#Contract Research Organization Growth
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Pharmaceutical Contract Research Organization Market Market

Pharmaceutical Contract Research Organization Market Share Insights
Reed Intelligence has recently published a new report titled ""Global Pharmaceutical Contract Research Organization Market."" This comprehensive report delves into crucial aspects of the Bluetooth fingerprint scanner industry, offering valuable insights for both established and new market participants. It covers key factors such as market share, profitability, production, sales, manufacturing processes, advertising strategies, technological innovations, major industry players, and regional market breakdowns, among other important details.
Get Free Sample Report PDF @ https://reedintelligence.com/market-analysis/global-pharmaceutical-contract-research-organization-market/request-sample
Pharmaceutical Contract Research Organization Market Share by Key Players
IQVIA
Syneos Health
Quintiles
PPD
Parexel
ICON
PRA Health Sciences
InVentiv
INC Research Holdings
CRL
Wuxi AppTec
Charles River
Envigo
Medpace Holdings
SGS
PSI CRO
Axcent Advanced Analytics
BIO Agile Therapeutics
Firma Clinical Research
Acculab Lifesciences
Azelix
CTSERV
PEPGRA
The report also covers several important factors including strategic developments, government regulations, market analysis, and the profiles of end users and target audiences. Additionally, it examines the distribution network, branding strategies, product portfolios, market share, potential threats and barriers, growth drivers, and the latest industry trends.
Pharmaceutical Contract Research Organization Market Segmentation
The report on the Global Pharmaceutical Contract Research Organization Market offers a thorough segmentation by type, applications, and regions. It details production and manufacturing data for each segment over the forecast period from 2024 to 2032. The application segment focuses on the different uses and operational processes within the industry. Analyzing these segments will provide insights into the various factors contributing to market growth and their significance.
The report is segmented as follows:
Segment By Type
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient
Finished Dosage Formulation
Segment By Application
Pharmaceutical and Biopharmaceutical Companies
Medical Device Companies
Academic Institutes
Pharmaceutical Contract Research Organization Market Segmentation by Region
North America
U.S
Canada
Europe
Germany
UK
France
Asia Pacific
China
India
Japan
Australia
South Korea
Latin America
Brazil
Middle East & Africa
UAE
Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
South Africa
Get Detailed Segmentation @ https://reedintelligence.com/market-analysis/global-pharmaceutical-contract-research-organization-market/segmentation
The market research report on the Global Pharmaceutical Contract Research Organization Market has been thoughtfully compiled by examining a range of factors that influence its growth, including environmental, economic, social, technological, and political conditions across different regions. A detailed analysis of data related to revenue, production, and manufacturers provides a comprehensive view of the global landscape of the Pharmaceutical Contract Research Organization Market. This information will be valuable for both established companies and newcomers, helping them assess the investment opportunities in this growing market.
Key Highlights
The report delivers essential insights into the Global Pharmaceutical Contract Research Organization Market.
The report covers data for the years 2024-2032, highlighting key factors that impact the market during this period.
It emphasizes technological advancements, government regulations, and recent market developments.
The report will explore advertising and marketing strategies, examine market trends, and provide detailed analysis.
The report includes growth analysis and forecasts, with predictions extending up to the year 2032.
The report highlights a detailed statistical analysis of the key players in the market.
It presents a comprehensive and extensively researched overview of the market.
Buy Pharmaceutical Contract Research Organization Market Research Report @ https://reedintelligence.com/market-analysis/global-pharmaceutical-contract-research-organization-market/buy-now
Contact Us:
Email: [email protected]
#Pharmaceutical Contract Research Organization Market Size#Pharmaceutical Contract Research Organization Market Share#Pharmaceutical Contract Research Organization Market Growth#Pharmaceutical Contract Research Organization Market Trends#Pharmaceutical Contract Research Organization Market Players
0 notes
Text
#Contract Research Organizations (Cros) Services Market#Contract Research Organizations (Cros) Services Market Trends#Contract Research Organizations (Cros) Services Market Growth#Contract Research Organizations (Cros) Services Market Industry#Contract Research Organizations (Cros) Services Market Research
0 notes
Text
The Business Research Company offers contract development manufacturing organizations market research report 2023 with industry size, share, segments and market growth
#contract development manufacturing organizations industry#contract development manufacturing organizations market trends#contract development manufacturing organizations market share#contract development manufacturing organizations market outlook#contract development manufacturing organizations market overview#contract development manufacturing organizations market size#global contract development manufacturing organizations market#contract development manufacturing organizations market analysis#contract development manufacturing organizations market research#contract development manufacturing organizations market report#contract development manufacturing organizations market data#contract development manufacturing organizations market forecast#contract development manufacturing organizations market growth
0 notes
Text
What is the Rot? Why is the Rot?
Spoiler Warning and Holy Wall of Text Batman Warning. I got WAY too into questioning the turbo-cancer here, hopefully my rambling makes sense.
So, the Rot is… weird, from a biological standpoint. Really weird, if you stop to think about it. It’s most frequently described as some variation of cancer, and it certainly fits the criteria for it. Caused by damage to DNA? Check. Multiplies uncontrollably? Check. Comes in both benign and malignant forms, one stationary and the other mobile? Big fat check. Heck, even the Rot cysts eating other creatures kind of fits, according to some research I’ve done – there are apparently cancer cells that will eat other cells, which makes sense in hindsight since cancer cells are cells that have lost important genetic restrictions, which may include whatever lets cells identify other cells as “do not eat.”
(I ain’t a biology whiz and I’m doing research on the fly while getting my thoughts out here, so take whatever I say about biology with a grain of salt)
So, Rot is clearly cancer of some kind, right? Case closed. Except when me and a friend of mine were talking Rain World theories on Discord, she brought up some interesting points that got me thinking.
First point: Rot cells obviously mutate in a way that affects FAR more than just cell replication and termination. Some of the cysts can HEAR. As far as I know, cells in the body do not hear sounds. They communicate via chemical signals and maybe, MAYBE react to temperature. Hearing involves complicated, specialized sensory apparatus to pick up on vibrations in the air. Even if you simplify it and say that it’s only vibrations, that’s STILL a multicellular thing, not a single-cell thing. It’s something that took millions of years to evolve on Earth, if not billions.
And while Rain World’s timeline goes on for long enough that it those kinds of mutations might happen eventually, Rot cysts have the ability to hear pretty much right from the start – because even the Proto-Long-Legs react to your presence like the Daddy Long Legs do, and the Rot in Spearmaster’s campaign, where Pebbles has recently contracted it, reacts the same way as it does in later campaigns. It’s already able to hear.
As far as I know, cancer just means the same cell duplicating over and over again. Are more mutations possible with each division, as errors are made in the DNA during splitting? Probably. But not to THAT extent. There’s no way a lump of cancer somehow mutated the exact complicated genetic blueprint needed to grow organs, at least not without outside interference.
Second point: Cases of Rot are way too consistent across the board. Now, we don’t have a huge sample size to work from, but from what we see from both Pebbles’ Rot, and Hunter Long Legs, they’re… pretty similar. Hunter Long Legs is basically a mobile Rot cyst. They move the same way, seem to grow the same way (starts as a growth inside/on the body before eventually freeing itself from whatever wall/flesh it grew from in some capacity and moving elsewhere), they have the same senses, and they even eat the same way, via something like phagocytosis (how white blood cells “eat” invading organisms via engulfing them and breaking them down in a sac in their main “body.”)
Now, this doesn’t tell us much, because cancer, when it does emerge, is pretty consistent in symptoms/what the mutated cells do once they start replicating. It’s pretty much the same regardless of whatever organism the cancer is happening in. But what ISN’T consistent is what causes the DNA error in the cancer cell in the first place. IRL, cancer can be caused by all kinds of things – smoking, radiation poisoning, being out in the sun too long, drinking deadly chemicals and whatnot, anything that damages DNA. But in RW, the only time we ever hear Rot talked about, or see it present, is in the context of an iterator having f*cked up while mucking around with DNA. Pebbles was trying to create an organism that could change his own genome, and No Significant Harassment created Hunter as a messenger and probably mucked something up in the process in his haste to get them to Moon.
This doesn’t mean that there aren’t other causes of it, of course, we’re working with a sample size of two in an apocalyptic world with who knows how much potentially DNA-damaging stuff around, but… that’s still awfully consistent.
So, combining these points and everything we know to be canon, Rot is:
an organism that lives inside another organism
Until a certain condition is met, it cannot harm said host organism.
Once said condition is met, it goes out of control, wreaking havoc on the organism’s systems and mutating, giving it sensory capabilities and an appetite
Said condition is apparently someone messing up when re-arranging genomes, in yourself or others
It is widespread across multiple different species, at least iterators and slugcats but potentially other species as well.
Once you have a bad case of it, it is apparently NOT CURABLE. Pebbles tried everything he could think of but apparently exhausted all of his options by the time of the Survivor/Monk campaigns.
So, with all the context FINALLY laid out, here’s my wild theory: Rot isn’t a cancer. It’s a symbiote turned parasite. Specifically, I believe it’s a symbiotic microbe that lives inside the cells that make up every other creature in Rain World, and is held in check by a specific gene that all species share, and altering or getting rid of that gene causes it to go berserk, taking over and eventually mutating the host cells.
Yeah, I did watch Parasite Eve let’s plays as a kid, why do you ask? Anyway, hear me out here.
There is precedence for single-celled organisms living inside of other single-celled organisms. They’re referred to as intracellular endosymbiots (hopefully I got the spelling right there), and the most well-known one is probably the mitochondria. The powerhouse of the cell is thought to be descended from some bacteria way, WAY back that was engulfed by a larger cell and not only survived it, but BENEFITED from it. Since then those ancient proto-mitochondria and eukaryotic cells have mutually evolved to be dependent on each other. So it’s entirely possible for something similar to have happened in Rain World.
However, I don’t think it happened NATURALLY, here. Because something that’s able to take over a cell entirely and begin wildly mutating it is NOT something your average cell wants inside of it. There’s a VERY high chance of extinction if you do that. Which means that of course those funky bio-tech loving Ancients either took a look at a wildly dangerous cellular parasite and went “hmmm we can use this” or made one themselves.
Why did they do this? Who knows! Currently, I’m tied between “they needed a better powerhouse for the cell to power the various weird adaptations they’re building into various creatures,” “there was some sort of disease that this parasite gave immunity against and they wanted to make use of it,” and “it gave their creations massively powerful regeneration factors that made them much easier to maintain.” Possibly it was all three. Whatever the reason, the Ancients either found or created this parasite, and put it into their creations’ cells, hoping to reap the benefits.
