#Global Coal Demand
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
The Future of Coal: Examining Import Trends, Global Demand, and India's Coal Industry
Coal continues to be an important component of the world energy scene. This blog explores the demand for coal around the world, looking at consumption patterns and influencing factors. Next, we focus on India, which is a significant participant in the coal mining sector. Lastly, we examine India's coal imports and evaluate how they contribute to the country's energy needs. You will obtain important insights into the changing dynamics of the global coal market and India's energy future by comprehending these interrelated aspects.

0 notes
Text
Coal Mining Industry Market Size and Projections

Introduction
Coal has long been a cornerstone of the global energy sector, serving as a crucial source of electricity generation and industrial fuel. Despite increasing environmental concerns and the emergence of renewable energy alternatives, the Coal Mining Market continues to demonstrate resilience and sustained growth. In this article, we will explore the factors driving the expansion of the coal mining industry, supported by statistical insights and industry trends.
Future Outlook
The future of the Coal Mining Market is marked by a blend of challenges and opportunities. While the transition towards cleaner energy sources and escalating environmental regulations present hurdles, the persistent demand for coal in emerging economies and industrial sectors offers avenues for growth and innovation. To navigate these dynamics successfully, the coal mining industry must embrace sustainable practices, leverage advanced technologies, and diversify their portfolios to remain competitive in a swiftly evolving energy landscape.
Market Size and Projections
Statistical data underscores a robust growth trajectory for the global Coal Mining Market. In 2020, the market was valued at USD 869.5 billion, with a projected compound annual growth rate CAGR of 2.8% from 2021 to 2027. This growth is fueled by rising energy demand from emerging economies, ongoing industrial development, and the persistent reliance on coal for electricity generation.
Regional Dynamics
The Asia Pacific region stands as the dominant force in the global coal mining market, boasting the largest market share in both production and consumption. Countries like China and India serve as major coal producers and consumers, driven by rapid urbanization, industrialization, and infrastructural expansion. North America and Europe also wield significant influence in the coal mining sector, albeit with a stronger emphasis on environmental regulations and transitioning towards cleaner energy sources.
Key Market Drivers: Several factors propel the growth of the coal mining industry:
Energy Demand: Coal remains a primary energy source for electricity generation, particularly in developing economies with burgeoning populations and expanding industrial sectors. The affordability and reliability of coal-fired power plants sustain its demand.
Industrialization: Coal is integral to industrial processes such as steel production, cement manufacturing, and chemical synthesis, driving demand for coal mining. Industries value coal for its high energy content and cost-effectiveness compared to alternative fuels.
Infrastructure Development: Coal plays a vital role in infrastructure projects like road construction, railway networks, and urban development. As nations invest in infrastructure to support economic growth and urbanization, the demand for coal for construction materials and energy remains strong.
Technological Advancements
The Coal Mining Industry witnesses continuous technological advancements aimed at enhancing efficiency, safety, and environmental sustainability. Innovations such as automated mining equipment, remote monitoring systems, and advanced coal processing technologies bolster productivity and slash operational costs. Furthermore, efforts are underway to develop cleaner coal technologies, including carbon capture and storage (CCS) and coal gasification, to mitigate environmental impacts.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite promising growth prospects, the coal mining market grapples with environmental concerns, regulatory pressures, and competition from alternative energy sources. Nevertheless, these challenges also foster opportunities for innovation and diversification. Coal mining companies are exploring cleaner coal technologies, expanding into renewable energy sectors, and investing in carbon offset projects to mitigate their environmental footprint and adapt to shifting market dynamics.
Conclusion
The coal mining market stands as a testament to resilience and growth, buoyed by factors like energy demand, industrialization, and infrastructure development. Despite encountering obstacles from environmental concerns and regulatory pressures, the industry adapts to changing market dynamics through technological innovation and diversification. As the world seeks to harmonize economic growth with environmental sustainability, coal mining companies play a pivotal role in shaping the future of the global energy sector Top of Form
#Coal Mining Industry#Coal Mining Industry Reports#Coal Mining Market Growth#Coal Mining Market Size#Coal Mining Market#Coal Mining Market Demand#Coal Mining Market challenges#Coal Mining Market in India#Coal Mining Market value#Global Coal Mining Market#Coal Mining Market competitors#Coal mining market analysis#Coal Mining Market Forecast#Coal Mining Market outlook#Coal Mining Industry research reports#Coal Mining Market research reports#Coal Mining Market major players#Coal Mining Market Share
0 notes
Text
Exploring the Dynamics of the Coal Mining Market Growth, Market Revenue and Future Outlook

The Coal Mining Market stands as a vital pillar in the global energy landscape, navigating constant evolution and diverse challenges. This exploration delves into the growth, size, demand, challenges, regional nuances, competitive forces, and the future outlook that characterize the intricate terrain of the Coal Mining industry.
Growth Trajectory: Illuminating the Coal Mining Market
Understanding the growth patterns in the Coal Mining Market is pivotal to gauging its economic impact and industry vitality. The industry has witnessed steady growth, driven by increasing global demand for coal as a primary energy source. The key highlights include an annual growth of 5%, indicating sustained demand, and developing economies contributing significantly to this upward trajectory.
Sizing Up: Coal Mining Market Size Analysis
The sheer scale of the Coal Mining Market is instrumental for stakeholders seeking to comprehend its economic footprint and potential opportunities. The market size is substantial, with a valuation of USD 50 billion in the last fiscal year. Variations in market size are influenced by factors such as coal reserves, production capacities, and regional demand.
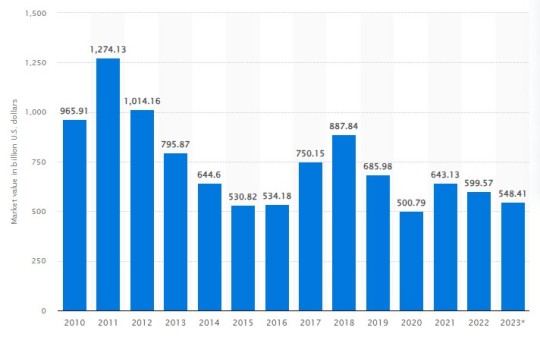
Meeting Demand: Coal Mining Market Demand Dynamics
The Coal Mining Market demand for coal remains a critical driver for the Market, impacting various industries, especially power generation and manufacturing. Despite global efforts to diversify energy sources, coal continues to meet a substantial portion of the world's energy demand.
