#Genetically Modified Seeds
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Genetically Modified Seeds: The Controversial Agricultural Revolution
Genetically modified (GM) crops are plants used in agriculture whose DNA has been modified using genetic engineering methods. The most common traits introduced to GM crops are herbicide tolerance and insect resistance. Herbicide Tolerance in Genetically Modified Seeds One of the earliest applications of genetic engineering in agriculture was to make crops tolerant to herbicides, so that weeds could be eliminated with herbicide spraying without killing the crops. Two main herbicide tolerance traits that have been introduced through genetic engineering are glyphosate tolerance and glufosinate tolerance. Glyphosate, marketed by Monsanto under the trade name Roundup, is a broad-spectrum herbicide that kills weeds but not crops engineered to be tolerant. Glufosinate is another broad-spectrum herbicide to which some crops have been engineered to be tolerant. These modifications allow farmers to spray herbicide over the top of entire fields and only kill the weeds, not the crops. Insect Resistance through Bt Technology Many GM crops are genetically engineered to produce one or more insecticidal proteins from the soil bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt). Known as Bt crops, they are insects resistant. Corn and cotton are the main crops engineered with Bt technology to be resistant to certain Lepidopteran or Coleopteran insect pests. The Bt proteins expressed in these GM crops only affect insect species within these orders and have no reported effects on other organisms including humans. Bt crops allow farmers to reduce or eliminate insecticide applications for key pests. Potential Benefits of GM Crops Besides reducing herbicide and insecticide use, Genetically Modified Seeds are promoted as having benefits such as increased crop yields through built-in pest and weed management, economic gains for farmers, increased food security by boosting global food supplies, and environmental benefits from reducing tillage needs. Many farmers have adopted GM crops due to economic and productivity advantages, reduced labor needs, and opportunities to farm more sustainably. Supporters argue that GM technology can play an important role in helping agriculture meet the challenging demands of feeding a growing global population. Skepticism and Criticism around GM Crops While GM crops have been embraced globally, controversy and skepticism also exists. Some criticism includes concerns over unknown long-term health and environmental risks, possibility of new superweeds and superpests developing resistance, lack of testing and regulation, domination of the seed industry by a few major corporations, and socioeconomic issues around licensing practices and seed patents. Opponents argue that natural plant breeding methods can achieve the same goals as GM without exposing the food supply or environment to potentially hazardous risks that genetic engineering may entail. There are also concerns that the spread of transgenes from genetically modified seeds to wild relatives or conventional crops cannot be prevented and could impact biodiversity. Developing countries are more cautious about adopting GM crops due to lack of local research capacity and health monitoring infrastructure.
Get more insights on Genetically Modified Seeds
Discover the Report for More Insights, Tailored to Your Language
French
German
Italian
Russian
Japanese
Chinese
Korean
Portuguese
Priya Pandey is a dynamic and passionate editor with over three years of expertise in content editing and proofreading. Holding a bachelor's degree in biotechnology, Priya has a knack for making the content engaging. Her diverse portfolio includes editing documents across different industries, including food and beverages, information and technology, healthcare, chemical and materials, etc. Priya's meticulous attention to detail and commitment to excellence make her an invaluable asset in the world of content creation and refinement.
(LinkedIn- https://www.linkedin.com/in/priya-pandey-8417a8173/)

#Genetically Modified Seeds#GMO Seeds#Genetically Engineered Seeds#Biotechnology#Agriculture#Crop Production#Food Production#Food Technology#Genetic Engineering#Genetic Modification
0 notes
Photo
The other thing you should be upset about: crops modified to be pesticide resistant so they can dump a shitton of toxins into the environment especially RoundUp which is a suspected carcinogen and dangerous to agricultural workers as well as ecosystems. And the weeds will evolve immunity in a few years anyway.
Support beneficial GMOs, but also support organic farming and a ban on RoundUp/glyphosphate (already illegal in France, Belgium, the Netherlands, and Germany). Fuck Monsanto.