Well, they got the benefits, but they also got a microbe that hijacked the cells and harnessed their pre-existing DNA blueprints to build organisms disguised as great big blobs of cancer. Which is not exactly ideal, but hey, they just had to figure out a way of keeping the cell hijacking from happening! And the way they ended up going about it was to alter the thing so that so long as there was a specific DNA sequence in the cell, it laid mostly dormant. All the benefits, none of the risks – so long as that specific string of genes remained intact.
And then BECAUSE it was so beneficial, they spread their artificial symbiote and it’s genetic reins throughout ALL of their creations, from the smallest pipe-cleaning slugs to the iterators. Which meant that as their purposed organisms replaced most of the original ecosystem, they spread the symbiote as well. Thus making it possible for pretty much ANY creature on the planet to come down with a bad case of the Rot. And with the iterators, I wouldn’t be surprised if this symbiote is tied to their self-destruction taboos. Try to cross yourself out? Well, it’s gonna maybe happen now, but it’ll be a slow painful death as you’re eaten alive from the inside and all your own parts turn against you, so was it really worth it?
And they never told their creations this perhaps even actively hid it, because why tell them the cause of the main deterrent to them mucking with their taboos? They might find a way around it. The iterators were left ignorant of how Rot works, and because of this they never figured out that Rot HAD a cure after all: rebuilding that genome that reins in the symbiote. Because why in the name of the Void would they repeat the same mistakes that gave them Rot in the first place, and potentially make it worse?
#rain world#rain world worldbuilding#serious musings#rain world headcanons#rw rot#the rot#rain world rot#rain world turbo cancer#which is not actually cancer#yes i Parasite Eved the shit out of the Rot#yes that is a verb now I take no criticisms#anywho the Rot is a byproduct of the ancients Fucking Shit Up on Purpose#and it DOES have a cure damn it#I'm not giving the robots not-actually-cancer and NOT giving them at least a chance to cure it#not mentioned above is the fact that depending on the genes altered along with the restraining gene#you might get rot with fun mutations like being able to jump from organism to organism#or Rot that outright assimilates cells from other organisms#amongst other things#plenty of FUN stories to play with there >:D
301 notes
·
View notes
Text
As digital scamming explodes in Southeast Asia, including so called “pig butchering” investment scams, the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) issued a comprehensive report this week with a dire warning about the rapid growth of this criminal ecosystem. Many digital scams have traditionally relied on social engineering, or tricking victims into giving away their money willingly, rather than leaning on malware or other highly technical methods. But researchers have increasingly sounded the alarm that scammers are incorporating generative AI content and deepfakes to expand the scale and effectiveness of their operations. And the UN report offers the clearest evidence yet that these high tech tools are turning an already urgent situation into a crisis.
In addition to buying written scripts to use with potential victims or relying on templates for malicious websites, attackers have increasingly been leaning on generative AI platforms to create communication content in multiple languages and deepfake generators that can create photos or even video of nonexistent people to show victims and enhance verisimilitude. Scammers have also been expanding their use of tools that can drain a victim’s cryptocurrency wallets, have been manipulating transaction records to trick targets into sending cryptocurrency to the wrong places, and are compromising smart contracts to steal cryptocurrency. And in some cases, they’ve been purchasing Elon Musk’s Starlink satellite internet systems to help power their efforts.
“Agile criminal networks are integrating these new technologies faster than anticipated, driven by new online marketplaces and service providers which have supercharged the illicit service economy,” John Wojcik, a UNODC regional analyst, tells WIRED. “These developments have not only expanded the scope and efficiency of cyber-enabled fraud and cybercrime, but they have also lowered the barriers to entry for criminal networks that previously lacked the technical skills to exploit more sophisticated and profitable methods.”
For years, China-linked criminals have trafficked people into gigantic compounds in Southeast Asia, where they are often forced to run scams, held against their will, and beaten if they refuse instructions. Around 200,000 people, from at least 60 countries, have been trafficked to compounds largely in Myanmar, Cambodia, and Laos over the last five years. However, as WIRED reporting has shown, these operations are spreading globally—with scamming infrastructure emerging in the Middle East, Eastern Europe, Latin America, and West Africa.
Most prominently, these organized crime operations have run pig butchering scams, where they build intimate relationships with victims before introducing an “investment opportunity” and asking for money. Criminal organizations may have conned people out of around $75 billion through pig butchering scams. Aside from pig butchering, according to the UN report, criminals across Southeast Asia are also running job scams, law enforcement impersonation, asset recovery scams, virtual kidnappings, sextortion, loan scams, business email compromise, and other illicit schemes. Criminal networks in the region earned up to $37 billion last year, UN officials estimate. Perhaps unsurprisingly, all of this revenue is allowing scammers to expand their operations and diversify, incorporating new infrastructure and technology into their systems in the hope of making them more efficient and brutally effective.
For example, scammers are often constrained by their language skills and ability to keep up conversations with potentially hundreds of victims at a time in numerous languages and dialects. However, generative AI developments within the last two years—including the launch of writing tools such as ChatGPT—are making it easier for criminals to break down language barriers and create the content needed for scamming.
The UN’s report says AI can be used for automating phishing attacks that ensnare victims, the creation of fake identities and online profiles, and the crafting of personalized scripts to trick victims while messaging them in different languages. “These developments have not only expanded the scope and efficiency of cyber-enabled fraud and cybercrime, but they have also lowered the barriers to entry for criminal networks that previously lacked the technical skills to exploit sophisticated and profitable methods,” the report says.
Stephanie Baroud, a criminal intelligence analyst in Interpol’s human trafficking unit, says the impact of AI needs to be considered as part of a pig butchering scammer’s tactics going forward. Baroud, who spoke with WIRED in an interview before the publication of the UN report, says the criminal’s recruitment ads that lure people into being trafficked to scamming compounds used to be “very generic” and full of grammatical errors. However, AI is now making them appear more polished and compelling, Baroud says. “It is really making it easier to create a very realistic job offer,” she says. “Unfortunately, this will make it much more difficult to identify which is the real and which is the fake ads.”
Perhaps the biggest AI paradigm shift in such digital attacks comes from deepfakes. Scammers are increasingly using machine-learning systems to allow for real-time face-swapping. This technology, which has also been used by romance scammers in West Africa, allows criminals to change their appearance on calls with their victims, making them realistically appear to be a different person. The technology is allowing “one-click” face swaps and high-resolution video feeds, the UN’s report states. Such services are a game changer for scammers, because they allow attackers to “prove” to victims in photos or real-time video calls that they are who they claim to be.
Using these setups, however, can require stable internet connections, which can be harder to maintain within some regions where pig butchering compounds and other scamming have flourished. There has been a “notable” increase in cops seizing Starlink satellite dishes in recent months in Southeast Asia, the UN says—80 units were seized between April and June this year. In one such operation carried out in June, Thai police confiscated 58 Starlink devices. In another instance, law enforcement seized 10 Starlink devices and 4,998 preregistered SIM cards while criminals were in the process of moving their operations from Myanmar to Laos. Starlink did not immediately respond to WIRED’s request for comment.
“Obviously using real people has been working for them very well, but using the tech could be cheaper after they have the required computers” and connectivity, says Troy Gochenour, a volunteer with the Global Anti-Scam Organization (GASO), a US-based nonprofit that fights human-trafficking and cybercrime operations in Southeast Asia.
Gochenour’s research involves tracking trends on Chinese-language Telegram channels related to carrying out pig butchering scams. And he says that it is increasingly common to see people applying to be AI models for scam content.
In addition to AI services, attackers have increasingly leaned on other technical solutions as well. One tool that has been increasingly common in digital scamming is so-called “crypto drainers,” a type of malware that has particularly been deployed against victims in Southeast Asia. Drainers can be more or less technically sophisticated, but their common goal is to “drain” funds from a target’s cryptocurrency wallets and redirect the currency to wallets controlled by attackers. Rather than stealing the credentials to access the target wallet directly, drainers are typically designed to look like a legitimate service—either by impersonating an actual platform or creating a plausible brand. Once a victim has been tricked into connecting their wallet to the drainer, they are then manipulated into approving one or a few transactions that grant attackers unintended access to all the funds in the wallet.
Drainers can be used in many contexts and with many fronts. They can be a component of pig butchering investment scams, or promoted to potential victims through compromised social media accounts, phishing campaigns, and malvertizing. Researchers from the firm ScamSniffer, for example, published findings in December about sponsored social media and search engine ads linked to malicious websites that contained a cryptocurrency drainer. The campaign, which ran from March to December 2023 reportedly stole about $59 million from more than 63,000 victims around the world.
Far from the low-tech days of doing everything through social engineering by building a rapport with potential victims and crafting tricky emails and text messages, today’s scammers are taking a hybrid approach to make their operations as efficient and lucrative as possible, UN researchers say. And even if they aren’t developing sophisticated malware themselves in most cases, scammers are increasingly in the market to use these malicious tools, prompting malware authors to adapt or create hacking tools for scams like pig butchering.
Researchers say that scammers have been seen using infostealers and even remote access trojans that essentially create a backdoor in a victim’s system that can be utilized in other types of attacks. And scammers are also expanding their use of malicious smart contracts that appear to programmatically establish a certain agreed-upon transaction or set of transactions, but actually does much more. “Infostealer logs and underground data markets have also been critical to ongoing market expansion, with access to unprecedented amounts of sensitive data serving as a major catalyst,” Wojcik, from the UNODC, says.
The changing tactics are significant as global law enforcement scrambles to deter digital scamming. But they are just one piece of the larger picture, which is increasingly urgent and bleak for forced laborers and victims of these crimes.
“It is now increasingly clear that a potentially irreversible displacement and spillover has taken place in which organized crime are able to pick, choose, and move value and jurisdictions as needed, with the resulting situation rapidly outpacing the capacity of governments to contain it,” UN officials wrote in the report. “Failure to address this ecosystem will have consequences for Southeast Asia and other regions.”
29 notes
·
View notes
Text
On May 28, 1914, the Institut für Schiffs-und Tropenkrankheiten (Institute for Maritime and Tropical Diseases, ISTK) in Hamburg began operations in a complex of new brick buildings on the bank of the Elb. The buildings were designed by Fritz Schumacher, who had become the Head of Hamburg’s building department (Leiter des Hochbauamtes) in 1909 after a “flood of architectural projects” accumulated following the industrialization of the harbor in the 1880s and the “new housing and working conditions” that followed. The ISTK was one of these projects, connected to the port by its [...] mission: to research and heal tropical illnesses; [...] to support the Hamburg Port [...]; and to support endeavors of the German Empire overseas.
