#Drupal 8 Migration Drupal 6 to 8 Drupal 7 to 8 migration Drupal 8 Content Migration Migrate Modules
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
The Benefits of Shared Web Hosting in San Antonio

In the digital age, businesses of all sizes must have a robust online presence. One of the key components of establishing an online presence is having a reliable web hosting service. Shared web hosting is a popular choice for many businesses in San Antonio, as it provides a cost-effective solution that allows multiple websites to share the resources of a single server. In this article, we will explore the benefits of shared web hosting San Antonio and why it is an excellent choice for businesses looking to establish their online presence.
1. Cost-Effective Solution
One of the primary reasons why businesses in San Antonio opt for shared web hosting is its affordability. Shared hosting plans are typically much cheaper compared to other hosting options such as dedicated or VPS hosting. With shared hosting, the cost of maintaining and managing the server is divided among multiple users, making it an attractive option for businesses on a limited budget.
2. Easy to Use
Shared web hosting in San Antonio is designed with ease of use in mind. Most hosting providers offer user-friendly control panels that allow businesses to manage their websites, domains, emails, and databases with ease. With just a few clicks, businesses can install popular content management systems like WordPress, Drupal, or Joomla, making it convenient for even non-technical users to set up their websites quickly.
3. Scalability
Flexibility and scalability are essential factors for businesses in San Antonio to consider when choosing a web hosting solution. Shared hosting plans offer scalability options that allow businesses to upgrade or downgrade their hosting resources as their needs change. This means that businesses can start with a basic shared hosting plan and easily upgrade to a higher-tier plan as their website traffic and resource requirements increase.
4. Technical Support
Another significant advantage of shared web hosting San Antonio is the availability of technical support. Reputable hosting providers offer 24/7 customer support to assist businesses with any technical issues or inquiries they may have. This ensures that businesses can quickly resolve any hosting-related problems and minimize any potential downtime that could affect their online presence.
5. Reliability and Uptime
Ensuring the reliability and uptime of a website is crucial for businesses in San Antonio. Shared web hosting providers utilize top-of-the-line servers that are optimized for performance and reliability. With advanced hardware and software optimizations, businesses can expect fast page load times, reducing bounce rates and improving SEO rankings. Additionally, reputable hosting providers offer a 99.9% uptime guarantee, minimizing any potential disruptions to businesses' online operations.
6. Enhanced Security Measures
Shared web hosting providers in San Antonio implement robust security measures to protect businesses' websites from potential threats. These measures include regular server monitoring, firewall protection, malware scanning, and automatic backups. By relying on shared hosting, businesses can take advantage of these security measures without the need for extensive technical knowledge or additional costs.
7. Free Website Migration
For businesses in San Antonio looking to switch hosting providers, shared web hosting often includes the benefit of free website migration. Reputable hosting providers offer professional assistance in transferring websites from the current hosting environment to their shared hosting servers. This eliminates the hassle and potential downtime associated with the migration process, allowing businesses to seamlessly transition to a new hosting provider.
8. Localized Hosting
Choosing a shared web hosting provider in San Antonio ensures that businesses' websites are hosted in local data centers. This localized hosting can positively impact website loading speeds and overall performance for visitors in the San Antonio area. Additionally, localized hosting can have SEO benefits, as search engines often prioritize locally hosted websites in search results for users in the same geographical location.
9. Additional Features and Resources
Shared web hosting plans in San Antonio often come with a range of additional features and resources to enhance businesses' online presence. These may include free SSL certificates for secure website connections, website builders for easy website creation, email hosting services, and access to website analytics tools. These added features provide businesses with the tools they need to create, manage, and analyze their websites effectively.
10. Community Support and Resources
Shared web hosting in San Antonio comes with the added benefit of a thriving community of users and resources. Businesses can access online forums, knowledge bases, and tutorials to find answers to common questions or troubleshoot any issues they may encounter. This community support can be invaluable in helping businesses make the most of their shared hosting and overcome any technical challenges.
In conclusion, shared web hosting in San Antonio offers businesses a cost-effective, easy-to-use, and reliable solution for establishing and maintaining their online presence. With a range of benefits such as scalability, technical support, enhanced security, and localized hosting, businesses can focus on their core operations while their websites are hosted on a stable and secure platform. Whether you are a small startup or an established business, shared web hosting in San Antonio can provide the necessary foundation for your online success.
Additional Information:
The San Antonio business landscape is highly competitive, making it essential for businesses to have a fast and reliable website to stand out from the competition.
Shared web hosting is an excellent option for startups and small businesses in San Antonio that have budget constraints but still require reliable hosting services.
When choosing a shared web hosting provider in San Antonio, it is crucial to consider factors such as server performance, customer support quality, and additional features that align with your business needs.
Businesses in San Antonio can benefit from leveraging the localized hosting advantage of shared web hosting, as it can improve their website's loading speed and SEO rankings for local searches.
0 notes
Text
AgProfessional Case Study.
INTRODUCTION
Farm Journal Media is a leading United States business information and media company serving the agricultural market. Started 140 years ago with the preeminent Farm Journal magazine, the company serves the row crop, livestock, produce and retail sectors through 26 branded websites, Newsletters and phone apps, 11 business magazines, 70 events, six nationally broadcasted television and radio programs; a robust mobile text marketing business; and an array of data-driven paid information products.
Valuebound helped Farm Journal Media with the redesigning of their 6 Magazine Sites that were built on Drupal 7. One of the redesigned site was Agprofessional. AgProfessional communication products provide agronomic and business management solutions to retailers/distributors, professional farm managers and crop consultants resulting in increased production and profitability in the food, fiber and energy marketplace.
CHALLENGE
The legacy magazine site was built on Drupal 7 and as the Farm Journal Editors and Webmasters were familiar with managing content with Drupal 7 CMS so it was their first choice to migrate content and upgrade the sites to Drupal 8.
The editorial team from Agprofessional needed to easily manage all content, allowing its classification into different taxonomies, ability to create articles, a dashboard for the editors and easy to use content moderation. The core of the project architecture is an implementation of Drupal 8 as content manager. The robust permission and content authoring experience made Drupal as the CMS of the choice for the stakeholders and the editors. The Old Site contains large amount of content which is needed to be migrated to new system. Drupal 8 has matured & efficient in migration system. The new application has to be performed in cross platforms including mobiles and Tabs. We have used a customised version of the Pixel theme for the new sites.


0 notes
Text
Top Drupal 8 migration tips that you needed to know before you start