Funny how that works
#gmo crops can be great but roundup is BAD. the WHO calls it a “probable” carcinogen which is more than enough evidence i don't want it to#be in my drinking water and soil and food and especially not for ag workers to be around it all the time#and also fuck that thing where they dont let farmers save seeds. and also the lack of seed diversity.#gmos#genetically modified#fuck monsanto#environmental issues#uncaptioned
276K notes
·
View notes
Text
#Corn crop#Corn production#Corn farming#Corn varieties#Corn seed#Maize#Corn harvest#Corn silage#Corn agriculture#Corn growth stages#Corn farming techniques#Corn planting#Genetically modified corn#Corn sustainability#Corn yield#Corn pests#Corn diseases#Corn rotation#Corn market#Corn nutrition#Corn products#Corn flour#Corn syrup#Sweet corn#Field corn#Corn ethanol#Corn feed#Corn prices#Corn trade#Corn industry
1 note
·
View note
Text
High Court Clears Path for Genetically Modified Crops in Kenya
A Kenyan court has dismissed a second legal challenge to the government’s decision to lift its decade-long ban on genetically modified crops, effectively allowing their continued cultivation and import. This ruling, made on Thursday by judge Lawrence Mugambi, builds on a 2023 decision in which an environment court ruled that no evidence showed GM crops posed risks to health or the…
#agriculture in kenya#biodiversity concerns GM crops#consumer opposition GM crops#drought-resistant crops Kenya#environmental impact GM crops#food security Kenya#genetically modified crops Kenya#GM crop ban lifted#GM crop regulation Africa#GM crops benefits risks#GM crops food security#GM crops legal battle#Kenya GM crop court ruling#Kenya GM crops#Kenyan agriculture economy#President Ruto GM crops#public perception GM crops#seed industry Kenya#smallholder farmers GM crops#traditional farming vs GM crops
0 notes
Text
Genetically Modified Seeds Market Trends: A Growing Agricultural Revolution

The genetically modified seeds market has revolutionized agricultural practices through the development of crop varieties that exhibit superior traits like herbicide tolerance and insect resistance. Genetically engineered seeds help farmers produce higher crop yields through traits that enhance stress tolerance, increase nutritional value, and prolong shelf life. Global demand for food isprojected to increase substantially due to the rising global population, which is estimated to reach nearly 10 billion by 2050. This growing global food demand can only be met through sustainable intensification of agricultural production with the help of GM seeds that boost productivity per acre of land. The Global genetically modified seeds market is estimated to be valued at US$ 20.34 Bn in 2024 and is expected to exhibit a CAGR of 10% over the forecast period of 2023 to 2030. Genetically modified seeds find widespread application in cultivating major crops like soybean, maize, cotton, canola and others. They help reduce dependence on pesticides and herbicides while maximizing agricultural output. The ability of GM seeds to withstand biotic and abiotic stressors makes them an indispensable tool for ensuring global food security. Key Takeaways
Key players operating in the genetically modified seeds market are Bayer CropScience, BASF SE, Syngenta, and JR Simplot Co. These leading seed companies are investing heavily in R&D to develop novel seed traits and capture greater market share. Growing global population coupled with changing dietary preferences is fueling the demand for food grains worldwide. Genetically modified seeds with traits like herbicide tolerance and insect resistance help boost agricultural productivity to meet this rising food demand. Several countries in Latin America, Asia and Africa are increasing their adoption of biotech crops due to the yield advantages offered by GM seeds. Global seed companies are also expanding to emerging nations to tap the vast growth opportunities in these markets. Market Key Trends
One of the major trends in the genetically modified seeds market is the development of drought-resistant and heat-tolerant seeds. With climate change leading to unpredictable weather patterns, GM seeds that can withstand extreme temperatures and water scarcity are gaining traction. Leading companies like Bayer are engaged in modifying crop genomes to produce varieties suited to arid conditions. Another prominent trend is the engineering of seeds that enhance nutrition. Biofortified seeds enriched with vitamins, minerals and nutrients can help address global micronutrient deficiencies. Meanwhile, gene-editing technologies like CRISPR are allowing for more precise genetic modifications without transgene integration. This is expanding the toolkit for breeders to develop proprietary biotech traits.
Porter's Analysis
Threat of new entrants: The high costs associated with R&D make it difficult for new companies to enter this market. Bargaining power of buyers: Large buyers like crop producers can negotiate lower prices due to high demand for GM seeds. Bargaining power of suppliers: A few large suppliers like Bayer and Syngenta dominate the GM seed supply chain which limits options for buyers. Threat of new substitutes: Alternatives such as organic seeds are still limited. Intensive R&D protects GM seeds from new substitutes. Competitive rivalry: Intense competition exists between major players to capture more market share through new product innovations and acquisitions. Geographical Regions North America accounts for the largest share of the GM seeds market currently due to widespread adoption in major crops like corn and soybean. The USA alone accounts for over 50% of global GM crop production. Asia Pacific is projected to grow at the fastest pace during the forecast period driven by population growth and rising demand for food. Countries like India and China are encouraging GM crop farming to boost agricultural yields to feed their large populations. Adoption of insect-resistant and herbicide-tolerant cotton seeds has been highest in India.
