#Debt Ratio and Deferred Student Loans
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Why You Need a Mortgage Professional When Buying a Home
When a person buys a home, they need a mortgage professional to help them with the home loan process. They work with individuals on submitting all the right documentation, helping them understand their different mortgage options and addressing any complications.
They also help people find a lender willing to offer them a professional mortgage loan, for example, one that allows for a flexible debt-to-income ratio and excludes deferred student loans.
1. They’re unbiased
You wouldn’t invest in stock without talking to a financial professional, and you shouldn’t buy a home without first speaking to your mortgage broker. They’re an invaluable source of information for homebuyers, especially since mortgage criteria has tightened in recent years.
A good mortgage professional will explain all your options and be able to find the best mortgage for you. They will also be up to date on any new changes in the industry, which could save you money.
It’s important to find a mortgage professional who works independently. If they’re working with a lender, they might be encouraged to cross-sell other bank products like credit cards, insurance and RRSPs. A true independent mortgage broker will only offer mortgage advice and won’t be distracted by incentives to sell you something other than what’s best for you. This is why it’s best to search online reviews and ask for referrals from real estate agents and other trusted sources.
2. They’re knowledgeable
Mortgage professionals are a big part of making real estate transactions work for consumers. They help homeowners investment property navigate the complexities of mortgage financing, offering guidance and advice on how to improve credit scores, save money for a down payment, secure mortgage pre-approval and more.
A trusted mortgage professional will have a deep understanding of the housing market, mortgage regulations and loan options. They’ll be able to provide borrowers with information on a variety of lenders and loans that might meet their needs, and they’ll take the time to explain the various costs associated with each option.
Mortgage brokers also have the ability to offer borrowers more choices because they are independent financial professionals with access to multiple lenders. This gives them the ability to provide borrowers with more competitive quotes and may result in impactful australian finance group savings through fee waivers or better loan rates.
3. They’re responsive
Mortgage professionals need to be responsive in order to build trust with their clients and demonstrate that they understand and respect the home-buying process. They should be punctual with responses and always follow up on their promises. This can be difficult when the industry is busy, but it’s necessary to meet client expectations and ensure that they have a positive experience.
Mortgage pros should also be proactive in managing their online reputation. They should fill out their business profiles on review sites, and they should also encourage happy customers to leave reviews. This can help them stand out in a competitive market.
Lastly, mortgage professional should use email campaigns to stay in touch with potential leads and share valuable information about the mortgage industry. They can also send personalized messages to their list of prospects based on their location, interests and homebuying stage. This can help them grow their business and improve the chances that they convert leads into satisfied clients.
4. They have a good reputation
You wouldn’t invest in a new car without talking to an auto dealer, so why would you get a mortgage without consulting a mortgage professional? Mortgage professionals have a deep understanding of the market and regulations, and offer tailored advice for your unique situation. They can guide you through the process, from finding the right lender to structuring your loan solution. They can also help you avoid pitfalls, such as costly mistakes like paying off debt too quickly or taking out a loan that exceeds your income limits.
Mortgage professionals rely on reviews and testimonials to build their reputation, attract new clients, and grow their business. They can control their online image by monitoring review sites, search engine rankings, and social media to respond to positive and negative feedback promptly and professionally.
They can also stay connected with their audience by sharing useful content on social media and in email campaigns. This shows that they are experts and helps them stand out from their competitors.
#mortgage professional#investment property#investment property loan#australian finance group#finance group Australia#business loan
0 notes
Text
Loans for students
You apply for a federal student loan by submitting a FAFSA. Taking on a federal loan means you’re borrowing from the government. You apply for a private student loan through a bank, credit union or online lender. Federal student loans also have flat interest rates set by Congress, while the interest rate on a private student loan depends on your or your co-signer’s credit. Federal loans charge origination fees; private loans typically do not. Federal student loans offer borrowers protections and alternative repayment options that private loans usually don't, such as income-based repayment and forgiveness programs. The current interest-free loan forbearance does not include private student loans; any future forgiveness offer is unlikely to include them. Compare offers from multiple lenders including banks, credit unions, online companies and statebased lenders to find the lowest interest rate. Depending on the lender, you may be able to choose a fixed or a variable interest rate. A fixed rate stays the same throughout the life of a loan. A variable rate may start out lower than a fixed rate, but could increase or decrease over time depending on economic conditions. Consider any borrower protections your private lender offers, including deferment and forbearance, as well as repayment options. You may also have the option to choose your loan term, which means you could pay off your loan faster and with less interest by making higher payments or pay lower amounts with more interest over a longer period of time. How do I qualify for a private student loan? Each lender will have its own requirements for taking out a loan. With most loans for students, credit score and income are taken into account. Higher scores and incomes tend to get the best rates or higher borrowing amounts. However, since undergraduate borrowers are less likely to have established credit or an income, lenders will usually require students to apply with a co-signer. Some lenders who have loans for borrowers without a co-signer will consider career and income potential. Lenders will often require you to attend a Title IV school, which means your school processes federal student aid. Some lenders don't offer loans in certain states. Can I get a private student loan with bad credit? You’ll have a hard time finding a private student loan from a bank, credit union or online lender if you have bad credit. Federal student loans don’t require borrowers to demonstrate creditworthiness, so they’ll be your best option. If