#Energy Sector Trends
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Exxon Mobil Corporation: Shaping the Energy Landscape with Innovation and Sustainability
Exxon Mobil Corporation, a global energy conglomerate, ranks among the world’s leading publicly traded energy companies. Renowned for its extensive presence in oil, gas, and petrochemical industries, Exxon’s operations span exploration, production, refining, and distribution. With a legacy dating back over a century, the company is recognized for its technological innovations and substantial…

View On WordPress
#Clean Energy Solutions#Corporate Legacy#Corporate Sustainability#Economic Impact#Energy Diversification#Energy Exploration#Energy Industry#Energy Innovation#Energy Sector Trends#Energy Transition#Environmental Concerns#Environmental Impact#Environmental Responsibility#Exxon Mobil Corporation#Fossil Fuels#Global Energy Conglomerate#Global Market Influence#Industry Leadership#Oil and Gas#Petrochemicals#Publicly Traded Companies#Refining Operations#Renewable Energy#Sustainability Initiatives#Technological Innovation
0 notes
Text
Market Focus: Energy sector likely to benefit from sharp oil price gains
Market sentiment is expected to improve following US CPI data meeting expectations and strong earnings reports from major banks. This optimism may drive a rebound in the FBM KLCI, supported by bargain hunting in undervalued stocks. Investors are also closely monitoring China’s Q4 2024 GDP and industrial production data, expected tomorrow. Sector Focus: energy • Energy Sector: Likely to benefit…
0 notes
Text
Seamless Intranet Applications for Singapore’s Shipping, Oil, and Gas Industries
In the dynamic landscape of Singapore’s shipping, oil, and gas sectors, seamless communication and efficient operations are paramount. As industries that thrive on precision, speed, and collaboration, leveraging cutting-edge intranet applications can redefine how organisations in these sectors operate, boosting productivity and resilience.

The Modern Challenges in Shipping, Oil, and Gas
Industries like shipping and oil and gas face a myriad of challenges:
Complex Operations: Managing global fleets, multi-national crews, and intricate logistics demands streamlined coordination.
Regulatory Compliance: Navigating stringent international and local regulations requires reliable and up-to-date data management.
Data Silos: Disconnected systems lead to inefficiencies, delayed decision-making, and resource wastage.
Cybersecurity Threats: The rise of digital operations brings increased vulnerability to cyberattacks.
Seamless intranet solutions tackle these challenges head-on by providing a unified digital framework that connects people, processes, and systems.
Key Features of Seamless Intranet Applications
Centralised Information Hub Modern intranet platforms act as a one-stop solution for all organisational data. Whether it’s vessel maintenance logs, crew schedules, or safety protocols, employees can access critical information in real-time, reducing delays and errors.
Enhanced Collaboration With features like instant messaging, video conferencing, and project management tools, teams across geographies can collaborate effectively. This is particularly crucial in industries where onshore and offshore teams need to synchronise operations seamlessly.
Advanced Security Protocols Industry-grade intranet applications come equipped with robust encryption, two-factor authentication, and intrusion detection systems to safeguard sensitive data from cyber threats.
Integration with Industry-Specific Tools Intranet systems can integrate with tools like enterprise resource planning (ERP) software, compliance management platforms, and IoT-enabled devices, offering a cohesive operational experience tailored to sector-specific needs.
Scalability and Customisation Scalable solutions ensure that the intranet grows with your business, adapting to new technologies and expanding requirements. Custom dashboards allow businesses to prioritise what matters most, from supply chain visibility to environmental performance metrics.
Benefits for Singapore’s Shipping, Oil, and Gas Industries
Improved Operational Efficiency: Minimise downtime with faster communication and streamlined workflows.
Regulatory Compliance: Stay ahead of compliance requirements with automated updates and centralised documentation.
Cost Reduction: Eliminate redundancies and optimise resource allocation through data-driven insights.
Enhanced Employee Engagement: Empower teams with user-friendly tools and access to training modules, improving morale and performance.
Sustainability Goals: Intranets that integrate with green logistics tools help businesses track and achieve environmental objectives.
Real-World Applications
Singapore’s position as a global maritime and energy hub makes it an ideal testing ground for innovative intranet solutions. For example:
Shipping: Streamlined fleet management with real-time data access ensures on-schedule deliveries and reduced operational costs.
Oil and Gas: Enhanced safety protocols through connected systems help reduce risks in high-stakes environments like offshore drilling platforms.
Why Invest in Seamless Intranet Applications?
In a world where digital transformation is no longer optional, adopting seamless intranet applications is a strategic necessity. These tools not only future-proof your business but also provide a competitive edge by fostering agility, collaboration, and innovation.
Conclusion
For Singapore’s shipping, oil, and gas industries, seamless intranet applications are more than just a technological upgrade—they’re a business imperative. By addressing core challenges, driving efficiency, and enhancing security, these solutions pave the way for sustained growth in an increasingly digital world.
Unlock the potential of your organisation with tailored intranet solutions designed to meet the unique demands of your industry. Embrace the change today, and lead your business into a connected, collaborative future.
#IoT-enabled intranet applications#Maritime digital transformation trends 2024#Advanced intranet for regulatory compliance#AI-powered intranet for shipping#Green logistics and intranet integration#How intranet applications improve shipping operations#Best intranet tools for oil and gas companies in Singapore#Seamless communication for shipping and maritime industries#Industry-specific intranet solutions for shipping and energy sectors#Streamlined workflows with intranet platforms in oil and gas#Seamless intranet applications#Intranet solutions for shipping industry#Intranet tools for oil and gas#Singapore shipping technology#Oil and gas industry intranet
0 notes
Text
Market Overview: Mixed Movements Amidst AI Concerns and Earnings Reports

In a turbulent day for U.S. stock markets, the Dow Jones Industrial Average declined by 234 points, or 0.60%, while the S&P 500 and NASDAQ Composite also faced setbacks, falling by 0.7% and 1%, respectively. The downturn was largely driven by mounting concerns over the slowing momentum in artificial intelligence (AI) technologies, which prompted a sell-off in semiconductor stocks.
AI Concerns Weigh on Chip Stocks
The tech sector, particularly chip stocks, experienced significant pressure. Leading the decline were NVIDIA Corporation (NASDAQ: NVDA), Broadcom Inc (NASDAQ: AVGO), and Wolfspeed Inc (NYSE: WOLF), all of which saw their share prices drop by approximately 2%. The apprehension surrounding AI's slowing progress has rattled investors, leading to a broader sell-off in the semiconductor industry.
Energy Sector Shows Resilience
Amidst the broader market decline, the energy sector displayed notable strength. Targa Resources Inc (NYSE: TRGP), Williams Companies Inc (NYSE: WMB), and Devon Energy Corporation (NYSE: DVN) were among the top gainers. Devon Energy, in particular, saw its stock rise following quarterly results that exceeded Wall Street's expectations. This positive performance highlights the sector's resilience despite the overall market volatility.
Major Stock Movements
Walt Disney (NYSE: DIS): Disney's stock fell sharply by 4%, reflecting ongoing concerns about the company’s performance and future prospects.
Shopify (NYSE: SHOP): Contrasting the general trend, Shopify's shares soared nearly 18%, driven by positive developments and investor optimism about its growth potential.
Airbnb (NASDAQ: ABNB): On the other end of the spectrum, Airbnb's stock dropped 13%, influenced by recent market challenges and potentially disappointing financial metrics.
S&P 500 Earnings Resilience
Despite the recent negative price action and growing recession fears, the earnings resilience of the S&P 500 remains a key highlight. The index's earnings have shown a level of robustness, which could offer some reassurance to investors amidst the current market volatility.
In summary, the market's recent performance underscores the complexity of current economic conditions. While AI concerns and specific sector movements have contributed to market declines, there are areas of strength and resilience, particularly in the energy sector and select stocks like Shopify. As always, investors should stay informed and consider these factors when making decisions.