First established in 1900 by Bernhard Nocht, chief of the Port Medical Service, the ISTK originally operated out of an existing building, but by 1909, when the Hamburg Colonial Institute became its parent organization (and Schumacher was hired by the Hamburg Senate), the operations of the ISTK had outgrown [...]. [I]ts commission by the city was an opportunity for Schumacher to show how he could contribute to guiding the city’s economic and architectural growth in tandem, and for Nocht, an opportunity to establish an unprecedented spatial paradigm for the field of Tropical Medicine that anchored the new frontier of science in the German Empire. [...]
[There was a] shared drive to contribute to the [...] wealth of Hamburg within the context of its expanding global network [...]. [E]ach discipline [...] architecture and medicine were participating in a shared [...] discursive operation. [...]
---
The brick used on the ISTK façades was key to Schumacher’s larger Städtebau plan for Hamburg, which envisioned the city as a vehicle for a “harmonious” synthesis between aesthetics and economy. [...] For Schumacher, brick [was significantly preferable] [...]. Used by [...] Hamburg architects [over the past few decades], who acquired their penchant for neo-gothic brickwork at the Hanover school, brick had both a historical presence and aesthetic pedigree in Hamburg [...]. [T]his material had already been used in Die Speicherstadt, a warehouse district in Hamburg where unequal social conditions had only grown more exacerbated [...]. Die Speicherstadt was constructed in three phases [beginning] in 1883 [...]. By serving the port, the warehouses facilitated the expansion and security of Hamburg’s wealth. [...] Yet the collective profits accrued to the city by these buildings [...] did not increase economic prosperity and social equity for all. [...] [A] residential area for harbor workers was demolished to make way for the warehouses. After the contract for the port expansion was negotiated in 1881, over 20,000 people were pushed out of their homes and into adjacent areas of the city, which soon became overcrowded [...]. In turn, these [...] areas of the city [...] were the worst hit by the Hamburg cholera epidemic of 1892, the most devastating in Europe that year. The 1892 cholera epidemic [...] articulated the growing inability of the Hamburg Senate, comprising the city’s elite, to manage class relationships [...] [in such] a city that was explicitly run by and for the merchant class [...].
In Hamburg, the response to such an ugly disease of the masses was the enforcement of quarantine methods that pushed the working class into the suburbs, isolated immigrants on an island, and separated the sick according to racial identity.
In partnership with the German Empire, Hamburg established new hygiene institutions in the city, including the Port Medical Service (a progenitor of the ISTK). [...] [T]he discourse of [creating the school for tropical medicine] centered around city building and nation building, brick by brick, mark by mark.
---
Just as the exterior condition of the building was, for Schumacher, part of a much larger plan for the city, the program of the building and its interior were part of the German Empire and Tropical Medicine’s much larger interest in controlling the health and wealth of its nation and colonies. [...]
Yet the establishment of the ISTK marked a critical shift in medical thinking [...]. And while the ISTK was not the only institution in Europe to form around the conception and perceived threat of tropical diseases, it was the first to build a facility specifically to support their “exploration and combat” in lockstep, as Nocht described it.
The field of Tropical Medicine had been established in Germany by the very same journal Nocht published his overview of the ISTK. The Archiv für Schiffs- und Tropen-Hygiene unter besonderer Berücksichtigung der Pathologie und Therapie was first published in 1897, the same year that the German Empire claimed Kiaochow (northeast China) and about two years after it claimed Southwest Africa (Namibia), Cameroon, Togo, East Africa (Tanzania, Burundi, Rwanda), New Guinea (today the northern part of Papua New Guinea), and the Marshall Islands; two years later, it would also claim the Caroline Islands, Palau, Mariana Islands (today Micronesia), and Samoa (today Western Samoa).
---
The inaugural journal [...] marked a paradigm shift [...]. In his opening letter, the editor stated that the aim of Tropical Medicine is to “provide the white race with a home in the tropics.” [...]
As part of the institute’s agenda to support the expansion of the Empire through teaching and development [...], members of the ISTK contributed to the Deutsches Kolonial Lexikon, a three-volume series completed in 1914 (in the same year as the new ISTK buildings) and published in 1920. The three volumes contained maps of the colonies coded to show the areas that were considered “healthy” for Europeans, along with recommended building guidelines for hospitals in the tropics. [...] "Natives" were given separate facilities [...]. The hospital at the ISTK was similarly divided according to identity. An essentializing belief in “intrinsic factors” determined by skin color, constitutive to Tropical Medicine, materialized in the building’s circulation. Potential patients were assessed in the main building to determine their next destination in the hospital. A room labeled “Farbige” (colored) - visible in both Nocht and Schumacher’s publications - shows that the hospital segregated people of color from whites. [...]
---
Despite belonging to two different disciplines [medicine and architecture], both Nocht and Schumacher’s publications articulate an understanding of health [...] that is linked to concepts of identity separating white upper-class German Europeans from others. [In] Hamburg [...] recent growth of the shipping industry and overt engagement of the German Empire in colonialism brought even more distant global connections to its port. For Schumacher, Hamburg’s presence in a global network meant it needed to strengthen its local identity and economy [by purposefully seeking to showcase "traditional" northern German neo-gothic brickwork while elevating local brick industry] lest it grow too far from its roots. In the case of Tropical Medicine at the ISTK, the “tropics” seemed to act as a foil for the European identity - a constructed category through which the European identity could redescribe itself by exclusion [...].
What it meant to be sick or healthy was taken up by both medicine and architecture - [...] neither in a vacuum.
---
All text above by: Carrie Bly. "Mediums of Medicine: The Institute for Maritime and Tropical Diseases in Hamburg". Sick Architecture series published by e-flux Architecture. November 2020. [Bold emphasis and some paragraph breaks/contractions added by me. Text within brackets added by me for clarity. Presented here for commentary, teaching, criticism purposes.]
#abolition#ecology#sorry i know its long ive been looking at this in my drafts for a long long time trying to condense#but its such a rich comparison that i didnt wanna lessen the impact of blys work here#bly in 2022 did dissertation defense in architecture history and theory on political economy of steel in US in 20s and 30#add this to our conversations about brazilian eugenics in 1930s explicitly conflating hygiene modernist architecture and white supremacy#and british tropical medicine establishment in colonial india#and US sanitation and antimosquito campaigns in 1910s panama using jim crow laws and segregation and forcibly testing local women#see chakrabartis work on tropical medicine and empire in south asia and fahim amirs cloudy swords#and greg mitmans work on connections between#US tropical medicine schools and fruit plantations in central america and US military occupation of philippines and rubber in west africa#multispecies#imperial#indigenous#colonial#landscape#temporal#see also us mosquito campaigns in panama and british urban planning in west africa and rohan deb roy work on india bengal entomology#ecologies#bugs#tidalectics#archipelagic thinking#plantations#intimacies of four continents#carceral geography
14 notes
·
View notes
Text

https://english.almayadeen.net/news/Economy/-israel--paying-heavy-price-for-its-widening-aggression--cnn
In late September, as "Israel's" almost year-long genocide in Gaza spread and its credit rating was reduced once more, Israeli Finance Minister, Bezalel Smotrich, claimed that, while under stress, the economy remained robust.
"Israel's economy bears the burden of the longest and most expensive war in the country's history," Smotrich said on September 28.
Karnit Flug, a former governor of "Israel’s" central bank, told CNN that a more intense war will "take a heavier toll on economic activity and growth."
The war has drastically deteriorated the situation in Gaza, driving it into an economic and humanitarian disaster long ago, while the West Bank is "undergoing a rapid and alarming economic decline," according to a UN study released last month.
The Lebanese economy, meanwhile, might shrink by much to 5% this year as a result of cross-border strikes between the Lebanese Resistance - Hezbollah - and "Israel", according to BMI, a market research organization owned by Fitch Solutions.
According to a worst-case scenario developed by Tel Aviv University's Institute for National Security Studies, "Israel's" economy might contract much worse.
Prior to the war on Gaza, the International Monetary Fund predicted the GDP of "Israel" would increase by 3.4% this year in contrast to the current predictions of 1% to 1.9%.
In addition, "Israel's" central bank cannot decrease interest rates to revive the economy since inflation is growing, fueled by rising salaries and ballooning government expenditure to support the war.
Related News
The Bank of Israel estimated in May that war costs could total $66 billion, including military outlays and civilian expenses, such as housing for thousands of Israeli settlers evacuated from the north. This is roughly 12% of "Israel's" GDP.
While Smotrich claimed that the economy will bounce back, economists are concerned the damage will far outlast the war.
Flug, the former Bank of Israel governor, says there is a risk the Israeli government will cut investment to free up resources for war, reducing the growth moving forward.
Researchers at the Institute for National Security Studies say a potential full withdrawal from Gaza and Lebanon would have "Israel" in a weaker position than before October 7, 2023.
“Israel is expected to suffer long-term economic damage regardless of the outcome,” they wrote.
High-income taxpayers leaving the occupation en masse would also make things worse. The occupation government has postponed releasing a budget for next year due to competing demands that make it difficult to balance the accounts.
The battle has doubled "Israel's" budget deficit — the gap between government expenditure and income, primarily from taxes — to 8% of GDP, up from 4% before the war.
Government borrowing has increased and become more costly, as investors seek greater returns on Israeli bonds and other assets. Multiple downgrades to "Israel's" credit ratings by Fitch, Moody's, and S&P are expected to hike the country's borrowing costs even higher.
In late August, the Institute for National Security Studies estimated that just one month of "high-intensity warfare" in Lebanon against Hezbollah combined with "intensive attacks" in the opposite direction that damage Israeli infrastructure could cause "Israel's" budget deficit to rise to 15% and its GDP to contract by up to 10% this year.
The Israeli government faces a growing fiscal crisis, unable to rely on stable tax revenues as many businesses collapse amid the ongoing war. Coface BDi estimates that 60,000 Israeli firms will shut down this year, significantly higher than the average of 40,000.
Avi Hasson, CEO of Startup Nation Central, warned that the Israeli tech sector will not sustain the blows and the government's “destructive” economic policies. The war has led many tech companies to register overseas despite local tax incentives, exacerbating an existing trend.
Other sectors like agriculture and construction are also suffering, struggling with labor shortages and rising prices. Tourism has seen a sharp decline, resulting in an estimated loss of 18.7 billion shekels ($4.9 billion) in revenue since the war began.
#palestine#free palestine#gaza#free gaza#jerusalem#current events#yemen#tel aviv#israel#palestine news
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Our Organizing Wins in 2023

Over the past year, EWOC had its busiest year yet with some truly extraordinary organizing wins. These include EWOC’s direct support in 14 successful union recognition wins and 15 more workplaces currently in a union drive. We’ve also connected 65 workplace campaigns and represented more than 7,000 workers to outside unions.
