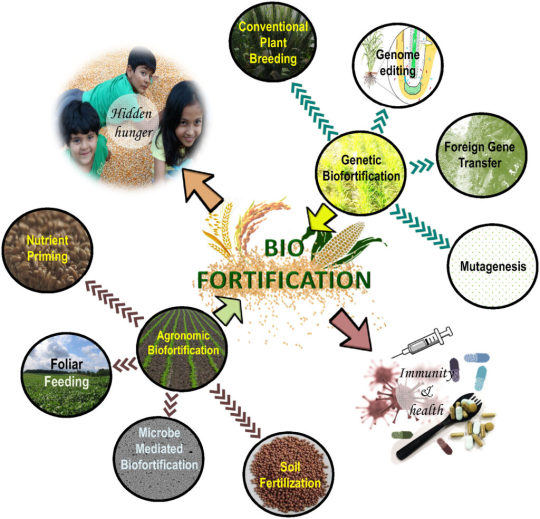
#Biofortification
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

MANAGE inaugurated a 3-day training program on "Harvesting Health: Empowering Agriculture with Bio-fortified Solutions" from September 23-25, 2024. A total of 11 participants from six states—Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Telangana, Chhattisgarh, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu—comprising senior and mid-level officers from the agriculture, veterinary, and Agri-allied sectors, are attending.
#MANAGE#AgriculturalExtension#AgriTech#FAO#Biofortification#Malnutrition#NutritionalFoodSecurity#AgricultureEmpowerment#ICRISAT#HarvestPlus#BalancedDiets#FoodSafety#MarketLinkages#ValueChainDevelopment#PolicyAdvocacy#BiofortifiedCrops#NutritionalBenefits#AgricultureTraining#GenderStudies
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
CURRENT AFFAIRS -15 AUGUST 2024
1. Bio fortified variety of crops Prime Minister released 109 high yielding, climate resilient and biofortified varieties of crops. These crops have been developed by the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) and release of new varieties of crops is the example of a “lab to land” programme. ICAR has been running crop-improvement programme to develop new crop varieties and hybrids with…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
A research group has developed an innovative method for the biofortification of leaves and other green plant tissues, increasing their content of healthy substances such as beta-carotene, the main precursor of vitamin A in the human diet. The work demonstrates that by using biotechnological techniques and treatments with high light intensity, the levels of beta-carotene in leaves can be multiplied up to 30 times by creating new places to store it without affecting vital processes such as photosynthesis. The results are published in the Plant Journal.
Continue Reading.
182 notes
·
View notes
Text
Green Banana Flour Market In-depth Insights, Revenue Details, Regional Analysis by 2035
The global green banana flour market is poised for steady expansion between 2025 and 2035, fueled by the increasing consumer preference for gluten-free and grain-free options, rising health awareness, and the growing integration of resistant starch in functional foods. Valued at USD 714.4 million in 2025, the market is projected to reach USD 1,141.8 million by 2035, expanding at a CAGR of 4.8% during the forecast period.
New market prospects are emerging as the health benefits of resistant starch-particularly for gut health, weight management, and blood sugar regulation-gain wider recognition. Technological progress in AI-driven agricultural analytics, sustainable banana farming, and biofortified banana flour production are poised to elevate the industry’s growth.
Furthermore, the surge in upcycled food trends and zero-waste manufacturing is opening new avenues for banana flour-based ingredients in sectors such as sports nutrition, baby foods, and plant-based proteins.
The global green banana flour sector presents significant opportunities, especially in the bakery segment, where banana flour enhances the nutritional profile of bread-one of the world’s most consumed foods. Consumers are also increasingly incorporating banana flour into smoothies, yogurt, and daily supplements to access its health benefits.
Gain Early Access to Market Insights – Request a Sample
Mergers and Acquisitions
Strategic collaborations and acquisitions are becoming critical growth drivers in the green banana flour market. Companies are focusing on vertical integration to secure sustainable banana supplies and investing in advanced food technology firms to enhance production quality.
Recent M&A activities reflect a trend towards expanding organic product lines and integrating eco-friendly processing methods
Key Takeaways
• The green banana flour market is expected to reach USD 1,141.8 million by 2035. • Rising demand for gut-health promoting ingredients and gluten-free alternatives are major growth drivers. • Technological innovation in AI-based farming and biofortification are emerging enablers. • Increasing incorporation of banana flour in functional foods, sports nutrition, and plant-based products is propelling market expansion.
Commercial Applications of Green Banana Flour in Food Industry
Green banana flour is no longer confined to health food stores. It’s widely used in commercial applications such as baking, snack manufacturing, baby food production, and even sports nutrition products.
Its functional properties, such as water retention and binding, make it a versatile ingredient.
Gluten-Free Product Trends Boosting Green Banana Flour Sales
The explosion of gluten-free food trends has played a pivotal role in green banana flour’s success. Food brands are launching gluten-free breads, pastries, and snacks, with green banana flour often cited as a superior alternative to rice or almond flour.
Innovations Shaping the Future of Green Banana Flour Production
Technological advancements such as freeze-drying and spray-drying methods are enhancing the quality and shelf-life of green banana flour. Innovations aimed at preserving the nutritional content are likely to set future benchmarks.
Recent Developments in the Market
• 2024: Major players launched organic and biofortified green banana flour variants. • 2025: Adoption of AI in agricultural monitoring systems for improved banana yields. • 2025: Introduction of green banana flour in functional snacks and beverages targeted at sports nutrition markets.