#Stock Market Update#Dow Jones Decline#S&P 500 Performance#NASDAQ Drop#AI Technology Impact#Semiconductor Stocks#NVIDIA Stock Analysis#Broadcom Stock Trends#Wolfspeed Performance#Energy Sector Strength#Targa Resources Gains#Williams Companies Stock#Devon Energy Results#Walt Disney Stock Drop#Shopify Share Surge#Airbnb Stock Decline#S&P 500 Earnings Resilience#Market Volatility#Tech Sector Pressure#Investing in Turbulent Markets
0 notes
Text
Industrial Miniature Circuit Breakers Market Geographical Expansion & Analysis Growth Development, Status, Recorded during 2017 to 2032
MCB and MCCB Market Projected to Reach USD 12.96 billion, at a 7.5% CAGR by 2030
Trends:
Several trends are shaping the industrial MCBs market:
• Growing IoT and automation adoption: Reliable circuit protection devices are needed since IoT and automation technologies are increasingly being used in industrial operations. Industrial MCBs are crucial parts of automated systems because they protect against electrical problems and improve the general security and effectiveness of industrial processes.
• There is a demand for intelligent and connected solutions, and industrial MCBs are evolving to include these features. This makes it possible to remotely monitor, diagnose, and operate electrical systems, which increases the effectiveness of maintenance and troubleshooting. The demand for intelligent industrial MCBs is being driven by the movement towards smart manufacturing and Industry 4.0.
Key Factors:
Several key factors are influencing the growth of the industrial MCBs market:
• Industrialization and infrastructure development: The need for industrial MCBs is being driven by continuing industrialization and infrastructure development initiatives around the world. To protect their electrical systems and equipment, industries like manufacturing, construction, oil & gas, and power generation need trustworthy circuit protection solutions.
• Safety and compliance rules: Reliable circuit protection devices are required in industrial contexts due to strict safety regulations and standards. Industrial MCBs offer an essential layer of defence against electrical problems, guaranteeing adherence to safety regulations and preventing accidents.
• Growth of electrical infrastructure: The need for industrial MCBs is driven by the growth of the electrical infrastructure, which includes substations, distribution networks, and data centres. Within these infrastructure projects, these circuit breakers are employed to protect and regulate electrical circuits.
In conclusion, developments like automation, IoT integration, energy efficiency, and the adoption of renewable energy sources have an impact on the market for industrial MCBs. The market's expansion is primarily being driven by industrialisation, safety requirements, the expansion of the electrical infrastructure, and the retrofit/replacement market. In order to satisfy the changing needs of industrial customers, manufacturers and suppliers should align their product lines with these trends and considerations.
Referrals to our Stringent datalytics company, trade journals, and websites that focus on market reports are encouraged. These sources frequently include thorough research, market trends, growth projections, competition analysis, and other insightful information about this market.
You can investigate the availability of particular reports linked to this market by going to our website or getting in touch with us directly. These reports frequently need to be purchased or subscribed to, but we provide comprehensive and in-depth information that can be valuable for businesses, investors, and individuals interested in this market.
“Remember to look for recent reports to ensure you have the most current and relevant information.”
Click Here, To Get Free Sample Report: https://stringentdatalytics.com/sample-request/industrial-miniature-circuit-breakers-market/10120/
Market Segmentations:
Global Industrial Miniature Circuit Breakers Market: By Company
• Kevilton Electrical Products
• Elmark
• Britec Electric
• R. STAHL EX-PROOF
• Siemens
• ABB
• Camsco Electric
• Iskra
• Dongguan Keiyip Electrical Equipment
• Schneider Electric
• China Suntree Electric
• Wenzhou korlen electric appliances
• Legrand
• Finolex
• Hager
• Eaton
Global Industrial Miniature Circuit Breakers Market: By Type
• B-MCB
• C-MCB
• D-MCB
Global Industrial Miniature Circuit Breakers Market: By Application
• Achitechive
• Power Industry
• Other
Global Industrial Miniature Circuit Breakers Market: Regional Analysis
The regional analysis of the global Industrial Miniature Circuit Breakers market provides insights into the market's performance across different regions of the world. The analysis is based on recent and future trends and includes market forecast for the prediction period. The countries covered in the regional analysis of the Industrial Miniature Circuit Breakers market report are as follows:
North America: The North America region includes the U.S., Canada, and Mexico. The U.S. is the largest market for Industrial Miniature Circuit Breakers in this region, followed by Canada and Mexico. The market growth in this region is primarily driven by the presence of key market players and the increasing demand for the product.
Europe: The Europe region includes Germany, France, U.K., Russia, Italy, Spain, Turkey, Netherlands, Switzerland, Belgium, and Rest of Europe. Germany is the largest market for Industrial Miniature Circuit Breakers in this region, followed by the U.K. and France. The market growth in this region is driven by the increasing demand for the product in the automotive and aerospace sectors.
Asia-Pacific: The Asia-Pacific region includes Singapore, Malaysia, Australia, Thailand, Indonesia, Philippines, China, Japan, India, South Korea, and Rest of Asia-Pacific. China is the largest market for Industrial Miniature Circuit Breakers in this region, followed by Japan and India. The market growth in this region is driven by the increasing adoption of the product in various end-use industries, such as automotive, aerospace, and construction.
Middle East and Africa: The Middle East and Africa region includes Saudi Arabia, U.A.E, South Africa, Egypt, Israel, and Rest of Middle East and Africa. The market growth in this region is driven by the increasing demand for the product in the aerospace and defense sectors.
South America: The South America region includes Argentina, Brazil, and Rest of South America. Brazil is the largest market for Industrial Miniature Circuit Breakers in this region, followed by Argentina. The market growth in this region is primarily driven by the increasing demand for the product in the automotive sector.
Visit Report Page for More Details: https://stringentdatalytics.com/reports/explosion-proof-circuit-breaker-market/10057/
Reasons to Purchase Industrial Miniature Circuit Breakers Market Report:
• To gain insights into market trends and dynamics: this reports provide valuable insights into industry trends and dynamics, including market size, growth rates, and key drivers and challenges.
• To identify key players and competitors: this research reports can help businesses identify key players and competitors in their industry, including their market share, strategies, and strengths and weaknesses.
• To understand consumer behavior: this research reports can provide valuable insights into consumer behavior, including their preferences, purchasing habits, and demographics.
• To evaluate market opportunities: this research reports can help businesses evaluate market opportunities, including potential new products or services, new markets, and emerging trends.• To evaluate market opportunities: this research reports can help businesses evaluate market opportunities, including potential new products or services, new markets, and emerging trends.
About US:
Stringent Datalytics offers both custom and syndicated market research reports. Custom market research reports are tailored to a specific client's needs and requirements. These reports provide unique insights into a particular industry or market segment and can help businesses make informed decisions about their strategies and operations.
Syndicated market research reports, on the other hand, are pre-existing reports that are available for purchase by multiple clients. These reports are often produced on a regular basis, such as annually or quarterly, and cover a broad range of industries and market segments. Syndicated reports provide clients with insights into industry trends, market sizes, and competitive landscapes. By offering both custom and syndicated reports, Stringent Datalytics can provide clients with a range of market research solutions that can be customized to their specific needs
Contact US:
Stringent Datalytics
Contact No - +1 346 666 6655
Email Id - [email protected]
Web - https://stringentdatalytics.com/
#Market Geographical Expansion & Analysis Growth Development#Status#Recorded during 2017 to 2032#Industrial Miniature Circuit Breakers#Circuit Protection#Electrical Safety#Industrial Automation#Energy Management#Electrical Distribution#Manufacturing Sector#Industrial Equipment#Industry Trends#Market Analysis#Electrical Engineering#Electrical Components#Market Dynamics#Industry Insights#Industrial Control#Electrical Systems#Power Distribution#Equipment Protection#Industrial Infrastructure#Market Forecast#Miniature Circuit Breaker Technologies#Electrical Industry#Safety Standards#Industrial Electronics#Circuit Breaker Market#Industrial Electrical Systems#Market Growth
0 notes
Text
The Green Revolution: Exploring the Disruptive Technologies Shaping the Future of the Green Economy

In today's rapidly evolving world, the urgency to address climate change and environmental degradation has propelled the concept of a green economy to the forefront of global discussions. As businesses, governments, and individuals recognize the need for sustainable solutions, disruptive technologies have emerged as key drivers of change. These groundbreaking innovations are reshaping traditional industries, revolutionizing energy production and consumption, transforming resource management, and paving the way for a more sustainable future.
The green economy encompasses a wide range of sectors, including renewable energy, waste management, sustainable agriculture, and green transportation. Within each of these sectors, disruptive technologies are playing a pivotal role in disrupting existing practices and opening up new possibilities.
