#GI Agriculture App
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
The Future of GPS Navigation and Tracking: Navigating Towards a Smarter Tomorrow
The Global Positioning System (GPS) has become an integral part of our daily lives, revolutionizing how we navigate and track our surroundings. From guiding drivers through bustling city streets to assisting logistics companies in managing their fleets, GPS technology is pivotal in various sectors. As we look to the future, advancements in GPS navigation and tracking promise to enhance our ability to move through the world more efficiently and safely. This analysis explores the evolution of GPS technology, the anticipated advancements, and its implications for consumers, industries, and academic institutions like Telkom University, which plays a crucial role in driving research and innovation in this field.
The Evolution of GPS Technology
Originally developed for military applications, GPS technology has permeated civilian life since the 1980s. Today, it is ubiquitous in smartphones, vehicles, and a wide array of devices, enabling users to access real-time location data. The technology relies on a network of satellites that transmit signals to GPS receivers, which then calculate the user's position based on the time it takes for signals to travel. global entrepreneurial university.
The accuracy of GPS has improved significantly over the years, evolving from a rough estimate of 100 meters to precise location tracking within centimeters. This evolution has been driven by the introduction of Differential GPS (DGPS), which uses ground-based reference stations to correct GPS signals, enhancing accuracy. The integration of GPS with other technologies, such as Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and the Internet of Things (IoT), has further expanded its applications and utility.
Future Trends in GPS Navigation and Tracking
1. Enhanced Accuracy and Reliability
As technology continues to evolve, the future of GPS navigation will see even greater accuracy and reliability. The advent of new satellite systems, such as the European Union��s Galileo and India’s NavIC, promises to enhance the global navigation satellite system landscape. These systems offer complementary capabilities to the existing GPS infrastructure, enabling users to receive signals from multiple satellite constellations, thus increasing accuracy.
In urban environments, where tall buildings can obstruct signals, advancements in multi-frequency GPS receivers and augmentation systems will help mitigate errors and improve performance. The integration of technologies like Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) positioning will provide centimeter-level accuracy, making GPS invaluable in applications such as agriculture, construction, and surveying.
2. Integration with Augmented Reality (AR)
The convergence of GPS technology with augmented reality is set to transform how we interact with our environment. AR applications that utilize GPS data can overlay digital information onto the physical world, providing context and enhancing the user experience. For instance, navigation apps could display directions directly onto the user’s surroundings through their smartphone or AR glasses, making navigation more intuitive.
This integration will be particularly beneficial in tourism, where users can receive historical information about landmarks as they explore new cities. Educational institutions like Telkom University can play a pivotal role in developing AR applications that leverage GPS data for educational purposes, fostering innovation and enhancing the learning experience.
3. Advancements in Tracking Technologies
The future of GPS tracking is poised for significant advancements, driven by the growing demand for real-time monitoring in various industries. Logistics and supply chain management are prime examples where tracking technology can provide substantial benefits. By integrating GPS with IoT devices, companies can monitor the location and condition of goods in transit, optimizing routes and reducing costs.
Moreover, GPS tracking technology will continue to evolve in personal safety applications. Wearable devices equipped with GPS will offer users real-time tracking capabilities, ensuring safety in emergencies. This technology can be particularly beneficial for vulnerable populations, such as children or the elderly, providing peace of mind for caregivers and families.
Telkom University is at the forefront of research in tracking technologies, focusing on developing solutions that address the needs of various industries. By fostering partnerships with local businesses, the university can help create tailored tracking systems that enhance operational efficiency and safety.
4. Privacy and Security Concerns
As GPS navigation and tracking become increasingly integrated into our daily lives, concerns about privacy and security will rise. The collection and sharing of location data raise critical ethical questions regarding user consent and data protection. Future developments in GPS technology must prioritize user privacy, ensuring that individuals have control over their data and understand how it is used.
Developing secure systems that prevent unauthorized access to location data will be paramount. Encryption technologies and secure data storage solutions will be essential in safeguarding users’ privacy while still allowing for the benefits of GPS tracking. Telkom University can contribute to this dialogue by conducting research on ethical data practices and developing secure GPS applications that respect user privacy.
5. The Role of Autonomous Vehicles
One of the most exciting frontiers in GPS navigation is its role in the development of autonomous vehicles. As self-driving technology advances, GPS will be crucial in enabling vehicles to navigate safely and efficiently. By integrating GPS with advanced sensors and machine learning algorithms, autonomous vehicles can make real-time decisions based on their environment.
Future GPS systems will need to support the high-speed data processing required for autonomous navigation. This involves not only accurate location tracking but also the ability to communicate with other vehicles and infrastructure, a concept known as Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) communication. Telkom University’s research initiatives in autonomous systems and smart transportation can help advance this field, preparing students for careers in this transformative industry.
Challenges Ahead
Despite the promising future of GPS navigation and tracking, several challenges must be addressed. One significant concern is the reliance on satellite signals, which can be affected by environmental factors such as weather, urban landscapes, and natural obstructions. Continuous innovation in alternative positioning technologies, such as terrestrial-based systems and hybrid solutions, will be essential to enhance reliability.
Moreover, the proliferation of GPS-enabled devices raises concerns about the digital divide, where access to these technologies may not be equitable. Ensuring that marginalized communities have access to GPS navigation and tracking technology will be crucial for fostering inclusivity in the digital age.
0 notes
Text
Geospatial Analytics Artificial Intelligence Market - Forecast(2024 - 2030)
Geospatial Analytics AI Market Overview
The Geospatial Analytics Artificial Intelligence Market is estimated to reach $172 million by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 30.0% from 2021 to 2026. Geospatial Analytics Artificial Intelligence generally called geospatial AI, GEOINT (geospatial intelligence) is the intersection of artificial intelligence and geospatial data. It collects and provides the geographical data for numerous geographical applications like weather centers, national labs and other agencies that specifically relay on these data for running their business. Owing to the use of geospatial AI real-time, feedback can be given nowadays related to the surroundings for instance traffic congestion and many others with the help of just simple smartphone applications. The availability of massive computational power, advancement in the field of artificial intelligence predominantly machine learning and deep learning along with increased availability of geospatial data from satellites are driving the growth of the market.
Report Coverage
The report: “Geospatial Analytics Artificial Intelligence Market” – Forecast (2021-2026)”, by Industry ARC covers an in-depth analysis of the following segments of “Geospatial Analytics Artificial Intelligence Market”.
By Data Source – Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS), Remote Sensing, Geo Tagging and Others By Solution - Hardware, Software, Services By Geospatial Data Model- Vector Data, Raster Data By Machine Learning- Unsupervised Learning, Reinforced Learning, Supervised Learning, Deep Learning, Semi-Supervised Learning. By Deployment- Cloud, On-Premises By Application- Real Estate, Sales & Marketing, Coastal Application, Agriculture, Fraud Detection, Surveying, Hazard Assessment, Natural Resource Management, Transportation and Logistics, National Labs, Weather Centers, Defense Agencies, Insurance, Others By Geography - North America (U.S, Canada, Mexico), South America(Brazil, Argentina and others), Europe(Germany, UK, France, Italy, Spain, Russia and Others), APAC(China, Japan India, SK, Aus and Others), and RoW (Middle east and Africa)
Request Sample
Key Takeaways
The rise in adoption of Geospatial Analytics Artificial Intelligence tools owing to their wide range of applications like monitoring of real time geographical data, traffic congestions, spatial analytics and others are driving the growth of the market.
The cloud deployment is dominating the market as the data integration can be done efficiently in the cloud with less complexity along with upsurge in use of cloud networks globally.
The APAC region is witnessing a significant growth in the market owing to the wide use of this solutions in the various enterprises.
Geospatial Analytics AI Market Segment Analysis - By Deployment
By Deployment Geospatial Analytics Artificial Intelligence Market is segmented as Cloud and On- Premises. The Cloud based deployment is witnessing significant growth in the market at 38.9% CAGR through 2026. The Web GIS is widely being adopted and used as it is significantly easier to use, deploy and integrate than on-premises GIS. In recent years the use of smart phones have made the integration of geographical information much easier. The smart phone mobile apps traces location and routing, spatial analytics, smart mapping, field data collection and others which is only possible through the web geospatial AI. The real time geographical data used by devices for instance smart phones, vehicle sensors, imaging sensors on drones are majorly extracted from the cloud. These factors are fueling the growth of the market.
Inquiry Before Buying
Geospatial Analytics AI Market Segment Analysis - By Geospatial Data Model
By Geospatial Data Type the market is segmented into Raster Data and Vector Data. Vector Data Model is witnessing a significant growth in the market at 33.3% CAGR through 2026. Points and line segments are used by the vector data model to identify the locations on the Earth. The vector data comprises verticals and paths owing to which the end users find it much easier to find the data. The vector data model consist of points, lines and polygons owing to which the cartographers find these symbols to represent real world features in the maps. These factors are driving the growth of the market.
Geospatial Analytics AI Market Segment Analysis - By Geography
The Global Geospatial Analytics Artificial Intelligence Market is dominated by APAC with a market share of 36.9% in 2020. The expanding usage of geospatial analytics AI tools, growth in internet penetration, rise in the developing industrial sectors and growth in infrastructural developments are boosting the growth of the market. The growth of cellular networks and real time communication for various applications for instance wireless broadband, mobile applications, GPS tracking and others are also driving the growth of the market in this region. Furthermore, ride sharing companies, Ola, Lyft, Uber and many others are also using it widely for the purpose of taking feedback from the customers and process the data to find out the density of cars and check the availability of drivers for ride. These factors are boosting the growth of the market.
Schedule a Call
Geospatial Analytics AI Market Drivers
Rise in the growth of geospatial analytics artificial intelligence due to its use in various applications:
One of the driving factors for upsurge of geospatial analytics intelligence tools are their versatile applications. In the communication from homes to workplaces and workplaces to home almost every day, the biggest problem is traffic congestion. The problem of traffic congestion is easily solved by the use of GIS application. It is adopted in most of the enterprises as it helps in real time data integration. The geospatial AI applications helps enterprises to improvise planning, resource allocation, decision making, multiplying supply chain efficiency, optimizing service delivery and other applications. The UAVs are used for variety of applications like inspection, mapping, surveillance, aerial videos and many other applications. All these applications of drones and UAVs are monitored through the use of geospatial analytics artificial intelligence. These factors are driving the growth of the market.