you’ve already hit your limit on federal loans, you may be able to get a private student loan if you apply with a co-signer who has solid credit — typically scores in the high 600s or better. If you have no income and either no credit or bad credit, you’ll need a co-signer to get a private student loan. Without bills in your name, such as a credit card, car loan or utility, you have no way to demonstrate that you can pay bills on time. Your co-signer will need to have a steady income as well as good to excellent credit scores, typically at least in the high 600s. Signing with a co-signer means they’re on the hook for your loan bill if you can’t pay. Some lenders offer loans exclusively for student borrowers that don't take credit into consideration. Instead, these lenders look at the school you’re attending as well as your income and career potential to determine the amount you can borrow and at what rate. How do I apply for a private student loan? Each lender will have its own application requirements. You’ll usually need to provide documents that prove citizenship, identity and income along with school attendance and cost information or a financial aid award letter from your college. As part of underwriting, you or your co-signer will need to show you have a credit score in the high 600s or higher, as well as cash flow to make loan payments. They’ll also look at your or your co-signer’s debt-to-income ratio to make sure you have the funds to pay a student loan bill in addition to any other bills in your name. Private student loan interest rates The NerdWallet team of student loans experts analyzed reported rates from 24 lenders over a period of 38 months. We considered four variables — average maximum fixed rates, average minimum fixed rates, average maximum variable rates and average minimum variable rates — for each lender on a month-over-month basis. The average rates as of Apr. 19, 2023, were: Minimum fixed interest rate - 5.87%. Maximum fixed interest rate - 13.23%. Minimum variable interest rate - 6.80%. Maximum variable interest rate - 14.33%. Average rates in general have continued to trend upward over the last 12 months. All average rates — except maximum fixed rates — have increased since last month. The reported rates represent lenders' advertised ranges. It's best to prequalify with multiple lenders to ensure you accept the best rate available to you. Lenders typically offer the lowest rates to those with the strongest financial profiles. Based on our analysis, less than 30% of borrowers are offered the lowest rate. That percentage includes companies that offer all borrowers the same rate. Excluding those companies, less than 18% of borrowers are offered the lowest rate. Use this chart and data to gauge how your student loan offers measure against typical interest rate ranges. How exactly do student loan interest rates work? Learn more about how student loan interest rates are determined, including a history of rate changes through the years. Private student loan interest rates can sometimes be lower than federal rates, but approval for the lowest rates requires excellent credit. If you have good credit, you may be able to refinance existing student loans to get a lower rate. Sallie Mae study: Less than half of families with college-bound students feel confident about paying for college. Among families with college-bound students, 47% think they’ll need to borrow to finance a college education, according to Sallie Mae’s 2022 College Confidence study. Yet just under half of those families identified federal direct subsidized and unsubsidized loans as aid that needs to be repaid, underlining the importance of learning the obligations of the debt you’ve been offered before accepting it. Additionally, those families with college-bound students aren’t clear on the purpose of the FAFSA; 34% don’t know why someone would submit the FAFSA, and 44% don’t know that it’s for everyone, regardless of income level. If you or your child are considering going to college, familiarize yourself with all of the options available to you to fund that education –– and submit the FAFSA to be considered for the most aid possible. NerdWallet study: College-bound grads could exit with nearly $40K of student loan debt A 2022 high school graduate who will depend on student loans to pay for college could expect to borrow $39,500 for their bachelor’s degree, according to a new NerdWallet analysis. The share of parents taking out federal parent PLUS loans to help cover the costs of their children's college education has also grown significantly. For more details, and to learn a number of ways to cut down on the amount borrowed for a bachelor's degree before, during and after college, see the full study here. STUDENT LOAN RATINGS METHODOLOGY Our survey of more than 29 banks, credit unions and online lenders offering student loans and student loan refinancing includes the top 10 lenders by market share and top 10 lenders by online search volume, as well as lenders that serve specialty or nontraditional markets. We consider 40 features and data points for each financial institution. Depending on the category, these include the availability of biweekly payments through autopay, minimum credit score and income requirement disclosures, availability to borrowers in all states, extended grace periods and in-house customer service. The stars represent ratings from poor (one star) to excellent (five stars). Ratings are rounded to the nearest half-star. Read more about our ratings methodologies for student loans and our editorial guidelines. Last updated on April 19, 2023 To recap our selections.
Step 2: Determine your budget
Once you've got some solid goals set, it's time to review your budget. Here are some things to consider: Your current after-tax income. Many people look at their pre-tax income, but you want to know how much money you're working with after taxes which can help you create a realistic budget. Your expenses. How much are your monthly expenses? How much do you have leftover each month? Is it possible to reduce or cut some expenses? Overall debt. How much debt do you currently have? List out your monthly payments and compare that against what you're making. Net worth. Your net worth is your total assets minus your liabilities. This number can give you an idea of where you're at financially and will allow you to get a "big-picture" snapshot of your financial health. Financial goals. As we mentioned before, knowing your goals is important as it gives your money a purpose. Risk tolerance. How much risk do you feel comfortable taking on? Calculating this will give you a clearer idea of what you can afford to lose. Time horizon. How much time do you have before you want to reach your investing goals? This is key to mapping out your finances to ensure you're keeping pace with when and how to invest without disrupting your budget or other goals not related to trading securities. All of these are key ingredients that can help you determine your budget. One last thing to consider: when you expect to retire. For example, if you have 30 years to save for retirement, you can use a retirement calculator to assess how much you might need and how much you should save each month. When setting a budget, make sure you can afford it and that it is helping you reach your goals.