One of the most significant areas where disruptive technologies are making an impact is renewable energy. Solar power, wind energy, and hydropower have long been recognized as viable sources of clean energy. However, recent advancements have propelled these technologies to new heights of efficiency and cost-effectiveness. The development of highly efficient solar panels, innovative wind turbine designs, and sophisticated energy storage systems has significantly enhanced the feasibility of renewable energy sources. Moreover, emerging technologies such as tidal and geothermal energy hold great promise in harnessing previously untapped sources of renewable power.
The intermittent nature of renewable energy sources has traditionally been a challenge for their widespread adoption. However, disruptive technologies are addressing this limitation through energy storage solutions. Advancements in energy storage technologies, such as lithium-ion batteries, flow batteries, and hydrogen storage systems, are unlocking the full potential of renewables. These technologies not only enhance grid stability but also enable the integration of renewable energy into existing infrastructure, reducing dependence on fossil fuels and accelerating the transition to a greener energy mix.
The transformation of energy management and distribution is another area where disruptive technologies are reshaping the green economy. Smart grids equipped with advanced sensors, communication networks, and automation allow for real-time monitoring and control of electricity supply and demand. By optimizing energy distribution, reducing transmission losses, and integrating decentralized renewable energy sources, smart grids enhance the overall efficiency and reliability of energy systems. Furthermore, the emergence of blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize the energy sector by enabling peer-to-peer energy trading, ensuring transparency and trust in transactions, and empowering energy consumers to actively participate in the market.
In the realm of sustainable agriculture, disruptive technologies are revolutionizing the way we grow food. Vertical farming, hydroponics, and aeroponics are transforming traditional farming methods, making agriculture more resource-efficient and less dependent on large land areas. These innovative approaches enable year-round crop cultivation, minimize water usage, and maximize productivity. Additionally, precision agriculture techniques, such as remote sensing, drones, and AI-powered analytics, optimize resource allocation, reduce environmental impact, and enhance overall crop yield.
The concept of a circular economy, where resources are used efficiently, waste is minimized, and materials are continuously recycled, is gaining momentum with the help of disruptive technologies. Advanced recycling technologies, including chemical recycling and waste-to-energy conversion, are enabling the recovery of valuable resources from waste streams. This not only reduces the strain on natural resources but also mitigates environmental pollution. Furthermore, innovations like 3D printing, which utilizes recycled materials, are revolutionizing traditional manufacturing practices, reducing waste generation, and promoting decentralized production.
Transportation, a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, is also undergoing a transformation driven by disruptive technologies. Electric vehicles (EVs) have gained significant traction, thanks to advancements in battery technology, increased range, and the establishment of robust charging infrastructure. The rise of autonomous vehicles and shared mobility services is revolutionizing urban transportation, reducing congestion, and optimizing energy consumption. Furthermore, the development of biofuels and hydrogen fuel cells holds promise for greener alternatives to traditional fossil fuel-based transportation.
Disruptive technologies are catalyzing a profound transformation within the green economy. From renewable energy and energy storage to sustainable agriculture, waste management, and green transportation, these innovative solutions are reshaping industries, driving economic growth, and addressing pressing global challenges. Embracing these technologies is not only an opportunity but a necessity as we strive to create a more sustainable and resilient future. By investing in and harnessing the transformative potential of disruptive technologies, we can accelerate the transition towards a greener, more sustainable world for generations to come.
The Rise of Disruptive Technology in the Green Economy
The green economy encompasses a wide range of sectors, including renewable energy, waste management, sustainable agriculture, and green transportation. Within each of these sectors, disruptive technologies are emerging as catalysts for change. These technologies are characterized by their ability to create significant shifts in existing markets, transform business models, and disrupt traditional practices. Their impact extends beyond economic considerations to encompass environmental sustainability and social progress.
Renewable Energy: Paving the Way for a Sustainable Future
Renewable energy is one of the key areas where disruptive technologies are reshaping the green economy. Solar power, wind energy, and hydropower have long been established sources of renewable energy. However, recent advancements in solar panel efficiency, wind turbine design, and energy storage systems have dramatically improved the feasibility and cost-effectiveness of these technologies. Additionally, emerging technologies like tidal and geothermal energy are showing promise in harnessing previously untapped sources of renewable power.
Energy Storage: Unlocking the Full Potential of Renewables
The intermittent nature of renewable energy sources poses a challenge to their widespread adoption. However, energy storage technologies are rapidly evolving to address this limitation. Innovations such as lithium-ion batteries, flow batteries, and hydrogen storage systems are paving the way for efficient and scalable energy storage solutions. These technologies not only enhance grid stability but also facilitate the integration of renewable energy into existing infrastructure, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and promoting a greener future.
Smart Grids and Energy Management: Revolutionizing the Power Sector
Disruptive technologies are also revolutionizing the way energy is managed and distributed. Smart grid systems, equipped with advanced sensors, communication networks, and automation, enable real-time monitoring and control of electricity supply and demand. This enables more efficient energy distribution, reduces transmission losses, and enables effective integration of decentralized renewable energy sources. Furthermore, the advent of blockchain technology has the potential to transform the energy sector by enabling peer-to-peer energy trading and ensuring transparency and trust in transactions.
Sustainable Agriculture: Growing Food for the Future
The agricultural sector is undergoing a transformation with the help of disruptive technologies. Vertical farming, hydroponics, and aeroponics are revolutionizing the way we grow crops, making agriculture more resource-efficient and less dependent on traditional farming methods. These technologies allow for year-round crop cultivation, reduce water usage, and eliminate the need for large land areas. Moreover, precision agriculture techniques, such as remote sensing, drones, and AI-powered analytics, optimize resource allocation, enhance productivity, and minimize environmental impact.
Circular Economy and Waste Management: Closing the Loop
Disruptive technologies play a pivotal role in promoting a circular economy, where resources are used efficiently, waste is minimized, and materials are continuously recycled. Advanced recycling technologies, such as chemical recycling and waste-to-energy conversion, are enabling the recovery of valuable resources from waste streams. Additionally, innovative approaches like 3D printing, which utilizes recycled materials, are reducing waste generation and enabling decentralized manufacturing. These technologies are reshaping traditional waste management practices, transforming waste into a valuable resource for creating new products and reducing environmental pollution.
Green Transportation: Journeying Towards Sustainable Mobility
The transportation sector is a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions. Disruptive technologies are tackling this challenge by promoting sustainable modes of transportation. Electric vehicles (EVs) are gaining momentum with advancements in battery technology, charging infrastructure, and increased range. Furthermore, autonomous vehicles and shared mobility services are revolutionizing urban transportation, reducing congestion, and optimizing energy consumption. Additionally, developments in biofuels and hydrogen fuel cells offer potential alternatives to fossil fuel-based transportation, paving the way for a greener mobility revolution.
Conclusion
The disruptive technologies within the green economy are transforming industries, economies, and societies. From renewable energy and energy storage to sustainable agriculture, waste management, and green transportation, these innovations are redefining traditional practices and offering sustainable solutions to pressing global challenges. As the urgency to address climate change intensifies, embracing and investing in these disruptive technologies is not just an opportunity but a necessity. By harnessing their transformative potential, we can accelerate the transition towards a greener, more sustainable future for generations to come.
#Disruptive technology in the green energy sector#Transformative innovations in the green economy#The future of green technology and sustainability#Advancements in renewable energy technologies#Energy storage solutions for a greener future#Smart grid systems and sustainable energy management#Revolutionizing agriculture with disruptive technologies#Sustainable farming practices and innovative technologies#Circular economy and waste management innovations#Green transportation and sustainable mobility solutions#Renewable energy revolution: disruptive technologies#Cutting-edge innovations in the green economy#Green technology trends shaping the future#Energy storage breakthroughs for renewable energy#Smart grid technology and efficient energy distribution#Sustainable agriculture: technological advancements#Disruptive waste management solutions for a circular economy#Future of transportation: green mobility technologies#Renewable energy innovations driving environmental sustainability#The role of disruptive technologies in the green revolution#Advancing the green economy through technology#Resource management in the age of green technology#Sustainable agriculture practices and technological breakthroughs#Circular economy: transforming waste through innovative technologies#Green transportation solutions and eco-friendly mobility#The impact of disruptive technology on renewable energy#Achieving sustainability through technological innovation#Efficient energy storage systems for a greener world#Smart grids and energy management in the green economy#Enhancing resource efficiency with disruptive green technologies
0 notes
Link
#market research future#blockchain in energy market#blockchain in energy sector#blockchain in energy industry#blockchain in energy trends
0 notes
Text
The Real Cost of the Fashion Industry

Atacama Desert, in Alto Hospicio, Iquique, Chile. (source)
The textile industry is destroying the world. The industry is wasting massive amounts of energy and materials, and polluting the air, the ground and the water supplies. It overwhelmingly exploits it's labour and extracts wealth from colonized countries, especially in Asia. I assume we all broadly understand this, but I think it's useful to have it all laid out in front of you to see the big picture, the core issues causing this destruction and find ways how to effectively move forward.