#Genetically Modified Seeds Market Growth#Genetically Modified Seeds Market Size#Genetically Modified Seeds Market Share
0 notes
Text
Genetically Modified Seeds Market Size and Growth Prospects: In-depth Analysis

In the world of agriculture, the advent of genetically modified (GM) seeds has sparked both excitement and controversy. These seeds, engineered to possess desirable traits such as pest resistance, herbicide tolerance, and improved yield potential, have revolutionized modern farming practices. As the global population continues to swell, placing increasing pressure on food production, the role of genetically modified seeds in addressing agricultural challenges has become ever more significant.
Understanding Genetically Modified Seeds:
Genetically modified seeds are the result of genetic engineering techniques that involve the alteration of an organism's genetic material to introduce beneficial traits. In agriculture, this typically involves the modification of crop plants to enhance characteristics such as resistance to pests, diseases, or environmental stressors, as well as to improve nutritional content and yield.
The process of creating genetically modified seeds often begins in laboratories, where scientists identify genes responsible for desired traits and introduce them into the plant's genome using various methods, including gene editing techniques like CRISPR-Cas9 or traditional genetic modification methods like recombinant DNA technology. Once developed, these genetically modified seeds undergo rigorous testing to ensure their safety and efficacy before being released to farmers.
Market Dynamics:
The genetically modified seeds market has witnessed significant growth over the past few decades, driven by several factors. One of the primary drivers is the increasing global demand for food in the face of population growth, urbanization, and changing dietary preferences. Genetically modified seeds offer the promise of higher yields, improved crop quality, and greater resilience to pests and environmental stresses, making them an attractive option for farmers seeking to optimize their productivity and profitability.
Moreover, the adoption of genetically modified seeds is also influenced by the growing need for sustainable agricultural practices. By reducing the reliance on chemical pesticides and fertilizers, genetically modified crops can help mitigate environmental degradation, minimize agricultural runoff, and conserve natural resources—a critical consideration in an era of climate change and dwindling arable land.
Controversies and Challenges:
Despite their potential benefits, genetically modified seeds remain a subject of intense debate and controversy. Critics raise concerns about their long-term environmental impact, potential health risks, and socioeconomic consequences. Questions surrounding issues such as seed ownership, farmer autonomy, and genetic diversity have fueled heated discussions and regulatory scrutiny in many parts of the world.
Additionally, the dominance of a few multinational corporations in the genetically modified seed industry has raised concerns about market concentration, intellectual property rights, and the equitable distribution of benefits. Critics argue that this concentration of power could exacerbate inequalities within the agricultural sector and hinder smallholder farmers' access to essential resources and technologies.
Future Outlook:
Looking ahead, the future of the genetically modified seeds market is likely to be shaped by ongoing technological advancements, regulatory developments, and shifting consumer preferences. Emerging technologies such as gene editing hold the promise of more precise and efficient genetic modifications, potentially opening up new avenues for crop improvement and innovation.
In conclusion, the genetically modified seeds market represents a complex and dynamic landscape characterized by innovation, controversy, and uncertainty. While genetically modified crops hold immense potential to address pressing agricultural challenges, their widespread adoption hinges on addressing legitimate concerns, fostering responsible stewardship, and promoting inclusive and equitable access to the benefits of biotechnology. As technology continues to evolve and societal values evolve, the future trajectory of the genetically modified seeds market will undoubtedly be shaped by a multitude of factors, each influencing the course of agricultural innovation and sustainability.
#Genetically Modified Seeds Market Growth#Recovered Carbon Black Trends#Recovered Carbon Black Shares
0 notes
Text
Illegal seeds?
