#Class 10 Math 5.2
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
MP Board Class 12th Maths Book Solutions in English Medium
MP Board Class 12th Maths Chapter 1 Relations and Functions
Chapter 1 Relations and Functions Ex 1.1
Chapter 1 Relations and Functions Ex 1.2
Chapter 1 Relations and Functions Ex 1.3
Chapter 1 Relations and Functions Ex 1.4
Chapter 1 Relations and Functions Miscellaneous Exercise
MP Board Class 12th Maths Chapter 2 Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Chapter 2 Inverse Trigonometric Functions Ex 2.1
Chapter 2 Inverse Trigonometric Functions Ex 2.2
Chapter 2 Inverse Trigonometric Functions Miscellaneous Exercise
MP Board Class 12th Maths Chapter 3 Matrices
Chapter 3 Matrices Ex 3.1
Chapter 3 Matrices Ex 3.2
Chapter 3 Matrices Ex 3.3
Chapter 3 Matrices Ex 3.4
Chapter 3 Matrices Miscellaneous Exercise
MP Board Class 12th Maths Chapter 4 Determinants
Chapter 4 Determinants Ex 4.1
Chapter 4 Determinants Ex 4.2
Chapter 4 Determinants Ex 4.3
Chapter 4 Determinants Ex 4.4
Chapter 4 Determinants Ex 4.5
Chapter 4 Determinants Ex 4.6
Chapter 4 Determinants Miscellaneous Exercise
MP Board Class 12th Maths Chapter 5 Continuity and Differentiability
Chapter 5 Continuity and Differentiability Ex 5.1
Chapter 5 Continuity and Differentiability Ex 5.2
Chapter 5 Continuity and Differentiability Ex 5.3
Chapter 5 Continuity and Differentiability Ex 5.4
Chapter 5 Continuity and Differentiability Ex 5.5
Chapter 5 Continuity and Differentiability Ex 5.6
Chapter 5 Continuity and Differentiability Ex 5.7
Chapter 5 Continuity and Differentiability Ex 5.8
Chapter 5 Continuity and Differentiability Miscellaneous Exercise
MP Board Class 12th Maths Chapter 6 Application of Derivatives
Chapter 6 Application of Derivatives Ex 6.1
Chapter 6 Application of Derivatives Ex 6.2
Chapter 6 Application of Derivatives Ex 6.3
Chapter 6 Application of Derivatives Ex 6.4
Chapter 6 Application of Derivatives Ex 6.5
Chapter 6 Application of Derivatives Miscellaneous Exercise
MP Board Class 12th Maths Chapter 7 Integrals
Chapter 7 Integrals Ex 7.1
Chapter 7 Integrals Ex 7.2
Chapter 7 Integrals Ex 7.3
Chapter 7 Integrals Ex 7.4
Chapter 7 Integrals Ex 7.5
Chapter 7 Integrals Ex 7.6
Chapter 7 Integrals Ex 7.7
Chapter 7 Integrals Ex 7.8
Chapter 7 Integrals Ex 7.9
Chapter 7 Integrals Ex 7.10
Chapter 7 Integrals Ex 7.11
Chapter 7 Integrals Miscellaneous Exercise
MP Board Class 12th Maths Chapter 8 Application of Integrals
Chapter 8 Application of Integrals Ex 8.1
Chapter 8 Application of Integrals Ex 8.2
Chapter 8 Application of Integrals Miscellaneous Exercise
MP Board Class 12th Maths Chapter 9 Differential Equations
Chapter 9 Differential Equations Ex 9.1
Chapter 9 Differential Equations Ex 9.2
Chapter 9 Differential Equations Ex 9.3
Chapter 9 Differential Equations Ex 9.4
Chapter 9 Differential Equations Ex 9.5
Chapter 9 Differential Equations Ex 9.6
Chapter 9 Differential Equations Miscellaneous Exercise
MP Board Class 12th Maths Chapter 10 Vector Algebra
Chapter 10 Vector Algebra Ex 10.1
Chapter 10 Vector Algebra Ex 10.2
Chapter 10 Vector Algebra Ex 10.3
Chapter 10 Vector Algebra Ex 10.4
Chapter 10 Vector Algebra Miscellaneous Exercise
MP Board Class 12th Maths Chapter 11 Three Dimensional Geometry
Chapter 11 Three Dimensional Geometry Ex 11.1
Chapter 11 Three Dimensional Geometry Ex 11.2
Chapter 11 Three Dimensional Geometry Ex 11.3
Chapter 11 Three Dimensional Geometry Miscellaneous Exercise
MP Board Class 12th Maths Chapter 12 Linear Programming
Chapter 12 Linear Programming Ex 12.1
Chapter 12 Linear Programming Ex 12.2
Chapter 12 Linear Programming Miscellaneous Exercise
MP Board Class 12th Maths Chapter 13 Probability
Chapter 13 Probability Ex 13.1
Chapter 13 Probability Ex 13.2
Chapter 13 Probability Ex 13.3
Chapter 13 Probability Ex 13.4
Chapter 13 Probability Ex 13.5
Chapter 13 Probability Miscellaneous Exercise
0 notes
Text
WBBSE solutions for class 10 maths chapter 5 ration and proportion ex 5.2
0 notes
Text
youtube
#এক_চলক_বিশিষ্ট_দ্বিঘাত_সমীকরণ #চলক #এক_চলক_বিশিষ্ট_দ্বিঘাত_সমীকরণ_সৃজনশীল
প্রিয় শিক্ষার্থী বৃন্দ এই ভিডিওতে নবম দশম গণিত বা SSC Maths এর এক চলকবিশিষ্ট সমীকরণ,দ্বিঘাত বিশিষ্ট সমীকরণ অর্থাৎ এসএসসি গণিত ৫.২,এসএসসি গণিত অনুশীলনী ৫.২ বা নবম দশম গণিত অনুশীলনী ৫.২এর সমীকরণ সমাধান নিয়ে আলচনা করা হয়েছে।অভেদ ও সমীকরণের মধ্যে পার্থক্য নিয়ে আলোকপাত করা হয়েছে।একচলক বিশিষ্ট স দ্বিঘাত সমীকরণের সমাধানের কৌশল নিয়ে এতে আলোকপাত করা হয়েছে। চলক কি চলক ও ধ্রুবকের মধ্যে পার্থক্য আলোচনা করা হয়েছে।
