#Gold GST Rate in India 2024
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
GST on Gold: Effects of Gold GST Rate in India 2024
In 2024, the effects of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) rate on gold continue to resonate throughout India's economy, impacting various stakeholders from consumers to industry players. Let's delve into the implications of the gold GST rate and how it shapes the landscape of the precious metal market:
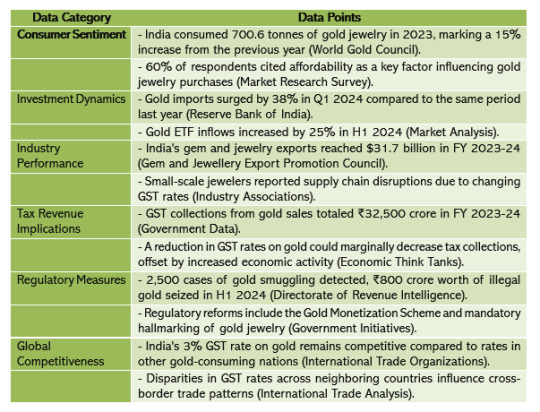
Consumer Sentiment: The GST rate directly influences the final price of gold for consumers. A lower GST rate makes gold more affordable, encouraging higher demand for jewelry, coins, and bullion among consumers. Conversely, a higher GST rate may deter purchases, particularly among price-sensitive buyers, impacting consumer sentiment and spending patterns.
Investment Dynamics: Gold is revered as a traditional investment asset and a hedge against economic uncertainties. The GST rate affects its attractiveness as an investment avenue. A lower GST rate enhances the appeal of gold investments, attracting investors seeking portfolio diversification and wealth preservation. Conversely, a higher GST rate may prompt investors to explore alternative investment options with potentially higher returns.
Industry Performance: The gold industry, encompassing miners, refiners, jewelers, and retailers, is intricately linked to the prevailing GST rate. A lower GST rate spurs demand for gold jewelry and ornaments, benefiting jewelers and retailers. However, fluctuating GST rates can disrupt supply chains, inventory management, and pricing strategies within the industry, posing challenges for stakeholders.
Tax Revenue Implications: The GST rate on gold significantly contributes to government tax revenues. While a lower GST rate stimulates demand and economic activity in the gold sector, it may lead to a reduction in tax collections. Conversely, a higher GST rate boosts government revenues but could dampen consumer spending and industry growth, necessitating a delicate balance between revenue generation and economic stimulus.
Regulatory Measures: Policymakers continuously monitor and adjust the gold GST rate to achieve broader economic objectives, address inflationary pressures, and ensure fiscal sustainability. Changes in the GST rate are often accompanied by regulatory measures aimed at curbing illicit activities such as smuggling and tax evasion, thereby safeguarding government revenue and market integrity.
Global Competitiveness: The GST rate on gold in India is juxtaposed with rates in other countries, influencing international competitiveness and trade dynamics. Disparities in GST rates between nations can incentivize cross-border trade, impacting domestic markets and necessitating policy responses to maintain a level playing field for industry participants.
In summary, the GST rate on gold in India is a critical determinant of consumer behavior, investment trends, industry dynamics, and government revenues. As policymakers navigate economic challenges and strive to foster growth, they must calibrate the gold GST rate judiciously, balancing the interests of stakeholders while ensuring fiscal prudence and regulatory effectiveness, you need the advice of experts such as efiletax Indeed.
#GST on Gold#Gold GST Rate#Gold GST Rate in India 2024#efiletax#taxes#gst services#gst filing chennai#gst update india#india gst#gold#gst filing
0 notes
Text
Exploring the 2024 Union Budget: International Tax Insights
What are the key details that taxpayers should be aware of regarding the 2024 tax changes?
Key Highlights
The Finance Minister of India presented the Union Budget 2024 on 23 July 2024. The Budget includes several positive proposals, such as tax incentives for small businesses, increased funding for infrastructure development, and measures to support sustainable energy initiatives. Thus, the purpose of these suggestions is to boost the economy, e-commerce growth in India and tackle several issues.
The Income Tax Act is due for a review, and the government has suggested much-needed changes, which are long overdue.
The base corporate tax rate for nonresident corporate taxpayers has been reduced from 40% to 35%.
The removal of angel tax provisions and the introduction of Equalisation Levy 2.0 will have a significant impact and are considered game changers.
The rationalization of the TDS Regime is a positive step forward and is sure to benefit the country's overall growth.
The removal of indexation to compute cost while calculating gains will significantly impact the capital gains tax regime. With the removal of the buyback tax, the tax incidence will now shift to the recipient.
The government has restated its commitment to simplifying processes, rationalizing GST rates, and expanding GST coverage to all sectors.
Customs duties will be waived for key sectors like healthcare, solar, critical minerals for renewable energy, and high-tech electronics. Additionally, there will be a reduction in customs duties for mobile phones, gold, precious metals, and the leather and textile industries.
Introduction of a one-time tax settlement scheme called Vivad se Vishwas (VSV) to help quickly resolve ongoing tax disputes.
