#Environmental Geospatial Studies
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Dictionary of GIS Terms

Aerial Photography Mapping: The creation of maps based on the interpretation and analysis of aerial photographs, utilizing differences in vantage points and angles to construct detailed representations of the Earth’s surface for planning and analysis.
Cartography and Map Design: The art, science, and technology of creating maps, involving the representation of spatial information visually in order to communicate geographic data effectively and accurately.
Climate Change Mapping: The process of using geographic data and mapping technologies to illustrate and analyze the effects of climate change, including rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events.
Consulting Service: Geospatial consulting services offer expert guidance on the strategic implementation and use of geospatial technologies. This includes Presales support, QA&QC, Staffing, Onshore and offshore support, Proof of support and Business process evaluation.
Data Services: In the context of geospatial solutions, data services refer to the processes and technologies used for managing, storing, retrieving, and distributing geospatial data, facilitating decision-making processes across. It comprises data conflation, data standardization, data management across different sectors.
Environmental Geospatial Studies: The application of geospatial technologies and analytical methods to environmental science, studying spatial patterns and processes affecting ecosystems, biodiversity, climate change, and natural resource management.
Enterprise GIS Framework: An enterprise GIS framework is an integrated approach to managing and utilizing geographic information throughout an organization. It enables the sharing of GIS resources, data, and applications across different departments, improving collaboration and efficiency.
Geographic Coordinate Systems: Frameworks that utilize latitude and longitude to pinpoint precise locations on the Earth’s surface, enabling accurate mapping and navigation worldwide.
Geographic Data Visualization: The technique of representing spatial data through graphical forms, including maps and 3D models, to help users understand geographic patterns, relationships, and trends more effectively, enhancing the interpretability of complex spatial information. Digital Terrain Model (DTM), Digital Elevation Model (DEM) are important 3D models to determine the type of terrain and assets.
Geographic Information Science Education: The academic field focused on teaching the principles, technologies, and applications of geographic information systems, including data collection, analysis, and visualization techniques.
Geofencing Technologies: Digital tools that create defined virtual perimeters around real-world geographic areas, enabling automated alerts or actions when objects enter or leave those boundaries.
Geospatial Big Data Analytics: The analysis of large volumes of geographic data from various sources to discover patterns, trends, and insights, supporting complex decision-making processes.
Geospatial Cloud Computing: This concept involves leveraging cloud technology to store, process, and manage geospatial data, enabling scalable and efficient access to GIS resources and data analysis capabilities from anywhere.
Geospatial Data Integration: The merging of geographical data from diverse sources into a coherent dataset, often involving the alignment of different coordinate systems, formats, and data models, to create a comprehensive spatial representation for analysis and decision-making.(Read More…)
#Consulting Service#Data Services#geospatial solutions#Environmental Geospatial Studies#GIS Application
0 notes
Text
My first published paper!
Please check out my first published paper contribution! I was involved with the field work portion of this study as part of my master's degree in geography at the University of Utah. It's always exciting to expand my knowledge of geospatial technologies and evolve in the world of environmental science.
#geography#lidar#pinyon-juniper#big data#mapping#science#biomass#university of utah#remote sensing#ecology#environment#professional
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Comprehensive GIS Services: Transforming Data into Actionable Insights
In a world where data drives decision-making, Geographic Information System (GIS) services have emerged as indispensable tools for businesses, governments, and organizations alike. GIS services encompass a vast array of tools, technologies, and techniques that allow users to visualize, analyze, and interpret spatial data. By bridging the gap between raw data and actionable insights, comprehensive GIS services enable users to understand complex relationships and trends within a geographical context, offering solutions across various industries, including urban planning, environmental management, transportation, and public health.
The Core of GIS Services: Integrating Spatial Data and Technology
At its essence, GIS services focus on integrating spatial data with cutting-edge technology to generate insights that are otherwise difficult to obtain. By capturing, storing, managing, analyzing, and displaying geographical data, GIS enables organizations to see beyond numbers and charts. This visual approach to data provides a geographic context that highlights patterns, trends, and relationships within datasets.
The foundation of GIS is built on spatial data, which represents the physical characteristics of locations and the relationships between them. Spatial data can come in various formats, including vector data, raster data, and geodatabases, which together can store information on boundaries, elevation, and even demographic factors. Comprehensive GIS services combine these data types with technological advancements to create interactive, visual maps, enabling users to make well-informed decisions.
Key Components of Comprehensive GIS Services
Comprehensive GIS services provide a range of functionalities, each designed to address specific needs of an organization:
Data Collection and Management: GIS services start with data acquisition, where organizations collect geospatial data using various methods, including satellite imagery, drones, and GPS. Once collected, this data needs to be stored, processed, and managed effectively. Modern GIS services often employ cloud-based platforms, allowing data to be securely stored and accessed from anywhere in the world.
Spatial Analysis: Spatial analysis lies at the core of GIS, enabling users to study relationships between different datasets. With spatial analysis tools, users can conduct activities like proximity analysis, overlay analysis, and network analysis, which can reveal crucial insights, such as identifying areas of high demand or determining optimal routes for transportation.
Geocoding and Mapping: Geocoding is the process of converting addresses into geographic coordinates, which can then be mapped to provide a visual representation of data points. Mapping, in turn, allows organizations to see the geographical distribution of their data, enabling them to visualize clusters, patterns, and outliers that would otherwise remain hidden.
Data Visualization: Through GIS services, data can be transformed into compelling visuals, such as heat maps, 3D models, and thematic maps. These visualizations simplify complex data, making it accessible to non-technical users and aiding in communicating insights to stakeholders. Visualization helps turn data into actionable insights by enabling users to interact with their data in real-time.
Remote Sensing and Image Analysis: Remote sensing uses satellite or aerial imagery to capture data over vast areas, allowing GIS professionals to monitor changes over time. Image analysis tools process these images, making it possible to track developments in environmental conditions, urban expansion, or disaster impacts. This technology provides a reliable means for tracking real-world changes that impact planning and policy-making.
Predictive Analysis and Modeling: By utilizing machine learning algorithms and predictive models, GIS services can forecast future events or trends. For instance, urban planners can use predictive modeling to estimate population growth in specific areas, enabling proactive planning for housing and infrastructure needs. Predictive GIS models also assist in risk assessment, particularly in areas prone to natural disasters.
Applications of GIS Services Across Industries
GIS services have far-reaching applications across numerous industries, driving efficiency and enabling better decision-making. Here are a few key sectors where GIS plays a transformative role:
Urban Planning and Development: GIS has become a cornerstone in urban planning, helping city planners design sustainable cities. With GIS, planners can analyze population density, land use, and transportation networks to create efficient urban layouts. GIS also aids in identifying optimal locations for infrastructure and services, balancing economic growth with environmental protection.
Environmental Management: Environmental organizations rely on GIS services for ecosystem monitoring, wildlife tracking, and environmental impact assessments. By visualizing deforestation rates, water levels, or pollution sources, GIS helps organizations understand ecological changes and manage conservation efforts effectively.