If your enterprise is deciding to move from Drupal 7 to Drupal 8, be prepared to embrace Drupal 8 migration. The principal task of migrating all your content and data is easier if you have properly planned and prepared. Since its release, Drupal 8 has been the city’s talk, and it is not just its features but the process of migration alongside which brings it to the front. We have outlined some tips here that you need to take care of – for a successful Drupal 8 migration.
The necessity of Drupal 7 to 8 migration?
Drupal 7 is gloaming. According to researches, it will reach its end of life by 2021. Drupal 8 is a contracting software product from Drupal 6 & 7 versions. It comprises of a full load of world-class technology and features. So, it is a good idea to upgrade from Drupal 7 to 8 now.
The following are a few crucial tips that you needed to know for a smooth migration:
Be prepared to migrate modules
Remember, it is a complicated process. Therefore, it is crucial to include the development team right from scratch. If you need help, it is better to choose a digital partner to finish the migration seamlessly. Having the right strategy makes the module migration process more manageable and successful.
Drupal 8 Content Migration
Content migration is the method of moving data from one website to another. This happens when one is moving data from an outdated website to a newer one. In our environment, data is transferred from Drupal 6 or 7 to Drupal 8. The main reason for any organization to migrate its content is to move on from their outdated website. You need to check the functionalities and features of your old website. Content auditing, like what functionalities are used and which ones are irrelevant to the new website, can be useful.
Have a Test Environment framework
The first step of all tasks is to create a backup of the live site. Performing the upgrade of Drupal 8 on a live site is not safe. If something goes wrong, you’ll not have to panic because the backup is always there – go back to the previous version and identify what went wrong.
Understand The Core Modules
Get the basic knowledge of how your site is built, and this should cover acquiring details of the actual inventory of the deployed Drupal modules. To know the details, navigate to Administer > Site building > Modules, or navigate the available updates page at admin/reports/updates.
Discover Module Details
However, It is not essential to have a 1-to-1 complete upgrade path for all the core modules, irrespective of Drupal’s software version. Refer to Drupal’s known issues page if you trip on modules that are not upgradeable. The knowledge resources can help you to prepare for various scenarios.
Ensure A smooth Installation
Initially, install a clean core version of Drupal so that it can acquire the Drupal 7 host server and database. This will help in finishing the migration without any complexity. Many things are structured and configured distinctly in Drupal 8, so hopping steps without the right preparation or understanding can cause severe issues/damages.
Configuring The Drupal 8 Site
Start with your configuration process once everything is launched successfully. i.e., wait until the migration and upgrade process to complete. This is because your migration and upgrade process will overwrite whatever configurations you do on the previous platform.
#Drupal 8 Migration Drupal 6 to 8 Drupal 7 to 8 migration Drupal 8 Content Migration Migrate Modules
0 notes
Text
WHAT YOU DON'T KNOW ABOUT BLUEHOST COMPANY!!!.
Today, I will give you genuine review on Bluehost hosting.
So let's start....
We’ve been a paying Bluehost web hosting customer throughout 2017 – 2021.That means we’ve been monitoring their cheapest “basic” shared hosting plan performance (both average load time and uptime) for 4+ years.This Bluehost review relies heavily on data, as well as the overall experience with their hosting features and customer support.In a nutshell, all Bluehost plans offer their customers 24/7 live chat, unmetered bandwidth, and five email accounts. Similarly to many other website hosting companies, they too offer their new users a free domain for the first year. Their plans start from $2.75/mo and include improved security, backups, and free SSL certificate. These help to keep your blog or website protected and safe.Overall, their last 24-month performance has been good. Bluehost is clearly at the top with its uptime (99.99%) and a fast load time of 405ms (0.4 seconds).Pros of Using Bluehost Hosting
1. Best Uptime – 99.99% – Throughout the YearUptime is one the most important aspects when choosing a web host – after all, if your site is down, your users can’t access it. So consistently good uptime should be one of your top priorities.After reviewing 30 web hosts, our benchmark for “good” uptime is 99.93%. That might seem pretty high, but it’s actually even slightly below average. Type those numbers into a calculator, and you’ll quickly see it translates into at least 26 minutes of downtime each month or just over five hours over the course of a year.So ideally, we don’t want to see anything less than that.The good news is that Bluehost easily surpasses this benchmark, comfortably keeping our test site live for 99.99% of the time during the last 34 months (2018-2021).Here’s the monthly breakdown of the past 12-months:January 2021 average uptime: 100% December 2019 average uptime: 100%November 2019 average uptime: 100%October 2019 average uptime: 99.96%September 2019 average uptime: 99.99%August 2019 average uptime: 99.99%July 2019 average uptime: 100%June 2019 average uptime: 99.98%May 2019 average uptime: 100%April 2019 average uptime: 100%March 2019 average uptime: 99.99%February 2019 average uptime: 100%Conclusion? Bluehost is one of the most reliable web hosting provider according to our uptime study.
2. Top 5 Website “Load” Speed – 405ms
A report from Google last year found that the vast majority of mobile websites are way too slow.That’s a problem for two major reasons. Google’s mobile-first index can either elevate or hide your site in user searches based on its loading speeds. Studies show that slow websites almost always translate into lower sales.So, after uptime, your host’s page loading times are the second most important thing that can literally make or break your site’s success.We have been keeping track of Bluehost’s performance since February 2018 using a third-party tool, Pingdom. And once again, we were pleased with the results — an average page loading speed of 405ms which places them as the 5th fastest site out of everybody that we’ve tested.
3. Low Introductory Pricing ($2.75/mo)
We’ll look into Bluehost’s full pricing and plans in just a moment.However, if you were to go check out the starting prices, you’ll notice the lowest advertised price is $3.95/month. That’s a pretty good deal considering they’ve supposedly reduced it already from $7.99/month originally.For that price, you get pretty much everything you need for a single website. That includes 50 GB SSD storage, unmetered bandwidth, a free SSL certificate, and more.So you’d be getting a pretty good value for the price, plus their consistent uptime and page loading speeds.The good news is that we’ve been able to work out a deal with Bluehost for our readers that takes the starting price down even further to $2.75/month.This is the lowest rate we’ve seen anywhere online (and trust us, our team spends way too much time online as it is). So it’s a great deal if you’re in the market for a new affordable host.
4. Good Security Options
Even though Bluehost is one of the “cheaper” options on the market, we have been pleased to see that they don’t cut too many corners or skimp on critical features like security.Bluehost provides a lot of good security options by default, including the free SSL certificate for each plan like we mentioned earlier.All plans also include a domain privacy feature that will help keep the personal information you used to sign up for a domain private. This prevents hackers from finding and using these personal details for phishing schemes to trick you or others into handing over sensitive information.SiteLock is included to help prevent malware attacks, which are unfortunately fairly common on WordPress sites. CodeGuard is another form for protection, which also provides daily backups so you can roll back previous versions of a site if it does get hacked.Postini, from Google, is the final security tool worth noting. It provides spam protection for your email, so anything suspicious is prevented from getting in your inbox.Altogether, this is a pretty decent security package to keep your site safe and sound.
5. Many Integrations, Apps, and eCommerce Features
Beyond the included security features, Bluehost also provides access to a huge number of different apps and integrations so you can use the most popular services on the web.For example, they have a domain manager if you’d rather just purchase and manage multiple domains through them. You can set daily, weekly, or monthly backups just in case.You can install WordPress with a single click (more on that in the next section below). You can also install other popular content management systems (CMS) like Drupal, Joomla, run an e-commerce shop, and more
6. ‘Official’ WordPress.org Recommended Host
WordPress is the most widely used website platform on the market.Of course, you can use almost any web hosting provider to create a WordPress site. But the fact that Bluehost is one of the few officially recognized partners is encouraging.
7. Easy to Use for Beginners
Some of the web hosts we’ve seen are best only for advanced users.LiquidWeb, for example, is great if you know what you’re doing. But they lack a user-friendly interface for non-technical people. So if you’re a beginner, you’d have a tough time getting a site live.The layout of Bluehost’s control panel (cPanel) makes it easy to use. You just need to point and click in most cases.It also has features for advanced users, but beginners too can easily install and start-up WordPress.Or, they can use the Bluehost website builder tools(such as Weebly or Drupal) to start with a template that you can customize by just dragging-and-dropping features.
8. 30-Day Money-Back Guarantee
Getting the best deal on web hosting usually means prepaying for a few months, a year or several years at a time.Bluehost is no different — more on that below. But they do offer a 30-day money-back guarantee on their plans.You can try out the service to gauge their performance for yourself, and then still ask for a refund if you’re not completely satisfied. We have a few words of caution, though.According to their terms, here’s what does and doesn’t fall under that guarantee:You can only get refunds on the web hosting cost, not any other products like domains or other add-ons.A $15.99 fee will be deducted if you received a free domain name in your plan.Any requests after 30 days will not be refunded.It’s not exactly a no-questions-asked policy like we’ve seen from some hosts. So make sure you’re OK with those points before signing up.
9. Customer Support
Bluehost offers everything from a knowledge base, to live chat, email ticket support, and even phone support. We tried out the live chat and Vinutha from Bluehost connected within two minutes.
Cons of Using Bluehost Hosting
Site Migrations Are Not FreeBluehost Pricing, Hosting Plans & Quick FactsBluehost’s Basic plan will cost you $3.95/mo (or $2.75 with our discount).Free domain? Yes for 1st year, then renews at $15.99.Ease of Sign-up: Easy two-page sign-up process.Payment Methods: Major credit cards and PayPal.Hidden Fees and Clauses: No refund on any domain names. Renewal rates for both domains and hosting increase.
Upsells: Some Upsells. Unfortunately, it’s a common occurrence in the web hosting industry and happens with a lot of different big-name hosting companies.
Account Activation: Most users enjoy instant activation. If the information is inaccurate or there’s suspicion of fraud, activation might get delayed.
Control Panel and Dashboard Experience: Simple and easy-to-use control panel.Installation of Apps and CMS (WordPress, Joomla, etc.): Mojo Marketplace makes app installation quick and easy.Do We Recommend Bluehost?Yes, we do.Bluehost has ranked at or near the top for both uptime and loading times for more than a year.In addition, they offer strong security support, a money-back guarantee, and plenty of user-friendly apps, all for one of the lowest rates in the industry ($2.75/month).So overall, Bluehost delivers strong performance and good value.So below is the Bluehost web hosting buy now button. Click to buy
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Drupal 7 to 9: Why, When and How Should You Migrate
Drupal is celebrating 20 years of an exciting journey of continued innovation. As a pioneer in content delivery across multiple channels, after 2 decades of existence it now stands at the forefront of the Digital Experience Platform (DXP) on the web, with sturdy content management tools, APIs for multichannel publishing, and one and the only digital hub to enable and support your digital presence.
Is it time to migrate from Drupal 6/7/8 to Drupal 9?
Since its launch in 2011, Drupal 7 became the popular content management tool to build websites and content-rich portals quickly. The open community support helped to make more than 11,000 contributing modules and more than 600 custom themes. The additional contributing modules played a considerable role in expanding the digital presence of enterprises with eCommerce, community platforms, project management, and many more valuable tools for day-to-day business.
As of today, almost 70% of the Drupal websites are running in Drupal 7 or lower versions. Although Drupal 7 gives us all the benefits of the content management tool along with the additional modules to drive your business, it’s time to migrate. Drupal 9 is the latest version released and the right choice to redefine the future of digital experience.
Drupal 9, an API-first platform with a powerful decoupled CMS, is a great fit to improve your user experience.
The question one might have is, "Do I need to migrate to Drupal 9 when my websites are running smoothly with the current version?”
As a Drupal development partner, our answer is “yes”. That’s because Drupal 7 is reaching the end of life by the end of November 2022. In 2018, Dries Buytaert announced the Drupal 7 end date as November 2021, but the Covid-19 impact extended it for one more year. If you continue to run your website on Drupal 7 after November 2022, you could face the following challenges.
Lack of Drupal 7 Code Support
Drupal 7 will stop getting community support officially. The leading hosting providers such as Acquia and Pantheon will stop the Drupal 7 support or provide little maintenance help at a higher cost. There is also a chance of the web pages being flagged as insecure in the third-party scanning tools. The other challenge includes integration with third-party systems.
Insufficient Security Support
The Official Drupal Security team will not extend support, stopping release of any security patches or available updates for Drupal 7 websites after November 2022. The outdated and insecure versions will leave your websites vulnerable to cybersecurity threats and data security compliance challenges.

Less Contributed Modules
Drupal community is based on thousands of contributed modules. Therefore, after the end date of Drupal 7, the community will reduce the effort to build the new modules or keep the Drupal 7 version updated. However, some of the contributed modules will run into several performance issues in the future.
Drupal 7 is reaching end-of-life; Drupal Association, Cloud hosting providers such as Acquia and Pantheon will soon withdraw the support.
Poor Website Performance
As we discussed earlier about the security support and the contributed modules that will expose you to vulnerabilities and decrease your website's SEO score. The overall lack of support will also directly or indirectly affect the website's performance.
Drupal 7, 8, and 9: The Journey
Drupal is in a transition phase after a steady version of Drupal 7 being used for a long time, covering 70% of the Drupal sites in the world. Drupal core platform depends on three major third-party libraries such as Symfony, Twig, and Guzzle, which means that we need to sync with their release timelines and their roadmaps.
Drupal 7 websites will face performance challenges as the contributed modules will no longer be supported for D7, and site security is expected to take a hit.
Just as Drupal 7 will end the support in November 2022, Drupal 8 will be stopping the support by November 2021. The most significant dependency in D8 is Symfony 3, and Symfony's official roadmap shows the end-of-life date to Symfony 3 as of November 2021. So the Drupal must adopt Symphony 4 or 5, which means switching to Drupal 9 is logical and imperative.
If you are on Drupal 8, all you need to do is keep your Drupal 8 site up-to-date, and you'll be ready for Drupal 9. Drupal 8 to 9 upgrade will be much faster and easier than the previous versions of Drupal.
Drupal 9: Digital Experience Platform for Future
As a future-ready Digital experience platform (DXP), Drupal 9 always stands apart from the rest of the CMS platforms with a decoupled /headless architecture. It gives you the freedom to publish the content across multiple channels, such as mobile, wearables, kiosks, and many other devices, while publishing it in just one place. In addition to that, it also gives the flexibility to use any front-end technology such as Angular, React, Vue, and Gatsby to display the content.
With Drupal 9, your marketing team always has the flexibility to define a No-code/less-code approach with the latest layout builder to publish content quickly with a responsive and SEO-friendly web page or a campaign landing page. It brings greater freedom to the marketers, allowing them to focus on the campaigns and the development team to focus on building next-generation digital experiences for the customers.
Conclusion
To sum it up, plan your migration path based on your unique business needs and goals. Identifying the proper roadmap to exceed expectations is imperative for your road to success, and Drupal 9 helps you with that. It facilitates easy migration, making the shift to a new version or undertaking future upgrades a seamless experience.
Please connect with ACL DIGITAL for end-to-end Drupal 9 migration and upgrade services, including design, development, strategy, integration, support, and maintenance to create engaging and customer-centric digital experiences.
0 notes
Text
INTERSERVER HOSTING REVIEW

InterServer Hosting Review
InterServer Hosting has been in the web hosting business since 1999, founded by John Quaglieri and Lavrik Michael in New Jersey, US. This hosting provides economic shared hosting, cloud hosting, and several other services that help individuals and business.One area in which InterServer excels is the provision of innovation-driven hosting services to its huge customer base. That is why highly reputed brands like Fortune 500 trust InterServer for their domain hosting. Additionally, InterServer is well known for its dedication in ensuring domain security and enhancing its reliability. The web host offers 24/7 live chat to sole issues at any given time.
General Information
1.Speed : 220 ms (January 2020 to February 2020 average)
2.UpTime :100% (January 2020 to February 2020 average)
3.Support : Phone support, ticketing system, email, 24/7 live chat
4. Apps : WordPress, Pebble, SitePad, Chyrp, HTMLy, Apache Roller, Serendipity, Dotclear, Textpattern, PivotX, Pubvana, Joomla, Drupal, e-commerce apps, CMSs, mailing lists, forums, and over 400 other apps.
5. Features : Unlimited storage, Unmetered bandwidth, Site Pad site builder, Unlimited emails, Content caching, Intershield protection, Website migration, Free SSL, Easy cPanel, Price- lock guarantee, Quick app installs, FTP access, Speed optimization, Money-back guarantee.

6. Plans : Cloud hosting/ Dedicated servers/ Shared hosting/Quick servers.
7. Site Transfer : Free site transfers
8. Price : Starts from as little as $5 per month (Standard web hosting)
The Pros and Cons of Using InterServer Hosting
1.Reliable uptime
InterServer performs UpTime exceptionally well when it comes to uptime, and you can expect your site to remain up while running most of the time.
2. Fast loading times
Besides high uptime, InterServer offers the best loading speed. On average, most of the sites hosted on InterServer respond within a record of time between 150 to 220 milliseconds. This means that InterServer is the best budget hosting provider.
3. Helpful customer support
Interserver gives best customer support and does help anytime whenever an issue is encountered with hosting through live chat, email, or phone line.
4. Competitive pricing
InterServer offers one of the most affordable website hosting price for individuals and businesses. InterServer’s price-lock guarantee, maintaining the initial prices, a 30-day money-back guarantee, refund of money if website hosting is cancelled.
5. Top-notch security
InterServer provides its unique security solution popularly known as InterShield. This tool helps to block attackers, scan for viruses and malware, and guard the whole system against other potential security risks.Further protection is made possible through the isolation of user accounts. Under the cPanel framework, no user can gain access to the account of another person. On top of that, users can drop PHP access and its privileges to avert the risk of file modification by PHP scripts.
6. Free site transfers
The free site transfer service helps users to move their existing domains to InterServer without much hassle. It is assured that the tech support will carry out the migration without any downtime.
7. Easy-to-use cPanel
InterServer offers a Linux-based cPanel that help users to get rid of the confusion they get while managing their accounts. The web host’s classic dashboard is made up of elements and tools for resellers, end-user site owners, and admins to make it easier to control the site.
8. E-commerce hosting
InterServer offers low-cost ecommerce hosting solutions that are meant to help create a Magento, WooCommerce, PrestaShop, OpenCart, or any other e-commerce store.
9. Cons
No uptime guarantees in their customer service agreement and Does not offer free domains.
INTERSERVER HOSTING PLANS
1.Standard Web Hosting: This plan costs $5 per month
2.ASP.NET web hosting: Costs $8.00 per month
3.Boost Web Hosting: This offering contains three different plans: The Standard plan ($5 per month), Boost 2 ($9.95 per month), and Boost 4 ($19.95 per month)
4.Reseller hosting: This category is made up of RS ONE, RS TWO, RS THREE, RS FOUR, and RS FIVE. The plans are priced at $19.95, $29.95, $39.95, $49.95, and $69.95 /month respectively.
5.Cloud VPS hosting: The cheapest plan under this category costs $6 per month while the top-tier plan costs $96 per month. Also, Windows VPS and WordPress VPS fall under this category, with their cheapest plans being priced at $10 per month and $6 per month, respectively.
Recommended
InterServer, gives access to unlimited resources, useful features, and top-grade security, all in one package. Additionally, InterServer is well known for its dedication to ensure domain security. Further to enhance its reliability, the web host offers 24/7 live chat support.
0 notes
Text
Reasons To Build eCommerce Enterprise On BigCommerce in 2020
With more than 100,000 online stores using BigCommerce, it is one of the most amazing stages for eCommerce endeavors. From normal estimated relationship to beasts and even privately owned businesses, everyone agrees that it is a veritable motivation for money offering. It gives a strong, versatile, and stable condition for associations moving from physical stores towards an undertaking level course of action. The allotment by industry type is:

In this article, we will look at the best 15 clarifications behind picking BigCommerce for building your webstore in 2020:
1 Ready To Use Website Themes and Templates
BigCommerce offers 50+ paid themes and 12 free subjects to peruse close by its Stencil Framework. You can pick them as indicated by your stock size, structures, show picture sizes, and adaptable improvement (AMP enabled) needs. They don't cost you beyond a reasonable doubt as you can pick from free themes or paid ones going limited for up to a few hundred bucks. They go with industry-express features and favorable circumstances like:

1.UX-obliging structure
2.Mobile responsiveness
3.Shopping truck auto-reviving
4.Translation arranged
5.Store Design gadget for visual showcasing
6.Page engineer and other customization extra things
7.They excuse a colossal bit of the improvement cycle and costs while 8.helping by giving industry-unequivocal structures. Auto-invigorating of these themes and formats is a cherry on the top!
2 Design Flexibility
Flexibility of design is a noteworthy element paying little mind to if you are building a store without any planning or migrating from other advancement.

It has various modules for front end structures like WordPress and Drupal (the two CMS and DXP) that grant you to continue with them after movement. Thusly it licenses you to investigate its own frontend capacities or to continue with your old course of action if you would lean toward not to relaunch your store.
Counting new things or pages is characteristic while most by far of the functionalities are managed by worked in eCommerce features. You can in like manner switch between any points with the help of its Stencil Framework.
3 SEO-Friendly
Site smoothing out is one of the fundamentals for your store as it ought to be found on Google with no issue. BigCommerce is a Google-obliging store with courses of action for all SEO best practices. While you can genuinely form the titles and URLs, it in like manner auto-makes them for you. Its SEO game plans license you to:

1.Write meta delineations truly in SEO boxes
2.Customize page title, meta marks, and legitimate names.
3.Use its SSL validation for getting space authority
4.Optimize your site for flexible customers through Google AMP
5.Include Alt messages for pictures, accounts, and other blended media content
6.Optimize your pages for Rich Snippets
7.Customize URLs to as per your target catchphrases
It is basic that by far most of its opponents give these features through outside applications requiring enrollment charges. This implies rehashing costs while BigCommerce has these features intrinsic. This is one motivation behind why it is acclaimed as a motivator for money stage in the business.
4 In-Built Marketing And Analytics Features
If you are looking for remarkable promoting features, BigCommerce has a ton in the backpack for you. Rather than other plan providers, here too, you don't need to pay for extra untouchable application enrollments. The going with features choose it an unquestionable choice among all other market alternatives:

1.Create and scatter coupons
2.Create and sell favoring vouchers
3.Create and insert advancing banners
4.Cart-level cutoff points
5.Email advancing help
6.Pre-demand blends
7.Automated interfacing with eBay, Amazon, and Facebook
8.SEO mechanical assemblies
On the assessment front, it's undertaking level examination give contributions regarding customer activity, truck surrender, division, and checkout direct channels. It similarly creates key data for the aggregate of your business channels as for stock turnover rates, demand following, and salary arranging. BigCommerce ERP integrations joins support for:
1.Microsoft Dynamics
2.SAP
3.Sage Accounting And Business Management Solutions
4.Quickbook Accounting Solutions
For more details: eCommerce iLabs
0 notes
Photo

Siteground Hosting Features & Tools Full Review - Best or Worst
In this blog, we will do Siteground Full tools and features Review and I Promise after reading this whole blog you will have no any confusion Regarding Siteground Hosting.
Introduction of Siteground
Siteground is one of recommended hosting provider by WordPress Officially & of-course the reason for the recommendation is the performance of their hosting. Recently they officially confirmed that they now use only Google Cloud Server for their hosting even for startup plan whose price starts from 6.99$ which I think the cheapest Google Cloud-based hosting. According to them, they are mainly based in Singapore but they have several data centre all over the world.


Technology Used By Siteground
Siteground has almost all the latest and best technology in their hosting like they recently integrated NGNIX and QUIC for better web speed even in slow connection. They use their own caching and optimization plugin named SG Optimizer for WordPress for better performance even they are improving it more and more.
I will introduce all technology used by them in tools section.
Siteground Speed Test and Server Response Time.
We have performed various Speed Test for siteground with different location based server and result were impressive.
View Full Speed Test
Some Samples of Siteground speed test are below
Google PageInsight
Gtmatrix
PingDom
-> 25 Locations
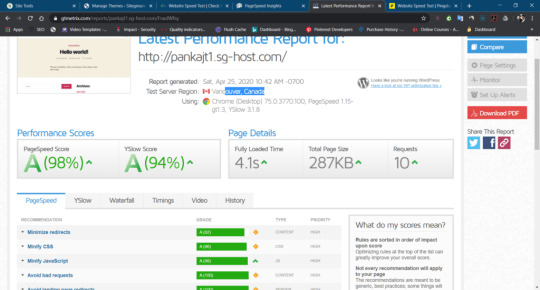
Siteground Speed test by Gtmatrix
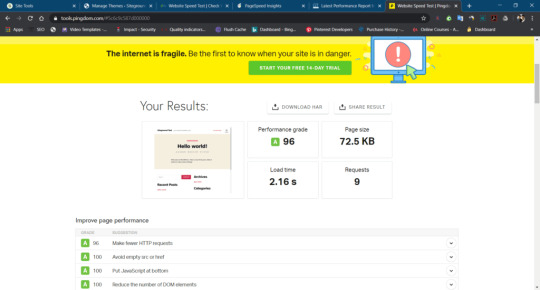
Siteground Speed Test By PingDom

Siteground Mobile Speed Score
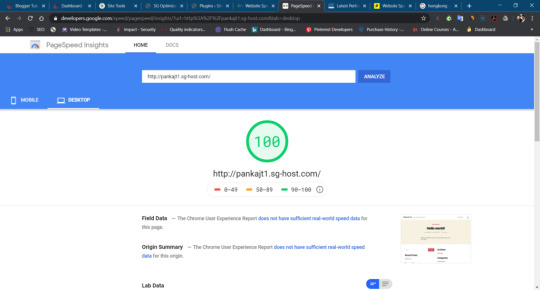
Siteground Desktop Speed Score
https://www.youtube.com/embed/htGg4RZlWOg
Siteground Hosting Live test
Siteground Hosting Uptime
According to Siteground, their uptime is 99.99%, which is accurate as they have cloud server (cluster of servers) means downtime is not an option in their Hosting.
Buy Siteground Hosting
-> Siteground India Hosting Review and alternative
Siteground Features and Tools available in Dashboard [cPanel]
I am really excited to tell you about siteground tools because I love them and the main reason for using siteground hosting for me is their tool. So let's explain their tools one by one.
1. App Manager
This tool is sounding its meaning from its name, i.e. App Manager will somehow manage your CMS application Automatically so that you do not need to install or delete them manually. Siteground App Manager has WordPress, Joomla, Drupal, Weebly, Magento, PrestaShop, ZenCart, OpenCart, phpBB, SMF, MediaWiki, Moodle, osTicket, vTiger, LimeSurvey, phpList, Piwigo. All these apps can be installed in siteground hosting automatically and you can manage them from siteground dashboard.

2. File Manager
Just like other hosting providers, You will get a file manager tool in siteground hosting to manage your hosting files. It has all the essential feature of a file manager like copy, paste, edit, rename, move, extract, compress etc.

3. FTP Accounts
Siteground hosting also provides FTP accounts for users to manage their files from third-party services like Filezilla. Here you can create, delete and manage FTP accounts.

4. MySQL Manager
MySQL tool will help you to create SQL database, manage SQL Users, Link SQL user to the database, Access SQL Database etc. This tool is really necessary even for WordPress users.

5. Backup
The backup tool creates an automatic backup of your website. This feature is really necessary even for professional developer because sometimes due to an unknown issue site get damaged and if you don't have a backup you will lose everything. In siteground backup tool, you can restore your site from last 30 days of backup.

6. SSL Manager
For making a website secure you must have an SSL certificate. Siteground Provides a free SSL certificate and a tool to manage it. from here you can directly install SSL certificate in a few clicks.

7. HTTPS Enforce
This feature of Siteground hosting will help you to forcibly serve all your content through the https protocol.
8. Protected URL
Protected URL is an Awesome security feature of siteground. You can secure any RL of your website with username and password. Only users with that credential can able to see that web page.

9. Blocked IPs
DDoS attack on any website is quite common, this feature of siteground will help you to block all those IPs that you think are harmful to your website. You can further unblock them anytime you want.
10. Site Scanner
Site Scanner is an addon product of siteground which is not available for free. You need to pay for it. It scans for malware in your website and tells location so that you can remove it manually. It has automatic removal feature but it is not very helpful for large websites with many scripts. Since it may remove your necessary files too.

11. Cloudflare Integration
Siteground has inbuilt Cloudflare integration to integrate Cloudflare free CDN to improve your website Speed and Code Optimization.

12. Caching
Website Caching is something that reduce server load and speedup your website. These days caching is just important as SSL for a website. Siteground have 3 Caching System, NGINX, Dynamic and Memcached.

13. WordPress Migration
Siteground have their Free WordPress Migration tool that need Siteground WordPress Migration Plugin to Migrate any website. They also offer free manual migration by their team.

14. Domain DNS Manager
When you map your domain to your hosting using a name server, then your domain provider will no longer manage your DNS setting. For this Particular Issue, siteground provide Domain DNS Manager tool from where you can Manage Parked Domain, Create and manage Subdomains, DNS Records, redirects etc.

15. Professional Emails
Professional emails are trending in these days. They show your quality and build trust among your audience and customer. Taking this into consideration, Siteground provides Free Professional Email accounts, Email Forwarder, Auto Responded, Email Filter, Authentication and Spam Filter. I love this particular service of any hosting provider not only siteground.

16. Website Statics
Site Statics tool really helps for those who are not too many techies in the field of web development or blogging. There are many things that you can track and see reports like Traffic Summary, Audience, Source, Behaviors, Error Logs, Access Log etc. This will help you to understand your website performance.

