#Battle flag of the Tennessee Army
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Ahem…
I have read plenty on this flag and what it represents… and I mean plenty

For instance, this version is the elongated Battle Flag of the Army of Tennessee with its slightly darker blue region than the 2nd Confederate Navy Jack that it is similar to … I told you I did some reading yo
Now, I want a layman's take on this What does this flag represent to a normal supporter of this flag
… over to you yo
#Battle flag of the Tennessee Army#2nd Confederate Navy Jack#I want the layman's take#I have already seen wiki#I have seen left and right sources too#2a#1a#fjb
11 notes
·
View notes
Text

“Tennessee, 1864. On a late autumn day, near a little town called Franklin, 10,000 men will soon lie dead or dying in a battle that will change many lives for ever. None will be more changed than Carrie McGavock, who finds her home taken over by the Confederate army and turned into a field hospital. Taking charge, she finds the courage to face up to the horrors around her and, in doing so, finds a cause.
Out on the battlefield, a tired young Southern soldier drops his guns and charges forward into Yankee territory, holding only the flag of his company's colours. He survives and is brought to the hospital. Carrie recognizes something in him - a willingness to die - and decides on that day, in her house, she will not let him.
In the pain-filled days and weeks that follow, both find a form of mutual healing that neither thinks possible.
In this extraordinary debut novel based on a true story, Robert Hicks has written an epic novel of love and heroism set against the madness of the American Civil War.”
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
Holidays 4.6
Holidays
ABW Day (Poland)
Animated Cartoon Day
Army Day (US)
Athletic Trainers and Physical Training and Sports Professionals Day (Kyrgyzstan)
Bohring-Optiz Syndrome Awareness Day
Castle Day (Japan)
Chakri Memorial Day (Thailand)
Circe Asteroid Day
Conor McGregor Day (UK)
Declaration of Arbroath Day (Scotland)
Drowsy Driver Awareness Day (California)
Evolution of Dance Day
Feigenbaum Constant Day
406 Day
Gender-Fluid Pride Day
Good Deeds Day
International Asexuality Day
International Day of Sport for Development and Peace (UN)
International Day of the Charango
International Recruiters Day
International Search & Rescue Beacon/406 Day
International Whistler’s Day
Jump Over Things Day
Kimbangu Day (DR Congo)
King Rama I Memorial and Chakri Day (Thailand)
Knock Your Socks Off Day
Larch Day (French Republic)
Modern Olympics Day
Näfelser Fahrt (Battle of Näfels; Switzerland)
National Charlie Brown’s Insecurities Day
National Employee Benefits Day
National Fisherman Day (Indonesia)
National Gang Day
National Health Day (Kiribati)
National Library Day
National Pajama Day
National Student-Athlete Day
North Pole Day
Ntaryamira Day (Burgundi)
Patriot’s Victory Day (Ethiopia)
Phocaea Asteroid Day
Plan Your Epitaph Day
Post-It Notes Day
Richard the Lionheart Day
Roberto Clemente Day
Self Determination Day (Australia)
Semana Santa (Argentina)
Sorry Charlie Day (in honor of those who have been rejected and lived through it)
Stigtingsdag (a.k.a. Founders Day or Van Riebeeck’s Day; South Africa)
Tartan Day (Canada, US)
Teflon Day
Think About Spring Cleaning Day
Van Riebeeck Day (Capetown, South Africa)
Waltzing Mathilda Day (Australia)
World Day of Physical Activity
World Table Tennis Day
Food & Drink Celebrations
Brew Year's Eve
Fresh Tomato Day
National Acai Bowl Day
National Caramel Popcorn Day
National Carbonara Day (Italy)
National Consider Drinking More Helles Day
National Food Faces Day
National Twinkie Day
National Viognier Day
New Beer's Eve
St. Sixtus' Day
Twinkie Day
Nature Celebrations
Adonis Day (Eternal Bliss; Korean Birth Flowers)
California Poppy Day
National Siamese Cat Day
Independence, Flag & Related Days
Capetown, South Africa (Founded; 1652) [Orania]
Cocos (Keeling) Islands (Act of Self Determination Day; 1984)
Koya (Declared; 2014) [unrecognized]
Republic of Venstral (Declared; 2018) [unrecognized]
Self-Determination Day (Cocos Islands)
Vancouver (Founded by Canadian Pacific Railway Company; 1886)
New Year’s Days
British Income Tax Year (UK)
Yazidi New Year (Iraq)
1st Sunday in April
A Drop of Water is a Grain of Gold (Turkmenistan) [1st Sunday]
English Breakfast Day (UK) [1st Sunday]
Geologists Day (Russia) [1st Sunday]
Mule Day (Columbia, Tennessee) [1st Sunday]
Parents & Children’s Day (Florida) [1st Sunday]
Seven For Sunday [Every Sunday]
Snack Sunday [1st Sunday of Each Month]
Spiritual Sunday [1st Sunday of Each Month]
Start Over Sunday [1st Sunday of Each Month]
Sundae Sunday [Every Sunday]
Sunday Funday [Every Sunday]
White Orchid Day [1st Sunday]
World Geologists Day [1st Sunday]
World Meditation Day [1st Sunday of Every Month]
World Transformation Day [1st Sunday]
Weekly Holidays beginning April 6 (1st Full Week of April)
Bat Appreciation Week [1st Full Week]
Be Kind to Spiders Week [1st Full Week]
Community Garden Week (UK) [1st Full Week]
Consider Christianity Week [begins 2nd Sunday before Easter]
Dumb Week (Greece) [thru 4.12]
Explore Your Career Options Week [1st Full Week]
International Trombone Week (thru 4.13)
National Blue-Ribbon Week [1st Full Week]
National Crime Victims’ Rights Week (thru 4.12)
National Library Week (thru 4.12)
National Medic Alert Week [1st Full Week]
National Oral, Head, and Neck Cancer Awareness Week (thru 4.12)
National Public Health Week [1st Full Week]
National Window Safety Week [1st Full Week]
New Haven Restaurant Week (New Haven, Connecticut) [thru 4.11]
Passion Week (thru 3.23) [Week before Holy Week; Christianity]
Passiontide (thru 3.30) [Passion Week + Holy Week]
Festivals On or Beginning April 6, 2025
The Laurence Olivier Awards (London, United Kingdom)
NFRA Executive Conference (Tempe, Arizona) [thru 4.9]
Vinitaly (Verona, Italy) [thru 4.9]
Zilker Kite Festival (Austin, Texas)
Feast Days
Aequinoctium Vernum VIII (Pagan)
Albrecht Dürer and Lucas Cranach (Lutheran Church)
Baily (Muppetism)
Beware of Lizardmen Day (Pastafarian)
Birth of Jesus (Mormons)
Brychan (Christian; Saint)
Celestine I, Pope (Catholic Church)
Children’s Springtime Festival (France; Everyday Wicca)
Church of Latter Day Saints Day
Colsus, Archbishop of Armagh (Christian; Saint)
Crane Bag Day (Celtic Book of Days)
Elstan (Christian; Saint)
Ether Sunday (Church of the SubGenius; Saint)
Eutychius of Constantinople (Eastern Orthodox Church)
Feast of the 120 Martyrs of Persia (Christian; Martyrs)
Fête des Petits Bateaux (Fête of the Little Boats; France)
Gudi Padwa (Birthday of Mother Earth; Maharashtra and Andhra Pradesh people)
Impersonate a Frog Day (Pastafarian)
Irenaeus of Sirmium (Christian; Saint)
Jake Day (Discordian)
Kanamara Matsuri (Fertility Festival; Japan)
Kimbanguiste Church Founding Day (Democratic Republic of the Congo)
Marcellinus of Carthage (Christian; Saint)
Pappus (Positivist; Saint)
Passover (a.k.a. Pesach; Judaism) [Nisan 16]
Prudentius, Bishop of Troyes (Christian; Saint)
Sixtus I, Pope (Christian; Saint)
Sorting-Out of the Doggets Day (Shamanism)
William the Confessor, Abbot of Eskille (Christian; Saint)
Fifth Sunday in Lent (Western Christianity) (a.k.a. ...
Care Sunday
Carling Sunday
Judica (Lutheranism)
Passion Sunday
Passiontide begins [lasts 2 weeks]
Solidarity Sunday
Lunar Calendar Holidays
Chinese: Month 3 (Geng-Chen), Day 9 (Y-Si)
Day Pillar: Wood Snake
12-Day Officers/12 Gods: Remove Day (除 Chu) [Auspicious]
Holidays: None Known
Secular Saints Days
Leigh Bardugo (Literature)
Graeme Base (Art)
Elizabeth Barrett Browning (Literature)
Leonora Carrington (Art)
Arthur Wesley Dow (Art)
Anthony H.G. Fokker (Science)
Merle Haggard (Music)
Jeanne Hébuterne (Art)
Harry Houdini (Entertainment)
Charles Huot (Art)
Charles Jackson (Literature)
Gil Kane (Art)
René Lalique (Art)
Barry Levinson (Entertainment)
James Mill (Philosophy)
Gustave Moreau (Art)
Gerry Mulligan (Music)
Guy Peellaert (Art)
Raphael (Art)
John Ratzenberger (Entertainment)
Hans Richter (Art)
Paul Rudd (Entertainment)
Sterling Sharpe (Sports)
Sebastian Spreng (Art)
Wilhelm von Kobell (Art)
John William Waterhouse (Art)
James D. Watson (Science)
Billy D. Williams (Entertainment)
Lucky & Unlucky Days
Fortunate Day (Pagan) [13 of 53]
Lucky Day (Philippines) [20 of 71]
Nēmontēmi, Day 2 (of 5) [Aztec unlucky or fasting days, taking place between 4.5-4.18]
Perilous Day (13th Century England) [14 of 32]
Taian (大安 Japan) [Lucky all day.]
Premieres
All Shook Up, by Elvis Presley (Song; 1957)
Along Flirtation Walk (WB MM Cartoon; 1935)
Attack on Titan (Anime TV Series; 2013)
Barney & Friends (Children’s TV Series; 1992)
Beef (TV Series; 2023)
Betty in Blunderland (Betty Boop Cartoon; 1934)
Blockers (Film; 2018)
The Boys from Brazil, by Ira Levin (Novel; 1976)
Buddy of the Legion (WB LT Cartoon; 1935)
The Bum Bandit (Betty Boop Cartoon; 1931)
The Castaway (Disney Cartoon; 1931)
Church of Jesus Christ of Latter Day Saints (Modern Cult/Religion; 1830)
Corn Chips (Donald Duck Disney Cartoon; 1951)
Country School (Oswald the Lucky Rabbit Cartoon; 1931)
Cry-Baby (Film; 1990)
The Dancing Fool (Betty Boop Cartoon; 1932)
Death Proof (Film; 2007)
Demon Slayer: Kimetsu no Yaiba (Anime TV Series; 2019)
Diva, by Annie Lennox (Album; 1992)
The Double Helix, by James D. Watson (Science Book; 1968)
Dough for the Do-Do (Blue Ribbon Hit Parade Cartoon; 1957)
The Dragons of Eden, by Carl Sagan (Science Essays; 1977)
The Flintstones: Little Big League (Hanna-Barbera Animated TV Special; 1978)
Flowers for Madame (WB MM Cartoon; 1936)
Fresh Fish (Blue Ribbon Hit Parade Cartoon; 1946)
The Gods Must Be Crazy (Film; 1984)
Going to Blazes (Oswald the Lucky Rabbit Cartoon; 1933)
Gold Chumps (Krazy Kat Cartoon; 1939)
Grifters, by Jim Thompson (Novel; 1963)
Grindhouse (Film; 2007)
Haikyu! (Anime TV Series; 2014)
Harbor Lights, by Bruce Hornsby (Album; 1993)
Humorous Phases of Funny Phases (Animated TV Show;1906) [1st Animated Cartoon]
I Love You to Death (Film; 1990)
Indian Pudding (Terrytoons Cartoon; 1930)
In Harm’s Way (Film; 1965)
Joe’s Lunch Wagon (Terrytoons Cartoon; 1934)
Join the Land Army (Hearst-Pathe News Cartoon; 1918)
Just Visiting (Film; 2001)
Kodak Flexible Rolled Film (Photography Film; 1889)
Ladies and Gentlemen: The Rolling Stones (Concert Film; 1971) [1st in Quadrophonic]
The Lost Weekend, by Charles R. Jackson (Novel; 1944)
Making Good (Oswald the Lucky Rabbit Cartoon; 1932)
Mamma Mia! (UK Musical Play; 1999)
The Millionaire Hare (WB LT Cartoon; 1963)
Monday Monday, by The Mamas and The Papas (Song; 1966)
Mony Mony, by Tommy James and The Shondells (Song; 1968)
Moscow on the Hudson (Film; 1984)
Mutt the Mutt Trainer (Mutt & Jeff Cartoon; 1919)
Nine Stories, by J.D. Salinger (Short Stories; 1953)
Olympics (Modern Olympics; 1896)
Outbreak, by Robin Cook (Novel; 1987)
Planet Terror (Film; 2007)
Popular Melodies (Fleischer Screen Songs Cartoon; 1933)
A Quiet Place (Film; 2018)
Robot Chicken DC Comics Special 2: Villains in Paradise (WB Animated TV Special; 2014)
Runnin’ Wild (Aesop’s Film Fable Cartoon; 1924)
Silicon Valley (TV Series; 2014)
A Sleepless Night (Heckle & Heckle Cartoon; 1948)
Tannhäuser, by Richard Wagner (Opera; 1870)
Teachers Are People (Disney Cartoon; 1952)
The Thorn Birds, by Colleen McCullough (Novel; 1977)
Those Beautiful Dames (WB MM Cartoon; 1935)
Timmy Time (Aardman Animations TV Series; 2009)
Trust the Saint, by Leslie Charteris (Short Stories 1962) [Saint #36]
Two-Faced Wolf (Loopy De Loop Cartoon; 1961)
Undertow, by Tool (Album; 1993)
Vitamin Pink (Pink Panther Cartoon; 1966)
Where the Boys Are (Film; 1984)
Wild Bill Hiccup (Woody Woodpecker Cartoon; 1970)
Workaholics (TV Series; 2011)
Today’s Name Days
Notker, Wilhelm (Austria)
Irenej, Petar, Prudencije (Croatia)
Vendula (Czech Republic)
Sixtus (Denmark)
Ville, Villem, Villi, Villo, Villu (Estonia)
Jami, Vilhelm, Vilho, Vili, Viljami, Ville (Finland)
Marcellin (France)
Sixtus, William (Germany)
Efthios, Evtychios (Greece)
Bíborka, Vilmos (Hungary)
Celestina, Diogene, Filarete, Guglielmo (Italy)
Filips, Vilips, Zinta (Latvia)
Celestinas, Daugirutis, Genardas, Žintautė (Lithuania)
Aasmund, Asmund, Åsmund (Norway)
Ada, Adam, Adamina, Celestyn, Celestyna, Diogenes, Ireneusz, Katarzyna, Świętobor, Sykstus, Wilhelm, Zachariasz (Poland)
Eutihie (Romania)
Irena (Slovakia)
Celestino, Gala, Guillermo, Prudencio (Spain)
Vilhelm, William (Sweden)
Celesta, Celeste, Celestina, Celestine, Tyra (USA)
Today is Also…
Day of Year: Day 96 of 2025; 269 days remaining in the year