A friend sent me the following video earlier, and I had to check into it! https://www.facebook.com/share/v/nzXCHT3mZQv5oddN/?mibextid=w8EBqM In the video, The Scaredy Cat Gardener shares that it is a good idea to check local and state laws beforehand because it may be ILLEGAL to sell or give away seeds from the plants in your garden… Immediately, I was like, “Whaaaaaaat?!” Yep, you heard that…

View On WordPress
#agriculture#civil#civil liberties#feed the nation#feed the world#garden#gardener#gardening#genetically modified#GMOs#government overreach#iowa#Murica#organic#rights#seed libraries#seed preemption#stupid laws#USA
0 notes
Text
Genetically Modified Seeds Market Expansion: Bridging the Food Gap
Genetically modification (GM) of seeds involves the modification of DNA of natural seeds, in order to increase tolerance against pests and herbicides, with the help of genetic engineering methods such as gene gun and agrobacterium tumefaciens. It also aids in improving the yield of the crop. Genetically modified seeds are gaining popularity over conventional seeds, owing to factors such as longer shelf life, improved yields, enhanced nutritional values, and capacity to sustain against climatic changes
#Genetically Modified Seeds Market Share#Genetically Modified Seeds Market Growth#Genetically Modified Seeds Market Demand
0 notes
Text
Exploring Innovations in the Genetically Modified Seeds Market: A Comprehensive Overview

Genetically modified seeds are seeds that have been transformed through recombinant DNA techniques, also known as genetic engineering or genetically modified organisms (GMOs). Such seeds are designed to resist pests or herbicides, or to increase crop yields. In recent times, genetically modified seeds have become predominant in many countries due to their advantages of providing higher crop yields along with resistance against pests and herbicides. However, there are also concerns regarding their impact on health and the environment. The global Genetically Modified Seeds Market is estimated to be valued at US$ 20.34 Bn in 2023 and is expected to exhibit a CAGR of 10% over the forecast period 2023 to 2030, as highlighted in a new report published by Coherent Market Insights. Growing Global Food Insecurity: The global population is expected to grow exponentially in the coming decades which has increased concerns around global food security. Genetically modified seeds have the potential to increase crop yields and help tackle the challenge of feeding the growing global population. Genetically modified crops have been reported to provide increased yields by reducing crop failures stemming from various diseases and pests. This makes them a viable solution to deal with growing concerns around food shortage and rising global food insecurity. Porter’s Analysis Threat of new entrants: The threat of new entrants is medium. The genetically modified seeds market requires high capital investment for R&D. Established players have strong brands and distribution network. Bargaining power of buyers: The bargaining power of buyers is high. Buyers can switch to alternative traditional seeds suppliers. Buyers have options to choose from multiple branded seeds in the market. Bargaining power of suppliers: The bargaining power of suppliers is low to medium. A few major players dominate the hybrid and GM seeds supply chain. Suppliers face pressure on prices from big buyers. Threat of new substitutes: The threat of substitutes is low. No close substitutes currently exist for GM seeds with superior crop traits and yields. Competitive rivalry: The competitive rivalry is intense. Major players compete on technology, traits, seeds quality and distribution reach. SWOT Analysis Strength: Genetically modified seeds offer superior yields and resistance to diseases and herbicides. Technological advancements enable development of new seed varieties. Weakness: High R&D costs increases seed prices. Strict regulations delay product approvals. Environmental and health concerns persist regarding GM crop impacts. Opportunity: Growing demand for food due to rising population presents opportunities. Adoption in developing regions is increasing. Development of biotech crops adapt to climate change impacts. Threats: Protectionist trade policies and non-tariff barriers restrict exports. Alternative natural and organic farming methods pose competition. Key Takeaways The global genetically modified seeds market is expected to witness high growth over the forecast period supported by increasing food demand and advances in biotechnology.
Regional Analysis: North America dominated the market in 2023 owing to large acreage under GM crop cultivation in countries like US and Canada. The US is the largest producer and exporter of GM seeds globally. Key players operating in the genetically modified seeds market are Bayer CropScience, BASF SE, Syngenta, and JR Simplot Co. Syngenta leads the market followed by Bayer. These major players invest heavily in R&D to develop new seed varieties offering herbicide tolerance and insect resistance traits. Opportunities lie in emerging markets of Asia Pacific and Latin America where GM crop adoption is rising.