17. Git Tools
The most advance and rare tool that any hosting provider is Git. It helps to create a Git repository of your application, which you can later access, download and edit on multiple local branches. You will be able to easily deploy updates, as well as compare differences between your local source code and your production or staging copies.
18. Cron Job Manager
Some WordPress Plugin and script need to work in the back end automatically. With the Cron Jobs tool you to automate commands or scripts on your site. You can set up scheduled tasks to run at a specific time or time interval. You need to be comfortable using and understanding Linux commands in order to create and run cron jobs seamlessly.
Is Siteground Better from Bluehost?
Yes, Because Siteground uses Google Cloud server and other advanced Technology.
Does Siteground Offer Free Domain?
No, they do not offer any free domain but you can buy new during hosting order.
Is siteground Slow?
No, Definitely not.
Why Siteground is So Expensive?
Siteground Is too much expensive because they are using Cloud server for hosting, means your shared hosting plan is from google cloud.
Which Siteground Hostin Plan is best?
Choosing a hosting plan depends on need of resources by your website. If you have a heavy website then you are definitely going to need a better plan.
Read More https://bloggertutor.com/siteground-hosting-tools-review/?feed_id=474&_unique_id=5f089a80593c2 #hosting
0 notes
Text
300+ TOP DRUPAL Interview Questions and Answers
Drupal Interview Questions for freshers experienced
1. What Is Drupal? Drupal (pronounced Dru-Pull) is an open source content management system offering a toolset that rivals those of most commercial alternatives. With integrated social media and e-commerce functionality, it provides unique value as part of your social media strategy. 2. How to create a folder and a module file in Drupal? Given that our choice of short name is "onthisdate", start the module by creating a folder in your Drupal installation at the path: sites/all/modules/onthisdate. You may need to create the sites/all/modules directory first. Create a PHP file and save it as onthisdate.module in the directory sites/all/modules/onthisdate. As of Drupal 6.x, sites/all/modules is the preferred place for non-core modules (and sites/all/themes for non-core themes), since this places all site-specific files in the sites directory. This allows you to more easily update the core files and modules without erasing your customizations. Alternatively, if you have a multi-site Drupal installation and this module is for only one specific site, you can put it in sites/your-site-folder/modules. The module is not operational yet: it hasn't been activated. We'll activate the module later in the tutorial. 3. How to name your module? The first step in creating a module is to choose a "short name" for it. This short name will be used in all file and function names in your module, so it must start with a letter and by Drupal convention it must contain only lower-case letters and underscores. For this example, we'll choose "onthisdate" as the short name. Important note: It is not just a convention that the short name is used for both the module's file name and as a function prefix. When you implement Drupal "hooks" (see later portions of tutorial), Drupal will only recognize your hook implementation functions if they have the same function name prefix as the name of the module file. It's also important to make sure your module does not have the same short name as any theme you will be using on the site. 4. Explain the menu system in Drupal? Define the navigation menus, and route page requests to code based on URLs. The Drupal menu system drives both the navigation system from a user perspective and the callback system that Drupal uses to respond to URLs passed from the browser. For this reason, a good understanding of the menu system is fundamental to the creation of complex modules. Drupal's menu system follows a simple hierarchy defined by paths. Implementations of hook_menu () define menu items and assign them to paths (which should be unique). The menu system aggregates these items and determines the menu hierarchy from the paths. For example, if the paths defined were a, a/b, e, a/b/c/d, f/g, and a/b/h, the menu system would form the structure: a a/b a/b/c/d a/b/h e f/g 5. How to interact with Drupal search system? There are three ways to interact with the search system: Specifically for searching nodes, you can implement nodeapi ('update index') and nodeapi ('search result'). However, note that the search system already indexes all visible output of a node, i.e. everything displayed normally by hook_view () and hook_nodeapi ('view'). This is usually sufficient. You should only use this mechanism if you want additional, non-visible data to be indexed. Implement hook_search (). This will create a search tab for your module on the /search page with a simple keyword search form. You may optionally implement hook_search_item () to customize the display of your results. Implement hook_update_index (). This allows your module to use Drupal's HTML indexing mechanism for searching full text efficiently. If your module needs to provide a more complicated search form, then you need to implement it yourself without hook_search (). In that case, you should define it as a local task (tab) under the /search page (e.g. /search/mymodule) so that users can easily find it. 6. How to Customize a Drupal Syndicate Feed Icon? For a recent project I needed to customize the feed icon in the Drupal theme I was creating. This wasn't as straight forward as I thought it would be. Being the drupal newbie that I am I went looking for it in the core templates and suggestions page only to come empty handed. Previously I found the solution to theming a search form by using the search-block-form.tpl.php template file and thought there would be one for the feed icon too. I found the solution to this in the function reference in the form of a theme hook. theme_feed_icon($url, $title) This function is internally called by drupal to generate the feed icon in the Syndicate block. Our Job is to override this function. 7. How to backup a Drupal site? Backing up your Drupal site is now very easy, you just need to download and install a module called Backup & Migrate. To install the module click on the Administer Modules check the Backup and Migrate module and enable it and save the settings. Then navigate to the Administer Content Management Backup and Migrate then do the following settings. Exclude the following tables altogether: select the table which you dont want to take backup. Give the backup file name. There are also options to compress the file before download, or add a datestamp. And then click Backup Database. Alternately you can take backups using PhpMyAdmin. 8. How to move a Drupal Site from One host/server to another on your NEW host? Upload your folder with the complete drupal installation to your home-directory. Once done, go to phpadmin on the new host, create a new mysql database, example "name_drpl1" and create a new mysql user. Create a password for this new mysql user, click "assign all privileges" to this user and assign the user to the new database. You now should have a new mysql database on the new host with a mysql user, eg. "name_drpl1" as database name and "name_username" as database user name. Import (upload) the database (which you exported from the old host earlier) with phpadmin to the new database. This might take a minute. If needed edit the file /sites/default/settings.php and edit at the section where you enter the database, location, username and password. You CAN enter the password either encrypted or not encrypted there. Chmod your "files" folder so it is writeable using your ftp client (filezilla), chmod to 777 Double check your .htaccess and /sites/default/settings.php and make changes in case they are needed. Change nameserves on your domain host and let them point to your new host's nameservers. Enter the new nameservers in your control panel where your domain names are hosted, overwriting the old ones. After some time (sometimes a day or two) your domain should point to the new host and drupal should be up and running on the new host. 9. How to move a Drupal Site from One host/server to another? Migrating Drupal On your OLD host: Backup your whole home directory from your ftp access using an ftp client like filezilla. Make a folder on your local harddisk and download the complete directory to that local folder. Backup your mysql database on your old host using phpadmin, select your mysql database, usually something like "name_drpl1". Select all fields, click "export" and save the database to your local harddisk. Leave default options enabled. You will receive a file similar to "name_drpl1.sql". This is your mysql database 10. How to install Drupal on a local WAMP server? Preparing your computer with a local installation of Drupal with WampServer is comparatively a trouble-free process to follow. Since WampServer will install an Apache-server, SQL, PHP and phpMySQL on your computer, with those tools you can install and run Drupal locally even without an internet connection.