Growth in 2023
EWOC has also supported workers in
Taking one form of collective action at 447 workplaces
Winning demands at 47 pre-union workplaces
Marching on the boss at 17 workplaces
Striking at two workplaces
EWOC accomplished these wins by mobilizing our volunteers in 2023
200 EWOC volunteer organizers supported worker organizers
67 EWOC volunteers made worker intake calls, guaranteeing that every worker who reached out to us received a call within 48 hours
75 EWOC volunteers took on the role of support organizers. These are typically organizers with decades of experience, who mentor younger organizers working on EWOC campaigns.
Our 2023 Campaigns
These are some of the incredible stories from campaigns in 2023.
Residents at Beth-Israel Deaconess hospital in Boston ran a petition campaign with support from EWOC volunteers. That campaign garnered a supermajority of signatures in less than a week, and management conceded to the overwhelming pressure. They won a $10,000-per-year housing stipend and additional benefits for the 700 residents on staff.
Twenty-six workers at a Juiceland warehouse in Austin, Texas, won a $2-per-hour pay increase after marching on their boss.
Workers at The Basement, an escape room in Los Angeles, worked with EWOC volunteers to learn the foundations of organizing. They then went on to work with Actors Equity and become the first unionized escape room in the U.S.
In New York City, workers at Hex&Co., a gaming cafe, worked with EWOC volunteers for more than a year to develop organizing skills before connecting with a union. Their successful union drive with Workers United sparked a wave of game store union organizing across New York City. Two more stores have since announced union drives.
In Princeton, New Jersey, 19 workers at Labyrinth Books, an independent bookstore, are unionizing with the Retail, Wholesale and Department Store Union (RWDSU) after working with EWOC for over a year to develop their organizing skills.
Workers at Barboncino in Brooklyn worked with EWOC volunteers one-on-one over the course of many months. They learned and applied their organizing skills to become the first unionized pizzeria in New York City. Leaders from this campaign have even become organizing volunteers with EWOC. They use their experience and skills to support other service workers interested in organizing across the city.
2023 Special Events
In addition to EWOC’s organizing support, we had a record year of training. About 480 workers participated in our foundational training program. This four-week program runs six times a year at no cost to participants. We also put on two “Train the Trainers” events, growing from 10 to 55 foundational program facilitators. This has greatly helped expand our capacity to support workers interested in our training.
In 2023, EWOC launched a fellowship program designed as a follow-up to the foundational training, specifically for workers engaged in ongoing workplace campaigns. Participants were invited to apply with their co-workers. We welcomed 49 participants split into four cohort sessions, each lasting six weeks.
EWOC also put on a number of events in 2023. We discussed many labor topics, including salting, corporate research and power mapping, the Cemex decision, and organizing in remote workplaces. Jane MacAlevey joined EWOC for training on winning a first contract, and members of UAWD and TDU came to speak about the power of strikes and contract campaigns. Adam Conover attended an EWOC volunteer call and gave us a shout-out on his show.
In 2023, EWOC released a 26-part video series entitled “Unionizing 101.” These short videos were designed to make unionizing accessible and fun. They broke down core organizing questions like leader identification, power mapping, and more! These videos have more than 6,000 views on YouTube alone.
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
Contract Hiring Mobile App Developers in 2024-25
In this digitally dependent world, one of the fastest-growing technologies is the introduction of mobile apps for brands. Businesses utilize apps to drive creation, quick access to information, customer communication, and engagement with the brand.
The growth rate of mobile-based applications is expected to be 14.3% from the year 2024 to 2030 – Grand View Research
This makes mobile app developers one of the most in-demand skills in the market. For a successful project, the presence of skilled professionals is essential and businesses are also inclined to hire app developers remotely. Read the complete guide and let’s reveal how contract hiring mobile app developers is beneficial for businesses.
Why is Contract Hiring Beneficial?
When to Hire Mobile App Developers on Contract and Not on Employment?
Identifying the Technology & Scope of Work for the Mobile App Project
Sources of Contract Hiring
Interviewing and Screening Candidates
Ideal Terms & Clauses for Contract Hiring
Setting up effective Remote Communication and Collaboration
Conclusion
Why is Contract Hiring Beneficial?
Contract work also commonly known as the gig economy is highly popular in the market. Businesses can easily fill the temporary skill gap in the company by indulging with contract workers on project to project basis.
However, the key aspect is that businesses should know when to opt. to hire remote app developers on a contract basis.
When to Hire Mobile App Developers on Contract and Not on Employment?
Project & Talent wise need only
If your project needs short-term assistance from a developer it’s best to hire contractors. And, if the requirements increase, you can scale up the work with the hired professional.
Cost Considerations
Organizations easily save money and resources by opting for contract developers instead of permanent employees. If you’ve tight budgets and short-term requirements, this would be the best option.
Requirement of a Specialized Skill
Contract developers are often specialized in one specific skill like React Native or Swift. When the project is dependent on one skill that you do not have in-house, then you can hire a professional from a pool of Talents who best fits your requirements.
Identifying the Technology & Scope of Work for the Mobile App Project
Before you start hiring mobile app developers, it’s critical to understand the scope of the app and project requirements in detail.
Understand the Problem the App solves and for whom
Perform market research to identify the need for an app among your target audience. Plan how the app is going to benefit the users and what is a list of problems that need to be solved via developing the app. The classic example could be the problem of consumer interaction. With the app’s introduction, a brand can promote more engagement and interaction with the target audience.
Understand the project requirements and related core features
Discuss with decision-makers what features the app must have for the users (the core feature and the differentiable features). Decide on the platforms the App will support (android, iOS, or both). You must also finalize project details beforehand like deliverables and deadlines.
Choose the right Technology Stack
Selecting the right technology stack sets the correct foundation for the app. Consider the purpose of the app while keeping the target audience in mind and select either a native or cross-platform stack.
1. Native Mobile App Development ensures optimal performance and ‘platform-specific’ capabilities.
iOS: Swift or Objective-C for programming, Xcode for development, UIKit for interface design.
Android: Kotlin or Java for programming, Android Studio for development, Android SDK for interface design.
2. Cross-Platform Mobile App Development ensures quick deployments, reusability of codes, and coverage of both platforms (Android & iOS).
React Native, Flutter, or Xamarin Frameworks offer the ability to write code once and deploy it across multiple platforms.
3. Other Tools, Libraries, and Databases to be identified might include Android Studio, Xcode, Firebase, Restful, SQLite, Room DB, SQL, MongoDB, Redux, etc.
Outline the Scope of Work & Document in detail
A well-defined scope of work sets the wheels in motion for an app development project. The clear SOW acts as a roadmap for the developer and client and reduces any chances of misunderstanding in the process.
Also well document the Team requirements, their roles & responsibilities, features & functionalities, tasks & deliverables, milestones & deadlines, expectations for UI/UX designs, testing guidelines, deployment & maintenance guidelines, etc.
Sources of Contract Hiring
Here are a bunch of options that one can select from to hire mobile app developers in 2024.
Leveraging Specialized Platforms,
There are freelance platforms available in the market like Upwork, and Fiverr, that have professional freelancers who can provide you with one-time developer services.
IT Agencies (B2B contract Hiring)
Consider hiring IT agencies like Sprybit that have a pool of talent who are not only pre-screened but also reliable for the project.
Networks
Ask in your Network, post on Facebook – LinkedIN – Reddit groups, reach out to Industry people, and ask for references.
Interviewing and Screening Candidates
Following a pre-decided screening process is essential to finding the right talent for your organization.
Review Past Work/Portfolio
Make sure to review the candidate’s portfolio related to the mobile development projects. Examine the projects that require similar skill sets as compared to your project and judge their proficiency. You can also inquire about those projects and codes to understand their level of knowledge.
Consider requesting some sample codes. The GutHub links can act as an excellent proof of skills. This step is necessary to make a calculated decision.
Screening of Technical Skill
Shortlisted candidates must be proficient in technical skills according to the project requirements. Hiring managers must conduct the right assessment that ensures the presence of skill expertise.
These assessments must be practical and should involve coding for varied purposes. With this, you can understand data structures and algorithm knowledge in the candidate.
Identify other important factors
Apart from technical skills, other non-technical factors are essential to be considered during the hiring process. Check the candidate’s communication skills to ensure they will be able to communicate their ideas and plans with other team members. Candidates must also possess problem-solving skills to navigate technical errors in codes if required.
There are multiple design principles for mobile apps to enhance user experience. Check if the app developer is aware of such technicalities to select the best possible resource for your project.
Ideal Terms & Clauses for Contract Hiring
Whether you are a newbie or an experienced professional; while contract hiring mobile app developers; the ideal terms to keep your data, time, money & idea safe remain an unmissable necessity.
Hiring from a Freelance Portal does check many boxes with their well-established policies and processes; which might be good but not always foolproof. Hiring freelancers directly or from IT Agencies engages us in co-building Terms & Conditions on mutual consensus or are pre-defined with our experience as a Vendor Compliance Policy. But, all-in-all, making sure that every safety measure for our Project is taken care of remains our sole responsibility.
Payment Terms
Unlike full-time employees, one can’t pay to contract professionals every month. Select among a wide range of options like hourly-rate, and project-basis. Transparency from the very beginning will help smooth project completion.
IP rights
Before starting the collaboration, clarity on IP i.e. intellectual property is essential. As in who is the owner of code, design, app interface, etc should be agreed on to avoid disputes in the future.
Confidential & Non-disclosure agreements
Once you allot work to these contract workers, you will be sharing confidential details of the company. Make an advance agreement and ask them to sign it before commencing the work.
Project Timeline & Quality Assurance Standards
Maintain the quality of the project by deciding in prior about project deadlines, submissions, and code quality in terms of programming languages.
Termination clause
State a prescribed reason for when can either of the parties end the agreement. This brings clarity to the table regarding moral, ethical and professional expectations your Organization has.
Dispute Resolution
In rare cases, the client and candidate might go into a dispute that needs to be solved for the project’s betterment. Laying out steps to clear disputes and solve them will act as guidance in case it’s required.
Indemnity & Liability
It is important to outline the obligations & responsibilities of each party during any case of losses, damages and/or legal claims arising during the course of the project.
Governing Law & Governing Body
Involving government laws, rights, and bodies can help in resolving disputes and save the project’s future. This way both parties can come to the same conclusion under legal principles.
Setting up effective Remote Communication and Collaboration
Remote work culture creates room for misunderstanding and unclear targets. However, the issue can be tackled if there’s a pre-decided communication system planned. From work allotment to final project submission, an effective communication plan benefits all the parties involved in the project.