Navigating Challenges: Coal Mining Market Challenges Unveiled
Challenges inherent in the Coal Mining industry require strategic approaches to ensure sustainable operations and compliance with evolving regulations. Environmental concerns, regulatory complexities, and the emergence of renewable energy sources are among the key challenges faced by the industry.
Regional Dynamics: Focus on Coal Mining Market in India
India plays a pivotal role in the Global Coal Mining Market, with unique dynamics shaping its industry landscape. The Coal Mining Market in India is characterized by extensive coal reserves and a significant contribution to the country's energy mix. Policy initiatives and technological advancements influence the growth trajectory of the Coal Mining Market in India.
Competing Forces: Coal Mining Market Competitors in the Limelight
The competitive landscape involves established industry leaders vying for market share and emerging players seeking to make their mark. Coal Mining Market Competitors engage in strategic alliances and investments in advanced mining technologies.
Future Outlook: Coal Mining Market Forecast and Outlook
The Coal Mining Market future outlook is influenced by global energy transitions, technological advancements, and evolving consumer preferences. The Coal Mining Market Forecast is optimistic, driven by sustained demand from industrial and power generation sectors.
Conclusion
The Coal Mining Market remains a dynamic force in the global energy sector, navigating growth, challenges, and evolving market dynamics. Stakeholders must stay attuned to these dynamics for informed decision-making in this critical industry.
#Coal Mining Industry#Coal Mining Industry Reports#Coal Mining Market Growth#Coal Mining Market Size#Coal Mining Market#Coal Mining Market Demand#Coal Mining Market Challenges#Coal Mining Market in India#Coal Mining Market Value#Global Coal Mining Market#Coal Mining Market Competitors#Coal Mining Market Analysis#Coal Mining Market Forecast#Coal Mining Market Outlook#Coal Mining Industry Research Reports#Coal Mining Market Research Reports#Coal Mining Market Major Players#Coal Mining Market Share
0 notes
Text
From the article:
From Europe to North America, an energy revolution is breathing new life into empty, long-forgotten coal mine shafts — by repurposing them into places to store renewable energy. Using “gravity batteries,” these underground facilities aim to tackle one of renewable energy’s greatest challenges: storage. The method is simple: Excess renewable energy is used to power winches that lift heavy weights — such as containers filled with sand or rock — up the mine shaft. When additional energy is needed, these weights are released, generating power as they descend. This approach not only gives these disused mines a second life but also offers economic and environmental benefits to communities once reliant on coal. Hundreds of thousands of abandoned mines — about 550,000 in the U.S. alone — pose economic, environmental and safety risks. In some areas, these old shafts have caused collapses or polluted groundwater, while in others, the loss of mining jobs has hit local economies hard. Meanwhile, as renewable energy scales up, storage limitations become a pressing issue, especially with solar and wind, which are naturally intermittent. This year, solar is expected to surpass coal as a leading global power source, according to the International Energy Agency, highlighting the need for reliable storage to balance supply and demand. During the U.K.’s 2020 lockdown, for example, National Grid warned of potential blackouts when energy demand dropped by 20 percent, leading to excess renewable power that went unused.
Gravity batteries offer a straightforward but powerful — and cost-effective — way to address both of these problems at once. Their potential is already being realized. In Rudong, near Shanghai, the first commercial grid-scale gravity battery was connected to the grid in December 2023. Capable of storing up to 100 megawatt hours of energy, it can power nine homes for an entire year using only stored electricity. Across China, nine additional projects are in development, while in Switzerland, a commercial demonstration unit has been connected to the national grid for testing since 2019, showcasing the technology’s promise on a global scale. And now, other countries, from Finland to Australia, are getting on board.
#hope#good news#solarpunk#renewable energy#hopepunk#solar energy#green energy#clean energy#wind energy#hydroelectric energy#global warming#climate change#environment#ecology#energy#electricity
533 notes
·
View notes
Text
"The UK’s greenhouse gas emissions fell by 3.6% in 2024 as coal use dropped to the lowest level since 1666, the year of the Great Fire of London, according to new Carbon Brief analysis.
Major contributions came from the closure of the UK’s last coal-fired power station in Nottinghamshire and one of its last blast furnaces at the Port Talbot steelworks in Wales.
Other factors include a nearly 40% rise in the number of electric vehicles (EVs) on the road, above-average temperatures and the UK’s electricity being the “cleanest ever” in 2024.
Carbon Brief’s analysis, based on preliminary government energy data, shows emissions fell to just 371m tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent (MtCO2e) in 2024, the lowest level since 1872.
Other key findings from the analysis include:
The UK’s emissions are now 54% below 1990 levels, while GDP has grown by 84%.
About half of the drop in emissions in 2024 was due to a 54% reduction in UK coal demand, which fell to just 2m tonnes – the lowest level since 1666.
Another third of the drop in 2024 emissions was due to falling demand for oil and gas, with the remainder down to ongoing reductions in non-CO2 greenhouse gases.
UK coal demand fell at power stations (one-third of the reduction overall) and at industrial sites (two-thirds). In 2024, the UK closed its last coal-fired power station, as well as the final blast furnace at the Port Talbot steelworks. Furnaces at Scunthorpe paused operations. Both sites are due to convert to electric-arc furnaces that do not rely on coal.
Oil demand fell 1.4% despite increased road traffic, largely due to the rise in the number of EVs. The UK’s 1.4m EVs, 0.8m plug-in hybrids and 76,000 electric vans cut oil-related emissions by at least 5.9MtCO2e, Carbon Brief analysis finds, only slightly offset by around 0.5MtCO2e from higher electricity demand.
The UK’s EV motorists each saved around £800, on average, in 2024 – some £1.7bn in total – relative to the cost of driving petrol or diesel vehicles.
Gas demand for heating increased, despite warmer average temperatures than in 2023, as prices eased from the peaks seen after the global energy crisis.
However, gas demand fell overall due to lower gas-fired electricity generation, thanks to higher electricity imports and increased output from low-carbon sources.
The UK would need to cut its emissions by a larger amount each year than it did in 2024, to reach its international climate goal for 2035, as well as its national target to reach net-zero by 2050...
Lowest since 1872

...
Apart from brief rebounds after the global financial crisis and the Covid-19 lockdowns, UK emissions have fallen every year for the past two decades."
