#Calculation of Standard Deviation in Grouped Data
Text
Calculation of Standard Deviation in Individual, Discrete & Continuous Series | Statistics
In this article, we will discuss about Calculation of Standard Deviation in Individual, Discrete & Continuous Series and measures of dispersion in Statistics. How to calculate Standard deviation
Standard Deviation
Standard deviation Measures of Dispersion in Statistics is the measure of the dispersion of statistical data. The standard deviation formula is used to find the deviation of the data…
View On WordPress
#Calculation of Standard Deviation#Calculation of Standard Deviation in Continuous Series#Calculation of Standard Deviation in Discrete Series#Calculation of Standard Deviation in Grouped Data#Calculation of Standard Deviation in Individual Series#Calculation of Standard Deviation in Ungrouped Data#How to Calculate Standard Deviation#How to Calculate Standard Deviation in Continuous Series#How to Calculate Standard Deviation in Discrete Series#How to Calculate Standard Deviation in Individual Series#Measures of Dispersion Statistics#Standard Deviation
0 notes
Text
my prof had us start analyzing some data for all groups across the whole entire class this semester before thanksgiving break and now im seeing he has apparently added in data for eight more groups since then im going to. AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA

#WHY THE HELL WAS THIS NOT IN BEFORE. better question why did you have us start analyzing the data when you knew damn well that not every#group’s data was in#personal#the engineering chronicles#the stats chronicles#am i supposed to be using this updated data?? or am i supposed to be using what he initially gave us. what the fuck#btw this is such a big deal bc i need to use the means and standard deviations of the whole class’s data so if those are different now. i#have to redo All the calculations ive done so far#and reformat my excel sheet which will be hellish#there’s not even a justifiable excuse for this we were The Last Section… he Had All The Data…. why was it not put in already#also the data in question was collected the week BEFORE we started analyzing it so. again. why
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
If MXTX's character's heights were real
The rest of the post is an unloading of all the fun I've had playing with the heights of most of the male adult characters from MXTX's novels. If you ever want to compare the heights of different male characters or pretend the novels don't exist in a magic-everyone-is-handsome-but-only-one-gay-relationship-can-exist-per-world alternate reality, this is your post.
I assume the average height of 19-year-old Chinese youths is 175.7 cm and the standard deviation is 6.5 cm (as of 2020, which was 3 years ago as of this post)
I referenced the Global Times article: "Average height of Chinese men sees the biggest rise of nearly 9 cm over 35 years: report" and a random height-percentile-in-different-countries website as it is literally impossible to find data on the standard deviation of height??
The inches and feet versions are at the end of the post, along with a comparison of a few of the heights
It all started with this chart by @jinxednoodle, which happens to be the first image if you google MXTX heights:

Free data? don't mind if I do…
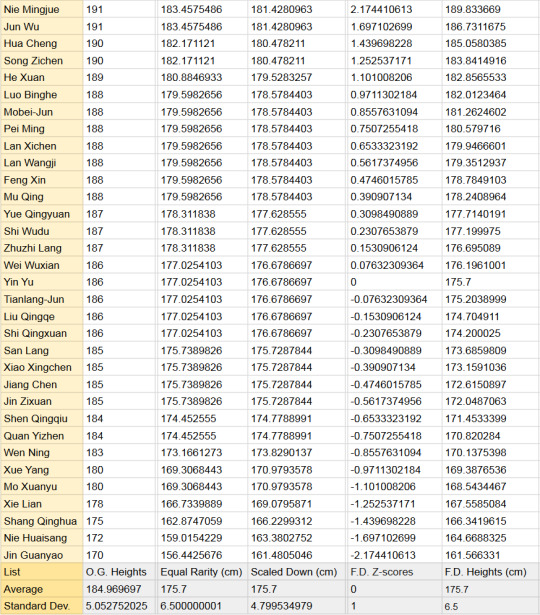
I finished with 3 final calculated columns
Equal Rarity
This column compares the characters' heights to one another by putting them in the context of the real-world equivalent height. Essentially, if you assume the distribution of heights is normal in MXTX-land and our sample accurately represents those heights (Neither is true, which is why this is Bad Math), being [character's name here]'s height in MXTX-land is as common as being ____ cm tall among a group of 19-year-old Chinese guys.
Perfect evidence that JGY is short
I divided each O.G. height by the average (~184.97) and standard deviation (the average difference between each number and the average) (5.05) of the O.G. heights, which gave me their z-scores (the number of standard deviations a number is from the average). I de-Z-scorified them by multiplying by 6.5 (the new STD) and adding 175.7 (the new average).
2. Scaled Down
This column just drags them small so they aren't giants compared to the rest of us
I divided the O.G. heights by their average (~184.97) and then multiplied by the 19CM average (175.7)
F.D. (Fixed Distribution) Heights
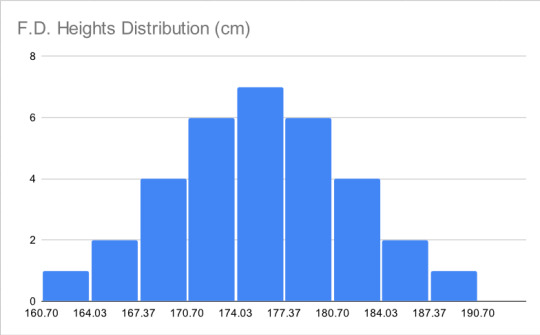
My personal favorite because it was the hardest to get right and my end goal all along. Heights are normally distributed, meaning if you mark all the heights along the horizontal axis and all the people with that height on the vertical, you should get a shape like the one below, with the exact average height in the exact middle, shorter people to the left, and taller to the right. I wasn't satisfied with only the average and standard deviation of my calculated samples matching real life, I wanted the distribution to match too

Below is the histogram of the O.G. heights. oof. Not the worst, because it only has one "hump" (one mode) and does have few extremely short people and few extremely tall people, but the shortest people have heights way further to the left of the mode than the tallest people's heights to the right of it. The data is heavily left-skewed. I think MXTX likes tall characters but cuts herself off at 191 cm (6'3.2") because any further is too tall to suspend disbelief.

