#Common Diseases For Kidney Transplantation
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Kidney Transplation Hospital In Ahmedabad - Common Diseases For Kidney Transplantation
Kidney Transplation Hospital In Ahmedabad

Kidney Transplation Hospital In Ahmedabad
Common Diseases For Kidney Transplantation
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Diabetes High Blood Pressure
Contact us for kidney transplation or visit website www.avionkidneyhospital.com/kidney-transplation-hospital-in-ahmedabad.php
Kidney Transplation Hospital In Ahmedabad, Kidney Transplation Hospital In Ahmedabad, Common Diseases For Kidney Transplantation, www.avionkidneyhospital.com/kidney-transplation-hospital-in-ahmedabad.php, Avion Kidney Hospital
#Kidney Transplation Hospital In Ahmedabad#Common Diseases For Kidney Transplantation#www.avionkidneyhospital.com/kidney-transplation-hospital-in-ahmedabad.php#Avion Kidney Hospital
0 notes
Text

Stopping Cystic Cells
More than half the patients with the inherited kidney disease ADPKD will need a kidney transplant. This study shows that the abnormal, cystic cells can be prevented from accumulating by inhibiting clustering of their centrosomes, cell machinery required for division – a potential novel treatment target
Read the published research article here
Image adapted from work by Tao Cheng and colleagues
Department of Medicine, Nephrology Division, Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, MO, USA
Image originally published with a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0)
Published in Journal of Clinical Investigation insight, May 2024
You can also follow BPoD on Instagram, Twitter and Facebook
#science#biomedicine#immunofluorescence#biology#centrosomes#cell division#kidney disease#kidney transplant#chromosomes
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
Sickle cell nephropathy, a complication not to be ignored, through a Moroccan case by Asmaa Biaz in Journal of Clinical Case Reports Medical Images and Health Sciences
Summary
Nephropathy is a major complication of sickle cell disease. Indeed, the kidneys are particularly sensitive organs to this disease.
We report a case of a patient with a major sickle cell syndrome; she was hospitalized in the nephrology department of Mohammed V Military Training Hospital, forend-stage renal failure. The family investigation revealed a composite S/O-Arab heterozygosity responsible for the severity of the clinical disorder.
Key words: Sickle cell nephropathy - End stage renal failure - Sickle cell major syndrome S/O-Arab.
Introduction
Sickle cell nephropathy (SCN) is a major complication of sickle cell disease. It manifest’s in various forms, including glomerulopathy, proteinuria, hematuria, and Renal tubular disorders, and frequently results in end-stage renal disease(ESRD). Hemolysis and vascular occlusion are the main factors promoting the manifestations of this disease. Dialysis and renal transplantation are the last resort for patient with SCN [1].
Through the case of a patient with a major sickle cell syndrome S/O-Arab complicated by end-stage renal failure, we will explain the pathophysiological mechanisms of this complication and emphasize the importance of biological monitoring.
Case report
The patient was 24 years old and was admitted to the nephrology department of the Mohammed V Military Training Hospital for incidental renal failure in the context of an impure nephrotic syndrome revealing sickle cell nephropathy. In his history, we retained a
follow-up since the age of 5 years in another hospital structure for a hemoglobinosis S treated by iterative transfusions with notion of acute renal failure during sickle cell crises.
The biological result showed an anemia at 7.7 g/dL, corrected serum calcium at 82 mg/L, serum phosphorus at 64 mg/L, intact parathyroid hormone 1-84 at 543 pg/L, Alkaline Phosphatase at 201 U/L.
Hemoglobin electrophoresis was ordered to this patient, but due to repeated transfusions, her electrophoretic profile remains uninterpretable. Therefore, hemoglobin electrophoresis (HBE) was performed in the parents as part of the hemoglobin phenotypic study. The HBE of both parents is performed on Capillarys (Sebia®) at alkaline pH followed by electrophoresis at acidic pH on Hydrasys (Sebia®) which showed a heterozygous Hb O-Arab variant in the mother and a heterozygous hemoglobinosis S (A/S) in the father.
Referring to the phenotypic study of Hb performed in the parents, it is concluded that the patient has a composite heterozygosity S/O-Arab explaining the severity of the renal manifestations.
The evolution was marked by the absence of improvement of her renal function and the aggravation of the uremic syndrome motivating her setting in peritoneal dialysis. The patient was treated with erythropoietin ARANESP 30µg/ per 2 weeks with a blood transfusion of 2 packed red blood cells on average every two months.
The patient died at the age of 26 years before benefiting from either a hemoglobin genotyping study or a renal transplant.
Discussion
Sickle cell disease is the most common hereditary hemoglobinopathy in the world. An estimated 300,000 children are born with this disease each year, three quarters of whom are born in sub-Saharan Africa [2]. It is characterized by extreme variability in terms of clinical manifestations, the most serious of which are renal manifestations.
The association S/O Arab is responsible for a major sickle cell syndrome, as in the case of our patient. Indeed, Hb O Arab stabilizes the intracellular polymerization of Hb S and leads to an irreversible sickle cell disease of red blood cells, thus expressing by a more severe clinical disorder. The clinical and biological manifestation of this association is similar to homozygous sickle cell disease and the association Hb S / Hb D Punjab. The onset is usually early, in infancy, and is marked by the classic triad of chronic hemolysis: anemia, jaundice and splenomegaly. Anemia is usually moderate outside of hemolytic attacks (Hb = 7 - 10 g/dL). The evolution is often marked by sickle cell complications. Osteoarticular complications are the most frequent, such as vaso-occlusive crises, septic arthritis and osteoporosis. Pneumonia, leg ulcers and vesicular lithiasis are also reported [3].
Sickle cell nephropathy is a major complication of sickle cell disease. The kidneys are particularly sensitive organs to the disease. Sickle cell disease substantially alters the structure and function of the kidneys and is the cause of several renal diseases and syndromes. Renal damage is more severe in SS homozygous patients than in other major sickle cell syndromes [4]. Approximately 5-18% of patients have SCN, thus increasing the risk of morbidity and mortality of the disease [5].
A number of studies have focused on this pathology, its evolution includes several stages; it starts with hyperfiltration, then the occurrence of microalbuminuria, then macroalbuminuria and finally the progression to renal failure. The prevalence of these complications increases with the age of the patients but can also be seen from a young age.
Two models have been proposed to explain the pathophysiology of SCN. Becker et al. showed that prostaglandin release following ischemic injury causes an increase in glomerular filtration rate (GFR). This increase leads to glomerular injury and eventually manifests as proteinuria and glomerulosclerosis [6]. Alternatively, Nath and Katusic [7] classified the manifestations of SCN into two different phenotypes: the hemolysis-endothelial dysfunction phenotype and the viscosity-vaso-occlusive phenotype. The hemolysis-endothelial dysfunction phenotype affects the renal cortex and leads to hyperfiltration and glomerulopathy; heme released due to intravascular hemolysis predisposes to proteinuria through its accumulation on the glomerular filtration barrier, which disrupts membrane selectivity by exerting cytotoxic effects on podocytes and endothelial cells [8]. On the other hand, the viscosity-vaso-occlusive phenotype is responsible for hematuria, papillary necrosis, and tubular acidosis [9].
Microalbuminuria, reflecting the early stages of renal damage, should be routinely sought in the follow-up assessment in this category of patients.
Decreased GFR, which suggests loss of kidney function, occurs with the progression of sickle cell disease and may be a sign of uncontrolled disease. Sickle cell patients have a higher risk of developing chronic kidney disease compared to the general population.
Specific treatment with an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or an angiotensin II
receptor antagonist should be considered in these patients in order to slow the progression of the renal disease. The prevention of microthrombosis and thus of renal damage requires the maintenance of a hemoglobin A level of more than 50% by regular blood transfusion as soon as sickle cell disease is diagnosed. The role of hydroxyurea in the prevention and/or treatment of renal function abnormalities in sickle cell disease remains to be studied [10].
Conclusion
Sickle cell nephropathy is a major complication of sickle cell disease. It must be systematically and early sought in all sickle cell patients to reduce the risk of morbidity and mortality of this disease.
