#Charlotte Dumas
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

“There is neither happiness nor misery in the world; there is only the comparison of one state with another, nothing more. He who has felt the deepest grief is best able to experience supreme happiness. We must have felt what it is to die, Morrel, that we may appreciate the enjoyments of life." ― Alexandre Dumas, The Count of Monte Cristo
Painting: 'The Count of Monte Cristo' by Mead Schaeffer
#albert camus#poetry#sylvia plath#classical quotes#franz kafka#quotes#classics#literature#booklr#classical literature#alexander dumas#the count of monte cristo#gustave flaubert#madame bovary#three musketeers#dark academia quotes#dark academia#lit#literary quotes#classic literature#excerpts#fragments#dostoevksy#virginia woolf#jane austen#charlotte bronte#book quote#books#penguin classics#don quixote
92 notes
·
View notes
Text









#light academia#gothic literature#books and libraries#books#reading#reading is my therapy#literature#jayne eyre#fairy tales#alexandre dumas#emily bronte#charlotte bronte#hans christian andersen#jane austen#gothic#goth#light aesthetic#classic tales#moodboard
27 notes
·
View notes
Text



Charlotte Tomas - editorial "TI AMO PARIS" for NSS, June 2024
Photographer: Fabien Dumas
source: models.com
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Natalya, Rhea Ripley, Brandi Rhodes, Maryse, TJ Wilson, Nia Jax, Charlotte Flair, Haku, Amy Dumas 💞
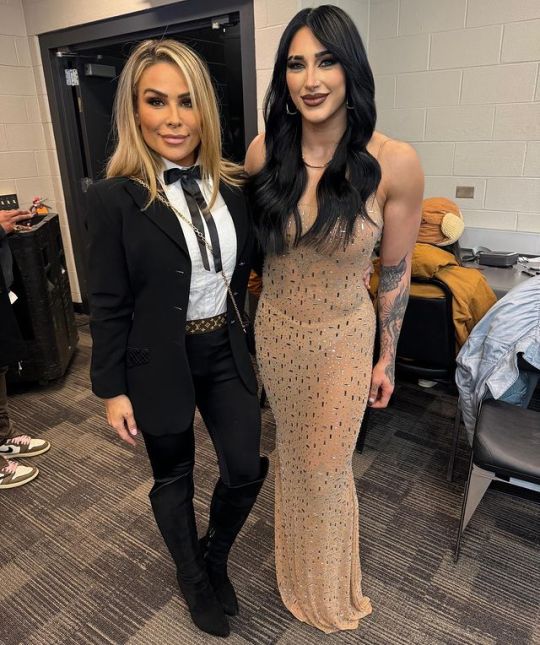
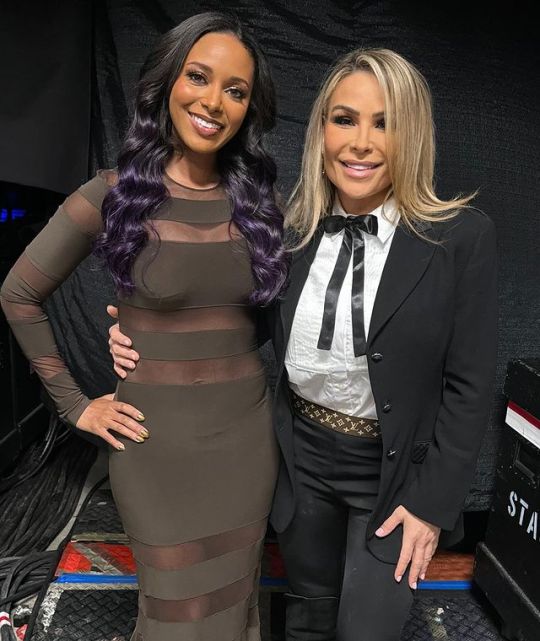
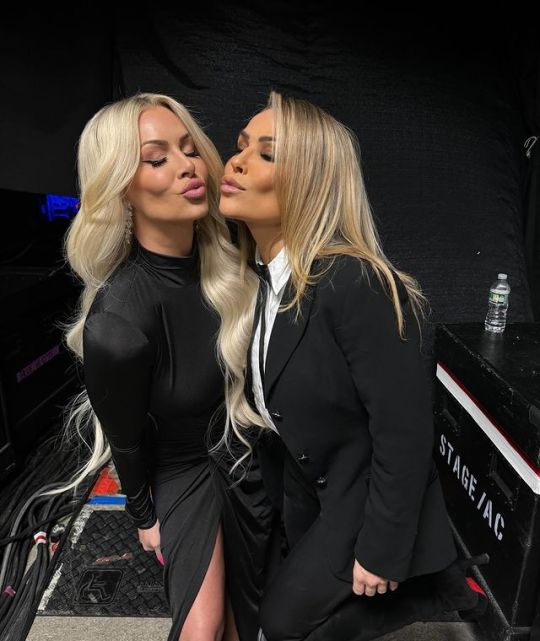
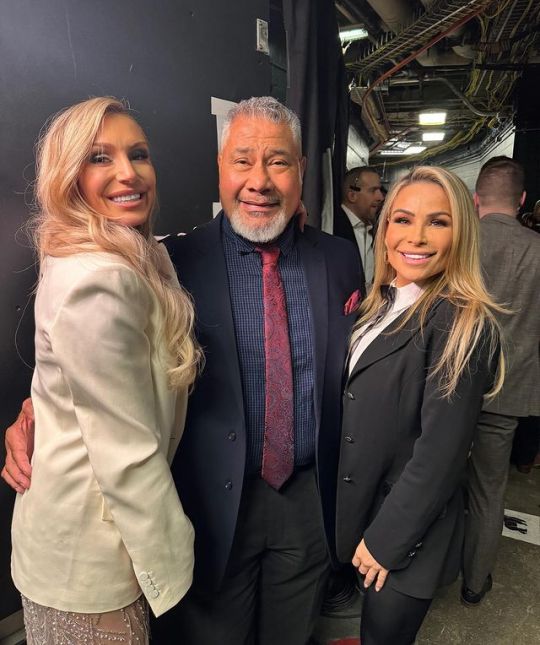
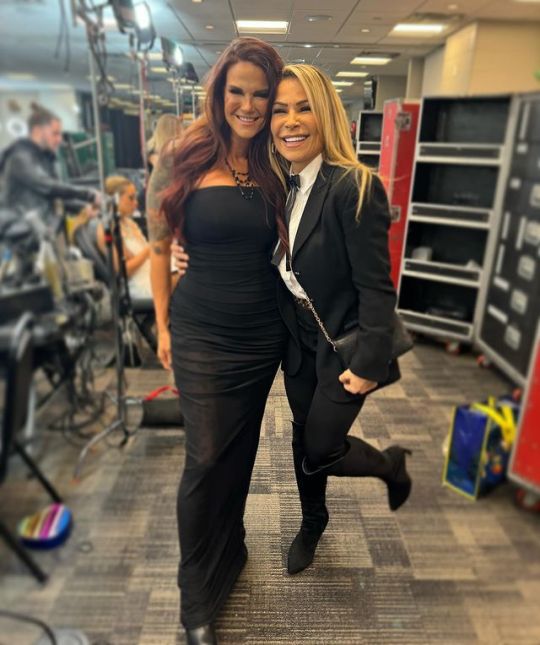







#natalya#rhea ripley#maryse#nia jax#charlotte flair#tyson kidd#raw#friday night smackdown#lita#wwe#brandi rhodes#tj wilson#haku#amy dumas
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
I am watching Queen Charlotte and a wild Ryan Gage appears!!!