Rise in internet penetration:
The rise in internet penetration has enhanced the use of Geospatial AI solutions through, cloud based deployment and on-premises deployment. It is due to the high speed internet that real time monitoring of devices is possible nowadays through which communication is also possible. The geospatial AI applications are used in real time diagnosis of patients through wireless broadband. All this is possible owing to the presence of internet. The patient receives first aid through the consultation of doctors’ on-route to the hospital. The ambulances are installed with wireless connectivity which runs through the availability of high speed internet. Furthermore, the national labs are using these geospatial AI for managing the chaos of natural disasters, improvement of crisis mapping, weather condition predictions as it allows real time monitoring of all the geographical information. All these applications are possible owing to the presence of high speed internet in almost all the locations around the globe nowadays. These factors are driving the growth of the market.
Geospatial Analytics AI Market Challenges
Cost related challenges:
Although the geospatial analytics artificial intelligence have many advantages owing to which these are used in various of applications such as natural resource management, coastal, marketing and others but the geospatial analytics artificial intelligence solutions are very costly. Owing to the high price of installation many small enterprises are unable to use these solutions. These factors are hindering the growth of the market.
Buy Now
Geospatial Analytics AI Market Landscape
Geospatial Analytics Artificial Intelligence Market is dominated by major companies such as Google Inc, Microsoft Corporation, Bentley Sytems, Harris Corporation, ESRI, Trimble Inc, Digital Globe, Geoblink, HEXAGON among others.
Acquisitions/Technology Launches
July 13, 2020- LuxCarta introduced its new product line named BrightEarth. BrightEarth uses artificial intelligence algorithms and these are a series of global geospatial product. This product line is delivered in the cloud as it is developed in the cloud.
December 23, 2020- Astraea, Inc. launched EarthAI Notebook. It analyzes roster data at scale and analyzes geospatial data.
#Geospatial Analytics Artificial Intelligence Market#Geospatial Analytics Artificial Intelligence Market Share#Geospatial Analytics Artificial Intelligence Market Size#Geospatial Analytics Artificial Intelligence Market Forecast#Geospatial Analytics Artificial Intelligence Market Report#Geospatial Analytics Artificial Intelligence Market Growth
0 notes
Text
AI and Agriculture: Driving Sustainable Farming Practices

In the developing world, agriculture stands as the backbone of economies, contributing 4% to the global GDP and over 25% for some nations. In India, where agriculture makes up 18-20% of the GDP and employs more than half of the population, the pressure to enhance farming efficiency is immense, especially with the global population surpassing 8 billion and continuing to grow. Artificial intelligence (AI), a transformative force in various industries, holds the potential to revolutionize agriculture, addressing challenges like climate change impacts and the need for increased productivity. This article explores how AI can make farming smarter and more sustainable, while also addressing the current status and challenges of AI adoption in agriculture.
Enhancing Efficiency with Farm Automation
Mechanizing Farm Tasks
AI-driven automation introduces efficiency by automating repetitive farming tasks such as weeding, harvesting, seeding, and spraying. Agricultural robots, often referred to as agriBOTS, are designed to handle these tasks, freeing farmers to focus on decision-making. Drones play a crucial role in monitoring crop health, and soil conditions, and even conducting field surveillance. They are also employed for cover crops through seeding drones and pesticide application through spraying drones.
Revolutionizing Harvesting
Developments are underway in fruit and vegetable harvesting robots. These robots utilize AI-assisted vision to estimate the readiness for harvesting and employ flexible-arm robots to pick fruits or vegetables accurately.
Sustainable Weeding
AI-driven automation has also addressed labour-intensive tasks like weeding. Weeding robots now autonomously locate and eliminate weeds in an environmentally friendly manner, providing an alternative to chemical-based weeding.
Autonomous Precision Tractors
Autonomous tractors, a more common sight now, not only optimize land preparation but also undertake precision planting, monitor soil quality, and apply fertilizers, contributing to resource-efficient and sustainable farming practices.
Informed Decision-Making through Predictive Insights
Weather Predictions
AI plays a vital role in predicting and forecasting local weather conditions, offering early warnings for natural hazards like droughts and floods. This enables farmers to plan their activities effectively, minimizing crop loss. AI systems also suggest optimal sowing and harvesting times based on climate predictions.
Crop Yield and Price Forecasting
Accurate crop yield predictions are crucial for global food production and distribution. AI models, particularly deep neural networks, accurately predict crop yields. Additionally, AI aids in forecasting crop prices, empowering farmers to make informed decisions for better profits.
Pest and Disease Management
AI, along with mobile phones and IoT, facilitates easy access to community knowledge on pests and crop diseases. Drones and mobile cameras capture images for AI systems and chatbots to identify pests, diagnose diseases, and recommend necessary actions. Apps like Plantix allow farmers to diagnose crop diseases through images captured on their mobile phones.
Soil Analysis
AI-driven systems analyze soil nutrients and quality, recommending suitable crops based on soil composition and predicting irrigation and fertilizer needs.
Precision Farming for Resource Efficiency
Smart Irrigation
Precision farming, incorporating AI, GPS, and GIS technologies, optimizes resource use. Farms are divided into zones, and soil composition, quality, and moisture content are analyzed for precise irrigation needs.
Intelligent Spraying
AI-driven intelligent spraying devices minimize the use of pesticides and chemicals, saving costs, improving yields, and promoting eco-friendly practices.
Current Status of AI Adoption in Agriculture
Despite slow but steady growth, AI adoption in agriculture faces challenges. According to Forbes, global spending on AI-powered farming is expected to triple to $15.3 billion by 2025. In India, the government allocated ~INR 8K crores to the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) last year for developing farming technologies. Microsoft's advisory services in India have improved farmers' average yield per hectare by 30%.
Challenges in AI Adoption
Data Requirements
AI systems demand substantial data for effective training, and collecting temporal data over large agricultural areas is challenging. Processing multi-temporal data from various sources introduces noise and anomalies, making data collection and preparation difficult.
Lack of Experience
The slow adoption of AI in farming is attributed to farmers' lack of experience with new technologies. To address this, solution providers should invest in farmer training to build confidence gradually.
Data Ownership and Security
Ambiguities in data ownership regulations pose legal concerns in AI adoption for agriculture. Data leaks, privacy breaches, and cyber-attacks are potential threats that need addressing.
Farmer-Engineer Gap
For successful AI applications in agriculture, collaboration between farmers and AI experts is crucial. However, a significant gap exists, necessitating efforts to bridge it.
Cost Considerations
Affordability and open-source options are essential for the widespread adoption of AI-driven farming tools and solutions.
Certifying the Future: Navigating the Agricultural Landscape with AI Expertise
As the agriculture sector embraces the transformative potential of artificial intelligence, individuals equipped with specialized skills become invaluable contributors to the sustainable farming revolution. Pursuing AI expert certification provides professionals with a comprehensive understanding of AI applications in agriculture. Additionally, AI certifications in related fields like cybersecurity certification, a critical aspect of AI implementation, can further enhance the skill set. To stay ahead in the field, individuals can opt for prompt engineer courses, ensuring they are well-versed in the latest technologies and methodologies.
The journey to upskilling in AI involves a strategic approach, combining foundational knowledge with practical expertise. Certifications like the AI developer certification offer a structured curriculum, enabling learners to navigate the complexities of AI adoption in agriculture. As the demand for AI-driven solutions in farming intensifies, being armed with recognized AI certifications not only validates one's expertise but also opens doors to opportunities in research, development, and implementation of smart and sustainable farming practices. These certifications act as passports to the future of agriculture, where AI plays a pivotal role in shaping the industry's trajectory towards efficiency and environmental consciousness.
AI and the Future of Agriculture
Artificial intelligence has revolutionized age-old farming practices, enabling smart and sustainable cultivation with higher yields and resource efficiency. If adopted on a large scale, AI holds the potential to drive the next agricultural revolution. Collaboration among farmers, governments, and AI experts is essential to facilitate seamless AI adoption in agriculture. For those looking to play an important role in this transformative journey, Blockchain Council offers the AI prompt engineer certification. As an authoritative group of subject experts and enthusiasts, the Blockchain Council is dedicated to evangelizing the research, development, and knowledge dissemination of blockchain technology for a better world. Recognizing the immense potential of artificial intelligence in agriculture, the AI certification equips individuals with the necessary skills to navigate the complexities of AI adoption. In a world where technology is rapidly evolving, Blockchain Council stands as a beacon, providing comprehensive and industry-recognized certifications to empower professionals in driving innovation and sustainability
0 notes
Text
Digital Agriculture in India: Challenges and Opportunities | Harisharan Devgan
Digital agriculture, also known as precision agriculture or smart farming, refers to the use of advanced technologies and digital tools in agricultural practices. In India, digital agriculture is gaining momentum and has the potential to revolutionize the farming sector. Here are some key aspects of digital agriculture in India:
Internet of Things (IoT): IoT technology allows farmers to collect real-time data from sensors and devices installed in the fields. These sensors measure various parameters like soil moisture, temperature, humidity, and crop growth. Farmers can access this data remotely and make informed decisions regarding irrigation, fertilization, and pest control.
Remote Sensing and GIS: Remote sensing technologies, including satellite imagery and drones, provide detailed information about crop health, vegetation index, and land mapping. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) help in analyzing and visualizing this data, enabling farmers to identify problem areas, monitor crop growth, and optimize resource allocation.
Farm Management Software: Farm management software platforms are designed to streamline and automate various farm operations. These platforms offer features like crop planning, inventory management, financial tracking, weather forecasting, and yield prediction. They provide farmers with valuable insights and analytics to improve productivity and profitability.
Mobile Applications: Mobile apps are widely used in digital agriculture to provide farmers with on-the-go access to information and services. These apps offer weather updates, market prices, pest and disease identification, crop advisory, and e-commerce platforms for buying and selling agricultural products.
e-NAM (National Agriculture Market): The e-NAM initiative is a digital platform that connects agricultural produce markets across India. It enables farmers to sell their produce online, access real-time market prices, and reach a wider buyer base. e-NAM promotes transparency, fair pricing, and reduces intermediaries in the agricultural marketing system.
Agri-FinTech: Agricultural FinTech companies leverage digital technologies to provide financial services tailored for farmers. These services include digital lending, crop insurance, mobile payment solutions, and access to credit. Agri-FinTech platforms simplify financial transactions, reduce paperwork, and provide farmers with access to formal financial services.
Agricultural Databases and Information Systems: Various government and private organizations have developed agricultural databases and information systems to facilitate data-driven decision-making. These platforms offer comprehensive agricultural information, including weather data, crop patterns, market trends, and government schemes. They empower farmers with knowledge and help them adopt best practices.
Capacity Building and Training: Government initiatives and private organizations conduct training programs and workshops to educate farmers about digital agriculture technologies. These capacity-building efforts aim to enhance digital literacy among farmers and enable them to effectively utilize digital tools for better farm management.
