagine it in the first person-
“I have a cow. He gave it to me. It is my cow. The cow is mine”.
And then replace it-
“Thou hast a cow. He gave it to thee. It is thy cow. The cow is thine.”
68K notes
·
View notes
Text
Struggling with emotional scenes? Here are some tips for writing emotion!
=========
1. While you’re writing, try to build an explanation for their feelings. What triggered their emotion? Is their reaction rational or are they overreacting? Do they fight, flight, fawn or freeze when provoked? Do they feel threatened?
=========
2. Show, don’t tell. Describe what is happening instead of plainly stating the situation. Try not to use words like sad, happy, devastated, in pain, angry, nervous, scared, or worried. They cut back on the emotional integrity of the scene and make it hard for readers to connect with your characters. Here are some different behaviors for different emotions.
-Eager-
Bouncing up and down
Unable to sit still
Breathing deeply
Fidgeting
Pretending to do something
Trying to stay busy
Constantly looking at the clock
-Nervous-
Red and hot face
Sweaty palms
Voice cracks
Shaky hands
Biting nails
Biting lips/inside of cheek
Wide eyes
Shallow breathing
Heart racing
-Excited-
Wide smile
Squeal/scream
Bouncing up and down
Fidgeting
Playing with hands
Tapping foot
Talking fast
Tapping pencil
Pacing back and forth
-Scared-
Curling up/bringing knees to head
Closing eyes
Covering ears
Stop breathing or breathing quickly
Biting nails
Shaking
Gritting teeth
Hugging/squeezing something tight
-Frustrated-
Stomping
Grunting/mumbling/yelling
Deep breaths
Red and hot face
Hitting/kicking something
Pointing
Straining/veins become more visible
-Sobbing-
Eyes filling up with tears
Eyes burn/turn red
Red cheeks
Face becomes puffy
Pursed lips
Holding head down
Hyperventilating
Fast blinking
Trying not to blink/holding back tears
-Happy-
Smiling wide
Laughing loudly
Cheeks hurting
Talking loudly
Higher pitched voice
Animated/expressive
-Upset-
Walking slowly/shuffling feet
Head down/avoiding eye contact
Biting inside of cheek
Dissociation
Keeping quiet
Fidgeting
-Bored-
Pacing back and forth
Sighing loudly
Complaining
Fidgeting
Blank face
Looking for something to do
Making up stories
Talking about random topics
=========
3. Try and bring some trauma into your character’s emotions. For example, something might happen that reminds them of a suppressed/traumatic memory. This is an easy way to hook your reader and have them really feel like your character is a real person with real emotions. They might have some internal conflict they need to work through and a certain situation reminds them of that. They might become irritable at the thought of their traumatic experience and they might snap at whoever is nearby.
=========
4. Most characters won’t dump their entire backstory or feelings in a conversation. Try and reserve your character’s emotions to make more interesting scenes later on. For example, your character may be triggered and someone may ask them what’s wrong. Will they give in, soften up and share? Or will they cut themself off and say they’re fine? Also take into account that your character might not know the other character very well and won’t be comfortable sharing personal information with them, like details regarding their trauma.
=========
5. Last but not least, you don’t need to have a major event happen to connect emotionally with your audience. You don’t have to kill off a character every time you need to spice up your story, even simple interactions can just help your readers understand your character better. Show how they react to certain topics or situations. Describe their feelings, their surroundings, their body language. Their defense mechanisms will help the audience to better understand what kind of person they are.
=========
#writerscommunity#writing community#writers community#writing help#creative writing#story writing#fiction writing#writers on tumblr#writeblr#writing#vocabulary#writing tips#helping writers#references for writers#writing reference#writing advice#writing resources#writing tips and tricks#grammar#english language#english#synonyms#linguistics#fanfiction tips#character building#creative writers#fanfic tips#creative expression#motivation#creative inspiration
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
Words You Always Have to Look Up
Nonplussed
Means “perplexed.”
But there is a further point of confusion that can send someone to the dictionary: since the mid-20th century, nonplussed has been increasingly used to mean “unimpressed” or “unsurprised,” and this use, though often considered an error, has made the confident deployment of this word a fraught issue for many.
Anodyne
Sometimes words sort of seem to telegraph their meaning: pernicious sounds like a bad thing rather than a good thing, and beatific sounds like something to be desired as opposed to something to be avoided.
This is all fairly subjective, of course, but the sounds of words can have an effect on how we perceive them.