I use an awful, unnecessarily complicated method after a few even worse attempts and split a normal distribution into 33 parts of equal area, then found the weighted average z-score of each section. I de-Z-scorified them by multiplying by 6.5 (the new STD) and adding 175.7 (the new average), producing the F.D. Heights column and this histogram:

I cannot tell you how many attempts I made before getting here. But my work was not done. Instead of starting with the O.G. heights, I had worked backward and needed to match my predetermined list of possible heights to the names. The order of who was at what height on my list was simple:
O.G. height was my first reference, but lots of characters are the same height. Their position in these "height blocks" was decided based on their appearance according to fandom.com. Anyone described as tall or strong-looking is put at the top and anyone delicate or synonymous is put near the bottom of the height block. Any additional selection was down by personal preference, which is why Yin Yu is exactly average (very evil of me), Mu Qing and Feng Xin are neighbors in height (to fuel the rivalry) and Yue Qingyuan is the tallest of his block (Big Bro vibes).
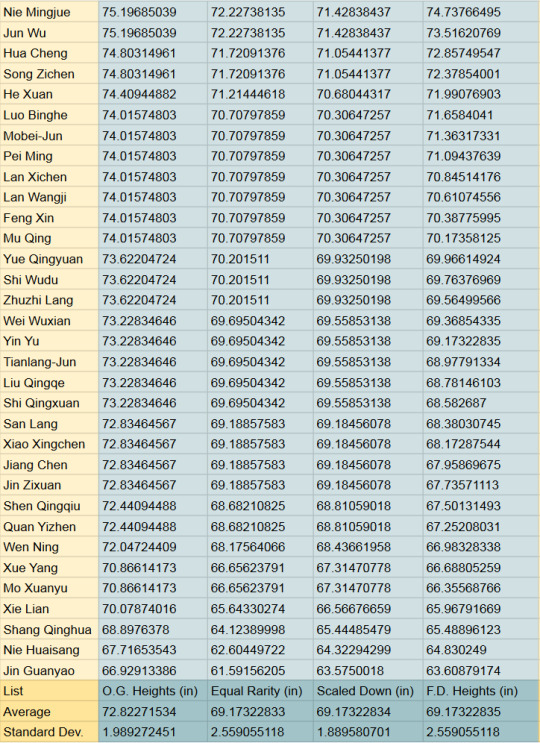
I didn't do the female heights because there were too few to make a good sample.
In Inches and Feet:

Example height differences, including an average 19-year-old female:

#bad math#mxtx#svsss#tgcf#mdzs#how do i tag this#reference#tall guys#China has a ThingTM with height#danmei#my posts
31 notes
·
View notes
Text
What are Bollinger Bands?
A series of trendlines serve as the definition of a Bollinger Band®, a technical analysis tool. They are represented as two standard deviations away from a simple moving average (SMA) of a security's price, both favorably and negatively, and can be customized to the user's preferences.
Technical trader John Bollinger created Bollinger Bands®, which are intended to increase the likelihood that investors will recognise when an asset is oversold or overbought.
Computing the security's simple moving average (SMA), often using a 20-day SMA, is the first step in computing Bollinger Bands®. The initial data point for a 20-day SMA is the average of the closing prices for the first 20 days. The following data point subtracts the price from the first data point, adds the price from day 21 and calculates the average, and so on. The security price's standard deviation will then be ascertained. The standard deviation calculates the deviation of a group of numbers from an average value.
Many traders hold the view that the market is more overbought or oversold the closer prices move to the upper band or the lower band, respectively. Since Bollinger Bands® are calibrated to use +/- two standard deviations around a SMA, we may anticipate that the observed price action will largely fall within these bands 95% of the time.
~Lakshya Kapoor
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
nahhh this lecturer is actually so evil. imagine teaching a basic statistics class, not covering relevant information in the lectures, giving rubbish data (everything is a likert scale with the responses in percentages and the grouping of the categories is weird/illogical) and then telling people to calculate the standard deviation (something which can't really be done with the data*) AND THEN refusing to answer people's emails until three days before the paper is due. lmfao. and he's the dean.
*if you disagree please tell me how, i am begging at this point
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
How Business Professionals Can Leverage Mathematics for Better Decision-Making
Math is more than just a subject for the classroom in today's data-compulsive business environment, it is a powerful tool that can significantly improve decision-making. Business experts who tackle mathematical principles and standards through business analytics training can make more educated, exact, and strategic choices. This is the way math can be utilized to advance business outcomes some of these are:
1. Data Understanding and Analysis
Arithmetic gives the establishment to observing and cracking information. Procedures like illustrative measurements, probability, and degeneration investigation empower experts to figure out patterns, make calculations, and reveal bits of knowledge from information. For example, utilizing accurate procedures like mean, median, and standard deviation helps in summing up and understanding the conveyance of data of interest. Regression analysis can analyze or predict future deals in the vision of verifiable information, permitting organizations to pursue active options.
2. Optimizing operations
Mathematicals assume a pivotal role in optimizing business tasks. Strategies from linear programming and business analytic training activities are utilized to take care of complicated problems, for example, asset assignment, production scheduling, and stock administration. Moreover, Linear programming can assist in determining the ideal product mix for manufacturing while simultaneously minimizing costs and satisfying demand restrictions. Furthermore, mathematical models help in stock administration by predicting the optimal stock levels to decrease holding costs and keep away from stockouts.
3. Financial Analysis and Planning
Financial management is well established in numerical standards. Business experts utilize different numerical models to assess and evaluate investment opportunities, estimate incomes, and oversee probabilities. When determining whether investments and projects are practicable, it is necessary to use tools like financial ratios, the internal rate of return, and net present value. helps in deciding the worth of future incomes according to modern standards, supporting the association of various investment options.
4. Risk Management
Math is basic in risk management. Probability theory and statistical analysis are utilized to assess and manage risks associated with business decisions. Like, risk assessment models and Monte Carlo recreations help in measuring the possible effect of vulnerabilities on monetary portfolios. Businesses can create plans to reduce their losses and increase their flexibility by understanding the possibility and impact of various data analytics.
5. Statistical surveying and Purchaser Insights
Mathematical methods help in analyzing consumer behavior and market trends in market research. Customers can be broken down into different groups and their preferences can be understood using methods like factor analysis and cluster analysis. For instance, cluster analysis groups customers with comparative ways of behaving or qualities, permitting organizations to fit promoting techniques to various portions. Factor analysis helps in identifying fundamental factors that impact customer choices, giving further experiences into market dynamics. Business analytics training trains professionals with these mathematical tools, enabling effective market research.
6. Vital Preparation
Math helps with vital preparation and prediction by giving apparatuses to display various situations and expect future results. Time series investigation is utilized to dissect verifiable information and conjecture future patterns. Businesses can anticipate market shifts, prepare for seasonal variations, and devise strategies to take advantage of upcoming opportunities by employing mathematical models. Business strategies can be better aligned with anticipated market conditions and informed decisions can be made with this proactive approach.
7. Improving Effectiveness with Algorithms
Automating processes and increasing productivity requires algorithms that are based on mathematical logic. From advancing stockpile chains to customizing client encounters, calculations can deal with huge measures of information rapidly and precisely. E-commerce platforms, for instance, use recommendation algorithms that look at user preferences and behavior to suggest relevant products. In a similar vein, optimization algorithms can optimize processes by determining the most effective resource allocation or delivery route.
8. Assessing
Advertising Campaigns Arithmetic aids in assessing the viability of advertising efforts through measurements and logical models. Procedures, for example, A/B testing, change rate investigation, and return for capital invested estimations give experiences into crusade execution. A/B testing, for instance, compares two versions of a marketing campaign to see which one delivers the best results. Businesses can improve their marketing strategies, allocate budgets more efficiently, and achieve better results by analyzing these metrics.
9. Optimal Pricing Strategies
A company's competitiveness and profitability are directly related to its pricing decisions. By analyzing cost structures, market demand, and competitor pricing, mathematics plays a crucial role in determining optimal prices. Procedures, for example, cost versatility examination and benefit advancement models help in deciding the best-evaluating systems. For example, understanding what changes in cost mean for requests permits organizations to set costs that expand income while staying cutthroat on the lookout.
10. Utilizing Simulation to Improve Decision-Making
Numerical recreations are integral assets for testing various situations and settling on informed choices. Recreation procedures, like Monte Carlo reenactments, permit organizations to demonstrate complex frameworks and survey the effect of different factors on results. This method aids in comprehending the potential benefits and risks of various strategies, resulting in more informed and self-assured decision-making.
Conclusion
Integrating business analytics training into business dynamics succession can essentially improve precision, proficiency, and critical understanding. Business professionals can make better-informed decisions and operate successful effects by utilizing mathematical techniques for data analysis, optimization, financial planning, risk management, and more. Businesses are better able to navigate complexities and seize opportunities that are becoming increasingly competitive when they understand and adopt mathematics management.
#business math#online math tutoring#math#math tutoring#mathematics#business analytics#data analytics#mathematics for better decision#business professionals#professional mathematics
0 notes
Text
Top Tips for Interpreting Kalyan Result Trends