Digital agriculture in India holds immense potential to increase farm productivity, optimize resource utilization, reduce input costs, and mitigate risks. However, it is essential to address challenges such as limited internet connectivity in rural areas, affordability of digital tools, and ensuring inclusivity for small and marginal farmers. Continued investment in digital infrastructure, farmer education, and policy support is crucial to realizing the full benefits of digital agriculture in India.
#precision agriculture#agriculture#farming#agriculturetechnology#farmer#farmingtechnologies#agripreneur#organicfarmer#cannabisresearch#agriculture technology#organicfarmerofmillionaire
0 notes
Text
Top Farmers Portal in India
As you know India is an agricultural country, agriculture is the backbone of India's economy. The present time is the time of new technology, farmers in the country are putting their full force in developing the field of agriculture by using new technologies in the field of agriculture. Agriculture is now being digitally done in India. The reason for all this is the rapid spread of agricultural information, news and services. In the time of digital technology, the farmer helpline is also supporting the farmers in the country with their full strength to develop the field of agriculture by shoulder to shoulder with the farmers.
Kisan Helpline is a portal where farmers get complete information about agriculture and agriculture related business. Information about products, machinery, research, etc. related to agriculture is provided in this portal. Detailed information about various policies, schemes, agricultural loans, market value of agricultural products, animal husbandry, fisheries, horticulture, loans and loans, sericulture, etc. are given here.
The main objective of creating Kisan Helpline portal is to provide all the information related to agriculture, agricultural news, information, crop related, government policy and planning, and agriculture related services etc. to the farmers of the country in a smooth and correct manner. Through this portal, an attempt has been made to provide a comprehensive, pure, reliable and single point source of information about India and its various aspects. And the farmer helpline disseminates the complete information and news to the farmers about the new technology of agriculture, new agricultural machinery, organic farming, animal husbandry, weather, government schemes and subsidy etc. To be strengthened and empowered.
The Kisan Helpline portal is ready to serve the country, society and farmers through self-understanding, new technology. Kisaan Helpline - Agri Marketplace | Sustainable Agriculture in India @ https://www.kisaanhelpline.com
#Kisaan Helpline#GI Agriculture App#Empowering Sustainable Agriculture in India#Kisan Portal#Seasonal Information#Agriculture in India#Indian Farmer App#Farmer Help#Kisan Help#Agriculture application#Kisan Help Desk#Agri Online Platform#Digital Smart Agriculture#Kisan helpline center#Call Center#Tollfree cm mobile number#किसान हेल्पलाइन नंबर#मुफ्त किसान हेल्प नंबर#कॉल सेंटर नंबर#खेती की जानकारी
0 notes
Text
Rise of a Digital Agriculture Platform-Agrojay Innovations Pvt Ltd.
Digital agriculture alludes to tools that carefully gather, store, examine and share electronic information as well as data along the farming value chain.
Now and then known as “smart farming” or “e-agriculture, digital farming incorporates exactness agribusiness. In contrast to exactness agriculture, advanced agribusiness impacts the whole agri-food value chain — previously, during, and after on-farm creation. Therefore, on-farm advancements, similar to yield mapping, GPS direction frameworks, and variable-rate application, fall under the space of exactness agriculture and digital agriculture. Then again, digital innovations engaged with e-commerce business stages, e-extension administrations, stockroom receipt frameworks, blockchain-empowered food traceability frameworks, tractor rental applications, etc. fall under the umbrella of digital agriculture however not accurate agriculture.
Digital agriculture encompasses a wide range of technologies, most of which have multiple applications along the agricultural value chain. These technologies include, but are not limited to:
· Cloud computing/big data analysis tools
· Artificial intelligence (AI)
· Machine learning
· Distributed ledger technologies, including blockchain and smart contracts
· Digital communications technologies, like mobile phones
· Digital platforms, such as e-commerce platforms, agro-advisory apps, or e-extension websites
· Precision agriculture technologies, including
o Sensors, including food sensors and soil sensors
o Guidance and tracking systems (often enabled by GPS, GNSS, RFID, IoT)
o Variable-rate input technologies
o Automatic section control
o Advanced imaging technologies, including satellite and drone imagery, to look at temperature gradients, fertility gradients, moisture gradients, and anomalies in a field
o Automated machinery and agricultural robots
On-farm efficiency
On-farm, accuracy agriculture innovations can limit inputs required for a given yield. For example, variables rate application (VRA) innovations can apply exact measures of water, fertilizer, pesticide, herbicide, etc. Various exact examinations find that VRA improves input use proficiency. Utilizing VRA nearby geo-spatial mapping, ranchers can apply contributions to hyper-confined areas of their homestead — here and there down to the individual plant level. Diminishing info use brings down expenses and decreases negative ecological effects. Besides, observational proof shows accuracy agriculture innovations can build yields.
Digital agriculture improves work profitability through improved farmer knowledge. E-extension takes into account cultivating information and abilities to diffuse requiring little to no effort. E-extension administrations can likewise improve farm profitability by means of choice to help benefits on portable applications or other advanced stages. Utilizing numerous wellsprings of data — climate information, GIS spatial mapping, soil sensor information, satellite/drone pictures, etc — e-extension stages can give ongoing proposals to farmers.
At long last, advanced farming improves work profitability through reduced work requirements. Robotization innate inaccuracy agribusiness — from “milking robots on dairy farms to greenhouses with automated climate control — can make yield and domesticated animals the executives increasingly proficient by lessening required labor.
Off-farm/market efficiency
Reducing information asymmetry
Value data influence serious markets’ productivity since it impacts price scattering, exchange, and farmers and customer welfare. Since the negligible expense of carefully conveying data approaches zero, digital agriculture can possibly spread value data. Likewise, cost data gave by Internet booths (“e-choupals”) in India prompted an expansion in farmers’ net benefits as profits lost monopsony power.
Matching buyers and sellers
Online business brings down the inquiry expenses of coordinating purchasers and sellers, possibly shortening the worth chain. Instead of experience many delegates, farmers can sell straightforwardly to consumers. Market get to administrations can likewise take care of the coordinating issue without fundamentally facilitating online transactions. These coordinating stages assist smallholders with organizing with purchasers and enter both local and worldwide worth chains. At last, it’s critical to take note of digital technologies that can likewise encourage coordination in financial and input markets, not only producer to-consumer output sales.
Lowering transaction costs in commercial markets:
Digital payments — whether integrated into e-commerce platforms or in mobile money accounts, e-wallets, etc. — reduce transaction costs inside rural markets. The requirement for sheltered, fast money related exchanges is especially evident in rustic territories. In addition, Digital payments can give passage to financial balances, protection, and credit. Utilizing conveyed record advances or brilliant agreements is another approach to lessen trust-related exchange costs in business markets. Numerous retail and food organizations have collaborated with IBM to create blockchain pilots related to food safety and traceability.
Agrojay is one of the best platforms for Digital agriculture
Agrojay Digital Agricultural platform will help the farmers for the following: 1. Farmers can directly connect with labs and research institutes.
2. Farmers can find agronomist for his crop, also he can give ratings and feedback to him.
3. Farmers can get pre harvesting predictions.
4. Farmers can directly connect with buyers and before harvesting, they can sell.
5. Farmers can easily connect with manufacturers of pesticides, fertilizer, Agri equipment.
6. Farmers can discuss their problems and solution with each other.
Download the app: https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.wowinfotech.agrojay
Agrojay Innovations Pvt. Ltd.
Check other blogs
Why Agronomist is Important in Agri Sector
Farmer Producer Organization
TOP 10 PROBLEM FACED BY FARMERS
Farmer Producer Organization
Digital Platform for Farmers
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Annotated Bibliography of Relevant Sources
Burgan, R, van Wagtendonk, J, Keane, Robert E, Burgan, Robert, & van Wagtendonk, Jan. (2001). Mapping wildland fuels for fire management across multiple scales: Integrating remote sensing, GIS, and biophysical modeling. International Journal of Wildland Fire, 10(3-4), 301–319. https://doi.org/10.1071/WF01028
This study compares the advantages and disadvantages of four different methods of fuel mapping: field reconnaissance, direct remote sensing, indirect remote sensing and biophysical modeling. None of these methods appear to be highly accurate or consistent in and of themselves. Yet, all of these methods represent a means of collecting data for synthesis within a geographic information system for the purpose of creating a map that is useful to land management. The authors propose a strategy which involves classifying biophysical setting, species composition and stand structure to assign fuel models, but acknowledge the enduring need for sensor technology that can penetrate a forest canopy to effectively analyze complex surface fuels.
Church, Richard, Adams, Benjamin, Bassett, Danielle, & Brachman, Micah L. (2019). Wayfinding during a wildfire evacuation. Disaster Prevention and Management., ahead-of-print(ahead-of-print). https://doi.org/10.1108/DPM-07-2019-0216
This will be an interesting article to read when it is published, because it is an example of using GIS to synthesize and analyze empirical data from a wildfire evacuation for the purpose of helping emergency managers to develop more effective wildfire evacuation plans. The authors used network analysis to compare volunteers’ selected routes with the shortest distance routes available, and found that only 31 percent of evacuees took a shortest distance route, and that factors such as the elevation of exits and downhill slope could have impacted wayfinding processes. Although this study is more of a spatiotemporal snapshot, more generalizable results could be produced with additional research.
Coops, Nicholas C., Ferster, Colin J, & Coops, Nicholas C. (2014). Assessing the quality of forest fuel loading data collected using public participation methods and smartphones. International Journal of Wildland Fire, 23(4), 585–590. https://doi.org/10.1071/WF13173
This study looks at the potential for citizens to contribute forest structure and fuels input data for use in the applied geographic information systems used by land managers. Citizen contributions could be especially helpful in data collection over broad areas because accurate characterization of forest fuels is dependent on frequent field measurements, as fuels are spatially variable, can change rapidly due to changing conditions, and are difficult to sense remotely under dense canopy. Eighteen volunteers were recruited at the University of British Colombia, and nine of those had extensive working experience in either wildfire suppression or fuels management. The volunteers used an app on their smartphones to collect and report data. For most components, professional measurements were only slightly closer to reference measurements than volunteered measurements, however, non-professional participants notably overestimated aspect and slope. Overall, when appropriate training is provided and adequate controls for accuracy are incorporated, this study found volunteer data collection to be suitable to help inform forest management decisions.
Danzer, SR, Watts, JM, Stone, S, Yool, SR, Miller, Jay D, Danzer, Shelley R, … Yool, Stephen R. (2003). Cluster analysis of structural stage classes to map wildland fuels in a Madrean ecosystem. Journal of Environmental Management., 68(3), 239–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-4797(03)00062-8
The authors of this study highlight the importance of quality baseline fuels data since we are not yet capable of assessing understory fuels with remotely sensed data. This assessment therefore combines field data collections with GIS, remote sensing, and hierarchical clustering to map the variability of fuels within and across vegetation types of 156 plots from a mountain range in the southwestern U.S. Vegetation classification was validated using an independent sample of 479 randomly located points and demonstrated substantial accuracy with a Kappa value of .80. However, the overall map, created by combining the land cover/vegetation type classification and fuel classes within vegetation type classifications received a relatively low Kappa of .50. This reduction in accuracy could be attributed to GPS errors, ecological overlap between adjacent vegetation types, and/or confusion of fuel classes in areas where overstory canopies obscured the understory.