DRUPAL Interview Questions 11. How to remove breadcrumbs from my Drupal pages? Breadcrumbs or breadcrumb trail is a navigation aid used in drupal interfaces. Normally it appears in between the top banner area and the page title. It gives users a way to keep track of their location within programs. Breadcrumbs are really useful in a comparatively bigger website with plenty of sections and subsections. But when it comes to smaller websites, it may found useless. In those cases you may either hide it using CSS (eg. .breadcrumb {display: none;}) or in the page.tpl.php file remove the line that says 12. How to add custom PHP codes in my Drupal pages or blocks? By default, drupal will not allow inserting PHP code directly inside a post or in a block. To do this, you need to activate a drupal module called PHP filter via, Administer Site building Modules. Even though this module ships with drupal, it remains disabled by default. 13. How can I create a custom region in my Drupal template? Adding a new region in your drupal template is not a hard thing, but its not as easy as adding a new block. It's basically a two-step process: define the custom region in your theme's .info file insert some PHP in your theme's page.tpl.php file wherever you would like the new region to appear 14. What does Views do and how do you use it? Views is a practical necessity for sites built on Drupal 6, and it's imperative that your developer understands how to take advantage of it. Earl Miles has written a great summary on the Views project page. 15. How can I add a new Block In Drupal? Adding a new block is a simple process in drupal 6. Go to Administer Blocks and click on the Add Block link (tab). Fill in the form with the necessary PHP/HTML code in the block body. And click the 'Save Block' button. 16. How can I customize my 404 - Page not found page? Create a new page with some extra information, so that your visitors don't ever plunge on to the default boring 404 - page not found error page. Once this page is created: Remember its node ID, Go to Administer > Site configuration > Error reporting Set Default 404 (not found) page to the node ID you just created Save your settings You can also use the Search 404 module as an alternative. 17. How to handle upgrades in Drupal? It's a fact of life that you'll have to upgrade your Drupal installation and contributed modules fairly frequently. Your candidate should mention: backing up the site, putting it into maintenance mode downloading the new version of the module uncompressing it running update.php testing the site aking the site out of maintenance mode Ideally, your candidate would also mention creating a development environment to minimize downtime. There is also a big difference between upgrading a module (process described above) and a Drupal minor version upgrade, which requires more careful patching. Drupal major version upgrades, which happen every couple years, are another can of worms entirely. 18. How do I show different Drupal themes on different pages? Yeah it's possible! You can apply different themes to different pages in your drupal site simply with the help of a cool module called 'Sections'. 19. How do I add images to Drupal? Image module allows users with proper permissions to upload images into Drupal. Thumbnails and additional sizes are created automatically. Images could be posted individually to the front page, included in stories or grouped in galleries. 20. How can I translate Drupal to my local language? The interface text (like the "Log in" button and the "Add new comment" text) is in English by default, but can be translated. For many languages, there are completed or partly completed translations available. (See the locale module on how to use them.) All languages need more translation contributions. Some have only incomplete versions of the text in core, so that parts of the interface will show up in English. Others may be complete but need corrections and improvements of the language. And no language has a complete set of translations for all contributed modules. 21. How do I remove the title 'Navigation' from the navigation block? To prevent the navigation block title or any other block title from appearing in the pages, just do the following. Navigate to Administer Site building Blocks and click the configure link next to the Navigation block. In the block configuration page, enter in the Block title filed. This will override the default title for the block and remove the title. 22. How do I get my site to have SEO-friendly URLs? The Pathauto module automatically generates URL/path aliases for various kinds of content (nodes, taxonomy terms, users) without requiring the user to manually specify the path alias. This allows you to have URL aliases like /category/my-node-title instead of /node/123. The aliases are based upon a "pattern" system that uses tokens which the administrator can change. 23. How can I enable clean URLs in Drupal? Drupal's default URL structure is like "http://www.sitename.com/?q=node/10″ This URL format can be hard to read, and can sometimes prevent search engines from indexing all your pages properly. In this case you can eliminate this "?q=" and clean the URLs through the following steps. Navigate to Administer Site configuration Clean URLs. By default, it will be disabled. Select enabled and click the save configuration button. You are done. You can make your URLs even more cleaner with the help of path module. Home Administer Site building Modules: enable the Path Module. 24. How can I change the favicon in my Drupal Site? Create your own favicon.ico file using any graphic tools or with the help of any online favicon generator tools like dnamicdrive. Navigate to admin site building themes and click the configure link next to your current theme. This will bring up the theme configuration page. Here you will see a section titled Shortcut icons settings. You can either upload your favicon file or specify the path to your customized icon file. The changes may not appear immediately in your browser, you need to clear your browser's cache and reload the page. If you have bookmarked your site, you may need to delete the bookmark and then recreate it again so that the new favicon will appear in the bookmarks menu. 25. Explain favicon in Drupal? A favicon (short for favorites icon), also known as a website icon or bookmark icon is a 1616 pixel square icon that appears near the address bar and in the bookmarks folder in a visitor's browser. By default, a drupal site shows that water drop kinda drupal logo as favicon. 26. How can I reset my Drupal admin password? Login to cPanel -> Databases box -> phpMyAdmin; Select the Druapl database folder from the left navigation bar. The page will refresh and and the Drupal database's tables will be displayed on it. Click on the SQL tab. In the text field write the following SQL query: update users set pass=md5('NEWPASS') where uid = 1; where "NEWPASS" is your new Drupal administrative password. Click the GO button to submit the query. If the query is executed correctly and no errors are displayed then you should be able to login with the new password. 27. How to install a new module in Drupal? After finding and downloading a module, the next step would be to copy it the modules folder. Most people copy the file to the default modules folder here http://sitename.com/drupal/modules this is where all the modules that ship with Drupal are stored so it seems somewhat logical to do this. But this folder is actually meant to store only Drupal's default modules. Instead you should go to http://sitename.com/drupal/sites/all folder, there you will see a readme.txt file. This file will clearly tell you the trick. You just need to create a new folder named modules here. Now copy the modules folder here. That's all, you have successfully installed the module. Next step would be to enable the module through the Admin interface. To do this navigate to Administer Site Building Modules. Here you will see a list off all installed modules, and our newly installed module will also be listed here. You just have to check the enable check box against the new module and then click the Save Configuration button. That's all. 28. How can I install a new theme in Drupal? This is another common question among Drupal newbies all time. After trying out all available themes under Drupals theme directory, we may naturally want to try new themes. Installing a new theme is very simple and straightforward. Follow the steps below. Download a new theme package. Note that themes for different Drupal versions are not compatible, version 5.x themes do not work with Drupal 6.x and reverse. Read any README or INSTALL files in the package to find out if there are any special steps needed for this theme. Upload the contents of the theme package to a new directory in the themes directory in your Drupal site. In Drupal 5.x & 6.x, you place your themes in /sites/all/themes/yourThemeName Click administer themes and enable the new theme (Drupal will auto-detect its presence). Edit your user preferences and select the new theme. If you want it to be the default theme for all users, check the default box in the themes administration page. 29. How to make my Drupal site offline to public, while it is under construction? You can set your Drupal site in off-line mode, while it is being developed. Just click Administer Site maintenance. There you can set the status to off-line. If you wants, you can also set your own custom off-line message. When set to Off-line, only users with the administer site configuration permission will be able to access your site to perform maintenance; all other visitors will see the site off-line message configured there. Authorized users can log in during Off-line mode directly via the user login page. 30. How does caching work in Drupal? One of the common (mostly unfounded) complaints about Drupal has been, "Drupal is slow." You want to hire a developer who understands Drupal's built in caching system, and what its limitations are. For example, Drupal 6's block cache will not appreciably speed up the page if the user is logged in. Ask your candidate to recommend some additional solutions to speed up Drupal's caching. These could include the Boost module, Varnish, Squid, Memcache or Pressflow. Ask if they've ever run into issues with Drupal's cache. 31. Can you please explain the difference between Core and Contrib in Drupal? The standard release of Drupal, known as Drupal core, contains basic features common to content management systems. These include user account registration and maintenance, menu management, RSS-feeds, page layout customization, and system administration. The Drupal core installation can be used as a brochureware website, a single- or multi-user blog, an Internet forum, or a community website providing for user-generated content. As of August 2011 there are more than 11,000 free community-contributed addons, known as contrib modules, available to alter and extend Drupal's core capabilities and add new features or customize Drupal's behavior and appearance. Because of this plug-in extensibility and modular design, Drupal is sometimes described as a content management framework. Drupal is also described as a web application framework, as it meets the generally accepted feature requirements for such frameworks. 32. What are System requirements for Drupal? A minimum base installation requires at least 3MB of disk space but you should assume that your actual disk space will be somewhat higher. For example, if you install many contributed modules and contributed themes, the actual disk space for your installation could easily be 40 MB or more (exclusive of database content, media, backups and other files). 33. Why ca not A Drupal user edit a node they created? Symptoms: An authorized Drupal user loses "edit" access to nodes they've created, even if they have appropriate node (or other module) access permissions. Or, user cannot edit a node that should be editable by them, based on access control or node access settings. No errors or warnings are presented to the user. Nothing in the Drupal watchdog log. Possible Cause: The user does not have permission to use the input filter currently assigned to the node. (An administrator or other privileged user may have changed the input filter settings, or, input filter permissions may have been changed to exclude the node author since the node was created. As a result, the user never had, or no longer has permission to use the input filter associated with the node.) 34. How Does Drupal Compare to Ruby on Rails? Another common alternative platform to Drupal is Ruby on Rails. We really don't have much to say about Ruby except that it is a framework moreso than a platform. There are some characteristically challenging web development tasks that are quite easy to do with Ruby, and there are others which are infinitely more complicated than they should be. One big difference is the fact that Ruby lacks the refined data object model found in Drupal that ensures interoperability between various aspects of the system, such as adding new modules to modify the operations of others. Whereas Drupal offers a self-generating database schema for many modules and underlying components of the platform, Ruby on Rails emphasizes a design philosophy holding that simplification of code conventions leads to better outcomes. While this all sounds good in principle, we have found there are certain tasks that make adherance to this philosophy an ideal moreso than a practical goal and breaking free from these conventions when necessary a daunting task (especially when integrating with external systems). 35. How Does Drupal Compare to Other Open Source CMS Systems? Drupal is also often compared with other open source content management systems including Joomla, Plone, Scoop, Silverstripe, Typo3, Graffitti, Moveable Type and Wordpress. There are characteristic features to all of these systems that make them appropriate in certain contexts, and most of them compare favorably to Drupal in one category of operation or another. Few of them, however, are capable of offering the balance between performance and functionality found in Drupal. 36. How Does Drupal Compare to Commercial CMS Systems? Drupal is often compared to a number of commercial content management systems including Crown Peak, Expression Engine, Clickability and Site Life in terms of capabilities. None of these systems offer the range of features that can be found in Drupal or the flexible, developer-friendly architecture that allows us to rapidly deploy dynamic web sites. In terms of sustainability, these platforms charactertistically lack the innovative approach to development embraced by the Drupal community, with updates and new features continually being added to the platform. These systems typically do surpass Drupal in terms of out-of-the-box reporting and metrics tools, generally providing views of data that is also stored in other systems. For instance, detailed page tracking information can just as easily be pulled from a CDN and integrated into a Drupal site for much less than the costs of per-seat licenses from a commercial vendor over a 1 month period. 37. What Kind of Support Is Available? A wide range of support services are available for organizations running Drupal sites. The Drupal community itself is an excellent resource for people looking to learn more about the platform or resolve specific issues that emerge using the system. Acquia offers an enterprise distribution of Drupal that includes uptime monitoring, email and telephone based troubleshooting support, and subscription plans for sites with varying performance requirements. For hosting, Our works with a variety of partners to deliver solutions to ensure sites are operational and can scale to meet changing traffic expectations. Rackspace is Our preferred hosting partner, and their 100% uptime guarantee allows us to focus on building great web sites without worrying about the network. Workhabit and Amazon S3 offer cloud hosting solutions that allow us to build sites that automatically scale to handle large peaks of traffic, and to provision new servers dynamically based on actual traffic conditions on any given day. 38. How Does Drupal Scale? Trellon has built Drupal sites and deployed them in very demanding scenarios, serving millions of page views a day. Drupal scalability and performance optimization is one of our core competencies, and we often work with existing web properties to find ways to improve their performance. Contact us to discuss your specific needs. 39. What Does Drupal Do? Drupal is the choice for many great web sites because it does a lot of different things very well, and allows different kinds of information to interact effectively through its flexible, open architecture. Compared with commercial or custom solutions, Drupal's feature set is far more economic and practical for most organizations. 40. Explain coding standards in Drupal? As per the Coding standards, omit the closing ?> tag. Including the closing tag may cause strange runtime issues on certain server setups. (Note that the examples in the handbook will show the closing tag for formatting reasons only and you should not include it in your real code.) All functions in your module that will be used by Drupal are named {modulename}_{hook}, where "hook" is a pre-defined function name suffix. Drupal will call these functions to get specific data, so having these well-defined names means Drupal knows where to look. We will come to hooks in a while. 41. What is CMS? A content management system (CMS) is a collection of procedures used to manage work flow in a collaborative environment. These procedures can be manual or computer-based. The procedures are designed to: Allow for a large number of people to contribute to and share stored data Control access to data, based on user roles. User roles define what information each user can view or edit Aid in easy storage and retrieval of data Reduce repetitive duplicate input * Improve the ease of report writing Improve communication between users In a CMS, data can be defined as almost anything – documents, movies, pictures, phone numbers, scientific data, etc. CMSs are frequently used for storing, controlling, revising, semantically enriching, and publishing documentation. Content that is controlled is industry-specific. For example, entertainment content differs from the design documents for a fighter jet. There are various terms for systems (related processes) that do this. Examples are web content management, digital asset management, digital records management and electronic content management. Synchronization of intermediate steps, and collation into a final product are common goals of each. cms,drupal,drupal cms,interview questions,technical,joomla,joomla cms,drupal interview question,content management system 42. Source Code The program must include source code, and must allow distribution in source code as well as compiled form. Where some form of a product is not distributed with source code, there must be a well-publicized means of obtaining the source code for no more than a reasonable reproduction cost preferably, downloading via the Internet without charge. The source code must be the preferred form in which a programmer would modify the program. Deliberately obfuscated source code is not allowed. Intermediate forms such as the output of a preprocessor or translator are not allowed. 43. Derived Works The license must allow modifications and derived works, and must allow them to be distributed under the same terms as the license of the original software. 44. Integrity of The Author’s Source Code The license may restrict source-code from being distributed in modified form only if the license allows the distribution of “patch files” with the source code for the purpose of modifying the program at build time. The license must explicitly permit distribution of software built from modified source code. The license may require derived works to carry a different name or version number from the original software. 45. No Discrimination Against Persons or Groups The license must not discriminate against any person or group of persons. 46. What are GNU Licenses ? Does free software mean using the GPL? Not at all—there are many other free software licenses. We have an incomplete list. Any license that provides the user certain specific freedoms is a free software license. 47. Why are so many Drupal versions available – 4.x, 5.x …? Which one should I use? It is recommended that you run the most current stable release. This can always be found at the Drupal Project page. However, if there are no compelling features in the latest version, a contrib module that is important to you isn’t ready or you don’t have time, there is no need to rush your upgrade as long as security updates are available for the version you are running. 48. Can I use Drupal on the command line? Yes, you can use drush – drush is a command line shell and Unix scripting interface for Drupal 49. What are hooks in Drupal ? Allow modules to interact with the Drupal core. Drupal’s module system is based on the concept of “hooks”. A hook is a PHP function that is named foo_bar(), where “foo” is the name of the module (whose filename is thus foo.module) and “bar” is the name of the hook. Each hook has a defined set of parameters and a specified result type. To extend Drupal, a module need simply implement a hook. When Drupal wishes to allow intervention from modules, it determines which modules implement a hook and calls that hook in all enabled modules that implement it. 50. what is Database abstraction layer in Drupal ? Allow the use of different database servers using the same code base. Drupal provides a slim database abstraction layer to provide developers with the ability to support multiple database servers easily. The intent of this layer is to preserve the syntax and power of SQL as much as possible, while letting Drupal control the pieces of queries that need to be written differently for different servers and provide basic security checks. Most Drupal database queries are performed by a call to db_query() or db_query_range(). Module authors should also consider using pager_query() for queries that return results that need to be presented on multiple pages, and tablesort_sql() for generating appropriate queries for sortable tables. 51. Explain the menu system in Drupal ? Purpose of menus ? Define the navigation menus, and route page requests to code based on URLs. The Drupal menu system drives both the navigation system from a user perspective and the callback system that Drupal uses to respond to URLs passed from the browser. For this reason, a good understanding of the menu system is fundamental to the creation of complex modules. Drupal’s menu system follows a simple hierarchy defined by paths. Implementations of hook_menu() define menu items and assign them to paths (which should be unique). The menu system aggregates these items and determines the menu hierarchy from the paths. For example, if the paths defined were a, a/b, e, a/b/c/d, f/g, and a/b/h, the menu system would form the structure: a a/b a/b/c/d a/b/h e f/g Note that the number of elements in the path does not necessarily determine the depth of the menu item in the tree. When responding to a page request, the menu system looks to see if the path requested by the browser is registered as a menu item with a callback. If not, the system searches up the menu tree for the most complete match with a callback it can find. If the path a/b/i is requested in the tree above, the callback for a/b would be used. The found callback function is called with any arguments specified in the “page arguments” attribute of its menu item. The attribute must be an array. After these arguments, any remaining components of the path are appended as further arguments. In this way, the callback for a/b above could respond to a request for a/b/i differently than a request for a/b/j. For an illustration of this process, see page_example.module. Access to the callback functions is also protected by the menu system. The “access callback” with an optional “access arguments” of each menu item is called before the page callback proceeds. If this returns TRUE, then access is granted; if FALSE, then access is denied. Menu items may omit this attribute to use the value provided by an ancestor item. In the default Drupal interface, you will notice many links rendered as tabs. These are known in the menu system as “local tasks”, and they are rendered as tabs by default, though other presentations are possible. Local tasks function just as other menu items in most respects. It is convention that the names of these tasks should be short verbs if possible. In addition, a “default” local task should be provided for each set. When visiting a local task’s parent menu item, the default local task will be rendered as if it is selected; this provides for a normal tab user experience. This default task is special in that it links not to its provided path, but to its parent item’s path instead. The default task’s path is only used to place it appropriately in the menu hierarchy. Everything described so far is stored in the menu_router table. The menu_links table holds the visible menu links. By default these are derived from the same hook_menu definitions, however you are free to add more with menu_link_save(). 52. How to interact with Drupal search system ? There are three ways to interact with the search system: Specifically for searching nodes, you can implement nodeapi(‘update index’) and nodeapi(‘search result’). However, note that the search system already indexes all visible output of a node, i.e. everything displayed normally by hook_view() and hook_nodeapi(‘view’). This is usually sufficient. You should only use this mechanism if you want additional, non-visible data to be indexed. Implement hook_search(). This will create a search tab for your module on the /search page with a simple keyword search form. You may optionally implement hook_search_item() to customize the display of your results. Implement hook_update_index(). This allows your module to use Drupal’s HTML indexing mechanism for searching full text efficiently. If your module needs to provide a more complicated search form, then you need to implement it yourself without hook_search(). In that case, you should define it as a local task (tab) under the /search page (e.g. /search/mymodule) so that users can easily find it. 53. What is a Module in drupal ? A module is software (code) that extends Drupal features and/or functionality. Core modules are those included with the main download of Drupal, and you can turn on their functionality without installing additional software. Contributed modules are downloaded from the Modules download section of drupal.org, and installed within your Drupal installation. You can also create your own modules; this requires a thorough understanding of Drupal, PHP programming, and Drupal’s module API. 54. Explain User, Permission, Role in drupal. Every visitor to your site, whether they have an account and log in or visit the site anonymously, is considered a user to Drupal. Each user has a numeric user ID, and non-anonymous users also have a user name and an email address. Other information can also be associated with users by modules; for instance, if you use the core Profile module, you can define user profile fields to be associated with each user. Anonymous users have a user ID of zero (0). The user with user ID one (1), which is the user account you create when you install Drupal, is special: that user has permission to do absolutely eveything on the site. Other users on your site can be assigned permissions via roles. To do this, you first need to create a role, which you might call “Content editor” or “Member”. Next, you will assign permissions to that role, to tell Drupal what that role can and can’t do on the site. Finally, you will grant certain users on your site your new role, which will mean that when those users are logged in, Drupal will let them do the actions you gave that role permission to do. You can also assign permissions for the special built-in roles of “anonymous user” (a user who is not logged in) and “authenticated user” (a user who is logged in, with no special role assignments). Drupal permissions are quite flexible — you are allowed to assign permission for any task to any role, depending on the needs of your site. 55. Explain the concept of node in drupal. A node in Drupal is the generic term for a piece of content on your web site. (Note that the choice of the word “node” is not meant in the mathematical sense as part of a network.) Some examples of nodes: Pages in books Discussion topics in forums Entries in blogs News article stories Each node on your site has a Content Type. It also has a Node ID, a Title, a creation date, an author (a user on the site), a Body (which may be ignored/omitted for some content types), and some other properties. By using modules such as the contributed Content Construction Kit (CCK) module, the core Taxonomy module, and the contributed Location module, you can add fields and other properties to your nodes. 56. Concept of Comment in Drupal . Comments are another type of content you can have on your site (if you have enabled the core Comment module). Each comment is a typically small piece of content that a user submits, attached to a particular node. For example, each piece of discussion attached to a particular forum topic node is a comment. 57 explain Taxonomy in drupal . Drupal has a system for classifying content, which is known as taxonomy and implemented in the core Taxonomy module. You can define your own vocabularies (groups of taxonomy terms), and add terms to each vocabulary. Vocabularies can be flat or hierarchical, can allow single or multiple selection, and can also be “free tagging” (meaning that when creating or editing content, you can add new terms on the fly). Each vocabulary can then be attached to one or more content types, and in this way, nodes on your site can be grouped into categories, tagged, or classified in any way you choose. 58 . How database system of drupal works ? Drupal stores information in a database; each type of information has its own database table. For instance, the basic information about the nodes of your site are stored in the Node table, and if you use the CCK module to add fields to your nodes, the field information is stored in separate tables. Comments and Users also have their own database tables, and roles, permissions, and other settings are also stored in database tables. 59. Explain the path system of drupal ? When you visit a URL within your Drupal site, the part of the URL after your base site address is known as the path. When you visit a path in your Drupal site, Drupal figures out what information should be sent to your browser, via one or more database queries. Generally, Drupal allows each module you have enabled on your site to define paths that the module will be responsible for, and when you choose to visit a particular path, Drupal asks the module what should be displayed on the page. For instance, this site (drupal.org) is (of course) built with Drupal. The page you are now viewing is http://drupal.org/node/19828, whose path is “node/19828?. The module that is responsible for this path is the core Node module, so when you visit this page, Drupal lets the Node module determine what to display. To determine the path to a particular page on your site, for purposes of creating a link, go to the page you want to link to and look at the URL in the address bar. By default the URL, after the base address of your site, will begin with ‘?q=’. When ‘Clean URLs’ are enabled you will see a directory structure in the URL. The “path” for use in a menu item is the part of the URL after the site’s base address and without the “?q=”. 60. Explain Region, Block, Menu in drupal .. Pages on your Drupal site are laid out in regions, which can include the header, footer, sidebars, and main content section; your theme may define additional regions. Blocks are discrete chunks of information that are displayed in the regions of your site’s pages. Blocks can take the form of menus (which are concerned with site navigation), the output from modules (e.g., hot forum topics), or dynamic and static chunks of information that you’ve created yourself (e.g., a list of upcoming events). There are three standard menus in Drupal: Primary Links, Secondary Links, and Navigation. Primary and Secondary links are built by site administrators, and displayed automatically in the page header of many themes (if not, you can enable their blocks to display them). Navigation is the catch-all menu that contains your administration menus, as well as links supplied by modules on your site. You can also create your own custom menus, and display them by enabling their blocks. You can customise menus in several ways, such as reordering menu items by setting their “weight” or simply dragging into place, renaming menu items, and changing the link title (the tooltip that appears when you mouse over a menu item). You can move a menu item into a different menu by editing the Parent property of the menu item. You can also add custom menu items to a menu, from the Add menu item tab of the Menu administration screen. To create a menu item, you will need to provide the path to the content (see above). In all cases a menu item will only be shown to a visitor if they have the rights to view the page it links to; e.g., the admin menu item is not shown to visitors who are not logged in. 101. What hardware does Drupal.org run on? 100. Drupal and Working with JavaScript 99. Why does Drupal need a database? What database… 98. How to create a static archive of a Drupal web… 97. Programming best practices and CMS(drupal) bes… 96. what are Drupal Distributions and Drupal inst… 95. Drupal coding standards 94. Drupal 8 classes and interfaces 93. Explain drupal advanced search 92. Drupal 8 , Changelog.txt – What’s new in Drupa… 91. Drupal Negatives and explanation on Usability,… 90. Explain Drupal Architecture 89. Drupal Version release dates 88. Drupal at a glance 87. Why you shouldn’t modify core drupal files ? 86. Explain hardcoding in drupal ? 85. Explain Theming in Drupal 8 ? 84. Steps for launching a drupal site ? 83. Explain drupal administration 82. How to configure .htaccess to ignore specific … 81. What are the steps for migrating drupal websit… 80. How to install and configure drupal 8 ? 79. How to Install Drupal ? 78. What are alpha, beta releases and release cand… 77. What do version numbers in drupal mean? 76. Explain Backward Compatibility in Drupal ? 75. Explain Security features of Drupal ? 74. What are Entity types in drupal ? 73. What is Bootstrap in drupal ? 72. What is drupal weight ? 71. What is triage ? 70. What is drupal trigger ? 69. What is theme and theme engine in drupal ? 68. What is teaser in drupal ? 67. What is render array in drupal ? 66. What is drupal region ? 65. What is permission in drupal ? 64. What is Git in drupal ? 63. What is DrupalCon and Druplicon ? 62. What is cron in drupal ? 61. What is critical path ? DRUPAL Questions and Answers pdf Download Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Drupal 8 on azure 7 reasons why it is a match made in heaven

