#FOR MONGOLIAN IT IS SOMETHING LIKE /ɬ~ɮ/
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text


YEAH- THATS APT- Also! I LOVE THE MONGOLIAN ON THIS ONE MY BRAIN WENT BRRRRRR!!!! I KNEW THESE WORDS FELT FAMILIAR! (After simp: öödrög/optimistic, teneg/silly or stupid)
Thanks for the tag Raf :D & YALLS NEED THERAPY OMGS!
Tags: @transfrogmer @giddyfenix @what-aboutno
Let's all be in a TV show!!!
> Do this quiz
> do this picrew (Based on urself + quiz answers)
> tag ppl
> profit.


Tags (/nf ofc):
@mxlilly @circus-of-horror @yourleastfavoriteguyinthechair @microsoupmouse @the-firefly-jar-system @punkrockinchair @theplushiesystem @coded-pup @florasolarsystem + ANYONE else who wants to join
#FLCKSKCKSKCKSKD GODS I LOVE MONGOLIAN#MONGOLIAN CAN STICK OUT LIKE A SORE THUMB COMPARED TO OTHER LANGUAGES WRITTEN IN CYRILLIC#THE LANGUAGE HAS VOWEL HARMONY & SO YOU WILL SEE OFT THE SAME VOWEL#OR SIMILAR VOWELS ACROSS THE SYLLABLES OF A WORD!!#ALSO Г <333 IT CAN BE READ AS [ɢ] & UVULAR CONSONANTS MAKE MY BTAIN GO MMMMMMMMM /POS#ALSO#CAN WE TALK ABOUT л???#FOR MONGOLIAN IT IS SOMETHING LIKE /ɬ~ɮ/#& THE LATERAL FRICATIVES ARW THW MOST SEXY SOUND EVER#& ANY LANGUAGE THAT USES IT IS AUTOMATICALLY SEXU#MONGOLIAN OBVI#KALAALLISUT INUKTITUT IÑUPIAQ YUPIK ALEUT 110%#WELSH YEAH ILL LET YOU GUYS OFF ON THIS ONE#NAHUATL WITHOUT A DOUBT#IN FACT NAHUATL IS SO SEXY IF HAS GOT AN AFFICATE WITH THIS SOUND THAT MARKS SO MANY OF ITS NOUNS 🥺🥺🥺#I GOTTA STOP BEFORE I GUSH TOO MUCH MORE#NO I LIED AMOTGWR COOL THING WITH MONGOLIAN IS THA- [gets shot]
11K notes
·
View notes
Text
Movelang #001 - Phonology and Sound System
Nophhurra, and hello again everyone! It's time for another post showing off my experimental conlang, Movelang! This time around, I'll be going over Movelang's sound system: the consonants and vowels used, along with a currently loosely-defined syllable structure, as well as allophony!

Admittedly, the Phonology has been one of the aspects of Movelang which has been altered several times over, and has gone through several iterations before reaching the point at which it exists in the present. Since the emphasis for this conlang was moreso on grammar than on the phonoaesthetic, I had largely loosely defined it at the start, with only a vague idea of what Movelang would sound like. At the start, I took a lot of inspiration from the Coptic Language, as well as several African and Caucasian Languages. Later on as I began being more deterministic about the phonetic inventory of the language, it did change from this original vision in several ways, but I ended up ultimately with something I really like!
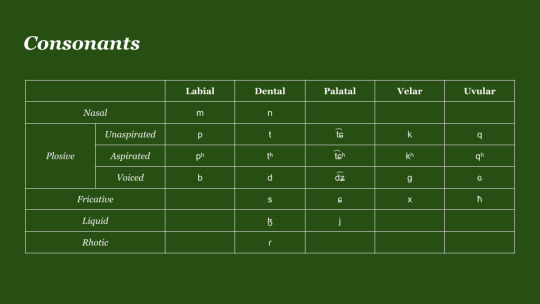
(My charts tend to prioritize neatness over exactness, so if there's a sound somewhere that doesn't exactly describe it completely correctly, please don't fight me 😭)
Phonemically, the consonant inventory consists of 2 nasals, 15 plosives, 4 fricatives, 2 liquids, and 1 tap. The plosives are split three ways by mode of articulation, where 5 stops are unaspirated: /p t t͡ɕ k q/, 5 stops are aspirated: /pʰ tʰ t͡ɕʰ kʰ qʰ/, and 5 are voiced: /b d d͡ʑ g ɢ/. Each mode of articulations contains a labial, dento-alveolar, palatal, velar, and uvular stop respectively. This was a choice inspired by both Ancient Greek, as well as the Coptic and Caucasian influence I mentioned earlier, and in an earlier version of the phonology, the palatal affricates were instead alveolar affricates: /t͡s t͡sʰ d͡z/. Accompanying the stops are 4 fricatives that roughly match 4/5 of the same manners of articulation: /s ɕ x ħ/. These were selected mainly for that reason, that they lie in the same POA as their stop counterparts, but I decided to throw in an oddball for the fricative furthest towards the back of the mouth. Originally, this was /h/ phonemically, but I was intrigued by Maltese's presence of /ħ/ as the sole voiceless fricative closest to the back of the mouth, so I decided to do this for Movelang, and I do love how it sounds! I personally think /x/ and /ħ/ pair nicely with each other! The Approximants and Nasals then weren't that hard to reckon, I simply filled in the gaps in the chart respectively. When I got to my /l/ sound though, I decided to make this a little bit different as well, and follow the lead of Mongolian, and make it /ɮ/ instead. I also made the decision to omit /w/ or any similar sound, since I have a habit of using this sound a lot whenever I make new sound systems, as a bit of a monkey-wrench to try and make myself work with.