Dean, DJ, Blackard, Jock A, & Dean, Denis J. (1999). Comparative accuracies of artificial neural networks and discriminant analysis in predicting forest cover types from cartographic variables. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture., 24(3), 131–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-1699(99)00046-0
The authors compare an artificial neural networks (ANNs) approach to GIS with a conventional model based on discriminant analysis (DA) with regards to effectiveness at predicting forest cover types. In this study, elevation of each 30x30-m raster cell was obtained directly from USGS digital elevation model (DEM) data. Results demonstrated that both ANN and DA models tended to confuse ponderosa pine, Douglas-fir, and cottonwood/willow cover types with each other, potentially due to geographic proximity. However, overall, the ANN model, with a predictive accuracy of 71.1 percent, was shown to be superior to the DA model, with a predictive accuracy of 58.4 percent.
Eva, E. K. (2010). A method for mapping fire hazard and risk across multiple scales and its application in fire management. Ecological Modelling., 221(1), 2–18. https://doi.org/info:doi/
This study presents an effective approach for mapping fire risk across large, complex geographies containing diverse ecosystems on multiple scales. The author uses FIREHARM, which is a C++ program capable of computing changes in fire characteristics over time using climate data, to predict fuel moisture and corresponding fire behavior, danger, and effects. This model does not provide spatially explicit information concerning fire spread. Instead, it assumes that every pixel or polygon experiences a head fire and simulates the resulting fire characteristics based on ensuing weather factors. A landscape is represented by series of polygons. Each polygon defines an area of similar characteristics (vegetation, fuel, site conditions), is assigned attributes related to fire behavior, and is also assigned a tree list (with attributes of species, diameter, height) which combine to estimate tree mortality for a region. In 2004, FIREHARM was validated by the results of a comparison with 54 sample plots from the Cooney Ridge and Mineral Primm wildfires, producing adequate predictions of fuel consumption within approximately 14 days. The model also had a 60 percent chance of accuracy in predicting canopy vs. non-canopy fire and scorch height and fire severity predictions compared well with observed conditions.
Gatzojannis, S, Galatsidas, S, Kalabokidis, Kostas D, Gatzojannis, Stylianos, & Galatsidas, Spyros. (2002). Introducing wildfire into forest management planning: towards a conceptual approach. Forest Ecology and Management, 158(1-3), 41–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-1127(00)00715-5
This study explains the process of using a geographic information system to synthesis existing information for the purpose of calculating fire danger and fire resistance per unit area (1 km2) and to map distribution within a forest. First, data is collected, next data is grouped into thematic layers, and finally the layers are synthesized for evaluation. The input data required to produce such a map involves taking an inventory of factors with both horizontal and vertical spatial distribution. Homogeneous information layers, such as landscape, are broken down into a series of variables (vegetation zones, land cover structure, aspect, slope, altitude). External factors include climate, landscape, human impact, and other special factors. Internal factor information layers relate to forest stand structure and describe fire resistance at the forest floor, understory, low crown, middle crown, and high crown levels. The mapping of these factors allows for spatial delineation of fire danger zones which decision makers in determining operational objectives and priorities for large geographical areas.
Ilavajhala, Shriram, Wong, Min Minnie, Justice, Christopher O., Davies, DK, Ilavajhala, S, Min Minnie Wong, & Justice, CO. (2009). Fire Information for Resource Management System: Archiving and Distributing MODIS Active Fire Data. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing a Publication of the IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Society., 47(1), 72–79. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2008.2002076
This paper describes the ways in which the combined technologies of remote sensing and GIS are able to deliver Moderate-resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) active fire data to resource managers and even e-mail customized alerts to users. When used as a mobile service, Fire Information for Resource Management System (FIRMS) is an application that can deliver fire information to field staff regarding potential danger. For example, in South Africa, when a fire is detected either using data from MODIS or from a weather satellite, a text message is sent to relevant personnel who can decide if/what action may be required. This strategy makes satellite-derived FIRMS data more accessible to natural resource managers, scientists, and policy makers who use the data for monitoring purposes and for strategic planning.
Kalabokidis, K. (2013). Virtual Fire: A web-based GIS platform for forest fire control. Ecological Informatics., 16, 62–69. https://doi.org/info:doi/
This research project, supported by the University of Athens in Greece and funded by Microsoft Research, describes the high-tech but user-friendly Virtual Fire system, a web-based GIS platform, which allows firefighting forces to share and utilize real-time data (provided by GPS, satellite, camera) for the purpose of locating resources (vehicles, aircrafts, water tanks) and associated shortest routes, monitoring fire ignition probability, and identifying high risk areas. Data from automatic weather stations also aids in fire prevention and early warning. With the ability to conveniently access this information in synthesized form, managers can design more effective and efficient operational plans. Future considerations involve moving to a cloud-based platform, which would allow for expansion to a broader area and the increased incorporation of mobile devices.
Karlsson Martin, Oskar, Galiana Martin, Luis, Montiel Molina, Cristina, Karlsson Martín, Oskar, & Galiana Martín, Luis. (2019). Regional fire scenarios in Spain: Linking landscape dynamics and fire regime for wildfire risk management. Journal of Environmental Management., 233, 427–439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.12.066
The authors of this study apply socioecological systems theory to the wildfire generations model, which describes and explains the appearance and transformation of large wildfires in relation to landscape dynamics within Mediterranean climatic regions. There is a focus on acknowledging the ways in which humans directly and indirectly affect fire regimes. National forest inventory data and existing maps are the data used to create fire scenarios for the Central Mountain Range in Spain via ArcGIS and SPSS23. Land use and land cover features, which relate certain fuel structures to certain fire behaviors, are assigned to 91 discrete geographical units. The resulting visual comparisons can be used to help managers optimize prevention and suppression strategies.
Koukoulas, Sotirios, Kazanis, Dimitrios, & Arianoutsou, Margarita. (2011). Evaluating Post-Fire Forest Resilience Using GIS and Multi-Criteria Analysis: An Example from Cape Sounion National Park, Greece. Environmental Management., 47(3), 384–397. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-011-9614-7
The ability to assess an ecosystem’s resilience, or its capacity to endure disturbances without a state change, is becoming more important in the face of an accelerated decrease in biodiversity and with the projected effects of climate change. This study uses geographic information systems (GIS) to assess post-fire resilience by synthesizing bioindicators, such as forest cover, density, and species richness with geo-indicators, such as fire history, slope, and parent material. The significance of each factor was assessed using sensitivity analysis in order to produce a map of areas at risk- “risk hotspots” – of losing resilience, allowing managers to prioritize resources in restoration efforts.
Kulakowski, D, Veblen, TT, Bigler, Christof, Kulakowski, Dominik, & Veblen, Thomas T. (2005). MULTIPLE DISTURBANCE INTERACTIONS AND DROUGHT INFLUENCE FIRE SEVERITY IN ROCKY MOUNTAIN SUBALPINE FORESTS. Ecology., 86(11), 3018–3029. https://doi.org/10.1890/05-0011
GIS technologies are especially helpful for spatially predicting indicators such as fire severity, which can be the result of complex interactions. This study examines the possible combined effects of interactions between the disturbances of fire, insect outbreaks, and storm blowdown upon fire severity. Pairwise overlay analyses were performed in order to assess these associations. The regression models created, unlike bivariate overlay analysis, allowed for the simultaneous predictions, hypothesis tests and assessment of effects. Results showed that local forest cover type was a significant factor affecting fire spread and severity in the Rocky Mountains, with Spruce-fir stands having the highest probability of burning at high severity. Maps created in GIS show weather variability only significantly affecting fire when fuel build up is sufficient. Pre-fire disturbance and topography were also found to influence burn severity and explain variability.
Michener, W. K. (1997). Quantitatively Evaluating Restoration Experiments: Research Design, Statistical Analysis, and Data Management Considerations. Restoration Ecology : the Journal of the Society for Ecological Restoration., 5(4), 324–337. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1526-100X.1997.00546.x
Ecological restoration projects (i.e. post-wildfire disturbance) can be very difficult to design and analyze quantitatively due to several factors: experimental units are often heterogeneous, multiple non-uniform treatments may be applied iteratively, replication is difficult or impossible, the effects of extrinsic and intrinsic disturbances may be poorly understood, and the goal of focus is typically the variability in system responses rather than mean responses. This author provides thorough explanations of each of these challenges, along with a variety of ways in which they might be addressed, including via the application of GIS technologies. GIS is described as a powerful tool in relation to this discipline because of its ability to quickly synthesis data using multiple layers, rename and reclassify attributes, analyze spatial coincidence and proximity, and provide quantitative and statistical measurements which can be used to identify potential restoration sites and to visualize and interpret results.
Schroeder, P, Kern, JS, Brown, Sandra L, Schroeder, Paul, & Kern, Jeffrey S. (1999). Spatial distribution of biomass in forests of the eastern USA. Forest Ecology and Management, 123(1), 81–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-1127(99)00017-1
Biomass is defined by the net difference between photosynthetic production and consumption (respiration, mortality, harvest, herbivory). This measurement is an important indicator of the carbon stored in forests, which can be released as atmospheric carbon into the air during a disturbance (i.e. wildfire) or function as atmospheric carbon sinks during periods of regeneration post-disturbance. While accurate measurements of biomass provide valuable information for decision makers and land managers, large scale estimations can be challenging (remote sensing techniques have met with little success). The authors of this widely-cited study decided to use preciously established methods to convert US forest inventory volume data into above and belowground biomass, downloaded from the USFS Forest Inventory and Analysis (FIA) database, which they then mapped in a geographic information system (GIS) by county. These maps provide a vivid visual representation of forest biomass density patterns over space which can be useful in predicting changes to the global carbon cycle and evaluating potential for increased biomass-carbon storage.
Smith, JE, Weinstein, DA, Laurence, JA, Woodbury, Peter B, Smith, James E, Weinstein, David A, & Laurence, John A. (1998). Assessing potential climate change effects on loblolly pine growth: A probabilistic regional modeling approach. Forest Ecology and Management, 107(1-3), 99–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-1127(97)00323-X
In this study, a geographic information system was used to integrate regional data including forest distribution, growth rate, and stand characteristics, provided by the USDA Forest Service, with current and predicted climate data in order to produce four different models predicting the potential effects of climate change upon the loblolly pine across the southern U.S. Results indicated a high likelihood of a 19 to 95 percent decrease in growth rates, varying substantially per region and primarily influenced by a relative change in carbon assimilation and CO2 concentrations. In this case, GIS seems particularly useful for synthesizing existing information from regional surveys and account for uncertainties to produce ecological risk assessments at large scales in a way that is useful to policy and decision makers (vs. lengthy reports that are difficult to parse through).