These can be achieved by establishing communication, collaboration & project management tools for your Project:
Inbuilt communication channels of Freelance Platforms
Slack
Microsoft Teams
Zoom
Google Meet
Jira
Asana
Trello
Basecamp
Google Workspace
Dropbox
Microsoft 365
Notion
Conclusion
Organizations’ idea to hire mobile app developers on Contract is spreading like a forest fire. Businesses now have access to partner freelancers and contract workers for short periods with ideal skills, and reliable talent.
Before starting your journey on the same path, make sure to remain transparent and pre-decide the essential factors like payment, timelines, IP & communication; and finally proceed to give life to your mobile app.
#hire remote developers#hire developers#hire mobile app developers#android app developers#ios app developers#contract hire developers#hire developers on contract#remote developers for hire#hire dedicate remote developers#hire pre vetted remote developers
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Tetrahed-Prominent IT services and staffing solutions- Best Permanent staffing solutions & contract staffing service provider
Tetrahed, Inc., a prominent provider of best IT services and staffing solutions based in Austin, Texas, has expanded its operations to India, demonstrating a dedication to delivering tailored solutions to meet the unique requirements of its clients. The company offers a comprehensive range of IT services, including cloud solutions, cybersecurity, AI/ML, network services, identity access management, and data analytics. With a deep understanding of the constantly evolving technological landscape, Tetrahed, Inc. ensures that its clients remain at the forefront of this competitive market. The company envisions becoming a globally trusted leader in IT services, driven by a robust and innovative delivery approach. Tetrahed, Inc. is committed to propelling every sector forward, enhancing productivity, and fostering innovation. The organization's recent expansion to India further solidifies its position as a key player in the IT services and staffing solutions industry.
Our company offers a range of services beyond IT, including business consulting and best enterprise solutions. We work with clients to develop innovative strategies that enhance operational efficiency, optimize processes, and drive sustainable growth. Our holistic approach enables clients to navigate the complexities of today's business environment with confidence.
Tetrahed is a company that specializes in providing innovative IT services and staffing solutions. They offer a range of flexible options such as contract-to-hire, contract staffing service provider, Top permanent staffing, and Top best IT staff augmentation services. Their global reach allows them to source top-tier talent irrespective of location requirements, providing onshore, offshore, onsite, and nearshore staffing solutions. Tetrahed is a reliable best IT staffing company that provides end-to-end staffing solutions to cater to client requirements. They have years of deep industry experience, offer real-time market analysis, and have a diverse network of qualified professionals. Tetrahed is a strategic partner that empowers organizations with the right blend of technology and talent to thrive in an ever-changing landscape.
Give Us A Call
(+1) 512 692 9119
www.linkedin.com/company/tetrahedinc
Our Locations
13785 Research Blvd, Ste 125 Austin, TX 78750

BEST IT STAFFING COMPANY IN INDIA & USA
#staffing company#temporary staffing#permanent staffing#it services#contract staffing#staffing#permanent staffing solutions#it staffing services#it staff augmentation#it staffing solutions#it staffing agency#staff augmentation solutions#staff augmentation company
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ditch the Debt, Drive Your Dreams: No Credit Check Van Leasing

Building your business shouldn't be held hostage by credit scores. Enter the world of "no credit check van leasing", a game-changer for entrepreneurs who need a reliable workhorse without the financial hurdles. Forget the stress of loan applications and credit inquiries; this innovative option lets you get behind the wheel and start hustling, regardless of your credit history.
But how does it work? Unlike traditional leasing, which relies heavily on credit scores, these specialized providers take a more holistic approach. They consider your income, business stability, and even alternative credit data to assess your suitability. This means freelancers, startups, and those with limited credit history have a fair shot at securing the van they need.
Here are some key benefits of no credit check van leasing:
1- Faster approval process: Say goodbye to weeks of waiting. With streamlined assessments, you could be driving your new van within days. 2- No credit score impact: Forget the anxiety of credit checks. This option protects your credit history, leaving you free to build it organically. 3- Flexible terms: Choose a lease duration and mileage that suits your needs, from short-term contracts to long-term flexibility. 4- Reduced upfront costs: Skip the hefty down payments. Most no-credit-check leases require minimal upfront investments, freeing up your capital for business growth. 5- Predictable monthly payments: Enjoy fixed installments for the duration of your lease, making budgeting a breeze. 6- Focus on what matters: With a reliable van at your disposal, you can concentrate on what truly drives your business, whether it's client satisfaction or market expansion.
No credit check van leasing isn't a magic bullet, but it's a powerful tool for entrepreneurs who need a boost. Remember, it's crucial to research reputable providers, compare lease terms, and ensure you understand all the associated costs. With careful planning and responsible financial management, you can leverage this option to fuel your business growth without breaking the credit bank.
So, are you ready to ditch the debt and drive your dreams? Explore the world of no credit check van leasing and unlock the freedom to navigate your entrepreneurial journey with confidence.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Navigating Economic Storms: Understanding and Responding to Recession in Canada
Introduction:
In the complicated world of economics, recessions are like storms on the horizon, affecting the financial well-being of people and the stability of organizations. In this blog post, we can delve into the intricacies of recession in the context of Canada, analyzing its reasons, effects, and techniques for weathering the monetary downturn.
Defining Recession in Canada:
A recession is a considerable decline in monetary pastime that lasts for an extended period. In Canada, that is measured by the valuable resource of consecutive quarters of a bad GDP boom. This economic contraction can cause mission losses, decreased client spending, and a stylish experience of financial lack of confidence.
The Causes of Recession:
An aggregate of domestic and international elements frequently brings about recessions. In Canada, shifts in global alternate patterns, fluctuations in commodity costs, and modifications in monetary policies all play a role. For instance, the 2008 financial catastrophe was driven by an international credit rating crunch reverberating through the Canadian economy. In 2023, researchers at Deloitte are among a developing chorus of economists, which consists of those at the most significant Canadian banks, watching for the monetary gadget to be successful. This is due to a mixture of things, which include the continued COVID-19 pandemic, delivery chain disruptions, and hard work shortages.
Impacts on Various Sectors:
Different sectors revel in recessions through several strategies. While industries like manufacturing and production can also face declines in production and layoffs, company-oriented sectors like healthcare and schooling will be inclined to be more resilient. For example, at some point in the 2008 recession, the housing market in Canada experienced a significant downturn, impacting the development of the organization and associated offerings. In 2023, the tight labor market and high costs can result in a profit-inflation spiral.
Government Responses and Interventions:
In reaction to recessions, governments implement several rules to stimulate financial growth and stability. These measures can encompass modifications to hobby expenses, financial stimulus applications, and targeted investments in key industries. For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, the Canadian authorities delivered sizeable economic resource packages to guide humans and groups. In 2023, the government may want to position comparable measures to guide the financial system.
Challenges and Opportunities for Individuals and Businesses:
For human beings, recessions can supply pastime uncertainty and monetary stress. Building a diverse capacity set and preserving a solid financial plan can help mitigate economic storms. As an alternative, businesses may additionally need to pivot their strategies, innovate, and find new markets to continue existing and thriving. In 2023, companies will also need to focus on supply chain resilience and complex paintings for improvement to stay competitive.
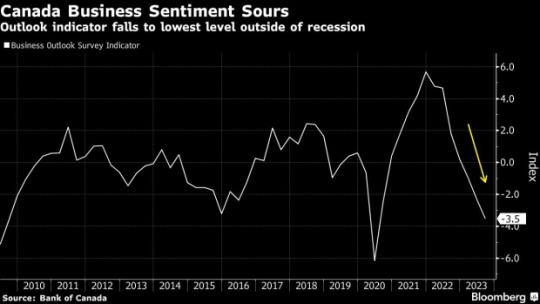
Canadian business sentiment has hit its lowest point since the 2020 Covid recession, as in line with Bank of Canada surveys. The statistics exhibits that while economic interest has slowed throughout numerous indicators, both firms and clients maintain to assume excessive inflation. Despite the slowdown, businesses are making plans greater frequent and considerable charge will increase, although hiring expectations have dipped. On the customer front, the exertions market remains considered definitely, with document-excessive expectations for salary increase. However, there's a excellent discrepancy between their perception of inflation and real figures. This standard decline in sentiment points closer to a deteriorating economic outlook, doubtlessly influencing the relevant bank's choice to maintain interest prices. The business outlook indicator fell for the 7th consecutive zone, signaling worries about slower sales increase and destiny projections. Firms also are reevaluating hiring and capital expenditure plans. The venture for policymakers lies in adjusting inflation expectations amid a cooling economy. Although corporations fear about income call for and credit, issues approximately price pressures and deliver chains are waning. Many believe that better quotes will hinder income and investments within the subsequent 12 months, and anticipate accomplishing the 2% inflation target will take longer than three years. For customers, perceptions of contemporary inflation continue to be excessive, with expectations for destiny inflation also improved. Higher fees are impacting foremost purchases, leading to a preference for discretionary spending. The Bank of Canada has maintained a consistent interest charge of five% however leaves the door open for capacity tightening inside the destiny. The next fee statement is scheduled for October twenty fifth, with September inflation information due on Tuesday.
Global Context and Interconnectedness:
Canada's monetary system is intricately related to the worldwide marketplace. Events like change tensions, geopolitical conflicts, and forex fluctuations have a proper effect on the Canadian economic machine. Recognizing those connections is essential for understanding the entire scope of a recession in Canada. In 2023, the continuing worldwide pandemic and delivery chain disruptions may also significantly impact the Canadian economy.
Conclusion:
As we navigate the complexities of a recession in Canada, staying knowledgeable and proactive is critical. By understanding the reasons, influences, and functionality techniques, individuals and groups can better prepare for financially demanding situations. Remember, even as recessions may supply turbulence, they also present model, boom, and resilience possibilities. In 2023, it's critical to stay vigilant and take proactive steps to weather the economic crisis.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
5 benefits of hiring structure contractors
Professionals are an essential part of the construction market as well as the homes they develop compose a substantial portion of our economy. They specialize in what's referred to as basic contracting, that includes various construction, demolition, and also site work. Construction is a company that's constantly developing, with brand-new fads ahead of the competition. With that said being claimed, what are the advantages of employing building professionals?
1. They get on the front lines
When it concerns building, service providers are on the cutting edge. They supervise large jobs as well as generally function closely with the client in order to ensure that the procedure is reliable as well as organized. They know what's taking place at a task right with, which makes them an invaluable source.
2. They have actually specialized knowledge
Service providers, specifically general contractors, have actually had years of experience in numerous fields so they can much better recognize what your details requirements are when it comes to contracting a task, carpenter cambridge uk .