For Allophony, most of this deals with the pronunciation of consonants. There are 3 major rules that come into effect when pronouncing consonants in particular places within a word. First, the nasals, /m n/, devoice to /m̥ n̥/ whenever they are preceded by a syllable that has an aspirated plosive in the coda, any of /pʰ tʰ t͡ɕʰ kʰ qʰ/. Secondly, /ɮ/ may devoice to /ɬ/ when next to any voiceless sound: a voiceless plosive or fricative. Finally, the alveolar tap /ɾ/ becomes trilled /r/ when it is geminated. These rules as you'll notice mostly depend on a sound's locale within a syllable, which I'll explain in greater detail when discussing syllable structure...
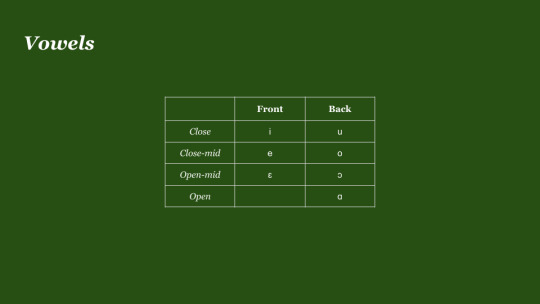
As for the vowels, these are quite simple. Movelang consists of seven phonemic vowels, which compliment the front and the back of the mouth. Movelang contains no phonemic length, tone, nasality, or anything else that would affect vowel quality in this way, at least phonemically, and only has these 7 plain oral vowels. There are 3 front vowels: /ɛ e i/, all of which are unrounded, and 4 back vowels: /ɑ ɔ o u/, all of which are rounded, except for the open back vowel.
In terms of vowel allophony, nothing really major happens to vowels. The only major rule which takes place with vowels, is that /ɑ/ goes to /a/ when near a palatal sound.

Additionally, the syllable shape in Movelang is pretty straightforward, it's pretty much CVC, but with a few additional caveats. The main difference, is that /j/ cannot be a coda consonant, which is reflected by the use of D for the coda consonant in my syllable shape notation, and additionally, only 6 consonants can end a word: /m t k q s r/, which is reflected by the use of K for a word-final coda consonant.
In addition to these tactical features, hiatus is permitted in Movelang, meaning that the onset consonant in syllables is optional even word-internally, and when this happens, the parallel vowels flow together smoothly, rather than having some epenthetic consonant placed between them, like a glottal stop. Gemination also happens quite frequently in Movelang, especially in compounds, and it is under these circumstances when /j/ technically can appear in the coda of a syllable, but only as a part of a geminate /j:/.
=-=-=-=
Alright! Well, that's pretty much it for phonology, at this point I'm going to try and stick to this phonology and not impulsively change it again, but knowing me, I can't make any promises XD. I hope you all enjoyed this look at the sound system! I look forward to posting some lexical samples in the next post, with these sounds intact, where I'll be showing you Movelang's class system in action! More on that later of course... Until then, I look forward to it, and I hope you all enjoyed this post! If you all have any questions, feel free to leave me a comment, or an ask!
8 notes
·
View notes