The Kalyan market, a significant part of the Satta Matka game, captivates many with its blend of chance and strategy.
Analyzing the Kalyan result trends is crucial for players aiming to enhance their predictions and improve their chances of winning. This blog provides top tips for interpreting Kalyan result trends effectively.
Collect Historical Data
The first step in interpreting Kalyan result trends is to gather extensive historical data. This includes past winning numbers, dates, and any patterns observed over time.
Many online platforms and forums offer archives of Kalyan results. Having a robust dataset is crucial for identifying recurring patterns and trends.
Analyze Frequency of Numbers
One of the fundamental aspects of interpreting Kalyan result trends is analyzing the frequency of numbers. Determine which numbers appear most often and which are rare.
By creating a frequency chart, you can visualize these patterns and use them to inform your future bets. Numbers that appear frequently may have a higher probability of being drawn again.
Identify Hot and Cold Numbers
In the context of Kalyan results, hot numbers are those that have appeared frequently in recent draws, while cold numbers are those that haven't appeared for a while.
Tracking these can help you decide whether to bet on a hot streak or anticipate a cold number making a comeback. Balancing bets between hot and cold numbers can enhance your strategy.
Utilize Statistical Tools
Statistical tools can significantly aid in interpreting Kalyan result trends. Techniques such as mean, median, mode, and standard deviation can provide deeper insights into the distribution of numbers.
For instance, calculating the mode helps identify the most frequently occurring numbers, while the standard deviation reveals the variability in the results.
Look for Number Pairs and Sequences
Examining number pairs and sequences is another effective strategy. Sometimes, specific pairs of numbers or sequences appear more frequently together.
Identifying these patterns can provide clues for future predictions. Create a chart of common pairs and sequences to keep track of their occurrences.
Consider Seasonal and Temporal Patterns
Kalyan result trends may also exhibit seasonal and temporal patterns. For example, certain numbers might appear more frequently during specific months or days of the week.
Analyzing these temporal trends can help you make more informed bets based on the time of year or day.
Use Probabilistic Models
Probabilistic models can enhance your understanding of Kalyan result trends. By calculating the probability of certain numbers or combinations appearing,
you can make more informed predictions. Bayesian analysis and Markov chains are two examples of probabilistic models that can be applied to Kalyan result data to forecast future outcomes.
Leverage Technology and Software
Technology offers a range of tools for analyzing Kalyan result trends. Various software and apps are available that provide advanced data analysis and pattern recognition capabilities.
These tools can save time and improve the accuracy of your predictions. Utilize prediction software, Satta Matka calculators, and dedicated analysis platforms to enhance your strategy.
Stay Updated with Expert Insights
Engaging with the Satta Matka community and staying updated with expert insights can provide additional perspectives on Kalyan result trends.
Online forums, blogs, and social media groups are excellent resources for sharing and gaining knowledge. Learning from experienced players can offer new strategies and approaches to interpreting trends.
Test and Refine Your Strategy
Finally, it’s essential to test and refine your strategy based on real-world results. Use a simulated environment or small bets to experiment with different approaches.
Track your performance, analyze outcomes, and adjust your strategy accordingly. Continuous refinement based on actual performance will improve your ability to interpret Kalyan result trends effectively.
Conclusion
Interpreting Kalyan result trends requires a combination of historical data analysis, statistical tools, and practical strategies. By collecting comprehensive data,
identifying patterns, leveraging technology, and staying informed, you can enhance your predictions and increase your chances of success in the Kalyan market.
Remember, while data and trends can guide your bets, the element of chance remains a core part of the Satta Matka game.
Read More: What the Latest Kalyan Result Means for Your Game Plan
0 notes
Text
How to Start Your Career in Data Analytics
There are countless opportunities in the fascinating field of data analytics. Here is a simple tutorial to get you started if you want to get into this field. We'll go over the fundamentals, necessary abilities, getting real-world experience, and networking.

1. Understand the Principles
Gaining an understanding of data analytics will put you on the correct track. In order to make wise decisions, data analytics entails gathering, processing, and analyzing data. Start by familiarizing yourself with the following important concepts:
Data Collection: The process of compiling data from multiple sources.
The practice of correcting or deleting inaccurate data is known as data cleansing.
Data analysis methods involve analyzing data to find trends or patterns.
It's not necessary to dive in headfirst. Start with resources that are appropriate for beginners, such as online guides and introductory classes.
2. Develop core skills.
To be effective in data analytics, you need a specific skill set. Focus on these essential areas:
Technical Skills: Master tools like Microsoft Excel for data manipulation, SQL for database queries, and data visualization software such as Tableau or Power BI. These tools help you organize and visualize data effectively.
Statistical Knowledge: Learn basic statistics, including mean, median, standard deviation, and probability. This knowledge helps you understand data trends and make predictions.
Programming Skills: Familiarize yourself with programming languages such as Python or R. Both are popular in data analytics for their ability to handle large datasets and perform complex calculations.
Several online platforms offer courses in these areas. For instance, Codecademy and DataCamp provide interactive lessons in Python and R tailored to data analytics.
3. Gain hands-on experience
Experience is crucial in data analytics. Start by working on small projects to apply your skills. Here’s how:
Personal Projects: Find publicly available datasets on sites like Kaggle or Google Dataset Search and try to analyze them. This can help you practice data cleaning, analysis, and visualization.
Internships: Look for internships or entry-level positions that offer real-world experience. These roles often provide valuable exposure to industry practices and tools.
Portfolio Development: Document your projects and results in a portfolio. Include examples of data analyses, visualizations, and any insights you’ve drawn. A strong portfolio can significantly enhance your job applications.
4. Build your professional network.
Networking is key to advancing your career. Connecting with professionals in the field can open doors and provide valuable insights. Here’s how to build your network:
Join Communities: Participate in online forums, LinkedIn groups, and local meetups related to data analytics. These platforms can offer advice, job leads, and support.
Attend Events: Go to industry conferences, webinars, and workshops. These events are great for learning about new trends and meeting potential employers or mentors.
Engage on Social Media: Follow industry leaders on platforms like Twitter and LinkedIn. Engaging with their content can keep you informed and connected to the latest developments in data analytics.
Gaining practical experience, developing a professional network, and grasping the fundamentals are all necessary for beginning a career in data analytics. You'll have no trouble landing a great job in this exciting sector if you put in the necessary effort and acquire the necessary tools. Take a deep breath, keep studying, and seize the fascinating prospects presented by data analytics! I appreciate you reading.
0 notes
Text
Time Management Status In SAP HR