#এক চলকবিশিষ্ট সমীকরণ#এক চলকবিশিষ্ট দ্বিঘাত সমীকরণ#এক চলকবিশিষ্ট দ্বিঘাত সমীকরণ সৃজনশীল#চলক#অভেদ কি#ধ্রুবক#একঘাত বিশিষ্ট সমীকরণ#নবম গণিত#দশম গণিত#নবম-দশম গণিত#এসএসসি গণিত#এসএসসি গণিত ৫.২#এসএসসি গণিত অনুশীলনী ৫.২#নবম দশম গণিত অনুশীলনী ৫.২#SSC Math#Class 9 Math 5.2#Class 9 Math#Class 10 Math Chapter 5.2#Class 10 Math 5.2#Class 9-10 Math Chapter 5.2#Class 9-10 Math 5.2#Class 9-10 Math#msu#ssc math#mathematics#Youtube
1 note
·
View note
Note
1,2, and 16 for the lighthearted asks?
1] What’s the last thing you did that made you feel proud of yourself?
So I’m taking a class where we learn how to do math the physics way, because we physicists don’t do math the way that mathematicians do it. The class average for our second quiz was 5.2 out of 10, and I got an 8.5 out of 10. Now, this is already good, because I’m above average and it’s a B. B’s, as I have learned as a physics major who used to be really good at academics in high school, are actually a good thing and not a symbol of being “ehh... whatever you’re barely good enough”.
Then my professor tells us that the top score for the quiz was an 8.5. Out of my seven person class of physics majors, math majors, and one dude who’s a comp sci/accounting double major, I got the top score.
It’s been a couple days since I got my quiz back and I’m still proud of it.
2] What was your last inner chuckle about?
Uh... probably a TAZ fanfic I read?
16] If you were a dragon what would you horde?
Chocolate and other candy.
21 lighthearted questions
3 notes
·
View notes
Link
#BalajiPublicationsMathematicsClass10#BalajiMathsBook#BalajiClass10MathsSolutionsChapter5#BalajiPublicationsSolutionsPdf#UPBoardSolutions
20 notes
·
View notes
Link
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
KSEEB SSLC Class 10 Maths Solutions
KSEEB SSLC Class 10 Maths Solutions
KSEEB SSLC Class 10 Maths Solutions Pdf download in both English Medium and Kannada Medium are part of KSEEB SSLC Class 10 Solutions. Here we have given Karnataka Board SSLC Maths 10th Standard Textbook Solutions according to latest NCERT state board syllabus.
Karnataka SSLC Class 10 Maths Solutions
Chapter 1 Arithmetic Progressions
Chapter 2 Triangles
Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables
Chapter 4 Circles
Chapter 5 Areas Related to Circles
Chapter 6 Constructions
Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry
Chapter 8 Real Numbers
Chapter 9 Polynomials
Chapter 10 Quadratic Equations
Chapter 11 Introduction to Trigonometry
Chapter 12 Some Applications of Trigonometry
Chapter 13 Statistics
Chapter 14 Probability
Chapter 15 Surface Areas and Volumes
Arithmetic Progressions Ex 1.1
Arithmetic Progressions Ex 1.2
Arithmetic Progressions Ex 1.3
Triangles Ex 2.1
Triangles Ex 2.2
Triangles Ex 2.3
Triangles Ex 2.4
Triangles Ex 2.5
Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Ex 3.1
Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Ex 3.2
Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Ex 3.3
Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Ex 3.4
Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Ex 3.5
Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Ex 3.6
Circles Ex 4.1
Circles Ex 4.2
Areas Related to Circles Ex 5.1
Areas Related to Circles Ex 5.2
Areas Related to Circles Ex 5.3
Constructions Ex 6.1
Constructions Ex 6.2
Coordinate Geometry Ex 7.1
Coordinate Geometry Ex 7.2
Coordinate Geometry Ex 7.3
Real Numbers Ex 8.1
Real Numbers Ex 8.2
Real Numbers Ex 8.3
Real Numbers Ex 8.4
Polynomials Ex 9.1
Polynomials Ex 9.2
Polynomials Ex 9.3
Quadratic Equations Ex 10.1
Quadratic Equations Ex 10.2
Quadratic Equations Ex 10.3
Quadratic Equations Ex 10.4
Introduction to Trigonometry Ex 11.1
Introduction to Trigonometry Ex 11.2
Introduction to Trigonometry Ex 11.3
Introduction to Trigonometry Ex 11.4
Some Applications of Trigonometry Ex 12.1
Statistics Ex 13.1
Statistics Ex 13.2
Statistics Ex 13.3
Statistics Ex 13.4
Probability Ex 14.1
Surface Areas and Volumes Ex 15.1
Surface Areas and Volumes Ex 15.2
Surface Areas and Volumes Ex 15.3
Surface Areas and Volumes Ex 15.4
5 notes
·
View notes
Link
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Yang is Stronk (I did the math)
Okay, we all know Yang is strong, but do we talk about it enough? I decided the answer is NO and so I did a bunch of back of the envelope calculations to figure out exactly how ridiculously powerful she is.