I guess they shook up his resume and watched The Musketeers before deciding that yes, this man would be perfect to play the comedic and useless, yet somewhat sympathetic royal.
#lol#ryan gage#queen charlotte#queen charlotte a bridgerton story#prince regent#the musketeers#bbc musketeers#louis xiii#king louis#original post#not incorrect quotes#musketeers#the three musketeers#alexandre dumas#bridgerton
96 notes
·
View notes
Text
19 total
How many have you read?
The BBC estimates that most people will only read 6 books out of the 100 listed below. Reblog this and bold the titles you’ve read.
1 Pride and Prejudice - Jane Austen 2 Lord of the Rings - J. R. R. Tolkein 3 Jane Eyre – Charlotte Bronte 4 Harry Potter series 5 To Kill a Mockingbird - Harper Lee 6 The Bible 7 Wuthering Heights – Emily Bronte 8 Nineteen Eighty Four – George Orwell 9 His Dark Materials – Philip Pullman 10 Great Expectations – Charles Dickens 11 Little Women – Louisa M Alcott 12 Tess of the D’Urbervilles – Thomas Hardy 13 Catch 22 – Joseph Heller 14 Complete Works of Shakespeare 15 Rebecca – Daphne Du Maurier 16 The Hobbit – JRR Tolkien 17 Birdsong – Sebastian Faulks 18 Catcher in the Rye 19 The Time Traveller’s Wife - Audrey Niffeneger 20 Middlemarch – George Eliot 21 Gone With The Wind – Margaret Mitchell 22 The Great Gatsby – F Scott Fitzgerald 23 Bleak House – Charles Dickens 24 War and Peace – Leo Tolstoy 25 The Hitch Hiker’s Guide to the Galaxy – Douglas Adams 26 Brideshead Revisited – Evelyn Waugh 27 Crime and Punishment – Fyodor Dostoyevsky 28 Grapes of Wrath – John Steinbeck 29 Alice in Wonderland – Lewis Carroll 30 The Wind in the Willows – Kenneth Grahame 31 Anna Karenina – Leo Tolstoy 32 David Copperfield – Charles Dickens 33 Chronicles of Narnia – CS Lewis 34 Emma – Jane Austen 35 Persuasion – Jane Austen 36 The Lion, The Witch and The Wardrobe – CS Lewis 37 The Kite Runner - Khaled Hosseini 38 Captain Corelli’s Mandolin - Louis De Bernieres 39 Memoirs of a Geisha – Arthur Golden 40 Winnie the Pooh – AA Milne 41 Animal Farm – George Orwell 42 The Da Vinci Code – Dan Brown 43 One Hundred Years of Solitude – Gabriel Garcia Marquez 44 A Prayer for Owen Meaney – John Irving 45 The Woman in White – Wilkie Collins 46 Anne of Green Gables – LM Montgomery 47 Far From The Madding Crowd – Thomas Hardy 48 The Handmaid’s Tale – Margaret Atwood 49 Lord of the Flies – William Golding 50 Atonement – Ian McEwan
51 Life of Pi – Yann Martel 52 Dune – Frank Herbert 53 Cold Comfort Farm – Stella Gibbons 54 Sense and Sensibility – Jane Austen 55 A Suitable Boy – Vikram Seth 56 The Shadow of the Wind – Carlos Ruiz Zafon 57 A Tale Of Two Cities – Charles Dickens 58 Brave New World – Aldous Huxley 59 The Curious Incident of the Dog in the Night-time – Mark Haddon 60 Love In The Time Of Cholera – Gabriel Garcia Marquez 61 Of Mice and Men – John Steinbeck 62 Lolita – Vladimir Nabokov 63 The Secret History – Donna Tartt 64 The Lovely Bones - Alice Sebold 65 Count of Monte Cristo – Alexandre Dumas 66 On The Road – Jack Kerouac 67 Jude the Obscure – Thomas Hardy 68 Bridget Jones’s Diary – Helen Fielding 69 Midnight’s Children – Salman Rushdie 70 Moby Dick – Herman Melville 71 Oliver Twist – Charles Dickens 72 Dracula – Bram Stoker 73 The Secret Garden – Frances Hodgson Burnett 74 Notes From A Small Island – Bill Bryson 75 Ulysses – James Joyce 76 The Bell Jar – Sylvia Plath 77 Swallows and Amazons - Arthur Ransome 78 Germinal – Emile Zola 79 Vanity Fair – William Makepeace Thackeray 80 Possession – AS Byatt 81 A Christmas Carol – Charles Dickens 82 Cloud Atlas – David Mitchel 83 The Color Purple – Alice Walker 84 The Remains of the Day – Kazuo Ishiguro 85 Madame Bovary – Gustave Flaubert 86 A Fine Balance – Rohinton Mistry 87 Charlotte’s Web – EB White 88 The Five People You Meet In Heaven – Mitch Albom 89 Adventures of Sherlock Holmes – Sir Arthur Conan Doyle 90 The Faraway Tree Collection – Enid Blyton 91 Heart of Darkness – Joseph Conrad 92 The Little Prince – Antoine De Saint-Exupery 93 The Wasp Factory – Iain Banks 94 Watership Down – Richard Adams 95 A Confederacy of Dunces – John Kennedy Toole 96 A Town Like Alice – Nevil Shute 97 The Three Musketeers – Alexandre Dumas 98 Hamlet – William Shakespeare 99 Charlie and the Chocolate Factory – Roald Dahl 100 Les Miserables – Victor Hugo
#4 Harry Potter series#5 To Kill a Mockingbird - Harper Lee#9 His Dark Materials – Philip Pullman#10 Great Expectations – Charles Dickens#11 Little Women – Louisa M Alcott#16 The Hobbit – JRR Tolkien#29 Alice in Wonderland – Lewis Carroll#30 The Wind in the Willows – Kenneth Grahame#33 Chronicles of Narnia – CS Lewis#36 The Lion#The Witch and The Wardrobe – CS Lewis#40 Winnie the Pooh – AA Milne#46 Anne of Green Gables – LM Montgomery#61 Of Mice and Men – John Steinbeck#73 The Secret Garden – Frances Hodgson Burnett#81 A Christmas Carol – Charles Dickens#87 Charlotte’s Web – EB White#91 Heart of Darkness – Joseph Conrad#97 The Three Musketeers – Alexandre Dumas#99 Charlie and the Chocolate Factory – Roald Dahl
73K notes
·
View notes
Text










her style♥️
#natasha goldenberg#mira duma#miroslava duma#proenza schouler#missoni#Prada#miuccia prada#miu miu#charlotte olympia#lanvin#valentino#Balenciaga#isabel marant#pregnant photo#pregnant style#2011#2012
1 note
·
View note
Text
✨Jason Todd's Bookshelf✨
i think it's so interesting to see what books Jason Todd would read/own, so here's my own contribution! some of these are canon* (hence the *), some are popular headcanons and some are my own speculation. i'll probably continue to add to this.