ISO Week: Day 7 of Week 14 of 2025
Celtic Tree Calendar: Fearn (Alder) [Day 20 of 28]
Chinese: Month 3 (Geng-Chen), Day 9 (Y-Si)
Chinese Year of the: Snake 4723 (until February 17, 2026) [Ding-Chou]
Coptic: 28 Baramhat 1741
Druid Tree Calendar: Rowan (April 1-10) [Day 6 of 10]
Hebrew: 8 Nisan 5785
Islamic: 7 Shawwal 1446
Julian: 24 March 2025
Moon: 67%: Waxing Gibbous
Positivist: 12 Archimedes (4th Month) [Pappus]
Runic Half Month: Ehwaz (Horse) [Day 8 of 15] (thru 4.9)
Season: Spring (Day 17 of 92)
SUn Calendar: 7 Cyan; Seventhday [7 of 30]
Week: 1st Full Week of April
Zodiac:
Tropical (Typical) Zodiac: Aries (Day 17 of 30)
Sidereal Zodiac: Pisces (Day 23 of 30)
Schmidt Zodiac: Pisces (Day 17 of 26)
IAU Boundaries (Current) Zodiac: Pisces (Day 26 of 38)
IAU Boundaries (1977) Zodiac: Pisces (Day 26 of 38)
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Holidays 4.6
Holidays
ABW Day (Poland)
Animated Cartoon Day
Army Day (US)
Athletic Trainers and Physical Training and Sports Professionals Day (Kyrgyzstan)
Bohring-Optiz Syndrome Awareness Day
Castle Day (Japan)
Chakri Memorial Day (Thailand)
Circe Asteroid Day
Conor McGregor Day (UK)
Declaration of Arbroath Day (Scotland)
Drowsy Driver Awareness Day (California)
Evolution of Dance Day
Feigenbaum Constant Day
406 Day
Gender-Fluid Pride Day
Good Deeds Day
International Asexuality Day
International Day of Sport for Development and Peace (UN)
International Day of the Charango
International Recruiters Day
International Search & Rescue Beacon/406 Day
International Whistler’s Day
Jump Over Things Day
Kimbangu Day (DR Congo)
King Rama I Memorial and Chakri Day (Thailand)
Knock Your Socks Off Day
Larch Day (French Republic)
Modern Olympics Day
Näfelser Fahrt (Battle of Näfels; Switzerland)
National Charlie Brown’s Insecurities Day
National Employee Benefits Day
National Fisherman Day (Indonesia)
National Gang Day
National Health Day (Kiribati)
National Library Day
National Pajama Day
National Student-Athlete Day
North Pole Day
Ntaryamira Day (Burgundi)
Patriot’s Victory Day (Ethiopia)
Phocaea Asteroid Day
Plan Your Epitaph Day
Post-It Notes Day
Richard the Lionheart Day
Roberto Clemente Day
Self Determination Day (Australia)
Semana Santa (Argentina)
Sorry Charlie Day (in honor of those who have been rejected and lived through it)
Stigtingsdag (a.k.a. Founders Day or Van Riebeeck’s Day; South Africa)
Tartan Day (Canada, US)
Teflon Day
Think About Spring Cleaning Day
Van Riebeeck Day (Capetown, South Africa)
Waltzing Mathilda Day (Australia)
World Day of Physical Activity
World Table Tennis Day
Food & Drink Celebrations
Brew Year's Eve
Fresh Tomato Day
National Acai Bowl Day
National Caramel Popcorn Day
National Carbonara Day (Italy)
National Consider Drinking More Helles Day
National Food Faces Day
National Twinkie Day
National Viognier Day
New Beer's Eve
St. Sixtus' Day
Twinkie Day
Nature Celebrations
Adonis Day (Eternal Bliss; Korean Birth Flowers)
California Poppy Day
National Siamese Cat Day
Independence, Flag & Related Days
Capetown, South Africa (Founded; 1652) [Orania]
Cocos (Keeling) Islands (Act of Self Determination Day; 1984)
Koya (Declared; 2014) [unrecognized]
Republic of Venstral (Declared; 2018) [unrecognized]
Self-Determination Day (Cocos Islands)
Vancouver (Founded by Canadian Pacific Railway Company; 1886)
New Year’s Days
British Income Tax Year (UK)
Yazidi New Year (Iraq)
1st Sunday in April
A Drop of Water is a Grain of Gold (Turkmenistan) [1st Sunday]
English Breakfast Day (UK) [1st Sunday]
Geologists Day (Russia) [1st Sunday]
Mule Day (Columbia, Tennessee) [1st Sunday]
Parents & Children’s Day (Florida) [1st Sunday]
Seven For Sunday [Every Sunday]
Snack Sunday [1st Sunday of Each Month]
Spiritual Sunday [1st Sunday of Each Month]
Start Over Sunday [1st Sunday of Each Month]
Sundae Sunday [Every Sunday]
Sunday Funday [Every Sunday]
White Orchid Day [1st Sunday]
World Geologists Day [1st Sunday]
World Meditation Day [1st Sunday of Every Month]
World Transformation Day [1st Sunday]
Weekly Holidays beginning April 6 (1st Full Week of April)
Bat Appreciation Week [1st Full Week]
Be Kind to Spiders Week [1st Full Week]
Community Garden Week (UK) [1st Full Week]
Consider Christianity Week [begins 2nd Sunday before Easter]
Dumb Week (Greece) [thru 4.12]
Explore Your Career Options Week [1st Full Week]
International Trombone Week (thru 4.13)
National Blue-Ribbon Week [1st Full Week]
National Crime Victims’ Rights Week (thru 4.12)
National Library Week (thru 4.12)
National Medic Alert Week [1st Full Week]
National Oral, Head, and Neck Cancer Awareness Week (thru 4.12)
National Public Health Week [1st Full Week]
National Window Safety Week [1st Full Week]
New Haven Restaurant Week (New Haven, Connecticut) [thru 4.11]
Passion Week (thru 3.23) [Week before Holy Week; Christianity]
Passiontide (thru 3.30) [Passion Week + Holy Week]
Festivals On or Beginning April 6, 2025
The Laurence Olivier Awards (London, United Kingdom)
NFRA Executive Conference (Tempe, Arizona) [thru 4.9]
Vinitaly (Verona, Italy) [thru 4.9]
Zilker Kite Festival (Austin, Texas)
Feast Days
Aequinoctium Vernum VIII (Pagan)
Albrecht Dürer and Lucas Cranach (Lutheran Church)
Baily (Muppetism)
Beware of Lizardmen Day (Pastafarian)
Birth of Jesus (Mormons)
Brychan (Christian; Saint)
Celestine I, Pope (Catholic Church)
Children’s Springtime Festival (France; Everyday Wicca)
Church of Latter Day Saints Day
Colsus, Archbishop of Armagh (Christian; Saint)
Crane Bag Day (Celtic Book of Days)
Elstan (Christian; Saint)
Ether Sunday (Church of the SubGenius; Saint)
Eutychius of Constantinople (Eastern Orthodox Church)
Feast of the 120 Martyrs of Persia (Christian; Martyrs)
Fête des Petits Bateaux (Fête of the Little Boats; France)
Gudi Padwa (Birthday of Mother Earth; Maharashtra and Andhra Pradesh people)
Impersonate a Frog Day (Pastafarian)
Irenaeus of Sirmium (Christian; Saint)
Jake Day (Discordian)
Kanamara Matsuri (Fertility Festival; Japan)
Kimbanguiste Church Founding Day (Democratic Republic of the Congo)
Marcellinus of Carthage (Christian; Saint)
Pappus (Positivist; Saint)
Passover (a.k.a. Pesach; Judaism) [Nisan 16]
Prudentius, Bishop of Troyes (Christian; Saint)
Sixtus I, Pope (Christian; Saint)
Sorting-Out of the Doggets Day (Shamanism)
William the Confessor, Abbot of Eskille (Christian; Saint)
Fifth Sunday in Lent (Western Christianity) (a.k.a. ...
Care Sunday
Carling Sunday
Judica (Lutheranism)
Passion Sunday
Passiontide begins [lasts 2 weeks]
Solidarity Sunday
Lunar Calendar Holidays
Chinese: Month 3 (Geng-Chen), Day 9 (Y-Si)
Day Pillar: Wood Snake
12-Day Officers/12 Gods: Remove Day (除 Chu) [Auspicious]
Holidays: None Known
Secular Saints Days
Leigh Bardugo (Literature)
Graeme Base (Art)
Elizabeth Barrett Browning (Literature)
Leonora Carrington (Art)
Arthur Wesley Dow (Art)
Anthony H.G. Fokker (Science)
Merle Haggard (Music)
Jeanne Hébuterne (Art)
Harry Houdini (Entertainment)
Charles Huot (Art)
Charles Jackson (Literature)
Gil Kane (Art)
René Lalique (Art)
Barry Levinson (Entertainment)
James Mill (Philosophy)
Gustave Moreau (Art)
Gerry Mulligan (Music)
Guy Peellaert (Art)
Raphael (Art)
John Ratzenberger (Entertainment)
Hans Richter (Art)
Paul Rudd (Entertainment)
Sterling Sharpe (Sports)
Sebastian Spreng (Art)
Wilhelm von Kobell (Art)
John William Waterhouse (Art)
James D. Watson (Science)
Billy D. Williams (Entertainment)
Lucky & Unlucky Days
Fortunate Day (Pagan) [13 of 53]
Lucky Day (Philippines) [20 of 71]
Nēmontēmi, Day 2 (of 5) [Aztec unlucky or fasting days, taking place between 4.5-4.18]
Perilous Day (13th Century England) [14 of 32]
Taian (大安 Japan) [Lucky all day.]
Premieres
All Shook Up, by Elvis Presley (Song; 1957)
Along Flirtation Walk (WB MM Cartoon; 1935)
Attack on Titan (Anime TV Series; 2013)
Barney & Friends (Children’s TV Series; 1992)
Beef (TV Series; 2023)
Betty in Blunderland (Betty Boop Cartoon; 1934)
Blockers (Film; 2018)
The Boys from Brazil, by Ira Levin (Novel; 1976)
Buddy of the Legion (WB LT Cartoon; 1935)
The Bum Bandit (Betty Boop Cartoon; 1931)
The Castaway (Disney Cartoon; 1931)
Church of Jesus Christ of Latter Day Saints (Modern Cult/Religion; 1830)
Corn Chips (Donald Duck Disney Cartoon; 1951)
Country School (Oswald the Lucky Rabbit Cartoon; 1931)
Cry-Baby (Film; 1990)
The Dancing Fool (Betty Boop Cartoon; 1932)
Death Proof (Film; 2007)
Demon Slayer: Kimetsu no Yaiba (Anime TV Series; 2019)
Diva, by Annie Lennox (Album; 1992)
The Double Helix, by James D. Watson (Science Book; 1968)
Dough for the Do-Do (Blue Ribbon Hit Parade Cartoon; 1957)
The Dragons of Eden, by Carl Sagan (Science Essays; 1977)
The Flintstones: Little Big League (Hanna-Barbera Animated TV Special; 1978)
Flowers for Madame (WB MM Cartoon; 1936)
Fresh Fish (Blue Ribbon Hit Parade Cartoon; 1946)
The Gods Must Be Crazy (Film; 1984)
Going to Blazes (Oswald the Lucky Rabbit Cartoon; 1933)
Gold Chumps (Krazy Kat Cartoon; 1939)
Grifters, by Jim Thompson (Novel; 1963)
Grindhouse (Film; 2007)
Haikyu! (Anime TV Series; 2014)
Harbor Lights, by Bruce Hornsby (Album; 1993)
Humorous Phases of Funny Phases (Animated TV Show;1906) [1st Animated Cartoon]
I Love You to Death (Film; 1990)
Indian Pudding (Terrytoons Cartoon; 1930)
In Harm’s Way (Film; 1965)
Joe’s Lunch Wagon (Terrytoons Cartoon; 1934)
Join the Land Army (Hearst-Pathe News Cartoon; 1918)
Just Visiting (Film; 2001)
Kodak Flexible Rolled Film (Photography Film; 1889)
Ladies and Gentlemen: The Rolling Stones (Concert Film; 1971) [1st in Quadrophonic]
The Lost Weekend, by Charles R. Jackson (Novel; 1944)
Making Good (Oswald the Lucky Rabbit Cartoon; 1932)
Mamma Mia! (UK Musical Play; 1999)
The Millionaire Hare (WB LT Cartoon; 1963)
Monday Monday, by The Mamas and The Papas (Song; 1966)
Mony Mony, by Tommy James and The Shondells (Song; 1968)
Moscow on the Hudson (Film; 1984)
Mutt the Mutt Trainer (Mutt & Jeff Cartoon; 1919)
Nine Stories, by J.D. Salinger (Short Stories; 1953)
Olympics (Modern Olympics; 1896)
Outbreak, by Robin Cook (Novel; 1987)
Planet Terror (Film; 2007)
Popular Melodies (Fleischer Screen Songs Cartoon; 1933)
A Quiet Place (Film; 2018)
Robot Chicken DC Comics Special 2: Villains in Paradise (WB Animated TV Special; 2014)
Runnin’ Wild (Aesop’s Film Fable Cartoon; 1924)
Silicon Valley (TV Series; 2014)
A Sleepless Night (Heckle & Heckle Cartoon; 1948)
Tannhäuser, by Richard Wagner (Opera; 1870)
Teachers Are People (Disney Cartoon; 1952)
The Thorn Birds, by Colleen McCullough (Novel; 1977)
Those Beautiful Dames (WB MM Cartoon; 1935)
Timmy Time (Aardman Animations TV Series; 2009)
Trust the Saint, by Leslie Charteris (Short Stories 1962) [Saint #36]
Two-Faced Wolf (Loopy De Loop Cartoon; 1961)
Undertow, by Tool (Album; 1993)
Vitamin Pink (Pink Panther Cartoon; 1966)
Where the Boys Are (Film; 1984)
Wild Bill Hiccup (Woody Woodpecker Cartoon; 1970)
Workaholics (TV Series; 2011)
Today’s Name Days
Notker, Wilhelm (Austria)
Irenej, Petar, Prudencije (Croatia)
Vendula (Czech Republic)
Sixtus (Denmark)
Ville, Villem, Villi, Villo, Villu (Estonia)
Jami, Vilhelm, Vilho, Vili, Viljami, Ville (Finland)
Marcellin (France)
Sixtus, William (Germany)
Efthios, Evtychios (Greece)
Bíborka, Vilmos (Hungary)
Celestina, Diogene, Filarete, Guglielmo (Italy)
Filips, Vilips, Zinta (Latvia)
Celestinas, Daugirutis, Genardas, Žintautė (Lithuania)
Aasmund, Asmund, Åsmund (Norway)
Ada, Adam, Adamina, Celestyn, Celestyna, Diogenes, Ireneusz, Katarzyna, Świętobor, Sykstus, Wilhelm, Zachariasz (Poland)
Eutihie (Romania)
Irena (Slovakia)
Celestino, Gala, Guillermo, Prudencio (Spain)
Vilhelm, William (Sweden)
Celesta, Celeste, Celestina, Celestine, Tyra (USA)
Today is Also…
Day of Year: Day 96 of 2025; 269 days remaining in the year
ISO Week: Day 7 of Week 14 of 2025
Celtic Tree Calendar: Fearn (Alder) [Day 20 of 28]
Chinese: Month 3 (Geng-Chen), Day 9 (Y-Si)
Chinese Year of the: Snake 4723 (until February 17, 2026) [Ding-Chou]
Coptic: 28 Baramhat 1741
Druid Tree Calendar: Rowan (April 1-10) [Day 6 of 10]
Hebrew: 8 Nisan 5785
Islamic: 7 Shawwal 1446
Julian: 24 March 2025
Moon: 67%: Waxing Gibbous
Positivist: 12 Archimedes (4th Month) [Pappus]
Runic Half Month: Ehwaz (Horse) [Day 8 of 15] (thru 4.9)
Season: Spring (Day 17 of 92)
SUn Calendar: 7 Cyan; Seventhday [7 of 30]
Week: 1st Full Week of April
Zodiac:
Tropical (Typical) Zodiac: Aries (Day 17 of 30)
Sidereal Zodiac: Pisces (Day 23 of 30)
Schmidt Zodiac: Pisces (Day 17 of 26)
IAU Boundaries (Current) Zodiac: Pisces (Day 26 of 38)
IAU Boundaries (1977) Zodiac: Pisces (Day 26 of 38)
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
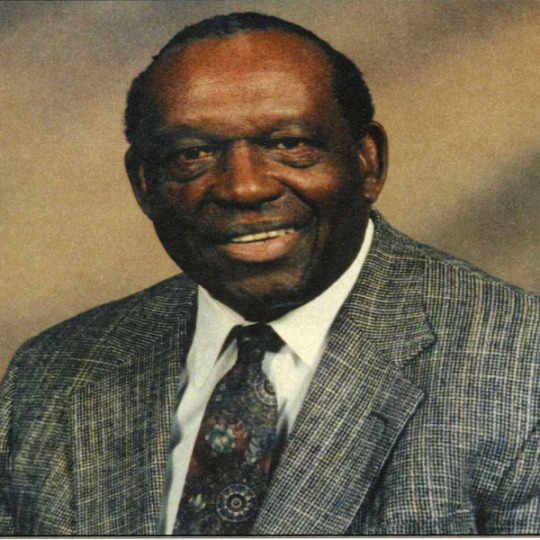