The concerning trend behind this ever-increasing devastation are shortening of trend cycles, lowering clothing prices and massive amount of wasted products. Still in year 2000 it was common for fashion brands to have two collections per year, while now e.g. Zara produces 24 collections and H&M produces 12-16 collections per year. Clothing prices have fallen (at leas in EU) 30% from 1996 to 2018 when adjusted to inflation, which has contributed to the 40% increase in clothing consumption per person between 1996 and 2012 (in EU). (source) As the revenue made by the clothing industry keep rising - from 2017 to 2021 they doubled (source) - falling prices can only be achieved with increasing worker exploitation and decreasing quality. I think the 36% degrees times clothing are used in average during the last 15 years (source) is a clear indication on the continuing drop in quality of clothing. Clothing production doubled between 2000 and 2015, while 30% of the clothes produced per year are never sold and are often burned instead (source), presumably to prevent the returns from falling due to oversupply.
These all factors are driving people to overconsume. While people in EU keep buying more clothes, they haven't used up to 50% of the clothes in their wardrobe for over a year (source). This overconsumption is only made much worse by the new type of hyper fast fashion companies like SHEIN and Temu, which are using addictive psychological tactics developed by social media companies (source 1, source 2). They are cranking up all those concerning trends I mentioned above.
Under the cut I will go through the statistics of the most significant effects of the industry on environment and people. I will warn you it will be bleak. This is not just a fast fashion problem, basically the whole industry is engaging in destructive practices leading to this damage. Clothing is one of those things that would be actually relatively easy to make without massive environmental and human cost, so while that makes the current state of the industry even more heinous, it also means there's hope and it's possible to fix things. In the end, I will be giving some suggestions for actions we could be doing right now to unfuck this mess.
Carbon emissions
The textile industry is responsible for roughly 10% of the global CO2 emissions, more than aviation and shipping industry combined. This is due to the massive supply chains and energy intensive production methods of fabrics. Most of it can be contributed to the fashion sector since around 60% of all the textile production is clothing. Polyester, a synthetic fiber made from oil which accounts for more than half of the fibers used in the textile industry, produces double the amount of carbon emissions than cotton, accounting for very large proportions of all the emissions by the industry. (source 1, source 2)
Worker exploitation
Majority of the textiles are produced in Asia. Some of the worst working conditions are in Bangladesh, one of the most important garment producers, and Pakistan. Here's an excerpt from EU Parliament's briefing document from 2014 after the catastrophic Rana Plaza disaster:
The customers of garment producers are most often global brands looking for low prices and tight production timeframes. They also make changes to product design, product volume, and production timeframes, and place last-minute orders without accepting increased costs or adjustments to delivery dates. The stresses of such policies usually fall on factory workers.
The wage exploitation is bleak. According to the 2015 documentary The True Cost less than 2% of all garment factory workers earned a living wage (source). Hourly wages are so low and the daily quotas so high, garment workers are often forced through conditions or threats and demand to work extra hours, which regularly leads to 10-12 hour work days (source) and at worst 16 hour workdays (source), often without days off. Sometimes factories won't compensate for extra hours, breaching regulations (source).
Long working hours, repetitive work, lack of breaks and high pressure leads to increased risks of injuries and accidents. Small and even major injuries are extremely common in the industry. A study in three factories in India found that 70% of the workers suffered from musculosceletal symptoms (source). Another qualitative study of female garment workers and factory doctors in Dhaka found that long hours led to eye strain, headaches, fatigue and weight loss in addition to muscular and back pains. According to the doctors interviewed, weight loss was common because the workers work such long hours without breaks, they didn't have enough time to eat properly. (source) Another study in 8 factories in India found that minor injuries were extremely common and caused by unergonomic work stations, poor organization in the work place and lack of safety gear, guidelines and training (source). Safety precautions too are often overlooked to cut corners, which periodically leads to factory accidents, like in 2023 lack of fire exists and fire extinguishers, and goods stacked beyond capacity led to a factory fire in Pakistan which injured dozens of workers (source) or like in 2022 dangerous factory site led to one dead worker and 9 injured workers (source).
Rana Plaza collapse in 2013 is the worst industrial accident in recent history. The factory building did not have proper permits and the factory owner blatantly ignored signs of danger (other businesses abandoned the building a day before the collapse), which led to deaths of 1 134 workers and injuries to 2 500 workers. The factory had or were at the time working for orders of at least Prada, Versace, Primark, Walmart, Zara, H&M, C&A, Mango, Benetton, the Children's Place, El Corte Inglés, Joe Fresh, Carrefour, Auchan, KiK, Loblaw, Bonmarche and Matalan. None of the brands were held legally accountable for the unsafe working conditions which they profited off of. Only 9 of the brands attended a meeting to agree on compensation for the victim's families. Walmart, Carrefour, Auchan, Mango and KiK refused to sight the agreement, it was only signed by Primark, Loblaw, Bonmarche and El Corte Ingles. The compension these companies provided was laughable though. Primemark demanded DNA evidence that they are relatives of one of the victims from these struggling families who had lost their often sole breadwinner for a meager sum of 200 USD (which doesn't even count for two months of living wage in Bangladesh (source)). This obviously proved to be extremely difficult for most families even though US government agreed to donate DNA kits. This is often said to be a turning point in working conditions in the industry, at least in Bangladesh, but while there's more oversight now, as we have seen, there's clearly still massive issues. (source 1, source 2)
One last major concern of working conditions in the industry I will mention is the Xinjiang raw cotton production, which is likely produced mainly with forced labour from Uighur concentration camps, aka slave labour of a suspected genocide. 90% of China's raw cotton production comes from Xinjiang (source). China is the second largest cotton producer in the world, after India, accounting 20% of the yearly global cotton production (source).
Pollution
Synthetic dyes, which synthetic fibers require, are the main cause of water pollution caused by the textile industry, which is estimated to account for 20% of global clean water pollution (source). This water pollution by the textile industry is suspected of causing a lot of health issues like digestive issues in the short term, and allergies, dermatitis, skin inflammation, tumors and human mutations in the long term. Toxins also effect fish and aquatic bacteria. Azo dyes, one of the major pollutants, can cause detrimental effects to aquatic ecosystems by decreasing photosynthetic activity of algae. Synthetic dyes and heavy metals also cause large amounts of soil pollution. Large amounts of heavy metals in soil, which occurs around factories that don't take proper environmental procautions, can cause anaemia, kidney failure, and cortical edoem in humans. That also causes changes in soil texture, decrease in soil microbial diversity and plant health, and changes in genetic structure of organisms growing in the soil. Textile factory waste water has been used for irrigation in Turkey, where other sources of water have been lacking, causing significant damage to the soil. (source)
Rayon produced through viscose process causes significant carbon disulphide and hydrogen sulphide pollution to the environment. CS2 causes cardiovascular, psychiatric, neuropsychological, endocrinal and reproductive disorders. Abortion rates among workers and their partners exposed to CS2 are reported to be significantly higher than in control groups. Many times higher amounts of sick days are reported for workers in spinning rooms of viscose fiber factories. China and India are largest producers of CS2 pollution, accounting respectively 65.74% and 11,11% of the global pollution, since they are also the major viscose producers. Emission of CS2 has increased significantly in India from 26.8 Gg in 2001 to 78.32 Gg in 2020. (source)
Waste
The textile industry is estimated to produce around 92 million tons of textile waste per year. As said before around 30% of the production is never sold and with shortening lifespans used the amount of used clothing that goes to waster is only increasing. This waste is large burned or thrown into landfills in poor countries. (source) H&M was accused in 2017 by investigative journalists of burning up to 12 tonnes of clothes per year themselves, including usable clothing, which they denied claiming they donated clothing they couldn't sell to charity instead (source). Most of the clothing donated to charity though is burned or dumbed to landfills (source).