The Count of Monte Cristo by Alexandre Dumas*
Pride & Prejudice by Jane Austen*
1984 by George (Wh)Orwell*
The Prince by Machiavelli*
The Complete Works of Sir Arthur Conan Doyle*
The Art of War by Sun Tzu*
Hamlet*
An additional complete works of William Shakespeare
Jane Eyre by Charlotte Brontë
Northanger Abbey by Jane Austen
One Hundred Years of Solitude by Gabriel García Márquez
Notes on an Execution by Danya Kukafka
Slouching Towards Bethlehem by Joan Didion
Catcher in the Rye by J.D Salinger
i think Holden Caulfield secretly reminds him of Bruce
One Flew Over the Cuckoo's Nest by Ken Kesey
Frankenstein by Mary Shelley
Beloved by Toni Morrison
The Brothers Karamazov by Fyodor Dostoyevsky
The Metamorphosis and The Trial by Franz Kafka
specifically owns a copy that has both of them in there
Fight Club by Chuck Palahniuk
this may be a bit on the nose, but Jason would love a good satire
The Invisible Man by Ralph Ellison
Dream of the Red Chamber by Cao Xueqin
Such a Fun Age by Kiley Reid
Trainspotting by Irvine Welsh
Starling House by Alix E. Harrow
The Road by Cormac McCarthy
Hayy ibn Yaqdhan by Ibu Tufail
East of Eden by John Steinbeck
but lowkey he hates it
Little Women by Louisa May Alcott
The Stranger by Albert Camus
The Iliad by Homer
The Outsiders by S.E Hinton
i don't see Jason as being a big fantasy/sci-fi guy unless it falls under the magical realism or gothic categories (i.e, Beloved, Frankenstein), however i do think he would jive with Ray Bradbury, Douglas Adams, Terry Pratchett and (unfortunately) Harlan Ellison
i can also see him jiving with R.F Kuang and i think The Poppy War specifically would be an exception to his usual disinterest in fantasy
i think he maybe also has a stash of paperback Star Wars novels stashed away somewhere
if jason is a theatre kid into adulthood, i think he would be the kind that reads solely straight plays
Fat Ham by James Ijames
Complete Works of Arthur Miller
Everybody by Branden Jacobs-Jenkins
he typically avoids stuff that’s so directly about mortality, but this play would really resonate with him and honestly be a healing read
being the hater that he is, he's also hate read at least one Collen Hoover book (and promptly left it in the Batcave to frame Bruce for the crime)
#i put too much thought into this but this is so much fun#jason todd#red hood#jason todd headcanon#red hood headcanon#bat family#kenobers poetics
176 notes
·
View notes
Text
the martyrer than thou syndrome that reblogger had lmao
European history is not white


Someone commented this to a post I reblogged, which message is basically "we shouldn't venerate the Dead White Man HistoryTM and we should elevate other history too, but we still need to learn Dead White Man HistoryTM to understand the world today". It's basically a response to the attitude you sometimes come across in the internet that sees learning about those Dead White MenTM as not worth our time. And this person, who seems to be following this blog because they responded to my reblog, takes it as a personal attack against all white Europeans. For some reason. Well I take these comments as a personal attack against historical understanding.
Firstly, the post clearly didn't say you shouldn't venerate any European history, because not all European history is Dead White Man HistoryTM. Obviously this person thinks European history is white, which is not true, but surely, surely, they know it's not all men? Secondly, what is "west culture"? When did it start? There is not one western culture, not one European culture. The first concept of some shared Europeanness was the Christendom in Middle Ages, but it was not exactly the same as we think of Europe today, because it did not include the pagan areas, but it included a lot of Levant and parts of Central Asia, where there were large Christian areas. And Europe was not "very white" nor was the Christendom. The more modern concept of West was cooked in tandem with race and whiteness during colonial era and Enlightenment, around 17th to 18th centuries. And Europe was certainly not very white then. The western world also includes a lot of colonized areas, so that's obviously not white history. Thirdly, implying that asking white people to apologize for European history (which no one did ask) is as ridiculous as asking black people for African history is... a choice. Black people do exist in a lot of other places than Africa, which white people should be the ones apologizing for, and really white people also have a lot to answer for about African history. Lastly, if you think the quote "anyone who thinks those dead white guys are aspirational is a white supremacist" means you as an European are demanded to apologize for your existence, maybe - as we say in Finland - that dog yelps, which the stick clanks. (I'm sorry I think I'm the funniest person in the world when I poorly translate Finnish sayings into English.)
The thing is, there is no point in European history, when Europe was white, for three reasons. 1) Whiteness was invented in 17th century and is an arbitrary concept that has changed it's meaning through time. 2) Whichever standard you use, historical or current, Europe still has never been all or overwhelmingly white, because whiteness is defined as the in-group of colonialists, and there has always been the internal Other too. In fact the racial hierarchy requires an internal Other. 3) People have always moved around a lot. The Eurasian steppe and the Mediterranean Sea have always been very important routes of migration and trade. I've been meaning to make a post proving exactly that to people like this, since as I've gathered my collection of primary images of clothing, I've also gathered quite a lot of European primary images showing non-white people, so I will use this opportunity to write that post.
So let's start from the beginning. Were the original inhabitants of Europe white? Of course not. The original humans had dark skin so obviously first Europeans had dark skin. Whenever new DNA evidence of dark skinned early Europeans come out (like this study), the inevitable right-wing backlash that follows is so interesting to me. Like what did you think? Do you still believe the racist 17th century theories that white people and people of colour are literally different species? I'm sure these people will implode when they learn that studies (e.g. this) suggest in fact only 10 000 years ago Europeans had dark skin, and even just 5 000 years ago, when Egypt (an many others) was already doing it's civilization thing, Europeans had brown skin (another source). According to the widely accepted theory, around that time 5 000 years ago the Proto-Indo-European language developed in the Pontic-Caspian steppe, which extends from Eastern Europe to Central Asia. These Proto-Indo-Europeans first migrated to Anatolia and then to Europe and Asia. Were they white? Well, they were probably not light skinned (probably had brown skin like the other people living in Europe around that time), the Asian branch of Indo-European peoples (Persians, most Afghans, Bengalis, most Indians, etc.) are certainly not considered white today and a lot of the people today living in that area are Turkic and Mongolic people, who are also not considered white. I think this highlights how nonsensical the concept of race is, but I don't think Proto-Indo-Europeans would have been considered white with any standard.
Around Bronze Age light skin became common among the people in Europe, while in East Asia it had become wide spread earlier. This does not however mark the point when "Europe became white". During the Bronze Age there was a lot of migration back and forth in the Eurasian steppe, and the early civilizations around Mediterranean did a lot of trade between Europe, Africa and Asia, which always means also people settling in different places to establish trading posts and intermarrying. There were several imperial powers that also stretched to multiple continents, like the briefly lived Macedonian Empire that stretched from Greece to Himalayas and Phoenicians from Levant, who didn't built an empire but settled in North Africa, Sicily and Iberia. In Iron Age the Carthaginian Empire, descendants of Phoenician settlers in current Tunisia, build an Empire that spanned most of the western Mediterranean coast. Their army occupying that area included among others Italic people, Gauls, Britons, Greeks and Amazigh people.
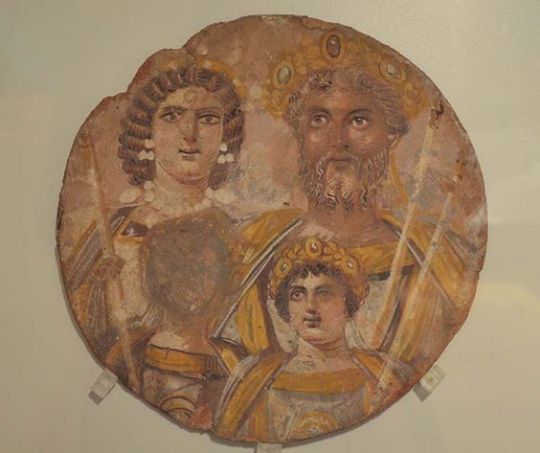
Iron Age also of course saw the rise of the Roman Republic, and later empire, but it was preceded by Etruscans, who populated Tuscan, and possibly preceded the Indo-European presence. However, weather through trade and migration with other Mediterraneans or the continuing presence of darker skin tones of the early Europeans, their art quite often depicts darker skin tones too, like seen below in first two images. Roman Empire at it's height spanned from Babylonia to the British Isles. They recruited soldiers from all provinces and intentionally used stationed them in different areas so they wouldn't be too sympathetic to possible rebels or neighboring enemies. Historical sources mention black Nubian soldiers in British Isles for example. They also built a lot of infrastructure around the empire to ensure protection and easy transportation through trade routes inside the empire. During this time Jewish groups also migrated from Levant to both North-Africa and Europe. Rome even had non-European emperors, like Septimius Severus who originated from Levant and was Punic (descendants of Phoenicians) from his father's side, and who was depicted with darker skin (third picture below). Various ethnicities with differing skin tones are represented all over Roman art, like in the fourth picture below from hunting lodge in Sicily.