Williams, D, Barry, D, Kasischke, Eric S, Williams, David, & Barry, Donald. (2002). Analysis of the patterns of large fires in the boreal forest region of Alaska. International Journal of Wildland Fire, 11(2), 131–144. https://doi.org/10.1071/WF02023
This study represents the first attempt to spatially correlate the distribution of fire activity in Alaska with climate, topographic, and vegetation cover features using GIS to provide a realistic assignment of fire cycle (frequency) for 11 distinct Alaskan ecoregions (where 96% of all fire activity occurs). GIS technologies can make use of Alaska’s state-wide initiative to digitize maps of fire perimeters from fire events from 1950 to 1999. Perimeter maps are created using a combination of ground and aerial surveys, and aerial photography or satellite imagery. Geospatial analysis showed fire frequency to be influenced by the complex interaction of elevation, aspect, lightening strike frequency, precipitation, forest cover, and growing season temperature.
Please send comments and questions to Melissa Hannah at [email protected] or click "Comments Are Welcome" at the top of the page.
1 note
·
View note
Text
How to Build a Mobile App for Agriculture Industry?
An agricultural application is a web, mobile or desktop application used in farms. The app enables users to manage farm equipment and implement farming strategies. For example, the app can be used to plan crop management activities such as planting and harvesting, track weather trends over time, and analyze soil quality.
Agriculture apps, like food delivery apps, ride-hailing apps, and task coordination apps, are comparable to other applications that include time management or scheduling. With the use of mobile apps for agriculture, a lot can be done in agribusiness, from providing hi-tech solutions to finding the best quality seeds to structured farming processes.

Trending technologies that could reshape the agriculture industry
Technologies in precision agriculture are reshaping the way farmers & agricultural companies look after their crops and how they manage it. Here are some techniques that seem more beneficial
Read More: Computer Vision Applications in Precision Agriculture
Geographic Information System GIS: In precision agriculture, GIS shines as an extremely valuable tool. With a geographic information system, farmers can get data like temperature, crop yield, plant health and also predict future changes based on that.
Drone Sync: The advent of drones has changed the way agriculture is done. Drones help in various ways from precision spraying, pest detection, trespassing, field vigilance & more.
5G technology: 5G is the next big thing to hit the digital world. It has the ability to deliver real-time data in quick ways and if it is used in the agriculture sector through mobile apps, it will give a great boost to agribusiness. Tracking, monitoring and other operations are done at lightning speed, which boosts smart agriculture.
Here are some features that an agribusiness owner must include in the agriculture app development process.
# Weather Forecast
One of the most important features in the agriculture app development process is the weather forecast. Using these features, farmers can identify the weather and suitability for growing crops, helping them take appropriate measures to insure their crops.
# Crop Disease Treatment
Incorporating crop disease treatment into agriculture app development is a beneficial feature as farmers can easily connect with experts who can help them with proper treatment advice.
This amazing feature allows farmers to communicate through video conferencing without physically going anywhere.
Read More: Role of artificial intelligence in food industry
# GPS Tracking
Adding GPS tracking features in agriculture app development can add more value to the app than you can imagine.
This feature allows the display of the entire farmland in a guide that helps farmers monitor crops at any given time.
# List of Items
Commodity listing is a great feature if your agriculture app development is essentially a marketplace where you list commodities like pesticides, seeds and equipment.
# Agricultural Schedule
Scheduling is an excellent feature to keep in the farming application to manage the crop schedule to benefit farmers and other agri-industry workforce.
# Calendar
Calendar is again one of the must-have features for agriculture app development. Using this feature, the farmer can provide a calendar to the laborers to keep the fields organized and perfect.
#Payment gateway
As in any other application, another important feature that an agriculture-based app must facilitate is a payment gateway.
Read More: Cost to develop on-demand Food Delivery App
How to build a mobile app for farmers/agribusiness?
To develop a mobile app for agribusiness, it is best to connect with USM, a leading mobile app development company that provides custom mobility solutions for agribusiness across the globe through latest & advanced mobile technologies like AI, IoT etc. Our skilled developers are highly experienced in providing qualified agriculture mobile app development services that will greatly enhance your business performance.
Building a farming app typically costs $20,199. However, the total average cost of app development can be less than $10,000 or more than $30,000. An agriculture app with a small number of features (also known as a "minimum viable product" or MVP) is more affordable than an app that has all the intended functionality.
It usually takes 269 hours to build a farming app. However, a farming app can be built in 133 hours or less than 400 hours. The exact timeline depends largely on how complex your app is. As a general rule, it will take longer if you need highly optimized designs, niche features, or non-standard release platforms.
In total,
An online agribusiness with agriculture app is a timely opportunity if you are starting or founding an agri-support business. Moreover, Rythu application development cost depends on app features, complexity, tech-stack and your decision regarding mobile application development company.
To develop agriculture app development you need to hire skilled mobile developers who can cut the mustard and save cost. For the right mobile technology solution to promote smart farming, our Android application development company in frisco team can walk shoulder to shoulder with you. Remember, we're only a mouse click away!
#agriculture app#agriculture app development#agriculture mobile app development services#agriculture mobile app development#agriculture-based app
0 notes
Text
Red eagle singlebox bedienungsanleitung

#RED EAGLE SINGLEBOX BEDIENUNGSANLEITUNG HOW TO#
#RED EAGLE SINGLEBOX BEDIENUNGSANLEITUNG FULL#
#RED EAGLE SINGLEBOX BEDIENUNGSANLEITUNG PASSWORD#
This item listing is for a single box of 20rds of IGMAN. To see the label for the product you need and the corresponding Safety Data Sheet, just click. 25 / round) Federal 223 Rem 55 gr FMJ BT American Eagle 20/Box 12. The high quality of RedEagle products is due to our partnerships with manufacturers known for exceptional production expertise, stringent quality control systems, and thorough regulatory compliance. With some RedEagle multiple active ingredient products such as Flu-Rimuron you even get more residual protection per ounce than with the big-name product. That lower RedEagle price also makes it possible to use a higher labeled rate and stay within your input budget. You can pay less and have the freedom to use them with the seed and other products you prefer. With a small company like RedEagle, you don’t have to do that. Many big-name agrichemical companies still expect you to pay a premium price for some of these products.
#RED EAGLE SINGLEBOX BEDIENUNGSANLEITUNG FULL#
But they all still work, and they meet your expectations for performance and value. Red Eagle SingleBox LCD Full HD Linux E2 Receiver (1x CI / 1x Kartenleser) 99,90 Protek 9911 LX HD Linux E2 Combo-Receiver (1x Sat-Tuner fest + 1x Tuner DVB-S2 oder DVB-C/T/T2 H.
#RED EAGLE SINGLEBOX BEDIENUNGSANLEITUNG HOW TO#
Whether you grow commodity row crops or specialty high-value crops, these are the products you already know when and how to use. Light Tactical Scope Reticle Optical Rifle Scope Fast Focus,T-eagle ER 1. A substantial and well-made single box with a. The RedEagle line of products includes many of the most proven and trusted chemistries in agriculture. Airsoft GI was founded in 2003 with the sale of just a single box of BBs and. end piece (blue grip and red grip have matching stylus colours). Singlebox gives you the ability to customize everything, including icons and colors, notification scheduling, ads & tracker blocking, dark theme and much much more.RedEagle Products Help Optimize the Economics of Crop Production Even better, by default, Singlebox runs each of your services/accounts/workspaces in sandbox environment, protecting you from cross-site trackers.
#RED EAGLE SINGLEBOX BEDIENUNGSANLEITUNG PASSWORD#
Singlebox lets you lock & protect your accounts from sneaky eyes with password or Touch ID. Leider kommt meine Fritzbox nicht mit 2x 1TB zurecht und ich wollte die zweite Festplatte jetzt ber den Red Eagle ins Netzwerk. Your workflow is cleaner than ever, finding what you need is easy.Īdditionally, Singlebox can be set as your default email client or calendar app and works with many popular email and calendar services such as Gmail, Google Calendar, Outlook, FastMail and more. Ich mchte meine externe Festplatte 1TB gerne im Netzwerk verwenden, hab das auch schon bei einer anderen via Fritzbox am laufen. Attach a red streamer at each point where a plug is installed. For example, draw a single box around all of the egfp bands. with one part East Hanover, NJ 07936 Royal D. Lost in tabs? Singlebox works like a smart web browser that lets you run and organize multiple web apps in a single place and switch between them easily using keyboard shortcuts. Ponceau Red is a stain that quantitatively binds a protein. Not limiting itself to messaging, Singlebox also supports thousands of web services, including GitHub, LinkedIn, Asana, Trello, Udemy, and many more. Konami issued several cardboard boxes that have design cues. You could even use five different Messenger or Slack accounts at once, if some inexplicable reason urges you to do so. Similarly, the box on the same side The Red/The Blu is on features the Team Fortress logo. This makes Singlebox the perfect tool to manage multiple business and private accounts all at the same time. Singlebox allows you to add each service many times. Singlebox supports a great variety of business and private messaging & chat services like Discord, Slack, WhatsApp, WeChat, Messenger, Telegram, Google Hangouts, Skype, Zendesk and many more. Neue Treiber 16025-Image-Info-jpg Image Info Model: Red Eagle Singlebox LCD Kernel: 4.0.1 Treiber: Gstreamer: 1.9.0 HDF-Version: 5.5 Build: 5 OpenHDF Teamimage basierend auf dem OE-Alliance git. Singlebox for Linux is an all-in-one messaging & emailing app - a single place for all your web services & accounts, including Discord, WhatsApp, Messenger, Slack, Telegram and many many more.

0 notes
Text
7 Essential technologies to live smart in our daily life

Introduction
We are in a digital era where we like more and more technologies doing stuff from our end. Some people are doing this because they are lazy and some are fond of doing this. Everybody is making efforts in living a fancy life and technology is an essential part of it. Starting from an alarm on a smartphone to a fresh tea from an electric kettle. Everything is technology. I'll mention some gadgets that are easy to use but very much impactful in our daily life These cool technologies cover almost every field.