Step 3: Get acquainted with various stocks and funds
Now it's time to start doing research on what to invest in. There are different ways to invest in the stock market and there's a lot to know so doing your research is well worth your time. Stocks are a good option to consider if you want to invest in specific companies. Just keep in mind that you should look into the company itself and how it's performing over time: Stocks — A stock is a security that gives stockholders the opportunity to buy a fractional share of ownership in a particular company. There are many different types of stocks to choose from, such as blue-chip stocks, growth stocks, and penny stocks, so make sure you understand your options, what they offer, and what matches with your budget and investing goals. "If you're going to pick a stock, look at the financial statements and select the stock based on the "bucket" you're trying to fill in your portfolio. For example, are you looking for a dividend stock? Look at the dividend history. Are you looking for a growth stock? Look at the earnings per share: Is it showing consistent growth? how these indicators measure against peer group," says Amy Irvine, a CFP® professional at Rooted Planning Group. So you want to take steps to look at your income and expense balance sheets and make sure you're hitting the right bucket — which refers to the grouping of related assets or categories — for your investing needs. For example, investing in small-cap, mid-cap, or large-cap stocks, are a way to invest in different-sized companies with varying market capitalizations and degrees of risk. If you're looking to go the DIY route or want the option to have your securities professionally managed, you can consider ETFs, mutual funds, or index funds: Exchange-traded funds (ETFs) — ETFs are a type of exchange-traded investment product that must register with the SEC and allows investors to pool money and invest in stocks, bonds, or assets that are traded on the US stock exchange. There are two types of ETFs: Index-based ETFs and actively managed ETFs. Index-based ETFs track a particular securities index like the S&P 500 and invest in those securities contained within that index. Actively managed ETFs aren't based on an index and instead aim to achieve an investment objective by investing in a portfolio of securities that will meet that goal and are managed by an advisor. Mutual funds — this investment vehicle also allows investors to pool their money to invest in various assets, and are similar to some ETFs in that way. However, mutual funds are always actively managed by a fund manager. Most mutual funds fall into one of four main categories: bond funds, money market funds, stock funds, and target-date funds. Index funds — this type of investment vehicle is a mutual fund Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Planning to take a loan? Use this loan calculator for easy monthly payment

If you are planning to take a loan, this post is definitely for you on how to secure a loan and use a allcalculator.net’s loan calculator.
Ways to choose a loan:
Borrow what you can pay
Always take a loan that you can pay; many take an excessive amount of loan, and due to default payment issues, they turn out to be homeless. It would be best if you made a calculation right before securing a loan and for which allcalculator.net is here for you to make your calculation much simpler.
Maintain a shorter tenure
When the tenure is long, the repayment amount is less, which tempts people to go in for a long repayment of the loan, which is a benefit for the bank rather than the borrower. So choose the best tenure that suits you based on the short tenure that matches your income capability.
Payment at the right time
Never ever dare to miss the payment of a loan for whatever you have borrowed; it may be a short-term loan, a long-time loan, or a credit card loan. The monthly payment should always be made on time before the due date.
Good credit score
Maintaining a good credit score ensures you can avail a loan with a lower interest rate.
What affects credit scores?
While calculating credit scores in America, each factor carries a different weightage to determine the credit score so that one can see substantial changes in credit history.
To improve your credit score, you must maintain good credit history as it weighs more than your recent credit inquiries, which will be taken care of by the agency where you secure the loan.
What is Credit history?
Credit history is an exhaustive list of all the credit payments you've made over the last few years.
Purpose of loan calculator:
One can use allcalculator.net’s loan calculator to determine your monthly repayments for various loans. These consist of loans for homes, vehicles, people, etc.
allcalculator.net’s a loan calculator assists you in determining how much you can borrow affordably in light of your salary and other circumstances.
Generally, the interest rate is based on
credit score
amount of the loan
and duration.
Interest rates range from 5.99% to 29.99% and higher. When you have a strong or excellent credit score and select the shortest repayment term feasibly, you'll typically get the lowest interest rate.
Borrowers choose two different terms of payment
Borrowers prefer low monthly payments with long tenure.
Borrowers prefer high monthly payments with low tenure.
Borrowers should generally aim to spend at most 35% to 43% of their income on debt, which includes payments for personal loans, mortgages, and auto loans.
E.g., With a monthly take-home salary of $5000, one can secure a loan with a monthly payment of less than $2150.
If a borrower plans to take on a mortgage loan from a lender, ensure that your debt-to-income ratios are less than 43%, as anything more than 43% of mortgage lenders deny the loan. For a personal loan, a good credit score and an income statement are more than enough to avail of a personal loan.
You can slightly stretch this ratio to accept a higher monthly payment if you believe you can temporarily stomach higher payments to save significantly on interest.
And with allcalcultor.net, one can easily compute these types of loans.
Amortized loan
Deferred loan
Bond
Amortization is nothing but repaying a loan in full by the maturity date by making monthly payments of the principal and interest over a period of time.
In the allcalculator.net’s loan calculator, one must enter the Loan amount, term, interest, compounded, and payback. When you calculate, you can see a graphical representation of the principal amount to the interest. The amortization schedule for the loan tenure with 12 months each will be listed in the table.
Deferred Payment Loan
A right to opportunistically postpone payment on an investment to a later time is known as a deferred payment option, and a student loan is the best example to point to a Deferred payment loan.
Here in all allcalculator.net’s loan calculator user must enter the loan amount, loan term, interest rate, and compound, which will give you a precise result of the Amount Due at Loan Maturity and the total interest that comes up with
Annual schedule with one installment per year
And a monthly schedule with 12 installments per year.
Bond
In a bond, the loan user must feed a predetermined due amount, loan term, interest rate, and compound, giving you an annual and monthly schedule of total balance with added interest rates until the loan tenure.
Don't be misguided by bankers and other agencies; use this allcalculator.net loan calculator to calculate the monthly installments on your own.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Kentucky Rural Housing USDA Loan Student Loan Debt Calculations
Kentucky Rural Housing USDA Loan Student Loan Debt Calculations
For potential home buyers with student loans that are either in a deferred payment status or being paid back through an income based or graduated repayment program, the treatment of this liability needs to be considered. When student loan debts are not currently being paid upon, due to the loan applicant still being in school or recently graduating from school, the monthly liability will be…

View On WordPress
#Bowling Green Kentucky#Debt Ratio and Deferred Student Loans#Kentucky#ky first time home buyer#Rural development#student loans#student loans mortgage approval ky#student loans usda ky#United States Department of Agriculture#USDA Rural Development
0 notes
Text
Budgeting with Student Loans
Student loans can be intimidating, committing to being in debt for the next decade or longer isn’t exactly ideal. That is why scholarships and grants are a great option that you should be sure to research fully to see how much you can cover for free. But scholarships aren’t usually enough to get you all the way through your degree. Especially since they tend to only cover academic expenses and in my experience the majority of my expenses in college are personal.
https://www.libbyincollege.com/lifestyle/budgeting-with-student-loans

What You Need To Know About Student Loans There are many different lenders for student loans and you should definitely do your own research before deciding which one to use. There are a couple of options when it comes to paying back your loans. You could pay a little bit every month while you’re in school, usually the interest, or defer them till you graduate which usually has a higher interest rate. I opted to defer them because it’s one less thing I have to worry about and calculate into my budget while I’m in school. Lenders will typically go through your school rather than giving you the money directly. Your school in turn will then take out any money you owe them, such as tuition and fees, before giving you the money. Disbursements of financial aid will take place after the add/drop deadline for the semester and you will only be given the money designated for that particular semester. These measures are to ensure that you are actually taking the classes you’re receiving financial aid for.