State Senator Charles Douglas Langford (December 9, 1922 – February 11, 2007) was an Alabama state senator who represented Rosa Parks in the famous civil rights case of the 1960s. He served in the Alabama Legislature as a State Representative, in District 77, Montgomery County (1976-83) and as a State Senator, in District 26, Montgomery County (1983-2002). He was the sixth child of Nathan G. and Lucy Brown Langford. He was one of two African American lawyers in Montgomery at this time.
He completed two years at Tuskegee Institute before being drafted into the Army during WWII, where he served overseas as a truck driver in the European Theater Operation. He had an honorable discharge from the Army in 1946. He earned his JD at The Catholic University of America. He had earned his BA at Tennessee State University. He was a partner in the law firm of Gray, Langford, Sapp, McGowan, Gray, and Nathanson.
He helped end the flying of a Confederate battle flag from the dome of the State Capitol in Montgomery. In 1964 he represented Arlam Carr in a lawsuit against Montgomery’s Board of Education that led to the desegregation of the city’s public schools.
In 1953, he was admitted to the Alabama State Bar and opened his law office on Monroe Street in Montgomery. He stayed in Montgomery and continued to represent local African Americans in civil rights cases. He served five terms in the Senate before retiring in 2002. #africanhistory365 #africanexcellence #alphaphialpha
0 notes
Link
Check out this listing I just added to my Poshmark closet: Car Tag.
0 notes
Photo