The development of new biomarkers has become increasingly essential for the early detection of sickle cell disease in order to improve the survival of patients with sickle cell disease.
Declaration of interest:
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
#Sickle cell nephropathy - End stage renal failure - Sickle cell major syndrome S/O-Arab#JCRMHS#Is Journal of Clinical Case Reports Medical Images and Health Sciences PubMed indexed.#clinical decision making#clinical images submissions
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Dr. Sidharth Kumar Sethi: India’s Leading Pediatric Nephrologist

Dr. Sidharth Kumar Sethi: India’s Leading Pediatric Nephrologist
Protecting the Tiny Kidneys: The Expertise of Dr. Sidharth Kumar Sethi
When it comes to the delicate health of children, finding the right specialist is paramount. For parents seeking exceptional pediatric nephrological care in India, Dr. Sidharth Kumar Sethi stands out as a beacon of hope. With his extensive expertise and compassionate approach, he has earned a stellar reputation as one of the best pediatric nephrologists in the country.
A Profile of Excellence
Dr. Sidharth Kumar Sethi is a highly qualified pediatrician with a specialized focus on kidney diseases affecting children. His impressive academic credentials, coupled with years of hands-on experience, have positioned him as a leading authority in the field. He has received rigorous training at renowned institutions, both in India and abroad, enabling him to stay at the forefront of advancements in pediatric nephrology.
Comprehensive Care for Young Patients
Dr. Sethi’s commitment to his young patients is evident in his comprehensive approach to care. He offers a wide range of services, including:
Diagnosis and management of kidney diseases: From common conditions to complex disorders, Dr. Sethi provides accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plans.
Renal transplantation: Offering hope and a new lease on life for children with end-stage kidney disease.
Dialysis care: Providing specialized care for children requiring dialysis to support kidney function.
Preventive care: Educating parents and caregivers about kidney health and promoting early detection of potential issues.
A Compassionate and Patient-Centric Approach
Beyond his medical expertise, Dr. Sethi is known for his compassionate and patient-centric approach. He takes the time to listen to parents’ concerns, explain complex medical information in understandable terms, and build strong relationships with his young patients. This empathetic demeanor creates a supportive environment where children and their families feel comfortable and confident in their care.
Why Choose Dr. Sidharth Kumar Sethi?
Extensive expertise: Dr. Sethi’s deep knowledge and experience in pediatric nephrology ensure the best possible care for your child.
Compassionate care: He treats each child with empathy and understanding, creating a supportive environment.
State-of-the-art treatment: Dr. Sethi stays updated with the latest advancements in the field to offer cutting-edge treatments.
Patient-focused approach: He involves parents in the decision-making process and provides clear communication.
If you are seeking the best possible care for your child’s kidney health, Dr. Sidharth Kumar Sethi is an excellent choice. His dedication to his patients, combined with his exceptional medical skills, make him a trusted name in pediatric nephrology in India.
To schedule an appointment With the Best Child Kidney Doctor in India, please contact: Name: Dr. Sidharth Sethi (Best Child Kidney Doctor in India) Address: Division of Pediatric Nephrology, Kidney Institute, Medanta, The Medicity, Gurgaon, Haryana, India, 122001 Phone: 0124–4141414 Website: www.pediatricnephrologyindia.com
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
For patients battling diabetes, a group of Chinese scientists and clinicians may offer a glimmer of hope. For the first time in the world, a patient’s diabetes has reportedly been cured using cell therapy.
The patient, a 59-year-old man who had been living with type 2 diabetes for 25 years, was at serious risk of complications from the disease. He had a kidney transplant in 2017, but had lost most of his pancreatic islet function which controls blood glucose levels, and relied on multiple insulin injections every day.
“He was at great risk of serious diabetes complications,” Yin Hao, a leading researcher at Shanghai Changzheng Hospital, told Shanghai-based news outlet The Paper earlier this month.
The patient received the innovative cell transplant in July 2021. Eleven weeks after the transplant, he was free of the need for external insulin, and the dose of oral medication to control blood sugar levels was gradually reduced and completely stopped one year later.
“Follow-up examinations showed that the patient’s pancreatic islet function was effectively restored,” Yin said. The patient has now been completely weaned off insulin for 33 months.
The medical breakthrough, achieved by a team of doctors and researchers from institutions including Shanghai Changzheng Hospital, the Centre for Excellence in Molecular Cell Science under the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Renji Hospital, all based in Shanghai, was published in the journal Cell Discovery on April 30.
“I think this study represents an important advance in the field of cell therapy for diabetes,” said Timothy Kieffer, a professor in the department of cellular and physiological sciences at the University of British Columbia in Canada.

Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the way our bodies convert food into energy.
What we consume is broken down into glucose – a simple sugar – and released into the bloodstream. Insulin, produced by the islets of the pancreas, is essential for regulating blood sugar levels.
In diabetes, this system is hijacked: either the body does not produce enough insulin, or it cannot use the insulin it produces effectively.
There are several types of diabetes, of which type 2 is the most common, affecting almost 90 per cent of sufferers. It is largely diet-related and develops over time.
Regardless of the type of diabetes, failure to maintain normal blood glucose levels over time can lead to serious side effects, including heart disease, vision loss and kidney disease.
According to the US Centres for Disease Control and Prevention, “there isn’t a cure yet for diabetes”.
Along with losing weight, eating well and taking medication, insulin is the mainstay of treatment for some, but this requires frequent injections and monitoring.
Scientists around the world are researching islet transplant as a promising alternative, mainly by creating islet-like cells from human stem cell cultures. Now, after more than a decade of work, the group of Chinese scientists has come a step closer.
The team used and programmed the patient’s own peripheral blood mononuclear cells, Yin said, which were then transformed into “seed cells” and reconstituted pancreatic islet tissue in an artificial environment.
While preclinical data from Kieffer’s team supports the use of stem cell-derived islets for the treatment of type 2 diabetes, the report by Yin and colleagues is, to Kieffer’s knowledge, “the first evidence in humans”.
Yin said the breakthrough was another step forward in the relatively new field of regenerative medicine – where the body’s own regenerative capabilities are harnessed to treat illness.
“Our technology has matured and it has pushed boundaries in the field of regenerative medicine for the treatment of diabetes.”
Globally, China has the highest number of people with diabetes. According to the International Diabetes Federation, there are 140 million people with diabetes in the country. Of those, about 40 million depend on lifelong insulin injections.
China’s diabetic population is disproportionately high, according to Huang Yanzhong, a senior fellow for global health at the Council on Foreign Relations.
In an article last year, he pointed out that while China accounted for 17.7 per cent of the world’s population, the country’s diabetic population made up a staggering quarter of the global total, placing a huge health burden on the government.
If this approach for cell therapy ultimately works, Kieffer said, “it can free patients from the burden of chronic medications, improve health and quality of life, and reduce healthcare expenditures”.
But to get there, he added, studies in more patients based on the findings of this Chinese study were needed.
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Kidney Diseases in Children - What Parents Need to Know

Kidney diseases are not just limited to adults; children can also be affected. As a parent or caregiver, it's essential to understand these conditions, recognize potential signs, and be prepared to navigate the challenges that come with pediatric kidney issues. In this article, we will shed light on kidney diseases in children, common pediatric kidney problems, early warning signs, and the necessary steps for parents and caregivers.
Understanding Pediatric Kidney Diseases
1. The Scope: Kidney diseases in children can encompass a wide range of conditions, from congenital anomalies to acquired diseases. These conditions may affect the structure or function of the kidneys, impacting their ability to filter waste and regulate fluids.
2. Congenital Kidney Conditions: Understanding congenital kidney issues in children is crucial for early detection and intervention. Some children are born with kidney issues, such as congenital anomalies like hydronephrosis, polycystic kidney disease, or renal agenesis. Hiranandani Hospital Kidney plays a significant role in providing specialized care and treatment for these conditions, ensuring that affected children receive the necessary medical attention and support for improved health outcomes.
3. Acquired Kidney Diseases: Children can also develop kidney diseases later in life due to infections, autoimmune disorders, or other underlying medical conditions. Early diagnosis and treatment are vital for managing these acquired conditions.