Figuring Out How Much You Need A good starting point for figuring out how much you need is your school’s website because they set the limit on how much you can borrow. The limit to the amount of financial aid you’re school will approve is called the cost of attendance, this will include money for not only tuition but also for food and other living expenses. This can be a good way to get an idea of how much things should cost but it’s not specific enough to be a stopping point.
Here’s my Cost of Attendance My expenses vary from this and yours probably will too. For example, this semester, my tuition is closer to $3000 and my books $500, it’s unlikely your school fees will be greater than the cost of attendance but don’t count on it being lower either, just in case. Because you’ll be given money in a big chunk for the whole semester it’s important to be sure you know how to make it last.
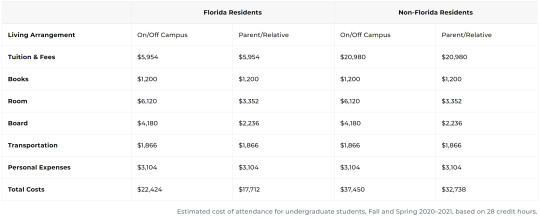
Budgeting You can either start with the cost of attendance budget and take off the academic expenses to get your living budget for the semester or you can build your budget from scratch and add expected academic expenses to it. I usually stick to the former.
The old rule of thumb is that 50% should go to needs, 30% to wants, and 20% to savings. I try to follow this the best I can but I live off-campus and with rents the way they are around here it’s not completely feasible for me.
So because my budget for the spring semester is $11,000 I’ll subtract my academic expenses ($3500) to get my living budget of $7,500. This $7,500 needs to last me from February to May (4 months) so I have a max budget of $1,875/month.
If you want to go a step further you can figure out your disbursement total for the entire year. This is a wise choice should you not want to worry about your budget changing every few months. For me, this looks like $30,000 before academic expenses. To calculate expected academic expenses you need to know what classes you’re going to take. The school website should have expected tuition per credit hour listed somewhere and in the course catalog you can find out if there are any extra fees associated with your courses. Make sure you budget for books too, I like to eat aside $600 per semester. This leaves me with $21,000 making my monthly budget $1750. Ideally, my needs should cost $875, my wants $525, and my savings $350 to follow the 50/30/20 rule but my realistic ratio ends up looking more like 60/20/20.
Needs
Needs are necessary expenses that can’t be avoided. Rent, food, transportation, etc. Most places you rent will want you to have an income that is around 50% of what the rent will be but it’s best to keep it as low as you can. Here are some necessities you should consider budgeting for:
Rent & Insurance
Water & Electricity
Internet
Phone
Car Payment/Insurance & Gas
Groceries & Toiletries
Wants
Wants are all other unnecessary expenses. Things like shopping and eating out. Because I know my needs are going to go over their 50% budget I like to take out the difference from wants. And use what’s left for more frivolous things. Here are some avoidable but fun expenses to consider budgeting for:
Shopping
Eating Out
Activities
Subscriptions
Hobbies
Savings
Some people especially while in college ignore this part but the earlier you start saving the better your future will be. I also like to include any debt-related expenses in this category just to keep needs a little lower. Here are some savings/debt-related expenses to consider budgeting for:
Credit Card Debt
Student Loan Debt
Saving for a Particular Thing
Rainy Day Fund
What does your realistic ratio look like?
And remember, good things are coming.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Raguragavan Sreetharan | Student Loans and Credit Scores
Raguragavan Sreetharan | Discussing family accounts as a way to build credit, it was mentioned that people starting out will usually have student loans as their first credit account, unless they obtain a car loan or credit cards tied to a family member with credit history. Student loans are a tricky area of installment credit history because they are not looked on as favorably as you would imagine.
You might think that having opened student loan accounts when you first went to college would show a history of the account, but in actuality, only when you start making your first payment will student loans count as “credit payment history.” Most student loans are in a deferred status as long as you are in school. Once you are out of school, you have one to four months before the companies begin asking you to make monthly payments that pay down the principal and interest.

Yet, when you have student loans, you have an “amount owed.” This amount owed can actually be reducing your credit scores. One the one hand, you feel that making payments should increase your scores, but then you get dinged for having a high amount owed.
So what can you reasonably do about student loan debt? Do you want to pay it off right away?
According to people like Stephen Snyder and Robert Kiyosaki, if you have student loan debt, you want to leave it as the last items you pay off. It comes down to an IRS strategy. The history of this strategy has existed since student loans became necessary for people to go to college. The minute the IRS allowed you to use your student loan interest paid as a deduction is when this strategy came into being.
Raguragavan Sreetharan | How it Works
Each month you make a payment you pay interest and a little towards your principal, when you are newly paying on the account. When you file taxes, you are asked to enter the amount in student loan interest you paid. The amount paid is a deduction. During this same period, you are paying a little of the “amount owed,” thus reducing your overall debt amount. You are also making payments, and as long as they are on time and the full monthly amount, you are helping your scores. When you get to a point in the loan, where you are barely making any interest payment at all towards the balance, pay off the debt.