First of all, Drupal 8 is the greatest release of Drupal. It is the most widely used enterprise web content management system. Developers like it and prefer for its speed and flexibility also. The main platform of Drupal has more than 200 in built features to help businesses to create memorable digital experiences.
Drupal 8 offers mobile-first approach and also supports responsive design. The content authoring in Drupal is easier. Drupal 8 helps in creating great online experiences for audiences across the globe with better globalization and multi-lingual support. Drupal 8 is being adopted twice as fast as Drupal 7 had been. Code of Drupal 8 includes object-oriented classes, interfaces, inheritance. It uses PHP standards and requires at least PHP 5.5.
Most common question is- Which is the right platform for hosting Drupal websites? There is not a complete solution which fits it all. Drupal 8 sites on Azure gives many business benefits. Go through the details of Drupal 8 at- Drupal 8 Is Not A CMS, It’s CMF.
Benefits of Drupal 8 on Azure-
Azure, the cloud platform operated by Microsoft, is an high-level hosting environment providing:
Managed web server instances (Web Worker Role)
Database services (SQL Azure)
Similarly, File storage and distribution (Azure Blob Storage)
CDN and caching for both the web server instances and the file distribution
Simple object storage (Azure Table)
And other related services (less useful for Drupal)
Reasons why Microsoft Azure is a good platform for Drupal hosting- 1. Drupal Web App-
It is very easy and also simple to migrate a Drupal website to Azure Web App. By following some easy steps, complete Drupal site can be moved within an hour. These simple steps include the creation of Azure website, the creation of MySQL database and copying it to Azure Web Apps and developing the code using version control tools such as Git BitBucket.
2. Pre-Installed Drupal Tools-
Developers using some popular version control tools such as Git and BigBucket. Azure has made these tools available pre-installed with just only plug-and-play with its platform. By using this, developers can continue to use these tools of their choice and also improve their development workflows.
3. Ready modules for authentication, file storage-
There are various ready made modules accessible in Drupal for commonly used tasks, For eg., authentication, controlling access and likewise distributed file storage. With the use of such modules, developers can save a lot of development time and as a result influence the ready made connectivity with Azure platform. Many of these modules uses libraries of Microsoft and these are stable and scalable also.
4. Caching tools-
Those websites having heavy content need to use caching tools. These tools are used to provide better search options for a hazard free user experience. Varnish and Memcache are caching tools and search experience enhancers like Apache Solr are popular within developers community. These tools are available as plug-ins with Microsoft Azure. It makes easy to integrate with the websites and also to increase the speed of website.
5. Application performance management with application insights-
Application insights is most useful service for web developers. This service helps developers to monitor the performance of their live web applications. It identifies the performance issues. Similarly, it provides necessary analytics tools to help the developers to analyze issues and use of application by the end users. With the use of insights, developers can continuously improve the performance. Insights can also improves the usability of their application. Application insights is correctly hosted within Microsoft Azure. It is free to use until the application has significant use.
6. Premium Partnership-
Microsoft Azure is Premium Technology supporter for Drupal. By this partnership it is more easy and also simple for Drupal developers to instantly start using Windows and Linux Virtual Machines, apps and infrastructure within Microsoft-managed data centers around the world. Using Visual Studio tools, developers can develop and debug apps fast. Due to the features such as built-in auto-scaling and pre-minute billing, organizations that uses Drupal can save money and agile.
7. Used by industries-
Not only organizations but also educational institutes are using the combination of Drupal and Azure for their web applications. For eg.,
1. Group INSEEC- It is one of the biggest international professional training providers which delivers high-quality training not only for luxury but also for hospitality customers.
2. Shezlong- It is an Egypt-based startup which offers online psychotherapy for millions of sufferers.
3. ESADE Business School- It is one of the major international professional training providers. So it delivers high-quality training and hospitality customers.
Final Words-
If you are searching for a hassle-free Drupal hosting, you should go with the various options provided by Microsoft Azure. It is highly secure and also offers great performance for delivering seamless digital experiences through your Drupal web application. Microsoft offers well documentation and videos for quick assistance.
Are you looking to develop a website for your business? We have a dedicated team that believes in benefits and effectiveness of hosting drupal website on azure platform. Develop a website with Solace that will help you to set you on your way to success of business. Contact us for your effective website development to stand out in the market.
0 notes
Text
Move On To Drupal 8, Be Ready For Drupal 9!

Change is the only constant and yet what one fears the most is change. But it is rightly said about change - “Don’t be afraid of change. You may lose something good, but you may gain something better.” We’ll like to say the same about the fear you hold for changing the current version of your Drupal 6/7 site to Drupal 8. Well, we also know that its more of a confusion than the fear of change, since you’re stuck between the two thoughts - whether to upgrade now to Drupal 8 or wait for Drupal 9. What if we say, we offer you a solution that will hit both the birds with one stone?
An Easy, Inexpensive & Drupal 9 Compatible Migration!