tl;dr: Yang can lift 180-270 kg/400-600 lbs over the shoulder, so maximum lifting weight is 450 kg/1000 lbs or more. Yang can endure at least 3.5-5.2 MN of force on her body, get right back up, and punch a mech. Oh, and when she punches said mech, she throws out 17-20 MN with a single punch. That’s 4 THOUSAND times more force than a professional boxer.
Calculations, math/science, and awesome pictures of Yang are below the cut, take with multiple tablespoons of salt bc I had to estimate on a lot of things.
Point 1: How much can Yang lift? Let’s talk about that ridiculous scene with the speaker

you know the one
Based on really quick graphic analysis and Yang’s height (5 ft, 8 inches), that speaker is around 57 inches long and 38 inches wide. Depth is hard to determine because of the angle, but I’m guesstimating it at 25 inches. This gives a total volume of 54,150 cubic inches.
So how heavy is that? Well I spent some time browsing Best Buy (I wonder what my facebook ads are gonna look like after this...) and a 17,827 in^3 speaker weighs 116 lbs. Judging by that ratio, the speaker Yang is holding is around 350 lbs.
BUT WAIT. The Best Buy speaker had two 15″ subwoofers whereas this speaker has two 23″ woofers. I don’t know much about speaker systems, but after looking up a few subwoofers it seems like they’re the heavy part of the speaker (rest of the speaker is more lightweight structural components and air). Using a volume to weight ratio of a subwoofer, the Yang speaker becomes around 740 lbs. Realistically, it’s not fully a subwoofer, so I’m estimating the actual weight in the neighborhood of 400-600 lbs.
Keep in mind that this is casual over-the-shoulder lifting. So I’d wager that her maximum lifting weight is at least double that (so 800-1200lbs, around 1 ton -- ~450 kg if you don’t use the filthy imperial system. Sorry for using imperial, it was easier given the specs on Best Buy). Btw if any of you lift weights regularly, feel free to chime in on this. Idk how shoulder lifting compares to maximum weight, so if you have a better estimate let me know!
Regardless though, Yang is able to just casually sling around 180-270 kg/400-600 lbs, which is uhhhh pretty hot very impressive. No wonder she makes this face afterwards:

Point 2: What is Yang’s durability? Remember that time she got punched into a concrete pillar and fucking BROKE THE PILLAR ?!

That’s right, she didn’t just crack it or dent it. It didn’t even split in half or anything. No, that column of solid concrete literally SHATTERED from the force of that mech punch.

So...that’s a lot of force, all of which was also imparted on Yang’s body. What’s the force required to break a concrete column? This fun video shows an axial compression test for a 6″ diameter concrete cylinder, which withstood 10,000 psi (pounds per square inch). That’s 700 kgf/cm^2 (kilograms of force per cm^2) or about 70 MPa (mega pascals). We’re going to use real people units for this bit fyi.
70 MPa to “pop” a column with a radius of 7.62 cm. The area that the force is being applied to is just the area of the circle -- 182.4 cm^2. Multiply that by the 70 MPa of pressure and we get over 1 million newtons as the force applied (approx. 1.25 mega newtons (MN) if you want a more exact number).
Cool, now let’s do it for Yang’s body smashing into a column. One important thing to note is that she’s hitting the column from the side. This is testing the tensile/flexural strength of the concrete, NOT the compressive strength. Since these columns are built to support a bunch of weight from above, they are weaker when hit from the side. This website says that tensile strength of concrete is 10-15% of its compressive strength, we’ll go with that as an estimate.
So we need something around 7-10.5 MPa to shatter a column of concrete from the side. The force exerted on the column is all from Yang’s body, and I’m going to estimate the contact area of that at around 0.5 m^2. That’s 3.5-5.2 MN, or 350,000-525,000 kgf (770,000-1,157,000 lbf). And given the strain rate at which the pillar shattered, the actually force imparted was probably significantly more than that, but it’s already pretty ridiculous.