Understanding Time Management Status in SAP HR
In the SAP Human Resources (HR) world, the Management Status plays a pivotal role in streamlining time recording, evaluation, and pa, payroll processes. This critical field within an employee’s master data record dictates how the SAP system will handle their working hours and attendance. Let’s dive into the meaning of Time Management Status and its various settings.
What is Time Management Status?
Time Management Status is a crucial indicator of an employee’s SAP HR record’s Planned Working Time info type (0007). It functions as a control mechanism, determining if and how the system processes an employee’s time data during time evaluation. Errors in assigning the proper status can lead to inaccurate time calculations and potential disruptions in payroll.
Common Time Management Statuses
Let’s break down the most frequently used Time Management Statuses:
0 (Blank): Time Evaluation BypassedEmployee’s actual work times are not recorded.
Time data is not processed by time evaluation.
1: Active Time Recording and EvaluationEmployee’s work times are recorded (e.g., time clock terminals, attendance entries).
Time evaluation processes the recorded time data.
2: Time Recording via Plant Data Collection (PDC)Work times are captured through production systems or terminals.
Time evaluation processes this data.
7: No Time Recording, Planned Work Schedules UsedNo actual work times are recorded.
The employee’s planned work schedule (info type 0007) forms the basis for time evaluation.
8: External EmployeesDesigned for external personnel.
Attendance data is recorded, but actual work times are not.
Time evaluation is still carried out.
9: Exception-Based Recording is ideal for scenarios where only deviations from the standard work schedule are tracked (e.g., absences and overtime).
Time evaluation incorporates these exceptions and the planned work schedule.
Impact on Payroll Integration
It’s crucial to note that the Time Management Status directly influences how time data flows into the payroll process. The status choice determines when wage types are generated and considered for salary calculations.
Best Practices
Careful Selection: Choose the Time Management Status meticulously based on the employee’s working arrangements and how their time data needs to be processed.
Consistency: Ensure consistency in applying Time Management Statuses across similar employee groups for efficient payroll processes.
Reporting: Leverage SAP HR reports to monitor and analyze the usage of Time Management Statuses for potential errors or anomalies.
In Conclusion
The Time Management Status is a seemingly small but potent field in SAP HR. Understanding its nuances is essential for accurate time tracking, efficient time evaluation, and seamless payroll integration. By carefully managing this status, HR professionals can ensure timely and error-free compensation processes.
youtube
You can find more information about SAP HR in this SAP HR Link
Conclusion:
Unogeeks is the No.1 IT Training Institute for SAP HR Training. Anyone Disagree? Please drop in a comment
You can check out our other latest blogs on SAP HR here – SAP HR Blogs
You can check out our Best In Class SAP HR Details here – SAP HR Training
———————————-
For Training inquiries:
Call/Whatsapp: +91 73960 33555
Mail us at: [email protected]
Our Website ➜ https://unogeeks.com
Follow us:
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/unogeeks
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/UnogeeksSoftwareTrainingInstitute
Twitter: https://twitter.com/unogeeks
0 notes
Text
Joining Six Sigma Training to Understand Variance and Deviation

Individuals enroll in Six Sigma training for a variety of reasons. Many of these reasons are related to their desire to advance their careers and enhance their organizations. First off, Six Sigma training gives people the chance to advance their knowledge and abilities in statistical analysis, problem-solving strategies, and process improvement procedures. This improves their chances of landing a job and gives them useful tools to help them be more productive and successful in their positions.
In this blog, we will learn why it is important to join a Six Sigma Training for understanding Variance and Deviation.
Understanding and managing variance and deviation are essential in the Six Sigma quality management. It drives process improvement and ensures consistent product and service quality. Two statistical measurements that shed light on the predictability, consistency, and stability of processes are variance and deviation

What is Variance in Six Sigma?
Variance is a term used in Six Sigma methodology to describe the spread or dispersion of data points inside a process. It expresses the degree to which a single data point deviates from the data set's mean or average value. Variance is a key idea in Six Sigma since it aids in determining how predictable and consistent a process is.
Data points from a process with minimal variation are tightly grouped around the mean, a sign of stability and predictability. Conversely, data points from a process with a large variance are further dispersed from the mean, indicating a higher degree of variability in the process's results.
Six Sigma practitioners can find areas for process improvement and put plans in place to eliminate errors, limit variability, and maximize performance by assessing variation. Variance analysis is frequently carried out to create a baseline understanding of process performance and find areas for improvement as part of the Measure phase in the DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) approach.
What is Six Sigma Standard Deviation or Deviation?
In statistics and Six Sigma methodology, standard deviation, often referred to simply as deviation, is a measure of the dispersion or spread of data points within a dataset. It quantifies how much individual data points deviate from the mean or average value of the dataset.
Standard deviation is calculated by taking the square root of the variance, which is the average of the squared differences between each data point and the mean. Essentially, it provides a measure of the average distance of data points from the mean.
A smaller six sigma standard deviation indicates that data points are closer to the mean, suggesting less variability in the dataset. Conversely, a larger standard deviation indicates greater variability, with data points spread out more widely from the mean.
In Six Sigma, standard deviation is a key metric for assessing process performance and variability. By analyzing standard deviation, practitioners can identify areas of improvement, reduce defects, and optimize processes to achieve better outcomes. Standard deviation analysis is often conducted as part of the Measure phase in the DMAIC methodology. It is to establish a baseline understanding of process performance and variability.
Why Join Six Sigma Training or Classes?
Mastery of Statistical Tools
Six Sigma training provides participants with a comprehensive understanding of statistical tools and methodologies used to analyze process data, including variance and deviation. Through hands-on exercises and practical examples, participants learn how to calculate and interpret these metrics to assess process performance effectively.
Problem-Solving Skills in Six Sigma Training
Six Sigma training or classes equips individuals with a structured problem-solving methodology. It includes DMAIC, which enables them to identify root causes of process variation and implement data-driven solutions to address them. By understanding the role of variance and deviation in process improvement, participants can drive meaningful change and achieve measurable results.
Process Optimization
By mastering variance and deviation analysis, Six Sigma practitioners can identify opportunities for process optimization and waste reduction. From streamlining manufacturing processes to enhancing product quality, it provides a systematic approach to driving continuous improvement and maximizing efficiency.
Career Advancement through Six Sigma Training
Six Sigma certification has a wide recognition and value among employers across industries. By completing Six Sigma training and obtaining certification, individuals demonstrate their proficiency in process improvement methodologies. It further enhances their career prospects. It can open doors to a wide range of career paths and advancement opportunities.
Joining Six Sigma Training for Career Success
Enrolling in Six Sigma Training is a wise investment in your career advancement and the success of your company. Individuals may effectively increase process performance, augment organizational efficiency, and realize their professional objectives. The training provides insights and growth opportunities to broaden the skill set or pursue certification as a Six Sigma practitioner.
Resource: https://www.mindcypress.com/blogs/quality-management/joining-six-sigma-training-to-understand-variance-and-deviation
0 notes
Text
Making Sense of Survey Results