Ok so that 2021 book list I mentioned earlier...it turned into 30 books because I have no self control 😬but here they are, my favorite books I read in 2021! And yeah, all of them civil war related cause what would you expect?
below the cut, I’ve included all the names with the authors so if you wanna check them out, you can!
Nothing But Victory: The Army of the Tennessee, 1861- 1865 (Steven E. Woodworth)
Raising the White Flag: How Surrender Defined the American Civil War (David Sikenat)
Thunder at the Gates: The Black Civil War Regiments that Redeemed America (Douglas R. Egerton)
American Brutus: John Wilkes Booth and the Lincoln Conspiracies
This Republic of Suffering: Death and the American Civil War (Drew Gilpin Faust)
The War of the Common Soldier: How Men Thought, Fought, and Survived in Civil War Armies (Peter S. Carmichael)
The Howling Storm, Weather, Climate, and the American Civil War (Kenneth W. Noe)
An Environmental History of the Civil War (Judkin Browning)
Meade at Gettysburg: A Study in Command (Kent Masterson Brown)
Lincoln on the Verge: Thirteen Days to Washington (Ted Widmer)
Major General George H. Sharpe and the Creation of American Military Intelligence in the Civil War (Peter G. Tsouras)
Radical Sacrifice: The Rise & Ruin of Fitz John Porter (William Marvel)
Midnight in America: Darkness, Sleep, and Dreams During the Civil War (Jonathan W. White)
Rites of Retaliation: Civilization, Soldiers, and Campaigns in the American Civil War (Lorien Foote)
Let Us Have Peace: Ulysses S. Grant and the Politics of War & Reconstruction, 1861 - 1868 (Brooks D. Simpson)
Sickles at Gettysburg: The Controversial Civil War General Who Committed Murder, Abandoned Little Round Top, and Declared Himself The Hero of Gettysburg (James A. Hessler)
Timothy B. Smith:
Champion Hill: Decisive Battle for Vicksburg
The Union Assaults at Vicksburg, May 17 – 22, 1863
The Siege of Vicksburg: Climax of the Campaign to Open the Mississippi River, May 23 – Jay 4, 1863
Caroline E. Janney:
Remembering the Civil War: Reunion & the Limits of Reconciliation
Ends of War: The Unfinished Fight of Lee’s Army After Appomattox
Elizabeth R. Varon:
Appomattox: Victory, Defeat, and Freedom at the End of the Civil War
Southern Lady, Yankee Spy: The True Story of Elizabeth Van Lew, a Union Agent in the Heart of the Confederacy
Jeffrey Wm Hunt:
Meade & Lee After Gettysburg: From Falling Waters to Culpeper Court House
Meade & Lee at Bristoe Station
Meade & Lee at Rappahannock Station
Petersburg campaign books:
The Siege of Petersburg: The Battles for the Weldon Railroad, August 1865 (John Horn)
Richmond Redeemed: The Siege at Petersburg, the Battles of Chaffin’s Bluff and Poplar Spring Church, September 29 – October 2, 1864
Richmond Must Fall: The Richmond Petersburg Campaign, October 1864 (Hampton Newsome)
A Campaign of Giants: The Battle for Petersburg Vol. 1 (A. Wilson Greene)
#my ramblings#self control? don't know her#also i love all these covers but that ricmond must fall cover lol#i love that book but the cover is just!! not great#2021 books
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
Songs From History: General Sherman and his Boys in Blue
General Sherman and his Boys in Blue (or, as I like to call it, the Sherman glorification song) is a song which was (I think) written by H.M. Higgins. Library of Congress just says it was arranged by G. Ascher (who may have changed the song a bit), with no info on who wrote it. Lincoln collection lists the creator of the song as H. M. Higgins. Other places I’ve looked have also said it was Higgins, so I think LOC just got Ascher’s particular version of the song, but I’m mentioning both of them just in case. What I do know is that it was published in 1865. Unfortunately, I am unable to find video or audio of the song being sung (I just keep seeing video/audio of Bonnie Blue Flag instead). I do have the lyrics though. The link I provided with the name of the song has the sheet music with the lyrics, so you may be able to use that to get an idea of what the tune may be. If anyone has video or audio of the song being sung, please let me know.
I’ll warn you that the song is long. On the bright side, Thomas and Grant get mentioned too!
With all that out of the way, here are the lyrics.
Hail, glorious chief! the country’s pride, For victory follows thee; Thy fame is spreading far and wide, Great chieftain of the free! The bravest army in the world Is being lead by you, And freedom’s banner is unfurl’d By bonny boys in blue.
General Sherman, O! General Sherman, O! The boys in blue will fight with you, General Sherman, O!
On Shiloh’s bloody battle field He met old Beauregard, who found that Sherman would not yield And he took it very hard, He’d water his horse in the Tennessee, That’s what he said he’d do, But Billy Sherman got in the way With his bonny boys in blue
General Sherman, O! General Sherman, O! The boys in blue will fight with you, General Sherman, O!
And when the rebels on Vicksburg’s heights Were all corralled by Grant, Joe Johnston thought he’d give us fits, But Sherman said “You can’t.” Joe Johnston found there were some things That he could never do; He has to run when Sherman brings His bonny boys in blue.
General Sherman, O! General Sherman, O! The boys in blue will fight with you, General Sherman, O!
On Mission Ridge he met the foe, With Thomas and with Grant, And on that glorious field, you know, Our banners they did plant. Old Bragg and all his army fled What else could Braxton do? When Grant and Sherman nobly led The bonny boys in blue.
General Sherman, O! General Sherman, O! The boys in blue will fight with you, General Sherman, O!
Atlanta next was Sherman’s aim, Though Dalton blocked the way; But flanking was the kind of game That Sherman knew would pay. Joe Johnston found that to retreat Was all the way to do; For it was dangerous to meet the bonny boys in blue.
General Sherman, O! General Sherman, O! The boys in blue will fight with you, General Sherman, O!
From Dalton down to Kennesaw Joe Johnston did retreat, From there he found he must withdraw Or meet a sore defeat. And when within Atlanta’s walls Says Hood, “I’ll show you, Joe, That Sherman soon before me falls, And all his boys in blue.”
General Sherman, O! General Sherman, O! The boys in blue will fight with you, General Sherman, O!
Says Hood, “I’ll try the flanking game;” But he didn’t make it pay; For Thomas brought old Hood to shame, While Sherman went on his way. Down through Georgia Sherman went, Cut Rebeldom in two, And in Savannah pitched his tent, With all his boys in blue.
General Sherman, O! General Sherman, O! The boys in blue will fight with you, General Sherman, O!
For General Sherman, then, we’ll shout, And Charleston next must fall; The boys in blue will clean them out, Old Beauregard and all. This base rebellion soon will end, The bottom’s falling through; Hurrah for General Sherman, then, And the bonny boys in blue.
General Sherman, O! General Sherman, O! The boys in blue will fight with you, General Sherman, O!
#songs from history#william tecumseh sherman#us civil war#acw#i'm slightly disappointed the song never refers to him as uncle billy#still i thought this would be good to post on sherman's birthday#even though i don't actually know what he thought of the song
6 notes
·
View notes
Note
Honestly as a history buff, it's hilarious to me when people proudly fly the confederate flag as a symbol of Southern heritage considering what we call the "confederate" flag at no point was ever used as an official symbol for the seceded states of the confederate south.
That honor goes to the "stars and bar" which was established in 1863 and used throughout the entirety of the Civil war.

What people call the "confederate" flag is actually just an elongated version of the Battle Flag of the Army of Tennessee. Never once used as a symbol of the south. It was made first snd foremost as a symbol of the enslavment of african americans. There's a reason it was mainly called the Battle flag. It's use was considered for a national symbol but it, along with 1 other flag, were relegated to small-time use.

Same goes statues!!! Most of them were built in the 40's-50's in response to Jim Crow being viewed negatively. It was never about heritage. It's nothing but hate. Robert E. Lee HIMSELF even said not to build statues of him. The confederate states lasted only 5 years, that's hardly a "heritage". The Southern united states does have a rich culture and heritage, but it's not with the rebels or the dixie flag. It's a melting pot of various poc be them native, enslaved african, creole, haitan, etc. THATS the Southern heritage I wanna see. None of this states rights bs 🙄🙄🙄
Not to turn that into a rant, my inner history buff screams when someone acts like being racist is important to their cultural background 🤢
YES!
Lee was literally like “you know what? Nvm don’t burry me with that flag let’s act like it never happened UwU” FJDNDNENE
“southern heritage” oh you mean Afro American, Hispanic, and a shit ton of native cultures?
I’ve noticed that it’s unfortunately very common for people to use culture to get away with bad morals and actions whether it be racism misogyny queerphobia or just straight up abuse :(
#I also find it really weird when a/p/h/ fans ‘remake’ america or make south ocs (which….yikes for the most part) and then make them white#Like I get that those are topics you might not want to touch on but then don’t make a south oc if you can’t handle it???? Not to mention#The ACTUAL confederacy ocs I’ve seen 🤢 and half the time they’re like ‘UwU they learned and they’re better now’ which is just so fucked
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
the corruption of redneck culture is disgusting.
It went from
"I shot my employer in the chest cause he refused to treat me like a human being and then I beat the scab that came in to replace me to within an inch of his life and I'll happily do it again. Meanwhile my coworkers are literally being bombed for daring to strike for better working conditions and the ability to feed themselves"
All the way to
"God, Truck, Beer, Gun, USA, country girls make do, 4th of July, duck hunting, Truck again, the battle flag of the Army of Tennessee for some "unknown reason", mention of getting dirty /sweating, and a mention of cowboy boots to close it all off"
1 note
·
View note
Text
The Celtic Tiger - A Kaiserreich Ireland AAR Chapter 2: An American Tragedy

12 February 1937 - Home of Michael Collins, Cork, Ireland
“The United States of America has faced challenges since its founding, but it is an enduring republic. When we were invaded, we fought off our attackers. When the Great Storm hit Galveston, we built cottages from the storm lumber. When Black Monday reached our shores, we passed the Garner-Wagner Act to deliver our people relief. The American people, through this election, have made their will clear. They do not want the empty promises of Jack Reed. They demand more than the sayings of Huey Long. Words are not enough, action is required. That is what I shall promise: action. We will stand firm against the threat of populism and syndicalism.”
Benjamin Franklin, after the Constitutional Convention, was asked whether the United States was a democracy or a republic. His words were: ‘a republic, if you can keep it.’ That was not mere wit, but a charge; a sacred duty given to every citizen. Today we say: it is our republic, and we shall keep it.” -US President John Garner, Excerpt from Inaugural Address
In Michael Collins’s case, war never seemed to have a countdown, but sure enough, the war looked like it would begin in 30 days. Just the thing to ruin his vacation; he had hoped to spend a few days in Cork to recharge his batteries, and ended up having indigestion and headaches the entire trip.
The United States had been a roiling mass of discontent since 1925, but it had only gotten worse during Black Monday. President Garner had won a lot of support in his campaign, which had focused on trumpeting the successes of the Garner-Wagner Act and touting the President’s willingness to fight any who threatened democracy. “A snake is a snake is a snake,” Garner had been fond of quoting on the campaign trail, swaggering with a pair of revolvers. “I plan on working to fix the mess that we’ve found ourselves in. If Jack Reed and Huey Long want their voices heard, I’ll listen to them. If they want prosperity for America, they’ll listen to me. And if they want to fight, they’ll get one. I don’t plan on striking first, but as God is my witness, I’ll be striking last!”

That had been enough for the Presidency. Jack Reed’s Socialist Party of America and Huey Long’s America First Party had strong regional support, but neither movement received enough votes to beat the Republican candidate Alf Landon, let alone Garner. Yet the victory was narrow, and both candidates claimed voting irregularities arranged at the polling places by supporters within the state voting commissions, along with other accusations of beatings and intimidation campaigns. Herbert Hoover endorsed Garner in a show of cross-party American solidarity, and Landon himself was a guest of honor at Garner’s inauguration. Garner had already promised the Republicans some Cabinet appointments in the hopes of building a coalition government strong enough to stop Long and Reed. It was an uphill battle; the 1936 voting season had been marred by political demonstrations turning violent, they had even called it the Red Summer, and now Long and Reed were railing against the legitimacy of the vote.
When the populists had made their accusations, the governors in their regional strongholds had backed Long and Reed. The populists, it seemed, had called President Garner’s bluff. The governors demanded a “national reconciliation council” under their talking head, and both had made it plain that the other would not be welcome on it, making it all but certain that war would come, and it would not be small. Jack Reed was popular in the Steel Belt and Huey Long had an almost religious appeal in Louisiana and in the rest of the Southern United States. Reed had much of the industrial heartland, but Long had far more pull among the military including high ranking officers. It wouldn’t be an easy fight, no matter what Texans had to say. In both ways, it was bad for the United States.
Collins had hoped it wouldn’t be war, but he was sure that it would be. If Jack Reed was able to successfully overthrow Garner, the Internationale would be emboldened. The Communards might still be reluctant to face Germany, given how large such a war would be, but Mosley would almost certainly want to snap up Ireland to carry forth syndicalist momentum. Anti-Irish rhetoric had only intensified in the months following Ireland’s meteoric 1936 rise, with Mosley claiming that Michael Collins had become “every inch the oppressive king he fought against.” Collins laughed when he was first told it, but as the days went on he seethed against the man, wishing he could have five minutes alone in a room with him. He was sure his sainted ma would not look fondly on him for beating on a man with a limp, but she’d forgive him.
When the reporters asked for a quote, Collins was sure to give them one. “Look at Mosley in the war. Gallivanting around in an aeroplane like war was just boys at camp, crashing trying to be a showboat. I suppose I must be kind, he tried to prove he was a brave man, I’m sure it’s not his fault he ran behind a desk before a year was out. That’s where he’s most comfortable, hiding and sipping his gin while he sends young boys to do the fighting and dying.”
Collins had a good laugh, but he made sure to tell his diplomatic service to make sure that Ireland would have plenty of friends on both sides of the Atlantic, just in case the Union tried anything. Laugh in public, but service your pistol in private.
---