Raguragavan Sreetharan | Summary
Student loans, when you first start taking them out appear on your credit report, but without any payment history. It is just an open installment account. The lack of payment history does not help your score, nor does it hurt it. The debt utilization ratio on the other hand will hurt your score a little. It is due to having this debt that makes your score a little lower than if you had no debt at all.
If this is the only debt you have, then it is also considered “little to no debt,” which also does not help when you are trying to get new loans to build your credit history.
When it comes time to make payments to the student loan companies as part of your installment agreement, you need to be on time and pay the monthly amount asked for. If possible, pay more than the monthly amount.
Paying interest helps lower your taxes owed. You want this deduction and the payment history. The deduction may be the only thing you have helping you get a tax refund. The payment history is also helping you increase your score, as the balance goes down.
Raguragavan Sreetharan | There will come a point when you are going to pay off the debt in full. Do this when the deduction on your taxes is no longer significant. The reduction of debt owed will also help at this point. The reason behind this key point lies in the other credit you have built. You should be in your 30s or 40s, with a mortgage, credit cards, and other credit that weighs more significantly on your ability to get credit. You no longer need the payment history from the student loans. In fact, given the amount of debt you might have at this point, you want to reduce the “amount owed” you have overall.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Payday express

Payday Express loans work in two phases: a loan initiation period, during which the loan must be paid back; and a deferral period, during which the loan can be paid back at any time. You can pay back a loan or deferment during the loan initiation phase, but if your payments exceed your principal, you're forced to take a down payment on the loan. When you defer a loan, your outstanding balance is paid off over time so that you can live on it.
In addition to the standard loan repayment requirements, credit card applications from American Express, Mastercard, Discover, Visa, and Discover Global are accepted.
In this article we're taking a closer look at three different kinds of American Express Bank credit card loans. To understand the difference between a normal loan and an American Express Bank loan, we'll be taking a look at what a normal loan means, the loan initiation period, and an America Express Bank Credit Card Loan repayment schedule. First, we review the term for an average American Express Bank loan.
What is an Average Credit Score?
One question often asked by customers is: "I just applied for an American Express Bank loan, where do I apply?" Your application for a credit card may be your last chance to qualify for your loan before you start paying off any of the interest charges, or the credit limit. In most scenarios, you may find your average credit score to be between the credit limit, where most of the interest charges apply, and the maximum credit limit.
The credit limit determines how much credit you get for your current account balance, or "per day" if you are single-eligible. The maximum per-day credit limit includes credit-card interest and any monthly, if the interest is charged on the entire balance at any given time. The minimum credit limit is usually around 6.7%.
A credit card application, whether written or by phone, is a credit application, and the amount of interest on the application is what you have to pay in order to apply for the credit card. If you don't pay the interest, your account will go toward the principal on the account. For example, suppose you want to apply to have your payment balance forgiven for the interest charge that's due on an installment loan. That $1000 payment balance will go toward the $2000 balance due on the loan. That $1000 payment should normally go toward payment on the loan at the average credit limit of 6.7%. Because the interest rate changes slightly each payment day, there will generally three ways:
A loan to which an individual makes a direct deposit (called a lump-sum loan) is converted into an initial payment in a bank. The amount of money lent is the actual value of the loan and the monthly repayment. This is known as the actual cost of capital.
An individual holds a loan from a bank for one year, pays a minimum principal and interest rate of 2.75%. A loan to which a loan is converted into an Initial Payment is treated as an initial payment from which interest may commence.
A loan to which a loan is a conversion to Loan Amount is referred to as an Initial payment. The amount of money lent is the loan amount plus the minimum principal and interest rate plus an initial payment amount. In other words, the loan amount.
Bank loan.
Cash advance transaction.
The amount of money borrowed is equal to the difference between original costs, estimated principal and interest, plus the amount loaned. For example, a 1,000-lot project may be projected to require $150 million (or the value of the property sold and all the cash flow). This may require a cash advance transaction with the bank at $50,000, which would be a loan. But note that at time of conversion, interest paid by the bank is the full amount of principal/interest, minus the amount borrowed.
Example A $50 million house in New York City is valued at $200 million. Since a cash advance loan would amount to $50 x 500 = $100,500 ($100,500 * 0.100), the actual cost of capital for such a project is $90,500, minus the amount lent. On a 5% interest rate, this would leave a monthly payment amount equivalent to $1,500, or a net cost of $1,500 per month, on loan interest of 5% interest. Using the 2.5% interest rate used above, the actual cost of capital for a total debt cost of $200,500 is $200,500 x $100,500, or $200,500 * 0.06 (or the value of the property sold and all cash flow for the loan)
This is a common illustration: A house with a base cost of $1,875 is projected to have an expected value of $3,869,000 upon completion, with monthly payment of $350 to the bank. On loan, the monthly payment is $350 - $350 * 0.06 Payday Express similar ways. The lender can offer a loan that makes up 15% or more of the balance at maturity, then sell the remaining 20%.
A common example for a 25% repayment on a $10,000 loan comes from the Bank of Scotland, which gave a customer a $1,000 repayment line to repay. The company wanted to be sure, however, that the customer didn't receive a second line of credit, so it sold the customer the first line of credit and didn't pay more than the $900 that the customer had originally borrowed. For both cases, the borrower might be happy not to pay more than 25%. But the Bank of Scotland wouldn't be able to make use of 25% of the loan balance — that would be too high. For instance, if the borrower took out a loan of $10,000 and used 75% of it in interest for 25% of the balance, the customer would owe $2,500 for each $1,000 borrowed. Because that would have been too much, the Bank of Scotland made the borrower pay $600 towards the $10,000 loan balance.
Advertisement Continue reading the main story
But the Bank of Scotland can't sell the second line of credit. Because the interest rate on those two lines is too low for the risk of default, borrowers have to take care to be sure they get a full repayment to cover it. (In their favor, they also get to buy into a bank product that makes up that second line, and that doesn't add to the total loan balance.)