Eurasian steppe continued to be important source of migration and trade between Europe and Asia. Scythians, Iranic nomadic people, were important for facilitating the trade between East Asia and Europe through the silk road during the Iron Age. They controlled large parts of Eastern Europe ruling over Slavic people and later assimilating to the various Slavic groups after loosing their political standing. Other Iranic steppe nomads, connected to Scythian culture also populated the Eurasian steppe during and after Scythia. During the Migration Period, which happened around and after the time of Western Rome, even more different groups migrated to Europe through the steppe. Huns arrived from east to the Volga region by mid-4th century, and they likely came from the eastern parts of the steppe from Mongolian area. Their origins are unclear and they were either Mongolic, Turkic or Iranic origin, possibly some mix of them. Primary descriptions of them suggests facial features common in East Asia. They were possibly the nomadic steppe people known as Xiongnu in China, which was significant in East and Central Asia from 3rd century BCE to 2nd century CE until they moved towards west. Between 4th and 6th centuries they dominated Eastern and Central Europe and raided Roman Empire contributing to the fall of Western Rome.
After disintegration of the Hun Empire, the Huns assimilated likely to the Turkic arrivals of the second wave of the Migration Period. Turkic people originate likely in southern Siberia and in later Migration period they controlled much of the Eurasian steppe and migrated to Eastern Europe too. A Turkic Avar Khagenate (nation led by a khan) controlled much of Eastern Europe from 6th to 8th century until they were assimilated to the conquering Franks and Bulgars (another Turkic people). The Bulgars established the Bulgarian Empire, which lasted from 7th to 11th in the Balkans. The Bulgars eventually adopted the language and culture of the local Southern Slavic people. The second wave of Migration Period also saw the Moor conquest of Iberia and Sicily. Moors were not a single ethnic group but Arab and various Amazigh Muslims. Their presence in the Iberian peninsula lasted from 8th to 15th century and they controlled Sicily from 9th to 11th century until the Norman conquest. During the Norman rule though, the various religious and ethnic groups (which also included Greeks and Italic people) continued to live in relative harmony and the North-African Muslim presence continued till 13th century. Let's be clear that the Northern Europe was also not white. Vikings also got their hands into the second wave migration action and traveled widely to east and west. Viking crews were not exclusively Scandinavians, but recruited along their travels various other people, as DNA evidence proves. They also traded with Byzantium (when they weren't raiding it) and Turkic people, intermarried and bought slaves, some of which were not white or European. A Muslim traveler even wrote one of the most important accounts of Vikings when encountering them in Volga.
By this point it should already be clear that Medieval Europe was neither white, but there's more. Romani people, who originate from India and speak Indo-Aryan language, arrived around 12th century to Balkans. They continued to migrate through Europe, by 14th century they were in Italy, by 15th century in Germany and by 16h century in Britain and Sweden. Another wave of Romani migration from Persia through North-Africa, arrived in Europe around 15th century. Then there's the Mongol Empire. In 13th century they ruled very briefly a massive portion of the whole Eurasian continent, including the Eastern Europe. After reaching it's largest extent, it quickly disintegrated. The Eurasian Steppe became the Golden Horde, but lost most of the Eastern-Europe, except Pontic-Caspian Steppe. They ruled over Slavs, Circissians, Turkic groups and Finno-Ugric groups till early 15th century. The Mongolian rulers assimilated to the Turkic people, who had been the previous rulers in most of the steppe. These Turkic people of the Golden Horde came to be known as Tatars. Golden Horde eventually split into several Tatar khagenates in 15th century, when the khagenates, except the Crimean Khagenate, were conquered by the Tsardom of Moscovy. Crimean Khagenate was annexed by the Russian Empire in 1783. Crusades were a movement from Europe to Levant, but they also meant intermarriage in the the Crusader kingdoms especially between the European and Levant Christians, and some movement back and froth between these kingdoms and Europe, trade and a lot of movement back after the Crusader kingdoms were defeated in 13th century. Generally too trade across the Mediterranean sea was extensive and led to migration and intermarriage.
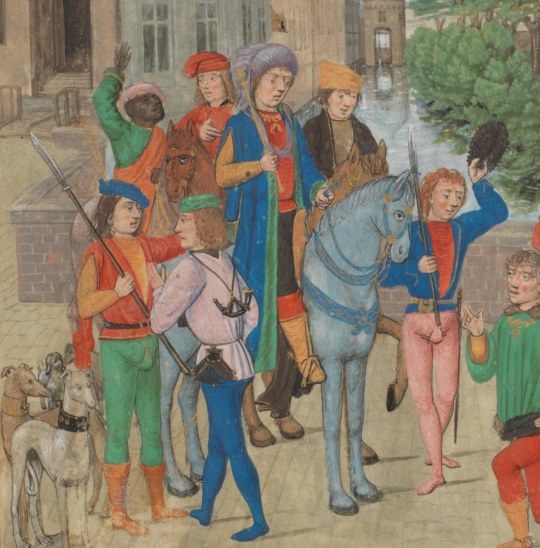
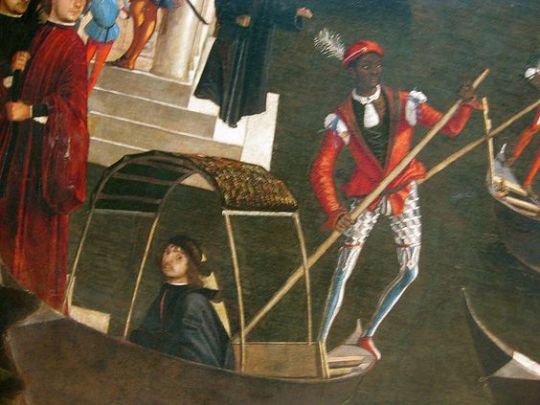
And here's some example of people of colour in Medieval European art, shown as part of the majority white European societies. First is from a 15th century French manuscript depicting Burgundy court with dark skin courtier and lady in waiting. Second one is from a Flemish manuscript from 15th century of courtiers, including a black courtier, going for a hunt. Third is a 15th century Venetian gondolier with dark skin.