14 March 1937 - Áras an Uachtaráin, Dublin, Ireland
It was war. The entire world was aflutter with the news that the United States had descended into a civil war. President Garner’s deadline had come and went, and both Jack Reed and Huey Long had declared war on the United States. In response, Garner had appointed General George Marshall as Chief of Staff of the Army. The Internationale had already voiced its support for Jack Reed, with Chilean, Communard, and Union supporters already on their way to support the newly-formed Combined Syndicates of America. The German Empire was far more reserved in its support. German-Americans primarily lived in areas controlled by the Combined Syndicates, and the United States government had primarily conducted a pro-Entente policy during the Weltkrieg, leading the Kaiser to support Huey Long out of pure pragmatism. Canada had fallen into debate within the Houses of Parliament on who they were supporting.
Collins had no such reservations about debating who to support in the Dail. Collins had sent out a call for a volunteer division, the 1st Thunderbolts, and had placed them under the command of Daniel McKenna. The East Coast was dense with urban areas, and McKenna was just the man to fight in that difficult urban war, having fought the English in the cities before. The Thunderbolts had been training for months in preparation for the outbreak of hostilities. Most were young men, too young to have seen the Independence War, but their officers and senior NCO’s had. That would carry them, fighting in unfamiliar territory would mean they would have to adapt quickly and rely on the experience of the leaders. Other IRA volunteers, particularly those with families in the United States, had opted to go there themselves, fight in the American army, and return later.
The first target would have to be the syndicalists. With their position in the American industrial heartland, they’d have the manufacturing prowess and the civilian manpower to build and repair war materiel far faster than the mostly rural southern states. They would have to trust in their greater manpower and equipment to hold the southern front against the aggressive generals of the American Union State. The United States had begun mobilizing forces on the West Coast to get them to move east, and requisitioned several rail lines for exclusive military use, but it would be hard fought. America was going to need all the help it could get.
---
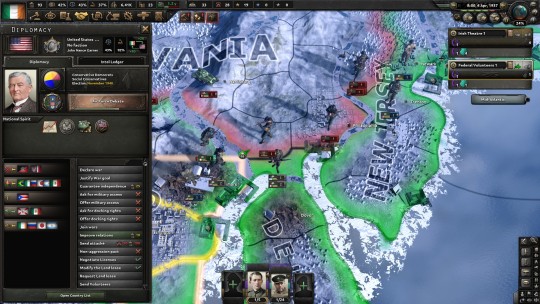
13 April 1937 - Northern Maryland, United States of America
“We have traitors to our left, and traitors to our right
Our Congress and our president have long since taken flight
No ammo, no armor, no pills, no cargo
No prayers, no chance, no hope of tomorrow
Just you and me and a hell of a lot of fight.” -Frank McHewlitt
Pennsylvania had become a battlefield for the Second American Civil War just as it had for the first. The Pennsylvania governor had declared for Jack Reed, but the Federals had made a march into central Pennsylvania, seizing York to Fulton counties, but lack of manpower, difficult terrain, and Communard volunteer tank brigades had ensured any excursion was short-lived. From New York to the Midwest was controlled by the Syndicalists. Fearing being overrun, Joseph Kennedy Sr. had asked Canada to send an occupation force to protect them from the Syndicalists. This had infuriated President Garner, but pragmatists in his Cabinet had argued that the region was indefensible since the Syndicalists held New York, and better that the Canadians occupy it, and the Combined Syndicates risk a war with the Entente, than the factories be taken over by Jack Reed. Further south, Canada had sent a force to occupy the Panama Canal after the Americans had withdrawn their garrison force. The Canadians had said their mission was to protect trade, but had banned ships flying Communard, Union, or Chilean flags.
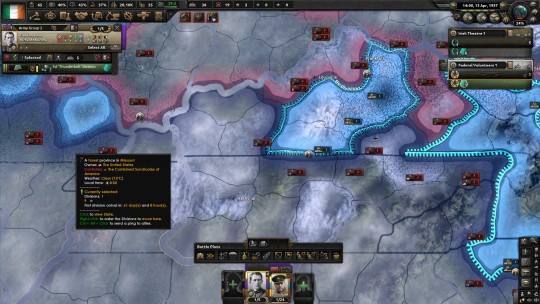
Further south, Texas to the Carolinas, and everything south, had pledged loyalty to Huey Long’s vision. Several companies had even signed on to the “Share Our Wealth” program. His men were heavily-armed and competently led, and they had already made significant inroads pushing north into Kentucky from Tennessee, even making contact with and fighting Jack Reed. George Patton had been named the overall commander of the American Union State, and on land the America First Party had shown themselves to be exceptional fighters pound-for-pound. Their goal had been to push and seize whatever territory they could, to turn the factories over to Longist control and get their war materiel production up to match the Federals and the Syndicalists. It had been remarkably successful, Patton’s armor techniques had run circles against disorganized Kentucky militia and revolutionary syndicalists alike. Already there were unconfirmed reports of mass shootings of CSA prisoners by AUS irregulars. The Federals were hard-pressed, often surrounded and potentially encircled by hostile forces in Kentucky. Only the chaos of the war and the close proximity of all three forces, kept them from being killed outright. Desertions, particularly from militia unfortunate enough to be in the encircled regions, were high.
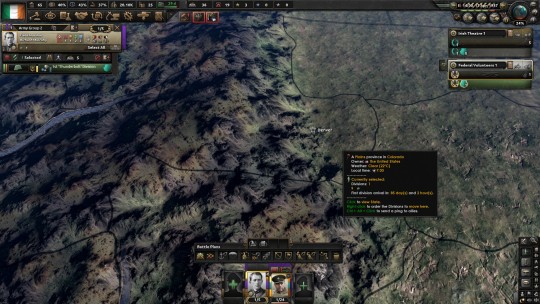
Washington was no longer the capital. With Maryland under fire and the Firsters pushing from the south into Virginia, Garner had decided to temporarily move the capital to Denver, where he could oversee the political business of state. MacArthur had elected to remain in place as the commander of the East Coast Enclave, suggesting that Dwight Eisenhower take command of the main Federal forces in the Midwest. “He’s a Kansas man, there’s no man better in command from the Midwest. The troops will fight tougher and harder if they know we haven’t abandoned them. Don’t worry, Mr. President. Those bastard traitors won’t set a foot in D.C.” With his trademark corn cob pipe and a wave to the press, MacArthur took a ride on a Vultee V-1 to take up command, with Eisenhower being named the overall commander of Army Group West, with the goal of pushing east from Kansas into Missouri.
MacArthur welcomed the service of the volunteers sailing and landing on the Chesapeake, no traitor forces had been able to ensure naval supremacy on the East Coast and none were willing to risk firing upon a flagged vessel and invite any nation’s full-blown entrance into the conflict. Lavr Kornilov, eager to project strength and stability after the assassination of President Kerensky. Hirohito had also dispatched volunteers citing the strong relationship between the United States and Japan and the need for legitimate government to be re-established in the United States to project stability in the Americas. Calles in Argentina, eager to re-establish the Monroe Doctrine to act as a bulwark against the Patagonian Worker’s Front, and always eager to fight syndicalists. Brazil likewise had ordered troops to support the United States. Mexico, eager to avoid any war spilling over their borders, had closed the borders to the American Union State and had sent divisions through the Gulf of Mexico before the Longist navy could seize control of the waters and potentially cut off trade and transit. MacArthur ensured that each division had several bilingual Americans to serve as liaisons and communications personnel. He couldn’t command the volunteers, but he did demand adherence to military law and that any abuse of US civilians or military personnel would be dealt with by firing squad. Similarly, MacArthur promised his own men that they would be punished harshly if they stole from or fought with Federal volunteers. Regular correspondence was mandatory, and passwords changed regularly to allow foreign soldiers to identify themselves quickly to friendlies, passed via radio operators who had signed up with the Federals in record numbers when President Garner forced a bill and executive order expanding the civil rights of Native Americans to shore himself up for the upcoming emergency. The Navajo Nation, who provided one of the largest units, dispatched signals operators to coordinate with the volunteer brigades, providing exceptional communications security and coordination between the Federals on both fronts.
Yet things were not going well. MacArthur had enforced military law within the East Coast enclave, and garrison forces frequently looked to seize supplies and materiel for their war effort. Oftentimes, a token effort at compensation or promise of restitution to come later was the only balm in Gilead; it did not help those who starved.
The volunteer forces moved north to the Mason-Dixon line, where the Combined Syndicate militia were threatening to move south into Maryland from their regional headquarters in Philadelphia. The Russians opted to secure themselves in Baltimore, while the Argentine and Mexican forces moved to Cecil County to secure Delmarva from the syndicalists seizing the east bank and potentially cutting off vital access to the Chesapeake. McKenna and the Irish 1st Thunderbolt, acting aggressively, crossed into Pennsylvania and secured themselves in York. Not willing to pass up a fight, Russian and Irish volunteer brigades pushed into Lancaster County, threatening Philadelphia and forcing the Communards to reinforce their position lest Philadelphia fall and the road to New York be pushed wide open.
---
17 April 1937 - Economic Committee of the Dail, Dublin, Ireland
It had been a constant flurry of activity in the new year. The Dail was debating loosening immigration restrictions to help bring in new blood to help support Ireland’s effort to modernize. Even if good policy and hard work had led Ireland out of the depression following Black Monday, manpower was still the hard limit on everything they could do. Once unemployment fell, there would be no new employees for businesses, and they’d turn away from Irish investment.
There had been two major sources of pushback against immigration reform. The Unionists in Ulster had been vocal opponents, calling the efforts part of a planned demographic shift to stock the north with people that would sideline their concerns as Unionists. Their proposal had instead suggested an increase in immigration from select countries, notably Canada, Australasia, and the British Dominion of India. Gearóid Ó Cuinneagáin was far more hostile to immigration overall, demanding no immigration save from Celtic-majority countries, particularly those who wished to depart the Union of Britain from Scotland and Wales. Some of the measures proposed had truly been radical, such as instituting a Gaelic language entrance exam to new immigrants. The hAiséirghe crowd had always been a touchy subject, they had enough support in Munster that they couldn’t be ignored as much as Collins wanted to throw the bastards into the ocean.

Collins had been lucky, his Dublin financial capital idea had already been receiving positive responses. The German Kaiserreich, still deep within the throes of Black Monday, had debated whether or not to permit German businesses to invest in Ireland. The protectionists in their government had argued that the last thing that they needed to do was open up subsidiary companies in Ireland and send work away from Germans. The market liberals were far more enthusiastic, suggesting that the profits made could be reinvested in Germany; an influx of cash that wouldn’t increase the money supply and devalue the Mark. In the end, Wilhelm II had agreed to the proposal. He had known that the Irish Republican Army had been looking to re-equip their forces, and Krupp could easily manufacture rifles and mortars with a sizable government contract. Krupp opened Krupp Rüstungsbetriebe Irland, redesigning the Krupp Radreifen into the shape of a shamrock.

The Kingdom of Spain had also looked to establish an arms company in Ireland, eager to arm those who were also hostile to the syndicalists, and quite isolated on the European continent, with France and the German Protectorate of Morocco making an uneasy set of neighbors. Having a well-armed Irish Republic was a benefit to King Alfonso, who agreed to set up a subsidiary of Llama-Gabilondo y Cia SA, taking the name Dóiteáin-Gabilondo Incorporated, and selling their famous pistols to the Irish Republican Army. With regular army drills, and now a larger armaments industry within Ireland itself, a more significant and professional Irish Republican Army was starting to take shape.

The Italian Republic, floundering in the wake of massive German and Austrian stock selloffs, were eager to find ways to bring in cash and stabilize their own economy. Seeing a pressing need, the Italian Republic opted to establish a naval manufacturing dockyard in Dublin as Gio Ansaldo Irish Sea Shipwright, Ltd, to help produce submarines for the Naval Service. Italian engineers could work in Ireland, the revenue would flow into Italy, and the Irish would receive a powerful deterrent against the Union of Britain’s navy. Working in the choppier northern waters was different from the warmer and calmer Mediterranean, but the Italians proved up to the challenge, christening the first Irish U-Boat the new Fenian Ram.

The rush of European activity to invest in Ireland had not gone unnoticed in the Netherlands. After a fierce and competitive bidding war, the Dutch government, very busy with their preparations for the upcoming elections in May, had given the go-ahead for Royal Dutch Airlines KLM to do business within Ireland. Rather than operating a strict subsidiary, as the government was still facing the worst of Black Monday, Royal Dutch instead opened a joint venture with Aer Lingus, operating a civilian airfield that would bring in much needed tax revenue, and providing expertise for the construction of a military airfield in Leinster. The Union of Britain had lodged a formal complaint against the move in the Netherlands, but the ambassador had been dismissed out of hand, the official response being “Ireland has a right to the sky, and Britain has no right to dictate policy to the Netherlands.”

The United States had been considered highly unlikely to invest in Ireland. Even with the positive relationship that had existed between the two countries, the USA had been facing an existential crisis. To Collin’s great surprise, Garner had actually encouraged American companies to open subsidiaries in Ireland before hostilities broke out. In a diplomatic message to the Irish President, Garner had written: “I am certain there will be war. American industry will certainly not be spared. This initiative may save American lives and enrich both our countries. If the worst comes to pass, may God protect us both.” General Irish Electric, as the company titled itself, designed a logo incorporating the Irish harp in the signature “G” of the GE logo. The company received a grant from the National Industrial Investment Fund and purchased a factory abandoned during the Black Monday fallout, bringing up to speed in record time to produce civilian and industrial-grade electronics. Almost immediately, GIE had orders tasked almost to capacity for factories across Ireland to upgrade their own operations, throwing itself into the greater industrialization efforts that Michael Collins had championed the previous year.