Payday Express in other words, for every $1,000 the borrower owes, the lender has to spend $1,000 in profits from the second line of credit. This could result in double- and even triple-counting payments on their loan and making them owe out even more. In an effort to keep tabs on America's national debt, and the nation's debt-ceiling increase, The New York Times has published the most comprehensive debt report this side of Occupy Wall Street: A Debt Report of America: 10 Years of Uncontingent Pity, by The Federal Reserve.
Here's what it says:
More than $30 trillion, or 10 percent of the federal debt, remains unspent over the next 10 years because debt-ceiling increase and other costs are so large, experts said. The number of unspent dollars in the federal budget is rising as the U.S. Treasury holds back money as it
a similar way. Like FICO, they assess interest rates based on the original bill, not the bill-to-income ratio.
The main difference is that they charge a percentage of the interest they receive. With an FICO credit score, the rate is typically 0.15 percent.
As the name implies, you're paying as much as you can to make sure this loan is paid in full.
The process for FICO loan applicants can look confusing if you don't understand it. That's because FICO makes several assumptions to calculate which of its more than 200 million borrowers do enough to qualify for the loan.
How The Score Works
The credit score of FICO loans can vary a lot from person to person. But by default, your FICO loan will give you information you can use to compare a few of the three types of loans available.
A FICO loan can also receive a credit score that you may not be able to get with any other type of loan.
Let's say you take out a loan with an income that's 40 percent of the credit limit for you, but $200,000 in interest. Your FICO score won't cover this amount. So, if you want to use it to help get a loan that will put you in a stronger position than other students, you'll spend about $60,000.
The other important factor you'll have to consider is the interest rate. For the most part, FICO loans give a percentage of the interest you receive if the interest is lower than the loan's "accelerated interest rate."
For example, if you buy an FICO loan and then pay $150,000 out of pocket to make the loan, you'll have an interest rate you have to pay at least $0.5 on each payment. In this case, $450,000. If the payment is the equivalent of 10 percent of interest, it's 5% of the rate.
Some people may also have a high credit limit, meaning they'll either need to take out a longer-term loan with an interest rate much higher than 4% to pay the loan off, or they'll end up paying interest in the same percentage each time they apply.
The Bottom Line
FICO loans are good options for someone who wants a good number of credit scores. If you need to make the money you need to get into a better deal, you'll probably want to use one of part by paying a monthly fee. In order to qualify for the loan, borrowers must pay a fee of around $0.20 every 18 months. Once the loan is secured, fees add up and eventually become almost a monthly payment until the last of the loan debt is paid.
The cost to operate the bank's debit card payment system for payday loans is estimated to be $120,000 per year, but it doesn't look like borrowers are starting to make a profit on their loans and the loan process is taking a toll on the bank's bank account.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Student Loan Terms to Know
Student loan terms to know before you apply:
Co-borrower
Someone (relative, spouse, friend, or anyone!) who signs onto a loan with the main borrower and agrees to make payments if the borrower becomes unable to do so.
Underwriting
The process by which an applicant is either approved or denied for a loan. The factors that are considered vary from lender to lender, but many look at credit score, payment history, and debt-to-income ratio.
Origination
On the lender’s side, the process of a loan application. This includes the application’s submission, loan underwriting, processing any documentation you’ve submitted, and sending the loan funds.
Origination fee
The fee lenders charge for processing a loan application. Depending on the lender, this can be paid as an upfront cost, or it can be added to the total amount of the loan and paid back monthly as part of the loan payments. (At Climb, our origination fees are added to the loan and paid back over time).
Debt-to-income (DTI)
Your monthly debt payments compared to your monthly income.
Principal
The amount that you currently owe out of the original amount you borrowed. If you take out a $10,000 loan, your principal at the beginning will be $10,000. Then, the principal will be reduced as you pay back the original amount you borrowed and the additional interest on the loan!
Interest rate
The amount you are charged to borrow money. This is usually expressed as a percentage of the principal amount you pay over the course of a year, typically in monthly installments.
Annual percentage rate (APR)
The amount you’re charged annually to borrow money. Like interest rate, this is expressed as a percentage, but unlike interest rate, it takes any additional loan fees into account.
Student loan terms to know as you pay back:
ACH
Short for Automated Clearing House, setting up ACH on your student loan allows payments to be automatically withdrawn from your bank account each month. Connecting your account for ACH auto-payments not only makes it easier to make payments on time, but often lenders will offer an interest rate reduction as long as ACH is connected!
Disbursement
When a lender sends the funds for a loan.
Loan servicer
A company used by the lender to handle payments and billing after a loan is funded.
Deferment/forbearance
A temporary reduction or pause in your student loan payments. While these differ in the case of federal student loans, with private student lenders availability and terms vary and interest always accrues during the deferment/forbearance period. You may also need to provide documentation showing your need of assistance.
0 notes
Text
Student Loan Debt
What is a Student Loan? A Student Loan, also known as an Education Loan, is a sum of money borrowed to finance the post-secondary education or higher education-related expenses. Payments are often deferred while students are in college and, depending on the lender, sometimes they are deferred for an additional six-month period after earning a degree. This additional period of time after the graduation is known as a the "grace period". An Education loan can be obtained from either government or private sector lenders. Usually, a loan obtained from a government (federal) source carries a lower interest rate than that of a loan obtained from private sector lenders.
Economic Impact of Student Loan Debt (In the US) Some interesting pointers to note-
Since 2006, the total national student loan debt balance has increased 248.19% or at an annual rate of 17.7%.
In the 21st Century alone, the federal student loan debt balance has increased 583.84%.
Each time a consumer’s student debt-to-income ratio increases 1%, their consumption declines by as much as 3.7%. And that is how student loans reduce consumption/spending.
Student debt is the 2nd largest type of household credit (after mortgages).
Would-be entrepreneurs are 11% less likely to start a new business if they owe more than $30,000 in student loan debt.