And as a side note, if we assume that the mech punches are fairly consistent, then she also was able to catch around that same amount of force with her hands and not move an inch.
Point 3: How much force can Yang dish back out? Let’s not forget that she completely DESTROYED a giant mechanical battlesuit in a single goddamn punch

Wow I’m...gay.
Okay this one is a bit of a challenge since we don’t know what the Atlesian Paladin is made out of. Who even knows what sort of cool metals and alloys they have going on in Remnant. I’m going to use mechanical properties for composite armor, which is what is used for modern tanks (the Paladin is sort of like a really mobile tank, right?).
Quick history, tank armor used to be made primarily from hot-rolled steel, because steel is awesome (really strong, durable, fails in a forgiving way). But unfortunately it wasn’t that great at stopping ballistics, especially as weapons got more sophisticated. Meanwhile the strongest class of materials (ceramics) weren’t used because they’re too brittle and thus prone to shattering, unlike metals which are more ductile and will usually dent or bend upon failure. But with the magic of composites, more modern tank armors like Chobham armor let you take advantage of the super high strength of ceramic materials without having to deal with brittleness and multiple hit capability problems.
That was a tangent, but basically composite armors consist of ultra-strong ceramics enclosed in a metal matrix of some sort (like a sandwich). It seems like the metals used are usually some combination of steel, titanium, aluminum, and alloys of those. We want to know what force it takes to annihilate one of these composites. When Yang punches the mech, it flies away and shatters upon landing. However, she also shatters one of it’s arms directly -- right after she catches the punch. So it’s safe to say that the number we’re looking for is the ultimate tensile strength. UTS is defined as the maximum stress that a material can withstand before fracture, conveniently labeled below.
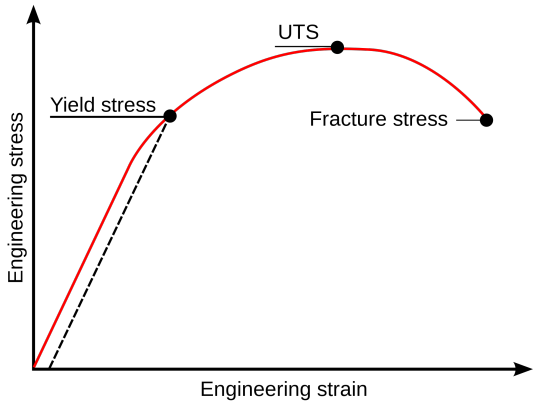
We have a bit of a problem here, which is that a lot of these composite armors are very new in development, and unfortunately most military groups don’t want to share the details of their defense materials and the resultant mechanical properties (very rude of them tbh). I checked out some general ceramic metal composite materials though, and got a fairly massive range of UTS values (like, 600-1900 MPa). We’ll take a relatively high value, since Remnant/Atlas is technologically advanced (giant mecha battle suits, ridiculously good prosthetics, etc.) Assuming UTS between, say, 1700-2000 MPa, then Yang would have to hit the mech with a corresponding amount of force concentrated just on her fist.
Surface area of her fist + Ember Celica we can estimate at 100 cm^2 (0.01 m^2). So that’s 17-20 MN of force in a single punch. Let me write that another way. Yang punches with 20,000,000 Newtons of force. This article says that most boxers punch with a maximum of 5,000 Newtons of force. Yang is 4,000 times stronger than a professional boxer.

I...did not expect THIS crazy of a result going into this, let me tell ya. I think I need to lie down...
Anyway, this was a lot of fun lol. Again, take with a heaping serving of salt since I’m not a professional in any of these areas (my only credential is 3/4 of an undergraduate Materials Science degree).
#this is how I procrastinate now apparently#please give this attention I spent multiple hours on this oh god what has m y life become#yang xiao long#rwby#character analysis + MATH#now where tf are her MUSCLES hmm??#lookin at you roosterteeth animation
92 notes
·
View notes
Text
QUADRATIC EQUATION
5.1 QUADRATIC EQUATION :
This content is part of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations
If P(x) is quadratic expression in variable x, then P(x) = 0 is known as a quadratic equation.

5.1 (a) General form of a Quadratic Equation :
The general form of quadratic equation is ax2 + bx + c = 0, where a,b,c are real numbers and Since , quadratic equations, in general are of the following types :-
(i) b = 0, i.e., of he type ax2 + c=0.
(ii) c = 0, i.e. of the type ax2 + bx = 0.
(iii) b = 0, c = 0, i.e. of the type ax2 = 0.
(iv) , i.e., of the type ax2 + bx + c = 0.
5.2 ROOTS OF A QUADRATIC EQUATION :
The value of x which satisfies the given quadratic equation is known as its root. The roots of the given equation are known as its solution.