Competition Outlook
The market is moderately fragmented, with companies investing in organic certifications, sustainable sourcing practices, and product innovation. Top players are expanding their e-commerce footprint to meet growing direct-to-consumer demand.
Partnerships with functional food brands and health-focused companies are likely to reshape competitive dynamics.
Market Share Analysis by Company
• Natural Evolution • International Agriculture Group (IAG) • NuNaturals Inc. • Kanegrade Ltd. • Woodland Foods • Other Companies (combined)
Transform Data into Action – Get the Full Market Report
Region-wise Insights
United States North America leads the market due to growing demand for gluten-free foods, gut health awareness, and banana flour applications in baking and functional foods. The rise of plant-based diets and novel processing technologies like enzymatic treatment and spray drying are boosting product innovation.
E-commerce is rapidly reshaping the distribution landscape. CAGR (2025-2035): 5.1%
United Kingdom In the UK, demand for clean-label, allergen-free ingredients and the use of resistant starch in gut-health products are key drivers. Premium banana flour offerings benefit from the expansion of the organic and non-GMO food categories.
Sustainability in sourcing and packaging is also influencing buying behavior. CAGR (2025-2035): 4.6%
European Union A shift toward high-fiber, prebiotics-rich foods, regulatory backing for clean-label products, and innovations like alternative flour blends are fueling the EU market. The application of banana flour in infant nutrition and protein-enriched foods is expanding rapidly. CAGR (2025-2035): 4.9%
Japan Japan’s market is driven by rising interest in digestive health, growing demand for plant-based functional foods, and innovative uses of banana flour in traditional snacks and desserts. Advances in precision food processing ensure high-quality, nutrient-rich offerings. CAGR (2025-2035): 4.5%
South Korea South Korea is becoming a major market, with growing demand for low-GI, gluten-free, and clean-label products. Advances in AI-based food formulation and processing technologies are aiding product development, while consumer demand for banana flour in protein bars and energy snacks continues to rise. CAGR (2025-2035): 5.0%
Green Banana Flour Market Segmentation
By Product Type: • Organic • Conventional
By Process: • Spray Dried • Sun Dried • Freeze Dried • Others
By Sales Channel: • Convenience Store • Specialty Store • Online Retailers
By Region: • North America • Latin America • Western Europe • Eastern Europe • East Asia • South Asia Pacific • Middle East and Africa
0 notes
Text
Agri Micronutrients Market shooting from $4.5B to $8.3B by 2034 🌻📈 (CAGR 6.3%)
Agricultural Micronutrients Market is experiencing a remarkable transformation, driven by the increasing need for sustainable agriculture and improved crop productivity. Valued at $4.5 billion in 2024, the market is set to reach $8.3 billion by 2034, growing at a healthy CAGR of 6.3%. Micronutrients such as zinc, iron, boron, and manganese are essential for plant growth, aiding in processes like photosynthesis, enzyme function, and resistance to disease. The rising demand for high-yield crops and healthy soil composition is compelling farmers worldwide to turn to these micro-elements. With food security becoming a global priority and arable land under stress, micronutrients are now the unsung heroes of modern farming.
Market Dynamics
The market’s momentum is being fueled by a mix of drivers and challenges. Technological advancements in precision agriculture — like GPS-guided soil mapping and sensor-based nutrient monitoring — are enabling more efficient application of micronutrients.
Click to Request a Sample of this Report for Additional Market Insights: https://www.globalinsightservices.com/request-sample/?id=GIS21475
Farmers can now deliver the right nutrient, in the right amount, at the right time. However, high raw material costs, a lack of awareness among farmers, and regional soil variability are posing challenges. Moreover, the fluctuating prices of key minerals used in micronutrient formulations are creating volatility. Still, the shift toward organic farming, government subsidies, and innovations in biofortification are helping counterbalance these hurdles, opening up new avenues for market expansion.
Key Players Analysis
A mix of global giants and emerging innovators are shaping the competitive landscape. Yara International, BASF SE, The Mosaic Company, and Nutrien dominate the market with wide product portfolios and global distribution networks. Their investments in R&D and collaborations with agricultural tech firms are keeping them ahead in innovation. Meanwhile, a wave of emerging players like Micro Green Solutions, Nutra Field Technologies, and Vital Soil Components is disrupting the market with niche formulations and organic micronutrient blends. These players are agile, experimental, and closer to the ground realities of farmers in emerging economies, positioning them well for future growth.
Regional Analysis
Asia-Pacific remains the undisputed leader, commanding over 55% of the global market share. Countries like India and China are at the forefront due to their massive agricultural footprint and adoption of advanced farming techniques. North America follows, driven by a tech-savvy farming community and regulatory emphasis on sustainable agriculture. In Europe, stringent nutrient management laws and a growing organic food trend are propelling the demand for eco-friendly micronutrient products. Latin America shows promising growth, especially in Brazil and Argentina, due to large-scale commercial farming. The Middle East and Africa are emerging markets, with governments pushing agricultural productivity in water-stressed regions using micronutrient solutions.
Recent News & Developments
The past year has seen a surge in strategic collaborations and product innovations. Companies like ICL Group and Wilbur-Ellis are integrating AI and drone technology to fine-tune micronutrient delivery. In Europe and North America, the push for eco-friendly agriculture is influencing pricing strategies, leading to an uptick in demand for organic micronutrient products. Supply chain disruptions due to geopolitical issues and climate change are prompting companies to localize their sourcing strategies. Meanwhile, precision agriculture is evolving rapidly, with GPS-enabled tools and smart sprayers enhancing micronutrient efficiency, reducing wastage, and improving ROI for farmers.