Most of the waste clothing from rich countries like European countries, US, Australia and Canada are shipped to Chile (source) or African countries, mostly Ghana, but also Burkina Faso and Côte d'Ivoire (source). There's major second-hand fashion industries in these places, but most of the charity clothing is dumbed to landfills, because they are in such bad condition or the quality is too poor. Burning and filling landfills with synthetic fabrics with synthetic dyes causes major air, water and soil pollution. The second-hand clothing industry also suppresses any local clothing production as donated clothing is inherently more competitive than anything else, making these places economically reliant on dumbed clothing, which is destroying their environment and health, and prevents them from creating a more sustainable economy that would befit them more locally. This is not an accident, but required part of the clothing industry. Overproduction let's these companies tap on every new trend quickly, while not letting clothing the prices in rich countries drop so low it would hurt their profits. Production is cheaper than missing a trend.
Micro- and nanoplastics
There is massive amounts of micro- and nanoplastics in all of our environment. It's in our food, drinking water, even sea salt (source). Washing synthetic textiles accounts for roughly 35% of all microplastics released to the environment. It's estimated that it has caused 14 million tonnes of microplastics to accumulate into the bottom of the ocean. (source)
Microplastics build up into the intestines of animals (including humans), and have shown to probably cause cause DNA damage and altered organism behavior in aquatic fauna. Microplastics also contain a lot of the usual pollutants from textile industry like synthetic dyes and heavy metals, which absorb in higher quantities to tissues of animals through microplastics in the intestines. Studies have shown that the adverse effect are higher the longer the microplastics stay in the organism. The effects cause major risks to aquatic biodiversity. (source) The health effects of microplastics to humans are not well known, but studies have shown that they could have adverse effects on digestive, respiratory, endocrine, reproductive and immune systems. (source)
Microplastics degrade in the environment even further to nanoplastics. Nanoplastic being even smaller are found to enter blood circulation, get inside cells and cross the blood-brain barrier. In fishes they have been found to cause neurological damage. Nanoplastics are also in the air, and humans frequently breath them in. Study in office buildings found higher concentration of nanoplastics in indoor air than outdoor air. Inside the nanoplastics are likely caused mostly by synthetic household textiles, and outdoors mostly by car tires. (source) An association between nanoplastics and mitochondrial damage in human respiratory cells was found in a recent study. (source)
Micro and nano plastics are also extremely hard to remove from the environment, making it even more important that we reduce the amount of microplastics we produce as fast as possible.
What can we do?
This is a question that deserves it's own essays and articles written about it, but I will leave you with some action points. Reading about these very bleak realities can easily lead to overwhelming apathy, but we need to channel these horrors into actions. Whatever you do, do not fall into apathy. We don't have the luxury for that, we need to act. These are industry wide problems, that simply cannot be fixed by consumerism. Do not trust any clothing companies, even those who market themselves as ethical and responsible, always assume they are lying. Most of them are, even the so called "good ones". We need legislation. We cannot allow the industry to regulate itself, they will always take the easy way out and lie to their graves. I will for sure write more in dept about what we can do, but for now here's some actions to take, both political and individual ones.
Political actions
Let's start with political actions, since they will be the much more important ones. While we are trying to dismantle capitalism and neocolonialism (the roots of these issues), here's some things that we could do right now. These will be policies that we should be doing everywhere in the world, but especially rich countries, where most of the clothing consumption is taking place. Vote, speak to others, write to your representative, write opinion pieces to your local papers, engage with democracy.
Higher requirements of transparency. Right now product transparency in clothing is laughably low. In EU only the material make up and the origin country of the final product are required to be disclosed. Everything else is up to the company. Mandatory transparency is the only way we can force any positive changes in the production. The minimum of transparency should be: origin countries of the fibers and textiles in the product itself; mandatory reports of the lifecycle emissions; mandatory reports of whole chain of production. Right now the clothing companies make their chain of production intentionally complex, so they have plausible deniability when inevitably they are caught violating environmental or worker protection laws (source). They intentionally don't want to be able to track down their production chain. Forcing them to do so anyway would make it very expensive for them to keep up this unnecessarily complex production chain. These laws are most effective when put in place in large economies like EU or US.
Restrictions on the use of synthetic fibers. Honestly I think they should be banned entirely, since the amount of microplastics in our environment is already extremely distressing and the other environmental effects of synthetic fibers are also massive, but I know there are functions for which they are not easily replaced (though I think they can be replaces in those too, but that's a subject of another post), so we should start with restrictions. I'm not sure how they should be specifically made, I'm not a law expert, but they shouldn't be used in everyday textiles, where there are very easy and obvious other options.
Banning viscose. There are much better options for viscose method that don't cause massive health issues and environmental destruction where ever it's made, like Lyocell. There is absolutely no reason why viscose should be allowed to be sold anywhere.
Governmental support for local production by local businesses. Most of the issues could be much more easily solved and monitored if most clothing were not produced by massive global conglomerations, but rather by local businesses that produce locally. All clothing are made by hand, so centralizing production doesn't even give it advantage in effectiveness (only more profits for the few). Producing locally would make it much more easier to enforce regulations and it would reduce production chains, making production more effective, leaving more profits into the hands of the workers and reducing emissions from transportation. When the production is done by local businesses, the profits would stay in the producing country and they could be taxed and utilized to help the local communities. This would be helpful to do in both exploited and exploiter countries. When done in rich countries who exploit poorer ones, it would reduce the demand for exploitation. In poor countries this is not as easily done, since poor means they don't have money to give around, but maybe this could be a good cause to put some reparations from colonizers and global corporations, which they should pay.
Preventing strategic accounting between subsidiaries and parent companies. Corporate law is obviously not my area of expertise, but I know that allowing corporations to move around the accounting of profits and losses between subsidiaries and parent companies in roughly 1980s, was a major factor in creating this modern global capitalist system, where corporations can very easily manipulate their accounting to utilize tax heavens and avoid taxes where they actually operate, which is how they are upholding this terrible system and extracting the profits from the production countries. How specifically this would be done I can't tell because again I know shit about corporate law, so experts of that field should plan the specifics. Overall this would help deal with a lot of other problems than just the fashion industry. Again for it to be effective a large economic area like EU or US should do this.
Holding companies accountable for their whole chain of production. These companies should be dragged to court and made to answer for the crimes they are profiting of off. We should put fear back into them. This is possible. Victims of child slavery are already doing this for chocolate companies. If it's already not how law works everywhere, the laws should be changed so that the companies are responsible even if they didn't know, because it's their responsibility to find out and make sure they know. They should have been held accountable for the Rana Plaza disaster. Maybe they still could be. Sue the mother fuckers. They should be afraid of us.
Individual actions
I will stress that the previous section is much more important and that there's no need to feel guilty for individual actions. This is not the fault of the average consumer. Still we do need to change our relationship to fashion and consumption. While it's not our fault, one of the ways this system is perpetuated, is by the consumerist propaganda by fashion industry. And it is easier to change our own habits than to change the industry, even if our own habits have little impact. So these are quite easy things we all could do as we are trying to do bigger change to gain some sense of control and keep us from falling to apathy.
Consume less. Better consumption will not save us, since consumption itself is the problem. We consume too much clothing. Don't make impulse purchases. Consider carefully weather you actually need something or if you really really want it. Even only buying second-hand still fuels the industry, so while it's better than buying new, it's still better to not buy.
Take proper care of your clothing. Learn how to properly wash your clothing. There's a lot of internet resources for that. Never wash your wool textiles in washing machine, even if the textile's official instructions allow it. Instead air them regularly, rinse them in cool water if they still smell after airing and wash stains with water or small amount of (wool) detergent. Never use fabric softener! It damages the fabrics, prevents them from properly getting clean and is environmentally damaging. Instead use laundry vinegar for making textiles softer or removing bad smells. (You can easily make laundry vinegar yourself too from white vinegar and water (and essential oils, if you want to add a scent to it) which is much cheaper.) Learn how to take care of your leather products. Most leather can be kept in very good condition for a very long time by occasional waxing with beeswax.
Use the services of dressmakers and shoemakers. Take your broken clothing or clothing which doesn't fit anymore to your local dressmaker and ask them if they can do something about it. Take your broken and worn leather products to your local shoemaker too. Usually it doesn't cost much to get something fixed or refitted and these expert usually have ways to fix things you couldn't even think of. So even if the situation with your clothing or accessory seems desperate, still show it to the dressmaker or shoemaker.