3. They're completely accredited
The process for getting a service provider certificate is fairly simple, and also the majority of states are now looking at methods to enhance the licensing process. When you hire a basic specialist, you can be sure that they're totally certified, at minimum by state licensing requirements.
4. They have a good reputation
One of the biggest advantages of working with service providers is their online reputation, which helps them obtain operate in their area of competence. This online reputation can assist get the sphere rolling on projects when other contractors may not want moving on with them. When you employ a general service provider, your building task has the chance to chase all every person reads about it!
5. They have modern tools.
Modern devices assist specialists when it pertains to building brand-new residence additions as well as improvement. Newer building can assist builders keep up to date with state-of-the-art modern technology as well as additionally make the procedure of construction easier than ever. This is something that new house builders will wish to keep in mind as they continue to build their residential properties.
6. They have the expertise to take care of tasks
One of the most outstanding advantage of hiring a general specialist is their capability to handle large-scale tasks, that includes handling individuals, managing financial resources, and also preparing in advance of what's coming. These sorts of service providers do not just delve into that project; they make the effort to research study and establish it in order to see exactly how it associates with their proficiency in the field.
7. They understand the ins and outs of growth
Since specialists have a lot experience in the field, they can clarify everything you need to understand about creating a project. They'll address any kind of concerns you may have as well as provide you a far better concept of just how to progress. Having this knowledge can assist your task run even more efficiently than it may if you were to take on the project yourself, cambridge carpenters .
8. They're leaders in the industry
Specialists are leaders in the industry as well as they strive to improve their business everyday. They deal with various other professionals as well as service providers in order to develop out tasks, which suggests that they're frequently learning from a few of the very best people in their field. This constant understanding helps obtain new understanding as well as see to it that they're on top of their video game at all times Thanks to professionals, building tasks are simpler than ever before. They steer the ship and make sure that it runs efficiently from starting to end. Their range of work can cover most if not every one of the work associated with a building project. By hiring general service providers for your task, you can be sure that it's mosting likely to run successfully and also go off without a hitch.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Clinical Trial Supplies Industry 2030 Driving Factors, Future Trends, Size & Key Vendors
The global clinical trial supplies market was valued at approximately USD 2.58 billion in 2023 and is forecasted to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.5% from 2024 to 2030. This growth is attributed to the increasing globalization of clinical trials and a rise in the number of biologics and biosimilar drugs being tested. The biopharmaceutical industry is also experiencing greater adoption of supply chain management systems aimed at improving operational efficiency and managing the pressures of high R&D costs. Supplies for clinical trials make up a substantial portion of total R&D spending, and these efficiencies are expected to propel market expansion in the coming years. In particular, the growing prevalence of biologics and temperature-sensitive drugs in clinical trials highlights the need for effective supply management.
Currently, the market is in a medium growth stage, and its expansion rate is accelerating. A defining feature of the clinical trial supplies market is its high level of innovation, as advancements in trial equipment, including cutting-edge imaging systems, monitoring tools, and diagnostic devices, are enhancing trial efficiency. This trend in innovation is driving greater demand for clinical trial supplies.
The market has also seen a moderate level of merger and acquisition (M&A) activity among leading companies. Many companies seek to provide comprehensive solutions for trial sponsors by acquiring specialized firms or expanding their service portfolios. With clinical trials taking place on a global scale, companies are extending their geographic reach to conduct trials across diverse regions, which enhances their market positioning.
The clinical trial supplies market operates under stringent regulations, enforced by agencies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA), to protect participant safety and rights. This regulatory environment encourages companies to establish a presence in multiple regions to meet the varying requirements. Expanding regionally also helps companies streamline operations and optimize resources to address regulatory compliance and logistical needs in different countries.
Gather more insights about the market drivers, restrains and growth of the Clinical Trial Supplies Market
Regional Insights:
North America Clinical Trial Supplies Market Trends
In 2023, North America held the largest market share, representing approximately 55.49% of the global clinical trial supplies market. This region conducts the highest volume of clinical trials worldwide, which significantly drives demand for trial supplies. Additionally, North America is home to many leading companies in this industry, along with high levels of technological penetration, which contribute to its market dominance.
United States
In the United States, the clinical trial supplies market is projected to grow at a substantial rate over the coming years. The presence of major contract research organizations (CROs), such as Quintiles, Covance, and PAREXEL International Corporation, further bolsters the market’s growth. However, there is a growing trend of shifting clinical trial sites outside the U.S. due to rising R&D costs and patient recruitment expenses. This shift is increasing the demand for cost-effective clinical supplies, thereby boosting market growth in emerging economies.
Asia Pacific Clinical Trial Supplies Market Trends
Asia Pacific is expected to be one of the fastest-growing regions in the clinical trial supplies market due to significant growth in clinical research. Key drivers for this regional expansion include lower per-patient costs and a diverse patient pool, which enhances recruitment efficiency. These factors make Asia Pacific an attractive region for clinical trials, contributing to the global market’s growth.
China
China, in particular, presents substantial growth opportunities for clinical trial supply companies due to its large, diverse patient population and expanding pharmaceutical sector. However, logistics and supply chain challenges in the country have deterred some biopharmaceutical companies from conducting trials there. China accounts for over 27% of global clinical trials as of 2023 and has shown strong growth over the past five years. To address these logistical challenges and capitalize on the market potential, companies like Catalent Pharma Solutions are entering the Chinese market, which is expected to further drive growth in the country’s clinical trial supplies sector.
Browse through Grand View Research's Category Medical Devices Industry Research Reports.
The global 3D ultrasound market size was estimated at USD 3.73 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.8% from 2025 to 2030.
The global lancets market size was valued at USD 5.90 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.7% from 2025 to 2030.
Key Companies & Market Share Insights
Leading companies in the clinical trial supplies market are adopting inorganic growth strategies, such as mergers, acquisitions, and partnerships, to strengthen their market positions. For example, in March 2023, Calyx, a provider of eClinical regulatory services, introduced Calyx Supply, a forecasting service designed to predict clinical trial supply needs through simulation and statistical design. Similarly, in April 2021, Catalent expanded its clinical supply services capabilities at its Philadelphia facility to support clients working on cell and gene therapies.
These strategic expansions and innovations underscore the competitive landscape of the clinical trial supplies market. By investing in enhanced capabilities and broadening their service offerings, key players are positioning themselves to meet the growing demands of a global clinical trial landscape characterized by a diverse range of drug types, regulatory requirements, and logistical challenges.
Key Clinical Trial Supplies Companies
Almac Group
Biocair
Catalent Inc.
KLIFO
Movianto
PCI Pharma Services
Sharp Services, LLC
Thermo Fischer Scientific Inc.
Marken
PAREXEL International Corporation
Order a free sample PDF of the Clinical Trial Supplies Market Intelligence Study, published by Grand View Research.
0 notes
Text
Investments in place matter. Public spaces such as parks and community centers as well as businesses such as restaurants and bars signal local prosperity, add a richness to the neighborhood, and enhance community wealth by attracting further investment.
Grocery stores are a crucial component of this ecosystem. And premium grocery chains focused on natural, organic, and specialty foods (commonly referred to as “fresh format” stores) such as Whole Foods and Trader Joe’s[1] not only provide healthy shopping options for residents, but also serve as markers of high-income, desirable areas, which contributes to increased property values and an image of security and stability. Conversely, the lack of these assets—or the proliferation of chains associated with poverty, such as dollar stores—can indicate to investors and developers that a community is struggling or lacks a clientele that would make investing profitable. These patterns can drive an upward or downward spiral of investment, concentrating wealth in already-wealthy areas while diverting it from struggling ones.
Community investment patterns are often influenced by race as well as wealth. Analyzing the distribution of grocery stores in several large U.S. cities, we find that premium grocery stores are less likely to be located in Black-majority neighborhoods, regardless of the average household income of those neighborhoods, and are substantially more likely to be located in neighborhoods where the Black population share is less than 10%.
In other words, businesses and the broader real estate and financing sectors are not investing even in prospering Black-majority neighborhoods, which devalues these communities and hinders opportunities for growth.
Devaluation of Black communities has led to disparities in food access
Uneven food systems across neighborhoods of varying racial compositions reveal ways that American society signals the value it places on the people in those communities.
The devaluation of Black neighborhoods is linked with redlining and mid-20th century “urban renewal” projects that labeled many Black neighborhoods as “slums” and demolished them. Meanwhile, federal, state, and local leaders invested in infrastructure that brought suburban white residents to and from urban cores, signaling the higher intrinsic value of white communities. These policies acted on the presumed lower value of people and assets in Black communities, which shows up in the kinds of amenities a community offers.
Federal Housing Finance Agency appraisal reports have allowed researchers to confirm that homes in Black neighborhoods are valued roughly 20% lower than equivalent homes in non-Black neighborhoods, and are nearly twice as likely to appraise below the contracted selling price. Similar devaluation patterns have been found in commercial real estate in Black-majority neighborhoods, which makes it difficult for Black entrepreneurs to get loans to start new businesses or invest in existing ones. Customer-facing businesses that do establish themselves in Black-majority neighborhoods face lower customer ratings and less revenue.
One part of the larger structure of business and commercial real estate devaluation in Black-majority communities is “food apartheid,” or disparities in access to food that have been produced by structural racism in residential and investment patterns, such as supermarket redlining. Though differences in food access are often blamed for elevated food insecurity and worse nutritional outcomes in Black communities, the relationship may not be as strong as is often believed, as our Brookings Metro colleagues pointed out in a 2021 report. They found that while there has been a tendency to frame the problem of food insecurity and poor nutrition in low-income neighborhoods as one of “food deserts” (areas with limited access to affordable and nutritious food), a number of recent studies have shown that greater access to food retailers does not correlate to reduced food insecurity, and that shoppers, even those without vehicles, do not necessarily choose to shop at the nearest supermarket.
Furthermore, the rise of food delivery services during the COVID-19 pandemic has resulted in greater access to grocery delivery services for most Americans living in traditionally defined “food deserts.” While financial insecurity and the higher cost of healthier food play a bigger role in food insecurity and nutritional deficits among low-income Americans, segregation and differing retail options in Black-majority neighborhoods still matter, because they are symptoms of a broader problem of devaluation and underinvestment in Black communities, which has real consequences for local wealth retention and development.
Beyond issues of access, this report presumes that store type is an economic statement of value that can spur or throttle investment in an area. The store types present in a community are a judgement of the level of investment a community is worthy of.
Premium grocery stores are absent from wealthy Black-majority communities
We analyzed the locations of premium grocery retailers in 10 U.S. metro areas with populations over 1 million and substantial numbers of high-income, non-rural census block groups with Black-majority populations.[2] We found strong evidence for underinvestment across all 10 metro areas.