Transportation and Logistics: GIS enables transportation companies to optimize routes, reduce fuel costs, and improve delivery times. Logistics companies use GIS to create accurate road networks and predict traffic patterns, allowing them to respond dynamically to delays or changes in demand. For public transit systems, GIS helps in planning routes, tracking fleet movements, and improving service efficiency.
Public Health: During pandemics or disease outbreaks, GIS services provide vital information for tracking infection rates and predicting spread patterns. By integrating demographic data with spatial analysis, public health officials can identify at-risk areas, allocate resources effectively, and develop targeted health interventions.
Agriculture: Precision agriculture has greatly benefited from GIS, allowing farmers to monitor crop health, manage water resources, and optimize fertilizer use. With GIS, farmers can create field-specific maps, analyze soil conditions, and make data-driven decisions, ultimately improving yield and sustainability.
Disaster Management and Emergency Response: GIS services play a critical role in disaster preparedness, response, and recovery efforts. By mapping hazard-prone areas and analyzing disaster patterns, emergency responders can develop contingency plans, evacuate high-risk areas, and allocate resources where they’re most needed during an emergency.
Advantages of GIS Services in Decision-Making
GIS services offer several significant advantages for organizations seeking data-driven decision-making solutions:
Enhanced Data Accuracy: GIS collects data from multiple reliable sources, ensuring that the resulting insights are accurate and up-to-date. This accuracy is particularly valuable in sectors where precision is essential, such as healthcare and disaster management.
Increased Efficiency: By automating data processing and analysis, GIS services save time and reduce labor costs. For instance, companies can quickly identify profitable locations for new stores or determine efficient routes for deliveries, improving overall operational efficiency.
Improved Resource Allocation: GIS helps organizations make informed decisions about resource allocation, enabling them to distribute their resources effectively. For instance, GIS allows city planners to decide where to place public amenities based on population density and accessibility.
Better Communication with Stakeholders: GIS visualization tools enable organizations to present complex data in a simplified, visually appealing format, making it easier to communicate findings to stakeholders, investors, or the general public. This transparency fosters trust and facilitates collaboration.
Predictive Capabilities for Proactive Planning: With predictive modeling, GIS services enable organizations to foresee future trends and plan accordingly. This forward-looking approach helps businesses and governments mitigate risks, manage resources effectively, and adapt to changing conditions.
Emerging Trends in GIS Services
The field of GIS is continuously evolving, with new trends shaping its future:
Integration with IoT and Real-Time Data: The Internet of Things (IoT) is adding a new dimension to GIS by enabling real-time data collection from sensors and connected devices. This integration allows for real-time monitoring of dynamic conditions, such as traffic flow or environmental changes, empowering organizations to make timely decisions.
AI and Machine Learning in Spatial Analysis: Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are transforming GIS by enabling advanced analysis of complex data sets. Machine learning models can detect patterns and anomalies that are invisible to traditional analysis methods, enhancing GIS’s predictive capabilities.
3D GIS and Augmented Reality (AR): As 3D modeling and augmented reality become more accessible, GIS is moving beyond two-dimensional mapping. 3D GIS enables users to visualize data in a more immersive and intuitive way, which is particularly useful in urban planning and environmental management.
Cloud-Based GIS Solutions: Cloud-based GIS services provide scalable, accessible platforms for data storage and processing, allowing teams to collaborate remotely and access their data from any location. This shift to the cloud is reducing the need for physical infrastructure, making GIS more accessible to organizations of all sizes.
Conclusion
Comprehensive GIS services have proven to be transformative tools for industries seeking data-driven insights to navigate complex challenges. By turning spatial data into actionable insights, GIS helps organizations make informed decisions, optimize resource allocation, and plan proactively for the future. As technology continues to advance, GIS services will likely become even more powerful, playing a pivotal role in shaping the future of data-driven decision-making across various sectors. For organizations looking to harness the power of spatial data, investing in GIS services is not just an option—it’s a necessity.
0 notes
Text
The Importance of Topography in Delhi, India
Topography plays a vital role in urban planning, environmental management, and infrastructure development. In a city like Delhi, which is constantly evolving and expanding, understanding the topographical features is essential for efficient and sustainable growth. From construction to environmental conservation, knowledge of topography in Delhi India provides critical insights into how the land is structured and how it can be used responsibly.
This blog explores the significance of topography, its applications in different sectors, and the benefits it brings to a rapidly developing city like Delhi.
What is Topography?
Topography refers to the detailed mapping and study of the surface features of an area, including its natural and man-made formations. These features include hills, valleys, rivers, roads, and buildings. Topographical maps are created using a combination of survey data, satellite imagery, and geospatial technology to accurately represent the terrain of a particular area.
In the context of topography in Delhi India, it involves analyzing the city's landscape to understand its elevation, slope, and other features. This information is crucial for various industries, particularly those involved in construction, land-use planning, and environmental protection.
The Importance of Topography in Urban Planning
Urban planning is one of the key sectors that rely heavily on topographical data. In a city like Delhi, where space is limited and population density is high, proper planning is essential to ensure that new developments do not adversely affect the existing infrastructure or the environment. Knowledge of topography in Delhi India helps urban planners design more efficient layouts for roads, buildings, and other infrastructure.
For instance, areas with steep slopes or high elevation may not be suitable for large-scale construction projects due to the risk of landslides or drainage issues. Conversely, low-lying areas may be prone to flooding during heavy rains, which could affect housing developments or transportation systems. By using topographical data, planners can identify the most suitable locations for different types of construction, ensuring that the city's infrastructure is both safe and sustainable.
Applications of Topography in Construction
Topographical surveys are essential in the construction industry, especially in a growing city like Delhi. Before starting any major construction project, developers need to understand the land's terrain to determine the best design and layout for buildings, roads, and other infrastructure. A detailed analysis of topography in Delhi India ensures that construction projects are built on stable ground and take into account any natural features that might impact the development.
For example, construction companies use topographical data to plan drainage systems, ensuring that rainwater flows away from buildings and roads. Additionally, topographical surveys can help identify potential hazards, such as areas prone to flooding or erosion, which could pose significant risks during construction. By analyzing the land's features, developers can create more efficient and resilient structures that withstand the challenges posed by the local environment.
Environmental Management and Conservation
Environmental conservation is another area where topography in Delhi India plays a critical role. As the city grows, it is essential to protect its natural resources and minimize the impact of development on the environment. Topographical data helps environmental experts identify areas that are particularly vulnerable to damage, such as wetlands, forests, or rivers.
By understanding the landscape's natural features, environmental planners can design conservation projects that preserve these areas while allowing for responsible development. For example, areas with steep slopes may be prone to soil erosion, which could damage nearby ecosystems or water sources. By using topographical data, environmental planners can create strategies to prevent erosion, protect wildlife habitats, and ensure that the city's natural resources are preserved for future generations.