-via CarbonBrief, March 12, 2025
#uk#united kingdom#europe#emissions#greenhouse gasses#fossil fuels#carbon emissions#coal#climate action#climate hope#good news#hope
683 notes
·
View notes
Text

Charles Ponder·
Quit trashing Obama's accomplishments. He has done more than any other President before him. Here is a list of his impressive accomplishments:
1. First President to be photographed smoking a joint.
2. First President to apply for college aid as a foreign student, then deny he was a foreigner.
3. First President to have a social security number from a state he has never lived in.
4. First President to preside over a cut to the credit-rating of the United States.
5. First President to violate the War Powers Act.
6. First President to be held in contempt of court for illegally obstructing oil drilling in the Gulf of Mexico.
7. First President to require all Americans to purchase a product from a third party.
8. First President to spend a trillion dollars on "shovel-ready" jobs when there was no such thing as "shovel-ready" jobs.
9. First President to abrogate bankruptcy law to turn over control of companies to his union supporters.
10. First President to by-pass Congress and implement the Dream Act through executive fiat.
11. First President to order a secret amnesty program that stopped the deportation of illegal immigrants across the U.S., including those with criminal convictions.
12. First President to demand a company hand-over $20 billion to one of his political appointees.
13. First President to tell a CEO of a major corporation (Chrysler) to resign.
14. First President to terminate America’s ability to put a man in space.
15. First President to cancel the National Day of Prayer and to say that America is no longer a Christian nation.
16. First President to have a law signed by an auto-pen without being present.
17. First President to arbitrarily declare an existing law unconstitutional and refuse to enforce it.
18. First President to threaten insurance companies if they publicly spoke out on the reasons for their rate increases.
19. First President to tell a major manufacturing company in which state it is allowed to locate a factory.
20. First President to file lawsuits against the states he swore an oath to protect (AZ, WI, OH, IN).
21. First President to withdraw an existing coal permit that had been properly issued years ago.
22. First President to actively try to bankrupt an American industry (coal).
23. First President to fire an inspector general of AmeriCorps for catching one of his friends in a corruption case.
24. First President to appoint 45 czars to replace elected officials in his office.
25. First President to surround himself with radical left wing anarchists.
26. First President to golf more than 150 separate times in his five years in office.
27. First President to hide his birth, medical, educational and travel records.
28. First President to win a Nobel Peace Prize for doing NOTHING to earn it.
29. First President to go on multiple "global apology tours" and concurrent "insult our friends" tours.
30. First President to go on over 17 lavish vacations, in addition to date nights and Wednesday evening White House parties for his friends paid for by the taxpayers.
31. First President to have personal servants (taxpayer funded) for his wife.
32. First President to keep a dog trainer on retainer for $102,000 a year at taxpayer expense.
33. First President to fly in a personal trainer from Chicago at least once a week at taxpayer expense.
34. First President to repeat the Quran and tell us the early morning call of the Azan (Islamic call to worship) is the most beautiful sound on earth.
35. First President to side with a foreign nation over one of the American 50 states (Mexico vs Arizona).
36. First President to tell the military men and women that they should pay for their own private insurance because they "volunteered to go to war and knew the consequences."
37. Then he was the First President to tell the members of the military that THEY were UNPATRIOTIC for balking at the last suggestion.
I feel much better now. I had been under the impression he hadn't been doing ANYTHING... Such an accomplished individual... in the eyes of the ignorant maybe.!.
199 notes
·
View notes
Text
President Trump’s relationship with climate change policy has been highly controversial and has drawn a significant amount of attention from politicians, environmentalists, and global leaders. While it is true that Trump has been a vocal skeptic of climate change science and has historically supported policies that many believe undermine global climate efforts, the assertion that he would "stop" the progress on climate change entirely is more complicated. There are several factors to consider that illustrate why it is unlikely that Donald Trump will be able to halt the progress on climate change entirely, even with policies that prioritize fossil fuel industries, deregulation, and skepticism towards international climate accords.
1. Global Movements and Public Opinion
One of the primary forces that will prevent Trump from halting climate progress is the widespread global movement in other nations in favor of addressing climate change. Over the past few decades, public awareness and concern over environmental degradation, the rise of extreme weather events, and the growing scientific consensus on climate change have catalyzed action at various levels. Even during Trump's tenure as president, the shift towards climate activism grew, with international agreements such as the Paris Agreement, corporate initiatives, and grassroots environmental movements gaining momentum.
Public opinion, especially in democracies, plays a significant role in shaping policy. In the United States, the majority of Americans support climate action, including a strong preference for clean energy and renewable resources. Despite Trump’s rhetoric, various cities, states, and businesses in the U.S. have continued to prioritize climate goals. For instance, states like California have implemented ambitious climate policies, such as transitioning to 100% renewable energy by 2045. Furthermore, a growing number of corporations have pledged to achieve net-zero emissions. The private sector’s movement towards sustainability, driven by consumer demand, investor pressure, and increasing environmental risks, represents a substantial force for climate action that extends beyond the federal government.
Even if Trump were to reverse or dismantle federal climate policies, the local and private sector commitments would likely remain largely unaffected. These bottom-up efforts represent a powerful counterbalance to federal inaction and are likely to continue advancing the fight against climate change regardless of the administration in power.
2. Economic Shift Toward Clean Energy
While Trump has been a staunch advocate for coal, oil, and gas, the global economic shift toward renewable energy is undeniable. The cost of renewable technologies, such as solar and wind power, has drastically decreased over the last decade. This economic shift makes clean energy an increasingly competitive and attractive option for both developed and developing countries. By 2025, it is estimated that the cost of solar energy will continue to fall, making it even more affordable and mainstream.
The renewable energy sector has seen significant growth in its employment. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), more than 11 million people worldwide were employed in the renewable energy industry by 2021, a figure that is expected to continue rising as nations transition away from fossil fuels. The growth of renewable energy markets is increasingly detached from political agendas, driven by technological innovation and economic pragmatism. Regardless of Trump’s policies, these forces are already in motion and will likely continue to expand, creating jobs, boosting economies, and driving global progress on climate change.
Additionally, as the consequences of climate change, such as extreme weather events, wildfires, and rising sea levels, continue to threaten communities and industries, the push for sustainable infrastructure and resilient urban planning grows. The cost of inaction will continue to drive investments in climate adaptation and mitigation technologies, further fueling the global transition to cleaner energy systems.
3. International Cooperation and Climate Diplomacy
Even during Trump’s presidency, when the United States withdrew from the Paris Agreement in 2017, international cooperation on climate change continued unabated. While the U.S. decision to exit the accord was a blow, it did not signal the end of global climate diplomacy. Many world leaders and climate organizations pushed forward with ambitious plans for carbon reduction, renewable energy investments, and international collaboration. The European Union, China, and India, as well as other nations, have made strides in combating climate change through national policies and international agreements.
Trump’s reluctance to engage with the Paris Agreement, as well as his opposition to climate-focused international cooperation, did not isolate the U.S. from the global conversation on climate change. The U.S. remained a key player in many climate-related issues at the local, corporate, and state levels, even if the federal government under Trump was less cooperative.