As seen in Table 1, in seven of the 10 metro areas studied, none of the Black-majority, non-rural block groups in the top quartile for household income were located within 1 mile of a premium grocery store and only in one metro area—Washington, D.C.—was the percentage above 5%. For block groups in the same income brackets but with less than a 10% share of Black residents, the percentage that were located within 1 mile of a premium grocery store ranged from 10% in Atlanta to 34% in Los Angeles. Furthermore, Black-majority block groups in each income quartile of all the metro areas studied had a lower chance of being within 1 mile of a premium grocery store than block groups in that metro area overall.[3]

While we see the same pattern of underinvestment in wealthy Black communities across all 10 cities in our sample, there are significant differences between metro areas as well. Figure 1 highlights the difference in the shares of Black and non-Black neighborhoods near premium grocery stores. The differences in premium grocery store prevalence in wealthy neighborhoods are lowest in the low-income metro areas (New Orleans and Memphis, Tenn., which have median household incomes below $60,000), and largest in Washington, D.C., New York, and Los Angeles (which are among the wealthiest metro areas in our sample).
Another difference appears when we look at low-income block groups. In some metro areas (Atlanta and Baltimore in particular), the deficit of premium grocery stores is similar across low-income and high-income Black neighborhoods. However, in two metro areas (Houston and Chicago), Black-majority communities in the bottom income quartile were actually more likely to be located near a premium grocery store than low-income communities with few Black residents. In both cases, the differences are small, and the low-income Black neighborhoods in question are in relatively dense urban areas adjacent to higher-income neighborhoods.
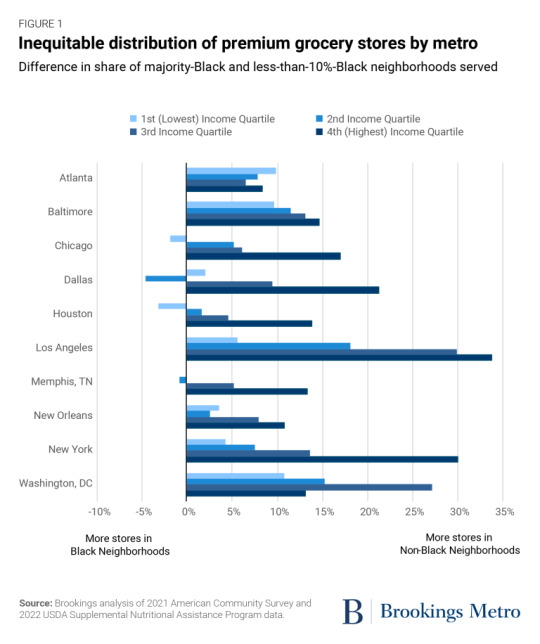
Comparing premium grocery store locations in the Washington, D.C. and Atlanta metro areas
The Washington, D.C. metro area is the highest-income metro area that we studied, with a median household income of $111,000 according to 2021 American Community Survey (ACS) 5-year estimates. It is also home to Prince George’s County and Charles County in Maryland, the second-highest and highest-income Black-majority counties in the country. Still, our analysis demonstrates the differences in investment distributions between Black-majority and predominantly white neighborhoods. For example, the absence of high-end retailers, including premium grocery outlets, in Prince George’s County has been a point of concern in those high-income Black communities for decades.
The Washington, D.C. area is home to roughly 20 Trader Joe’s and Whole Foods locations each, as well as two local organic chains: MOM’s Organic Market and Yes! Organic Market. The national chains are much more likely to be located in neighborhoods with few Black residents across the income spectrum, while the two local chains show a much smaller racial disparity. In the case of Yes! Organic Market, this is partly a consequence of the fact that all of their stores are located in the urban core—often in gentrifying areas—and thus close to historically Black communities. However, it may also be evidence that locally owned stores are less likely to undervalue Black neighborhoods than national chains with less familiarity with the areas where they operate.
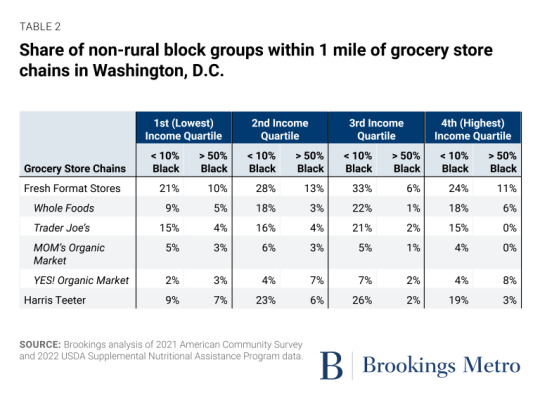
As seen in Figure 2, a belt of high-income block groups with Black-majority populations wraps roughly a third of the way around the Capital Beltway in the District’s eastern and southern suburbs. However, while high-income areas in other parts of the Washington, D.C. suburbs are scattered with Whole Foods, Trader Joe’s, and MOM’s Organic Market locations, the two MOM’s locations in the belt are near its ends, in areas with less predominately Black populations, and neither of the national chains has any locations in the belt. In fact, while each of the chains has a single location in Prince George’s County and none in Charles County, these stores are located within a mile of each other, and very near the University of Maryland’s flagship campus, in a part of the county that is not majority-Black.
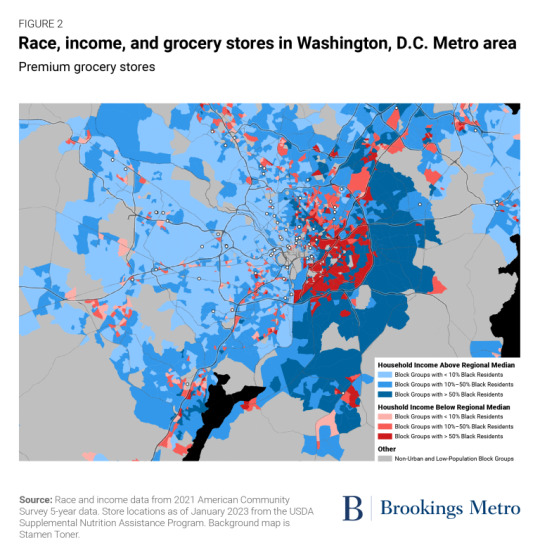
A similar pattern is seen in the locations chosen by the Kroger-owned conventional grocery retailer Harris Teeter (Figure 3), which began to move into the Washington, D.C. area in the early 2000s and has focused its expansion on upscale markets. Although Harris Teeter is now the third-largest grocery chain in the region with 44 stores, it has no stores in Charles County and only two in Prince George’s County—neither in a Black-majority neighborhood and both near the county’s border with majority-white Baltimore suburbs.
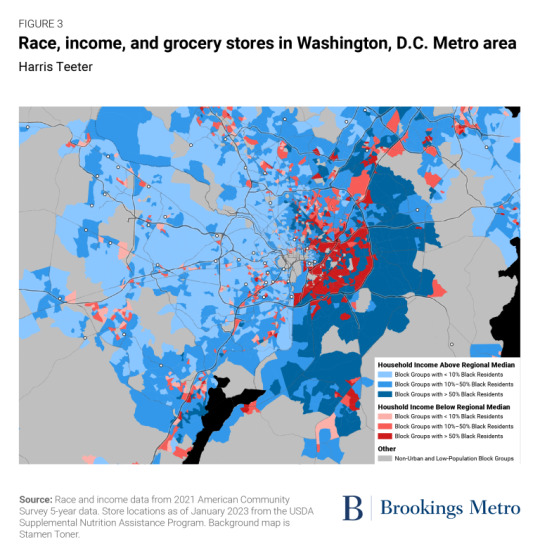
The distribution of premium grocery chains in Atlanta, shown in Table 3 and Figure 4, provides a good comparison to Washington, D.C., since Atlanta has the smallest percentage of top-quartile block groups within 1 mile of a premium grocery store among the metro areas we studied. While relatively few block groups in the Atlanta area are located near premium grocery stores, nearly all of those that are have few Black residents.
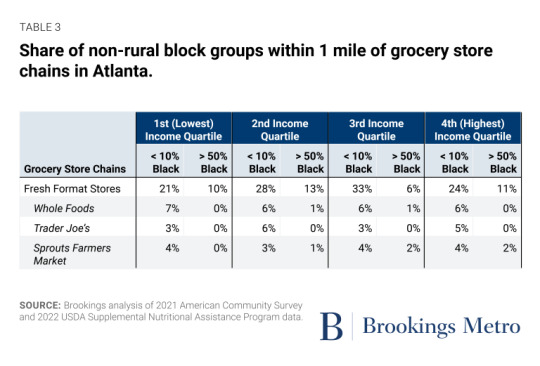
Premium grocery stores are rare overall in the Atlanta area, but the ones that are present are nearly all confined to a corridor running north of downtown that has some of the region’s smallest shares of Black residents. The major suburban “edge city” job clusters of Buckhead and Perimeter Center are also home to pairs of premium grocery stores.
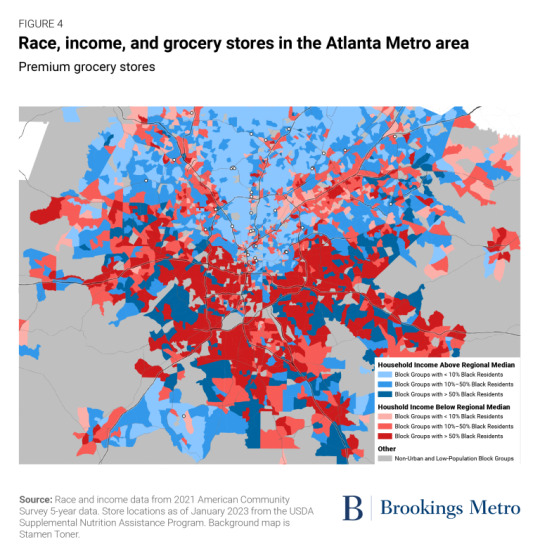
Dollar stores are more common in Black-majority communities at all income levels
The absence of premium grocers from even high-income Black-majority communities is an example of the disinvestment side of food apartheid. However, there is a second component to the different food retail ecosystems in Black and non-Black (especially white) neighborhoods: the prevalence of less-desirable food options. Studies have shown that the prevalence of fast-food restaurants is positively correlated with the percentage of Black residents in urban neighborhoods in the U.S. Similar trends have been found for liquor stores.