Early Warning Signs
1. Urinary Changes: Keep an eye out for changes in your child's urinary habits. Frequent urination, painful urination, or bedwetting beyond a certain age can be indicators of kidney issues.
2. Swelling: Noticeable swelling in the face, limbs, or abdomen may be a sign of kidney problems, as impaired kidney function can lead to fluid retention.
3. High Blood Pressure: Hypertension is not exclusive to adults. Elevated blood pressure in children can sometimes point to underlying kidney issues.
4. Growth and Development: Poor growth or delayed development could be attributed to chronic kidney disease, affecting the body's ability to absorb essential nutrients.
5. Fatigue and Anemia: Kidney problems may cause anemia and fatigue, as the kidneys play a role in producing erythropoietin, a hormone that stimulates red blood cell production.
.
Read For More Blog: Causes and Treatments for Acne and Prevention Tips
Navigating Pediatric Kidney Care
1. Timely Consultation: If you notice any warning signs, consult a pediatric nephrologist promptly. Early diagnosis and intervention can significantly improve outcomes.
2. Diagnostic Tests: Your child may undergo various tests, including blood work, urinalysis, imaging studies, and kidney biopsies, to determine the nature and extent of kidney disease.
3. Treatment Approaches: Treatment will depend on the specific kidney condition. It might involve medications, dietary changes, or even dialysis in severe cases. Some children may require a kidney transplant.
4. Emotional Support: Pediatric kidney diseases can be emotionally challenging for children and their families. Seek emotional support through counseling or support groups to help your child cope.
5. Monitoring and Follow-up: Regular follow-up appointments and ongoing monitoring are crucial to ensure the effectiveness of treatment and the overall well-being of the child.
Conclusion
Kidney diseases in children may present unique challenges, but with awareness, early detection, and timely intervention, the prognosis can be positive. As a parent or caregiver, your vigilance is key to safeguarding your child's kidney health. At Hiranandani Hospital Powai we are here to support you through this journey, providing expert care and guidance for pediatric kidney issues. Your child's health is our priority, and we are dedicated to helping them lead a healthy, kidney-empowered life.
#hiranandani hospital reviews#hiranandani hospital powai covid#hiranandani powai hospital#hiranandani hospital powai
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Diabetes and Kidney Disease: The Connection and How to Protect Your Kidneys

Looking for a doctor near you in Brooklyn 11213 to help you manage your diabetes and kidney disease?
Visit Prasad Medical Center, where our team of experts will work with you to develop a personalized treatment plan to help you control your blood sugar levels, protect your kidneys, and improve your overall health.
Introduction:
Diabetes is a chronic health condition that affects how your body turns food into energy.
When you have diabetes, your body either resists the effects of insulin—a hormone that regulates the movement of sugar into your cells—or doesn’t produce enough insulin to maintain normal glucose levels.
Over time, high blood sugar can damage many parts of your body, including your kidneys.
Diabetic kidney disease, also known as diabetic nephropathy, is a common complication of diabetes.
It occurs when high blood sugar damages the tiny blood vessels in your kidneys, making it difficult for them to filter waste products from your blood.
If diabetic kidney disease is not treated, it can lead to kidney failure, a serious condition that requires dialysis or a kidney transplant.
You can reach our dialysis centers in Brooklyn in these places
What happens to your kidneys when you have diabetes?
When you have diabetes, high blood sugar can damage the tiny blood vessels in your kidneys.
This damage can make it difficult for your kidneys to filter waste products from your blood.
Over time, as the blood vessels in your kidneys become more damaged, your kidneys may not be able to function as well as they should.
This can lead to a buildup of waste products in your blood, which can cause a variety of health problems, including:
High blood pressure
Fluid retention
Anemia
Weakness and fatigue
Bone disease
Heart disease
Stroke
Kidney failure

How to protect your kidneys if you have diabetes:
The best way to protect your kidneys if you have diabetes is to control your blood sugar levels. You can do this by following your treatment plan, which may include taking medication, eating a healthy diet, and exercising regularly.
Know more about: OUR SPECIALIZED TREATMENTS - NEPHROLOGY
Here are some other tips for protecting your kidneys:
Monitor your blood pressure regularly: High blood pressure can damage your kidneys even further, so it’s important to monitor your blood pressure regularly and work with your doctor to keep it under control.
Maintain a healthy weight: Obesity is a risk factor for both diabetes and kidney disease. If you are overweight or obese, losing weight can help improve your blood sugar levels and reduce your risk of kidney disease.
Eat a healthy diet: A healthy diet for people with diabetes and kidney disease is low in saturated and trans fats, sodium, and sugar. It is also high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
Exercise regularly: Exercise can help improve your blood sugar levels, blood pressure, and overall health. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
Don’t smoke: Smoking damages your blood vessels and can make kidney disease worse. If you smoke, talk to your doctor about quitting.
When to see a doctor:
If you have diabetes, it is important to see your doctor regularly for checkups and kidney function tests. This is especially important if you have any of the following symptoms:
Swelling in your feet, ankles, or hands
Fatigue
High blood pressure
Blood or protein in your urine
Changes in urination
If you have any of these symptoms, your doctor may refer you to a nephrologist, a specialist in kidney diseases in Brooklyn.
Finding the best doctor near you in Brooklyn:
If you are looking for a doctor in Brooklyn to help you manage your diabetes and kidney disease, there are a few things you can do to find the best doctor near you:
Ask your primary care physician for a referral
Search for doctors in your area who specialize in diabetes and/or kidney disease
Read online reviews of doctors in your area.
Talk to your friends and family members who have diabetes and/or kidney disease to see who they recommend.
Once you have found a few doctors that you are interested in, you can schedule a consultation to learn more about their approach to treating diabetes and kidney disease.
Conclusion:
Diabetes and kidney disease are serious conditions, but they can be managed with proper care. By following your treatment plan, eating a healthy diet, and exercising regularly, you can help protect your kidneys and live a long and healthy life.
If you are looking for a doctor to help you manage your diabetes and kidney disease, there are a few things you can do to find the best doctor near you in Brooklyn.
#best doctor in brooklyn#doctors near brooklyn#best neurologist doctor in new york#clinic near me brooklyn#doctors near new york ny#the best neurologist in brooklyn#the best doctors in new york#medical doctor in brooklyn#best doctors in brooklyn#doctor in brooklyn ny#brooklyn clinic near me
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Best Hospital in Lucknow for Urology & Kidney Transplant- Wellsun Super specialty Hospital
Urology is a medical specialty that focuses on the diagnosis and treatment of conditions related to the urinary tract system in both males and females. This includes the kidneys, bladder, ureters, and urethra. Urologists are trained to manage various urological conditions such as urinary tract infections, kidney stones, prostate problems, and urinary incontinence.
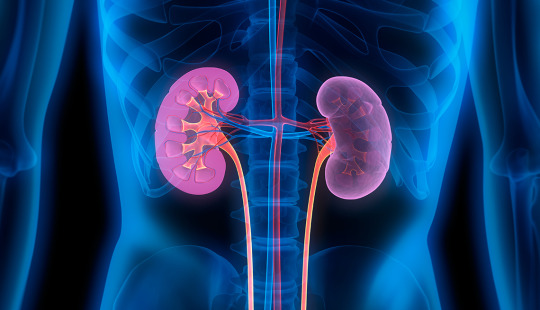
Kidney transplant, on the other hand, is a surgical procedure in which a healthy kidney from a donor is transplanted into a person with end-stage kidney disease. This procedure is typically performed when other treatments, such as dialysis, are no longer effective in managing kidney failure. Kidney transplant offers the potential for improved quality of life and long-term survival for individuals with kidney failure.
It's important to consult with a qualified urologist or transplant surgeon for personalized advice and treatment options related to urology and kidney transplant.
What our expert say’s
Urology is a medical specialty that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of conditions related to the urinary tract system in both males and females. This includes the kidneys, bladder, urethras, and urethra. Urologists are trained to manage various urological conditions, including but not limited to:
1. Urinary tract infections (UTIs): Symptoms may include frequent urination, pain or burning during urination, cloudy or bloody urine, and a strong urge to urinate.