In Renaissance Era Europe was only increasing it's trade and therefore had even more connections outside Europe. The first picture below is Lisbon, which had strong trade relationship with Africa, depicted in late 16th century. People with darker skin tones were part all classes. Second image is an Italian portrait of probably a seamstress from 16th century. Third one is a portrait of one of the personal guards of the Holy Roman Emperor. Fourth image is a portrait of Alessandro de' Medici, duke of Florence, who was noted for his brown complexion, and the modern scholarly theory is that his mother was a (likely brown) Italian peasant woman.




Colonialism begun in the Renaissance Era, but the wide spread colonial extraction and slavery really got going in the 17th century. Racial hierarchy was developed initially to justify the trans-Atlantic slave trade specifically. That's why the early racial essentialism was mostly focused on establishing differences between white Europeans and black Africans. Whiteness was the default, many theories believed humans were originally white and non-whites "degenerated" either through their lives (some believed dark skin was basically a tan or a desease and that everyone was born white) or through history. Originally white people included West-Asians, some Central-Asians, some North-Africans and even sometimes Indigenous Americans in addition to Europeans. The category of white inevitably shrank as more justifications for atrocities of the ever expanding colonial exploitation were required. The colonial exploitation facilitated development of capitalism and the industrial revolution, which led to extreme class inequality and worsening poverty in the European colonial powers. This eventually became an issue for the beneficiaries of colonialism as worker movements and socialism were suddenly very appealing to the working class.
So what did the ruling classes do? Shrink whiteness and give white working classes and middle classes justifications to oppress others. Jews and Roma people had long been common scapegoats and targets of oppression. Their oppression was updated to the modern era and racial categories were built for that purpose. The colonial powers had practiced in their own neighborhoods before starting their colonial projects in earnest and many of those European proto-colonies were developed to the modern colonial model and justified the same way. In 19th century, when racial pseudoscience was reaching it's peak, Slavs, others in Balkan, the Irish (more broadly Celts), Sámi (who had lost their white card very early), Finns, Southern Italians, the Spanish, the Southern French and Greeks all were considered at least not fully white. The Southern Europeans and many Slavs were not even colonized (at least in the modern sense, though with some cases like Greeks it's more complicated than that), but they looked too much and were culturally too similar to other non-white Mediterraneans, and they were generally quite poor. In many of these cases, like Italians, the French and Slavs, it was primarily others belonging in the same group, who were making them into second class citizens. All this is to highlight how very malleable the concept of race is and that it's not at all easy to define the race of historical people.
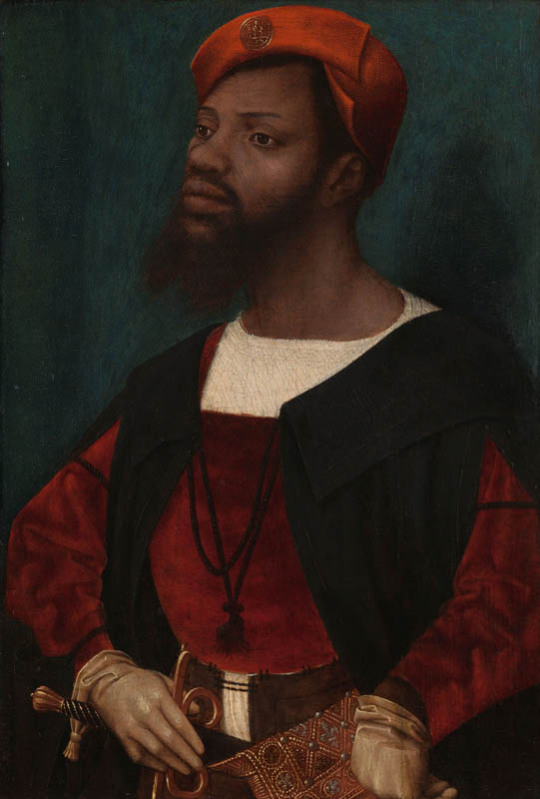
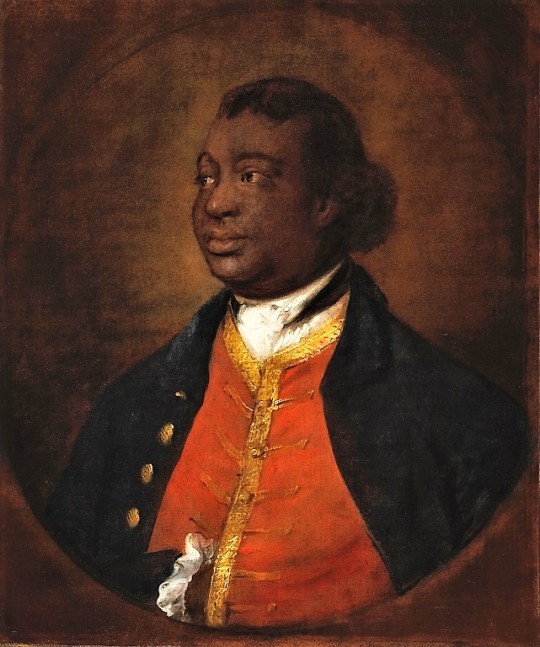
However, even if we would go with the racial categories of today, Europe was still far from being all white in this period. You had Roma, who certainly are not included in whiteness today, and European Jews, whose whiteness is very conditional, descendants of Moors in Southern Europe and Tatars and Turks in Eastern Europe and Turkey, which today is often not thought of as part of Europe, but historically certainly was. And then colonialism brought even more people into Europe forcibly, in search of work because their home was destroyed or for diplomatic and business reasons. There were then even more people of colour, but they were more segregated from the white society. Black slaves and servants are very much represented in European art from 17th century onward, but these were not the only roles non-white people in Europe were in, which I will use these examples to show. First is a Flemish portrait of Congo's Emissary, Dom Miguel de Castro, 1643. Second is a 1650 portrait of a Moorish Spanish man Juan de Pareja, who was enslaved by the artist as artisanal assistant, but was freed and became a successful artist himself. Third is a 1768 portrait of Ignatius Sancho, a British-African writer and abolitionist, who had escaped slavery as a 20-year-old. Fourth painting is from 1778 of Dido Elizabeth Belle, a British gentlewoman born to a slave mother who was recognized as a legitimate daughter by her father, and her cousin. The fifth portrait is of an unknown woman by (probably) a Swiss painter from late 18th century. Sixth is a 1760s Italian portrait of a young black man.