4. Technological Innovation and Climate Solutions
The energy sector, which has traditionally relied on fossil fuels, is undergoing a profound transformation. Advances in battery technology, electric vehicles, and green hydrogen are already making renewable energy more feasible for widespread use. As technology continues to develop, renewable energy solutions will become more efficient, less expensive, and more scalable.
Furthermore, the global push for climate action will continue to stimulate innovation. Even if Trump were to curtail government funding for green technology, private investment in clean energy and sustainability is projected to increase. Major companies are making significant strides to reduce their carbon footprints, from Google’s goal of running on 100% renewable energy to Tesla’s push for mass adoption of electric vehicles. Corporate pressure and consumer demand will continue to drive innovation and reduce reliance on fossil fuels, limiting the potential for any one individual, including Trump, to stop the progress on climate change.
5. The Resilience of Local and State-Level Action
Despite the Trump administration’s rollback of federal climate policies, local and state governments in the U.S. have continued to push forward with their climate initiatives. States like California, New York, and Washington have continued to prioritize climate action, passing laws that mandate emission reductions, promote renewable energy development, and require climate adaptation strategies.
This decentralized approach to climate action ensures that the United States remains a significant actor in the global effort to combat climate change. Even if Trump were to reintroduce policies that weaken federal regulations, states and cities would likely continue their push for climate policies in line with the global scientific consensus. This “bottom-up” approach is a vital counterbalance to the federal government’s actions and is indicative of a broader commitment to addressing climate change that transcends individual political figures.
Read the Conclusion at https://www.thescientistblog.com/blog/you-cant-stop-destiny
#climate change#government#hope#landscape#global warming#inspiration#philanthropy#climate crisis#democrat#republican
127 notes
·
View notes
Text
by Michael Rubin
Hamas paraded three Israeli hostages before cameras prior to turning them over to the Red Cross on Feb. 8. The three were emaciated like concentration camp survivors. They may have been the lucky ones. Hamas meanwhile delays the release of a dual Russian-Israeli citizen due to his health. The hostages did not learn about the deaths of their loved ones on Oct. 7, 2023, until their release. Nor was the starvation of prisoners the only Holocaust parallel. Just as the Nazis did, Hamas executed special needs children and babies it had seized during its invasion of Israel.
Biden’s team recognized but would not lift a finger to rectify the ICRC’s Jewish exception, even though several of those hostages were Americans.
A core function of the International Committee of the Red Cross is to visit and monitor prisoners. Historically, the ICRC would visit Israeli prisons. After it neglected to visit Jewish hostages in Gaza, Israel suspended its access. That the Red Cross made a greater issue about such suspensions while Hamas tortured, abused, starved, and, in some cases, executed Jewish civilians in its custody suggests that the Red Cross considers the welfare of Jews to be an exception to its mission.
Less than two weeks after Hamas seized more than 200 men, women, and children, President Joe Biden said, “I asked Israel that the global community demand that the International Red Cross be able to visit hostages. I just demanded that the United States fully — a just demand that the United States fully supports.”
Yet, when Israel made the demand and Hamas rejected it, the White House continued channeling hundreds of millions of dollars in aid to ICRC. The message was clear: Biden’s team recognized but would not lift a finger to rectify the ICRC’s Jewish exception, even though several of those hostages were Americans.
Had Biden withheld funding to the ICRC until the group visited all hostages, Mirjana Spoljaric, a Swiss diplomat who heads the group, may not have been so willing to throw Jews under the bus for the sake of the group’s good relations with Hamas. Instead, the group continues to allow Hamas to subject Jewish women to harassment and abuse upon their release. Moral clarity and backbones matter.
Alas, the ICRC’s willingness to sacrifice its mission upon its antipathy toward Jews is not a one-time occurrence. It took the ICRC headquarters more than 75 years to recognize Israel’s Magen David Adom’s chapter because of objections over its Jewish star. It had no trouble recognizing the Islamic Red Crescent, however.
Nor is the ICRC alone. The United Nations Relief and Works Agency effectively became an enabler of Hamas terrorism, if not a Hamas arm. Its employees participated in the Oct. 7, 2023, massacre. Its hospitals doubled as Hamas command posts. And released hostages said they were kept at times in UNRWA facilities. Yet, its commissioner-general Philippe Lazzarini, an ICRC leadership alum, deflects criticism and accountability. Instead, he seemingly embraces the ICRC’s Jewish exception.
ICRC rot runs deeper. Agnes Callamard, the secretary-general of Amnesty International, cited ICRC’s Israel denunciations to justify her own advocacy for Hamas.
Antisemitism remains the world’s oldest hatred, and Jews are the canary in the coal mine. Antisemitism’s victims are not just Jewish, however. The institutional antisemitism and embrace of a Jewish exception in international organizations such as the ICRC and the U.N. erode their moral standing.
Israeli Foreign Minister Eli Cohen was right when, in 2023, he said the Red Cross had “no right to exist” if it did not visit the hostages in Gaza. His only error was he did not go far enough. The moral bankruptcy not only of the ICRC but also of organizations ranging from UNRWA to the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization to the United Nations International Children’s Emergency Fund raises questions about whether it is time to cull them.
83 notes
·
View notes
Text
MYKOLAIV, UKRAINE—Kateryna Nahorna is getting ready to find trouble.
Part of an all-female team of dog handlers, the 22-year-old is training Ukraine’s technical survey dogs—Belgian Malinois that have learned to sniff out explosives.
The job is huge. Ukraine is now estimated to be the most heavily mined country on Earth. Deminers must survey every area that saw sustained fighting for unexploded mines, missiles, artillery shells, bombs, and a host of other ordnance—almost 25 percent of the country, according to government estimates.
The dogs can cover 1,500 square meters a day. In contrast, human deminers cover 10 square meters a day on average—by quickly narrowing down the areas that manual deminers will need to tackle, the dogs save valuable time.
“This job allows me to be a warrior for my country … but without having to kill anyone,” said Nahorna. “Our men protect us at war, and we do this to protect them at home.”
A highly practical reason drove the women’s recruitment. The specialized dog training was done in Cambodia, by the nonprofit Apopo, and military-aged men are currently not allowed to leave Ukraine.
War has shaken up gender dynamics in the Ukrainian economy, with women taking up jobs traditionally held by men, such as driving trucks or welding. Now, as mobilization ramps up once more, women are becoming increasingly important in roles that are critical for national security.