Disaster Management and Risk Mitigation
Delhi, like many other major cities, faces various natural and man-made disasters, including floods, earthquakes, and urban flooding. Understanding topography in Delhi India is crucial for disaster management and risk mitigation efforts. By analyzing the terrain, disaster management teams can identify areas that are more likely to experience flooding during monsoon seasons or areas at higher risk of earthquake damage.
Topographical maps help authorities plan evacuation routes, locate safe areas for shelter, and design infrastructure that can withstand natural disasters. In flood-prone areas, for instance, topographical data can be used to design flood defenses, such as embankments or drainage systems, to prevent water from accumulating in low-lying areas. Similarly, areas with unstable terrain can be reinforced to reduce the risk of landslides or building collapse during an earthquake.
Applications in Agriculture and Water Management
In addition to urban planning and construction, topography in Delhi India is also important for agriculture and water management. Farmers and agricultural planners use topographical data to determine the best locations for planting crops, building irrigation systems, and managing soil health. Topographical surveys can identify areas with the right slope and drainage for agriculture, helping farmers optimize their land use and increase crop yields.
Moreover, topographical data is critical for water management projects. In a city like Delhi, where water scarcity is a growing concern, understanding the land's natural features can help planners design more efficient water distribution systems. By analyzing the terrain, water management experts can determine the best locations for reservoirs, pipelines, and other infrastructure to ensure that water is distributed efficiently throughout the city.
Technological Advancements in Topographical Surveys
Advancements in technology have revolutionized the way topographical surveys are conducted. Traditional surveying methods, which involved manual measurements and physical mapping, have been replaced by more advanced tools such as drones, GPS systems, and satellite imagery. These tools allow surveyors to gather accurate data on topography in Delhi India more quickly and efficiently than ever before.
Drones, for example, can capture high-resolution images of the terrain from above, providing detailed information about the land's surface features. GPS systems allow surveyors to pinpoint exact locations and elevations, ensuring that topographical maps are highly accurate. These technological advancements have made topographical surveys more accessible and cost-effective, allowing more industries to benefit from this valuable data.
Conclusion
Understanding topography in Delhi India is essential for various industries, including urban planning, construction, environmental conservation, disaster management, and agriculture. By providing detailed information about the landscape's features, topographical surveys help ensure that development projects are safe, efficient, and sustainable.
Whether it's designing a new housing development, managing water resources, or protecting natural habitats, topographical data provides the critical insights needed to make informed decisions. As Delhi continues to grow and evolve, the importance of topographical surveys will only increase, helping to shape a more resilient and sustainable future for the city.
#topography in delhi India#Cavity Mapping in delhi#utility mapping services in delhi India#shijay projects#shijay
0 notes
Text
Energy Jobs
A major concern in shifting to a clean energy economy is the loss of many jobs that people have worked in for decades. It is not so simple as putting non-renewable energy employees into renewable energy jobs. These jobs require training, and people who lose jobs as we decrease non-renewable energy reliance need a way to financially sustain themselves.
Lost Jobs
According to Reimagining the Economy in 2023, over one million people worked in fossil fuel production. Not all of these people automatically have skills that easily transfer into clean energy, and some of those jobs are trades that have not required college degrees.
As of 2022, the oil industry was made up of 71% male employees. 73% of employees were white, with no large racial differences from the overall workforce average. Globally, fossil fuels made up about 32 million jobs in the same year.
The coal industry decreased by about 7,000 employees in 2022. Natural gas increased by 7,000, and oil by 279.
In the U.S., decreasing fossil fuel production is expected to displace close to 2 million workers by 2050.
Additionally, most fossil fuel jobs are centered away from the coasts, in states like Texas, the Midwest, and near the Appalachian mountains.
New Jobs
From 2021 to 2022, clean energy jobs grew 3.9% to about 3.1 million jobs. By 2030, the clean energy transition is expected to have created 30 million new jobs. But that doesn’t mean that they’re available to workers leaving the fossil fuel industries.
Many fossil fuel jobs are not near the coasts, for one, while many solar and wind jobs are.
A study in 2023 found that geospatial distance is a primary barrier to transitioning fossil fuel workers to green jobs.
The International Energy Agency (IEA) claims that 14 million new jobs will be created in clean energy, and an additional 16 million fossil fuel workers will shift into clean energy jobs. However, the IEA also estimates that about 60% of clean energy jobs created by 2030 will require post-secondary training. The exact training will depend on the job, but overall, most people interested in the clean energy industry are advised to major in Chemistry, Biology, or Environmental Engineering. Contrastingly, the most sought after degrees in fossil fuel jobs are Petroleum Engineering and Mechanical Engineering. It will likely be very difficult for workers to switch their specializations in this way.
These new jobs will also have risks unless worker protection policies are enacted and upheld. Newer and quickly growing industries, such as solar, are less likely to have labour protections and unions. Around 17% of U.S. fossil fuel jobs have a union, which is relatively high compared to the average of 10% across industries. Clean energy jobs have about a 12.4% union rate, surpassing the general average but still below fossil fuels. In other words, if workers are qualified for clean energy jobs, there is yet another reason for them to resist investing their work in clean energy. Meanwhile, those who do still switch to a clean energy job might see far fewer benefits from their employment.
Moving Forward
With a changing labour force and new growing industries, it is important to realize who will be disadvantaged by switching from the fossil-fuel reliant economy that has been built. Decreasing non-renewable energy production means fewer jobs on which people have been building their livelihoods.
The IEA believes that many of these fossil fuel jobs require skills that translate well to clean energy. With the growth in clean energy jobs expected to outnumber the loss in fossil fuel jobs, the concern then is making sure fossil fuel workers have the resources to make that switch. What are workers expected to do if they can’t physically reach those jobs?
Morgan Frank from the University of Pittsburgh has proposed one possible solution. The areas of machinery, infrastructure, and working with tools are ones that many fossil fuel jobs prepare you for. Workers might want to focus on searching for such jobs, not only within the industries of clean energy.
There is no way to perfectly ensure that every person finds the job they need in the energy-shifting economy. We still have a responsibility to facilitate this transition as much as possible, because shifting to clean energy is about what we owe to the earth and to each other. That includes clean air, parks, and fresh water, but also the ability to afford food, shelter, and amenities since everything is increasingly expensive.