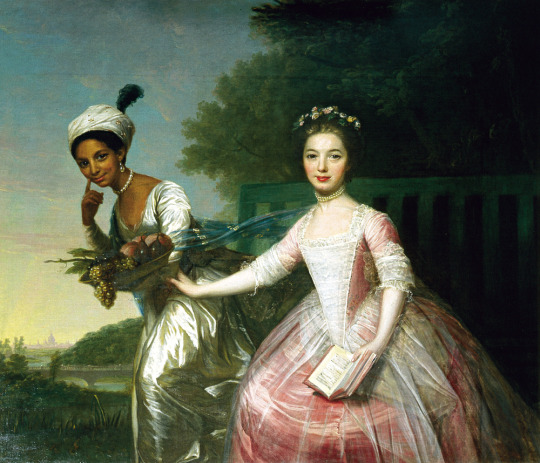
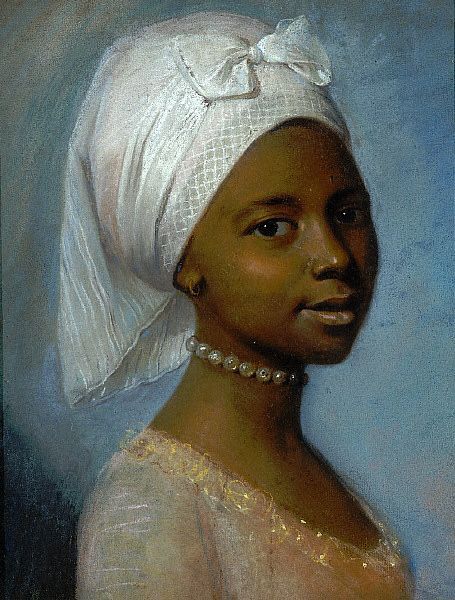

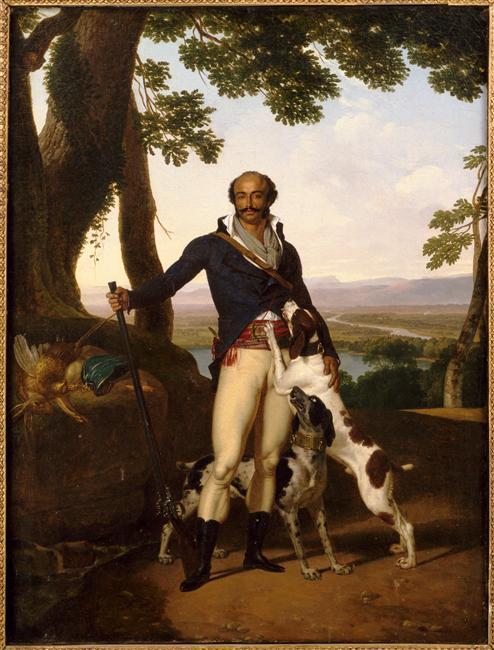
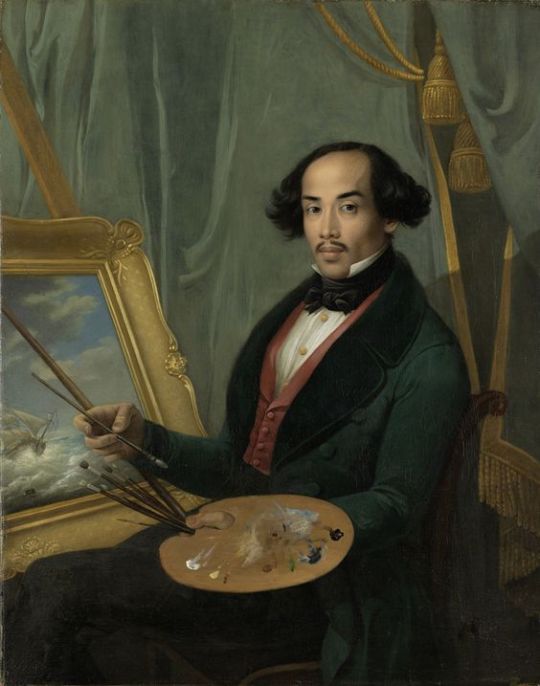
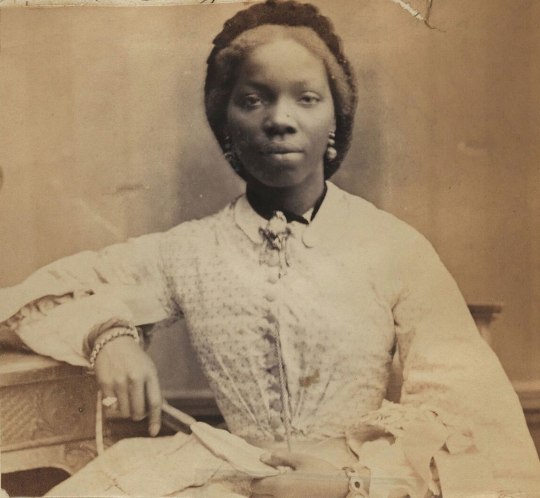
In late 18th century England abolished slavery in British Isles first, then in early 19th century in the whole British Empire, thanks to the continuous campaign of free Black people and some white allies, notably Quakers. Around the same time slavery was abolished in France (briefly till Napoleon got to power) after the French revolution. This meant there were a lot more free black people in Europe after that. In 18th century the Europeans, British especially, were colonizing Asia as much they could, which meant that in 19th century there started to also be a lot more Asian, especially Indian people in Europe. First picture below is of Thomas Alexander Dumas, who was son of a black slave woman and a white noble French man and became a general in the French revolutionary army. His son was one of the most well-known French authors, Alexander Dumas, who wrote The Count of Monte Cristo and The Three Musketeers. Second portrait is of Jean-Baptiste Belley, a Senegalese former slave, who became French revolutionary politician. Third portrait is from 1810 of Dean Mahomed, an Indian-British entrepreneur, who established the first Indian restaurant in London. Forth is Arab-Javanese Romantic painter Saleh Syarif Bustaman, who spend years in Europe. Fifth is a 1862 photo of Sara Forbes Bonnetta, originally named Aina, princess of Edbago clan of Yoruba, who was captured into slavery as a child, but later freed and made Queen Victoria's ward and goddaughter. She married a Nigerian businessman, naval officer and statesman, James Pinson Labulo Davies (sixth picture).