Collecting data through surveys is a vital step in gaining insights, but the true value lies in the ability to analyze and interpret that data effectively. Survey results are like a treasure trove of information waiting to be unlocked. However, for many, the prospect of diving into data analysis can be daunting. In this article, we’ll demystify the process of making sense of survey results and offer practical steps to turn raw data into actionable insights.
1. Understand Your Objectives:
Before you begin analysis, remind yourself of the survey’s objectives. What questions were you trying to answer? What insights were you seeking? This clarity will guide your analysis and help you focus on the most relevant data.
2. Data Cleaning and Preparation:
Raw survey data can be messy. Start by cleaning and organizing the data. Remove duplicate responses, check for outliers or inconsistencies, and ensure that data is correctly formatted for analysis. This step sets the foundation for accurate results.
3. Quantitative Analysis:
For quantitative data (numerical values), start with descriptive statistics. Calculate measures like mean, median, and standard deviation to understand the central tendency and spread of your data. Create visualizations such as histograms, bar charts, and scatter plots to visualize patterns and trends.
4. Qualitative Analysis:
If your survey includes open-ended responses, qualitative analysis is key. Organize responses into themes or categories. Techniques like content analysis or sentiment analysis can help uncover common sentiments or ideas among respondents.
5. Cross-Tabulation and Comparative Analysis:
Cross-tabulation involves analyzing the relationship between two or more variables. This helps uncover patterns or differences in responses based on demographic or other factors. Comparative analysis lets you compare responses across different groups to identify trends and disparities.
6. Correlation and Regression:
Use correlation analysis to understand the strength and direction of relationships between two variables. Regression analysis can help predict one variable based on the values of others. These techniques provide deeper insights into causality and predictive patterns.
7. Visual Representation:
Visualizations are powerful tools to communicate findings effectively. Create graphs, charts, and heatmaps that illustrate your key insights. Visual representations make it easier for stakeholders to grasp complex information quickly.
8. Identify Key Findings:
Based on your analysis, pinpoint the most significant findings. What trends, patterns, or correlations emerge from the data? Clearly articulate these key insights to guide decision-making.
9. Contextualize Results:
Avoid drawing premature conclusions. Contextualize your findings by considering external factors that might influence the results. Understanding the broader context ensures that your insights are accurate and actionable.
Read More
0 notes
Text
72 stock market terms for new investors

Certainly! Here are 72 stock market terms that are commonly encountered by new investors:
If you want to learn more about trading then joinInvestingdaddy.com.