General form of a quadratic equation is :
ax2 + bx + c = 0
or 4a2x2 + 4abx + 4ac = - 4ac [Multiplying by 4a]
or 4a2x2 + 4abx = - 4ac [By adding b2 both sides]
or 4a2x2 + 4abc + b2 = b2 - 4ac
or (2ax + b)2 = b2 - 4ac
Taking square root of both the sides
2ax + b =
or
Hence, roots of the quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 are and
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
MP Board Class 12th Maths Book Solutions in Hindi Medium
MP Board Class 12th Maths Chapter 1 संबंध एवं फलन
Chapter 1 संबंध एवं फलन Ex 1.1
Chapter 1 संबंध एवं फलन Ex 1.2
Chapter 1 संबंध एवं फलन Ex 1.3
Chapter 1 संबंध एवं फलन Ex 1.4
Chapter 1 संबंध एवं फलन विविध प्रश्नावली
MP Board Class 12th Maths Chapter 2 प्रतिलोम त्रिकोणमितीय फलन
Chapter 2 प्रतिलोम त्रिकोणमितीय फलन Ex 2.1
Chapter 2 प्रतिलोम त्रिकोणमितीय फलन Ex 2.2
Chapter 2 प्रतिलोम त्रिकोणमितीय फलन विविध प्रश्नावली
MP Board Class 12th Maths Chapter 3 आव्यूह
Chapter 3 आव्यूह Ex 3.1
Chapter 3 आव्यूह Ex 3.2
Chapter 3 आव्यूह Ex 3.3
Chapter 3 आव्यूह Ex 3.4
Chapter 3 आव्यूह विविध प्रश्नावली
MP Board Class 12th Maths Chapter 4 सारणिक
Chapter 4 सारणिक Ex 4.1
Chapter 4 सारणिक Ex 4.2
Chapter 4 सारणिक Ex 4.3
Chapter 4 सारणिक Ex 4.4
Chapter 4 सारणिक Ex 4.5
Chapter 4 सारणिक Ex 4.6
Chapter 4 सारणिक विविध प्रश्नावली
MP Board Class 12th Maths Chapter 5 सांतत्य तथा अवकलनीयता
Chapter 5 सांतत्य तथा अवकलनीयता Ex 5.1
Chapter 5 सांतत्य तथा अवकलनीयता Ex 5.2
Chapter 5 सांतत्य तथा अवकलनीयता Ex 5.3
Chapter 5 सांतत्य तथा अवकलनीयता Ex 5.4
Chapter 5 सांतत्य तथा अवकलनीयता Ex 5.5
Chapter 5 सांतत्य तथा अवकलनीयता Ex 5.6
Chapter 5 सांतत्य तथा अवकलनीयता Ex 5.7
Chapter 5 सांतत्य तथा अवकलनीयता Ex 5.8
Chapter 5 सांतत्य तथा अवकलनीयता विविध प्रश्नावली
MP Board Class 12th Maths Chapter 6 अवकलज के अनुप्रयोग
Chapter 6 अवकलज के अनुप्रयोग Ex 6.1
Chapter 6 अवकलज के अनुप्रयोग Ex 6.2
Chapter 6 अवकलज के अनुप्रयोग Ex 6.3
Chapter 6 अवकलज के अनुप्रयोग Ex 6.4
Chapter 6 अवकलज के अनुप्रयोग Ex 6.5
Chapter 6 अवकलज के अनुप्रयोग विविध प्रश्नावली
MP Board Class 12th Maths Chapter 7 समाकलन
Chapter 7 समाकलन Ex 7.1
Chapter 7 समाकलन Ex 7.2
Chapter 7 समाकलन Ex 7.3
Chapter 7 समाकलन Ex 7.4
Chapter 7 समाकलन Ex 7.5
Chapter 7 समाकलन Ex 7.6
Chapter 7 समाकलन Ex 7.7
Chapter 7 समाकलन Ex 7.8
Chapter 7 समाकलन Ex 7.9
Chapter 7 समाकलन Ex 7.10
Chapter 7 समाकलन Ex 7.11
Chapter 7 समाकलन विविध प्रश्नावली
MP Board Class 12th Maths Chapter 8 समाकलनों के अनुप्रयोग
Chapter 8 समाकलनों के अनुप्रयोग Ex 8.1
Chapter 8 समाकलनों के अनुप्रयोग Ex 8.2
Chapter 8 समाकलनों के अनुप्रयोग विविध प्रश्नावली
MP Board Class 12th Maths Chapter 9 अवकल समीकरण
Chapter 9 अवकल समीकरण Ex 9.1
Chapter 9 अवकल समीकरण Ex 9.2
Chapter 9 अवकल समीकरण Ex 9.3
Chapter 9 अवकल समीकरण Ex 9.4
Chapter 9 अवकल समीकरण Ex 9.5
Chapter 9 अवकल समीकरण Ex 9.6
Chapter 9 अवकल समीकरण विविध प्रश्नावली
MP Board Class 12th Maths Chapter 10 सदिश बीजगणित
Chapter 10 सदिश बीजगणित Ex 10.1
Chapter 10 सदिश बीजगणित Ex 10.2
Chapter 10 सदिश बीजगणित Ex 10.3
Chapter 10 सदिश बीजगणित Ex 10.4
Chapter 10 सदिश बीजगणित विविध प्रश्नावली
MP Board Class 12th Maths Chapter 11 त्रि-विमीय ज्यामिति
Chapter 11 त्रिविमीय ज्यामिति Ex 11.1
Chapter 11 त्रिविमीय ज्यामिति Ex 11.2
Chapter 11 त्रिविमीय ज्यामिति Ex 11.3
Chapter 11 त्रिविमीय ज्यामिति विविध प्रश्नावली
MP Board Class 12th Maths Chapter 12 रैखिक प्रोग्रामन
Chapter 12 रैखिक प्रोग्रामन Ex 12.1
Chapter 12 रैखिक प्रोग्रामन Ex 12.2
Chapter 12 रैखिक प्रोग्रामन विविध प्रश्नावली