2. Kidney stones: Symptoms can include severe pain in the back or side, blood in the urine, frequent urination, and pain during urination.
3. Prostate problems: Common conditions include benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and prostate cancer. Symptoms may include difficulty urinating, weak urine flow, frequent urination (especially at night), and blood in the urine.
4. Urinary incontinence: This refers to the involuntary loss of urine. Symptoms can vary depending on the type of incontinence but may include leakage during physical activity, coughing, or sneezing, frequent urination, and a sudden strong urge to urinate.
5. Erectile dysfunction: This is the inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for sexual intercourse. It can be a symptom of various underlying conditions, including vascular disease, diabetes, or psychological factors.
It's important to note that these are just a few examples, and there are many other urological conditions with their own specific symptoms. If you are experiencing any urological symptoms or concerns, it is recommended to consult with a urologist for proper evaluation and diagnosis.
Feel Free to Call Our 24*7 Consultant ,
email id- [email protected]
Mobile no : 18008991200,+91-6389010203
#hospital#medicine#multispecialityclinic#wellsun#healthcare#health tips#medical care#health and wellness#doctors#city
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
What Is A Dual Organ Transplant? When Do You Need A Dual Organ Transplant?

A combined or dual organ transplant is a viable option for those who have suffered multiple organ failures wherein the patient will receive two organs simultaneously during one surgical procedure. A dual organ transplant may usually include a combined liver and kidney transplant or a pancreas and kidney transplant. Whether a liver and kidney transplant or a pancreas and kidney transplant, both organs must be replaced when they fail to function properly. The most common type of dual organ transplant is a kidney-pancreas transplant, which is performed on patients with type 1 diabetes who also have end-stage renal/kidney failure.
When Do You Need Dual Organ Transplant?
When you suffer from end-stage diseases like kidney failure and liver failure associated with comorbidities such as diabetes, congenital defects, autoimmune disorders, chronic infections, or long-term damage from substance abuse, you may have to undergo dual organ transplantation. Some patients may have a genetic predisposition to develop multiple organ failure, while others may experience organ damage as a result of an accident or injury. Patients undergo liver and kidney transplants because their liver and kidney fail to function. Those who have to undergo pancreas and kidney transplantation have kidney failure and suffer from insulin resistance (diabetes) simultaneously. Liver and kidney transplantation is recommended in case of Chronic Kidney Disease and defects in the liver at the same time.
Visit a top multispecialty hospital if you or your loved one needs a dual organ transplant in Old Airport Road.
What to Expect from Dual Organ Transplant?
There are many advantages of dual organ transplants. Some of these are:
Two Organ Transplants Simultaneously
One of the significant benefits of a dual organ transplant is that you receive two organs simultaneously and do not need to undergo two surgeries separately.
Less Suffering
Undergoing surgery may drain a patient. When two organs are transplanted in one surgery, the patient is relieved from undergoing two surgeries. Thus, a dual organ transplant helps the patient avoid additional surgeries and recover faster.
Long-Term Outcomes
For patients with end-stage organ diseases, a dual organ transplant can greatly improve their quality of life and increase their life expectancy.
Steps Involved in Dual Organ Transplant
There are different steps involved in the transplantation of various organs.
Kidney and Liver Transplant
To perform kidney and liver transplants together, the patient has to undergo a series of tests and evaluations such as a comprehensive medical evaluation, blood tests, and imaging studies, to determine if they are healthy enough to undergo the transplantation surgery. The liver and kidneys are often received from a deceased donor. The size of the liver must exceed 2% of the recipient's body weight. After the liver implantation, the single kidney is implanted into the right or left of the liver transplantation.
The liver will be transplanted in the following procedure:
The doctor will make an incision in your abdomen.
Blood vessels will be separated from your diseased liver.
The diseased liver will be replaced with a healthy liver.
The blood vessels will be reconnected.
The incision will be closed and the patient will be moved to the recovery room.
To transplant a kidney, the doctor will follow the procedure mentioned below:
The surgeon will place your kidney in the area of the lower abdomen. The new kidney is placed under the existing kidney. The existing kidney is removed if the doctor finds it is cancerous or leads to increased blood pressure.
Kidney and Pancreas Transplant
A simultaneous kidney and pancreas transplant is required when a patient suffers from kidney failure and diabetes and needs a very high insulin dose to control diabetes. Once the doctor confirms that you require a kidney and pancreas transplant through a complete medical assessment, blood tests, imaging tests, etc., you will wait for a donor kidney and pancreas. The doctor will test the compatibility when the donor's kidney and pancreas are available.
During the procedure, the surgeon will place the new kidney below the left side of the abdomen and connects the blood vessels to the kidney. The vein and artery are then connected to the new kidney, and the ureter of the new kidney is also connected to your bladder. After that, the new pancreas is placed below the right side of the abdomen and connects the blood vessels. The kidney and pancreas combined surgery take almost 5 to 7 hours and you may have to stay in the hospital for up to 2 weeks.
The surgeon will monitor your condition for the next few days after the surgery, whether it is a combined liver and kidney transplant or a kidney and pancreas transplant. If everything is found normal, you will be discharged from the hospital with a post-transplant care module, which includes regular check-ups and monitoring of the function of the new organs. By following these guidelines and taking immunosuppressant medications as prescribed, patients can help ensure the long-term success of their dual organ transplant.
Risks Involved in Dual Transplants
Risks in dual organ transplants depend on the health of the patients. Since your surgeon will monitor your entire health, there is less chance of risk during the surgery. In rare cases, a patient undergoing dual transplant surgery may suffer bleeding, pain, and other infections.
Currently, dual organ transplant has emerged as an effective way for those who have suffered an acute disease. This transplant procedure is recommended when there is no other option left. The organs are received normally from a deceased patient, and you will be on a waiting list until the organs are available.
Consult a nephrologist in Old Airport Road if you require dual organ transplant services.
FAQs
Name some complications of organ transplant.
Rejection, infection, high blood pressure, and delayed graft function are common complications of organ transplants.
Which is the most complicated organ to transplant?
Lungs are the most complex organs for transplant as they are more susceptible to infections.
Can two organs be transplanted together?
Yes, two organs can indeed be transplanted together. This procedure is called a combined or dual organ transplant.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Leukocytes or nitrites present 75% sensitivity and 82% specificity; all you need for simple cystitis
Culture positive if >10^5 CFU or 10^2 CFUs with symptoms; necessary for pyelonephritis/complicated UTI
CT will show obstruction, calculi, gas-forming infections
Men: STI, prostatitis, urethritis
Tx: Macrobid 100 mg x5 days, Bactrim DS bid x3 days
Pyelo: FQs, CTX, zosyn, cefepime if low risk for MDR
Meropenem, IV FQs, CTX, zosyn, cefepime for high risk MDR
Recurrent UTIs: pyridium, post coital abxs, urogyn referral, daily ppx with Bactrim, Macrobid, or Keflex
Pyelo f/u: PRN, urology, or urogyn f/u
Highest prevalence among uncircumcised males <3 months
In peds pts, enterococcus is not a contaminant in the urine culture as it typically is in adults
You want to avoid renal scarring; any other organism other than E.coli has increased risk of causing renal scarring in kids
US recommended in kids <2 years with first febrile UTI, any age with recurrent UTI, any age with fam hx of kidney/uro disease, poor growth, HTN, failure to respond to tx
Voiding cystourethrogram for anatomical eval and for reasons listed above
Simple cystitis tx:
Infants: cephalosporin; Keflex 50-100 mg/kg qd divided bid x5 days. Allergy? Can use Bactrim, Augmentin, rarely ciprofloxacin
Pts 1 month to 2 years: IV CTX, gentamicin; cefdinir 14 mg/kg qd divided bid x10 days
If no improvement in 48-72 hours, change abxs and pursue imaging
For infants, you need to do f/u imaging if not done in hospital
Pregnant women have acute cystitis, not simple cystitis because pregnant women are not simple
Abxs in pregnancy: beta lactam, Macrobid (not in first trimester), Fosfomycin; duration of therapy is 5-7 days
Bactrim avoided during pregnancy. Cefpodoxime is another one safe in pregnancy.