We have been an active Drupal community member since the past 6+ years, 7+ Drupal projects supported, 5000+ successfully delivered international projects and 500+ international Drupal projects - out of which 100+ projects are of Drupal Migration. And hence, we can help you in migrating your current Drupal 6/7 site to Drupal 8 and that too in a way that you will not have to spend a single penny for migrating to Drupal 9 in future. There’s a bunch of rational reasons to back this statement and offer of ours, which we’ll like to share with you:
Change in Drupal Philosophy Previously, every Drupal upgrade was considered to be tedious and more of a technical task as compared to its counterpart CMS platforms. This is because Drupal 8 was created with a philosophy of bridging the gap between the technical developer and a layman-like admin. And taking this philosophy of positive change, Drupal 9 is going to bridge the gap of upgrade issue by introducing compatibility between its older and newer version - making the entire process effortless and inexpensive.
Upgrade-based Modules The compatibility between the older and newer version of Drupal majorly depended upon the modules and themes used while building the older version. Until and unless these modules and themes aren’t upgraded, the migration was a time-taking task and tedious task that required technical assistance. This has been changed with the change in the upgrade path of the content, which makes the migration easier if prepared
Drupal Core Deprecating Policy Drupal 8 capable of introducing new APIs and features against the old ones. And once these new ones are launched, the old ones automatically get deprecated. Though these old APIs cannot be removed in the minor release of Drupal 8, it will be removed in the next major version of Drupal 9. Hence, if you migrate to Drupal 8 now, the migration to Drupal 9 can easily be done with just a handful of changes to make it compatible.
Looking at the above three major reasons, it must be clear to you that migrating to Drupal 9 from Drupal 8 is far easier as compared to the migration from Drupal 6/7 to Drupal 9. Dries Buytaert, the founder of Drupal, has also shared similar information about planning to be done for Drupal 9. According to him, Drupal 9 is basically built in Drupal 8 instead of a different codebase, altogether. This implies that the new features are added as backwards-compatible code and experimental features, which means once the code is stable the old functionality will be deprecated.
Dries, in his blog on ‘Plan for Drupal 9’, has quoted contributed module authors as one of the core reasons behind the easy migration from Drupal 8 to Drupal 9. On this, he says that these are the module authors are already well-equipped with the upcoming technologies of Drupal 9 and hence they can priorly work in a manner that is Drupal 9 compatible. AddWeb, being one of these contributing members of the community, can assure you of the easy and inexpensive migration to Drupal 9 as and when it arrives.
Why Vouch for Drupal 9? Now, after grasping all the above information regarding the upcoming major release of Drupal 9, you must be wondering what’s in Drupal 9 to vouch for. Let us throw some light on the same, to be able to bring some clarity for you. Drupal 9 is all about eliminating the use of deprecated modules and APIs. Drupal 8, which runs on the dependency of Symfony 3, will run out from the market by November 2021. And hence, it is highly advisable to upgrade and avail the benefits of all that’s latest!
Concluding Words: As an expert #Drupal-er and active community member, AddWeb is all set to offer you with this amazing opportunity to migrate from your current Drupal 6/7 site to Drupal 8, in a way that the future migration to Drupal 9 will be super easy and inexpensive. Share your details with us in here and let our Drupal Migration Experts get back to you. In case, of any queries or suggestions feel free to get in touch with us!
Source: AddWeb Solution
0 notes
Text
Why Choose Joomla as Your eCommerce Platform in 2019

Akin to all major CMS platforms out in the market, Joomla isn’t different in the fact that it is also an open source platform you can choose to create various kinds of websites for setting up your business online. You might even want to seek professional assistance from a Joomla Development company in India. Now you might be wondering “Why is it any different if I use a platform other than Joomla if it’s all the same?” Glad you asked, and here’s a list of reasons as to why-
1) Ease of Installation: This is especially the case with the latest Joomla versions (Joomla 3.5 and Joomla 4 in general). In addition to being a lightweight platform, Joomla installation is a 3-step process and takes less than 15 seconds to complete. The whole process is rid of unnecessary detail filling.
2) Free of cost: Employing an efficient platform is a compromising task in the majority. Either the framework isn’t up to the standard and on the occasion that is the case, it usually doesn’t come in cheap. Joomla is an anomaly to the fact that despite being free of cost, a developer has all the necessary tools to create their preferred form of a website.
3) Flexibility: Joomla isn’t really too technical a language hence making it extremely user-friendly, especially for beginners and amateurs. Also, the access control list is an amazing addition to promote feasibility as it delivers you the means to manage a large number of customer groups easily. Migrating from a different host to Joomla also has been a lot easier of late due to adding ons.
4) Additional Features and Customisation: ● Joomla supports the PHP7 version that assists your website performance. ● Joomla is multilingual as it supports around 70 different languages. ● Various in-built editing functions (for instance WYSIWYG editor) pave a way for you to edit your website even if you aren’t aware of coding. ● The Drag and Drop image feature is a surefire way of boosting website performance. ● A regular developer using Joomla can now effortlessly insert modules within their articles. ● Latest Joomla versions come with over 10000 plugins, templates, and modules for quality web designing.
5) Superlative Security: The hackers these days are capable of XSS attacks and SQL injections via system function. This is becoming a regular occurrence now and to tackle the situation, Joomla comes with in-built secured layers and prompt extensions. These layers ensure CSRF protection along with other concerns, while extensions add a host of Captchas that act as a barrier to all major threats. This way all sensitive customer data is secured from online vulnerabilities when using Joomla.
6) Third party extensions: Unlike other major platforms like WordPress and Drupal that come with inbuilt extensions, Joomla depends on third-party extension providers. This is a desired addition as these extensions give a larger variety of designing and customization tools to the user. To put it straight, Joomla lays out more option to make your website more appealing.
7) SEO friendly functionality: As mentioned earlier, Joomla pages are extremely lightweight despite being functional. This is a blessing for SEO purpose since the page loading is much quicker, and that enables the crawlers to locate and read your web page at a brisk pace. Viewer trafficking is taken care of when using Joomla.
8) Extensive Community: Joomla boasts a core of highly skilled and experienced IT technicians that are capable of putting forth a reliable solution to any developer’s query. Though WordPress has a larger community base, that also is the consequence of a bloated user base. As a result, the time taken to address an individual query takes lesser time with Joomla.
Conclusion: Though not as extensive as a major platform like WordPress, Joomla is more than good enough for answering your web development needs. This platform is especially popular among small scale businesses who are content with fewer complex websites and that suits the website ranking algorithm. You must also hire Joomla Developers who are seasoned enough to cater to your needs. Do you want to establish a business presence online and need assistance? We at FutureProfilez provide complete Web Development services to all scale businesses at economical prices.
0 notes
Text
Drupal 7 to 8 Upgrade and Migration Guide | Hostperl
Likewise with all significant site changes, the update from Drupal 7 to 8 might be intimidating to design. In spite of the time investment, fully recognizing the advantages of Drupal 8 will be certainly justified regardless of your while. Read on to become familiar with how updating will help your business through expanding proficiency, security, and an improved in overall experience for your team.

Essential Benefits of Upgrading to Drupal 8
So for what reason would it be advisable for you to move up to Drupal 8, as opposed to remaining with Drupal 7 or moving to another platform like WordPress?
Guarantee your application is secure.
Drupal 7 is planned to arrive at its finish of life in November 2021. This implies it won't get security updates or bug fixes after that point, except if you buy a support contract from an outsider seller.
The Drupal community already took every necessary step for straightforward migration paths.
The Migrate module has been moved into Drupal 8 core code, and the community has included relocation contents to move most Drupal 6 and Drupal 7 setup and content to Drupal 8. If you were moving to another platform, you would need to build up your new data structures, themes, and migration scripts yourself. With Drupal 8 you can use the endeavors of the community to migrate your data structures and content with less exertion.
Moving up to Drupal 8 will encourage your upgrade to Drupal 9.
While the Drupal 7 to Drupal 8 change requires a migration of setup and requires, the Drupal 8 to Drupal 9 redesign won't require a migration. The Drupal community is coming back to a redesign set up system, much like between past versions.
Drupal 9 will be built off of Drupal 8, with its outsider conditions refreshed and some old code removed. This will bring about a smoother progress between Drupal 8 and 9.
You might be wondering: why not hold up until Drupal 9 to migrate, if the experience will be fundamentally the same as? Drupal specialists are recommending updating currently to take advantage of all the Drupal 8 enhancements listed above, and to prepare for the Drupal 9 upgrade. Since Drupal 8 will likewise arrive at its finish of life in November of 2021!
0 notes
Link