Browse Full Report : https://www.globalinsightservices.com/reports/agricultural-micronutrients-market/
Scope of the Report
This report offers a deep dive into the type, application, form, and regional breakdown of the Agricultural Micronutrients Market. It includes both qualitative and quantitative analysis covering growth drivers, challenges, competitive landscape, and future opportunities. Segments such as chelated vs. non-chelated micronutrients, application methods like soil, foliar, fertigation, and end-users including farmers, cooperatives, and research organizations are meticulously analyzed. Moreover, the study explores market behavior across regions and forecasts performance up to 2034. It is designed to help stakeholders — ranging from investors to policymakers — make informed, data-driven decisions in the agricultural ecosystem.
Discover Additional Market Insights from Global Insight Services:
Pea Protein Market : https://www.globalinsightservices.com/reports/pea-protein-market/
Ice Cream Market ; https://www.globalinsightservices.com/reports/ice-cream-market/
Agricultural Micronutrients Market : https://www.globalinsightservices.com/reports/agricultural-micronutrients-market/
Food Contact Paper Market : https://www.globalinsightservices.com/reports/food-contact-paper-market/
Wet Pet Food Market : https://www.globalinsightservices.com/reports/wet-pet-food-market/
#agriculture #micronutrients #sustainablefarming #precisionagriculture #soilhealth #cropnutrition #planthealth #agritech #organicfarming #zincfertilizers #boronbenefits #smartfarming #farminnovations #yieldboost #agriculturalreform #farmingtech #agroindustry #cropyield #plantgrowth #greenfarming #ecofriendlyagriculture #climatefarming #biofortification #agroscience #nutrientmanagement #foodsecurity #cropscience #farmingfuture #soilscience #smartagriculture #sustainablesoil #fertilizertech #farmerfirst #agribusiness #foodinnovation #modernfarming #farminginsights #precisioncropcare #smartsoil #organicgrowth #greentechnology
About Us:
Global Insight Services (GIS) is a leading multi-industry market research firm headquartered in Delaware, US. We are committed to providing our clients with highest quality data, analysis, and tools to meet all their market research needs. With GIS, you can be assured of the quality of the deliverables, robust & transparent research methodology, and superior service.
Contact Us:
Global Insight Services LLC 16192, Coastal Highway, Lewes DE 19958 E-mail: [email protected] Phone: +1–833–761–1700 Website: https://www.globalinsightservices.com/
0 notes
Text
Will the vegetables of the future be fortified using tiny needles?
New Post has been published on https://sunalei.org/news/will-the-vegetables-of-the-future-be-fortified-using-tiny-needles/
Will the vegetables of the future be fortified using tiny needles?

When farmers apply pesticides to their crops, 30 to 50 percent of the chemicals end up in the air or soil instead of on the plants. Now, a team of researchers from MIT and Singapore has developed a much more precise way to deliver substances to plants: tiny needles made of silk.
In a study published today in Nature Nanotechnology, the researchers developed a way to produce large amounts of these hollow silk microneedles. They used them to inject agrochemicals and nutrients into plants, and to monitor their health.
“There’s a big need to make agriculture more efficient,” says Benedetto Marelli, the study’s senior author and an associate professor of civil and environmental engineering at MIT. “Agrochemicals are important for supporting our food system, but they’re also expensive and bring environmental side effects, so there’s a big need to deliver them precisely.”
Yunteng Cao PhD ’22, currently a postdoc Yale University, and Doyoon Kim, a former postdoc in the Marelli lab, led the study, which included a collaboration with the Disruptive and Sustainable Technologies for Agricultural Precision (DiSTAP) interdisciplinary research group at the Singapore-MIT Alliance for Research and Technology (SMART).
In demonstrations, the team used the technique to give plants iron to treat a disease known as chlorosis, and to add vitamin B12 to tomato plants to make them more nutritious. The researchers also showed the microneedles could be used to monitor the quality of fluids flowing into plants and to detect when the surrounding soil contained heavy metals.
Overall, the researchers believe the microneedles could serve as a new kind of plant interface for real-time health monitoring and biofortification.
“These microneedles could be a tool for plant scientists so they can understand more about plant health and how they grow,” Marelli says. “But they can also be used to add value to crops, making them more resilient and possibly even increasing yields.”
The inner workings of plants
Accessing the inner tissues of living plants requires scientists to get through the plants’ waxy skin without causing too much stress. In previous work, the researchers used silk-based microneedles to deliver agrochemicals to plants in lab environments and to detect pH changes in living plants. But these initial efforts involved small payloads, limiting their applications in commercial agriculture.
“Microneedles were originally developed for the delivery of vaccines or other drugs in humans,” Marelli explains. “Now we’ve adapted it so that the technology can work with plants, but initially we could not deliver sufficient doses of agrochemicals and nutrients to mitigate stressors or enhance crop nutritional values.”
Hollow structures could increase the amount of chemicals microneedles can deliver, but Marelli says creating those structures at scale has historically required clean rooms and expensive facilities like the ones found inside the MIT.nano building.
For this study, Cao and Kim created a new way to manufacture hollow silk microneedles by combining silk fibroin protein with a salty solution inside tiny, cone-shaped molds. As water evaporated from the solution, the silk solidified into the mold while the salt forms crystalline structures inside the molds. When the salt was removed, it left behind in each needle a hollow structure or tiny pores, depending on the salt concentration and the separation of the organic and inorganic phases.