Additional Resources
1. Reimagining the Economy
2. 2022 Industry Demographics
3. Displaced Workers
4. Reassigning Fossil Fuel Workers
5. Job Location Problems
#clean energy#renewable energy#renewable resources#wind energy#solar wind#energy industry#jobs#economy#us politics#fossil fuel industry#article#research#resources#environment#climate change#politics
1 note
·
View note
Text
Scientists unlock the secrets to an Alpine flower's survival
08.08.24 - A team of scientists from EPFL and other research institutes have identified just how an Alpine flower is surviving by adapting its genes to local habitats. This discovery has important implications for the protection of ecosystems under threat. In the Alps, adventurous hikers aren’t the only ones to regularly climb to new heights. Several plant species are doing the same in response to climate change, as warmer temperatures threaten their survival. Today, scientists are working with environmental conservation organizations to better understand the strategies used by these species and predict their migration, in order to help protect Switzerland’s biodiversity. A research team that includes EPFL scientists began studying this process in 2013, combining geographic information systems with molecular ecology (landscape genomics). Their findings – published in the July issue of Evolutionary Applications – can help answer a question that has puzzled biologists until now: at what scale does natural selection operate? The study clearly indicates that natural selection works on a very localized level and can vary significantly, even within the same plant species. That means a multiscale framework is essential for making effective observations about how the natural selection process works. Mapping and genomics In the study, researchers used drones and a light-detection and ranging (LiDAR) system installed on a helicopter to produce topographic models of four valleys in the Vaud Alps at an unprecedented spatial resolution of 6 cm to 32 m. At the same time, the researchers collected samples of a plant representative of the local ecosystem – the Alpine rock-cress (Arabis alpina) – at the four sites. This plant produces white flowers and grows in rocky, sandy mountain soil as well as in cracks in mountain rocks. The researchers extracted the whole genome of plants from each of the four sites in order to identify genotype variations. When they combined the results with the geographic data, they discovered that the species’ genome varied significantly between valleys based on the specific environmental conditions in each one (sunlight, humidity, air temperature, surface slope and orientation, etc.). In other words, they saw just how the plant fights for survival in response to its local habitat. Now, for the first time, we’re able to detect natural selection signatures at the right scale Stéphane Joost, senior scientist in the Geospatial Molecular Epidemiology Group (GEOME) at EPFL’s Laboratory for Biological Geochemistry (LGB) A multiscale approach Stéphane Joost, the corresponding author and a senior scientist in the Geospatial Molecular Epidemiology Group (GEOME) at EPFL’s Laboratory for Biological Geochemistry (LGB), explains: “For a long time, these kinds of studies used topographical models with a spatial resolution of just 25–50 m and that were supplied mainly by the Swiss Federal Office of Topography. Now, for the first time, we’re able to detect natural selection signatures at the right scale.” So what new information does this reveal? Joost gives the example of a defense mechanism that the Alpine rock-cress uses to ward off plant-eating insects. These insects are often found under the large mountain rocks where Alpine rock-cress grows. To protect its leaves, the plant produces a sugary sap that repels the insects. “We found a significant association between a gene involved in this defense mechanism and a variable that measures surface roughness – but only when the variable is calculated at a spatial resolution of 2 m,” says Joost. “The association can’t be detected or doesn’t exist at other resolutions.” He believes the study shows how important it is to carry out multiscale analyses in order to identify the full range of local adaptation strategies that are crucial to the survival of a given species. The study also highlights another important point: even though the Alpine rock-cress… http://actu.epfl.ch/news/scientists-unlock-the-secrets-to-an-alpine-flower- (Source of the original content)
0 notes
Text
Astronomy has long been dominated by skilled amateurs, but the widespread adoption of the internet and smartphones has made geospatial data ubiquitous, and directions once only available on paper maps can now be updated in real time on your smartphone, taking traffic conditions into account. Scientific relationships are also changing. Crowdsourced scientific data has transformed the way protein folding was obscured 15 years ago. Relevance everywhere. That evolution will continue to be driven by how data is collected. Credit: Emory University, Xiao Huang According to the authors, urban planning, transportation and environmental monitoring have been particularly influenced by crowdsourced information, with user-generated data providing "unprecedented real-time views and community-driven perspectives that often lead to more responsive and adaptive decision-making processes." The same kind of data is also providing the commercial sector with more informed, customer-centric product development and marketing strategies.The significance of this change lies in the power it has given ordinary people to contribute and influence a field traditionally dominated by experts and authorities.This democratization has not only diversified the types of data available, but also provided richer, more multifaceted insights into human behavior and environmental change. But the researchers said that despite such changes, there is still a need for a comprehensive and holistic view that links different data sources, such as social media platforms, to application areas such as public health and remote sensing. "Our aim is to fill this gap and provide a comprehensive view of the uses and potential of crowdsourced geospatial data," said Professor Xiao Fan of Emory University. "In this study, we provide a thorough analysis of the current efforts, potentials, and obstacles associated with crowdsourced geospatial data from two fundamental perspectives: human observation and Earth observation." Earth observation refers to data recorded by large organizations, such as academic or government institutions, as opposed to human observations on social media, for example. Combining these two perspectives, the researchers identified seven specific challenges: ensuring data quality and accuracy, protecting data privacy, training and educating non-experts, continuing data collection, resolving legal and ethical issues, and interpreting data. Their paper summarizes the current state of each field and possible paths forward. "Crowdsourced geospatial data plays an important role and has great potential in enhancing human and Earth observation," said Huang. "This data, provided by the public through various platforms, provides high-resolution spatiotemporal observations that may be missed by traditional methods. This comprehensive review paper highlights the democratization of data collection and its impact on various fields, and emphasizes the need to integrate these non-traditional data sources for more comprehensive and nuanced understanding and decision-making." The researchers identified three key future directions: leveraging the power of the crowd to expand the reach of geospatial crowdsourcing, cultivating a sustainable crowdsourcing ecosystem from motivation to retention, and translating crowdsourced geospatial data into real-world impact.
0 notes
Text
Above and Beyond: The Evolution of Global Satellite Data Services
Astute Analytica, a team of experts with extensive experience, has recently published a new report on the Global Satellite Data Services Market. The report provides valuable insights into the market’s competitive environment, growth prospects, and upcoming opportunities. It covers the strategies adopted by major global players in the industry, including mergers, achievements, revenue offshoring, R&D, development plans, progression growth, and collaboration.
Global satellite data services market was valued at US$ 8,368.91 million in 2022 and is projected to surpass valuation of US$ 44,356.60 million by 2031 at a CAGR of 21% during the forecast period 2023–2031.
Get Customized Reports with your Requirements :- https://www.astuteanalytica.com/request-sample/satellite-data-services-market
Report Scope
The report delves into the industry structure, sales, revenue, price, and gross margin of the global Satellite Data Services Market. It also presents information on major producers’ production locations, market shares, industry ranking, and profiles.
The research is based on primary and secondary statistics sources, including up-to-date government regulations, market information, and industry data. The data were collected from manufacturers, distributors, end users, industry associations, government-industry bureaus, industry publications, industry experts, third-party databases, and in-house databases.
Recent Market Trends
The global market report provides valuable insights into the major drivers and regional dynamics of the global keyword market, as well as current trends within the industry. The report also discusses the major players across each regional market and emphasizes the importance of technology and data for the industry’s future.
Competitive Landscape
The Global Satellite Data Services Market features a competitive landscape characterized by multinational corporations alongside regional players. The intense competition drives innovation and collaboration, with a focus on expanding product portfolios and meeting diverse consumer preferences for keywords.
Key Companies
Airbus SE
Earth-i Ltd
East View Geospatial Inc.
EOS Data Analytics (EOSDA)
ICEYE
ImageSat International (ISI)
L3Harris Technologies, Inc.
LAND INFO Worldwide Mapping
Maxar Technologies
NV5 Geospatial Solutions, Inc.