#Genetically Modified Seeds Market Share#Genetically Modified Seeds Market Growth#Genetically Modified Seeds Market Demand#Genetically Modified Seeds Market Trend
0 notes
Text
Asia Pacific Genetically Modified (GMO) Seeds Market Outlook, 2022-2029
BlueWeave Consulting, a leading strategic consulting and market research firm, in its recent study, estimated the Asia-Pacific Genetically Modified (GMO) Seeds Market size at USD 5.65 billion in 2022. During the forecast period between 2023 and 2029, BlueWeave expects the Asia Pacific Genetically Modified Seeds Market size to grow at a significant CAGR of 9.57% reaching a value of USD 9.77 billion by 2029. Asia-Pacific Genetically Modified (GMO) Seeds Market is propelled by the growing population and demand for food driving the adoption of high-yielding genetically modified crops for enhanced agricultural productivity. Technological advancements in biotechnology and seed development, coupled with a rising need for pest-resistant and drought-tolerant crops, contribute to market growth. Government initiatives supporting the adoption of genetically modified seeds for sustainable agriculture further fuel the market growth. Also, the awareness about the benefits such as improved crop yields and reduced environmental impact drives farmer acceptance of GMO seeds. Overall, the Asia-Pacific Genetically Modified (GMO) Seeds Market is shaped by a complex interplay of technological, economic, and regulatory factors.
Opportunity – Increasing Adoption of Biofuels
The Asia-Pacific Genetically Modified (GMO) Seeds Market is experiencing significant growth due to the increasing adoption of biofuels. The trend is driven by various factors, such as the elevated cost of crude oil, the inconsistent supply of fossil fuels, and the associated political and environmental issues related to fossil fuels. Also, the growing environmental awareness among consumers is contributing to a rising demand for biofuels. Further, biofuels, derived from various crops like soybeans, sugarcane, and corn, play a crucial role in ensuring environmental sustainability, reducing dependence on fossil fuels, and minimizing pollution. Farmers across Asia Pacific are increasingly adopting GMO plants and seeds which would help them cultivate with enhanced yields, a trend expected to drive the growth of the Asia-Pacific Genetically Modified (GM) Seeds Market during the forecast period.
Sample Request @ https://www.blueweaveconsulting.com/report/asia-pacific-genetically-modified-seeds-market/report-sample
Impact of Escalating Geopolitical Tensions on Asia-Pacific Genetically Modified (GMO) Seeds Market
Escalating geopolitical tensions, such as the Russia-Ukraine war, have significantly impacted the Asia-Pacific Genetically Modified (GMO) Seeds Market. The conflict disrupted the global supply chain, leading to increased uncertainty and volatility in seed markets across the region. Supply chain disruptions affected the timely availability of GMO seeds, disrupting planting schedules and causing uncertainties for farmers. Also, heightened geopolitical tensions can lead to shifts in trade dynamics, affecting import and export patterns of GMO seeds in the Asia-Pacific region. These disruptions pose challenges for stakeholders in the agricultural sector, impacting production, pricing, and overall market stability. As geopolitical tensions continue to evolve, the Asia-Pacific GMO Seeds Market remains susceptible to ongoing uncertainties and challenges, necessitating adaptive strategies for industry players.
Asia-Pacific Genetically Modified (GMO) Seeds Market – By Sales Channel
By sales channel, Asia-Pacific Genetically Modified (GMO) Seeds Market is divided into Direct Sales, Modern Trade, and E-Retailers segments. The modern trade segment is the largest, reflecting a growing preference for organized retail channels in the region. The segment encompasses various established retail formats, contributing significantly to the distribution and sales of genetically modified seeds. The shift toward modern trade underscores evolving consumer preferences and the adoption of efficient supply chain mechanisms, influencing the dynamics of the GMO seeds market in the Asia-Pacific region.
Competitive Landscape
Asia-Pacific Genetically Modified (GMO) Seeds Market is fiercely competitive. Major companies in the market include JK Agri Genetics Limited, Nufarm, Bayer AG, Syngenta Crop Protection AG, J.R. Simplot Company, Mahyco, Cibus, and Stine Seed Company. These companies use various strategies, including increasing investments in their R&D activities, mergers, and acquisitions, joint ventures, collaborations, licensing agreements, and new product and service releases to further strengthen their position in the Asia-Pacific Genetically Modified (GMO) Seeds Market.
Contact Us:
BlueWeave Consulting & Research Pvt. Ltd
+1 866 658 6826 | +1 425 320 4776 | +44 1865 60 0662
0 notes
Text
Genetically Modified (GMO) Seeds Market Set To See Strong Growth by 2030

The genetically modified (GMO) seeds market refers to the production, sale, and distribution of seeds that have been genetically modified using biotechnology techniques. These seeds have been engineered to possess certain desired traits, such as resistance to pests, diseases, or herbicides, increased yields, and improved nutritional content.