1. Healthcare industry
Smart toothbrush

Smart toothbrush - Daily technologies - Indivtech A smart toothbrush is not only a smart way to brush, the cleaning of each tooth and the whole mouth use to be cleaned properly. This device is supported by a motor that offers you brush positions, speed, feedback, and how oral hygiene can be improved. It has high-quality sensors that collect data on your brushes, missed spots, pressures, etc. You can follow this important information on your smartphone and gain insights into how your oral health might be improved. Imagine if you have missed a small portion while brushing, you can easily see that, how smart! IMBED

IMBED - Daily technologies - Indivtech MIT researchers have already constructed a genetically modified sensor that can easily diagnose bleeding from the stomach or other gastrointestinal (GI) issues. The prototype device, called IMBED, can eventually be reduced to a minimum to enhance the ingestion or need of food of a human patient so that doctors can treat or diagnose a spectrum of intestinal disorders better. Cool? Not only cool, it's also a very much important thing especially when you're a regular sufferer of stomach aches. CGM
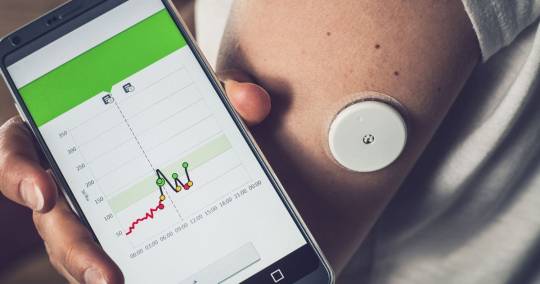
CGM - Daily technologies - Indivtech Now you don't have to inject your fingertips regularly to measure your diabetes level. It will be done automatically below your skin layer 24*7. It takes a bit more time but made for more care for you.
2. Fitness Industry
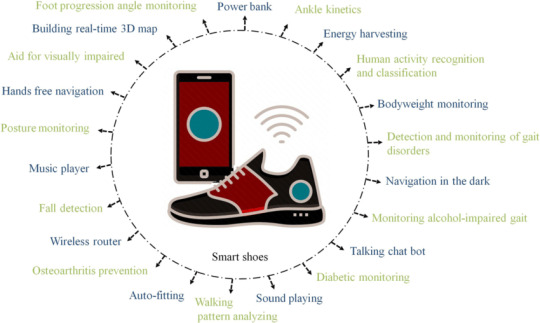
Smart shoes
Smart shoes If you're an athlete or sports freak person, Smart shoes are being invented for you because smart shoes use to provide individual feedback for analysis of health, fatigue, posture, steps, calories, and the creation of accurate health and injury prevention data. It can be connected to Bluetooth devices with almost no effort and offers individualized tutoring through a smartphone app in real-time. Lacing System

Nike 'Self-Lacing' Smart Shoes Lacing System is an electronic adjustment of your shoe to the shape of your foot. Get the right fit in every game, in every step. Check battery levels, and more by just using your smartphone.
3. Infrastructure Industry
Touchless Transaction Devices

Touchless Transaction Devices Touchless Transactions include contactless payment, gathering, and tracking of data. We've got that smart where we're making transactions even without touching anything except the card. This is what technology brought to us. Automated Fare Collection

Automated fare collection Automated Fare Collection is a ticketing system that lets passengers pay for tickets using ticket selling machines or internet services. These systems were made up of money and tokens but now are replaced with smart cards.
Conclusion
In this article, we've tried to elaborate on the top 3 industries that got revolutionized by technologies. There are almost all industries got upgraded by new technologies. Like in the safety industry there are gadgets like Child and Pet Finder and Infant Monitor. In Agriculture Industry we've got Robotic lawnmowers and Solar parasol. In Food Industry there are Smart Refrigerators. In Hospitality Industry we've Climate Control Devices and Central heating systems. technology is everywhere. you just have to pick the right option for you. That will be possible when you will understand your difficulties or in what aspect you are lacking behind the world. First, understand your requirement, and then go for it! Next Article Read the full article
#7Essentialtechnologiestolivesmartinourdailylifeindivtech#Automatedfarecollection#BestTechnologies#imabhihere#indivtech#indivtech.com#Technologies#TouchlessTransactionDevices
0 notes
Text
Smart Agriculture Market | Industry Insight 2021-2028


The global smart agriculture market share is estimated to be valued at $54,949.90 million by 2028, surging from $26,642.60 million in 2020, at a noteworthy CAGR of 10.90%.
Covid-19 Impact on Smart Agriculture Market
The global market for smart agriculture is estimated to experience a medium growth amid the COVID-19 pandemic. This growth is the result of increased demand for remote sensing technologies and other type of farm management software tools, which may lead to higher adoption of smart agriculture technologies during the COVID-19 period. Therefore, demand for smart agriculture is projected to witness a rise.
Furthermore, certain key vendors operating in smart agriculture are focusing on the wireless technologies for staying in the competition. For instance, SensoTerra, Europe based IT company, in May 2020, announced that they launched new wireless systems for farm connectivity and data analysis of field with cloud. This sensor system helps in improving the connectivity with the help of real time application via smartphones. All such factors are predicted to positively impact the global smart agriculture market forecast amid the pandemic.
Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, there is a shortage of labors to work in agricultural field. Therefore, most of the farmers are using digital agriculture devices than ever before. These factors are anticipated to create lucrative investment opportunities in the market during the forecast period.
How Technology lead to higher adoption of Smart Agriculture Market Pre and Post COVID-19? Get in Touch with our Expert Analyst@ https://www.researchdive.com/connect-to-analyst/235
Global Smart Agriculture Market Trends Analysis
The enormous growth of the global smart agriculture market is mainly attributed to increasing application of remote sensing, VRT, GIS, guidance technology, and GPS in smart agriculture for increasing the productivity. Now-a-days, farm operating expenses are very high; therefore, farmers are adopting technologies that will decrease their dependency on farmers and labors. Technologies such as agricultural drones with cameras are mostly used for applications such as weeding, spraying, harvesting, and pruning of farmlands. These types of advancements are creating awareness among people to adopt smart agriculture technologies and thus fueling the market growth.
Lack of knowledgeable workers in smart agriculture market and their usage may create a crack between the execution and understanding of the concepts in smart agriculture. Such key issues may create a negative impact on the smart agriculture system across the globe during the forecast period.
The increasing adoption of smartphones with software and hardware devices applications may create huge opportunities for the market in the future. Also, quick availability of smart farming applications (apps) for monitoring weather and climate conditions in low cost are some of the factors that are expected to raise the demand for climate smart agriculture market. Furthermore, the companies involved in the global smart agriculture are following effective strategies to use IoT in agriculture and launch of innovative products to grow in the market. For instance, Topcon Agriculture, California based electrical & electronic manufacturing company, in November 2019, announced that they have launched a new cloud-based platform tool, this will help farmers to integrate connectivity and data analytics during farming. Such technological advancements may further lead to lucrative market opportunities in the market in the upcoming years.
Global Smart agriculture Market, Segmentation
The global smart agriculture market trend is segmented based on agriculture, component, and region.
Agriculture:
The agriculture segment is further classified into precision agriculture, livestock, aquaculture, and greenhouse. Among these, the precision agriculture type sub-segment is anticipated to have the fastest as well as dominant growth and surpass $19,743.00 million by 2028, with an increase from $9,283.20 million in 2020.
The market growth of precision agriculture can be attributed to its popularity among the farmers due to increasing need for optimum crop production with limited availability of resources. Moreover, rising pressure on farmers for food supply system owing to rapidly growing population is driving the use of modern technologies in agricultural products, which may fuel the growth of precision agriculture market. All such factors may create a positive impact on the sub-segment throughout the forecast period.
Component:
The component segment is further divided into solution, service, and connectivity technology. The solution sub-segment is anticipated to have a dominating sub-segment in the global market and register a revenue of $30,244.50 million during the analysis timeframe.
This growth is projected to increase demand for solutions in smart agriculture technologies such as livestock monitoring technology. Moreover, increasing demand for dairy and milk products in developing countries, and growing livestock and agricultural sectors are expected to witness increased demand of solutions in smart agriculture technologies. These aspects may aid in the generation of a lucrative revenue for the market throughout the forecast period.
Region:
The smart agriculture market for the North American region is projected to witness dominant growth. This market generated a revenue of $10,923.50 million in 2020 and is further projected to reach up to $22,804.20 million by 2028.
The demand for smart agriculture is growing in the North America region specifically because of factors such as increasing prevalence of precision farming across the region. Moreover, countries such as Canada and the US adopted technologies such as precision farming technology, therefore it is the major reason for the high share of this region in the smart agriculture market. Furthermore, farmers across the region are increasingly using smart agri-equipment such sensors, display devices, farm management software, steering, and guidance systems. All such factors are anticipated to boost the market in the North America region.
Get Access to the Exclusive PDF Sample of Smart Agriculture Market@ https://www.researchdive.com/download-sample/235
Key Players in the Global Smart agriculture Market
Some of the leading global smart agriculture market insight players are AgJunction, AGCO, AgEagle Aerial Systems, Inc., DEERE & COMPANY, Raven Industries, Inc., Trimble Inc., Afimilk, LumiGrow, Inc., Topcon Positioning Systems, Inc., and DeLaval.
Along with the company profiles of the key players in the market, the report includes the Porter’s five forces model that gives deep insights into the competitive environment of the market.
0 notes
Text
Geospatial Analytics Market
Market Dynamics:
Advancement in AI, ML and technological advancement is a major driving factor for the geospatial analytics market. Artificial intelligence and machine learning developments are assisting in improving corporate efficiency. For companies and governments to obtain reliable data insights, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning is becoming increasingly important. Nearly 80% of consumer datasets are georeferenced, and GeoAI's area of application has expanded dramatically as its usage in agriculture, transportation, climate forecasting, and the military has grown. For instance, Cray announced enhanced capabilities in June 2019 to empower data scientists and engineers innovating in the Geospatial AI sector. AI and ML save considerable time and energy by performing numerous tasks, such as classification of images, object detection, semantic segmentation, and segmentation of instances. Demand for geospatial analytics is projected to increase considerably as suppliers of geospatial analytics solutions progressively offer clients AI- and ML-based software solutions. However, increasing individual concerns related to confidential data and geoprivacy is expected to restrict geospatial analytics's growth in the upcoming years. Individuals who are worried about the privacy of their location-based data might refuse to allow crucial location data to be collected, which is required by some geospatial analytics apps.
Download free sample: https://www.datamintelligence.com/download-sample/geospatial-analytics-market
Covid 19 Analysis:
Manufacturing, logistics, transportation, retail, education, mining, telecom, oil & gas, and utility businesses have all suffered as a result of the lockdown. In the healthcare industry, however, the use of geospatial analytics to combat COVID-19 is on the rise. Healthcare experts, government decision-makers, and ground-level organizations have partnered to collect real-time data on COVID-infected patients and disseminate geographic information about the COVID-19 prone area in order to raise public awareness and slow the virus's spread. The Tunisian Ministry of Public Health, for example, created a georeferenced database of hospital bed capacity in June 2020. High-density locations with the highest demand for COVID-19 vaccinations are identified using geospatial analytics. Geospatial analytics improves supply chains by analyzing real-time data and enabling tracking and visualization.