Stock: Ownership in a company, represented by shares.
Shares: Units of ownership in a company.
Market Capitalization: Total value of a company's outstanding shares.
Dividend: Distribution of a portion of a company's earnings to its shareholders.
Initial Public Offering (IPO): The first sale of a company's stock to the public.
Bull Market: A market characterized by rising stock prices.
Bear Market: A market characterized by falling stock prices.
Volatility: Degree of variation of a trading price series over time.
Index: A measure of the performance of a group of stocks.
Blue Chip Stocks: Stocks of large, well-established companies with a history of stable earnings.
Penny Stocks: Stocks with a low share price, typically traded over-the-counter.
Market Order: An order to buy or sell a stock at the current market price.
Limit Order: An order to buy or sell a stock at a specific price or better.
Bid Price: The price at which a buyer is willing to purchase a stock.
Ask Price: The price at which a seller is willing to sell a stock.
Spread: The difference between the bid and ask prices.
Volume: The number of shares traded in a stock or market.
Liquidity: The ease with which an asset can be bought or sold without impacting its price.
Earnings Per Share (EPS): A company's profit divided by its number of outstanding shares.
Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio: A measure of a company's valuation relative to its earnings.
Dividend Yield: A company's annual dividend divided by its stock price.
Book Value: The value of a company's assets minus its liabilities.
Return on Investment (ROI): The gain or loss on an investment relative to its cost.
Short Selling: Selling a stock that the seller does not own, with the intention of buying it back at a lower price.
Margin: Borrowed money used to purchase securities.
Margin Call: A demand by a broker for additional funds to cover potential losses.
Portfolio: A collection of investments owned by an individual or institution.
Asset Allocation: The distribution of investments across different asset classes.
Diversification: Spreading investments across different assets to reduce risk.
Market Order: An order to buy or sell a stock at the current market price.
Limit Order: An order to buy or sell a stock at a specific price or better.
Stop-Loss Order: An order to sell a stock if its price falls below a specified level.
Day Trading: Buying and selling stocks within the same trading day.
Swing Trading: Buying and holding stocks for several days or weeks to capitalize on short-term price movements.
Long Position: Owning securities with the expectation that their value will increase.
Short Position: Selling securities with the expectation that their value will decrease.
Candlestick Chart: A type of chart that displays the open, high, low, and closing prices of a security.
Moving Average: A calculation used to smooth out price data by creating a constantly updated average price.
RSI (Relative Strength Index): A momentum oscillator that measures the speed and change of price movements.
MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence): A trend-following momentum indicator that shows the relationship between two moving averages of a security's price.
Market Sentiment: The overall attitude of investors toward a particular market or security.
Fundamental Analysis: Analysis of a company's financial statements and other factors to determine its intrinsic value.
Technical Analysis: Analysis of past market data, primarily price and volume, to forecast future price movements.
Alpha: A measure of an investment's performance relative to a benchmark index.
Beta: A measure of a stock's volatility relative to the overall market.
Standard Deviation: A measure of the dispersion of returns for a given security or market index.
Risk: The potential for loss or variability in investment returns.
Volatility: The degree of variation of a trading price series over time.
Portfolio Management: The process of managing a collection of investments to achieve specific financial goals.
Asset Allocation: The distribution of investments across different asset classes to optimize risk and return.
Diversification: Spreading investments across different assets to reduce risk.
Rebalancing: Adjusting the weightings of assets in a portfolio to maintain desired risk levels.
Buy and Hold Strategy: A long-term investment strategy in which an investor holds securities for an extended period regardless of short-term market fluctuations.
Dividend Reinvestment Plan (DRIP): A program that allows investors to reinvest dividends to purchase additional shares of the issuing company's stock.
Direct Stock Purchase Plan (DSPP): A program that allows investors to purchase shares of a company's stock directly from the company without going through a broker.
401(k): A retirement savings plan sponsored by an employer that allows employees to contribute a portion of their wages to individual retirement accounts.
One of the best way to start studying the stock market to Join India’s best comunity classes Investing daddy invented by Dr. Vinay prakash tiwari . The Governor of Rajasthan, the Honourable Sri Kalraj Mishra, presented Dr. Vinay Prakash Tiwari with an appreciation for creating the LTP Calculator.
LTP Calculator the best trading application in India

You can also downloadLTP Calculator app by clicking on download button.

IRA (Individual Retirement Account): A tax-advantaged retirement savings account that individuals can contribute to on a regular basis.
Roth IRA: A type of individual retirement
0 notes
Note
can you explain the difference between the bell curves we often see on tumblr polls, and normal distribution, which is what users tend to label poll results as? and can you say it like i'm kinda stupid
of course!! so, in its most basic form, the normal distribution is a way of representing data so they can show, simply put, the "norm." this means that almost anyone (literally 99.8%) of the population fits within three standard deviations of the mode (most common answer). a standard deviation is the average amount of difference (variation) thats found in a set of data for answers around the mode:
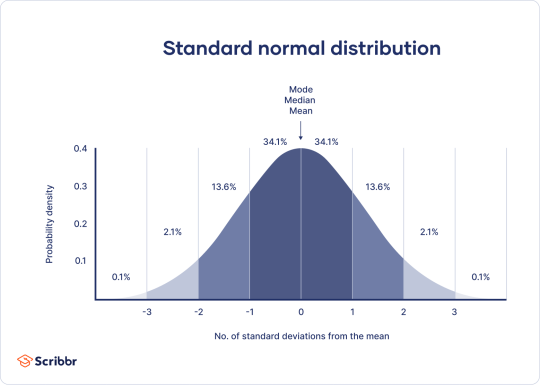
it looks like this! 68% of the population falls within one standard deviation, 95% within two, and 99.8% within 3 standard deviations. this is done so we can look at data and assume we've represented just about everyone, and find who is significantly different (for example, someone who eats 10,000 spiders a day).
the most common example ive seen is IQ. The mode is an IQ of 100 with a standard deviation of 10. So, 68% of people have an IQ of 90-110, 95% have an IQ of 80-120, and 99.8% of 70-130. If we have a room of 100 people, we can assume they all have an IQ between 70 and 130. If they don't, then they are a statistically significant outlier (adn shouldnt be counted).
So, in tumblr poll terms, if you have 10 options (especially a 1-10 likert scale), its not likely to naturally be a normal distribution, BUT! its very easy for it to be a symmetrical distribution, with a mode (the most amount of answers) in the middle and a steady decline in answers on either side, making it symmetrical. however, unless the data follow the 68, 95, 99.8% pattern, its not "Normal."