For Download Sample Report Click Here: https://www.globmarketreports.com/request-sample/255904
The global GMO seed market has been growing in recent years, driven by the increasing demand for food and the need for higher crop yields to meet the growing population’s food requirements. The market is dominated by a few multinational companies such as Monsanto, Syngenta, Bayer CropScience, DowDuPont, and BASF, who invest heavily in research and development of new GMO seed technologies.
However, the GMO seed market is also controversial due to concerns about the safety and environmental impact of genetically modified crops. Many consumers and environmental groups argue that GMO crops could harm biodiversity and potentially pose risks to human health, while the industry argues that GMO crops are safe and beneficial.
The use of GMO seeds is regulated by different regulatory bodies around the world, with some countries having strict regulations and others allowing GMO crops to be grown more widely. The debate over the use of GMO seeds is likely to continue as the market continues to grow, and concerns about food security and sustainability become increasingly pressing.
0 notes
Note
Thinking about sex toys but they’re living plants…
Venus flytraps that were genetically modified to have tongues that go so deep inside you
Tulip flower where it’s flowery insides are sticky with a new type of pollen that resembles cum
Cactus plants that were modified so instead of sharp spikes they have bumps that feel so good going in and out of your hole
Lily of the valleys whos small white bulbs suck on your skin n clit so well
Sunflowers whose seeds contain aphrodisiacs
Ivy/vine plants that have a hive mind and all they want is you
.
784 notes
·
View notes
Note
from the same authors of "do you think zayne cum is cold?" we also have: do you think xavier cum shine in the dark, or that he shines when he comes (like that blonde female character from the boys, that i forgot the name)?
I know you are only message fics for now and i dont know if something like this would fit that format, but if you can i would love to read anything about this ♡
I’m gonna be honest with you nonnie, I’m VERY out of touch with modern media (I’ve watched like. 4 series in my entire life and a total of like 20 movies all in all) so I have no idea what you’ve just referenced, BUTTTT I do believe I have an answer to your question!! Of course this is all based off my silly headcanons, so take my opinion with a grain of salt🙏🏽 Of course, this is pretty NSFW, and the reader is gender-neutral as always!
To anyone else reading this, my requests are still closed!! These are just my ramblings, or old requests I had🫶🏽
Tip jar!
Masterlist

Metaphorically speaking, Xavier’s cum is pretty much lighter fluid
In the sense that this man’s diet is absolutely disastrous… can a person even live on an almost-purely-carnivorous diet???
Naturally that makes his cum a lot more bitter than it normally would be, so unless his lover wants to choke on battery acid every time they swallow his cum, they ought to sit down with him and have a few serious conversations regarding sex vs food
Either he pulls out of their mouth before he cums when they’re sucking him off, or he gets a little more greens in him in order to improve his own taste… fair enough, I would think!
Xavier doesn’t really mind; after all, he’s still eating lots of red meat, he just now balances that out with more fruits and veggies… and he still gets the overwhelming pleasure of watching his partner swallow his release with a much more pleased hum than they ever did, their thumb reaching out to catch any drops that spill out of the corner of their mouth
It drives him half mad, but he guesses that’s a small price to pay
Now that we’ve got the metaphorical part out of the way, let’s get to this interesting point: does he, or does he not glow when he climaxes?
I wouldn’t say that his cum glows, because if it did, I think his other bodily fluids would too
From a fictional anatomical standpoint, I highly doubt that his lover wouldn’t notice if his saliva had a bit of a glow (something they’d surely notice while making out or having a hearty meal, for example)
So I do believe his cum is as normal as normal could be for a man like him
I do believe, though, since he’s not 100% human (or, at the very least, not from Earth) that doesn’t mean he’s fully normal
I think that he would have abnormally thick cum, and I would assume that that has to do with his biological make-up
Given how people from Philos lead extremely long lives (given Xavier’s age, I’d give them a lifespan of 500+), and given how literally none of the characters from Philos have any siblings, I think it would be safe to assume that their seed isn’t very potent to start with
So if a person will live half a millennium and be able to have just 1 kid their entire life, I do believe that their cum would be stickier and thicker in order to have a higher chance of “taking” by not spilling out immediately
So I honestly think that Xavier’s cum is genetically modified for breeding purposes
And regardless of whether or not his significant other has the ability to become pregnant and/or even wants it at all, his brain has him wired to have a bit of a breeding kink that he can’t even help
But of course, he’ll always listen to and respect his partner’s wishes!