Venture Companies
Airbus Ventures
BAE Systems
MMC Ventures
Seraphim Space
True Ventures
Procure Complete Research Report Now:- https://www.astuteanalytica.com/industry-report/satellite-data-services-market
Key Market Aspects
The report covers several key aspects of the global keyword market, including:
Executive Summary: Summarizes vital studies, market trends, drivers, challenges, and macroscopic pointers.
Study Analysis: Covers major companies, vital market segments, the scope of products offered, and the years measured.
Company Profile: Screens each firm based on products, value, SWOT analysis, and other significant features.
Manufacture by Region: Offers data on imports and exports, sales, production, and key companies in all studied regional markets.
Segmentation Outline
By Service
Data Analytics
Land and Water State of Agriculture and Environment Analysis
Historic Agricultural and Environmental Metrics
Identify Trends from Satellite Indices
Crop Performance
Natural Resource Management
Risk Management
Image Data
Geospatial
Others
By Technology
Optical and Radar Imagery Technology
Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) Active Remote Sensing Technology
Geospatial Technology
Others
By Application
Land Satellite Data Range
Agriculture Harvest Monitoring & Field Segmentation
Security Surveillance
Infrastructure & Construction Monitoring
Mapping of Areas affected by Natural Disasters
Interferometry
Oil Pipeline Monitoring
Sea/Maritime Satellite Data Range
Prevention of Illegal Fishing
Coastal Security
Monitoring Port and Sea Traffic
Ice Monitoring and Iceberg Tracking
Natural and Man-Made Catastrophe Responses
Others
By Industry
Defense & Security
Crime Mapping
National Mapping & Topographic Agencies
Surveillance
Energy & Power
Mining And Mineral Exploration
Oil And Gas Operation
Agriculture
Environmental
Engineering & Infrastructure
Marine
Forestry
Transportation & Logistics
Insurance and Finance
Media And Entertainment
Others
By Region
North America
The U.S.
Canada
Mexico
Europe
Western Europe
The UK
Germany
France
Italy
Spain
Rest of Western Europe
Eastern Europe
Poland
Russia
Rest of Eastern Europe
Asia Pacific
China
India
Japan
Australia & New Zealand
South Korea
ASEAN
Rest of Asia Pacific
Middle East & Africa
Saudi Arabia
South Africa
UAE
Rest of MEA
South America
Argentina
Brazil
Rest of South America
Interested to Procure the Research Report? Inquire Before Buying:- https://www.astuteanalytica.com/request-sample/satellite-data-services-market
About Astute Analytica:
Astute Analytica is a global analytics and advisory company that has built a solid reputation in a short period, thanks to the tangible outcomes we have delivered to our clients. We pride ourselves in generating unparalleled, in-depth, and uncannily accurate estimates and projections for our very demanding clients spread across different verticals. We have a long list of satisfied and repeat clients from a wide spectrum including technology, healthcare, chemicals, semiconductors, FMCG, and many more. These happy customers come to us from all across the globe.
They are able to make well-calibrated decisions and leverage highly lucrative opportunities while surmounting the fierce challenges all because we analyze for them the complex business environment, segment-wise existing and emerging possibilities, technology formations, growth estimates, and even the strategic choices available. In short, a complete package. All this is possible because we have a highly qualified, competent, and experienced team of professionals comprising business analysts, economists, consultants, and technology experts. In our list of priorities, you-our patron-come at the top. You can be sure of the best cost-effective, value-added package from us, should you decide to engage with us.
Get in touch with us
Phone number: +18884296757
Email: [email protected]
Visit our website: https://www.astuteanalytica.com/
LinkedIn | Twitter | YouTube | Facebook | Pinterest
0 notes
Text
North America Airborne LiDAR Market Research By Growth Regions, Forecast 2024-2032.

The North American airborne LiDAR market is being driven by the quick adoption of LiDAR technology in a number of industries, such as forestry, infrastructure, and urban planning. The LiDAR (Light Identification and Running) technology provides high-goal 3D information that is invaluable for planning, surveying, and natural observation applications. It measures distances to the Earth's surface using laser pulses.
One of the key factors fueling the growth of the North America airborne LiDAR market is the region's robust infrastructure development initiatives. Governments and private sector entities are leveraging LiDAR technology to collect accurate topographic and terrain data for infrastructure planning, construction, and maintenance projects.
From road and railway alignment surveys to floodplain mapping, airborne LiDAR has emerged as a critical tool for enhancing the efficiency and precision of infrastructure development processes. Moreover, the forestry sector in North America is increasingly turning to airborne LiDAR for forest inventory and management purposes. LiDAR data enables forest managers to assess tree heights, canopy structures, and biomass distribution with unprecedented accuracy, leading to more informed decision-making and sustainable forest management practices. As concerns about deforestation and climate change grow, the demand for airborne LiDAR solutions in the forestry sector is expected to continue rising.
Request Free Sample Report - Receive a free sample report to preview the valuable insights and data we offer.
In addition to infrastructure and forestry applications, airborne LiDAR is also being deployed for urban planning and environmental monitoring across North America. Cities are utilizing LiDAR data to create detailed 3D models for urban development projects, transportation planning, and disaster management. Furthermore, environmental agencies are leveraging LiDAR technology to monitor changes in land cover, detect habitat disturbances, and assess the impact of natural disasters such as wildfires and hurricanes.
Many major companies providing a broad range of LiDAR services and solutions define the North American airborne LiDAR industry. Leading innovators in airborne LiDAR technology include Teledyne Optech, Leica Geosystems AG, and RIEGL Laser Measurement Systems GmbH. They are constantly creating cutting-edge sensors and software to satisfy the changing demands of clients in many industries. In the future, growing awareness of LiDAR's potential across numerous sectors, expanding need for geospatial data, and technological improvements will all fuel growth in the North American airborne LiDAR market. LiDAR technology is predicted to become more widely used as it gets more accessible and affordable, which will spur market expansion and create new avenues for cooperation and innovation.
About US
At Market Research Future (MRFR), we enable our customers to unravel the complexity of various industries through our Cooked Research Report (CRR), Half-Cooked Research Reports (HCRR), Raw Research Reports (3R), Continuous-Feed Research (CFR), and Market Research & Consulting Services. MRFR team have supreme objective to provide the optimum quality market research and intelligence services to our clients. Our market research studies by products, services, technologies, applications, end users, and market players for global, regional, and country level market segments, enable our clients to see more, know more, and do more, which help to answer all their most important questions. To stay updated with technology and work process of the industry, MRFR often plans & conducts meet with the industry experts and industrial visits for its research analyst members.