If it's extremely cheap, don't buy it. Remember that every clothing is handmade. Only a small fraction of the cost of the clothing will be paying the wages of the person who made it with their hands. If a shirt costs 5 euros (c. 5,39 USD), it's sewer was only payed mere cents for sewing it. I'm not a quick sewer and it takes me roughly 1-2 hours to cut, prepare and sew a simple shirt, so I'm guessing it would take around half an hour to do all that for a factory worker on a crunch, at the very least 15 minutes. So the hourly pay would still be ridiculously low. However, as I said before, the fact that the workers in clothing factories get criminally low pay is not the fault of the consumer, so if you need a clothing item, and you don't have money to buy anything else than something very cheep, don't feel guilty. And anyway expensive clothing in no way necessarily means reasonable pay or ethical working conditions, cheep clothing just guarantee them.
Learn to recognize higher quality. In addition to exploitation, low price also means low quality, but again high price doesn't guarantee high quality. High quality allows you to buy less, so even if it's not as cheep as low quality, if you can afford it, when you need it, it will be cheaper in long run, and allows you to consume less. Check the materials. Natural fibers are your friends. Do not buy plastic, if it's possible to avoid. Avoid household textiles from synthetic fibers. Avoid textiles with small amounts of spandex to give it stretch, it will shorten the lifespan of the clothing significantly as the spandex quickly wears down and the clothing looses it's shape. Also avoid clothing with rubber bands. They also loose their elasticity very quickly. In some types of clothing (sport wear, underwear) these are basically impossible to avoid, but in many other cases it's entirely possible.
Buy from artisans and local producers, if you can. As said better consumption won't fix this, but supporting artisans and your local producers could help keep them afloat, which in small ways helps create an alternative to the exploitative global corporations. With artisans especially you know the money goes to the one who did the labour and buying locally means less middlemen to take their cut. More generally buy rather from businesses that are located to the same country where the production is, even if it's not local to you. A local business doesn't necessarily produce locally.
Develop your own taste. If you care about fashion and style, it's easy to fall victim to the fashion industry's marketing and trend cycles. That's why I think it's important to develop your personal sense of style and preferences. Pay attention at what type of clothes are comfortable to you. Go through your wardrobe and track for a while which clothing you use most and which least. Understanding your own preferences helps you avoid impulse buying.
Consider learning basics of sewing. Not everyone has the time or interest for this, but if you in anyway might have a bit of both, I suggest learning some very simple and basic mending and reattaching a button.
Further reading on this blog: How to see through the greenwashing propaganda of the fashion industry - Case study 1: Shein
Bibliography
Academic sources
An overview of the contribution of the textiles sector to climate change, 2022, L. F. Walter et al., Frontiers in Environmental Science
How common are aches and pains among garment factory workers? A work-related musculoskeletal disorder assessment study in three factories of south 24 Parganas district, West Bengal, 2021, Arkaprovo Pal et al., J Family Med Prim Care
Sewing shirts with injured fingers and tears: exploring the experience of female garment workers health problems in Bangladesh, 2019, Akhter, S., Rutherford, S. & Chu, C., BMC Int Health Hum Rights
Occupation Related Accidents in Selected Garment Industries in Bangalore City, 2006, Calvin, Sam & Joseph, Bobby, Indian Journal of Community Medicine
A Review on Textile and Clothing Industry Impacts on The Environment, 2022, Nur Farzanah Binti Norarmi et al., International Journal of Academic Research in Business and Social Sciences
Carbon disulphide and hydrogen sulphide emissions from viscose fibre manufacturing industry: A case study in India, 2022, Deepanjan Majumdar et al., Atmospheric Environment: X
Microplastics Pollution: A Brief Review of Its Source and Abundance in Different Aquatic Ecosystems, 2023, Asifa Ashrafy et al., Journal of Hazardous Materials Advances
Health Effects of Microplastic Exposures: Current Issues and Perspectives in South Korea, 2023, Yongjin Lee et al., Yonsei Medical Journal
Nanoplastics and Human Health: Hazard Identification and Biointerface, 2022, Hanpeng Lai, Xing Liu, and Man Qu, Nanomaterials
Other sources
The impact of textile production and waste on the environment (infographics), 2020, EU
Chile’s desert dumping ground for fast fashion leftovers, 2021, AlJazeera
Fashion - Worldwide, 2022 (updated 2024), Statista
Fashion Industry Waste Statistics & Facts 2023, James Evans, Sustainable Ninja (magazine)
Everything You Need to Know About Waste in the Fashion Industry, 2024, Solene Rauturier, Good on You (magazine)
Textiles and the environment, 2022, Nikolina Šajn, European Parliamentary Research Service
Help! I'm addicted to secondhand shopping apps, 2023, Alice Crossley, Cosmopolitan
Addictive, absurdly cheap and controversial: the rise of China’s Temu app, 2023, Helen Davidson, Guardian
Workers' conditions in the textile and clothing sector: just an Asian affair? - Issues at stake after the Rana Plaza tragedy, 2014, Enrico D'Ambrogio, European Parliamentary Research Service
State of The Industry: Lowest Wages to Living Wages, The Lowest Wage Challenge (Industry affiliated campaign)
Fast Fashion Getting Faster: A Look at the Unethical Labor Practices Sustaining a Growing Industry, 2021, Emma Ross, International Law and Policy Brief (George Washington University Law School)
Dozens injured in Pakistan garment factory collapse and fire, 2023, Hannah Abdulla, Just Style (news media)
India: Multiple factory accidents raise concerns over health & safety in the garment industry, campaigners call for freedom of association in factories to ‘stave off’ accidents, 2022, Jasmin Malik Chua, Business & Human Rights Resource Center
Minimum Wage Level for Garment Workers in the World, 2020, Sheng Lu, FASH455 Global Apparel & Textile Trade and Sourcing (University of Delaware)
Rana Plaza collapse, Wikipedia
Buyers’ compensation for Rana Plaza victims far from reality, 2013, Ibrahim Hossain Ovi, Dhaka Tribune (news media)
World cotton production statistics, updated 2024, The World Counts
Dead white man’s clothes, 2021, Linton Besser, ABC News
#fashion#fashion industry#sustainability#sustainable fashion#sustainable clothing#environment#climate change#i will be continuing the series of how to see through fashion industry propaganda at some point#i just felt compelled to write this because i feel like people so often miss the forest for the trees in this conversation
505 notes
·
View notes
Text
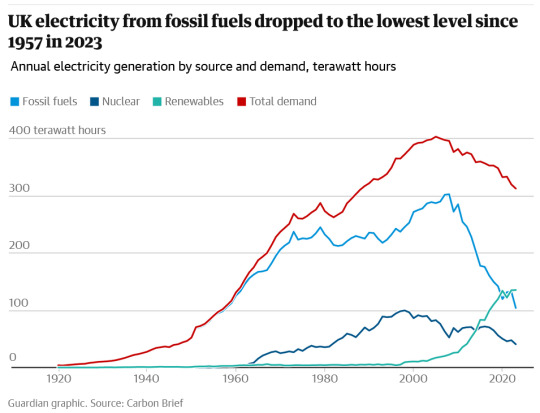
"The amount of electricity generated by the UK’s gas and coal power plants fell by 20% last year, with consumption of fossil fuels at its lowest level since 1957.
Not since Harold Macmillan was the UK prime minister and the Beatles’ John Lennon and Paul McCartney met for the first time has the UK used less coal and gas.
The UK’s gas power plants last year generated 31% of the UK’s electricity, or 98 terawatt hours (TWh), according to a report by the industry journal Carbon Brief, while the UK’s last remaining coal plant produced enough electricity to meet just 1% of the UK’s power demand or 4TWh.
Fossil fuels were squeezed out of the electricity system by a surge in renewable energy generation combined with higher electricity imports from France and Norway and a long-term trend of falling demand.
Higher power imports last year were driven by an increase in nuclear power from France and hydropower from Norway in 2023. This marked a reversal from 2022 when a string of nuclear outages in France helped make the UK a net exporter of electricity for the first time.
Carbon Brief found that gas and coal power plants made up just over a third of the UK’s electricity supplies in 2023, while renewable energy provided the single largest source of power to the grid at a record 42%.
It was the third year this decade that renewable energy sources, including wind, solar, hydro and biomass power, outperformed fossil fuels [in the UK], according to the analysis. Renewables and Britain’s nuclear reactors, which generated 13% of electricity supplies last year, helped low-carbon electricity make up 55% of the UK’s electricity in 2023.