In Mykolaiv, in the industrial east, Nahorna and her dogs will soon take on one of the biggest targets of Russia’s military strategy when they start to demine the country’s energy infrastructure. Here, women have been stepping in to work in large numbers in steel mills, factories, and railways serving the front line.
It’s a big shift for Ukraine. Before the war, only 48 percent of women over age 15 took part in the workforce — one of the lowest rates in Europe. War has made collecting data on the gender composition of the workforce impossible, but today, 50,000 women serve in the Ukrainian army, compared to 30,000 before the war.
The catalyst came in 2017, years before the current war began. As conflict escalated with Russia in Crimea, the Ukrainian government overturned a Soviet-era law that had previously banned women from 450 occupations.
But obstacles still remain; for example, women are not allowed jobs the government deems too physically demanding. These barriers continue to be chipped away—most recently, women have been cleared to work in underground mines, something they were prevented from doing before.
Viktoriia Avramchuk never thought she would follow her father and husband into the coal mines for DTEK, Ukraine’s largest private energy company.
Her lifelong fear of elevators was a big factor—but there was also the fact that it was illegal for women to work underground.
Her previous job working as a nanny in a local kindergarten disappeared overnight when schools were forced to close at the beginning of the war. After a year of being unemployed, she found that she had few other options.
“I would never have taken the job if I could have afforded not to,” Avramchuk said from her home in Pokrovsk. “But I also wanted to do something to help secure victory, and this was needed.”
The demining work that Nahorna does is urgent in part because more than 55 percent of the country is farmed.
Often called “the breadbasket of Europe,” Ukraine is one of the world’s top exporters of grain. The U.K.-based Tony Blair Institute for Global Change, which has been advising the Ukrainian government on demining technology, estimates that landmines have resulted in annual GDP losses of $11 billion.
“Farmers feel the pressure to plow, which is dangerous,” said Jon Cunliffe, the Ukraine country director of Mines Advisory Group (MAG), a British nonprofit. “So we need to do as much surveying as possible to reduce the size of the possible contamination.”
The dogs can quickly clear an area of heavy vegetation, which greatly speeds up the process of releasing noncontaminated lands back to farmers. If the area is found to be unsafe, human deminers step in to clear the field manually.
“I’m not brave enough to be on the front line,” 29-year-old Iryna Manzevyta said as she slowly and diligently hovered a metal detector over a patch of farmland. “But I had to do something to help, and this seemed like a good alternative to make a difference.”
Groups like MAG are increasingly targeting women. With skilled male deminers regularly being picked up by military recruiters, recruiting women reduces the chances that expensive and time-consuming training will be invested in people who could be drafted to the front line at a moment’s notice. The demining work is expected to take decades, and women, unlike men, cannot be conscripted in Ukraine.
This urgency to recruit women is accelerating a gender shift already underway in the demining sector. Organizations like MAG have looked to recruit women as a way to empower them in local communities. Demining was once a heavily male-dominated sector, but women now make up 30 percent of workers in Vietnam and Colombia, around 40 percent in Cambodia, and more than 50 percent in Myanmar.
In Ukraine, the idea is to make demining an enterprise with “very little expat footprint,” and Cunliffe said that will only be possible by recruiting more women.
“We should not be here in 10 years. Not like in Iraq or South Sudan, where we have been for 30 years, or Vietnam, or Laos,” Cunliffe said. “It’s common sense that we bring in as many women as we can to do that. In five to 10 years, a lot of these women are going to end up being technical field managers, the jobs that are currently being done by old former British military guys, and it will change the face of demining worldwide because they can take those skills across the world.”
Manzevyta is one of the many women whose new job has turned her family dynamics on their head. She has handed over her previous life, running a small online beauty retail site, to her husband, who—though he gripes—stays at home while she is out demining.
“Life is completely different now,” she said, giggling. “I had to teach him how to use the washing machine, which settings to use, everything around the house because I’m mostly absent now.”
More seriously, Manzevyta said that the war has likely changed many women’s career trajectories.
“I can’t imagine people who have done work like this going back and working as florists once the war is over,” she laughed.
57 notes
·
View notes
Text
Deciphering India's Coal Shortage: Myth, Perception, or Reality? | Eninrac Reports
Exploring the Global Coal Demand: Plateaued in the West, Strong Growth in the East. Analyzing India's Coal Situation

0 notes
Text
Exploring the Growth Trajectory of the Coal Mining Industry by 2027

Coal has long stood as a cornerstone of the global energy sector, serving as a primary source for electricity generation and industrial fuel. Despite mounting concerns about environmental impacts and the emergence of renewable energy alternatives, the coal mining market continues to demonstrate resilience and steady growth. In this blog, we will delve into the factors propelling the growth of the coal mining market, supported by statistical insights and industry trends.
Market Size and Projections:
Statistical data unveils a robust growth trajectory for the global Coal Mining Market. In 2020, the market size was estimated at USD 869.5 billion, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 2.8% from 2021 to 2027. This growth is underpinned by increasing energy demand from emerging economies, industrial expansion, and the persistent reliance on coal for electricity generation.
Regional Dynamics:
The Asia Pacific region dominates the global coal mining market, boasting the largest market share in both production and consumption. Nations like China and India emerge as major coal producers and consumers, fueled by rapid urbanization, industrial growth, and infrastructure development. North America and Europe also wield significant influence in the coal mining market, albeit with a stronger emphasis on environmental regulations and transitioning to cleaner energy sources.
Key Market Drivers:
Several factors are steering the growth of the coal mining market:
Energy Demand: Coal remains a primary energy source for electricity generation, particularly in developing economies with burgeoning populations and expanding industrial sectors. The affordability and reliability of coal-fired power plants sustain its demand.
Industrialization: Coal finds extensive use in industrial processes such as steel production, cement manufacturing, and chemical synthesis, driving demand for coal mining. Industries leverage coal for its high energy content and cost-effectiveness compared to alternative fuels.
Infrastructure Development: Coal plays an indispensable role in infrastructure endeavors, including road construction, railway networks, and urban expansion. As countries invest in infrastructure to bolster economic growth and urbanization, the demand for coal for construction materials and energy remains robust.
Technological Advancements:
The coal mining industry is witnessing technological innovations aimed at enhancing efficiency, safety, and environmental sustainability. Innovations such as automated mining equipment, remote monitoring systems, and advanced coal processing technologies bolster productivity and curtail operational costs. Moreover, endeavors are underway to develop cleaner coal technologies like carbon capture and storage (CCS) and coal gasification to mitigate environmental impacts.