The government of India is currently engaged in modernizing its international tax policies and administration. This initiative encompasses the implementation of a variety of tax incentives and rate reductions, as well as the substantial digitalization of critical processes.
Tax Insights: Introduction
During the presentation of the Union Budget for 2024-2025, the Union Minister for Finance & Corporate Affairs, Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman underscored the budget's emphasis on several identified priorities aimed at expediting the journey toward the goal of Viksit Bharat.
The Finance Minister highlighted the government's ongoing efforts to simplify taxes, improve taxpayer services, and reduce legal disputes. Thus, the taxpayers have responded positively to these efforts.
In the fiscal year 2022-23, Smt. Sitharaman highlighted that 58 percent of corporate tax revenue was contributed by the simplified tax regime. Additionally, over two-thirds of taxpayers chose to adopt the new personal income tax regime based on the data available.
During the budget presentation, the Finance Minister also announced a number of attractive benefits designed to provide tax relief to salaried individuals and pensioners who choose the new tax regime. The Union Budget for the fiscal year 2024-2025 has incorporated a range of provisions and amendments, underscoring the government's dedication to establishing a streamlined and effective tax framework.
What is the major objective of the International tax sector?
International taxation serves various objectives, such as ensuring fair distribution of tax burdens, preventing the illegal avoidance of taxes, fostering economic growth, and facilitating international collaboration. However, the following are the primary purposes of the International tax sector.
Preventing Double Taxation
Encouraging International Trade and Investment
Preventing Tax Evasion and Avoidance
Equitable Distribution of Taxing Authority
The encouragement of International collaboration
Union Budget 2024 International tax updates
Following are the International tax sector updates:
Rationalisation of taxes and rates
E-commerce operators from foreign countries, who supply or facilitate the e-commerce supply of goods or services into or relating to India, are currently burdened with India’s digital service tax, the equalisation levy, which is imposed at a significant 2 percent of the gross consideration. The impending discontinuation of this tax will bring a welcome relief and is scheduled to take effect from 1 August 2024.
From fiscal year 2024–2025, foreign companies will have a reduced corporate tax rate of 35 percent, down from 40 percent.
Relief/beneficial provisions
Angel tax is a tax that private companies have to pay when they issue shares to someone at a price higher than the fair market value of the shares. The government's proposed Finance Bill aims to get rid of angel tax starting from April 1, 2024. This will be a great relief for companies that receive investments, including those from foreign sources.
The safe harbour rules will be expanded, and the transfer pricing assessment procedure will be streamlined.
IFSC-regulated finance companies may be exempt from thin capitalization rules as long as they meet certain conditions. This would put them on the same level as banks, some NBFCs, and insurance companies.
Other changes
A new presumptive taxation regime is being considered for cruise ship operations conducted by non-residents in India, effective from the fiscal year 2024–25. This regime would deem 20% of the specified gross receipts as business income. Additionally, Cruise Ship Operators (CSOs) would be exempt from the presumptive taxation regime for non-resident shipping businesses. Specific group companies of these CSOs receiving lease rentals would also be eligible for tax exemption until the fiscal year 2029–30.
With effect from 1st October 2024, a significant change has been implemented in the tax treatment related to share buybacks by domestic companies. The tax burden has now been transferred from the company to the shareholders. The consideration received by the shareholder will be taxable as a "dividend" at applicable tax rates without any deduction for expenses, potentially resulting in a capital loss. Shareholders must proactively consider tax treaty benefits or dividend deductions available to them.
Before April 1, 2024, if a taxpayer transferred a capital asset through a gift, will, or irrevocable trust, it was not considered a "transfer" under the Income Tax Act. Therefore, no capital gains tax was applied to the transferor. Starting April 1, 2024, this rule will only apply to transfers by individuals or Hindu undivided families. This means that gifts or transfers to an irrevocable trust of any capital asset by other taxpayers will be subject to capital gains tax.
Procedural matters
Currently, there is a time limit of seven years to pass an order deeming a person to be in default for failure to deduct or deposit TDS for resident payees. However, there is no such time limit for non-resident payees. Similarly, no time limit has been prescribed for cases of failure to collect or deposit tax at source (TCS). It is proposed to provide a common limitation period of six years for passing such an order for both resident and non-resident payees. A similar timeline has been prescribed for passing orders in the case of TCS provisions.
Effective April 1, 2025, a proposal to streamline compliance for non-resident liaison offices and introduce penalties for delayed compliance will take effect. Currently, the requirement dictates that the statement of activities must be filed within 60 days from the end of the fiscal year. The proposed changes will entail the specification of new timelines through established rules.
Applications for advance rulings that have been transferred from the Authority for Advance Rulings to the Board for Advance Rulings may be withdrawn by October 31, 2024, if they have not already been disposed of.
Non-locals and international businesses can settle ongoing legal disputes through the new conflict resolution program called the Direct Tax Vivad Se Vishwas Scheme 2024.
Last words
The national, state, and union territory governments of India are actively promoting foreign investment to drive economic transformation. While this presents promising opportunities, it's important for investors to approach this with caution, as both risk and opportunity are closely intertwined in India's investment landscape.
0 notes