Market Segmentation:
– By Type
· Surface and Field Analytics
· Geovisualization
· Network Analysis
· Artificial Neural Networks (ANN)
· Others
– By Technology
· Remote Sensing
· GPS
· GIS
· Others
Competitive Landscape:
The global Geospatial Analytics market is consolidated, with the top 5 companies accounting for over 50% of global sales. Hexagon AB, ESRI Inc., L3 Harris Technologies, Atkins PLC, and General Electric dominate the global Geospatial Analytics market. These companies have used various strategies such as expansions, new product launches, agreements, partnerships, joint ventures, acquisitions, and others to increase their footprints in this market.
In 2020, Hexagon AB acquired PAS global. Customers will gain access to a comprehensive software portfolio to manage the industrial lifecycle, from plant design and maintenance to real-time situation awareness in the control room, cybersecurity risk management, and industrial digital transformation, thanks to the combination of PAS and Hexagon.
In September 2020, ESRI Inc Acquired frames, which would help it enhance its 3D capabilities. This will allow frames and Esri users to gather and analyze 3D data from the aerial, drone, and ground-based sensors in a fully automated end-to-end procedure.
In 2018, SPRING Technologies, a software supplier specializing in integrated solutions for optimizing machining workflows through machine tool simulation, toolpath verification and optimization, and machine tool management, has been acquired by Hexagon AB.
View Full Report: https://www.datamintelligence.com/research-report/geospatial-analytics-market
Enquiry Before Buying: https://www.datamintelligence.com/enquiry/geospatial-analytics-market
About Us
DataM Intelligence was incorporated in the early weeks of 2017 as a Market Research and Consulting firm with just two people on board. Within a span of less than a year, we have secured more than 100 unique customers from established organizations all over the world.
For more information:
Sai Kiran
Sales Manager at DataM Intelligence
Email: [email protected]
Tel: +1 877 441 4866
Website: www.datamintelligence.com
0 notes
Text
Learn About the Cultivation of Herbal Crops from the Kisaan Helpline
वर्तमान समय में कोरोना वायरस के इस दौर में यदि देखा जाए तो हर चीज संक्रमित (Infected) हो सकती है। इंफेक्शन और महामारी के इस संकट में जिस प्रकार लगातार संक्रमण बढ़ रहा है, उसे देखते हुए यदि हम हर्बल चीजों की तरफ बढ़े तो ज्यादा बेहतर होगा। क्योंकि हर्बल चीजें मुख्य रूप से प्राकृतिक होती हैं तो हमें नुकसान नहीं पहुंचाती हैं। यदि हम हर्बल उत्पादों का इस्तेमाल करते हैं, तो शायद हमारा जीवन बेहद सुखद और पीड़ा रहित हो सकता है। जड़ी बूटी और औषधि युक्त पौधों को उगाना उनकी देखभाल करना ही हर्बल खेती कहलाता है। उनमें ऐसे औषधीय गुण होते हैं जो बड़ी से बड़ी बीमारी ठीक करने में सक्षम होते हैं। साथ ही हर्बल प्रोडक्ट, जड़ी बूटी और औषधि से हमारा आंतरिक सिस्टम (Immunity power) मजबूत होता है और हम लंबे समय तक स्वस्थ रह सकते हैं।
हर्बल खेती के लिए मुख्य फसलें जैसे- तुलसी, चीया सीड, चिरायता (कालमेघ), गिलोय, हल्दी, सफ़ेद मूसली, कलौंजी, मेंथा, चाय, कॉफ़ी, आंवला, जटामांसी, मुलेठी, तेज पत्ता, दाल चीनी, संतरा, एलोवेरा आदि अनेक फसलें है जिनकी खेती आसानी से की जा सकती हैं और लाभ कमाया जा सकता हैं।
जड़ी बूटी और औषधीय पौधों की खेती वर्तमान समय में फायदे वाली खेती हैं। औषधीय पौधों का उपयोग आयुर्वेदिक चिकित्सा पद्धति में किया जाता है, जिसकी मांग देश की आयुर्वेदिक कंपनियों के साथ-साथ अंतररष्ट्रीय बाजार में भी रहती है। हर्बल खेती के जितने ज्यादा फायदे गिनाये जाए उतने कम है क्योंकि औषधीय गुण वाली यह जड़ी बूटियां सदैव ही प्रत्येक इंसान को फायदा देने का ही काम करती हैं। वर्तमान समय में हर्बल उत्पाद की मांग बहुत ज्यादा बढ़ गई है, इसलिए इसका सबसे बड़ा फायदा उत्पादक को मिल सकता है. Kisaan Helpline - Agri Marketplace - Sustainable Agriculture in India @ https://www.kisaanhelpline.com
जड़ी बूटी और औषधीय पौधों की खेती कैसे करें.
सर्वप्रथम हर्बल खेती के लिए ��पको एक पर्याप्त भूमि का चयन करना होगा। उसके बाद आपको यह देखना होगा कि जो पहले से खेती का काम कर रहे हैं, उनके पास जाकर उनसे उर्वरक और बीज से जुड़ी सभी जानकारी ले लेनी चाहिए। तत्पश्चात जड़ी बूटियों के बारे में जानकारी भी आपको प्राप्त करनी चाहिए कि आपको आसानी से जड़ी बूटियां कहां से और कैसे मिल सकते हैं। खेती के सभी गुण प्राप्त करने के बाद आप आसानी से हर्बल खेती का व्यवसाय आरंभ कर सकते हैं। और हर्बल खेती से सम्बंधित फसलों की सम्पूर्ण जानकरी किसान हेल्पलाइन के पोर्टल पर उपलब्ध हैं। जड़ी बूटी और औषधीय पौधों की खेती के लिए अनुकूल समय, जलवायु, मिट्टी, खेत की तैयारी, खाद एवं उर्वरक, सिंचाई, कटाई और उत्पादन से जुड़ी सम्पूर्ण जानकारी किसान हेल्पलाइन के पोर्टल पर उपलब्ध हैं. Kisaan Helpline @ https://www.kisaanhelpline.com
#Kisaan Helpline#GI Agriculture App#Empowering Sustainable Agriculture in India#Kisan Portal#Seasonal Information#Agriculture in India#Indian Farmer App#Farmer Help#Kisan Help#Agriculture application#Kisan Help Desk#Agri Online Platform#Digital Smart Agriculture#Kisan helpline center#Call Center#Tollfree cm mobile number#किसान हेल्पलाइन नंबर#मुफ्त किसान हेल्प नंबर#कॉल सेंटर नंबर#खेती की जानकारी
0 notes
Photo

Illustration Photo: Alexander Frick, Jr. uses a smart device to review data and plans his customized seed application for the day (credits: USDA Photo Media by Lance Cheung / Public domain)
GIZ-SAIS Investment Readiness Programme 2022 for African AgriTech and FoodTech Startups
‘Scaling Digital Agriculture Innovations through Startups’ (SAIS) is a project implemented by the Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH on behalf of the German Federal Ministry for Economic Cooperation and Development (BMZ). The overall goal of the project is to support African startups in scaling their digital innovations; these innovations should enable users in the agriculture or food sectors to increase their income. Up to 18 startups are selected annually to participate in a nine-month Investment Readiness Programme fully funded by the German Federal Ministry for Economic Cooperation and Development (BMZ). The aim of the Investment Readiness Programme is to support more African startups in improving their business models, gaining access to investors and business partners, and achieving greater impact. Seven output indicators (also called investment readiness criteria or investment readiness output indicators) have been defined to assess and monitor the investment readiness level of selected startups.
You can apply if your innovation is listed in one of the following categories or technologies.
Categories Building digital expertise for farmers (eSkills, eLiteracy), eLearning, precision farming, access to market, access to finance, digital payment, supply chain management, food delivery, animal and crops health, soil fertility, logistics and transport, e-commerce, gamification, big data, data analysis, open data, data protection, data security, cybersecurity, crowdsourcing, digital storytelling.
Technologies Internet of things, precision farming (chipcards, sensors, drones, remote sensing system) artificial intelligence (AI), virtual/augmented reality, 3D-printer, robotics, digital learning software (eLearning system, MOOC platforms, open educational resources), database, blockchain, information-management systems (IMS), monitoring, controlling systems, GIS (Geo-Information Systems) /Mapping, SMS-services, web platforms, Apps, social media, big data analysis systems.
Who can apply for the Investment Readiness Program? SAIS is looking for innovative startups that are about to scale rapidly and apply digital solutions to the agriculture and food sector which enable their users to improve their income. In addition, digital products or services that help mitigate the impact of COVID-19 are a plus and will be taken into special consideration.
Please note that early-stage startups will not be considered for the program.
Application Deadline: August 31, 2021
Check more https://adalidda.com/posts/AEcxSoZxqEtQT943L/giz-sais-investment-readiness-programme-2022-for-african
0 notes
Text
Mobile Mapping Market Research Report - Global Forecast till 2026
Mobile Mapping Market Research Report - Global Forecast till 2026
Market Snapshot
Mobile mapping market systems is a highly accurate method of gathering geospatial data from mobile vehicles. The system comprises various types of components such as positioning sensors, laser scanners, LiDAR, radar mounted digital cameras, or numerous types of remote sensing devices mounted on mobile platforms such as boats, SUVs, and all-terrain vehicle (ATV) depending upon the end-use application. The result from such systems comprises GIS data, digital maps, and georeferenced images and videos. 3D mobile mapping is one of the most important geospatial technologies available, which can change the way environments are visualized, measured, analyzed, and cataloged. Mobile mapping is used for land surveying, laser scanning, map creation, aerial surveys, facility/road management, and various other applications
Global Mobile Mapping Market has been categorized based on Component, Solution, Application, User Type, and End-User. Based on component, the global mobile mapping market is divided into hardware, software, and services. The hardware segment accounted for the largest share of the global market. Hardware includes sensors and scanners. Based on solution, the global mobile mapping market is categorized into location based, indoor mapping, asset management, 3D mapping, and others. The location based solution segment accounted for the largest share of the global market. By application, the global mobile mapping market has been categorized into land surveys, aerial surveys, bridge planning, and others. The land survey segment accounted for the largest share of the global market. Based on user type, the global mobile mapping market has been segmented into enterprises and individuals. The enterprises segment accounted for the largest share of the global market.