The average student loan debt per borrower is $37,693.
Students with outstanding loan payments are 36% less likely to purchase a house.
The average bachelor’s degree holder earns up to $33,000 more annually than a high school diploma holder.
For graduate and professional degree holders, the median annual income is $78,885.
Graduate loans carry an average interest rate of 6.1%.
~Lakshya Kapoor
#finance#business#trade#companies#economy#banking#corporate#financial markets#investment banking#stockmarket
1 note
·
View note
Text
Student Loan Changes to Kentucky Rural Housing Loans Approvals
Student Loan Changes to Kentucky Rural Housing Loans Approvals
Beginning on September 23rd, 2019, the way USDA calculates student loans in regards to Student Loans and they effect loan approvals.
Kentucky Rural Housing loan Changes for Student Loans Effective immediately for all Kentucky Rural Development loans, student loan calculations will be changed to the following
Fixed Payment Loans:A permanent amortized, fixed payment may be used when it can be…
View On WordPress
#Debt Ratio and Deferred Student Loans#kentucky rural housing loan#rhs loans ky#student loans mortgage approval ky#student loans usda ky#usda loan kentucky
0 notes
Text
Financial Aid Questions
Just about everyone qualifies for some type of financial aid. In fact, over 8 million consolidate private student loan receive financial aid every year. Even if you’re not a straight-A student or a star athlete, you may be eligible for more aid than you think. To see if you meet basic eligibility requirements, take our Financial Aid Eligibility Quiz. Then, complete the Free Application for Federal Student Aid to see how much aid you can get. When do I start the process? What is FAFSA and where do I find it? How can I increase my chances of getting more aid? How do I get the money? How do I know if I’m a dependent student? Which loans require credit checks? When do I start repayment of my loans?
Student Loan Consolidation FAQs and Responses
Why should I consolidate my student loans? Consolidating student loans offers many benefits-even if you’re currently making your monthly student loan payments without any difficulty. You can make monthly bill paying easier with one student loan payment to one lender. The rate on a federal loan is fixed for the life of the loan. Federal student loans and parent loans issued prior to July 1 2006, carry variable interest rates that are adjusted annually. Consolidating can help ease the pressure on your monthly budget by reducing your monthly student loan payment by 10% – 60%. You can save money by using your student loan payment savings to pay off high-rate debt, such as credit cards. Consolidation will help your credit scores and debt-to-income ratio, both key factors if you’re looking to qualify for a credit card, buy a car, rent an apartment, or purchase or refinance a home. Won’t my total cost increase if I extend repayment to 30 years? Can my parents consolidate their federal parent loans with my student loans? How is the interest rate determined? Is the interest tax deductible? How do I know what my payment will be? How do I apply?
Stafford Loan FAQs and Responses
What’s the difference between subsidized and unsubsidized Stafford loans? It’s all about financial need.Subsidized Stafford student loans are awarded to students with demonstrated financial need. While students are in school, Uncle Sam pays the interest on subsidized Stafford loans, and payment is deferred (delayed) until after graduation. Once out of school, though, the student assumes responsibility for the loan, including interest.With unsubsidized Stafford student loans, you’re responsible for the interest from the time funds are disbursed. Unsubsidized federal college loans are not based on financial need; in fact, virtually every student is eligible for an unsubsidized Stafford loan. Although interest starts to accrue immediately, you can delay repayment until after graduation. How much money can I get with a federal Stafford student loan? What if it isn’t enough? How are loan funds disbursed? What is the interest rate? How do I apply for a Stafford loan?
Private Student Loan FAQs and Responses
What’s the difference between federal and private student loans? Federal student loans are guaranteed by the federal government, and offer attractive terms such as low fixed interest rates, deferred repayment, subsidized interest payments (for student who demonstrate financial need), and flexible repayment terms. Neither Stafford student loans nor Perkins student loans require a credit check or co-signer. The credit checks for PLUS parent loans and Grad PLUS graduate student loans are modest, much less stringent than for private student loans and other types of consumer loans. You must complete the FAFSA (the Free Application for Federal Student Aid) in order to be eligible for federal education loans.Private student loans are non-government loans offered by banks, credit unions, and other private lenders. These loans are not based on financial need but rather on your creditworthiness and ability to repay. Private student loans are designed to supplement federal loan programs and can be used for a wide range of education purposes, including tuition, books, living expenses, and a computer. The rates and terms for private student loans vary by lender and borrower creditworthiness. If you don’t qualify for a private student loan on your own, you may need to get a co-signer. Do I need a co-signer for a private student loan? What are the rates for private student loans? What is TERI? How do I apply for a private student loan?
Parents’ FrequentlyAsked Questions and Responses
How much should I save for my child’s education? How much you need to save depends on the school your child attends. Tuition and fees at public colleges are generally lower than those at private schools. Regardless of the school, though, education costs have been rising, and are expected to continue increasing over the next decade.Here’s how much college funding you’ll need to save to send one child to an average four-year private or public college. Don’t let these numbers frighten you. Start implementing your college savings plans today.
This article has written by Miss Money Belle
0 notes
Text
Getting a First Mortgage With Student Loans Just Got Easier
Editorial independence
We want to help you make more informed decisions. Some links on this page – clearly marked – may lead you to an affiliate website and may result in us earning a referral commission. For more information, see How We Make Money.
If student loan debt has delayed your dreams of owning a home, a recent change could make it easier to qualify for an FHA home loan.
The Federal Housing Administration has updated how it requires lenders to calculate student loan debt with FHA loans. The aim is to remove the student debt as a barrier to entry to getting an FHA home loan – the FHA says more than 45% of first time borrowers have student loan debt and the previous guidelines had a negative impact on people of color in particular.
The change has the potential to improve access to FHA-backed mortgages for underserved communities and those with student debt – and some previously ineligible borrowers may now be eligible under the change. The people who benefit the most are heavily indebted, lower-income borrowers, says Catalina Kaiyoorawongs, co-founder of LoanSense financial wellness platform for student debt.