Contact us:
Market Research Future (part of Wants tats Research and Media Private Limited),
99 Hudson Street,5Th Floor, New York, New York 10013, United States of America
Sales: +1 628 258 0071 (US) +44 2035 002 764 (UK)
Email: [email protected]
0 notes
Text
Earth Observation Data Analysis: Unlocking the Potential of Satellite Imagery
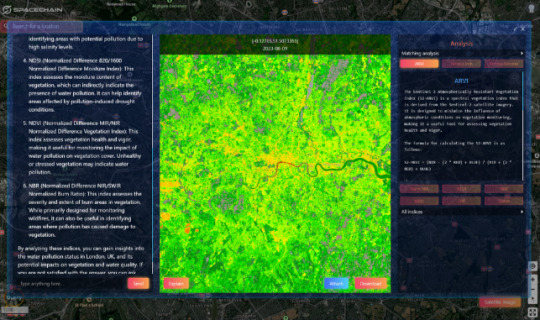
In today's digital age, advancements in technology have made it possible to gather vast amounts of data from outer space. Earth observation data, collected by satellites orbiting the planet, provides valuable insights into various aspects of our planet's environment, resources, and changes over time. Analyzing this data can lead to groundbreaking discoveries and help us better understand and address pressing global issues.
One of the key benefits of Earth observation data is its ability to capture changes in the Earth's surface over time. By analyzing satellite imagery, scientists can track deforestation, monitor changes in land use, and assess the impact of natural disasters. This data is crucial for conservation efforts, urban planning, and disaster response.
Earth observation data analysis also plays a vital role in climate research. Satellite data can help scientists monitor key climate indicators such as sea surface temperatures, ice coverage, and greenhouse gas emissions. By studying this data, researchers can improve climate models, predict future trends, and develop strategies for mitigating the effects of climate change.
In addition to environmental monitoring, Earth observation data analysis can also be used in various industries such as agriculture, mining, and infrastructure development. By analyzing satellite imagery, farmers can optimize crop yields, miners can locate mineral deposits, and urban planners can identify suitable locations for construction projects.
However, the sheer volume of Earth observation data can be overwhelming, requiring sophisticated data analysis tools and techniques. Machine learning algorithms, spatial analysis software, and cloud computing platforms are commonly used to process and interpret satellite imagery. These tools enable researchers to extract meaningful information from massive datasets and make informed decisions based on the analysis results.
As the demand for Earth observation data analysis continues to grow, there is an increasing need for skilled professionals. Data scientists, remote sensing specialists, and geospatial analysts are in high demand as organizations seek to harness the power of satellite imagery for a wide range of applications.
By leveraging the insights gained from satellite imagery, we can address environmental challenges, advance scientific research, and improve decision-making processes. As technology continues to advance, the possibilities for Earth observation data analysis are truly limitless.
Furthermore, earth observation data analysis plays a crucial role in climate change research. By analyzing satellite data, scientists can measure greenhouse gas emissions, track global temperature trends, and monitor the melting of polar ice caps. This information is essential for understanding the impacts of climate change and developing strategies to mitigate its effects.
In conclusion, earth observation data analysis is a powerful tool for studying and monitoring our planet's environment. By analyzing satellite imagery and other remote sensing data, researchers can gain valuable insights into various environmental phenomena and make informed decisions about resource management, disaster response, and climate change mitigation efforts. Governments, businesses, and organizations need to invest in earth observation data analysis to better understand and protect our planet for future generations. Contact our team to learn what next-level earth intelligence can do for your business. https://www.scsolutions.ai/
0 notes
Text
Cesium: Transforming AEC Visualisation for the Future of Architectural Design
Using cutting-edge technologies has become essential in the always-changing field of architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) to improve collaboration, expedite procedures, and provide outstanding results. The addition of Cesium to AEC viewers is one of these developments that sets the bar high and promises to revolutionize the way that architectural designs are perceived and experienced.
Recognising Cesium and Unlocking the Potential of Geographical Visualisation
Fundamentally, Cesium is a geospatial platform that gives programmers the ability to produce incredibly precise, dynamic, and immersive 3D maps and visualizations. Cesium, which was first created by Analytical Graphics, Inc. (AGI), has quickly acquired popularity in several industries, including AEC, due to its unmatched ability to represent geospatial data with unmatched accuracy and realism.
AEC and Cesium's Marriage: A Digital Match Made in Heaven
Envision a situation where clients, engineers, and architects may examine a proposed building project in unparalleled detail and realism within a virtual environment. Cesium's incorporation into AEC viewers has made this idea a tangible reality rather than just a pipe dream.
AEC experts may produce dynamic, interactive models of architectural projects that go beyond conventional static representations by utilizing Cesium's potent rendering engine and geospatial data visualization capabilities. With Cesium, users may become fully immersed in a project, whether it's for visualizing intricate construction structures, recreating real-world surroundings, or analyzing spatial relationships.
The Benefits Clearly Show Why Cesium Is Important for AEC Visualisation
Enhanced Visualisation: With Cesium, architects, engineers, and contractors can see their work in rich, detailed three-dimensional settings, giving stakeholders a clear picture of the spatial linkages and design intent.
Enhanced Collaboration: Teams can work together more efficiently, share insights, and make decisions in real time, no matter where they are, by centralizing project data via Cesium-powered AEC viewers.
Simplified Workflow: Cesium's strong tools and user-friendly interface simplify the design and review process, cutting down on mistakes, streamlining procedures, and quickening project completion dates.
Client Involvement: Cesium enables customers to engage in immersive interactions with architectural ideas, promoting more buy-in and confidence in the project's success.
Case Study: Utilising Cesium
Imagine a major urban development project where a variety of parties must work together to design and implement the project, such as architects, urban planners, and city authorities. Cesium can be integrated into the project's AEC viewer, allowing the team to:
Consider the proposed development of the topography, the built environment, and the surrounding cityscape.
Make use of sophisticated simulations and visualizations to examine how the project will affect pedestrian access, traffic flow, and environmental variables.
A highly immersive and interactive format should be used to present the design to community stakeholders and local officials, allowing for real-time feedback and input.
Learn about the full range of Cesium services offered by nCircle Tech, which provides AEC professionals with state-of-the-art geospatial visualization solutions. Realize Cesium's full potential for streamlined project workflows and engaging architectural experiences. See how our experience can help you realize your vision.
Towards the Future: Cesium-Based AEC Visualisation
The use of technologies such as Cesium in architectural design and construction is only going to grow in the future. The possibilities are endless, ranging from augmented reality (AR) experiences that let users explore virtual models on-site to real-time collaboration tools that link teams geographically.
0 notes
Text
How Remote Sensing and GIS in India Are Shaping the Future of Technology and Environment
Remote sensing and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are two technologies that have dramatically changed how we understand and interact with our planet. In India, these technologies are not just advancing; they're significantly shaping the future of technology and the environment. This blog explores how remote sensing and GIS are being used in India, their impact, and the role of education, particularly at the Symbiosis Institute of Geoinformatics (SIG), in promoting these fields.

The Basics of Remote Sensing and GIS
Remote sensing is the science of obtaining information about objects or areas from a distance, typically from aircraft or satellites. Conversely, GIS is a system designed to capture, store, manipulate, analyze, manage, and present spatial or geographic data. Together, they offer powerful tools for monitoring and managing the Earth's resources and environment.