“It’s a pretty simple fabrication process. It can be done outside of a clean room — you could do it in your kitchen if you wanted,” Kim says. “It doesn’t require any expensive machinery.”
The researchers then tested their microneedles’ ability to deliver iron to iron-deficient tomato plants, which can cause a disease known as chlorosis. Chlorosis can decrease yields, but treating it by spraying crops is inefficient and can have environmental side effects. The researchers showed that their hollow microneedles could be used for the sustained delivery of iron without harming the plants.
The researchers also showed their microneedles could be used to fortify crops while they grow. Historically, crop fortification efforts have focused on minerals like zinc or iron, with vitamins only added after the food is harvested.
In each case, the researchers applied the microneedles to the stalks of plants by hand, but Marelli envisions equipping autonomous vehicles and other equipment already used in farms to automate and scale the process.
As part of the study, the researchers used microneedles to deliver vitamin B12, which is primarily found naturally in animal products, into the stalks of growing tomatoes, showing that vitamin B12 moved into the tomato fruits before harvest. The researchers propose their method could be used to fortify more plants with the vitamin.
Co-author Daisuke Urano, a plant scientist with DiSTAP, explains that “through a comprehensive assessment, we showed minimal adverse effects from microneedle injections in plants, with no observed short- or long-term negative impacts.”
“This new delivery mechanism opens up a lot of potential applications, so we wanted to do something nobody had done before,” Marelli explains.
Finally, the researchers explored the use of their microneedles to monitor the health of plants by studying tomatoes growing in hydroponic solutions contaminated with cadmium, a toxic metal commonly found in farms close to industrial and mining sites. They showed their microneedles absorbed the toxin within 15 minutes of being injected into the tomato stalks, offering a path to rapid detection.
Current advanced techniques for monitoring plant health, such as colorimetric and hyperspectral lead analyses, can only detect problems after plants growth is already being stunted. Other methods, such as sap sampling, can be too time-consuming.
Microneedles, in contrast, could be used to more easily collect sap for ongoing chemical analysis. For instance, the researchers showed they could monitor cadmium levels in tomatoes over the course of 18 hours.
A new platform for farming
The researchers believe the microneedles could be used to complement existing agricultural practices like spraying. The researchers also note the technology has applications beyond agriculture, such as in biomedical engineering.
“This new polymeric microneedle fabrication technique may also benefit research in microneedle-mediated transdermal and intradermal drug delivery and health monitoring,” Cao says.
For now, though, Marelli believes the microneedles offer a path to more precise, sustainable agriculture practices.
“We want to maximize the growth of plants without negatively affecting the health of the farm or the biodiversity of surrounding ecosystems,” Marelli says. “There shouldn’t be a trade-off between the agriculture industry and the environment. They should work together.”
This work was supported, in part, by the U.S. Office of Naval Research, the U.S. National Science Foundation, SMART, the National Research Foundation of Singapore, and the Singapore Prime Minister’s Office.
0 notes
Text
Explore the development direction of organic fertilizer equipment
The development direction of organic fertilizer equipment is moving towards high efficiency, intelligence, environmental protection and sustainability. The following is a specific analysis:
1. Intelligent monitoring and remote control: In the future, organic fertilizer equipment will be more intelligent, and remote monitoring and fault diagnosis of equipment will be realized through Internet of Things technology. Operators can view the operating status of equipment in real time through mobile phones or computers, adjust parameters in time, and improve production efficiency.
2. Automated production process: The equipment will have a higher level of automation, reduce manual intervention, improve production efficiency and product quality.
3. Environmental protection and energy saving: The equipment will use energy-saving materials and processes to reduce energy consumption and pollution emissions.
4. Resource recycling: The equipment will pay more attention to the recycling of resources and reduce waste emissions. For example, the waste gas generated during the fermentation process of the organic fertilizer production line can be treated by the biological deodorization system and discharged to the standard, and the wastewater can be reused after treatment to achieve zero emissions.
5. Market demand and policy support: With the enhancement of environmental awareness and the development of sustainable agriculture, the market demand for organic fertilizers will continue to grow. The increase in consumer demand for green and organic agricultural products has driven the development of the organic fertilizer equipment market.
6. Technological innovation: Research and development of new fermentation technologies, such as microbial fermentation technology, biofortification technology, etc., to improve fermentation efficiency and product quality.
7. Intelligent control system: The introduction of advanced sensors and automatic control systems to achieve intelligent management and optimized operation of equipment.
In summary, the development direction of organic fertilizer equipment will focus on intelligence, environmental protection, high efficiency and sustainability, and promote the green transformation and sustainable development of agriculture.

0 notes
Text
The Role of Biotech in Food Security and Nutrition

Food security isn’t just a buzzword where I work—it’s the daily problem we solve. Every time we map a gene sequence, field-test a drought-tolerant crop, or pilot biofortified seed varieties, we’re dealing with real-world hunger, nutritional gaps, and fragile supply chains. I’ve spent years in biotech labs and field collaborations focused on one goal: helping more people get the food they need, with the nutrients they’re missing, in the face of unpredictable climate and rising costs. Biotechnology gives us the tools to do that. It lets us breed faster, grow smarter, and deliver value at the cellular level. From pest-resistant cotton in India to iron-rich beans in East Africa, I’ve seen how this science shows up in people’s meals. Here’s what that work looks like behind the scenes—and why it matters.