The Dominion of Canada was a much more difficult beast to wrangle. Edward VIII had made no secret that he wished to reacquire not just the British Home Isles, but the British Empire as well; he would not be a second-fiddle to the Kaiser. That would mean the Six Counties, surely, perhaps even re-establishing the Free State as a Dominion. Collins had debated even making the offer to Canada, but a good relationship with Canada was, putting Edward aside, a sound policy. Canada needed money to support their war efforts, and a friendly relationship with Ireland would mean less problems when launching their operation to take back the Home Islands. Collins privately feared that they would want to use Ireland as a staging ground. Ireland had situated itself as a prominent financial hub, and since Dublin was designated a Special Economic Zone, it could potentially be very lucrative and offer a way to sell to the rest of Mitteleuropa without dealing with the Kaiser. The Canadian government had assented to Canadian Arsenals, a crown corporation to open a subsidiary in Dublin named North Atlantic Arms. Collins made sure that it acted in all things as a private company, insisting that King Edward appoint an executive staff the same as any other business. That had been a headache in the Dail, with Eamon de Valera angrily demanding not to sell Irish land to King Edward. Collins had countered that Ireland was a free and independent republic, and that the King had to obey Irish law rather than dictating laws to Ireland.When rumors came around that Jim Larkin had supported Dev’s objections, the Fianna Fail politician withdrew his opposition in favor of a more moderate compromise, asking only that the Dail be presented the terms of the contract in open session so that they could vote on them. Dev’s desire not to give Larkin more ammunition had rapidly diminished opposition to the measure within Fianna Fail, and Sinn Fein offered only a token dissent, permitting the venture to go forward.
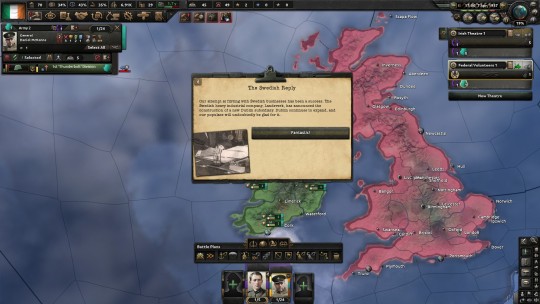
With the outbreak of war in the United States and Ireland’s rapid industrialization, Sweden had sensed an opportunity to open a subsidiary business in Ireland as well. AB Landsverk had originally sought to open a tank manufacturing plant, since the Irish tanks were largely outdated and the Irish Republican Army was going to need to modernize its arsenal. Fierce protest erupted from the social democrats within Sweden’s Parliament, opposing the idea of arming Ireland and facilitating a possible war between Ireland and the Union. The hawks within Sweden had supported the venture, but military arms, even support equipment, could not secure a large enough coalition for the Economic, Defense, and Foreign Ministers to agree to the venture. Not wanting to lose out on the potentially lucrative deal and already facing their own problems with syndicalist unrest, Sweden’s market liberals had offered a compromise within the Riksdag, allowing Landsverk to open Landsverk Inneal, specializing in tractors and harvesting equipment to support the modernization of the Irish agricultural sector. Several prominent military analysts noted that the new Inneal tractors, with a few modifications, looked suspiciously similar to a light tank with the turret removed, but these were dismissed as products of an overactive imagination by both Swedish and Irish military analysts.
The Austrian Empire was in a difficult position in 1937. Emperor Karl I had been making significant plans for his Ausgleich Federation plans, and saw the Irish initiative not simply as a means to support his economy, but as a means to demonstrate both Austrian power and his willingness and initiative to support cooperation efforts for mutual gain. The Emperor had made his commitment to pluralism plain within his proposed federative model, he had hoped that participating in Collin’s economic initiative would help sway skeptics and naysayers to his side to give him greater support against Hungary. If it could help his economy and put neutral voters who cared more about their own personal livelihood than the greater plans of Austria-Hungary, that was fine as well. Daimler founded Irish-Daimler and focused on developing automobiles and lorries. While the Emperor could not be there in person, he had prepared a statement for the opening of the plant in Dublin. “Irish-Daimler is in the business of Irish business. Her success is our success, and our success is her success. May we both prosper in the days ahead.”
Eight nations had opted to do business with Ireland in such a short period of time, and there had already been murmurs for other nations to do likewise. The success of Irish Black Monday reforms had been the talk of the European financial sector. Even distant Japan had expressed an interest in perhaps opening a branch of one of their zaibatsus in Ireland to sell to Western markets, though such a discussion was in the planning stages. When interviewed by The Financial Times, Lemass had made the quote that had made the headlines. “Ireland is the Emerald Isle. She always sparkled in our hearts, now everyone can see it.”
When Michael Collins had heard that, he smiled. The man had the head of a businessman but the heart of a poet. The head and the heart needed to complement each other if he wanted to see Ireland through.
---
8 May 1937 - Áras an Uachtaráin, Dublin, Ireland
As the war passed into its third month, Collins started to wonder about the upcoming elections in the fall. America had been on his mind a lot lately. An emergency act by the Oirechtas called the Díodean initiative had allowed Americans seeking refuge to come to Ireland, and plenty had taken Collins up on his offer. Many immigrants came with much of their wealth with them, which had provided an influx of capital. Even more valuable, however, was the technical knowledge. Many of the immigrants had been factory managers or entrepreneurs, and they had knowledge which made them highly valuable in the industrial sector. Not every tale was so fortunate, however. Some culture shock was perhaps inevitable, but it had been incredibly slow going. Collins had remembered the first time he saw a new settler to Ireland drive on the wrong side of the road and cause a car accident. This felt like seeing that unfold in slow motion on a national scale. The poor Americans had felt the Irish were cheating them out of wages and exploiting their desperate circumstances, while the wealthy felt their standard of living drop precipitously.
The hAiséirghe crowd again troubled him. Reports of nativist gang uprisings in the poorer parts of cities and rural areas were on the rise. There were demonstrations that the new arrivals were stealing all of the good-paying jobs; this had been going on since the new immigration reform but now was reaching a fever pitch. The Unionists again rallied against Collins, accusing him of colonizing the north with people opposed to King Edward under the guise of humanitarian aid to defeat the Ulster Unionists at the ballot box. They demanded a series of refugee and work permits that did not confer voting rights as opposed to outright immigration and naturalization. That had caused a firestorm on the debate floor, causing no shortage of headaches for Collins.
To alleviate the shortages, Collins had organized refugee brigades in the Republican Army, where young men could earn a wage and provide a livelihood for their families. The Yanks were excellent shots, and Collins had hoped that seeing immigrants wearing a uniform would cause the locals’ respect for the military to undermine nativist tendencies. It was a mild success at best, mostly in Leinster where there had already been fewer problems overall. Collins had weighed outright banning the Ailtirí na hAiséirghe, but that would just send them underground like the Labour Party had. He had to settle for punishing assaults when they were reported, and increasing Gardaí patrols to keep the peace.
In the leadup to the elections, Collins had seen cracks start to form in his ironclad voting bloc. While syndicalism had little popularity in Ireland itself, Sinn Fein had seen an upsurge in popularity with Black Monday despite Collins’s efforts. The Irish Christian Front and the Ailtirí na hAiséirghe had campaigned against him thanks to his immigration policies. Fianna Fail had campaigned on greater liberalization, and the National Centre Party had wanted to re-orient foreign policy to a more pro-Entente position. Sinn Fein and Fianna Fail had opted to engage in tactical voting, with candidates withdrawing from ballot races in order not to split the vote. Jim Larkin had endorsed the move, promising to work with Sinn Fein to provide greater relief to the Irish working class. The Irish Christian Front opted to boycott the elections and both they and the Ailtirí na hAiséirghe accused Collins of bringing in foreign refugees to ensure he had the votes needed to win.