[Note: "Third year this decade" refers to the UK specifically, not global; there are several countries that already run on 100% renewable energy, and more above 90% renewable. Also, though, there have only been four years this decade so far! So three out of four is pretty good!]
Dan McGrail, the chief executive of RenewableUK, said the data shows “the central role that wind, solar and other clean power sources are consistently playing in Britain’s energy transition”.
“We’re working closely with the government to accelerate the pace at which we build new projects and new supply chains in the face of intense global competition, as everyone is trying to replicate our success,” McGrail said.
Electricity from fossil fuels was two-thirds lower in 2023 compared with its peak in 2008, according to Carbon Brief. It found that coal has dropped by 97% and gas by 43% in the last 15 years.
Coal power is expected to fall further in 2024 after the planned shutdown of Britain’s last remaining coal plant in September. The Ratcliffe on Soar coal plant, owned by the German utility Uniper, is scheduled to shut before next winter after generating power for over 55 years.
Renewable energy has increased sixfold since 2008 as the UK has constructed more wind and solar farms, and the large Drax coal plant has converted some of its generating units to burn biomass pellets.
Electricity demand has tumbled by 22% since its peak in 2005, according to the data, as part of a long-term trend driven by more energy efficient homes and appliances as well as a decline in the UK’s manufacturing sector.
Demand for electricity is expected to double as the UK aims to cut emissions to net zero by 2050 because the plan relies heavily on replacing fossil fuel transport and heating with electric alternatives.
In recent weeks [aka at the end of 2023], offshore wind developers have given the green light to another four large windfarms in UK waters, including the world’s largest offshore windfarm at Hornsea 3, which will be built off the North Yorkshire coast by Denmark’s Ørsted."
-via The Guardian, January 2, 2024
#uk#united kingdom#england#scotland#wales#northern ireland#electricity#renewables#renewable energy#climate change#sustainability#hope posting#green energy#fossil fuels#oil#coal#solar power#wind power#environment#climate action#global warming#air pollution#climate crisis#good news#hope
395 notes
·
View notes
Text
Veiled by discussion of headline global trends in new renewables capacity investment is the fact that almost all the incremental progress is currently being made in one country: China. Trumpeting 2023’s 50 percent growth in annual global capacity installations as a global achievement is wrongheaded, given that China by itself delivered nearly 80 percent of the increment. And the IEA, for its part, expects China to continue to be the sole meaningful over-achiever. It recently revised upwards by 728 GW its forecast for total global renewables capacity additions in the period 2023–27. China’s share of this upward revision? Almost 90 percent. While China surges ahead, the rest of the world remains stuck. This raises a crucial question. What is different about the development of solar and wind resources in China from the rest of the world? The main answer is that in China, such development is capitalist in only a very limited sense. Certainly, the entities centrally involved in building out new solar and wind farms in China are companies. But almost all are state-owned. Take wind. Nine of the country’s top 10 wind developers are owned by the government, and such state-owned players control in excess of 95 percent of the market. Moreover, the state is far from being a passive shareholder in these companies. The companies are best seen as instruments wielded by the state in the service of achieving its industrial, geopolitical, and – increasingly – environmental objectives. The best example of this concerns the gargantuan ‘clean energy bases’ first announced by President Xi Jinping in 2021. To be built mainly in the Gobi and other desert areas by 2030, these new bases will have a combined capacity of in excess of 550 GW – more than Europe’s total solar and wind capacity at the time of this writing. Such development is as far from ‘capitalist’ as is imaginable. This is the state, in its most centralized and authoritative form mustering whatever resources it needs at its disposal to ensure that it delivers what it has said it will deliver. Add to this the fact that the banks financing all the new renewables development in China are generally also state-owned and directed, and a stark reality comes into focus. This is essentially central planning in action. Does the profit motive figure? To be sure, it does. But usually only marginally, and it is ridden roughshod over whenever Beijing deems fit.
111 notes
·
View notes
Text
1.20.25 • Today the United States Climate Alliance delivered a letter to UN Climate Change Executive Secretary Simon Stiell, making it clear to the global community that our climate work will continue regardless of federal action or inaction.
If you're not familiar with the U.S. Climate Alliance, they are a bipartisan climate action coalition of 24 governors representing approximately 55% of the U.S. population and 60% of the U.S. economy.
To read their letter, read more here or explore their press release on their website. Onward!
•••
Mr. Simon Stiell, Executive Secretary
United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change
P.O. Box 260124
D-53153 Bonn, Germany
January 20, 2025
Dear Executive Secretary Stiell,
We write as co-chairs of the United States Climate Alliance, a bipartisan coalition of two dozen governors representing nearly 60 percent of the U.S. economy and 55 percent of the U.S. population, to make it clear to you, and the rest of the world, that we will continue America’s work to achieve the goals of the Paris Agreement and slash climate pollution.
As you know, this is not the first time we’ve responded to this challenge in the U.S. Our coalition was launched after the President’s decision to withdraw our country from the Paris Agreement back in 2017. Since then, our reach, resolve, and impact have only grown.
In fact, our states and territories are now on track to meet our near-term climate target by reducing collective net greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions 26 percent below 2005 levels by 2025. Our recent progress reflects a wave of ambitious state policies and federal funding enacted over the last few years – and it builds on our coalition’s 15-year trend of cutting emissions while simultaneously growing our economies. We have continued to ramp up our longer-term commitments as well, pledging to reduce GHG emissions at least 50-52 percent by 2030 and 61-66 percent by 2035, below 2005 levels, in alignment with the U.S. Nationally Determined Contribution. Most importantly, this action is bringing better health, cleaner air, good-paying jobs, new economic development, and lower costs to our communities.
Our states and territories continue to have broad authority under the U.S. Constitution to protect our progress and advance the climate solutions we need. This does not change with a shift in federal administration. States across our coalition are implementing a suite of policies and programs to secure our net-zero future, including statewide and regional carbon markets, 100 percent clean energy standards, and methane reduction programs for the oil and gas, waste, and agricultural sectors, among many others. We are also deploying billions of dollars to eliminate pollution in our communities and sustain our country’s clean energy boom.
It’s critical for the international community to know that climate action will continue in the U.S. The Alliance will bring this message to the United Nations Climate Change Conference in Brazil (COP30) later this year – just as we have at every COP since our coalition’s founding – as we work to implement our climate goals. We are also committed to tracking and reporting on our progress and look forward to working with you and the global community to identify the most impactful ways to do so. The Alliance is proud to publish an annual report each year on our latest action, and we are enclosing here our most recent report for your reference.
We will not turn our back on America’s commitments. For our health and our future, we will press forward.
Sincerely,
Governor Kathy Hochul, Co-Chair
State of New York
Governor Michelle Lujan Grisham, Co-Chair
State of New Mexico
#us climate alliance#environmentalism#climate action#climate change#us politics#traumerica#good news
22 notes
·
View notes
Note
Do you have a list on your mind like "ohh this dude/girl is gay" lol I am pansexual so I am curious, I can't help but wonder. Especially in this sector, just because an idol hold a pride flag in a concert doesn't mean that they are part of the community or they are supportive. I hate that shit,,,
Hmm, this is only about energy. I can't really say this is how they are in reality, some come to mind that have shown a strong preference for me, Beomgyu, Mark (NCT), Huening Kai , I.N. I would expect Sunoo, not going to lie, but energetically he doesn't show that, not sure I believe the energy, sorry lol. But like I said they live in Korea and can't really express it, maybe Mark would, as he is Canadian and more open-minded to the idea. Now I also do see interest for women in Kai and Beomgyu, but their energy leans more towards men.
For girls, I have seen preferences for women, but I need to read more for them to see if I see a trend, but for these 4, I have seen a trend of them being attracted to men or being with men, so I will go with these 4, not sure I remember anyone else.
Bisexual energy seems more frequent. I get a few that just prefer women Jake, Sunghoon, Jay, Yeonjun, Seungmin. I haven't done much readings for Ateez and SVT on this topic (although there is an ask for Ateez that I will do, because girl wants to know their energy on that) and preferences do not show up either for them, so unsure about them.