We Use Genetic Modification to Maximize Output in Tough Conditions
I work with teams that design crop traits for specific regional stressors. Drought, salinity, pests—you name it. When we develop drought-tolerant maize, it's because farmers in sub-Saharan Africa can’t afford to lose another harvest. We’re not guessing which traits might help—we’re engineering the plant to hold on to moisture longer, produce more under less, and resist pests without constant chemical intervention.
These aren’t lab-bound ideas. They’re planted, harvested, and evaluated by growers working on plots where every square meter matters. Pest-resistant cotton, Bt brinjal (eggplant), and herbicide-tolerant soybeans are all commercialized products we’ve helped scale, not academic curiosities.
Yields aren’t just going up—they’re becoming more stable, which is just as important. A 10% bump in output is useful. But predictable harvests that don’t crash in heat waves or insect infestations? That’s what builds food security.
We Use Biofortification to Tackle Hidden Hunger
I’ve worked on vitamin A–enhanced rice projects, and I’ve seen how skeptical policymakers become strong supporters once the data hits. Golden Rice was one of the first biofortified crops I helped push toward regulatory review, and the science behind it changed how we design for nutrition.
In many low-income regions, food is available but dangerously low in essential nutrients. That's where biotech closes the gap. We’ve engineered cassava with higher zinc, maize with more lysine, and beans with higher iron content. These aren't food supplements; they’re staple crops redesigned to deliver what diets lack—directly through everyday meals.
We’ve learned to match our work to what people already eat. Changing dietary habits takes decades. Changing crop profiles can take a few growing seasons when the biotech pipeline works efficiently.
We Reduce Chemical Dependency with Smarter Crops
One of the most satisfying parts of biotech work is helping farmers cut their input costs. In projects we’ve run across Southeast Asia and Latin America, we’ve replaced multiple pesticide sprays per season with a single genetically engineered resistance trait.
That’s not just a cost saving. It reduces environmental exposure, protects non-target species, and keeps farm workers safer. Herbicide-tolerant crops also enable conservation tillage, which keeps soil intact and improves water retention—critical in arid and semi-arid zones where we’re working to stabilize yields.
We still run extensive field trials to test these benefits over time. But when I visit partner farms and see farmers using less spray and getting better crops, it’s a clear reminder that biotechnology isn’t just about better science—it’s about better farming.
We Extend Shelf Life and Reduce Food Loss with Gene Editing
I’ve worked on CRISPR-edited bananas that resist bruising and last longer post-harvest. Those traits don’t sound dramatic until you see the difference in truckload losses. In high-temperature regions, perishable crops often rot before they reach market—not because of quality, but because the supply chain is unforgiving.
By editing genes that control ethylene production (the ripening hormone), we’re slowing down spoilage without adding chemicals or refrigeration. Tomatoes, lettuce, and even leafy greens are getting shelf-life upgrades using similar techniques.
This reduces food waste not only at the consumer level, but across the transport and distribution chain. It’s biotech supporting efficiency, especially in places that lack cold storage infrastructure.
Food Safety and Public Confidence Depend on How We Communicate
Every time we bring a new crop forward, there’s a conversation about risk—and there should be. But those conversations have to be driven by science, not fear. That’s why I sit in on regulatory reviews, public outreach sessions, and technical Q&As with local governments.
We share everything—gene sequences, trial data, allergen profiles, environmental impact assessments—because transparency earns trust. And once communities understand that these crops aren’t strange or dangerous, but carefully tested and targeted tools, the resistance fades.
Food security doesn’t just come from better seeds. It comes from public confidence that those seeds are safe, beneficial, and responsibly managed.
Policy Determines Whether Good Science Reaches Farmers
I’ve worked in regions where the science was ready, but the politics weren’t. That delay costs time, investment, and—frankly—lives. When biotech crops are stuck in regulatory bottlenecks, it slows adoption and leaves vulnerable communities with fewer options.
On the flip side, I’ve seen what happens when policy supports the science. China’s recent move to approve gene-edited crops is going to open the door for massive yield gains in rice and soy. Brazil’s flexible regulatory system has helped launch some of the most successful biotech crop portfolios in the world.
As developers, we can only take things so far. Governments have to meet us halfway with science-based policies that allow innovation to scale safely and fairly.
How Biotech Supports Global Nutrition
Boosts yields – Through drought, pest, and disease resistance
Enhances nutrients – With biofortified crops targeting deficiencies
Reduces waste – With longer-lasting fruits and vegetables
Lowers input needs – By cutting pesticide and fertilizer use
Adapts to climate – By building resilience into crop genetics
Innovation Only Matters if It Reaches the Plate
Biotechnology isn't just about improving crops. It’s about connecting lab innovation to the dinner table—especially where nutrition and access are most at risk. Every project I support—whether it’s a gene-edited rice variety or a vitamin-rich legume—is tied to real problems we’re solving with farmers, governments, and food producers on the ground.
What makes this work powerful is its reach. A single biotech breakthrough doesn’t just change a seed. It changes a harvest, a diet, and a future. And when we get it right—scientifically, ethically, and collaboratively—those changes feed millions.
Biotechnology isn’t just about smarter crops; it’s about smarter solutions to global hunger and nutrition challenges. For more insights on how science meets the real world, visit Tumblr.
0 notes
Video
youtube
Chickpea Biofortification: A Nutrient Powerhouse! #sciencefather #resear...
0 notes
Text
Can Technology Solve the World’s Hunger Problems?