Pyelo in pregnancy: consider intraamniotic infection and placental abruption; it’s not an indication for delivery. Can tx with IV CTX or zosyn.
You have to recheck UA after treatment of asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnant pts; 30% don’t clear it
Macrobid and Bactrim should be avoided in pregnancy; Macrobid more so in the first trimester; avoid Bactrim throughout pregnancy
Febrile neonate: tachypnea, irritability, cyanosis, poor feeding; <1% of term infants have UTIs. Limited data for preterm infants.
Term infants tend to get E. coli. In preterm infants, coagulase neg staph and Klebsiella are more common; really small premies can have candida.
Hematogenous spread can occur in premies.
Neonates: UA, culture, blood culture, lumbar puncture; imaging, voiding cystourethrogram
Broad spectrum abxs in babies: Ampicillin and gentamicin for 10 to 14 days
CTX can increase serum free bilirubinà increased jaundice
Kids can have impaired renal growth that resolved
Catheter Associated UTI = CAUTI; no need to screen unless pt is symptomatic
Pyuria is not enough to diagnose UTI in pts with indwelling catheters; you need a culture, which you compare to previous culture. Percutaneous nephrostomy tubes, stents – get urology involved. Tx with broad spectrum abxs until you get culture results. Tx 7-14 days. Levofloxacin x5 days if not severely ill; 3 days for pts under 65 w/o upper UTI sxs
For transplant pts, there’s more resistance to cipro and Bactrim
For transplant pts with simple cystitis: FQs, 3rd gen cephalosporins x10-14 days; zosyn, meropenem, cefepime if complicated and call ID
Do not screen (these are guidelines, not what we always do): peds pts, functionally impaired adults, long term care facility pts, diabetics, pts w/ renal transplants, pts with spinal cord injuries
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Homeopathy for CKD: Tackling High Creatinine Levels Naturally
Natural Remedy for Kidney Failure Without Dialysis
Kidney failure is a critical medical condition that disables the kidneys to remove toxins and waste products from the blood. Patients with chronic kidney disease or failure are generally recommended dialysis or transplantation of the kidneys. However, patients are searching for natural remedies that could be used in place of or to avoid the use of such invasive treatments as dialysis and transplantation. One such alternative is homeopathic chronic kidney disease treatment, which has shown promise in improving kidney function and alleviating the symptoms of kidney failure.

Homeopathy is a holistic medicine that focuses on the patient as a whole rather than an isolated symptom. This system of medicine works under the principle of "like cures like." Highly diluted substances are used to stimulate the body's natural healing process. For patients with kidney disease, homeopathy can be a natural and non-invasive option that tries to restore the function of kidneys and improve overall health.
Homeopathic Treatment for Kidney Failure
Homeopathic medicine has gained respect for its applications in treating or managing kidney problems and preventing progressing to end-stage kidney failure. The benefits from homeopathic therapy for kidney disease are numerous :
Control of Creatinine Levels. Creatinine values are usually significant when kidney activity is compromised; hence, Homeopathic chronic kidney disease treatment is commonly used to manage it
Improved Circulation of Blood: Good circulation is the condition for a healthy kidney, and specific homeopathic treatment will also help improve blood circulation to provide oxygen and nutrients for the kidneys to work at their best.
Detoxification: Homeopathic treatment will encourage the detoxification processes in the body, and therefore, it will help remove wastes and toxins in the body which otherwise put pressure on the kidneys.
Reducing Inflammation: There is usually some inflammatory process seen with kidney disease. Homeopathy kidney problem medication reduces inflammation of the kidneys. This can then help in lessening the suffering from pain, swelling, and discomfort.
Controlling Fluid Retention: In kidney failure, fluid retention, which causes edema in legs, ankles, and other areas, is quite common.
Improved Energy Levels: Patients suffering from kidney failure often grow weak and fatigued. Homeopathic remedies are believed to improve energy levels by uplifting general well-being and making a body function properly.
Minimal Side Effects: One of the main advantages of homeopathic cure for chronic kidney disease is its gentle nature. Conventional medicines can cause side effects or damage other body parts but have no such issue with homeopathy treatments.
Chronic Kidney Disease Treatment at Bharat Homeopathy
Bharat Homeopathy, located in Gurgaon, is known for its specialized approach to managing chronic kidney disease (CKD) through homeopathic treatments. With a team of experienced practitioners and nephrologists, Bharat Homeopathy offers personalized treatment plans that are tailored to each patient’s unique needs.
Bharat Homeopathy provides a safe, natural, and effective alternative for patients with CKD against dialysis. The high creatinine treatment plan slows the disease's progression, reduces high creatinine levels, lowers proteinuria, and enhances the function of the kidneys.
Bharat Homeopathy has treated a range of kidney diseases. Some of them are:
Chronic Kidney Disease
Acute Kidney Injury
Polycystic Kidney Disease
Glomerulonephritis
Nephrotic Syndrome
The homeopathic cure for chronic kidney disease protocols aims to enhance the strength of the kidneys, improve their filtering ability, and restore normal functioning. This would enable patients to control their disease without dialysis or a kidney transplant.
Specialists in Creatinine Treatment by Bharat Homeopathy
High creatinine levels are the most common marker of impaired kidney function, which may lead to renal failure if not treated. Specialists at Bharat Homeopathy diagnose the root causes of high creatinine levels instead of just hiding the symptoms.
Here, Bharat Homeopathy's nephrologists interact closely with the patient to monitor their creatinine level and change treatment plans accordingly to ensure that a patient receives the best possible care and management in his or her kidney condition.
Nephrology Specialists at Bharat Homeopathy Gurgaon
The nephrologists at Bharat Homeopathy are skilled in diagnosing and Treatment for kidney failure, and they collaborate with other healthcare professionals to ensure that patients receive comprehensive care. They use diagnostic tools such as urine tests, blood tests, and imaging studies to assess kidney function and monitor disease progression.
One of the main advantages of treatment at Bharat Homeopathy is the clinic's patient-centered approach. Every patient is treated as an individual, and Treatment for kidney failure plans are specifically tailored to their unique health needs and conditions. The aim is to improve kidney function, alleviate symptoms, and enable patients to live a high quality of life without dialysis.
Conclusion
Chronic kidney disease and even kidney failure are life-changing conditions, but there is a proper treatment in which a significant amount of health improvement is noticed. Homeopathic kidney failure treatment without dialysis offers a proper, safe, and effective alternative to dialysis and other invasive procedures. The underlying causes of kidney disease and the promotion of the body's inherent capacity to heal are addressed in order to restore kidney function and prevent additional damage caused by the disease.
Nephrologists, along with the best homeopaths at Bharat Homeopathy Gurgaon, make it possible for an individual who suffers from renal failure to obtain proper care from them. Treating the person as a whole, the doctors in Bharat Homeopathy provide their patients with custom-tailored treatment and make them look towards a holistic, natural approach to the management of chronic kidney diseases and renal failures. Patients can improve their renal health, lower creatinine levels, and restore their vitality using homeopathic kidney failure treatment without dialysis, dietary modifications, and lifestyle interventions without the aid of dialysis.
Explore natural kidney treatments tailored for you. Click here to learn more
#cure for chronic kidney disease#kidney failure treatment without dialysis#homeopathy kidney problem medication#treatment for kidney failure
0 notes
Text
Overcoming End-Stage Renal Disease with Kidney Transplantation: A New Lease on Life

Kidney transplantation serves as a lifeline for individuals struggling with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) or advanced kidney dysfunction. This transformative procedure offers the chance for improved health and a better quality of life for those facing kidney failure. At Miart, we specialize in advanced kidney transplant services. In this blog, we will explore the complexities of kidney transplantation, including its overview, types, causes, recent advancements, and a balanced discussion of its benefits and drawbacks.
Kidney transplantation involves implanting a healthy kidney from a living or deceased donor into a recipient whose kidneys can no longer function properly. This surgery is regarded as the most effective long-term solution for end-stage renal disease (ESRD), offering recipients the chance to restore normal kidney function and lead a more active, healthier life.