One thing I’ve noticed about Xavier, however, is that his eyes tend to lose their shine when he’s being forward and open about his sexual desires
He’s putty in his lover’s hands, yes, but once he takes control? Those angel eyes have a very intentional purpose, and he’s making that message come across loud and clear
Like a turbulent ocean, deep and all-consuming, his gaze leaves no doubts about what he wants
Now, here’s my headcanon: I like to think that when he’s close, his eyes get their shine back; so much so that they would be mistaken for tears
Maybe it’s the emotional attachment to the person he’s yearned for all these years, maybe it’s because of his own EVOL making its appearance
But for some reason, as he begins to lose control, his eyes do shine quite a bit, almost like freshly-cut sparkling sapphires
It’s quite dazzling and a bit surprising to witness for the first time, since Xavier doesn’t usually exhibit non-human behavior
But it makes that seraphic face seem all the more otherworldly; the contrast between how beautiful he is and how downright filthy his actions can be when he’s buried to the hilt inside them makes their head spin
After he’s spilled inside them amidst soft sighs and sweet moans, his eyes do go back to normal after a few seconds of closing them in bliss, so they might miss it if they’re not paying close attention
Kind of hard to look away though, when your lover looks like that

Taglist: @verynormalsstuff @angry-and-yandere @nxx-jordiepord @honestlyjustablog @dawnbreakersgaze @tartartagliaboo @lucis-noctiana @riinari-sa @reika-desu @tikitsune @roll-of-royces @lemonsupernova @loveyoutodeep @belovedof @obiwanmcprobie @kalatipunan @eurekazz @bifedebruxa @thescribeswife @mysticangel123 @xenasolos @jvnluvr @dann-acalle @rin-sv14 @yololesgo @an-ever-angry-bi @semi-orangeapple @lavanderbliss @myturnwhen @winterlvod @carsonology @respitable @stellisangelicus-world @kvsqkiii @bitchynightmarepost @snoozeflare @spotted-salamander @cindywasneverhere @ladyparamount @sncrly0urs @huntersmoon1 @musiclover2119 @girl-who-lives-in-delusion @milktsukii @fromdeepspace-withlove @granddearduck @skriblobz @nadinefromwhere @imhere2dosomething @saerotonins @cantescapethevoid @teewritessmth @lovra974 @straykidz143 @reishuus @xinnn6 @vyntagei @bakahimesama (more in replies!)
Sign up for my taglist here!
#imagine#headcanons#hcs#hc#headcanon#smut#xavier#xavier smut#xavier x reader#xavier love and deepspace#xavier lnds#xavier lads#xavier l&ds#xavier shen#shen xinghui#shen xinghui x reader#shen xinghui smut#otome games#love and deepspace#lnds#lads#l&ds#lnds xavier#xavier shen x reader#xavier shen smut#xavier x mc#xavier x you#xavier love and deepspace x reader#spicy
437 notes
·
View notes
Text
Military Chaff and genetically modified seeds that grow in contaminated soil 🤔
#pay attention#educate yourselves#educate yourself#knowledge is power#reeducate yourselves#reeducate yourself#think about it#think for yourselves#think for yourself#do your homework#do your own research#do some research#do your research#ask yourself questions#question everything#military chaff#government corruption#evil lives here#news