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
A short note on your ability to help fight climate change
I've noticed a trend in some liberal spaces to laugh at the idea of personal responsibility in trying to prevent catastrophic climate change. The story goes, "The government has been telling us for years to recycle and bike to work and use reusable water bottles and that we can make a difference! But really 100 companies are responsible for 71% of global emissions, so this is all bunk actually, and putting the responsibility on all our shoulders when it's those guys who need to change! Me putting up string lights doesn't make a difference actually in the big picture." I want to push back on this a little as a scientist and climate advocate, and I want to give you some things to be aware of. First, those 100 companies are all energy companies, not companies like Amazon. They are the big producers of coal, oil, and gas worldwide. And that coal and natural gas are what are burned to provide the electricity that powers all our lives. The demand for that is every single thing you do that uses electricity. It is a massive collective phenomenon. That natural gas is what you likely burn to heat your house in the winter, and possibly how you cook your food. You might be doing so right now. Unless you have an electric car or scooter etc, gasoline is what powers your car. Many of your purchases are shipped across oceans with diesel. The demand for energy is from all of us. Many cities, at least in the US have CO2 budgets you can look up. If you do, you will see plots like this:


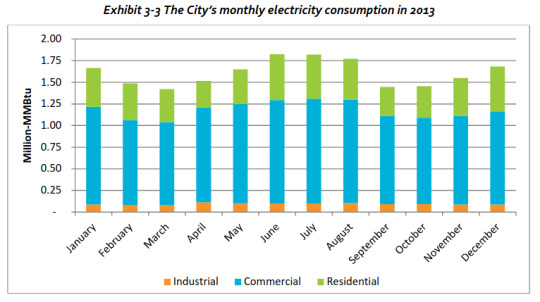

These are from a report prepared by the US National Energy Technology Lab about the nearby city of Pittsburgh PA, one of the two largest cities in the state of Pennsylvania. These are really simple plots, so take a minute to look at them, and actually note the y-axis. MMBtu is a unit of energy. One average single family home in the US uses about 50 MMBtu. The y-axis here is in millions of MMBtu. First, I want you to note that the greenhouse gas emissions are about an even 3-way split in if they come from electricity, natural gas, or transportation. All the renewable energy in the world would only impact one of those three categories. If all 100 of those energy companies replaced all their coal and oil with solar panels this year, that would only cut a third of these emissions. Only things that use electricity can be made lower emissions by switching to renewables and nuclear. For example, 1/3rd of the CO2 in this city comes from transportation and most of that is cars. Some of it is trucks, some of it is buses, but most of it is people driving around. This is why community organizers and climate activists want you to bike, take the bus, or get an electric or hybrid car. The total effect of everyone driving is actually massive! "But" I hear you say. "American infrastructure is car-centric! There are no buses where I live or I can't use them! And I can't afford to buy a new electric car." Yeah. I know. It sucks. But cities don't actually have enough money to rebuild the city to fix this, or to buy everyone new cars. But you can look up if your city has any sort of bond measure or sales tax to support public transit, or community feedback about it and try to support those things. But think about this. If the next time everyone in the city went to buy a new car, if they just checked if there was a hybrid in their price range and got that, then that would shift the composition towards being more electricity and less burning gasoline. This is what everyone calls "Electrification" and only by electrifying things can you reduce emissions in those sectors. Otherwise they stay totally flat and we just can't afford that. Let's look at the second plot, the city's monthly consumption broken down by electricity and natural gas. We see that the electricity is very flat over the year. Looking at the third plot, this is dominated by commercial use. Think like, big hospitals. This is not dominated by industry. It might be, depending on your city! But this electricity can come from renewable energy with grid scale and distributed storage. And there are programs in place now to try to bring these down. What about natural gas? Looking at the final plot we see that that is mostly residential. This is from heating and gas stoves. This is why you have heard your local city leaders talking about replacing your gas stove with electric or your gas furnace with a heat pump. These residential uses, summed over the whole population, contribute very significantly to the greenhouse gas emissions. [Note, check here if your electricity is still primarily from Coal. If so, natural gas has significantly less emissions than coal and you should wait to electrify until your electricity is itself mostly natural gas, renewables, and nuclear.] This is why you keep seeing programs offering tax rebates and other tools to give you benefits for switching from natural gas. This means your city or county leaders have assessed that it would be beneficial now to do this to start reducing that huge residential natural gas emissions source. If anyone you know owns a home, they could check and see if they could pay the same to replace old appliances with electric versions vs new natural gas ones, possibly with the help of government incentives. See the DOE page on heat pumps. If they did, it would help because again, the government can't come in and change your appliances for you.
But what about those 100 companies and their fossil fuels? None of this stops that, or lowers the carbon emissions from the electricity that makes everything run. True! But there are genuinely people working on that and you can too. Note that many of the easy actions your government could take to address this would cost you a lot of money and be deeply inequitable. For example, tripling the price of gas. The reason for all these government incentives is to try to get people to make these changes without doing that. So see if community solar is legal in your area, or if you can choose your electricity provider, or take other action to demonstrate interest in renewables. Email your elected officials and demand a cap-and-trade (or invest) program. Vote yes for these programs. If you work for a large company or institution, talk to someone about if the company could negotiate a Power Purchase Agreement. Look into stand-alone-battery storage even if solar isn't in your budget or wouldn't be efficient where you live because there being distributed battery storage helps reduce the peaking needs of the Grid and reduces demand for fossil fuels (and helps you save money and get through power outages). Learn about nuclear power and understand that it has to stay for us to get off fossil fuels. Keep protesting pipelines. Finally, most city greenhouse gas emissions budgets like the above don't include the emissions from consumption and shipping. Aka, the full supply chain emissions to get things delivered to cities (and it is, primarily, TO cities). Thus they are mostly under-estimates of the aggregate day to day impacts of the general populace. Moral or the story: Buy local, ride your bike, recycle your glass and do it properly, genuinely look into electrifying your transport and appliances as you are able, and then get involved in your community to do more. Don't kid yourself that you aren't part of the collective action problem. If you live in a major city in a developed country you are. You can't fix it yourself, but also it can't be fixed without your engagement, and all those PSAs and tax rebates and community organizing are the hard work of doing just that.
Note: This post is US-centric and the situation is very different in different countries. If you have anything to add that is more relevant to your country feel free to!
#ramblings#climate change#climate action#environmentalism#Seriously like check if you could save money long term with any of these things
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
As Election Day unfolded, speculation swirled about what a new administration in Washington might mean for cities, metropolitan areas, and communities across the nation. Over the past four years, President Biden’s administration ushered in unprecedented federal investments in industries, infrastructure, clean energy, and more. Now, the election results offer a clearer sense of the future for the place-based, locally led solutions that state and local leaders have championed in recent years.
Ample evidence suggests that the incoming Trump administration, backed by a compliant legislature, will prioritize tax cuts and deregulation. The president-elect has also signaled opposition to social safety net programs, diversity initiatives, climate policies, and immigration reforms. Yet the potential impacts on critical areas such as artificial intelligence, workforce development, and infrastructure remain uncertain.
To explore these issues, this compendium brings together insights from Brookings Metro scholars, examining how the next four years might shape cities, regions, and communities across the United States and the related impacts on people, economy, and environment. It leads off with a look at the nation’s evolving demographic trends, which will profoundly influence places regardless of who occupies the White House.
One thing is certain: state and local leaders, across both public and private sectors, will face a dramatically different federal landscape starting in January. At Brookings Metro, our mission is to partner with these leaders to ensure that our research and expertise inform practical, scalable policy solutions. In this time of uncertainty and heightened federal challenges, it is more important than ever that we do so.
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
In 2023, renewable energy attracted 37% of unlisted investments in Africa, marking a significant shift. This sector now outpaces financial services, which have long been the dominant choice, according to the latest report from the European Investment Bank (EIB) released on November 7. This change highlights a major turning point, with capital moving away from fossil fuels, which now make up just 4% of investments, in favor of more sustainable solutions. Investors are increasingly drawn to green assets, which are seen as vital for resilience in Africa, a continent facing growing climate challenges.
This trend aligns with the global search for sustainable and cost-effective alternatives. As African countries remain particularly vulnerable to the effects of climate change, developing green infrastructure is viewed not only as an ecological necessity but also as a strategic economic opportunity. The perspectives of African banks reflect this shift: 67% of those surveyed see the climate transition as an opportunity, and 79% have set specific climate-related goals. While this positioning points to a growing commitment to renewable energy, there are still challenges to overcome.
11 notes
·
View notes