Challenges and Opportunities:
Despite its growth potential, the coal mining market grapples with challenges such as environmental concerns, regulatory pressures, and competition from alternative energy sources. Nevertheless, these challenges also present avenues for innovation and diversification. Coal mining entities are exploring cleaner coal technologies, diversifying into renewable energy sectors, and investing in carbon offset initiatives to mitigate their environmental footprint and adapt to evolving market dynamics.
Future Outlook:
The future of the Coal Mining Market is characterized by a blend of challenges and opportunities. While the transition towards cleaner energy sources and escalating environmental regulations pose hurdles, the sustained demand for coal in emerging economies and industrial domains offers avenues for expansion and innovation. The coal mining industry must navigate these dynamics by embracing sustainable practices, adopting advanced technologies, and diversifying portfolios to maintain competitiveness in a swiftly evolving energy landscape.
Conclusion:
The coal mining market continues to showcase resilience and growth, propelled by factors like energy demand, industrialization, and infrastructure development. Despite confronting challenges from environmental and regulatory fronts, the industry is adapting to shifting market dynamics through technological innovation and diversification. As the world endeavors to strike a balance between economic prosperity and environmental sustainability, coal mining entities play a pivotal role in shaping the trajectory of the global energy sector.
#Coal Mining Industry#Coal Mining Industry Reports#Coal Mining Market Growth#Coal Mining Market Size#Coal Mining Market#Coal Mining Market Demand#Coal Mining Market challenges#Coal Mining Market in India#Coal Mining Market value#Global Coal Mining Market#Coal Mining Market competitors#Coal mining market analysis#Coal Mining Market Forecast#Coal Mining Market outlook#Coal Mining Industry research reports#Coal Mining Market research reports#Coal Mining Market major players#Coal Mining Market Share
0 notes
Text
Exploring the Coal Mining Market Growth, Share, and Major Players

The Coal Mining Market stands as a fundamental pillar, providing the essential fuel for global energy production. This comprehensive exploration delves into the nuanced intricacies of the market, shedding light on its growth trajectories, size, demand dynamics, challenges, global presence, competitive landscape, forecasts, research reports, and the major players shaping the industry's trajectory.
Fueling Progress: The Growth Trajectory of Coal Mining Market
The market serves as an indispensable contributor to the world's energy demands. In understanding the growth trajectory, it's essential to dissect the factors propelling its expansion. The Global Coal Mining Market has experienced commendable growth, boasting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3% over the last five years. This sustained growth is attributable to the unwavering reliance on coal for electricity generation, particularly in emerging economies.
Regional Dynamics:
Regional disparities in growth patterns exist, with Asia-Pacific dominating the coal mining landscape. China, India, and Australia emerge as pivotal contributors, fueled by their burgeoning economies and significant coal reserves.
Sizing Up the Industry: Coal Mining Market Size and Demand
Understanding the market's size and the dynamics driving coal demand is imperative for stakeholders seeking holistic insights into the industry. The current valuation of the Global Coal Mining Market exceeds USD 695 billion, indicative of its substantial influence. The demand for coal surpasses 8 billion metric tons annually, driven primarily by the insatiable energy needs of industries and the power sector.
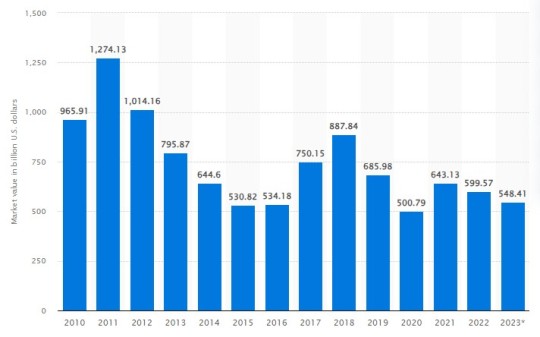
Click here – To Know more about this industry
Meeting Energy Needs: Exploring Coal Mining Market Demand
The demand for coal intricately aligns with global energy requirements, making it imperative to dissect the factors shaping demand and its pivotal role in meeting diverse energy needs.
Energy Generation Backbone:
Coal's significance in electricity generation remains pronounced, contributing to over 40% of the world's electricity. The reliable and consistent energy output from coal-fired power plants positions it as a critical contributor to the global energy mix.
Overcoming Hurdles: Coal Mining Market Challenges
Despite its integral role, the coal mining industry faces a myriad of challenges, ranging from environmental concerns to the shifting dynamics of the global market.
Environmental Concerns and Market Dynamics:
Stringent environmental regulations pose a substantial challenge, prompting the industry to pivot towards cleaner technologies and sustainable mining practices. The perpetual challenge lies in finding the delicate balance between meeting energy needs and environmental stewardship. The evolving landscape of the global energy market, with a growing emphasis on renewable sources, presents a challenge for the coal mining industry. Adapting to these market dynamics requires strategic foresight and innovative approaches.
Global Reach of the Global Coal Mining Market
The coal mining industry's influence extends far beyond national borders, necessitating an examination of the global landscape and the role of key players in shaping its dynamics.
Major Players and Market Competitors:
Leading companies, including Coal India Limited, China Shenhua Energy, and BHP Billiton, command the industry. Their strategic investments, technological advancements, and sustainable practices contribute significantly to their competitive positions on the global stage. The competition within the coal mining sector is fierce, with major players engaging in strategic maneuvers to secure resources and market dominance. Collaboration, innovation, and sustainability initiatives define their competitive strategies.
Forecasting the Future: Coal Mining Market Forecast
Anticipating future trends and trajectories is integral for strategic planning within the coal mining industry. Despite challenges and the growing emphasis on renewable energy, the coal mining market is forecasted to maintain a stable trajectory with a modest annual growth rate of 2%. The continued demand for coal in steel production and power generation contributes to this resilience.
Insights from the Earth: Coal Mining Market Research Reports
Informed decision-making within the industry relies on robust research, emphasizing the significance of Coal Mining Market Research Reports in providing actionable insights for stakeholders. An annual influx of 25 comprehensive research reports enriches the industry's knowledge base. These reports cover diverse aspects, including market dynamics, technological advancements, and regulatory changes, offering valuable guidance for strategic planning.
Pillars of the Industry
Certain players lead the way, steering the industry towards innovation and sustainability. Coal Mining Market Major players, such as Peabody Energy and Glencore, are pioneers in clean coal technologies and sustainability practices. Their efforts align with the industry's evolution towards more environmentally responsible mining, ensuring a balance between energy needs and environmental stewardship.
Conclusion
The Coal Mining Market remains a linchpin in global energy production, overcoming challenges and evolving to meet changing demands. As the industry navigates environmental concerns, explores cleaner technologies, and adapts to market dynamics, its steadfast role in powering economies underscores its enduring significance.