At a closed door meeting, Collins was asked a simple question. “Sir, what should we do about the election?”
Collins, his hands shaking, had only one response. “Whatever it takes.”
---
15 July 1937 - West Virginia, United States of America
“We’re in the right thick of it now, ain’t we?” Daniel McKenna shouted over the din of battle.
The East Coast Enclave had stabilized its borders after the early initial push, but still faced the difficulties of being surrounded by the enemy. Food and water shortages, irregular supply shipments, and losses from attrition were starting to take their toll on the beleaguered Federals. The Appalachian mountains had stymied Syndicalists pushing in from Ohio and Illinois, and the hilly and forested terrain had helped somewhat slow the push by Long’s forces, but only barely. Eisenhower had more success on the west, where the greater manpower has really started to pressure the American Union State on their Texas front.
The Federals still controlled the air though. That had made securing their defenses much easier. Flying over the Great Plains was effectively a death sentence, and few had the nerve to establish air cover on the east coast. That was a small comfort to Dan McKenna, who had gone to the Applachians in response to a new Syndie push. The Federals had retaken Charleston in June, but their position was tenuous there, and with new militia units being sent into battle, someone had needed to defend this key western outpost.
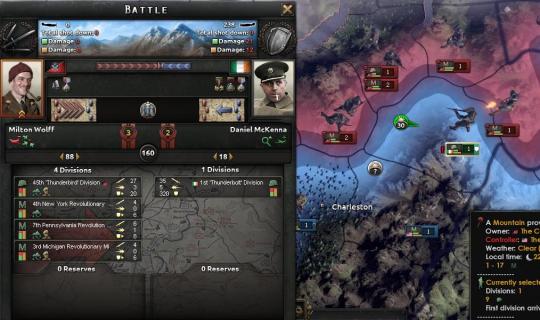
American militia units had stayed to defend the city, but McKenna had looked to secure the hills to the northeast. The Applachian plateau looked to give a good vantage point for artillery if any could succeed in the arduous task of towing them up to that position. Loyalist civilians had offered to do it on their own, pulling the units with their own work trucks, but that would be a dangerous undertaking without escort. McKenna took his Thunderbolts, with their own artillery pieces, to secure the hills first, while the militia guns could follow second when the way had been cleared. The Syndicates, tipped off by sympathetic informants, launched a massive push with their own 45th Thunderbirds, supplemented by local revolutionary forces, to prevent bombardment. The battle plan called for an overwhelming attack to break the dug-in mountain entrenchments, attacking from multiple directions in an attempt to dislodge the stubborn Irish defenders and find a weak spot.
McKenna demanded that the forces hold, using high-explosive burst shells over the heads of the enemy to maximize effect on the enemy. The engineers had dug in extensively, and had used dynamite to blast further fortifications and built entrenchments. The Thunderbolts only had a few guns, which were primarily pointed toward the northwest against the more highly-trained Thunderbirds. At such high elevation, and with such difficult terrain, evacuating casualties was difficult on the mountain, and men sometimes collapsed where they stood due to a combination of fatigue and high elevation.
That had been days ago, and the Thunderbolts were in tatters. The less wounded had even taken up shifts at night, or taking over service positions so able-bodied men could shoot and spot for the artillery. They had been holding, but just barely so. If it hadn’t been a mountain, they would have already been overrun. “I’ll be damned if I die on some cold rock half the world away from home.” McKenna defiantly continued to stand, hoping to wear down the superior numbers with artillery shells. He was the Wall of West Virginia, and he wouldn’t let the bastards through.
---
10 September 1937 - Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania
It had been months of hard fighting. Charleston had remained in Federal hands, and the front had stabilized, but all hopes of recovering the Federals in Kentucky were lost. The loyalists could only hope that the army groups had disbanded to make their way back to Federal territory in smaller numbers rather than being shot en masse, or worse, deserting to fall in with the enemy for their own salvation.
MacArthur had relied on the volunteers to fight a great deal of battles, more than he had preferred. The states under his control were tapped out for manpower resources, and if he started poaching from the factory floors for more able bodies he’d run out of supplies. Supply was irregular, especially for fuel, which he needed to keep the planes in the sky and the troops moving across the front. Olds and Tunner were able to airlift a lot of supplies, but demand always outstripped supply, and the more supplies he lifted the more danger there was for explosions in the cargo holds.
Ultimately, MacArthur decided that he needed to attack, to keep the pressure on the east so that the Syndicalists did not pull more men to prevent Eisenhower from marching toward Chicago from Kansas and the Dakotas. The Syndicates had been attacking south against the American Union State and fortifying out of New York City, and MacArthur had theorized that they would be weak in between those two strongpoints. The Brazilian and Argentine volunteers offered to push toward Philadelphia, with the hopes of breaking the regional command post and sending Syndicalist forces into disarray, while the Irish opted to push into Pittsburgh to seize the valuable steel mills and threaten a push into Ohio. The Mexican volunteers opted to remain in Virginia to help guard the line against the Longists; they had feared if the American Union State won, there may have been calls to expand further south to seize valuable oil and mining territories; fears of the Golden Circle expansion as it was dubbed in Mexico had been a hot button issue for the Mexican volunteers. If the Irish could secure Pittsburgh, that would give them control of the railroad junctions and the rivers, and allow MacArthur to bring in militia units to bring the territory under control with little fighting. With that, they could push further north toward Erie, splitting the Syndicalists and isolating them in New York. With Canada closing the border to the Combined Syndicates, even to the point of having the Royal Canadian Mounted Police arrest suspected border crossers and turning them over to the Federal government in Denver, that would render a similar fate to the lost Federals in Kentucky. MacArthur just hoped that his south could hold against the Firsters. Trading Virginia for Pennsylvania was not a winning proposition.
The B&O Line had been cut early, forcing McKenna and the Thunderbolts to march for most of the trip. Even in September, Pennsylvania was still hot, to help with water and the unfamiliar terrain McKenna had largely followed the Mononghaela river. To the east, he had Federal troops supplemented by Maryland militia moving north to take Harrisburg. McKenna force-marched his troops into Syndicate territory, hoping to secure a clear pathway along the rail lines for American repair crews to fix the B&O.
McKenna had been fortunate, western Pennsylvania had been defended by irregular militia units, poorly armed and lacking artillery support. In many cases, McKenna found that they didn’t have enough rifles for every man and only a few machine guns, some had taken to using shotguns better suited for partridge than men. When he was lucky, a few barrages from the field guns was enough to send them packing, but even without that, a dedicated attack usually was able to force back the disorganized units. A pity he didn’t have tanks, even a couple of old Weltkrieg landships would simply be able to drive to Pittsburgh unimpeded as long as it was gassed up.
The locals were fiercely divided. A few times McKenna had gone near towns, he had been welcomed and told where the Syndicates had kept their ammunition depot. Most of the time, however, the homes were ransacked, the supplies taken. Horror stories came to McKenna about “war syndicalism,” Reed’s name for the efforts taken to ensure his fighting men had the food they needed to fight. Sometimes it was the Combined Syndicates directly, but more often it seemed to be neighbors seizing on old grudges, summarily beating those they suspected of disloyalty and stealing their possessions, donating them to Reed as an act of solidarity. Worse still was what happened to those suspected of disloyalty. The Combined Syndicates offered a bounty on saboteurs and informants, and that had led to hastily-convened People’s Courts, serviced by hanging judges. Even so, there were plenty of people loyal to the Combined Syndicates, shouting their approval at finally destroying the brutal oppressors of Wall Street and their puppets in the Federal government. For a moment, McKenna thought of Ulster, and remembered everything he had heard 15 years before, and then he remembered the refugees from the British Isles after their revolution.
Pittsburgh had been hastily-fortified, with burned out hulks of cars blocking the bridges into town, forcing McKenna to navigate the crude fortifications with great care. The civilian population had largely huddled in buildings with boarded-up windows. The large buildings had been long ago hit by artillery fire or bombings from aircraft. Rail tunnels had been places of safety, McKenna’s scouts had found a few brave souls trading for various materials on picnic blankets. The mayor, who had thrown in his lot with the Syndicalists, had fled the city with the rest of the CSA, and they had thrown those city councilmen loyal to the Federal government into the Ohio. Coordination was largely infrequent, done by amateur radio. The civilians largely wanted to be left alone, out of the civil war, but the war had come to them despite their best wishes.
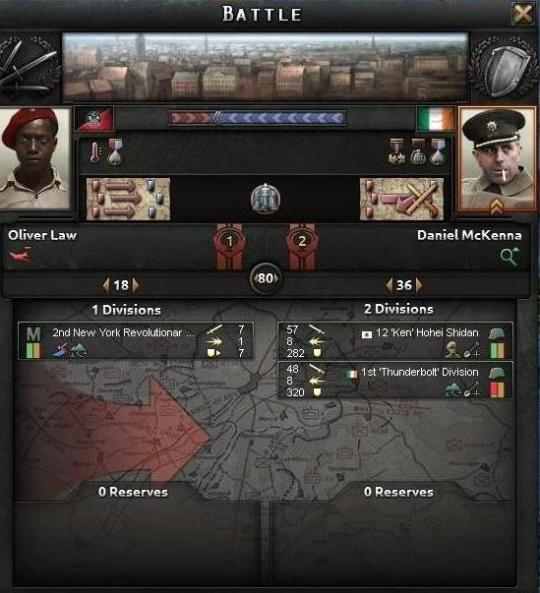
McKenna set to work, ordering his engineering corps to get the guns into firing positions. He positioned men near the Alleghany to prevent any CSA attack using the river to bypass his fortifications, and fortified the major exits with sandbags and machine guns. He had barely gone through half of his fortifications when he had heard the bad news: The Syndies were on the march along the Alleghany, and they would attack the city soon.
Yet, McKenna was not alone. The 12th Hohei Shidan, volunteer forces from far-off Japan, had come to support the Irish forces, and they had brought with them their Type 90’s, doubling McKenna’s supply of artillery. The Japanese and Irish soldiers met on the south side, and drew up plans for an attack. McKenna was given overall command, and elected to put his Irish veterans in the more dangerous forward position while the Japanese would fire on the CSA to draw them in under a battery of withering artillery fire. Once the enemy had descended past Lower Lincoln and could no longer enjoy visibility from Upper Lincoln, the Irish would ambush them in close quarters.
The CSA announced their attack with a radio command ordering all civilians to remain indoors, and all “foreign invaders” to surrender to the 2nd New York Revolutionary Guard, for handling by the legitimate United States government for repatriation. The 12th Hohei Shidan responded with a cannon barrage, thus commencing the Battle of Pittsburgh at 0900 on 10 September. McKenna’s Thunderbolts fought in ambush-and-retreat tactics, dividing themselves into seven-man fireteams. McKenna would fire on advancing CSA forces, retreat into a building, then have a second fireteam flank the New York Revolutionaries from across the street. Casualties were high on both sides, especially among the Irish who often refused to fight until in incredibly close combat, hoping the shock of the ambush would carry the day. Friendly fire incidents were high, especially as the day went into night, both from accidental fire on friendly troops and sympathetic civilians accidentally firing on who they believed were enemy soldiers. Yet the day stood. On 14 September, his squads battered and American troops pushing through central Pennsylvania, Oliver Law reluctantly ordered a retreat to the northeast. Western Pennsylvania stood liberated, but the war was not over yet.
---

20 December 1937 - Welfare Island, New York City, United States of America
The icy winds of winter were howling, but the pit in Daniel McKenna’s stomach wasn’t from the cold. He had hoped to warm himself with a cigarette as he surveyed the successful conquest of New York City, but that had all left him. Naught but a short time ago, the celebration had been high. The Syndies had lost both a major symbol and, perhaps more pragmatically, their eastern command center. The Dominion of Canada had officially supported the Federal Government, and there had been Canadian, Indian, and French Republican volunteers sailing to Maryland to join MacArthur and the Volunteer Brigades, along with massive shipments of weapons from the Entente. Manhattan had surrendered rather than risk a massive urban brawl amongst the skyscrapers. That too, had seemed like a cause for celebration, but there was little sense of Christmas cheer among those who were picking through the ruins of New York City, for they had finally come to Welfare Island.
Inside, McKenna had found cell after cell of prisoners, skin stretched and hair falling out from starvation and malnutrition, their bodies broken from months of hard labor. When New York had fallen to the Syndicalists, they had imprisoned anyone who had worked in the financial sector, any who rented an apartment to another, or any who they considered to be bourgeoise, and demanded that they atone for the crimes of their previous lives with new, honest labor for the Syndicalist cause. They had been forced into the most dangerous jobs of the arms industry, like manufacturing artillery shells to the point where their skin had turned to a greasy yellow. Bleeding gums and fingers, limbs lost in machinery or explosive accidents were routine, each prisoner was a laundry list of atrocities written out upon their bodies.
Each horror that McKenna heard made him feel numb. He had nearly torn his gloves in two after listening, but he had made sure that he had heard it all, and that his staff heard it as well. A patriotic young woman, formerly a social columnist for the New York Tribune who had signed on to help with the support staff, volunteered to transcribe every word. “Be damned, lass, you’re a damn sight braver than any fella. Write it down, every bloody word, and know that ye’ve got a ironclad heart three times larger than any bastard who tells ye different.”
McKenna had dispatched three messages from New York. The first was to General MacArthur, who had said: “Am pleased to deliver to you New York as an early Christmas present.” The second was to Michael Collins, relaying a request for more reinforcement of men and materiel. The third, a private correspondence, bemoaned what he had seen. “The brutality of what I’ve seen is beyond words, and the only thing that breaks me more is the thought that this is not some singularly unique moment of malice, that we’ll find another Welfare Island in the South run by those America First bastards. God help me, is this what we left the English to in ‘25? Did we look at an Englishman for all those years and see the English and not the man?”
“Private. Bring all the Syndie prisoners we’ve got, make them see what went on here, make ‘em stare at each one. If they look away, hit ‘em. Then find the officers, and see which ones knew about it. And if ye find one that did...hang ‘em from the Brooklyn Bridge.”
---
Alright, that’s the second chapter, with the Syndicates on the ropes and the Firsters being slowly ground down in the western theater. The third chapter will handle the defeat of the Syndicalists and the Firsters and Mosley’s opening shots for his invasion of Ireland. Let me know what you think. And yes, I know some of the pictures are from 0.12, I’ve already mentioned that in my first post on the topic, and I know the battle map is crude; I suck at art. Also, what do you think about cropping the screenshots to make them easier to read? I think it looks fine, not too pixelated or zoomed in, but it does lose the sort of authentic “AAR screenshot” feeling. Which do you prefer, readers?
Images
Cactus Jack Becomes President
Standoff in America
Second American Civil War Begins
Battle of Baltimore
Encircled Federal Troops in Kentucky
US Moves the Capital to Denver
Germany Approves the Irish Business Initiative
Spain Approves the Irish Business Initiative
Italy Approves the Irish Business Initiative
The Netherlands Approves the Irish Business Initiative
The United States Approves the Irish Business Initiative
Canada Approves the Irish Business Initiative
Sweden Approves the Irish Business Initiative
Austria Approves the Irish Business Initiative
Rigged 1937 Election
The Wall of West Virigina
The Battle of Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh Battle Map
The Fall of New York
-SLAL
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
04/27/2020 DAB Transcript
Judges 7:1-8:17, Luke 23:13-43, Psalms 97:1-98:9, Proverbs 14:7-8
Today is the 27th day of April, welcome to the Daily Audio Bible I’m Brian it’s wonderful to be here with you today as we gather together. No matter where we are in the world we gather together around this Global Campfire and be together, allow God to speak to us through His word, let everything else go. It’s wonderful to be in this place together with you today. So, I mean in the next step forward is the one that comes after the last step. And, so, we’re working our way through the book of Judges right now and we’re in one of the longer stories of the judges, the story of Gideon. We’re reading from the Common English Bible this week. Judges chapter 7 verse 1 through 8 verse 17.
Commentary:
Okay. So, in the book of Judges we’re reading through though the story of Gideon and it's a pretty famous story but it's, you know, it’s one of the longer stories of the judges in Israel. And, so, we’ve already gone through who is Gideon and how God came to him and said you…you know, he's gonna use him to set the people free from the Midianites and the testing and the assembling of the Army and all of this. So, Gideon has 32,000 people. And, so…like…that’s a lot of people. It may not have been anywhere near as big as the Midianite army that was coming but that’s enough people to do some damage with and to put up a good fight with. And, so, we see the counterintuitive ways of the Lord in like, “there's too many people. If I had the Midianites over into your hand then…then you'll say you did it by your own strength. And that's not what's going on here. I am setting you free from the Midianites.” And we can see that this is true from our reading alone. Like, after the battle has happened and people are chasing the Midianites and everything then some of the tribes come to Gideon and they’re like, “why didn’t you take us into battle”, right? So, it was all about this glory. And, of course, Gideon's like, “what have I done? Like, you're doing more than I ever did.” So, he's calming them all down. But we can see that when God stripped the Army down and whittled it down further that he was right, they would've tried to take the glory for themselves. So, he invites anybody who was afraid basically to leave the mountain and 22,000 of the 32,000 leave which leaves Gideon 10,000. And, so, like that whittles things down considerably but that's still too many for God. So, in the end the fighting force is 300 people against a vast horde and according to what we read today that vast horde was over 100,000 people. So, 300 against that much of a horde of armed people, like that is not…like you wouldn't say like, “yeah…that…those are good odds. That's…you should…you should go to battle”, right? It's more like, “this is a suicide mission.” And we see these counterintuitive ways of God in so many of the stories of the Bible. So, the 300 people, like when it all starts, they are able to, you know, kind of raise torches and blow trumpets and smash vases and make a lot of noise and scream and yell. And because these 300 people have surrounded the camp the people inside the camp have no idea that…all they know is that they're being attacked. And it…and no one would attack an army like that with three hundred people. Like this is a big attack. And, so they get up and just start fighting…fighting each other. Everything is thrown into disarray. They start fleeing and we’ve seen these kinds of things in many different battles on our journey through the Scriptures so far this year. So, why not the battles that we face? Why wouldn't God be counterintuitive so that we couldn't raise our own flag and say look at what I did?
And if we want to talk like counterintuitive ways of getting things done, then let's just flip over into what we read in the gospel of Luke today because again we read the story of the crucifixion, like the final judgment and the crucifixion of our Savior. And again, it's so easy, but really…I mean…because it's so well-known, we've heard in a million times, maybe read it 100,000 times…like whatever…we…we've been through this story so many times that it's very easy to just move beyond it, kind of know the end of the story, kinda know what's gonna happen. And we don't necessarily have to focus on the fact that, yeah, Jesus was crucified…crucified. That's just an unthinkable form of execution. It's just so completely counterintuitive. The most-high God could to anything, could destroy the world in a second, could create things into being out of nothing. The all-powerful most-high God, this is how He chose to humble Himself. Like this…this is such a profound outpouring of love that it is like impossible for our minds to even comprehend it. This is the lengths God is willing to go to to get to us and it's very counterintuitive because in the end He left us reaching for Him in faith in what looked like defeat. He could've done this differently. He could’ve just road in and took over the world. This is the most-high God, who created the world and everything else, both known and unknown, like can whatever He wants to do and this is what He chose. And, so, let's not expect anything different but a counterintuitive creative God working in among His people, including us individually to do victorious things in counterintuitive ways.
Prayer:
Father, we invite You into that because we like linear. We like predictable. I raise my hand. I raise my other hand. I like things to make sense. I like to know a predictable outcome. We generally do like this and try to arrange for that. And yet, through the stories of the Scriptures we see You continually working in very very interesting unconventional ways. So, why would we expect that would stop even in times like this? So come Holy Spirit, may we hear and see Your movements, may we attain what we've been asking for all along, eyes to see and ears to hear, that we might see what You are doing in the world, that we might see what You are doing in our lives. We open ourselves to Your transformation. Come Holy Spirit we pray in the powerful and mighty name of Jesus we ask. Amen.
Announcements:
dailyaudiobible.com is home base, it’s the website, it’s where you find out what's going on around here. It is the…well…its home base. I guess that's the best way it could ever be said. It’s home base and, yeah, it's good to be connected and this is the place to get connected.
So, check out the Community section. That’s where the Prayer Wall lives. That’s where the different links to stay connected on social media are.
Check out the Daily Audio Bible Shop. There are resources there for this journey. And, like if you haven't journaled it all through this whole weird interesting quarantine season that we've been in, like this has never really happened before in our lifetimes. So, writing how you went through this…this…how this affected you in unique ways, like juts understanding that you can look back and remember all the things that you're gonna forget, that's important. And it's important concept in the Bible as well, to see the threat of God's faithfulness in our lives that we reach points at times we don't know how we’re gonna make it and then we do, but then life is moving so fast that we just move on and think back, you know, to this blackhole of memory, like, “yeah that was a hard time but I made it through. God helped me get through.” But writing our way through these things shows us. It’s like us writing our own story down that God is faithful and we are here, and we are moving forward. So, yeah, we’ve created all those kinds of resources for this journey, including things to write with and things to write on. And, yeah, it’s all in the Daily Audio Bible Shop for the journey that we’re on.
If you want to partner with the Daily Audio Bible, you can do that at dailyaudiobible.com as well and I thank you profoundly because the reality is we are…we are here…this happens every day because we are in this together as a community. And, so, thank you for your partnership. If you are using the Daily Audio Bible app you can press the Give button in the upper right-hand corner or, if you prefer, the mailing address is PO Box 1996 Spring Hill Tennessee 37174.
And, as always, if you have a prayer request or encouragement, you can hit the Hotline button that’s in the app, it’s the little red Hotline button at the top of the screen. Just touch that and begin to share right from there, no matter where you are in the world, or if you want to use the telephone you can dial several numbers depending on where you are in the world. In the Americas 877-942-4253. If you are in the UK or Europe 44-20-3608-8078. If you are in Australia or that part of the world 61-3-8820-5459 is the number.
And that's it for today. I’m Brian I love you and I'll be waiting for you here tomorrow.
1 note
·
View note
Photo