Anodyne doesn’t give us many clues in that way. It turns out that anodyne is a good thing: it means “serving to alleviate pain” or “innocuous,” from the Greek word with similar meanings.
Supercilious
Used to describe people who are arrogant and haughty or give off a superior attitude.
It comes from the Latin word meaning “eyebrow,” and was used in Latin to refer to the expression of arrogant people, and this meaning was transferred to English.
Amusingly, the word supercilious was added to some dictionaries in the 1600s—a time when many Latin words were translated literally into English—with the meanings “pertaining to the eyebrows” or “having great eyebrows.”
Stochastic
In scientific and technical uses, it usually means “involving probability” or “determined by probability,” and is frequently paired with words like demand, model, processing, and volatility.
Comes from the Greek word meaning “skillful at aiming,” which had become a metaphor for “guessing.”
It’s a term that had long been used by mathematicians and statisticians, and has come into more public discourse with stochastic terrorism, the notion that accusations or condemnations of a person or group can lead to violence against that person or group. This allows those who make the initial accusations to seem innocent from any specific violent act, but stochastic terrorism is a way to identify the motives for such an attack as being set in motion by the words of another person.
Anathema
Means “something or someone that is strongly disliked”.
Initially used to refer to a person who had been excommunicated from the Catholic church.
Came from Greek through Latin into English with the meaning of “curse” or “thing devoted to evil,” but today refers to anything that is disapproved of or to be avoided.
There is a strangeness about the way this word is used in a sentence. Because anathema is usually used without an or the, as in “raincoats are anathema to high fashion” or “those ideas are anathema in this class” it may seem just odd enough to send people to the dictionary when they encounter it.
Bemused
So close in sound to amused that they have blended together in usage, but they started as very different ideas: bemused originally meant “confused” or “bewildered,” a meaning stemming from the idea of musing or thinking carefully about something, which may be required in order to assess what isn’t easy to understand.
Many people insist that “confused” is still the only correct way to use bemused, but the joining of meanings with amused has resulted in the frequent use of this word to mean “showing wry or tolerant amusement,” a shade of meaning created from the combination.
Words with meanings that seem to crisscross or intersect are sure to send us to the dictionary.
Solipsistic
Means “extremely egocentric” or “self-referential.”
Comes from the Latin roots solus ("alone," the root of sole) and ipse ("self").
As this Latinate fanciness implies, this is a word used in philosophical treatises and debates.
The egocentrism of solipsism has to do with the knowledge of the self, or more particularly the theory in philosophy that your own existence is the only thing that is real or that can be known.
Calling an idea or a person solipsistic can be an insult that identifies a very limited and usually self-serving perspective, or it can be a way to isolate one’s perspective in a useful way.
It’s a word with an abstract meaning, which is a good reason to check that meaning from time to time.
Tautology
A needless or meaningless repetition of words or ideas.
It’s a word about words that can be used in academic writing or as a hifalutin way of saying “redundancy,” as in “a beginner who just started learning.”
Since we value both clarity and originality, especially in writing, tautology is a word that usually carries a negative connotation and is used as a way to criticize a poorly formed sentence or a poorly argued position.
Perspicacious
The ability to see clearly is a powerful metaphor for being able to understand something.
Being perspicacious means having an ability to notice and understand things that are difficult or not obvious, and it comes from the Latin verb meaning “to see through.”
Means “perceptive,” and is often used along with words that have positive connotations like witty, clever, wise, alert, and insightful (another word that uses seeing as a metaphor for understanding).
Peripatetic
Means “going from place to place,” and comes from the Greek word that means “to walk.”
You can say someone who moves frequently has a “peripatetic existence,” or someone who has changed careers several times has had a “peripatetic professional trajectory.”
The root word “to walk” is usually more of a metaphor in the modern use of this word—it means frequent changes of place, yes, but it doesn’t necessarily mean that you are wearing out your shoes.
The original use of this word did use “walking” as a more literal image, however: it was a description of the way that the philosopher Aristotle preferred to give lectures to his students while walking back and forth, and the word has subsequently taken on a more metaphorical meaning.
Source ⚜ More: Writing Basics ⚜ Writing Resources PDFs
#grammar#langblr#writeblr#studyblr#linguistics#dark academia#vocabulary#light academia#writing prompt#literature#poetry#writers on tumblr#poets on tumblr#writing reference#spilled ink#creative writing#fiction#novel#words#writing resources
1K notes
·
View notes