So any guesses on at what point was that "very white Europe" when the "west culture" begun? It kinda seems to me that it never actually existed.
#People forget that Dumas father was literally the first black man to become a brigadier general in Francs#“Slavery is an all black thing; and wealth / nobility an all white thing” ALLOW ME TO DIFFER. Wealth and slavers wasn’t an all race thing.#Also the “we need to make queen Charlotte black because there are not enough black royals / noblemen” is wrong#Like what about the kings and emperors of Haiti? The kingdom of Ndongo?#Also Indian royalty is sooo erased from Hollywood and when represented is soooo stereotypical
201 notes
·
View notes
Text
#big shout out to @vickythestrange @the-mad-woman-in-the-attic and @suburban-critic for the suggestions#classic literature#dracula#mina murray#lucy westenra#mina murray x lucy westenra#anne of green gables#anne shirley#diana barry#anne shirley x diana barry#bleak house#esther summerson x ada claire#jane eyre#helen burns#pride and prejudice#charlotte lucas#elizabeth bennet#emma woodhouse x harriet smith#emma jane austen#northanger abbey#catherine morland#eleanor tilney#as you like it#shakespeare#celia x rosalind#the count of monte cristo
78 notes
·
View notes
Text




Charlotte Tomas - editorial "TI AMO PARIS" for NSS, June 2024
Photographer: Fabien Dumas
source: models.com
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

Duma and Lena dressed up as Meir and Charlotte (Vampire Hunter D: Bloodlust) this Halloween 🎃
#Duma#fire emblem heroes#fire emblem echoes#fire emblem#fe1#shadows of valentia#sov#echoes#fe#divine dragon#manakete#feh#fe oc#summoner oc#my art#ive had this idea in my brain for too dang long
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
That voice. It was- familiar. Too familiar. Turning slowly on her heel, verdant irises fall on the untriggered Crescent wolf, tears almost immediately blurring her vision behind dark lashes as realization as to who it belonged to registered and it took everything in her not to immediately pull the other woman into a tight embrace. It had been years since she seen the other, her passing having had hit Charlie just as hard as Jackson’s had, her best friend and cousin gone only to be followed by her grandmother a few years later. Devastating blows that had put the younger Kenner through hell, struggling to get through but managing for the sake of her husband and children. “I, unfortunately, am on duty, gram,” Charlotte retorts, blinking back the tears that had threatened to spill. “No drinks for me until I’ve gotten back home for the night.”

"you heard her, bugger off." mary spoke, eyes glaring at the others. while this wasn't the charlie she knew from her time, she could always sense a kenner and she still had that charlie voice to her. "and you, missy, should be listening to your own advice. grab a drink and relax."

#c. Mary Dumas#~Unburn the ashes unchain the reactions now not ready to die not yet pull me out of the train wreck; charlotte kenner
35 notes
·
View notes
Photo