Chain dollar stores are one example of food retailers that have targeted Black-majority urban neighborhoods for store locations, often saturating these communities with outlets and making it more difficult for local businesses and other grocery chains to become established. While dollar stores can fill a need in low-income neighborhoods, they are often regarded as predatory businesses that harm communities more than they benefit them, due to very low wages, displacing other grocery options while failing to sell fresh food, store design that increases the rate of armed robberies, and OSHA and FDA violations that put customers and employees at risk.
As shown in Table 4, in every metro area in our cohort except Washington, D.C. (where dollar stores are less prevalent overall, likely due to the metro area’s substantially higher incomes), Black-majority neighborhoods in the top income quartile were more likely to have a dollar store within 1 mile than high-income neighborhoods with a share of Black residents lower than 10%. Furthermore, in six of the 10 metro areas (New York, Los Angeles, Chicago, Houston, New Orleans, and Memphis), most Black-majority neighborhoods in the top income quartile were within 1 mile of a dollar store. In fact, in New York and Chicago, Black-majority neighborhoods in the top income quartile were more likely to be near a dollar store than non-majority-Black neighborhoods in any income quartile.

Figure 5 shows the situation in Chicago, where dollar stores are concentrated in and near Black-majority areas, including the higher-income ones south of the city. Dollar stores are significantly less common in areas with few Black residents. While chain dollar stores are much more numerous than fresh-format grocery stores, they still concentrate in neighborhoods with lower incomes and higher shares of Black residents. Many of these neighborhoods have not just one, but a cluster of several dollar stores—making it especially hard for businesses that compete with them to become established.
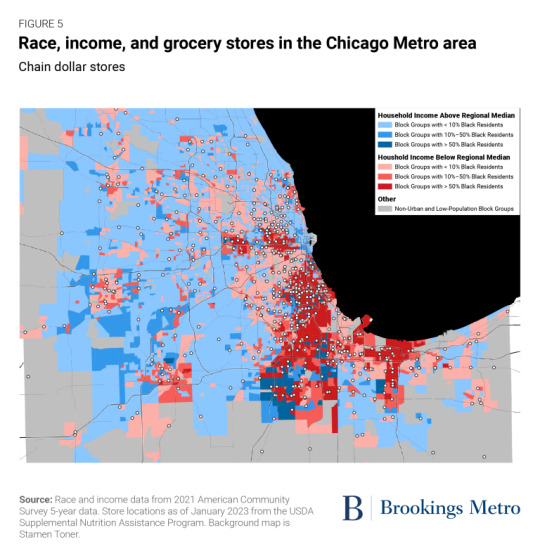
As shown in Figure 6, Black-majority block groups were more likely than block groups with a share of Black residents lower than 10% to be within 1 mile of a dollar store for each income quartile in each metro area, with two exceptions: the highest quartile in Washington, D.C. (where dollar stores are especially rare) and the lowest quartile in Dallas (where the racial differences in dollar store locations are smallest overall). And while there is an overall trend toward more dollar stores in Black-majority neighborhoods, the patterns in each metro area are very different.
Dallas has especially small differences—never more than 7 percentage points—in dollar store prevalence between Black-majority block groups and those with Black population shares lower than 10%, while there is a very large variation in dollar store prevalence by income, with roughly 85% of lowest-quartile and 30% of highest-quartile block groups within 1 mile of a dollar store. And among cities with substantial racial disparities, these disparities follow different patterns with income. In Washington, D.C., dollar stores are most over-represented in low-income Black neighborhoods, while the difference is smaller in third-quartile neighborhoods and negative in neighborhoods in the fourth income quartile. On the other hand, Atlanta, Baltimore, and New Orleans show similar disparities across income quartiles, while Houston, Los Angeles, Memphis, Chicago, and New York show the biggest disparities in high-income neighborhoods, which have few dollar stores when they have few Black residents but far more when they are majority-Black.
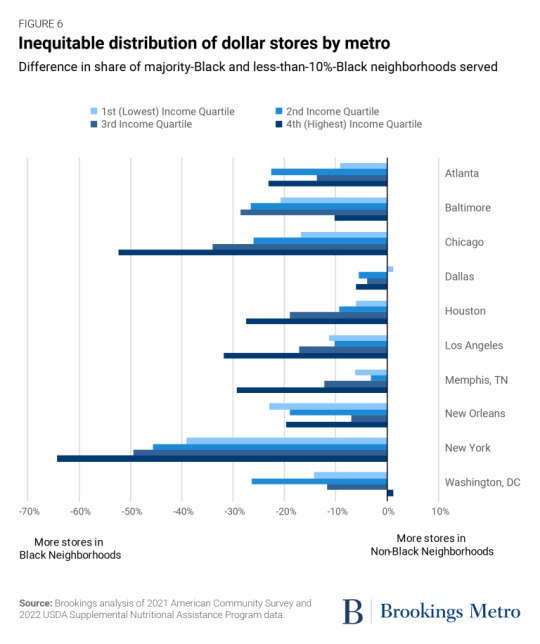
Like other local assets, grocery stores influence investment decisions
No single asset type alone determines the value of a place or the willingness of entrepreneurs, businesses, developers, and private individuals to invest in it. Rather, community, consumption, institutional, and other asset types are all part of a unified ecosystem that creates value and indicates potential investment opportunities.
The decisions food retailers make have obvious direct impacts on residents, such as the length of a trip to their preferred store. But their indirect impacts can be even more important. The presence of premium (or discount) retail in a community can drive the decisions of other retailers to locate in or avoid the community, thus strengthening or weakening the tax base. Furthermore, the presence of premium amenities in a community makes it more appealing to wealthier residents, which raises home values and potentially contributes to firms’ decisions on where to locate offices.
The less obvious outcomes of these choices—including their implications for place-based, racialized wealth divides—are no less important. Local assets and infrastructure matter to community well-being and development, and the differences in grocery store chains indicate a broader structural issue of financing practices and corporate underinvestment in Black communities. The tendency to frame this solely as a problem of access has led to suggestions that delivery services can bring about equality between communities. However, disparities in access were always just a symptom of a deeper and more fundamental problem of devaluation and divestment that need to be directly addressed.
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
Clinical Trial Supplies Market Segments by Application 2030
The global clinical trial supplies market was valued at approximately USD 2.58 billion in 2023 and is forecasted to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.5% from 2024 to 2030. This growth is attributed to the increasing globalization of clinical trials and a rise in the number of biologics and biosimilar drugs being tested. The biopharmaceutical industry is also experiencing greater adoption of supply chain management systems aimed at improving operational efficiency and managing the pressures of high R&D costs. Supplies for clinical trials make up a substantial portion of total R&D spending, and these efficiencies are expected to propel market expansion in the coming years. In particular, the growing prevalence of biologics and temperature-sensitive drugs in clinical trials highlights the need for effective supply management.
Currently, the market is in a medium growth stage, and its expansion rate is accelerating. A defining feature of the clinical trial supplies market is its high level of innovation, as advancements in trial equipment, including cutting-edge imaging systems, monitoring tools, and diagnostic devices, are enhancing trial efficiency. This trend in innovation is driving greater demand for clinical trial supplies.
The market has also seen a moderate level of merger and acquisition (M&A) activity among leading companies. Many companies seek to provide comprehensive solutions for trial sponsors by acquiring specialized firms or expanding their service portfolios. With clinical trials taking place on a global scale, companies are extending their geographic reach to conduct trials across diverse regions, which enhances their market positioning.
The clinical trial supplies market operates under stringent regulations, enforced by agencies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA), to protect participant safety and rights. This regulatory environment encourages companies to establish a presence in multiple regions to meet the varying requirements. Expanding regionally also helps companies streamline operations and optimize resources to address regulatory compliance and logistical needs in different countries.
Gather more insights about the market drivers, restrains and growth of the Clinical Trial Supplies Market
Regional Insights:
North America Clinical Trial Supplies Market Trends
In 2023, North America held the largest market share, representing approximately 55.49% of the global clinical trial supplies market. This region conducts the highest volume of clinical trials worldwide, which significantly drives demand for trial supplies. Additionally, North America is home to many leading companies in this industry, along with high levels of technological penetration, which contribute to its market dominance.
United States
In the United States, the clinical trial supplies market is projected to grow at a substantial rate over the coming years. The presence of major contract research organizations (CROs), such as Quintiles, Covance, and PAREXEL International Corporation, further bolsters the market’s growth. However, there is a growing trend of shifting clinical trial sites outside the U.S. due to rising R&D costs and patient recruitment expenses. This shift is increasing the demand for cost-effective clinical supplies, thereby boosting market growth in emerging economies.
Asia Pacific Clinical Trial Supplies Market Trends
Asia Pacific is expected to be one of the fastest-growing regions in the clinical trial supplies market due to significant growth in clinical research. Key drivers for this regional expansion include lower per-patient costs and a diverse patient pool, which enhances recruitment efficiency. These factors make Asia Pacific an attractive region for clinical trials, contributing to the global market’s growth.
China
China, in particular, presents substantial growth opportunities for clinical trial supply companies due to its large, diverse patient population and expanding pharmaceutical sector. However, logistics and supply chain challenges in the country have deterred some biopharmaceutical companies from conducting trials there. China accounts for over 27% of global clinical trials as of 2023 and has shown strong growth over the past five years. To address these logistical challenges and capitalize on the market potential, companies like Catalent Pharma Solutions are entering the Chinese market, which is expected to further drive growth in the country’s clinical trial supplies sector.
Browse through Grand View Research's Category Medical Devices Industry Research Reports.
The global 3D ultrasound market size was estimated at USD 3.73 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.8% from 2025 to 2030.
The global lancets market size was valued at USD 5.90 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.7% from 2025 to 2030.
Key Companies & Market Share Insights
Leading companies in the clinical trial supplies market are adopting inorganic growth strategies, such as mergers, acquisitions, and partnerships, to strengthen their market positions. For example, in March 2023, Calyx, a provider of eClinical regulatory services, introduced Calyx Supply, a forecasting service designed to predict clinical trial supply needs through simulation and statistical design. Similarly, in April 2021, Catalent expanded its clinical supply services capabilities at its Philadelphia facility to support clients working on cell and gene therapies.
These strategic expansions and innovations underscore the competitive landscape of the clinical trial supplies market. By investing in enhanced capabilities and broadening their service offerings, key players are positioning themselves to meet the growing demands of a global clinical trial landscape characterized by a diverse range of drug types, regulatory requirements, and logistical challenges.
Key Clinical Trial Supplies Companies
Almac Group
Biocair
Catalent Inc.
KLIFO
Movianto
PCI Pharma Services
Sharp Services, LLC
Thermo Fischer Scientific Inc.
Marken
PAREXEL International Corporation
Order a free sample PDF of the Clinical Trial Supplies Market Intelligence Study, published by Grand View Research.
0 notes