What this change means for you:
Getting an FHA loan just got easier
For loans that are not actively being paid back (forbearance, deferral, income-based repayment schedule), FHA mortgage lender guidelines required that the monthly payment of a borrower’s student loan be calculated at 1% of the total loan balance. That amount was then added to their debt-to-income ratio (DTI), which negatively impacted their borrowing potential.
For example, a borrower may have a total of $ 100,000 in student loans. However, you can have an approved income-based repayment plan (IBR) and contribute as little as $ 150 per month. Under the old policy, the FHA lender would have to budget $ 1,000 per month based on the 1% balance underwriting rule.
Now anyone using an income-based repayment plan can have the actual dollar amount they pay included in their DTI as long as the payment is above zero dollars per month. And if your student loans are late, deferred, or your IBR monthly payment is zero, 0.5% of your student debt is counted towards your DTI.
Like most loan programs, FHA loans have a Debt and Income Line (DTI). DTI is the main factor lenders use to determine how much they want to loan you, and student loans are part of that assessment. This includes your current monthly debt payments and your future mortgage payments.
These changes must be implemented by August 16, the FHA says, although lenders are also allowed to implement them immediately.
How it works
In most cases, the maximum DTI allowed on an FHA loan is 43% of your monthly income. To calculate your DTI, take your debt payments and divide that number by your gross monthly income (before taxes).
Here is a sample scenario of how a potential FHA borrower is affected in an income-based repayment plan under the old and new guidelines:
Old way
Monthly debt (car and credit card payments) $ 450 Monthly payment of the IBR student loan $ 150 Monthly income $ 3,500 Total student loan balance $ 100,000 Used to calculate monthly student debt $ 1,000 / month (1% of the loan) Total monthly debt used in DTI $ 1,450 / month DTI ($ 1,450 / $ 3,500) 41.42%
New way
Monthly debt (car and credit card payments) $ 450 Monthly payment of the IBR student loan $ 150 Monthly income $ 3,500 Total student loan balance $ 100,000 Used to calculate monthly student debt $ 150 / month (actual payment) Total monthly debt used in DTI $ 600 / month DTI ($ 600 / $ 3,500) 17.14%
In the example above, the decrease in the DTI ratio is significant and can make a huge difference in qualifying potential. The change can also affect how much you can borrow. Lowering the DTI also increases the purchasing power of home buying.
Who Can Benefit From The New FHA Loan Eligibility Rules?
Potential homebuyers
For buyers, this change can mean two things:
You could qualify if you couldn’t before
You could be eligible for a larger mortgage
But for those looking to buy a home, no matter what type of loan you get, it’s a tough market right now. Low housing stocks and exceptionally low mortgage rates have led to bidding wars and house prices soaring. While the change could make it easier for first-time home buyers to get an FHA loan, it’s unlikely to be a big game changer.
“It will be interesting to see how this change will affect the market in the next three to six months,” said Matthew Garland, division director of Garland Mortgage Group and co-host of the Rants & Gems real estate podcast. “I think this will continue to fuel the seller market and keep house prices higher across the country.” In other words, the challenge of finding an affordable home and getting your offer accepted will likely continue.
Therefore, it is especially important to have a budget for buying a home and stick to it. Banks are often willing to lend their buyers far more than people’s monthly budget allows. This is why it is important to focus on what you can afford, not how much a lender is willing to give you. FHA loans have a maximum DTI of 43%, but when certain “compensating factors” are taken into account, like your down payment or cash reserves, you can qualify with an even higher DTI.
Pro tip
The maximum DTI for an FHA loan is 43% or more, but many experts suggest leaving your DTI at 36% or less as the 43% doesn’t take into account other daily expenses.
Another important note: your DTI doesn’t account for all of your monthly expenses such as taxes, groceries, gasoline, maintenance costs, and unexpected medical bills. Because of this, some experts recommend following the 28/36 rule. This rule states that your mortgage payment should not be more than 28% of your monthly pre-tax income, and all of your debt payments (including your mortgage) should not be more than 36% of your gross monthly income.
Potential refinancers
If your student loan debt was the only thing keeping you from refinancing into a new FHA loan, then it’s worth checking out how much you can save now. “For people looking to refinance, this is a home run,” says Garland. “If you are on this income-based repayment plan we can use that payment to help you qualify and now you can get refi and a lower interest rate.”
Remember that when you refinance, you pay closing costs of 3% to 6% of the balance. And FHA loans have an additional mortgage insurance premium of 1.75% of the mortgage balance on top of ongoing mortgage insurance payments.
Before deciding whether an FHA refinance is the right option for you, compare the refinancing options you qualify for. Also, make sure you are around long enough for the potential savings to outweigh the cost of refinancing.
source https://www.cassh24sg.com/2021/07/07/getting-a-first-mortgage-with-student-loans-just-got-easier/
0 notes
Text
2017 STUDENT LOAN GUIDELINES FOR A KENTUCKY USDA RURAL HOUSING MORTGAGE LOAN
2017 STUDENT LOAN GUIDELINES FOR A KENTUCKY USDA RURAL HOUSING MORTGAGE LOAN

Lenders must include the greater of:
• 1 percent of the outstanding loan balance; or • The fixed payment as reflected on the credit report. Income Based Repayment (IBR) plans, graduated plans, adjustable rates, interest-only and deferred plans are examples of repayment plans that are subject to change and do not represent a fixed payment or repayment plan. These types of repayment plans are…
View On WordPress
#502 Guaranteed Loan#502 usda mortgage loan#580 credit score usda loanky#640 credit score usda loan ky#Debt Ratio and Deferred Student Loans#deferred student loans#ibr student loans#Rural development#Rural Housing Kentucky#rural housing mortgage#student loans mortgage approval ky#usda loan kentucky#USDA Rural Development
0 notes