Applications in India
India has embraced remote sensing and GIS across various sectors, including agriculture, forestry, urban planning, disaster management, and environmental protection. These technologies play a crucial role in crop monitoring, forest surveys, urban expansion studies, flood and drought management, and assessing the impacts of climate change. By providing accurate and timely data, they help policymakers make informed decisions.
Impact on Technology and Environment
The impact of remote sensing and GIS on technology and the environment in India is profound. Technologically, they have led to the development of sophisticated software and tools that can analyze vast amounts of spatial data. Environmentally, they offer unmatched capabilities in tracking changes, assessing damage, and planning for conservation efforts. For instance, remote sensing data helps identify polluted areas and track the health of rivers and forests over time, enabling targeted conservation actions.
The Role of Education
Education plays a pivotal role in the growth and development of remote sensing and GIS technologies. Recognizing this, numerous institutions across India offer courses designed to equip students with the necessary skills and knowledge. These courses range from short-term certifications to full-fledged degree programs, including GIS courses in India and remote sensing and GIS courses.
Symbiosis Institute of Geoinformatics (SIG)
At the forefront of geospatial education in India is the Symbiosis Institute of Geoinformatics (SIG), located in Pune. SIG offers a comprehensive range of programs tailored to the needs of this rapidly evolving field. Among these programs are the PG diploma in remote sensing and GIS, the remote sensing and GIS course, and the GIS remote sensing course. These programs are designed to meet the industry's demand for skilled professionals leveraging GIS and remote sensing technologies to address real-world challenges.
Why Choose SIG?
Choosing to study at SIG comes with numerous advantages. First, the institute provides access to state-of-the-art facilities and software, giving students hands-on experience with the tools and technologies they will use in their careers. Second, SIG's curriculum is industry-aligned, ensuring that graduates are not just academically proficient but also ready to meet the challenges of the professional world. Finally, SIG boasts a strong alumni network and industry connections, offering students valuable opportunities for internships and placements.
The Future of Remote Sensing and GIS in India
The future of remote sensing and GIS in India looks bright. As the country continues to develop and face environmental challenges, the demand for advanced geospatial technologies and skilled professionals is set to grow. Institutions like SIG are crucial in meeting this demand, training the next generation of experts who will continue to shape the future of technology and the environment in India.
Conclusion
Remote sensing and GIS are not just tools for observing the Earth; they are instruments for change, offering new ways to tackle technological and environmental challenges. India's commitment to these technologies, supported by institutions like the Symbiosis Institute of Geoinformatics, is paving the way for a future where informed decisions lead to sustainable development and environmental conservation. As we continue to harness the power of remote sensing and GIS, our planet's possibilities for innovation and protection are limitless.
#remote sensing and gis course#gis courses in india#gis remote sensing course#pg diploma in remote sensing and gis
0 notes
Text

In the world of geospatial analysis, a comprehensive process is undertaken by surveyors Shellharbour to collect, analyse, and interpret data about the Earth's surface. This technique, crucial for a myriad of applications ranging from environmental studies to urban planning, involves a series of intricate and fascinating steps.
0 notes
Text
Satellite Data Services Market 2024 — By Growth Rat, Share, Analysis, Outlook and Forecast To 2034
The Satellite Data Services market report offered by Reports Intellect is meant to serve as a helpful means to evaluate the market together with an exhaustive scrutiny and crystal-clear statistics linked to this market. The report consists of the drivers and restraints of the Satellite Data Services Market accompanied by their impact on the demand over the forecast period. Additionally, the report includes the study of prospects available in the market on a global level. With tables and figures helping evaluate the Global Satellite Data Services market, this research offers key statistics on the state of the industry and is a beneficial source of guidance and direction for companies and entities interested in the market. This report comes along with an additional Excel data-sheet suite taking quantitative data from all numeric forecasts offered in the study.
Get Sample PDF Brochure @ https://www.reportsintellect.com/sample-request/2515115
Key players offered in the market: Airbus SE Harris Geospatial Solutions DigitalGlobe Satellite Imaging Corporation Planet Labs ICEYE URSA Space Systems SATPALDA Geospatial Services Earth-i
Additionally, it takes account of the prominent players of the Satellite Data Services market with insights including market share, product specifications, key strategies, contact details, and company profiles. Similarly, the report involves the market computed CAGR of the market created on previous records regarding the market and existing market trends accompanied by future developments. It also divulges the future impact of enforcing regulations and policies on the expansion of the Satellite Data Services Market.
Scope and Segmentation of the Satellite Data Services Market
The estimates for all segments including type and application/end-user have been provided on a regional basis for the forecast period from 2024 to 2034. We have applied a mix of bottom-up and top-down methods for market estimation, analyzing the crucial regional markets, dynamics, and trends for numerous applications. Moreover, the fastest & slowest growing market segments are pointed out in the study to give out significant insights into each core element of the market.
Satellite Data Services Market Type Coverage: - Image Data Data Analytics
Satellite Data Services Market Application Coverage: - Energy & Power Engineering & Infrastructure Environmental Agriculture Maritime Others
Regional Analysis:
North America Country (United States, Canada) South America Asia Country (China, Japan, India, Korea) Europe Country (Germany, UK, France, Italy) Other Countries (Middle East, Africa, GCC)
Also, Get an updated forecast from 2024 to 2034.
Discount PDF Brochure @ https://www.reportsintellect.com/discount-request/2515115
The comprehensive report provides:
· Complete assessment of all opportunities and threats in the global market.
· Satellite Data Services Market recent advancements and major events.
· A thorough study of business policies for the growth of the Satellite Data Services Market leading players.
· Concluding study about the growth plot of Satellite Data Services Market for upcoming years.
· Detailed understanding of Satellite Data Services Market particular drivers, restraints, and major micro markets.
· Favorable impression inside vital technological and market latest trends hitting the Satellite Data Services Market.
Reasons to Purchase Satellite Data Services Market Research Report
· Develop a competitive approach based on the competitive landscape
· Build business strategy by identifying the high growth and attractive Satellite Data Services market classifications
· Identify potential business partners, gaining targets and business buyers
· Design financial investment policies based on estimated high potential segments
· Prepare management and tactical presentations using the Satellite Data Services market data
· Plan for new product promotion and portfolio in advance
Covid-19 Impact Analysis: Our research analysts are highly focused on the Satellite Data Services Market covid-19 impact analysis. A whole chapter is dedicated to the covid-19 outbreak so that our clients get whole and sole details about the market ups & downs. With the help of our report the clients will get vast statistics as to when and where should they invest in the industry.
About Us: Reports Intellect is your one-stop solution for everything related to market research and market intelligence. We understand the importance of market intelligence and its need in today’s competitive world.
Our professional team works hard to fetch the most authentic research reports backed with impeccable data figures which guarantee outstanding results every time for you.