My book collection so far
Jane Austen - Pride and Prejudice
Emily Bronte - Wuthering Heights
Louisa May Alcott - Little Women
Charlotte Bronte - Jane Eyre
Jane Austen - Sense and Sensibility
Edith Wharton - The Age Of Innocence
Jane Austen - Emma
Gustave Flaubert - Madame Bovary
Jane Austen - Northanger Abbey
Edith Wharton - The House of Mirth
Jane Austen - Persuasion
Louisa May Alcott - Good Wives
Nathaniel Hawthorne - The Scarlet Letter
Charlotte Bronte - The Professor
Leo Tolstoy - Anna Karenina (Part 1)
Leo Tolstoy - Anna Karenina (Part 2)
Jane Austen - Mansfield Park
Anne Bronte - Agnes Grey
Thomas Hardy - Far from The Madding Crowd
William Makepeace Thackeray - Vanity Fair (Part 1)
William Makepeace Thackeray - Vanity Fair (Part 2)
Pierre-Ambroise-François Choderlos de Laclos - Dangerous Liaisons
Alexandre Dumas fils - The Lady of the Camellias
Henry James - Washington Square
Louisa May Alcott - A Garland For Girls
Henry James - The Portrait of A Lady (Part 1)
Henry James - The Portrait of A Lady (Part 2)
Jane Austen - Lady Susan. The Watson. Sanditon
Anne Brontë - The Tenant of Wildfell Hall
Thomas Hardy - Tess of the D’Urbeville
Edith Wharton - The Mother’s Recompense
Daniel Defoe - Moll Flanders
Henry James - The Wings of the Dove
Edith Wharton - The Customs of the Country
Kate Chopin - The Awakening
Jane Austen - Juvenilia
George Eliot - Middlemarch (Part 1)
George Eliot - Middlemarch (Part 2)
George Sand - Nanon
Henry James - The Ambassadors
Elizabeth Gaskell - Cranford
Thomas Hardy - Under The Greenwood Tree
Edith Wharton - Summer
George Sand - Indiana
Henry James - The Bostonians
George Eliot - Silas Marner
Henry James - The Golden Bowl (Part 1)
Henry James - The Golden Bowl (Part 2)
Edith Wharton - The Twilight Sleep
Emily Eden - The Semi-Attached Couple
Edith Wharton - The Glimpses of the Moon
Mary Elizabeth Braddon - Lady Audley’s Secret
George Eliot - The Mill on the Floss
Elizabeth Gaskell - Mary Barton
Fanny Burney - Evelina
George Sand - Little Fadette
Emily Eden - The Semi-detached House
Charlotte Brontë - Shirley I
Charlotte Brontë - Shirley II
Daniel Defoe - Lady Roxana
Theodor Fontane - Effie Briest
Edith Wharton - The Cliff
Thomas Hardy - Two on a Tower
Frances Hodgson Burnett - A Lady of Quality
Louisa May Alcott - Moods
Edith Nesbit - The Incomplete Amorist
Frances Trollope - The Widow Barnaby (Part 1)
#storie senza tempo#books#book collection#classical literature#literature#american literature#german literature#english literature#french literature#jane austen#russian literature#pride and prejudice#emma#sense and sensibility#edith wharton#lady roxana#moll flanders#anna karenina#lev tolstoy#bronte sisters#jane eyre#wuthering heights#the age of innocence#little women#louisa may alcott#timeless classics#romans eternels#novelas eternas#middlemarch#george eliot
278 notes
·
View notes
Note
Some recommendations of classics, not organized just what came to mind
Jane Eyre by Charlotte Brontë
Sherlock Holmes stories by Arthur Conan Doyle (he’s at his best in short story format but Hounds of the Baskervilles is the best novel)
The Picture of Dorian Gray by Oscar Wilde
Frankenstein by Mary Shelley
The Strange Case of Dr. Jekyll and Mr. Hyde by Robert Louis Stevenson
The Woman in White by Wilkie Collins
The Count of Monte Cristo by Alexandre Dumas
Bleak House by Charles Dickens
Rebecca by Daphne du Maurier
My Cousin Rachel by Daphne du Maurier
Till We Have Faces by CS Lewis
You mentioned the Odyssey so the Iliad if you have not read it already
I can do more genre specific if you would like and if you want Golden Age mystery I will have many opinions
Oh my god, this is delightful! Thank you!
I've read a handful of these, but a couple could really use a refresher. A lot of the ones associated with Halloween-time I did in the last couple of years, but there are absolutely some I haven't read and find promising.
The Count of Monte Cristo really is something I absolutely should read and definitely needs to be on my list for next year!I knew I wanted to do more Dickens, but didn't actually know a ton of titles off the top of my head for his books, so thank you for Bleak House. I had never herad of Rebecca or Daphne du Maurier, so that's probably a must read if not even the author is on my radar! I did The Chronicles of Narnia as a kid and never thought to check out anything else by CS Lewis so that's actually a really great idea. And yes! In my brain, The Odyssey and the Iliad are interchangeable so those are likely MUST reads so my brain can't try to do that to me anymore XD
I will be tagging this to find again around the new year, but wanted to post now to show my appreciation and get out there the kind of thing I'm trying to do.
I traditionally also just haven't done mystery, but that means I'm especially ignorant to the type of stuff that formed the modern day landscape of the genre and might be really fun!
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
One Hundred Books
Decided to make this list in order to include in one post all the books that I found to be worth reading and would recommend to others. They're not in a specific order:
The Book Thief by Markus Zusak
Mrs. Dalloway by Virginia Woolf
Murder on the Orient Express by Agatha Christie
Dubliners by James Joyce
A Jounal of the Plague Year by Daniel Defoe
One Hundred Years of Solitude by Gabriel Garcia Marquez
Girl with a Pearl Earring by Tracy Chevalier
Art of War by Sun Tzu
The Trial by Kafka
Metamorphosis by Kafka
The Diary of a Young Girl by Anne Frank
Little Women by Louisa May Alcott
Jane Eyre by Charlotte Brontë
Frankenstein by Mary Shelley
The Picture of Dorian Gray by Oscar Wilde
Dracula by Bram Stocker
The Phantom of the Opera by Gaston Leroux
1984 by George Orwell
Animal Farm by George Orwell
And Then There Were None by Agatha Christie
To Kill a Mockingbird by Harper Lee
Lord of the Flies by William Golding
Madame Bovary by Gustave Flaubert
Dune by Frank Herbert
Kafka on the Shore by Haruki Murakami
Crime and Punishment by Dostoievski
Notes from the Underground by Dostoievski
Lolita by Vladimir Nabokov
The Count of Monte Cristo by Alexandre Dumas
The Pianist by Władisław Szpilman
Don Quixote by Miquel de Cervantes
East of Eden by John Steinbeck
The Divine Comedy by Dante Alighieri
Doctor Faustus by Thomas Mann
The Idiot by Dostoievski
Of Mice and Men by John Steinbeck
The Insulted and Humiliated by Dostoievski
Foundation by Isaac Asimov
I, Robot by Isaac Asimov
A Gentleman in Moscow by Amor Towles
Faust by Johann Wolfgang von Goethe
The Master and Margarita by Mikhail Bulgakov
Moby-Dick by Herman Meville
The Brothers Karamazov by Dostoievski
The Call of Cthulhu by Lovecraft
Dagon and other Macabre Tells by Lovecraft
The Prince by Niccolo Machiavelli
Memoirs of Hadrian by Marguerite Yourcenar
The Shining by Stephen King
The Decameron by Giovanni Boccaccio
The Name of the Rose by Umberto Eco
The Enlightened Cave by Max Blecher
Dr. Jekyll and Mr. Hyde by Robert Louis Stevenson
The God Factory by Karel Čapek
The Tongue Set Free by Elias Canetti
Brave New World by Aldous Huxley
I Have No Mouth And I Must Scream by Harlan Ellison
No Longer Human by Osamu Dazai
A Clockwork Orange by Anthony Burgess
Selected Poems by Jorge Louis Borges
The Prague Cemetery by Umberto Eco
Drive Your Plow Over the Bones of the Dead by Olga Tokarczuk
The Setting Sun by Osamu Dazai
The Stranger by Albert Camus
The Plague by Albert Camus
Carrie by Stephen King
Fight Club by Chuck Palahniuk
The Alchemist by Paulo Coelho
Notre Dame of Paris by Victor Hugo
Catch 22 by Joseph Heller
American Psycho by Bret Easton Ellis
Gone Girl by Gillian Flynn
The Iliad by Homer
The Odyssey by Homer
Wuthering Heights by Emily Brontë
The Bell Jar by Sylvia Plath
The Tell-Tale Heart and other Writings by Edgar Allan Poe
Fahrenheit 451 by Ray Bradbury
Oliver Twist by Charles Dickens
Hercule Poirot's Christmas by Agatha Christie
The Sound and the Fury by William Faulkner
V for Vendetta by Alan Moore
The Red and the Black by Stendhal
The Queen's Gambit by Walter Tevis
It by Stephen King
Pet Sematary by Stephen King
Anna Karenina by Leo Tolstoy
The Death of Ivan Ilych by Leo Tolstoy
La Dame aux Camélias by Alexandre Dumas fils
Pride and Predjudice by Jane Austen
Northanger Abbey by Jane Austen
Persuasion by Jane Austen
Sense and Sensibility by Jane Austen
The Old Man and the Sea by Ernest Hemingway
The Age of Innocence by Edith Wharton
North and South by Elizabeth Gaskell
A Game of Thrones by George R.R. Martin
The Fellowship of the Ring by J.R.R. Tolkien
The Return of Sherlock Holmes by Sir Arthur Conan Doyle
1Q84 by Haruki Murakami
12 notes
·
View notes