TL;DR: Migrating my website from Drupal 7 to Hugo
Jump directly to the end titled Migration to Hugo
Initial website
Looking back at my website’s history, the domain was first registered sometime in 2003. Back then, it was mostly a couple of html pages. Being (and still) a novice in web, my website was mostly on ideas from others. IIRC, for the bare html one, I took a lot of look wise details from Miss Garrels’ website.
First blog
My initial blog was self-hosted with a blogging software in PHP, named PivotX The website for it still works, so hopefully the project is still alive. It was pretty good a tool for the purpose. Very lean and had support for data backends in both, MySQL and flat files. The latter was important to me as I wanted to keep it simple.
Drupal
My first interaction with Drupal was with its WSOD. That was it until I revisited it when evaluating different FOSS web tools to build a community site for one of my previous employer.
Back then, we tried multiple tools: Jive, Joomla, Wordpress and many more. But finally, resorted to Drupal. What the requirement was was to have something which would filter content under nested categories. Then, of the many things tried, the only one which seemed to be able to do it was Drupal with its Taxonomy feature, along with a couple of community driven add-on modules.
We built it but there were other challenges. It was hard to find people who were good with Drupal. I remember to have interviewed around 10-15 people, who could take over the web portal and maintain it, and still not able to fill the position. Eventually, I ended up maintaining the portal by myself.
Migrating my website to Drupal
The easiest way to deal with the maintenance was to have one more live portal running Drupal. My website, which back then, had ambitious goals to also serve an online shopping cart, was the perfect candidate. So I migrated my website from PivotX to Drupal 6. Drupal had a nice RSS Import module which was able to pull in most of the content, except the comments on each article. I think that is more a limitation of RSS Feeds. But the only data import path I could find back then was to import content through RSS Feeds.
Initially, Drupal looked like a nice tool. Lots of features and a vibrant community made it very appealing. And I always desired to build some skills Hands-On (that’s how the job market likes it; irrespective of the skills, it is the hands-on that they evaluate) by using Drupal both, at the employer’s community portal and my personal website.
Little did I know that running/maintaining a website is one aspect; where as extending it, is another (mostly expensive) affair.
Drupal 7
That was the first blow. For a project serving as a platform, Drupal was a PITA when dealing with migrations. And it is not about migrations to a different platform. Rather an upgrade from one major release to another.
Having been using Debian for quite some time, this approach from Drupal brought back memories from the past, of when using Red Hat Linux and SuSE Linux distribution; where upgrades were not a common term, and every major release of the distribution people were mostly recommended to re-install.
Similar was the case with Drupal. Every major release, many (core) modules would be dropped. Many add-on modules would lose support. Neither the project nor the community around it, was helpful anymore.
But somehow, I eventually upgraded to Drupal 7. I did lose a lot of functionality. My nested taxonomy was gone and my themes were all broken. For the web novice that I am, it took me some time to fix those issues.
But the tipping point came in with Drupal 8. It took the pain to the next level repeating the same process of dropping modules and breaking functionalities; never did I hear much of backward compatibility on this platform.
Hugo
For quite some time I kept looking for a migration path away from Drupal 7. I did not care what it was as long as it was FOSS, and had an active community around it. The immediate first choice was WordPress. By this time, my web requirements had trimmed down. No more did I have outrageous ideas of building all solutions (Web, Blog, Cart) in a single platform. All I did was mostly blog and had a couple of basic pages.
The biggest problem was migration. WP has a module, that does migration. But, for whatever annoying reason, the free version of it would only pick 7 articles from the total. And it did not import comments. So the annoyance and my limitations with web technologies was still prone to with WP. This migration path did not enthuse me much: it was more like a Hindi idiom: आसमान से गिरे और खजूर में अटके
I also attempted Jekyll and Hugo. My limited initial attempts were disappointing. Jekyll had an import module, which IIRC did not work proper. Similar was the case with Hugo, which has a module listed on its migration page, drupal2hugo, which sets a disappointment in the beginning itself.
With nothing much left, I just kept postponing my (desperate) plans to migrate.
Migration to Hugo
Luckily, I was able to find some kind soul share migration scripts to help migrate from Drupal 7 to Hugo. Not everything could be migrated (I had to let go of comments) but not much was I in a position to wait more.
With very minimal changes to adapt it to my particular setup, I was able to migrate most of my content. Now, my website is running on markdown generated with Hugo. More than the tool, I am happy to have the data available in a much standard format.
If there’s one thing that I’m missing on my website, it is mostly the commenting system. I would love to have a simple way to accept user comments integrated into Hugo itself, which would just append those comments to their respective posts. Hopefully soon, when I have (some more) free time.
<?php define('DRUPAL_ROOT', __DIR__); include_once(DRUPAL_ROOT . '/includes/bootstrap.inc'); drupal_bootstrap(DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_FULL); $nids = db_query('SELECT DISTINCT(nid) FROM {node}') ->fetchCol(); $nodes = node_load_multiple($nids); foreach($nodes as $node) { $front_matter = array( 'title' => $node->title, 'date' => date('c', $node->created), 'lastmod' => date('c', $node->changed), 'draft' => 'false', ); if (count($node->taxonomy_vocabulary_2[LANGUAGE_NONE])) { $tags = taxonomy_term_load_multiple( array_column( $node->taxonomy_vocabulary_2[LANGUAGE_NONE], 'tid' ) ); $front_matter['tags'] = array_column($tags, 'name'); } if (count($node->taxonomy_vocabulary_1[LANGUAGE_NONE])) { $cat = taxonomy_term_load_multiple( array_column( $node->taxonomy_vocabulary_1[LANGUAGE_NONE], 'tid' ) ); $front_matter['categories'] = array_column($cat, 'name'); } $path = drupal_get_path_alias('node/'.$node->nid); if ($path != 'node/'.$node->nid) { $front_matter['url'] = '/'.$path; $content_dir = explode('/', $path); $content_dir = end($content_dir); } else { $content_dir = $node->nid; } $content = json_encode( $front_matter, JSON_PRETTY_PRINT|JSON_UNESCAPED_SLASHES|JSON_UNESCAPED_UNICODE ); $content .= "\n\n"; $tmp_file = '/tmp/node.html'; file_put_contents($tmp_file, $node->body['fr'][0]['value']); $body = shell_exec('html2markdown '.$tmp_file); unlink($tmp_file); //$body = $node->body['fr'][0]['value']; $content .= $body; $dir_name = '/tmp/hugo/content/'.$node->type.'/'.$content_dir; mkdir($dir_name, 0777, true); file_put_contents($dir_name.'/index.md', $content); }
via Planet Debian
0 notes
Text
Professional WordPress Design and Development
Professional WordPress Design and Development
Download
Introduction
WHO IS THIS BOOK FOR? It was the dichotomy between the almost trivial effort required to create a WordPress-based blog and publish a ‘‘first post’’ to the world and the much more detailed, broad understanding required to effect mass customization that led us to write this book. Many books on the market provide guidance to beginning bloggers by walking you through the typical functions of creating, configuring, and caring for your WordPress site. Our goal was to bridge the gap between an expert PHP developer who is comfortable reading the WordPress Codex in lieu of a manual and the casual WordPress user creating a public persona integrated with social networking sites and advertising services, with a tailored look and feel.
In short, we hope to appeal to a range of developers, from the person looking to fine-tune a WordPress theme to a more advanced developer with a plugin concept or who is using WordPress in a large enterprise integrated into a content management system. We do this by exploring WordPress from the inside out. Our goal for this book is to describe the basic operation of a function, and then offer guidance and examples that highlight how to take it apart and reassemble that function to fit a number of needs. WordPress users who are not hardened PHP developers may want to skim through the developer-centric section, whereas coders looking for specific patterns to implement new WordPress functionality can start in the middle and work toward the end
HOW THIS BOOK IS STRUCTURED
This book is divided into three major sections: Chapters 1 through 4 are an overview of the WordPress system, its major functional elements, and a top-level description of what happens when a WordPressgenerated web page is displayed. Chapters 5 through 8 build on this foundation and dive into the core of WordPress, describing internal code flow and data structures. This middle section is strongly developer-oriented, and describes how to extend WordPress through plug-ins and customize it via themes. The last section, Chapters 9 through 15, combines a developer view of user experience and optimization with the deployer requirements for performance, security, and enterprise integration. The following is a detailed chapter-by-chapter overview of what you can expect to find in this book.
Chapter 1, ‘‘First Post,’’ contains a brief summary of the history of the WordPress software core, explores some popular hosting options, why community matters in a content-centric world, and concludes with the basics of do-it-yourself WordPress installation and debugging.
Chapter 2, ‘‘Functional Overview,’’ examines each of the major sections of the WordPress system as seen by a typical user in the course of writing, editing, and managing a blog. This chapter covers the basic mechanics of the WordPress Dashboard, plugins, settings, permissions and users, and content management features, laying the foundation for dissecting their internals in later chapters. If you’re a beginning WordPress user, you should find this overview sufficient to develop proficiency in basic WordPress authoring and management tasks.
Chapter 3, ‘‘Code Overview,’’ starts with the mechanics of downloading the WordPress distribution and describes its basic contents and filesystem layout. A top-to-bottom code flow walks you from an index or specific post URL, through the process of selecting posts, assembling content, and generating the displayed HTML. This chapter is a map for the more detailed code tours in the developer-focused section.
Chapter 4, ‘‘Tour of the Core,’’ examines the essential PHP functions comprising the basic WordPress engine. It serves as an introduction to the developer-focused middle section of the book and also lays the foundation for the deployment-, integration-, and experience-focused chapters in the last section. This chapter also covers using the core as a reference guide, and why it is best not to hack the core code to achieve desired customizations.
Chapter 5, ‘‘The Loop,’’ is the basis for the developer-centric core of this book. The WordPress main loop drives the functions of creating and storing content in the MySQL database, as well as extracting appropriate chunks of it to be sorted, decorated, and nested under banners or next to sidebars, in both cases generating something a web browser consumes. This chapter disassembles those processes of creating, saving, and publishing a new post as well as displaying content that has been stored in the WordPress MySQL databases. The underlying database functions and the management of content metadata are covered in more detail to complete a thorough view of WordPress’s internal operation.
Chapter 6, ‘‘Data Management,’’ is the MySQL-based counterpart to Chapter 5. The core functions create, update, and manipulate entries in multiple MySQL database tables, and this chapter covers the database schema, data and metadata taxonomies used, and the basic relations that exist between WordPress elements. It also includes an overview of the basic query functions used to select and extract content from MySQL, forming a basis for extensions and custom code that needs to be able to examine the individual data underlying a blog.
Chapter 7, ‘‘Plugin Development,’’ starts with the basic plugin architecture and then explores the hook, action, and filter interfaces that integrate new functionality around the WordPress core. This chapter demonstrates the interposition of functions into the page composition or content management streams and how to save plugin data. Examples of building a plugin using a simple framework outline the necessary functionality of any plugin. This chapter also covers creation of widgets, simpler-to-use plugins that typically add decoration, additional images, or content to a blog sidebar; many plugins also have a widget for easier management. Publishing a plugin to the WordPress repository and pitfalls of plugin conflict round out the discussion of WordPress’s functional extensions.
Chapter 8, ‘‘Theme Development,’’ is the display and rendering counterpart to Chapter 7. Plugins add new features and functions to the core, whereas themes and CSS page templates change the way that content is shown to readers. Starting with the basic Sandbox theme, this chapter covers writing a theme, building custom page templates, theme installation, and how thematic elements are used by the functions described in previous chapters. This chapter ends the deep developer-focused middle section of the book.
Chapter 9, ‘‘Content Aggregation,’’ looks at WordPress from a services point of view. If a blog represents your public persona or online presence, it has to pull content from a variety of tools and content sources. This chapter delves into web services interfaces, WordPress APIs, feeds into and out of WordPress, and making WordPress entries show up in Facebook pages.
Chapter 10, ‘‘Crafting the User Experience,’’ looks at a WordPress installation from the perspective of a regular or potential reader. Usability, testing, and the ease of finding information within a WordPress blog form the basics, with added emphasis on web standards for metadata and search engine optimization so a blog, or a specific blog post, can be found through an appropriate Google search. Whereas Chapter 9 covers pulling external content into your WordPress instance, this chapter shows how to get your content to show up elsewhere on the Web. Alternatives for adding search functionality, one of WordPress’s weaknesses, are discussed, along with content accessibility and delivery to mobile devices.
Chapter 11, ‘‘Scalability, Statistics, Security, and Spam,’’ deals with good and bad popularity. Keeping a WordPress installation safe from inevitable comment spammers as well as malicious attackers is a key part of configuration and management, and this chapter covers the more popular security and antispam plugins and features. Traffic analysis tools indicate how well certain content types, functions, ad campaigns, promotions, or links are driving readership and how this informs traffic management.
Chapter 12, ‘‘WordPress as a Content Management System,’’ goes beyond blogging to examples of WordPress as a system for managing the life cycle, integration, and distribution of networked content. Integration with other open source content management systems including Drupal and Joomla rounds out this chapter.
Chapter 13, ‘‘WordPress in the Enterprise,’’ tackles issues of scale and integration. WordPress may address deficiencies in ‘‘enterprise scale’’ content management tools, and building on the mechanisms covered in Chapter 12, this chapter shows how to use WordPress with a variety of enterprise facilities ranging from identity management to Microsoft ASP/.NET services.
Chapter 14, ‘‘Migrating to WordPress,’’ provides an overview of moving content from an existing blog or content management system into WordPress, and examines issues of importing media such as images, video, or formatted data. This chapter also covers mechanisms for redirecting existing sites to a WordPress installation.
Chapter 15, ‘‘WordPress Developer Community,’’ is an introduction to contributing to the WordPress ecosystem by working on the core, submitting plugins or themes, adding to the documentation canon, and assisting other developers. An overview of WordPress sister projects such as bbPress for forums is provided along with a brief summary of other developer resources and a glossary of WordPress-context sensitive terms
Via TimoBook
0 notes
Text
Reasons That Make Drupal An Ideal CMS For Education Websites
Drupal is a widely acclaimed CMS as it offers a rich array of features that facilitate the creation of visually appealing and functionally robust websites. Big brands such as the White House, Twitter, IKEA, and McDonald’s are just a few names that have their websites running on this platform. The CMS caters to diverse requirements and has the versatility that makes it suitable for varied businesses. Education is one of the verticals that finds it ideal as a development platform. The fact that premier institutions such as Oxford, Harvard, and MIT have Drupal powered websites reinforces this statement. If you are running an educational institution, here are some reasons that you should consider custom drupal development as the best option for your website.

1. Multi-site functionality
Educational institutions and universities need to maintain multi-facet websites to fulfill the needs of different departments. Drupal, with its built-in multi-site functionality, offers a role-based control structure that enables complete ownership for the departments and reduces the overall IT expenditure.
2. Multi-language functionality
Multi-language support is another essential requirement for an education website as it needs to address students with different vernacular and cultural backgrounds. Drupal 8 provides extensive multi-language support as it is available in more than 110 languages.
3. Responsive design
Responsiveness is assured for institutions that opt for Drupal website design. Since the CMS extends responsive experiences out of the box, these sites can run seamlessly across a range of devices. Institutions with high student demographics can leverage this feature to connect with a larger user base.
4. Social media integration Drupal comes with integrated social media capabilities, making user engagement easier for the websites. Universities and colleges can use this functionality for integrating social media campaigns through YouTube, Twitter, Pinterest, etc.
5. Robust security
Hacking attacks are a major concern for educational sites as they house sensitive student data on them. Consequently, there is a need to choose a digital platform that adheres to best security standards. Drupal makes an apt choice because of its responsive and proactive security, with its frequent updates and security fixes.
6 Workflow modules
With Drupal’s powerful workflow modules, universities and colleges can avail a granular control for every content publication operation. It is possible to notify the employees to complete their tasks so that the project moves forward at an optimal pace.
7.User access control
Another feature that makes Drupal perfect for educational websites is the access control features it provides. It is possible for them to give different access rights for different users such as professors, alumni, students, and other visitors.
8.Community support
Drupal CMS has an extensive community support, with a large number of community groups across the globe. Many of the members have worked on developing educational portals and are willing to extend their support to those in need.
Conclusion
Considering these features that this CMS platform offers, it is advisable to choose it for developing educational websites. At Drupal India, we are a leading Drupal development partner that has catered feature-rich websites to some renowned clients from the education segment. From suggesting the best Drupal themes for education site to ensuring that it has all the required functionalities, we make sure that the client gets a solution that adds value to their business. In addition to design and development services, we also cater Drupal theme customization, migration, upgrades, maintenance and support services.
Originally published on http://drupalindia.co.in/
0 notes