The global mobile mapping market has been segmented into North America, Europe, the Middle East & Africa, South America, and Asia-Pacific. North America holds the largest share in the global mobile mapping market. The regional market has witnessed significant growth owing to the presence of key players such as Google Inc., Apple Inc., and Microsoft Corporation and their investments in the development of mobile mapping solutions across the US, Canada, and Mexico
A few of the key players operating in the global mobile mapping market are Trimble Inc, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, Google, Pasco Corporation, The Sanborn Map Company Inc., Huron Geomatics Inc, Topcon Corporation, 3D Laser Mapping, Apple Inc., NavVis, Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson, NGC Aerospace Ltd, FARCO Technologies Inc, Microsoft Corporation, Hexagon AB, TomTom International BV, IGI GmbH, Hyper-Tech, and Gexcel. These players have been continuously investing in research & development to provide best-in-class and comprehensive mobile mapping solutions to the targeted end-user
Global Mobile Mapping Market is projected to expand at a 15.88 % CAGR during the forecast period.
REQUEST FREE SAMPLE REPORT@ https://www.marketresearchfuture.com/sample_request/5747
Key Developments
In February 2018, Trimble launched its MX9 mobile mapping solution for survey, engineering, and geospatial professionals. This solution combines a vehicle-mounted mobile LiDAR system, multi-camera imaging, and field software to capture precise, efficient, and high-volume data for mobile mapping applications such as road surveys, topographic mapping, 3Dmodeling, and asset management.
In January 2019, Apple Inc. added a turn-by-turn direction feature to its Apple Maps to improve GPS navigation and make ride-hailing easier for iPhone users and to support cab-hailing apps such as Uber and Ola in India
In January 2018, TomTom launched the TomTom Auto Stream, an innovative map delivery service for autonomous driving and advanced driver assistance systems. This enables vehicles to build a horizon for the road by streaming the latest map data from the ‘TomTom’ cloud, enhancing the comfort and safety of the driver
In February 2019, Microsoft Corporation partnered with TomTom NV, a Dutch mapping company, to offer Microsoft Azure customers access to build location-aware applications and extend the latter’s high-quality location technologies to expand its customer base. This partnership provided TomTom’s map data and services to Azure Maps, which helps enterprises and developers create map-based software and Internet of Things (IoT) solutions.
Segmentation
Global Mobile Mapping Market is segmented based on Component, Solution, Application, User Type, and End-User.
Based on component, the global mobile mapping market is divided into hardware, software, and services. The hardware segment is divided into cameras, sensors, laser scanners, others. Further, the service segment is divided into professional and managed.
Based on solution, the global mobile mapping market is segmented into location based, indoor mapping, asset management, 3D mapping, and others
Based on application, the global mobile mapping market has been categorized into land survey, aerial surveys, bridge planning, and others.
Based on user type, the global mobile mapping market has been segmented into enterprises and individuals
Based on end-user, the global mobile mapping market has been segmented into agriculture, real estate & construction, energy & power, marine transport, manufacturing, aviation & aerospace, mining, IT & telecom, healthcare, media & entertainment, and others
Regional Analysis
Geographically, the global mobile mapping market has been segmented into the Asia-Pacific, North America, Europe, the Middle East & Africa, and South America
North America leads the mobile mapping market in terms of market share. The regional market has witnessed significant growth due to the presence of key players such as Google Inc., Apple Inc., and Microsoft Corporation and their investments in the development of mobile mapping solutions across the US, Canada, and Mexico. Europe holds the second-largest share in the mobile mapping market. The region has witnessed rapid growth in the implementation of mobile mapping technology across various industry verticals such as manufacturing, government, banking & financial services, real estate, telecommunication, and transportation.
GET COMPLETE REPORT@ https://www.marketresearchfuture.com/reports/mobile-mapping-market-5747
About Market Research Future:
At Market Research Future (MRFR), we enable our customers to unravel the complexity of various industries through our Cooked Research Report (CRR),Half-Cooked Research Reports (HCRR), Raw Research Reports (3R),Continuous-Feed Research (CFR), and Market Research & Consulting Services.
Contact:
Market Research Future
Office No. 524/528, Amanora Chambers
Magarpatta Road, Hadapsar
Pune – 411028
Maharashtra, India
+1 646 845 9312
Email: [email protected]
0 notes
Text
Technology can empower farmers to beat COVID blues
agriculturemonitoring
COVID pandemic has created an unprecedented level of disruption across the world. The sheer nature of the event has pressed the reset button on many traditional practices. From manufacturing to the services sector, this black swan event has brought in a paradigm shift in their operating models. In this context, the agriculture sector is no exception.

Globally, agricultural activity has been severely impacted due to lack of labour availability, restriction on mobility, and closure of key agricultural produce markets amid strict social distancing measures. As a result, the Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO) estimates that as many as 132 million people are likely to go hungry this year owing to the global economic recession. This will be over and above the 690 million people who are facing acute food shortage now. Unless the nations take immediate collective steps, a food emergency in some nations can’t be ruled out.
In this perspective, technology can play a critical role in avoiding such an impending crisis. Usually, the food supply chain involves a chain of activities that touch upon producers, consumers, input providers, processing and storage, transportation, and marketing. With the help of digital technologies such as machine learning, artificial intelligence, the internet of things, satellite technology (geo-plotting and geo-location mapping), big data, and sensors among others, the efficiency of the whole food supply chain can be improved. This can play a vital role in boosting food production within a short period apart from supplementing farmers’ income. As the world fights this ‘once in a century’ event, any boost in farmers’ income can go a long way in fighting the COVID-induced economic slowdown.
Solutions powered by AI, ML & data analytics key to drive productivity:
Starting from land selection to crop choice, ploughing, weeding, sowing, irrigating, and harvesting can be done better through the intervention of digital technologies such as machine learning. Take for example the case of differentiating between healthy and disease-infested crops. Usually, it is difficult to determine whether a particular crop is disease-infested or not at the early stage of infestation as it is not obvious to the normal eye. However, through the assistance of ML-driven image processing, the grower- whether a farmer or an agricultural expert- can determine which crops are healthy.
Similarly, disease-infested fungi, bacteria, or viruses can not only be detected but also various plant disease management measures such as application of pesticides, uprooting, and destruction of diseased plants can be undertaken.
The machine learning algorithm can enable the grower in suitable crop selection based on historical agro-climatic data, crop pattern, yield variations, and demand-supply dynamics through finding out patterns and correlations. Predictive models on crop yield can be drawn through machine learning, artificial intelligence, and data analytics. Any sort of predictability in crop production during these uncertain times can provide a cushion to farmers’ income apart from enabling agro-based enterprises to plan their investment.
Moreover, digital technologies such as artificial intelligence coupled with data analytics play a critical role in precision agriculture, which is the need of the hour to tide over any shortfall in food production due to this global pandemic. Especially, solutions powered by these technologies enable growers to predict various conditions related to crop including weather conditions, presence of diseases or pests, plant nutrition levels apart from analysing the data like temperature, precipitation, moisture level, and windspeed among others. In developing nations like India and most of South East Asia, early forecasting on weather and climatic conditions has a lot of bearing on output. AI-driven agriculture solutions also generate timely advisory on procurement and marketing, which help in generating a higher return on investment for the grower.
Similarly, digital agriculture is incomplete without the deployment of AI-powered chatbots, which are the major interfaces between the users and service providers. As it is physically impossible to reach out to each grower by any service providers, smart agriculture practices demand man and machine interface. Through the chatbots, conversational virtual assistants give out advisories to growers on various cultivation-related matters. With the penetration of smartphones across the globe, a grower can receive assistance in real-time, enabling him to take required actions. Robotics and autonomous systems (RAS) used mainly in the agriculture sector in developed economies have their foundations on AI and automation.
Satellite technology works as a great enabler:
Ever improving satellite technology has been working as a great enabler for the agriculture sector globally. Through this technology, farmers are not only able to receive advisories on weather and other climatic conditions, but even field management decisions such as irrigation and fertilization can be aptly taken, which are critical components of precision agriculture. For instance, farmers can determine over or under irrigation in a vast patch of land through this technology. Such precision in water management boosts productivity and saves costs for growers. Fertilization is another area that gets support from this technology. With the increasing penetration of agri-financing companies such as insurance firms and banks, satellite technology has proven to be a boon in settling claims along with lending decisions.
Precision agriculture hinges on the combined technologies of Global Positioning System (GPS) and Geographic Information System (GIS). These two segments can be taken as the derivatives of satellite technology. Through these technologies, site-specific farming has been made possible as real-time geospatial data helps in farm planning, field mapping, crop choice, soil sampling, and yield mapping among others. The data generated through GIS also enables agtech companies to prescribe site-specific recommendations, resulting in higher productivity.
Coupled with GIS & GPS, sensor technology has brought in drastic changes in the field of agriculture. For instance, soil moisture sensors can measure the moisture content of a crop on a real-time basis. In case of any variations from the desired level, it is being informed to the grower on an app. Moreover, an intelligent irrigation management system can be designed based on these data. Whenever soil moisture varies, the extent of irrigation can be altered. IoT-powered sensors can also be deployed to gauge temperature and determine crop patterns. Apart from these new-age technologies, even drones have slowly made inroads into the field of agriculture. From taking up the image to the application of pesticides and insecticides, drone technology is slowly evolving in the field of agriculture.
Mobile-based ‘SaaS’ platform makes access easy:
Easy access to technological solutions is vital for effective implementation. In this perspective, innovations in the field of agriculture have reached the last mile due to the wide penetration of mobile phones. Most ‘SaaS’(software as a solution)-based platforms are accessible on android-powered handsets, making it easy for farmers to receive the critical inputs on crop growth in time. Also, predictive analytics-based solutions on yield and productivity enable farmers to plan their investments.
Usually, these cloud-based platforms gather data from the field, which are transmitted to the service provider. In return, the agtech firm analyses these data with the help of AI, ML, big data-powered algorithms and find patterns for recommendations. Then, these recommendations are sent back to the grower. As cloud-based platforms are agile and available on subscription-based pricing models, users can get the benefit without committing a lot of upfront investment.
Farmsio’s platform provides integrated solutions:
Farmsio, a pioneer service provider in agtech space, provides holistic applications touching upon every aspect of farming. Starting from providing smart weather solutions to crop production, pest and disease alerts, supply chain management, and market-facing advisories, all are available on this platform. This android-based solution can fit in for both farmers of small landholdings and growers pursuing commercial agriculture.
Conclusion:
The COVID-induced slowdown is going to change all facets of the economy in multifarious ways. After the wide adoption of farm mechanisation across the globe in the pre-COVID era, post-COVID-world is likely to witness acceleration in the adoption of digital technologies. So, those players, be it the growers or agro-based companies, which can adopt these technologies faster, will have a fast-mover advantage.
0 notes