Contact Us: [email protected] Phone No: + 1–706–996–2486 US Address: 225 Peachtree Street NE, Suite 400, Atlanta, GA 30303
#Satellite Data Services Market#Satellite Data Services#Satellite Data Services Trends#Satellite Data Services Growth
0 notes
Text
Scientists map biodiversity changes in the world's forests
31.05.24 - A group of EPFL and ETH Zurich scientists have mapped the biodiversity in forests worldwide. Their data, when combined with climate projections, reveal trends that could support ecosystem conservation and restoration efforts. According to the latest figures from the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, forests cover just over 4 billion hectares of the Earth’s surface, or one-third of its total land.* The benefits of forests are numerous: they provide raw materials, act as carbon sinks, help regulate the climate and protect the planet, provide a home for biodiversity, and serve as a source of well-being. Yet the latest survey suggests that around 31% of tree species are threatened with extinction.** Efforts are under way to build the resilience of forest ecosystems. But which parts of the world are experiencing the biggest changes? Which regions should be prioritized for protection? Which tree species are most resilient to the local impacts of climate change? Scientists at EPFL have teamed up with colleagues at ETH Zurich to answer these questions and more. Their findings, published today in Nature Communications, provide key insights for policymakers and planners, helping to guide sustainable forest management practices around the world. This is the largest study of its kind in terms of scale and number of species. Our findings provide an overview of forest biodiversity across the entire planet, not just in regions that are already well-documented. Devis Tuia, professor at Environmental Computational Science and Earth Observation Laboratory Detailed distribution maps of over 10,000 tree species For this study, co-led by EPFL’s Environmental Computational Science and Earth Observation Laboratory (ECEO) and two research groups at ETH Zurich, scientists combined almost 26 million tree observations with geospatial data on climate and soil conditions as well as geographical dispersion constraints, which contain tree species within their reported native ranges. “We wanted to avoid prediction errors, such as species that would be predicted to be found in a given location simply because the climate was suitable although they are invasive,” says Nina van Tiel, a PhD student at ECEO. For their sample, the team selected the 10,590 most widespread of the 73,000 known tree species on the planet, excluding rarer ones at this stage. “We included trees with 90 or more recorded observations – the threshold above which our predictive models become sufficiently robust,” explains van Tiel. “This is the largest study of its kind in terms of scale and number of species,” says Devis Tuia, an associate professor at ECEO. “Our findings provide an overview of forest biodiversity across the entire planet, not just in regions that are already well-documented.” The scientists also used their models to predict species distribution under different climate and temperature scenarios through to 2100. “Predicting the future is always fraught with uncertainty, but the sheer number of species we included in our models gives us an idea of how biodiversity will shift in response to climate change,” adds Tuia. The data, compiled in map form, show the incredible diversity of forest ecosystems worldwide. The lines on the maps demarcate species with similar characteristics and genetic relationships. Each site is associated with a unique set of tree species and lineages – a result of historical and environmental factors. “The overall findings are in line with our expectations,” says Loïc Pellissier, an associate professor at ETH Zurich’s Department of Environmental Systems Science. Using the maps, scientists can also calculate the area of habitat of different species around the world. “As expected, species in boreal forests are distributed over large areas,” explains Pellissier. “But our models also show that certain tropical trees have very wide ranges, which relates to the findings of hyperdominant species… http://actu.epfl.ch/news/scientists-map-biodiversity-changes-in-the-world-s (Source of the original content)
0 notes
Text
Satellite Data Services Market Size Share Forecast (2024-2034)
The Satellite Data Services market report offered by Reports Intellect is meant to serve as a helpful means to evaluate the market together with an exhaustive scrutiny and crystal-clear statistics linked to this market. The report consists of the drivers and restraints of the Satellite Data Services Market accompanied by their impact on the demand over the forecast period. Additionally, the report includes the study of prospects available in the market on a global level. With tables and figures helping evaluate the Global Satellite Data Services market, this research offers key statistics on the state of the industry and is a beneficial source of guidance and direction for companies and entities interested in the market. This report comes along with an additional Excel data-sheet suite taking quantitative data from all numeric forecasts offered in the study.
Get Sample PDF Brochure @ https://www.reportsintellect.com/sample-request/2515115
Key players offered in the market: Airbus SE Harris Geospatial Solutions DigitalGlobe Satellite Imaging Corporation Planet Labs ICEYE URSA Space Systems SATPALDA Geospatial Services Earth-i Land Info Worldwide Mapping
Additionally, it takes account of the prominent players of the Satellite Data Services market with insights including market share, product specifications, key strategies, contact details, and company profiles. Similarly, the report involves the market computed CAGR of the market created on previous records regarding the market and existing market trends accompanied by future developments. It also divulges the future impact of enforcing regulations and policies on the expansion of the Satellite Data Services Market.
Scope and Segmentation of the Satellite Data Services Market
The estimates for all segments including type and application/end-user have been provided on a regional basis for the forecast period from 2024 to 2034. We have applied a mix of bottom-up and top-down methods for market estimation, analyzing the crucial regional markets, dynamics, and trends for numerous applications. Moreover, the fastest & slowest growing market segments are pointed out in the study to give out significant insights into each core element of the market.
Satellite Data Services Market Type Coverage: - Image Data Data Analytics
Satellite Data Services Market Application Coverage: - Energy & Power Engineering & Infrastructure Environmental Agriculture Maritime Others
Regional Analysis:
North America Country (United States, Canada) South America Asia Country (China, Japan, India, Korea) Europe Country (Germany, UK, France, Italy) Other Countries (Middle East, Africa, GCC)
Also, Get an updated forecast from 2024 to 2034.
Discount PDF Brochure @ https://www.reportsintellect.com/discount-request/2515115
The comprehensive report provides:
Complete assessment of all opportunities and threats in the global market.
Satellite Data Services Market recent advancements and major events.
A thorough study of business policies for the growth of the Satellite Data Services Market leading players.
Concluding study about the growth plot of Satellite Data Services Market for upcoming years.
Detailed understanding of Satellite Data Services Market particular drivers, restraints, and major micro markets.
Favorable impression inside vital technological and market latest trends hitting the Satellite Data Services Market.
Reasons to Purchase Satellite Data Services Market Research Report
Develop a competitive approach based on the competitive landscape
Build business strategy by identifying the high growth and attractive Satellite Data Services market classifications
Identify potential business partners, gaining targets and business buyers
Design financial investment policies based on estimated high potential segments
Prepare management and tactical presentations using the Satellite Data Services market data
Plan for new product promotion and portfolio in advance
Covid-19 Impact Analysis: Our research analysts are highly focused on the Satellite Data Services Market covid-19 impact analysis. A whole chapter is dedicated to the covid-19 outbreak so that our clients get whole and sole details about the market ups & downs. With the help of our report the clients will get vast statistics as to when and where should they invest in the industry.
Contact Us: [email protected] Phone No: + 1-706-996-2486 US Address: 225 Peachtree Street NE, Suite 400, Atlanta, GA 30303
#Satellite Data Services Market#Satellite Data Services Market trends#Satellite Data Services Market future#Satellite Data Services Market size#Satellite Data Services Market growth#Satellite Data Services Market forecast#Satellite Data Services Market analysis
0 notes