Types of Kidney Transplants
Living Donor Transplant: A kidney is donated by a living person, usually a family member or close friend.
Deceased Donor Transplant: The kidney comes from a deceased donor, typically someone who has signed up for organ donation or whose family consents to donation after death.
Causes of Kidney Transplantation
High Blood Pressure: Chronic hypertension causes damage to the small blood vessels in the kidneys and reduces their ability to function properly. Prolonged uncontrolled high blood pressure is a common cause of kidney disease.
Genetic Conditions: Inherited genetic disorders can lead to kidney problems, making transplantation necessary. Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is an example of a genetic condition resulting in kidney failure.
Autoimmune Diseases: Autoimmune diseases, like lupus and vasculitis, may lead to inflammation and kidney damage. In some cases, this damage can progress to the point where transplantation is the best treatment option.
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): The primary cause for many kidney transplants is the progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD) to End Stage Kidney Disease. Conditions such as diabetes and high blood pressure can contribute to the gradual deterioration of kidney function, leading to the need for transplantation.
Diabetes: Uncontrolled diabetes is a risk factor for kidney disease. High blood sugar levels may damage blood vessels in the kidneys and impair the ability to filter waste from the blood over time.
New Developments in Treatment
Recent advancements in kidney transplantation include:
Robotic-assisted Surgery: Robotic-assisted surgery has been introduced to enhance the precision of the transplant procedure in properly selected patients. This minimally invasive approach can lead to smaller incisions, quicker recovery times and reduced pain for recipients.
Stem Cell Therapy: Research in stem cell therapy is exploring the use of stem cells to promote kidney regeneration and reduce the risk of rejection. While still in the experimental stage, this approach holds promise for improving long-term outcomes and reducing dependence on immunosuppressive medications.
Desensitization Therapies: These therapies aim to overcome barriers related to incompatible donors. They involve techniques to reduce the recipient's immune system response, allowing transplantation even when there are blood type or antibody mismatches.
Organ Preservation Techniques: Advanced methods for preserving donor kidneys before transplantation have been developed. These techniques optimize the organ's condition, ensuring better functionality and reducing the risk of complications after transplantation.
Precision Medicine: Precision medicine is advancing in kidney transplantation - tailoring immunosuppressive medications to the specific genetic and immune profile of the recipient helps minimize side effects and improve the overall success of the transplant.
Benefits of Kidney Transplantation
Freedom from Dialysis: Transplantation eliminates the need for frequent and time-consuming dialysis sessions.
Potential for Living Donor Transplant: Living donor transplants offer the advantage of a quicker and more controlled process.
Reduced Healthcare Costs: Despite initial costs, kidney transplantation can be more cost-effective than long-term dialysis in the long run.
Improved Quality of Life: Transplantation often restores normal kidney function, allowing recipients to lead more active and fulfilling lives.
Long-term Survival: Kidney transplantation is associated with a higher long-term survival rate compared to long-term dialysis.
Drawbacks of Kidney Transplantation
Limited Availability of Organs: The demand for kidneys far exceeds the supply, leading to long waiting times for suitable donors.
Surgical Risks: Like every surgery, there are inherent risks involved in the transplantation procedure.
Financial Costs: While cost-effective in the long term, the initial expenses of transplantation, including surgery and lifelong medication, can be significant.
Risk of Rejection: The recipient's immune system may recognize the transplanted kidney as foreign and attempt to reject it.
Immunosuppressive Medications: These medications, while essential for preventing rejection, can lead to side effects and increased susceptibility to infections.
Kidney transplantation marks a significant breakthrough in medical science, offering hope to individuals battling kidney failure. While it provides many benefits, it is essential to recognize the potential risks and ongoing challenges tied to this transformative procedure. With advancements in renal transplants in Kerala, Miart continues to lead the way, emphasizing the importance of organ donation and groundbreaking research in the field.
0 notes
Text
Choosing the Best Kidney Doctor in Chandigarh for Your Health Needs
When it comes to your health, choosing the right healthcare provider is crucial, especially when dealing with complex conditions like kidney diseases. The Best Kidney Doctor in Chandigarh can provide you with expert advice, personalized care, and effective treatments that are vital for managing kidney-related issues.
Kidney diseases are becoming increasingly prevalent due to lifestyle factors such as poor diet, lack of exercise, and an increase in chronic conditions like diabetes and hypertension. When kidney problems arise, it is essential to seek medical attention from a qualified Nephrologist in Chandigarh, a specialist trained in the diagnosis and treatment of kidney diseases. These specialists are not only capable of managing common kidney conditions but also have the expertise to tackle more complicated renal issues that require specialized care.
At Alchemist Hospitals' Department of Renal Diseases, patients can receive top-notch care from experienced nephrologists who understand the intricate nature of kidney health. The hospital offers comprehensive services ranging from routine check-ups to advanced diagnostic procedures, ensuring that all your renal health concerns are addressed.
A Nephrologist in Chandigarh offers a wide range of services including:
Diagnosis of Kidney Disease: Early detection is key to preventing the progression of kidney disease. A nephrologist can help identify the signs and provide early intervention.
Dialysis Services: For patients whose kidneys are no longer functioning well, dialysis becomes a crucial part of life. Nephrologists at leading hospitals can manage dialysis schedules and ensure that the process is as comfortable as possible.
Kidney Transplant Consultation: In cases where kidney failure occurs, a nephrologist can provide guidance on kidney transplant options and the necessary care before and after the transplant.
Preventive Care and Lifestyle Advice: Kidney disease can often be prevented by managing risk factors like hypertension and diabetes. Nephrologists offer valuable advice on diet, exercise, and other lifestyle changes to help maintain kidney health.
Choosing a Nephrologist in Chandigarh is a crucial decision. It’s important to consult a professional who not only provides medical treatment but also offers empathetic care. With the right expert, you can manage your kidney health and lead a fulfilling life.
To get started, visit the Department of Renal Diseases at Alchemist Hospitals and take the first step towards ensuring optimal kidney health under the care of the Best Kidney Doctor in Chandigarh.
0 notes
Text
Kidney Failure Treatment in Kandivali: Comprehensive Care at Apex Group of Hospitals
Kidney failure, also known as renal failure, is a serious medical condition that occurs when the kidneys lose their ability to filter waste and excess fluids from the blood effectively. This can lead to a dangerous build-up of toxins in the body, causing a variety of symptoms, including swelling, fatigue, nausea, and confusion. In severe cases, kidney failure can be life-threatening without proper treatment. If you're looking for reliable kidney failure treatment in Kandivali, Apex Group of Hospitals is a trusted name in providing specialized care for kidney-related issues, including chronic kidney disease (CKD) and acute kidney failure.
In this article, we will discuss kidney failure, its symptoms, causes, and the advanced treatment options available at Apex Group of Hospitals in Kandivali.
Understanding Kidney Failure
Kidney failure is classified into two main types: acute kidney failure and chronic kidney failure. Both conditions can have a significant impact on a person’s health, and timely intervention is crucial for managing the disease and improving quality of life.
1. Acute Kidney Failure (AKF)
Acute kidney failure develops suddenly, often in response to another illness, injury, or medical procedure. It can occur over a short period of time, ranging from a few hours to a few days. Common causes of AKF include:
Dehydration or severe blood loss
Heart attack or heart failure
Severe infections or sepsis
Blockages in the urinary tract, such as kidney stones
Certain medications that damage the kidneys
While acute kidney failure is reversible in many cases with prompt treatment, it requires immediate medical attention.
2. Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
Chronic kidney disease is a long-term condition where kidney function deteriorates gradually over several months or years. The main causes of CKD include diabetes, high blood pressure, glomerulonephritis (inflammation of the kidneys), and polycystic kidney disease. CKD can progress to end-stage renal failure, which requires dialysis or a kidney transplant for survival.
Symptoms of Kidney Failure
Kidney failure can manifest with various symptoms, depending on the severity and underlying cause of the condition. Some common signs include:
Swelling in the legs, ankles, or feet (edema)
Decreased urine output, or dark, foamy urine
Fatigue and weakness
Nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite
Shortness of breath
Confusion or difficulty concentrating
High blood pressure
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is crucial to seek medical attention promptly to diagnose and address the underlying issue.