#Coal Mining Industry#Coal Mining Industry Reports#Coal Mining Market Growth#Coal Mining Market Size#Coal Mining Market#Coal Mining Market Demand#Coal Mining Market challenges#Coal Mining Market in India#Coal Mining Market value#Global Coal Mining Market#Coal Mining Market competitors#Coal mining market analysis#Coal Mining Market Forecast#Coal Mining Market outlook#Coal Mining Industry research reports#Coal Mining Market research reports#Coal Mining Market major players#Coal Mining Market Share
0 notes
Text
The cryptocurrency hype of the past few years already started to introduce people to these problems. Despite producing little to no tangible benefits — unless you count letting rich people make money off speculation and scams — Bitcoin consumed more energy and computer parts than medium-sized countries and crypto miners were so voracious in their energy needs that they turned shuttered coal plants back on to process crypto transactions. Even after the crypto crash, Bitcoin still used more energy in 2023 than the previous year, but some miners found a new opportunity: powering the generative AI boom. The AI tools being pushed by OpenAI, Google, and their peers are far more energy intensive than the products they aim to displace. In the days after ChatGPT’s release in late 2022, Sam Altman called its computing costs “eye-watering” and several months later Alphabet chairman John Hennessy told Reuters that getting a response from Google’s chatbot would “likely cost 10 times more” than using its traditional search tools. Instead of reassessing their plans, major tech companies are doubling down and planning a massive expansion of the computing infrastructure available to them.
[...]
As the cloud took over, more computation fell into the hands of a few dominant tech companies and they made the move to what are called “hyperscale” data centers. Those facilities are usually over 10,000 square feet and hold more than 5,000 servers, but those being built today are often many times larger than that. For example, Amazon says its data centers can have up to 50,000 servers each, while Microsoft has a campus of 20 data centers in Quincy, Washington with almost half a million servers between them. By the end of 2020, Amazon, Microsoft, and Google controlled half of the 597 hyperscale data centres in the world, but what’s even more concerning is how rapidly that number is increasing. By mid-2023, the number of hyperscale data centres stood at 926 and Synergy Research estimates another 427 will be built in the coming years to keep up with the expansion of resource-intensive AI tools and other demands for increased computation. All those data centers come with an increasingly significant resource footprint. A recent report from the International Energy Agency (IEA) estimates that the global energy demand of data centers, AI, and crypto could more than double by 2026, increasing from 460 TWh in 2022 to up to 1,050 TWh — similar to the energy consumption of Japan. Meanwhile, in the United States, data center energy use could triple from 130 TWh in 2022 — about 2.5% of the country’s total — to 390 TWh by the end of the decade, accounting for a 7.5% share of total energy, according to Boston Consulting Group. That’s nothing compared to Ireland, where the IEA estimates data centers, AI, and crypto could consume a third of all power in 2026, up from 17% in 2022. Water use is going up too: Google reported it used 5.2 billion gallons of water in its data centers in 2022, a jump of 20% from the previous year, while Microsoft used 1.7 billion gallons in its data centers, an increase of 34% on 2021. University of California, Riverside researcher Shaolei Ren told Fortune, “It’s fair to say the majority of the growth is due to AI.” But these are not just large abstract numbers; they have real material consequences that a lot of communities are getting fed up with just as the companies seek to massively expand their data center footprints.
9 February 2024
#ai#artificial intelligence#energy#big data#silicon valley#climate change#destroy your local AI data centre
74 notes
·
View notes
Text
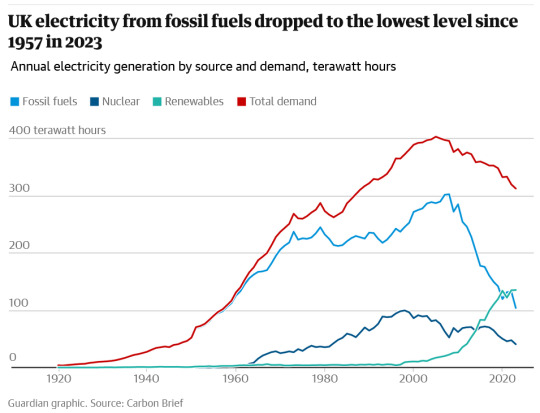
"The amount of electricity generated by the UK’s gas and coal power plants fell by 20% last year, with consumption of fossil fuels at its lowest level since 1957.
Not since Harold Macmillan was the UK prime minister and the Beatles’ John Lennon and Paul McCartney met for the first time has the UK used less coal and gas.
The UK’s gas power plants last year generated 31% of the UK’s electricity, or 98 terawatt hours (TWh), according to a report by the industry journal Carbon Brief, while the UK’s last remaining coal plant produced enough electricity to meet just 1% of the UK’s power demand or 4TWh.
Fossil fuels were squeezed out of the electricity system by a surge in renewable energy generation combined with higher electricity imports from France and Norway and a long-term trend of falling demand.
Higher power imports last year were driven by an increase in nuclear power from France and hydropower from Norway in 2023. This marked a reversal from 2022 when a string of nuclear outages in France helped make the UK a net exporter of electricity for the first time.
Carbon Brief found that gas and coal power plants made up just over a third of the UK’s electricity supplies in 2023, while renewable energy provided the single largest source of power to the grid at a record 42%.
It was the third year this decade that renewable energy sources, including wind, solar, hydro and biomass power, outperformed fossil fuels [in the UK], according to the analysis. Renewables and Britain’s nuclear reactors, which generated 13% of electricity supplies last year, helped low-carbon electricity make up 55% of the UK’s electricity in 2023.
[Note: "Third year this decade" refers to the UK specifically, not global; there are several countries that already run on 100% renewable energy, and more above 90% renewable. Also, though, there have only been four years this decade so far! So three out of four is pretty good!]
Dan McGrail, the chief executive of RenewableUK, said the data shows “the central role that wind, solar and other clean power sources are consistently playing in Britain’s energy transition”.
“We’re working closely with the government to accelerate the pace at which we build new projects and new supply chains in the face of intense global competition, as everyone is trying to replicate our success,” McGrail said.
Electricity from fossil fuels was two-thirds lower in 2023 compared with its peak in 2008, according to Carbon Brief. It found that coal has dropped by 97% and gas by 43% in the last 15 years.
Coal power is expected to fall further in 2024 after the planned shutdown of Britain’s last remaining coal plant in September. The Ratcliffe on Soar coal plant, owned by the German utility Uniper, is scheduled to shut before next winter after generating power for over 55 years.