In these pictures, all the data are symmetrical! a lot of data looking at people are (which is why it shows up so frequently in polls). But, if you have data spread across 10 points, we dont like that because it makes it harder for us to group people into the "norm."
whats great about statistics though is that we can make it work for us. if we have symmetrical data, we can fuck around with (okay, "calculate") the standard deviations to figure out how to make data fit into the normal distribution.
why do we love normal distributions anyway? imagine youre opening a bowling alley. a normal distribution of shoe size is going to show you what shoes to get for 99.8% of your customers! You can order more sizes for people within one standard deviation, fewer for people 1-2 standard deviations away, and the least for those 2-3 standard deviations away.
its not dumb to not know this! if youve never taken a statistics class or never needed to know the importance or uses for a normal distribution, its not really knowledge you need! im glad you asked. i looooove stats and the ways we can use it and make it work for us. thanks for asking!!
tl:dr: a normal distribution follows a very specific distribution of percentages. a symmetrical distribution can be any percentages, as long as they follow a pattern. all normal distributions are symmetrical, not all symmetrical distributions are normal.
0 notes
Text
In statistics, we have studied the classification of data into a grouped and ungrouped frequency distribution. These data can be pictorially represented using different graphs such as bar graphs, frequency polygons and histograms and so on. Also, we know that the three measures of central tendencies are mean, median and mode. In this article, we will discuss how to find the mean of the grouped data using different methods such as direct method, assumed mean method and step deviation method with many solved example.
Table of Content:
Mean
Standard deviation
Standard deviation of grouped data
Interpretation of Standard deviation
Steps to Calculate Standard Deviation for Grouped Data
Standard deviation of Grouped Data Example
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Read more HERE
0 notes
Text
Assignment(Week 1): Hypothesis Testing and ANOVA
Preview:
This assignment aims to directly test my hypothesis by evaluating, based on a sample of 2412 U.S. cannabis users aged between 18 and 30 years old (subsetc5), my research question with the goal of generalizing the results to the larger population of NESARC survey, from where the sample has been drawn. Therefore, I statistically assessed the evidence, provided by NESARC codebook, in favor of or against the association between cannabis use and mental illnesses, such as major depression and general anxiety, in U.S. adults. As a result, in the first place I used ols function in order to examine if depression ('MAJORDEP12') and anxiety ('GENAXDX12') disorders, which are both categorical explanatory variables, are correlated with the quantity of joints smoked per day when using the most ('S3BQ4'), which is a quantitative response variable. Thus, I ran ANOVA (Analysis Of Variance) method (C->Q) twice and calculated the F-statistics and the associated p-values for each disorder separately, so that null and alternate hypothesis are specified. Furthermore, I used ols function once again and tested the association between the frequency of cannabis use ('S3BD5Q2E'), which is a 10-level categorical explanatory variable, and the quantity of joints smoked per day when using the most ('S3BQ4'), which is a quantitative response variable. In this case, for my third one-way ANOVA (C->Q), after measuring the F-statistic and the p-value, I used Tukey HSDT to perform a post hoc test, that conducts post hoc paired comparisons in the context of my ANOVA, since my explanatory variable has more than 2 levels. By this way it is possible to identify the situations where null hypothesis can be safely rejected without making an excessive type 1 error. In addition, both means and standard deviations of joints quantity response variable, were measured separately in each ANOVA, grouped by the explanatory variables (depression, anxiety and frequency of cannabis use) using the groupby function. For the code and the output I used Spyder (IDE).


When examining the association between the number of joints smoked per day (quantitative response variable) and the past 12 months major depression diagnosis (categorical explanatory variable), an Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) revealed that among cannabis users aged between 18 and 30 years old (subsetc5), those diagnosed with major depression reported smoking slightly more joints per day (Mean=3.04, s.d. ±5.22) compared to those without major depression (Mean=2.39, s.d. ±4.16), F(1, 2368)=7.682, p=0.00562<0.05. As a result, since our p-value is extremely small, the data provides significant evidence against the null hypothesis. Thus, we reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternate hypothesis, which indicates that there is a positive correlation between depression diagnosis and quantity of joints smoked per day.

When testing the association between the number of joints smoked per day (quantitative response variable) and the past 12 months general anxiety diagnosis (categorical explanatory variable), an Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) revealed that among cannabis users aged between 18 and 30 years old (subsetc5), those diagnosed with general anxiety reported smoking marginally equal quantity of joints per day (Mean=2.68, s.d. ±3.15) compared to those without general anxiety (Mean=2.5, s.d. ±4.42), F(1, 2368)=0.1411, p=0.707>0.05. As a result, since our p-value is significantly large, in this case the data is not considered to be surprising enough when the null hypothesis is true. Consequently, there are not enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternate, thus there is no positive association between anxiety diagnosis and quantity of joints smoked per day.



ANOVA findings within the subset of daily cannabis users aged 18 to 30 years old (subset c5) revealed a significant association between the frequency of cannabis use (categorized into 10 ordered groups) and the number of joints smoked per day (a quantitative response variable), with F(9, 2349) = 52.65 and a p-value of 1.76e-87, which is less than the significance level of 0.05 (expressed in scientific notation).
In subsequent post hoc comparisons examining the mean number of joints smoked per day across different pairs of cannabis use frequency categories, it was observed that individuals using cannabis every day (or nearly every day) reported a significantly higher average daily consumption of joints (Every day: Mean = 5.66, s.d. ±7.8; Nearly every day: Mean = 3.73, s.d. ±4.46) compared to those using 1 to 2 times per week (Mean = 1.85, s.d. ±1.81) or less. Consequently, there are specific pairs where the frequency of cannabis use and the quantity of joints smoked exhibit a positive correlation.

To analyze the relationship between the frequency of cannabis use and the daily number of joints smoked most frequently, I employed the Tukey Honestly Significant Difference (HSD) test as part of post hoc paired comparisons following an ANOVA. The table provided delineates the variations in smoking quantity across different frequency groups of cannabis use. It aids in pinpointing instances where we can reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternative hypothesis, denoted as "reject equals true." Conversely, instances marked as "reject equals false" indicate situations where rejecting the null hypothesis might lead to an increased risk of committing a type 1 error.
1 note
·
View note