Causes of Kidney Failure
Several conditions and lifestyle factors can contribute to kidney failure. Some of the most common causes include:
Diabetes: High blood sugar levels over time can damage the kidneys' filtering units, leading to diabetic nephropathy.
Hypertension (High Blood Pressure): Uncontrolled high blood pressure can damage blood vessels in the kidneys, leading to kidney damage.
Chronic Glomerulonephritis: Inflammation of the kidney’s filtering units can lead to kidney damage over time.
Polycystic Kidney Disease: A genetic disorder that causes cysts to form in the kidneys, impairing their function.
Obstructions: Blockages in the urinary tract, such as kidney stones or an enlarged prostate, can lead to kidney damage if left untreated.
Infections: Kidney infections or urinary tract infections (UTIs) can damage the kidneys if not properly treated.
Kidney Failure Treatment at Apex Group of Hospitals in Kandivali
If you or a loved one is dealing with kidney failure, it is essential to seek expert care from experienced nephrologists who can provide the best possible treatment. Apex Group of Hospitals in Kandivali offers advanced and comprehensive treatment options for kidney failure, ensuring that patients receive timely and effective care. Here’s a look at the treatments provided:
1. Diagnosis and Monitoring
At Apex Group of Hospitals, the first step in treating kidney failure is accurate diagnosis. A thorough assessment, including blood tests (such as serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen), urine tests, and imaging tests like ultrasounds or CT scans, will help doctors evaluate kidney function and determine the extent of damage. Regular monitoring is also essential to track the progression of kidney disease, especially in cases of chronic kidney failure.
2. Medications and Lifestyle Modifications
In the early stages of kidney failure or for patients with chronic kidney disease, medications and lifestyle changes may help manage the condition and prevent further damage. The experienced nephrologists at Apex Group of Hospitals may recommend:
Blood pressure management: Controlling hypertension is crucial for slowing down kidney damage.
Diabetes management: Proper control of blood sugar levels can prevent kidney damage in diabetic patients.
Dietary modifications: Reducing salt, protein, and potassium intake can help relieve kidney stress and prevent further complications.
Medications: Prescriptions for managing symptoms such as high blood pressure, fluid retention, or high phosphorus levels.
3. Dialysis
For patients with end-stage kidney failure or severe acute kidney failure, dialysis may be necessary to filter waste and excess fluids from the blood. Apex Group of Hospitals offers both hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis options:
Hemodialysis: Involves using a machine to filter the blood outside the body, typically done in a hospital setting.
Peritoneal Dialysis: Involves using the lining of the abdomen (the peritoneum) to filter waste from the blood. This can be done at home with proper training.
Dialysis helps manage kidney failure temporarily, but it does not cure the condition. It is typically used for patients whose kidneys are no longer able to function sufficiently.
4. Kidney Transplantation
For patients with end-stage renal failure, a kidney transplant may be the best option for restoring kidney function. Apex Group of Hospitals provides expert kidney transplant services, including:
Pre-transplant evaluation: Comprehensive testing to determine whether a patient is a suitable candidate for a kidney transplant.
Living and deceased donor kidney transplants: The hospital facilitates both living donor and deceased donor kidney transplants, depending on availability.
Post-transplant care: After a successful kidney transplant, the hospital provides follow-up care to monitor kidney function and prevent complications such as rejection or infections.
5. Palliative Care
In cases where kidney failure cannot be reversed or treated with dialysis or a transplant, palliative care may be offered to manage symptoms and improve the quality of life. This includes pain management, controlling nausea and fatigue, and offering emotional support to both the patient and their family.
Why Choose Apex Group of Hospitals for Kidney Failure Treatment in Kandivali?
Apex Group of Hospitals in Kandivali stands out as one of the best healthcare providers for kidney failure treatment due to its:
Expert Nephrologists: The hospital has a team of highly skilled nephrologists who specialize in treating kidney diseases and provide comprehensive care tailored to each patient’s needs.
State-of-the-Art Facilities: With advanced diagnostic tools, dialysis units, and transplant services, Apex Group of Hospitals ensures that patients receive the highest standard of care.
Patient-Centered Approach: The hospital emphasizes individualized care and focuses on improving the quality of life for patients with kidney disease.
Comprehensive Kidney Care: From diagnosis and medication to dialysis and transplantation, Apex Group of Hospitals offers complete kidney care under one roof.
Conclusion
Kidney failure is a serious condition that requires expert care and timely intervention. If you or a loved one is seeking kidney failure treatment in Kandivali, Apex Group of Hospitals provides world-class nephrology services, including diagnosis, medications, dialysis, and kidney transplantation. With a team of experienced nephrologists and state-of-the-art facilities, you can trust Apex Group of Hospitals to provide comprehensive care for kidney disease and improve your health outcomes. Reach out to Apex Group of Hospitals today and take the first step toward better kidney health.
0 notes
Text
Chronic Kidney Disease in India
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is an emerging public health issue in India, affecting millions of people across the country. The prevalence of kidney disease has been steadily increasing, driven by factors such as poor lifestyle choices, increased rates of diabetes and hypertension, inadequate healthcare access, and a lack of awareness about kidney health. As CKD progresses to end-stage renal disease (ESRD), kidney transplant becomes one of the most viable treatment options, offering patients a chance to regain normal kidney function and improve their quality of life. In this article, we will explore the causes of CKD in India, its impact on individuals and communities, and how kidney transplant plays a critical role in managing this condition.
What is Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)?
Chronic Kidney Disease is a condition characterized by the gradual loss of kidney function over time. Kidneys are essential organs that filter waste and excess fluids from the blood, help regulate blood pressure, produce red blood cells, and maintain overall fluid and electrolyte balance. When kidney function deteriorates, waste products accumulate in the blood, leading to a range of serious health issues such as high blood pressure, anemia, weak bones, and cardiovascular problems.
CKD is typically classified into five stages, with stage 1 being the mildest and stage 5 representing end-stage renal disease (ESRD), where the kidneys are no longer able to function adequately, and the patient requires dialysis or a kidney transplant for survival.
The Prevalence of CKD in India
The prevalence of CKD in India has been rising steadily due to several interconnected factors. According to various studies, it is estimated that around 1 in 10 adults in India suffer from some form of CKD. This figure is concerning, given the vast population of India. The risk of developing CKD is higher among individuals with diabetes, hypertension, or a family history of kidney disease. Additionally, unhealthy lifestyle choices such as poor diet, lack of exercise, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption contribute to the growing incidence of kidney disease.
Diabetes and hypertension are the leading causes of CKD in India. With the increasing prevalence of these conditions, the number of people affected by CKD is expected to rise even further in the coming years. Moreover, there is a significant lack of awareness about kidney disease, leading many individuals to seek medical help only when the disease has already progressed to an advanced stage.
Causes and Risk Factors for CKD in India
Several factors contribute to the high rates of CKD in India. These include:
Diabetes and Hypertension: These two conditions are the most common risk factors for CKD. Diabetes can damage the small blood vessels in the kidneys, impairing their ability to filter waste products. High blood pressure can also cause kidney damage by putting extra strain on the kidneys’ blood vessels.
Poor Lifestyle Choices: A diet high in salt, sugar, and unhealthy fats, combined with a lack of physical activity, significantly increases the risk of developing CKD. Obesity, which is becoming more prevalent in India, also contributes to kidney disease, as it increases the likelihood of developing diabetes and hypertension.
Genetic Factors: In some cases, CKD can be hereditary, with certain genetic conditions such as polycystic kidney disease (PKD) being more common in some families. People with a family history of kidney disease are at higher risk.
Lack of Early Detection: Many people with CKD are unaware they have the disease until it reaches an advanced stage. This is due to the lack of regular screening and early detection programs, as well as a general lack of knowledge about the importance of kidney health.
Infections and Overuse of Medications: Certain infections, such as urinary tract infections (UTIs), if left untreated, can cause kidney damage. Additionally, the overuse of medications, particularly non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can lead to kidney damage.
Environmental Factors: In some regions of India, exposure to pollutants, contaminated water, and chemicals can contribute to kidney disease.