MP Board Class 12th Maths Chapter 13 प्रायिकता
Chapter 13 प्रायिकता Ex 13.1
Chapter 13 प्रायिकता Ex 13.2
Chapter 13 प्रायिकता Ex 13.3
Chapter 13 प्रायिकता Ex 13.4
Chapter 13 प्रायिकता Ex 13.5
Chapter 13 प्रायिकता विविध प्रश्नावली
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
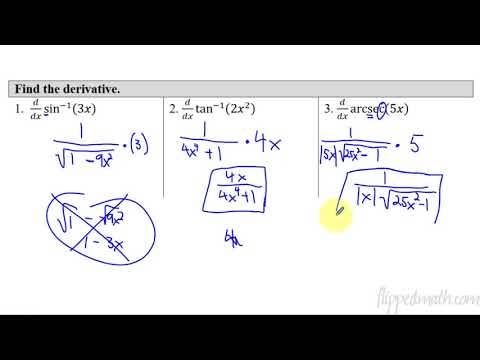
10.4 Usubstitution Trig Functionsap Calculus

10.4 U-substitution Trig Functionsap Calculus Answers
10.4 U-substitution Trig Functionsap Calculus Pdf
10.4 U-substitution Trig Functionsap Calculus Problems
10.4 U-substitution Trig Functionsap Calculus Worksheet
Calculus II, Section 7.4, #67 Integration of Rational Functions by Partial Fractions One method of slowing the growth of an insect population without the use of pesticides is to introduce into the population a number of sterile males that mate with fertile females but produce no o spring. Let P represeent. AP Calculus AB Mu Alpha Theta Welcome to AP Calculus AB! Contact me here. Need more review? Browse the Algebra II and Pre-Calculus Tabs. AP ® Calculus AB and BC. COURSE AND EXAM DESCRIPTION. AP COURSE AND EXAM DESCRIPTIONS ARE UPDATED PERIODICALLY. Please visit AP Central. Mathematics 104—Calculus, Part I (4h, 1 CU) Course Description: Brief review of High School Calculus, methods and applications of integration, infinite series, Taylor's theorem, first order ordinary differential equations. Use of symbolic manipulation and graphics software in Calculus. Note: This course uses Maple®.
Math 104: Calculus I – Notes
Section 004 - Spring 2014
10.4 U-substitution Trig Functionsap Calculus Answers
Syllabus
Concept Videos

Skeleton NotesComplete Notes Title More Remainder 10.6, 10.9 Remainder 10.6/10.9 Series Estimation & Remainder Sections 10.8-10.10 Sections 10.8-10.10 Taylor (and Maclaurin) Series Section 10.7 Section 10.7 Power Series Introduction Section 10.6 Section 10.6 Alt. Series Test and Abs. Conv. Conv. Tests Section 10.5 Section 10.5 The Ratio and Root Tests Section 10.4 Section 10.4 The Comparison Tests Section 10.3 Section 10.3 The Integral Test Section 10.2 Section 10.2 Introduction to Series Section 10.1 Section 10.1 Sequences Section 9.2 Section 9.2 Linear Differential Equations Section 7.2 Pt 1Pt 2 Section 7.2 Separable Differential Equations Section 8.8 Section 8.8 Probability and Calculus Odd Ans. Section 8.7 Pt. 1Pt. 2Section 8.7 Improper Integrals L'Hopital Section 8.4 Pt. 1Pt. 2Section 8.4 Partial Fraction Decomposition Section 8.3 Pt. 1Pt. 2Section 8.3 Trig. Substitution Section 8.2 Pt. 1Pt. 2Section 8.2 Integrating Trig. Powers Section 8.1 Pt. 1Pt. 2 Section 8.1 Integration By Parts Section 6.6 Section 6.6 Center of Mass Section 6.4 Section 6.4 Surface Area of Revolution Section 6.3 Section 6.3 Arc Length Section 6.2Section 6.2 Volumes Using Cylindrical Shells Section 6.1 Section 6.1 Volumes Using Cross-Sections disk/washer Review Calc I Review Calc I ReviewLimit, Derivative, and Integral Area b/w CurvesArea b/w Curves Video Example U-substitution Graphs you should know
Print out the skeleton notes before class and bring them to class so that you don't have to write down https://foxspain82.tumblr.com/post/657282647494672384/achievement-unlocked-2watermelon-gaming. Hide paragraph marks in microsoft word for mac. everything said in class. If you miss anything, the complete notes will be posted after class.