Renewable energy has increased sixfold since 2008 as the UK has constructed more wind and solar farms, and the large Drax coal plant has converted some of its generating units to burn biomass pellets.
Electricity demand has tumbled by 22% since its peak in 2005, according to the data, as part of a long-term trend driven by more energy efficient homes and appliances as well as a decline in the UK’s manufacturing sector.
Demand for electricity is expected to double as the UK aims to cut emissions to net zero by 2050 because the plan relies heavily on replacing fossil fuel transport and heating with electric alternatives.
In recent weeks [aka at the end of 2023], offshore wind developers have given the green light to another four large windfarms in UK waters, including the world’s largest offshore windfarm at Hornsea 3, which will be built off the North Yorkshire coast by Denmark’s Ørsted."
-via The Guardian, January 2, 2024
#uk#united kingdom#england#scotland#wales#northern ireland#electricity#renewables#renewable energy#climate change#sustainability#hope posting#green energy#fossil fuels#oil#coal#solar power#wind power#environment#climate action#global warming#air pollution#climate crisis#good news#hope
396 notes
·
View notes
Text
Excerpt from this New York Times story:
Last year was the hottest on record, and global average temperatures passed the benchmark of 1.5 degrees Celsius above preindustrial times for the first time. Simultaneously, the growth rate of the world’s energy demand rose sharply, nearly doubling over the previous 10-year average.
As it turns out, the record heat and rapidly rising energy demand were closely connected, according to findings from a new report from the International Energy Agency.
That’s because hotter weather led to increased use of cooling technologies like air-conditioning. Electricity-hungry appliances put a strain on the grid, and many utilities met the added demand by burning coal and natural gas.
All of this had the makings of a troubling feedback loop: A hotter world required more energy to cool down homes and offices, and what was readily available was fossil-fuel energy, which led to more planet-warming emissions. This dynamic is exactly what many countries are hoping to halt through the development of renewable energy and the construction of nuclear power plants.
Put another way, the I.E.A. estimated that if 2024’s extreme weather hadn’t happened — that is, if weather was exactly the same in 2024 as in 2023 — the global increase in carbon emissions for the year would have been cut in half.
It’s not all bad news: Increasingly, the global economy is growing faster than carbon emissions. “If we want to find the silver lining, we see that there is a continuous decoupling of economic growth from emissions growth,” said Fatih Birol, the executive director of the agency.
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
On April 21, Ali Hussein Julood, a 21-year-old living in the Iraqi town of Rumaila, on the outskirts of one of the world’s largest oil fields, died from leukaemia. He was told by doctors that pollution from gas flared in the nearby field, which is operated by British Petroleum (BP), had likely caused his cancer. “Gas flaring” is a low-cost procedure used by oil companies to burn off the natural gas expelled during drilling. [...] [I]t also contributes to global warming [...]. Some of the pollutants released during this process, such as benzene, are known to cause cancers and respiratory diseases. Ali, who had been battling cancer for six years when he died, was only the latest victim of the environmental degradation caused by international oil companies like BP in Iraq.
In towns and villages near the country’s vast oil fields, thousands of other men, women and children are still living under smoke-filled skies and suffering avoidable health problems because company executives insist on putting profit before lives. [...]
[A] confidential report from the Iraqi health ministry recently obtained by the BBC blamed pollution from gas flaring, among other factors, for a 20 percent rise in cancer in Basra, southern Iraq between 2015 and 2018. A second leaked document, again seen by the BBC, from the local government in Basra showed that cancer cases in the region are three times higher than figures published in the official nationwide cancer registry.
Like many other problems and crises that are devastating the lives of ordinary Iraqis today, the chain of events that led to the poisoning of southern Iraq’s skies by international oil companies also started during colonial times.
---
In the early 20th century, as its navy transitioned from coal to petrol, Britain found itself in increasing need of oil to run its empire and fuel its numerous war efforts. [...] In 1912, Britain formed the Turkish Petroleum Company (TPC) with the purpose of acquiring concessions from the Ottoman Empire to explore for oil in Mesopotamia. Following World War I, it brought modern-day Iraq under its own mandate [...]. By 1930, the TPC was renamed the Iraqi Petroleum Company (IPC) and was put under the control of a consortium made up of BP, Total, Shell and several other American companies. Together, they pushed for a series of “concession agreements” with the newly formed Iraqi government which would give them exclusive control of Iraq’s oil resources on pre-defined terms for long periods. By 1938, the IPC and its various subsidiaries had already secured the right to extract and export virtually all the oil in Iraq for 75 years. These concessions were granted to the IPC and its subsidiaries while Iraq was ruled by British-installed monarchs and under de facto British control. Thus the state had almost no negotiating power against the British-led consortium [...] In 1955, the Iraqi government started to voice its desire to use the gas being flared in Rumaila and Zubair for electricity generation. In 1960, while negotiating a concession with the IPC, then-Iraqi Prime Minister Abd al-Karim Qasim formally asked the company to let Iraq exploit the gas that it was not using. The same demand came up again and again [...], but IPC and its subsidiaries repeatedly turned the Iraqi government down. [...]
Following the 2003 invasion, the Iraqi oil industry was once again privatised as a result of pressure from the US and the International Monetary Fund (IMF). As was the case in the early 20th century, any negotiations on oil extraction rights took place when Iraq was still under foreign occupation [...]. When the process of auctioning off oil fields in southern Iraq began in 2008, the Iraqi government offered foreign oil companies long contracts of up to 25 years, reminiscent of the early concessions agreements with the IPC. These included stabilisation clauses, which insulated foreign companies from legal changes that might emerge over the course of their contracts. This meant that the companies were, and continue to be, unaffected by any environmental regulations passed by the Iraqi government to reduce pollution [...].
---
Looking back at the development of the oil industry in southern Iraq makes apparent that the kind of pollution that killed Ali has been in the making for some 70 years. His death – like the deaths of many others who succumbed to pollution-related cancers in his country – was not an unavoidable tragedy, but the natural consequence of a long history of colonial violence and extractive capitalism.
Predatory colonial practices that began over a century ago caused southern Iraq’s vast oil reserves to be left under the sole control of foreign companies today – companies that over and over again put profit before the lives of the Iraqi inhabitants of the lands they exploit.
Ali’s death is yet more proof that colonial violence is far from over and that it has many different faces.
---
Text by: Taif Alkhudary. “Southern Iraq’s toxic skies are a colonial legacy.” Al Jazeera (English). 12 June 2023. [Some paragraph breaks/contractions added by me.]
340 notes
·
View notes