The Impact of CKD on Individuals and Society
The impact of CKD in India is profound, affecting not only the individuals suffering from the disease but also their families and the healthcare system. As CKD progresses to ESRD, patients often face significant challenges in managing their health.
Physical and Emotional Strain on Patients
The progression of CKD can lead to debilitating symptoms, including fatigue, swelling, shortness of breath, and difficulty concentrating. The need for dialysis – a process that filters the blood when the kidneys can no longer do so – can be physically exhausting and mentally taxing. Dialysis is time-consuming and requires regular visits to healthcare facilities, often multiple times a week. This not only interferes with patients’ daily activities but also has a profound impact on their emotional well-being. Many dialysis patients experience depression, anxiety, and social isolation due to the constraints of the treatment.
Economic Burden
The economic burden of CKD is significant. Dialysis treatment is costly and can drain financial resources, especially for low-income families. Additionally, the inability to work due to illness further exacerbates the financial strain on families. The cost of kidney transplant surgery, although higher in the short term, is often more economical in the long run compared to ongoing dialysis treatments.
Strain on the Healthcare System
The rising prevalence of CKD places a tremendous burden on India's healthcare system. Dialysis requires considerable resources, including specialized equipment, trained medical staff, and facilities. The demand for kidney transplants also increases, which can overwhelm the healthcare infrastructure. This results in long waiting times for patients and puts additional strain on hospitals and medical professionals.
Kidney Transplant as a Solution
For individuals with end-stage renal disease, a kidney transplant offers the best chance for survival and a better quality of life. A kidney transplant involves surgically implanting a healthy kidney from a living or deceased donor into the patient’s body. This new kidney takes over the role of filtering waste and excess fluids from the blood, providing the recipient with a restored level of kidney function.
Kidney transplant offers several unique advantages over dialysis:
Improved Quality of Life: Kidney transplant recipients often experience a better quality of life than dialysis patients. The transplant eliminates the need for regular dialysis sessions, allowing patients to resume normal activities, such as work and social engagements.
Increased Life Expectancy: Studies show that kidney transplant recipients live longer than those who remain on dialysis. While dialysis can extend life, it does not offer the same long-term survival benefit as a transplant.
Reduced Healthcare Costs: Although the initial cost of a kidney transplant is high, it is generally more cost-effective in the long run compared to years of dialysis. Kidney transplant reduces the need for regular hospital visits and other ongoing medical costs associated with dialysis.
Better Psychological Well-being: Kidney transplant can significantly improve the emotional well-being of patients. The sense of relief from the burdens of dialysis and the hope for a healthier future leads to improved mental health and overall happiness.
Fertility and Family Planning: Kidney transplant can restore fertility in both men and women, making family planning possible for individuals who may have struggled with infertility due to kidney disease or dialysis.
The Need for Increased Awareness and Prevention
Despite the many benefits of kidney transplant, the reality is that many people in India suffer from CKD without proper awareness or early intervention. To combat the rising burden of CKD, it is essential to focus on preventive measures, including:
Early Detection: Regular screening for kidney disease in high-risk populations (e.g., people with diabetes, hypertension, or a family history of kidney disease) is crucial for early diagnosis and management.
Public Awareness Campaigns: Educating the public about kidney health, the risk factors for CKD, and the importance of regular check-ups can help prevent the disease from progressing to a severe stage.
Improved Healthcare Access: Ensuring that individuals have access to affordable healthcare services and dialysis options is critical for managing CKD and providing timely treatments like kidney transplant.
Conclusion Chronic Kidney Disease is a growing challenge in India, with a significant number of people affected by the condition. The rise in CKD is largely due to lifestyle changes, increased rates of diabetes and hypertension, and limited awareness about kidney health. As kidney disease progresses to end-stage renal disease, kidney transplant offers patients a new lease on life, providing improved health, increased life expectancy, and better quality of life. However, addressing the root causes of CKD through early detection, public awareness, and preventive healthcare measures will be key to curbing the spread of this disease in the future. Kidney transplant offers hope to millions, but tackling the broader public health issue requires collective effort and systemic change. For more details visit https://kidneytransplant.hospital/?kidney-transplant=benefits-of-kidney-transplant
0 notes
Text
Best Center for Kidney Treatment – Advanced Nephrology Care at Preethi Hospitals, Madurai
Understanding Kidney Health: Why It Matters
Kidneys play a vital role in maintaining overall health by filtering toxins, balancing fluids, and regulating blood pressure. With increasing lifestyle disorders and genetic predispositions, kidney diseases are becoming more prevalent. Finding the best center for kidney treatment is crucial for managing and preventing further complications.
Common Kidney Diseases and Their Impact
Kidney ailments range from mild infections to chronic conditions that require long-term management. Some of the most common kidney-related issues include:
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): A progressive condition that can lead to kidney failure if untreated.
Kidney Stones: Hard deposits formed from minerals that cause severe pain and block urine flow.
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Recurrent infections can damage the kidneys over time.
Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD): A genetic disorder that causes cysts in the kidneys, impairing their function.
Kidney Failure: A severe condition requiring dialysis or kidney transplant.
Why Choose Preethi Hospitals, Madurai for Kidney Treatment?
Preethi Hospitals, Madurai, is recognized as one of the best centers for kidney treatment due to its comprehensive approach to nephrology care. The hospital provides state-of-the-art diagnostic tools, advanced treatment methods, and a patient-centric approach.
Advanced Diagnostic Facilities
Early detection is crucial for effective kidney treatment. Preethi Hospitals offers cutting-edge diagnostic tests, including:
Blood and urine tests to assess kidney function
Ultrasound and CT scans for structural analysis
Biopsy procedures for detecting chronic conditions
Expert Nephrology and Urology Care
At Preethi Hospitals, a dedicated team of nephrology specialists and urologists work together to provide personalized treatment plans. The hospital excels in treating both acute and chronic kidney conditions through:
Medical management of kidney disorders
Minimally invasive procedures for kidney stones and UTIs
Dialysis services for end-stage kidney disease
Kidney transplant programs for advanced cases
Cutting-Edge Dialysis Services
For patients with chronic kidney disease, dialysis is a life-saving procedure that helps remove toxins and excess fluids from the body. Preethi Hospitals provides:
Hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis options
Advanced dialysis machines for effective treatment
Strict infection control measures for patient safety
Minimally Invasive Treatments for Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are a painful and recurring issue for many individuals. At Preethi Hospitals, patients receive advanced treatments like:
Laser Lithotripsy: A non-invasive method that breaks down kidney stones using laser energy.
Shock Wave Lithotripsy (SWL): High-energy sound waves to disintegrate stones for easy passage.
Ureteroscopic Stone Removal: A precise procedure for larger stones that cannot pass naturally.
Comprehensive Kidney Transplant Services
For patients with end-stage renal disease, kidney transplantation is the best solution. Preethi Hospitals offers:
Pre-transplant evaluation and donor matching
Advanced surgical procedures with high success rates
Post-transplant care for long-term health
Lifestyle and Preventive Care for Kidney Health
Maintaining kidney health requires more than just medical treatment. At Preethi Hospitals, patients receive guidance on lifestyle changes to prevent kidney diseases, including:
Hydration: Drinking adequate water to flush out toxins.
Balanced Diet: Reducing salt, sugar, and processed foods to lower the risk of kidney damage.
Regular Exercise: Managing weight and blood pressure to protect kidney function.
Avoiding Unnecessary Medications: Overuse of painkillers can harm the kidneys over time.
Patient-Centric Approach and Holistic Care
Preethi Hospitals prioritizes patient care by offering:
24/7 emergency support for kidney-related conditions
Affordable treatment options for all economic backgrounds
Counseling and rehabilitation services for kidney disease patients
Conclusion: Trust Preethi Hospitals for the Best Kidney Care
If you are searching for the best center for kidney treatment, Preethi Hospitals, Madurai, is a trusted name in nephrology care. With advanced technology, expert medical professionals, and a holistic approach, the hospital ensures the best outcomes for kidney patients.
Prioritize your kidney health today—consult with the experts at Preethi Hospitals for world-class kidney care!

0 notes