10.4 U-substitution Trig Functionsap Calculus Pdf
My Penn Page | Penn Math 104 Page| Penn Undergraduate Math | Advice | Help|
10.4 U-substitution Trig Functionsap Calculus Problems
10.4 U-substitution Trig Functionsap Calculus Worksheet
Version #1 The course below follows CollegeBoard's Course and Exam Description. Lessons will begin to appear starting summer 2020. BC Topics are listed, but there will be no lessons available for SY 2020-2021
Unit 0 - Calc Prerequisites (Summer Work) 0.1 Summer Packet
Unit 1 - Limits and Continuity 1.1 Can Change Occur at an Instant? 1.2 Defining Limits and Using Limit Notation 1.3 Estimating Limit Values from Graphs 1.4 Estimating Limit Values from Tables 1.5 Determining Limits Using Algebraic Properties (1.5 includes piecewise functions involving limits) 1.6 Determining Limits Using Algebraic Manipulation 1.7 Selecting Procedures for Determining Limits (1.7 includes rationalization, complex fractions, and absolute value) 1.8 Determining Limits Using the Squeeze Theorem 1.9 Connecting Multiple Representations of Limits Mid-Unit Review - Unit 1 1.10 Exploring Types of Discontinuities 1.11 Defining Continuity at a Point 1.12 Confirming Continuity Over an Interval 1.13 Removing Discontinuities 1.14 Infinite Limits and Vertical Asymptotes 1.15 Limits at Infinity and Horizontal Asymptotes 1.16 Intermediate Value Theorem (IVT) Review - Unit 1
Unit 2 - Differentiation: Definition and Fundamental Properties 2.1 Defining Average and Instantaneous Rate of Change at a Point 2.2 Defining the Derivative of a Function and Using Derivative Notation (2.2 includes equation of the tangent line) 2.3 Estimating Derivatives of a Function at a Point 2.4 Connecting Differentiability and Continuity 2.5 Applying the Power Rule 2.6 Derivative Rules: Constant, Sum, Difference, and Constant Multiple (2.6 includes horizontal tangent lines, equation of the normal line, and differentiability of piecewise) 2.7 Derivatives of cos(x), sin(x), e^x, and ln(x) 2.8 The Product Rule 2.9 The Quotient Rule 2.10 Derivatives of tan(x), cot(x), sec(x), and csc(x) Review - Unit 2
Unit 3 - Differentiation: Composite, Implicit, and Inverse Functions 3.1 The Chain Rule 3.2 Implicit Differentiation 3.3 Differentiating Inverse Functions 3.4 Differentiating Inverse Trigonometric Functions 3.5 Selecting Procedures for Calculating Derivatives 3.6 Calculating Higher-Order Derivatives Review - Unit 3
Unit 4 - Contextual Applications of Differentiation 4.1 Interpreting the Meaning of the Derivative in Context 4.2 Straight-Line Motion: Connecting Position, Velocity, and Acceleration 4.3 Rates of Change in Applied Contexts Other Than Motion 4.4 Introduction to Related Rates 4.5 Solving Related Rates Problems 4.6 Approximating Values of a Function Using Local Linearity and Linearization 4.7 Using L'Hopital's Rule for Determining Limits of Indeterminate Forms Review - Unit 4
Unit 5 - Analytical Applications of Differentiation 5.1 Using the Mean Value Theorem 5.2 Extreme Value Theorem, Global Versus Local Extrema, and Critical Points 5.3 Determining Intervals on Which a Function is Increasing or Decreasing 5.4 Using the First Derivative Test to Determine Relative Local Extrema 5.5 Using the Candidates Test to Determine Absolute (Global) Extrema 5.6 Determining Concavity of Functions over Their Domains 5.7 Using the Second Derivative Test to Determine Extrema Mid-Unit Review - Unit 5 5.8 Sketching Graphs of Functions and Their Derivatives 5.9 Connecting a Function, Its First Derivative, and Its Second Derivative (5.9 includes a revisit of particle motion and determining if a particle is speeding up/down.) 5.10 Introduction to Optimization Problems 5.11 Solving Optimization Problems 5.12 Exploring Behaviors of Implicit Relations Review - Unit 5
Unit 6 - Integration and Accumulation of Change 6.1 Exploring Accumulation of Change 6.2 Approximating Areas with Riemann Sums 6.3 Riemann Sums, Summation Notation, and Definite Integral Notation 6.4 The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus and Accumulation Functions 6.5 Interpreting the Behavior of Accumulation Functions Involving Area Mid-Unit Review - Unit 6 6.6 Applying Properties of Definite Integrals 6.7 The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus and Definite Integrals 6.8 Finding Antiderivatives and Indefinite Integrals: Basic Rules and Notation 6.9 Integrating Using Substitution 6.10 Integrating Functions Using Long Division and Completing the Square 6.11 Integrating Using Integration by Parts (BC topic) 6.12 Integrating Using Linear Partial Fractions (BC topic) 6.13 Evaluating Improper Integrals (BC topic) 6.14 Selecting Techniques for Antidifferentiation Review - Unit 6