Published on September 23, 2024
Hunger remains one of the world's most significant challenges, affecting millions of people daily. While progress has been made, a vast number of people in developing countries still struggle to access nutritious food. With advancements in technology, many experts now question whether innovations can address this issue more effectively. Can technology really help us eradicate hunger?
In this article, we explore the role of technology in addressing hunger problems and how it is already making a difference. We'll also look at future possibilities and challenges that come with relying on technology to tackle one of the world's most enduring problems.
Understanding the Hunger Problem
Hunger isn't just a lack of food; it's also about the lack of access to nutritious and affordable food. Many developing countries face challenges such as poor infrastructure, drought, war, and poverty. According to the United Nations, approximately 828 million people were undernourished globally in 2022. This figure is a stark reminder that hunger is a global crisis that needs comprehensive solutions.
Traditional methods of addressing hunger have relied on food aid, but these are often short-term solutions that do not tackle the root causes. This is where technology comes into play.
How Technology Is Already Helping
1. Agriculture and Farming Innovations
One of the biggest technological advances in recent years is in agriculture. Drones, sensors, and smart irrigation systems are being used to improve farming efficiency. Farmers can now monitor their crops remotely, identifying potential problems such as water shortages or disease outbreaks before they become critical.
In developing countries, mobile apps are being introduced to help farmers learn about the best practices in farming, weather forecasts, and market prices. For example, platforms like FarmLogs provide real-time data to farmers, helping them make informed decisions about their crops.
2. Food Production and Distribution
3D food printing is one of the more futuristic technologies being developed to combat hunger. While still in its early stages, the idea is that 3D printers could produce nutritious food using sustainable ingredients such as plant proteins. This technology could be especially helpful in areas where food production is limited.
Improving the food supply chain is another area where technology is making a difference. Blockchain technology is being tested to create transparent and secure food supply chains. This ensures that food gets to the right places, reducing waste and inefficiencies in the process.
3. Food Fortification
Malnutrition is a major issue in many regions. Many people have enough food but lack access to the vitamins and minerals needed for a healthy diet. Biofortification—adding nutrients to crops during the growing process—is an innovative solution. Scientists are working on developing genetically modified crops that contain higher levels of essential nutrients like Vitamin A and iron. Golden Rice, for example, has been biofortified with Vitamin A to help combat blindness caused by malnutrition.If you read more interesting social life stories. Click Here
1 note
·
View note
Text
Food Fortifying Agents Market Future Outlook: Analyzing Size, Share, and Growth Patterns
The global food fortifying agents market size is expected to reach USD 169.47 billion by 2030, expanding at a CAGR of 9.1% from 2024 to 2030, according to a new report by Grand View Research, Inc. The market is driven by rising awareness of the need for nutrient-rich diets, particularly in developing regions where deficiencies are common. Government regulations and initiatives mandating fortification to combat malnutrition also play a significant role. Additionally, the growing health and wellness trend is increasing demand for functional foods and beverages enriched with essential nutrients. The expansion of the global food and beverage industry, combined with advancements in fortification technologies, facilitates the integration of these agents into various products, further boosting market growth.

Companies are investing in research and development to create more effective and sustainable fortifying agents. For instance, biofortification, which involves enhancing the nutritional profile of crops during the growth phase, is gaining traction. Partnerships and collaborations between food manufacturers and biotechnology firms are leading to the development of novel fortifying compounds with improved absorption and health benefits. Regulatory bodies in various regions are updating and expanding their fortification guidelines to include a broader range of nutrients and food products. Additionally, the market is witnessing the introduction of fortified foods targeted at specific demographics, such as children, pregnant women, and the elderly, to meet their unique nutritional needs.
Innovations in microencapsulation technology are also playing a crucial role in the market. Microencapsulation involves enclosing nutrients in a protective coating, enhancing their stability and bioavailability. This technology allows for better incorporation of fortifying agents into various food matrices without compromising taste, texture, or shelf life. Improved nutrient delivery and absorption are critical in ensuring that fortified foods provide the intended health benefits, making microencapsulation a valuable tool for manufacturers.
Companies are developing new technologies. For instance, in February 2022 Xampla, based in Cambridge, developed a plant-based material from pea protein to protect vitamins in clear beverage bottles from UV degradation. This innovation allows the use of clear, recyclable bottles, preferred by consumers, without vitamin loss. The company received USD 1.28 million from Innovate UK to scale production and is partnering with Britvic to implement the technology. Britvic, known for fortifying drinks with vitamins C, D, and B, has moved brands like Fruit Shoot and 7UP to clear bottles to enhance recycling. Xampla's technology effectively addresses a key industry challenge.
For More Details or Sample Copy please visit link @: Food Fortifying Agents Market Report
Food Fortifying Agents Market Report Highlights
Based on type, vitamin food fortification agents dominated the market, accounting for 28% of global revenue in 2023. Widespread deficiencies and health benefits drive government initiatives and consumer demand for fortified foods
Based on application, dairy and dairy-based products dominated the market with a 25.1% revenue share in 2023. Their widespread consumption, nutritional profile, and distribution capabilities make them ideal for nutrient fortification
North America accounted for a share of 30.4% in 2023, driven by its advanced food industry, consumer awareness, and supportive regulations
Gain deeper insights on the market and receive your free copy with TOC now @: Food Fortifying Agents Market Report
We have segmented the global food fortifying agents market on the basis of type, application, and region.