94 notes
·
View notes
Text
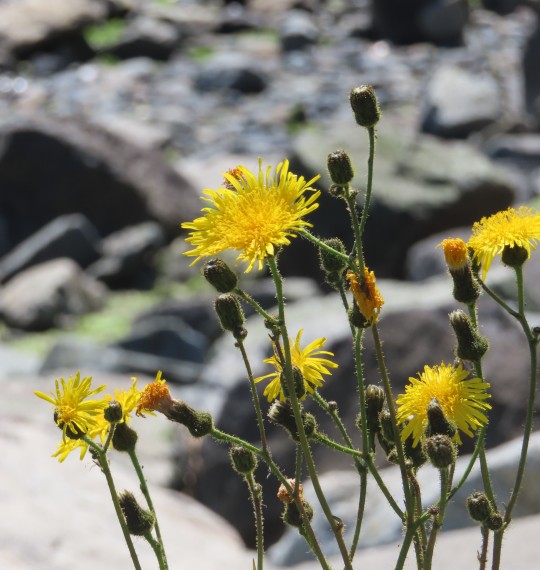
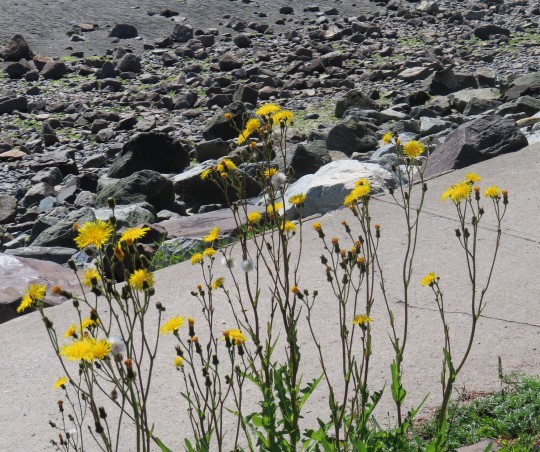
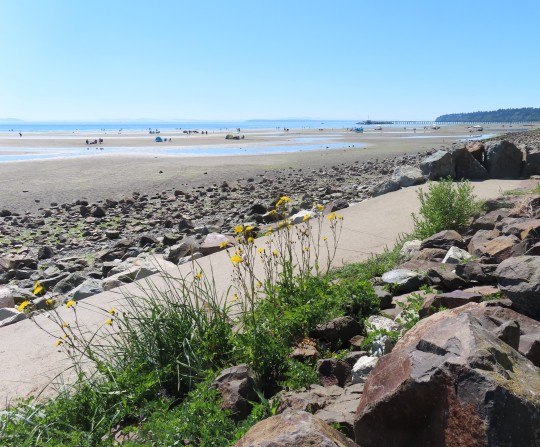



Sonchus arvensis (perennial sow-thistle)
Round-up
A perennial sow-thistle enjoys a sunny day at the beach. This plant is native to Eurasia but is often described (by farmers) as a noxious, invasive weed, and is now 'naturalized' throughout North America, South America, Russia, New Zealand and Australia. Like it's relative the dandelion, it arrived from Europe during the Age of Exploration and it's probably been growing in North America for five hundred years. I have no doubt that the first seeds arrived on someone's muddy boot.
The Minnesota Wildflowers website reports, "This species is a rapid colonizer from deep, extensive underground root systems. Once listed as a Minnesota state noxious weed, it is now widely established throughout the state but is not as problematic agronomically as was once thought. Round-up Ready crops took care of much of the problem." '
Round-up (2,4-d) is a powerful broad-spectrum herbicide used extensively in modern agriculture. Round-up Ready crops include soy, corn, canola, alfalfa, sugar beets and cotton and Round-up resistant wheat is under development. Round-up has been extensively tested and under normal concentrations it is not considered injurious to human health but this research is controversial and many lawsuits are pending. In 2023, 91% of the corn, 95% of soybeans, and 94% of cotton produced in the United States were from genetically modified, herbicide-resistant strains. For everybody's sake, I hope these safety studies are correct.
A final note: as a gardener you are advised to wear long pants, a long sleeved shirt, gloves, goggles and a mask when applying Round-up, not that anybody does. Personally, I never use the stuff. I get rid of weeds the old-fashioned way - I use my hands.
#flowers#photographers on tumblr#sow thistle#Round-up#invasive plants#fleurs#flores#fiori#blumen#bloemen#White Rock beach#Vancouver
62 notes
·
View notes
Text
‘One of the most infamous modern-day monopolies is the biotech agricultural company Monsanto. The company specializes in environmentally toxic, genetically modified crops and seeds, and utilizes patents to dominate seed markets. In India, 95 percent of cottonseed is controlled by Monsanto, as Indian companies have been locked into joint ventures and licensing arrangements for the last couple of decades. Every patented seed is the "intellectual property" of Monsanto, entitling them to royalties, thereby raising the costs of seeds.’
‘Perhaps most shockingly, these patented seeds have come to include "gene use restriction technology" — seeds that will not produce viable offspring seeds. In this way farmers are forced into buying new seeds every year, rather than harvesting them out of the previous year's crops. The swelling of Indian farmers' debt — along with increasing farmer suicides — are a product of what Indian environmentalist and ecofeminist Vandana Shiva has dubbed Monsanto's "seeds of suicide."’
-Hadas Thier, A People’s Guide to Capitalism
56 notes
·
View notes