Unit 7 - Differential Equations 7.1 Modeling Situations with Differential Equations 7.2 Verifying Solutions for Differential Equations 7.3 Sketching Slope Fields 7.4 Reasoning Using Slope Fields 7.5 Euler's Method (BC topic) 7.6 General Solutions Using Separation of Variables 7.7 Particular Solutions using Initial Conditions and Separation of Variables 7.8 Exponential Models with Differential Equations 7.9 Logistic Models with Differential Equations (BC topic) Review - Unit 7
Unit 8 - Applications of Integration 8.1 Average Value of a Function on an Interval 8.2 Position, Velocity, and Acceleration Using Integrals 8.3 Using Accumulation Functions and Definite Integrals in Applied Contexts 8.4 Area Between Curves (with respect to x) 8.5 Area Between Curves (with respect to y) 8.6 Area Between Curves - More than Two Intersections Mid-Unit Review - Unit 8 8.7 Cross Sections: Squares and Rectangles 8.8 Cross Sections: Triangles and Semicircles 8.9 Disc Method: Revolving Around the x- or y- Axis 8.10 Disc Method: Revolving Around Other Axes 8.11 Washer Method: Revolving Around the x- or y- Axis 8.12 Washer Method: Revolving Around Other Axes 8.13 The Arc Length of a Smooth, Planar Curve and Distance Traveled (BC topic) Review - Unit 8
Unit 9 - Parametric Equations, Polar Coordinates, and Vector-Valued Functions (BC topics) 9.1 Defining and Differentiating Parametric Equations 9.2 Second Derivatives of Parametric Equations 9.3 Arc Lengths of Curves (Parametric Equations) 9.4 Defining and Differentiating Vector-Valued Functions 9.5 Integrating Vector-Valued Functions 9.6 Solving Motion Problems Using Parametric and Vector-Valued Functions 9.7 Defining Polar Coordinates and Differentiating in Polar Form 9.8 Find the Area of a Polar Region or the Area Bounded by a Single Polar Curve 9.9 Finding the Area of the Region Bounded by Two Polar Curves Review - Unit 9
Unit 10 - Infinite Sequences and Series (BC topics) 10.1 Defining Convergent and Divergent Infinite Series 10.2 Working with Geometric Series 10.3 The nth Term Test for Divergence 10.4 Integral Test for Convergence 10.5 Harmonic Series and p-Series 10.6 Comparison Tests for Convergence 10.7 Alternating Series Test for Convergence 10.8 Ratio Test for Convergence 10.9 Determining Absolute or Conditional Convergence 10.10 Alternating Series Error Bound 10.11 Finding Taylor Polynomial Approximations of Functions 10.12 Lagrange Error Bound 10.13 Radius and Interval of Convergence of Power Series 10.14 Finding Taylor Maclaurin Series for a Function 10.15 Representing Functions as a Power Series Review - Unit 8
Version #2 The course below covers all topics for the AP Calculus AB exam, but was built for a 90-minute class that meets every other day. Lessons and packets are longer because they cover more material.
Unit 0 - Calc Prerequisites (Summer Work) 0.1 Things to Know for Calc 0.2 Summer Packet 0.3 Calculator Skillz
Unit 1 - Limits 1.1 Limits Graphically 1.2 Limits Analytically 1.3 Asymptotes 1.4 Continuity Review - Unit 1
Unit 2 - The Derivative 2.1 Average Rate of Change 2.2 Definition of the Derivative 2.3 Differentiability (Calculator Required) Review - Unit 2
Unit 3 - Basic Differentiation 3.1 Power Rule 3.2 Product and Quotient Rules 3.3 Velocity and other Rates of Change 3.4 Chain Rule 3.5 Trig Derivatives Review - Unit 3
Unit 4 - More Deriviatvies 4.1 Derivatives of Exp. and Logs 4.2 Inverse Trig Derivatives 4.3 L'Hopital's Rule Review - Unit 4
Unit 5 - Curve Sketching 5.1 Extrema on an Interval 5.2 First Derivative Test 5.3 Second Derivative Test Review - Unit 5
Unit 6 - Implicit Differentiation 6.1 Implicit Differentiation 6.2 Related Rates 6.3 Optimization Review - Unit 6
Unit 7 - Approximation Methods 7.1 Rectangular Approximation Method 7.2 Trapezoidal Approximation Method Review - Unit 7
Unit 8 - Integration 8.1 Definite Integral 8.2 Fundamental Theorem of Calculus (part 1) 8.3 Antiderivatives (and specific solutions) Review - Unit 8
Unit 9 - The 2nd Fundamental Theorem of Calculus 9.1 The 2nd FTC 9.2 Trig Integrals 9.3 Average Value (of a function) 9.4 Net Change Review - Unit 9
Unit 10 - More Integrals 10.1 Slope Fields 10.2 u-Substitution (indefinite integrals) 10.3 u-Substitution (definite integrals) 10.4 Separation of Variables Review - Unit 10
Unit 11 - Area and Volume 11.1 Area Between Two Curves 11.2 Volume - Disc Method 11.3 Volume - Washer Method 11.4 Perpendicular Cross Sections Review - Unit 11

0 notes