0 notes
Text
Gummy Supplement Market to Witness Unprecedented Growth in Coming Years
The global gummy supplement market is projected to reach USD 48.5 billion by 2028 from USD 24.6 billion by 2023, at a CAGR of 14.5% during the forecast period in terms of value. An increase in diseases, disposable incomes, and awareness of fortified food products is driving the gummy supplements market. The chewy texture of gummies is a distinctive feature that appeals to individuals of all age groups, making them an attractive product for consumption. Gummies are a tasty and enjoyable delight to eat because of their appealing soft, spongy texture. Gummies are a simple and portable supplement option because they are frequently provided in small, sealed packets or containers. They are a well-liked option for time-pressed consumers searching for a quick and delectable treat because they are simple to transport and enjoy when traveling.

The desire to eat healthier has gradually increased interest in seeking convenient and enjoyable ways to supplement their diets. Gummies offer a fun and tasty alternative to traditional supplement formats like pills and capsules. The demand for gummy supplements is driven by the aging population seeking more palatable ways to consume dietary supplements. Gummy supplements' ability to mask unpleasant Flavors and Odors has made them an attractive option for consumers across all ages.
Gummy Supplements Market Drivers: Rising rate of vitamin-deficiency diseases and undernutrition
Micronutrient deficiencies significantly impair immune systems, hinder infant growth and development, and limit human potential, leading to higher morbidity and mortality rates. Deficiencies in iron, vitamin A, zinc, folate, vitamin B12, vitamin D, and iodine can have severe health consequences, including increased susceptibility to infections, birth defects, blindness, stunted growth, cognitive impairment, poor school performance and productivity, and even death. Adolescent girls, women of reproductive age (15-49 years), pregnant and lactating women, and young infants are particularly vulnerable to the adverse effects of micronutrient deficiency due to their high nutritional requirements. Scientific studies have shown that improving diets, fortifying staple foods and condiments, biofortification, and supplementation can boost micronutrient intake in the general population or among those with higher needs. This can reduce maternal and child morbidity, impaired neurocognitive development, and mortality associated with micronutrient deficiencies.
Gummy supplements, such as vitamins, are designed to be more palatable than traditional vitamin tablets and capsules, increasing the likelihood of regular consumption. Additionally, vitamins that are soluble, chewable, sticky, or in powder form tend to be easier to digest. Vitamin C and B2 (riboflavin) are the most frequently incorporated vitamins in multivitamin gummies.
Download PDF Brochure: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/pdfdownloadNew.asp?id=39376426
Vitamin Gummies was one of the types Which Accounted Highest Market Share in North America
Vitamin gummies, a type of gummy supplement, are becoming increasingly popular due to their convenience and appealing taste. They offer a tasty and easy way to get essential vitamins and minerals without the need to swallow pills or capsules. Available in a variety of Flavors and shapes, they are enjoyed by both adults and children.
The popularity of vitamin gummies has surged in North America, driving significant growth in the gummy supplements market. This trend is fuelled by the rising incidence of vitamin deficiencies and undernourishment, alongside an increasing demand for vitamin C and D supplements. The need for personalized supplement solutions has further boosted this market. However, while vitamin gummies can be a convenient and enjoyable addition to one’s diet, they should not replace a healthy, balanced diet. A well-rounded diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, remains essential for providing the necessary nutrients for optimal health.
Request Sample Pages: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/requestsampleNew.asp?id=39376426
US is one of the Major Market for Gummy Supplement in North America
The United States is one of the leading markets for gummy supplements in North America. In recent years, the popularity of gummy supplements has surged due to several factors. These include a rise in vitamin deficiencies, a growing demand for vitamin C and D supplements, and the increasing need for personalized supplement solutions. Gummy supplements offer a convenient and flavourful way to address vitamin deficiencies and support health and wellness goals.
The key players in the gummy supplements market include GSK Plc. (UK), Haleon Group of Companies (UK), Church & Dwight Co., Inc. (US), Amway (US), Bayer AG (Germany), Nestle (Switzerland), Unilever (UK), and Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (Japan).
#Gummy Supplement Market#Gummy Supplement#Gummy Supplement Market Size#Gummy Supplement Market Share#Gummy Supplement Market Growth#Gummy Supplement Market Trends#Gummy Supplement Market Forecast#Gummy Supplement Market Analysis#Gummy Supplement Market Report#Gummy Supplement Market Scope#Gummy Supplement Market Overview#Gummy Supplement Market Outlook#Gummy Supplement Market Drivers#Gummy Supplement Industry#Gummy Supplement Companies
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
Cross-Industry Collaborations in the Carotenoids Market

Introduction:
In an era of interconnectedness and shared expertise, cross-industry collaborations are emerging as catalysts for innovation, driving advancements in diverse fields including nutrition, healthcare, agriculture, and cosmetics. Within the carotenoids market, collaboration between stakeholders from different industries is fostering synergies, accelerating research, and expanding market opportunities.
This article explores the significance of cross-industry collaborations in the carotenoids market, recent examples of successful partnerships, and their impact on product development, sustainability, and market growth.
According to Next Move Strategy Consulting, the global Carotenoids Market is predicted to reach USD 2.43 billion by 2030 with a CAGR of 4% from 2024-2030.
Download FREE Sample: https://www.nextmsc.com/carotenoids-market/request-sample
The Power of Collaboration:
Cross-industry collaborations bring together complementary expertise, resources, and perspectives to tackle complex challenges and seize new opportunities. By pooling knowledge from diverse fields such as biotechnology, food science, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics, collaborators can leverage synergies, accelerate innovation cycles, and drive meaningful outcomes. In the carotenoids market, collaborations between researchers, manufacturers, suppliers, and end-users are facilitating the development of novel products, technologies, and applications with enhanced efficacy, safety, and sustainability.
Key Areas of Collaboration:
Cross-industry collaborations in the carotenoids market span a wide range of areas, including research and development, ingredient sourcing, formulation technology, and market access. For example, collaborations between food companies and agricultural suppliers are driving advancements in sustainable farming practices, biofortification, and crop breeding to enhance the nutritional content of staple crops with carotenoids.
Similarly, partnerships between pharmaceutical companies and research institutions are advancing the development of carotenoid-based therapies for various health conditions, including age-related macular degeneration (AMD), cancer, and cardiovascular diseases.
Geographical Analysis:
Europe emerges as the dominant force in the carotenoids market throughout the forecast period, driven by multiple commercial expansions and the active involvement of top market players operating and investing in the region. The continuous commitment and strategic initiatives of these key industry players significantly contribute to the robust growth and overall prominence of the carotenoids market in Europe thereby driving the market growth. The carotenoids market in the Asia-Pacific region is experiencing substantial growth, primarily driven by the presence of a large population in the region.
The significant demographic size in Asia-Pacific offers an expansive consumer base for the carotenoids market. The region's growing awareness of the health benefits and application of carotenoid products across various applications, including food, healthcare, and cosmetics, further fuels the market's expansion. The burgeoning food and beverage industry in the Asia-Pacific region complements the growth of the carotenoid market.
As this industry expands, there is an increased demand for natural additives and ingredients, including carotenoids, to meet consumer preferences for clean-label and healthier products. This presents a significant opportunity for carotenoid manufacturers to tap into the growing market in the Asia-Pacific region and cater to the evolving needs of food and beverage companies in this thriving market.
Recent Examples of Collaborations:
In recent years, there have been several notable examples of successful cross-industry collaborations in the carotenoids market. For instance, a partnership between a biotechnology company and a food manufacturer resulted in the development of a novel microalgae strain engineered to produce high levels of astaxanthin, a potent carotenoid with antioxidant properties. This collaboration enabled the commercialization of sustainable, plant-based astaxanthin supplements with superior purity and potency, meeting the growing demand for natural health products.
Similarly, a collaboration between a cosmetics company and a research institution led to the development of a patented delivery system for carotenoids in skincare formulations. By combining expertise in nanotechnology, dermatology, and cosmetic science, the partners created liposomal encapsulation technology that enhances the stability, bioavailability, and skin penetration of carotenoids, offering consumers effective protection against UV-induced oxidative stress and premature aging.
Future Outlook and Opportunities:
As the carotenoids market continues to expand and diversify, cross-industry collaborations are expected to play an increasingly vital role in driving innovation, sustainability, and market growth. With advancements in biotechnology, formulation technology, and consumer insights, collaborators can unlock new opportunities for developing novel products and applications that address evolving consumer preferences and market trends.
Moreover, collaborations between industry stakeholders and academic institutions can accelerate research and development efforts, foster knowledge exchange, and shape the future direction of the carotenoids market.
Inquire before buying: https://www.nextmsc.com/carotenoids-market/inquire-before-buying
Competitive Landscape:
The top market players operating in the carotenoids market are Koninklijke DSM, BASF SE, Chr. Hansen A/S, Kemin Industries, Lycored Ltd., Fuji Chemical Industry Co Ltd., Dohler Group Se, Allied Biotech Corporation, Farbest Brands, Excelvite Sdn. Bhd. and others. These market players are adopting various strategies such as product launches and collaborations to remain dominant in the market.
BASF and Cargill expanded their partnership to offer high-performance enzyme solutions to animal protein producers. This collaboration aims to provide innovative enzyme-based solutions, generating distinctive value for animal feed customers. The extended partnership includes the development, production, marketing, and sale of customer-centric enzyme products and solutions.
Recent News:
In a recent development, a company announced a strategic partnership with [Research Institution] to explore the therapeutic potential of carotenoids in combating inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD). Leveraging expertise in microbiology, immunology, and nutritional science, the partners will conduct preclinical studies to investigate the anti-inflammatory effects of carotenoids on gut health and immune function. This collaboration underscores the growing interest in leveraging carotenoids as natural remedies for chronic inflammatory conditions, paving the way for future dietary interventions and therapeutic applications.
Furthermore, a Ingredient Supplier and a Food Company announced a collaborative initiative to develop sustainable sourcing practices for carotenoid-rich ingredients. By working together to establish fair trade agreements, promote regenerative agriculture, and support smallholder farmers, the partners aim to ensure a stable and ethical supply chain for carotenoids while preserving biodiversity and environmental integrity. This collaboration reflects a shared commitment to sustainability and responsible sourcing in the carotenoids market, addressing growing consumer demand for transparent and ethical food production practices.
Conclusion:
Cross-industry collaborations are driving innovation, sustainability, and market growth in the carotenoids market, enabling stakeholders to harness the full potential of these valuable compounds for health, nutrition, and well-being. By fostering partnerships between researchers, manufacturers, suppliers, and end-users, collaborators can leverage collective expertise and resources to overcome challenges, seize opportunities, and create meaningful impact across diverse sectors.
As the pace of innovation accelerates and consumer expectations evolve, collaborative approaches will continue to shape the future of the carotenoids market, unlocking new possibilities for improving human health, environmental sustainability, and societal well-being.
#carotenoids#food and beverages#carots#market research'#global market#industry analysis#healthy eating
0 notes