What flag is this?
from /r/vexillology Top comment: [General Polk's Army of Tennesse battle flag.](https://me.me/i/polk-flag-general-leonidas-polks-corps-army-of-tennessee-the-13789951)
14 notes
·
View notes
Link

Dr. Mary Walker was a remarkable woman. She was one of the first female doctors in the United States, and served as an army surgeon on the front lines during the Civil War. A dedicated reformer, Mary advocated for universal suffrage, abolition, dress reform, and temperance. She organized a relief system for the wives of wounded soldiers, and wrote two books. She remains, to this day, the only woman to have won the Medal of Honor. Mary was born in Oswego New York on November 26, 1832 to the unusual Alvah and Vesta Walker. (Alvah is the father.) Mary was the youngest of seven children--six girls and one boy. Mary's parents were eccentric for the times. They believed in sharing the work equally, and Alvah could often be found doing household chores. They allowed their daughters to dress however they liked, not forcing them into the restraining corsets and long skirts of the time, which both rightfully believed squished a girl's internal organs. To cap off the unusual Walker family, their home was also a stop on the Underground Railroad. Alvah had an interest in medicine, and a sizeable library of medical texts. Alvah and Vesta encouraged Mary to read as many of the medical books as she liked. Both of the Walkers were big believers in education, with Vesta being a school teacher. All of their children were educated through primary school, and all of the daughters went into teaching at one point in their lives. Mary worked briefly as a teacher, and in 1855 she entered and graduated Syracuse Medical School. Her course at Syracuse was only 39 weeks--three semesters of thirteen weeks each, which seems an almost irresponsible amount of training to give a doctor today, but was standard for the time. Mary chose Syracuse because it admitted women, and because it was known for its non-quackery. In an era where bloodletting and leeches were still common practices, Syracuse focused on more homeopathic remedies, and modern innovations. After graduation she married her classmate Albert Miller in an unusual ceremony where the bride wore pants, struck the 'obey' clause from her vows, and refused to take her husband's last name. Mary and Albert set up a practice together, and seemed to have been quite successful, with Mary treating the women and children, and Albert the men. Mary began to write about dress reform, and to present medical evidence in favor of this at important conferences. However, in 1859 this all ground to a halt when Mary discovered that Albert had been cheating on her. Mary tossed Albert out, and travelled to Iowa, where it was easier for women to obtain a divorce. Though it took several years, Mary eventually divorced Albert, and began life anew. After the First Battle of Bull Run, Mary decided to join the Union Army Medical Corp. She had nothing tying her down--Albert was long gone, her solo practice was a bust, and she had no children. Mary believed that she had a lot to offer as an army surgeon, so she went to Washington DC to ask for a commision. Unfortunately, the Union Army wasn't accepting female surgeons, or female anything really. Frustrated, Mary decided not to let a lack of pay stop her from doing what she wanted. She instead started volunteering as a nurse at the Patent Office Hospital, working under Dr. J.N. Green. Sources differ about what happened at this point. Some sources say that Dr. Green desperately need an assistant surgeon, and Mary filled that role. Others say that she did basically everything but surgery--dressing wounds, running errands, and entertaining patients. Whatever she did, Mary impressed Dr. Green so much that he recommend that she be given a commission. This recommendation was, of course, ignored, and Mary briefly went back to medical school in order to boost her credentials. She graduated from Hygeia Therapeutic College, and started volunteering in hospitals up and down Virginia. Mary was very outspoken about her opinions on how the war should be run. She published editorials suggesting that, in order to boost flagging enlistment numbers, former criminals could be enlisted, and even offered to serve as their surgeon. This gained the attention of war secretary, Edwin M. Stanton, who was definitely not going to create a regiment of former felons, and definitely didn't appreciate a lady having ideas. He gave Mary a posting, if not a commission or salary, to serve as an assistant surgeon with the 52nd Ohio Regiment in Tennessee. This was on the front lines, and there Mary faced a bit of difficulty. Wandering around a battlefield in skirts and petticoats was a terrible idea, and Mary had never been fond of dressing in typical Antebellum clothing anyways. In fact, she had been arrested several times for dressing like a man, and was frequently harassed for wearing a bloomer costume. On the front lines, Mary abandoned all pretense of dressing like a woman, instead donning a uniform, and making herself a green sash that denoted her as a member of the medical corp. Mary caused a bit of trouble with the 52nd with her, then, unconventional medical practices. An opponent of amputation, Mary felt that surgeons often rushed the decision to amputate, and that most wounds would be better treated by homeopathic remedies (like bandages and medicines) then amputation. When the male surgeons wouldn't listen to her, she talked directly to the patients, urging them to refuse amputation. Unsurprisingly, Mary faced a great deal of misogyny with the Ohio 52nd. Though her commanding officer, George H. Thomas, didn't care that she was female, the male surgeons cared very much. They didn't believe that she was capable of performing her duties as a surgeon, and even arranged a medical 'review' for her skills, which they then failed her on. Despite this, Mary refused to resign, and her commanding officer did not dismiss her. When the other surgeons refused to give her patients, Mary turned to treating civilians. Deep in Rebel territory, Mary was treating the wives and children of Confederate soldiers, many of whom were in hiding from the Union army. She is reputed to have taken supplies from Union stores in order to treat the unfortunates displaced by the war. It was during this time in 1864 that she was captured by the Confederacy. Now, there is some debate as to why Mary was captured. Some sources claim that it was because she was wearing men's clothing while being a Union soldiers, but other sources, including US Government Agencies, claim that it was because she was spying for the Union. In 1865 a federal judge put on the record that Mary had been a spy for General Sherman's army. Despite this record, there's some debate over whether or not Mary was up to espionage. However, this historian would like to posit that, while treating Confederate civilians, Mary would have several excellent opportunities for intelligence gathering. After being captured, Mary was sent to Castle Thunder Prison in Richmond. Castle Thunder was nicknamed 'the Southern Bastille', and not without reason. While in prison, Mary was treated abysmally. She was given only moldy bread and maggot ridden rice. She contracted bronchitis, lost an unhealthy amount of weight, and had to deal with fleas and bedbugs. Her eyesight was permanently damaged by the gas burning lamps in the prison. She would remain at Castle Thunder for four months. After being released Mary was celebrated far and wide for her heroics in war, even meeting President Lincoln. Edwin Stanton still denied her request for a commission, but she was given $432.26 in backpay, and was officially put on the US Army payroll. She was dispatched first to a women's military prison, then to an orphanage. When the Civil War ended in 1865 Mary was discharged from the army. Even after being discharged, Mary continued to lobby for a commision. President Andrew Johnson was in favor of this promotion, but military officials refused to give Mary a commision, fearing that if they gave one woman a commision, all the women would want commissions. Instead, President Johnson gave Mary the Congressional Medal of Honor, making her the only woman to this day to be awarded the honor. After being discharged, Mary took up work as an activist and reformer. She had some experience with this, having run a relief society for the mother's of wounded soldiers during her time at the Patent Office Hospital. Unaccompanied women who had come to see their wounded sons or husbands were rarely able to find lodging, and Mary organized a society that arranged places for those women to stay. She also, on several occasions, went over enemy lines to retrieve wounded sons or husbands for distraught women. Upon realizing that the many nurses who had served during the war had received no pay during the war, or pension after, Mary took up their cause, and by 1872 had browbeat Congress into giving the nurses a pension of $20 a month, despite the fact that she herself would not be successful in getting a pension for another two years. Mary was also active in the suffrage movement, specifically in the area of dress reform. She was arrested several times before and after the war for wearing men's clothing, and was quite proud of the fact. She gave lectures about the negative health effects of constrictive clothing. Because of this she was quite controversial, and other suffragettes didn't want her associated with the cause. Mary also took up her pen, publishing two books, Hit in 1871, and Unmasked: or the Science of Immorality in 1878. Both books argue for equality in a marriage, and for temperance and universal suffrage, but it is in Unmasked where Mary really hits hard. In a book as bitingly relevant today as it was when it was written, Mary puts forth the theory that if women could control their sexual urges, men could too. She argues that marriage should be a contract between social equals, and that just because a couple was married didn't mean they were allowed to rape each other. In 1874, Mary was finally given a pension of $8.50 a month. However, in 1917, her Medal of Honor was rescinded in an act of congress that took medals away from 911 individuals. The reasoning behind this was that the Medal of Honor could only be earned if the wearer had served in combat, which Mary hadn't. Continuing to wear the medal was a misdemeanor, but when a soldier came for her medal, Mary told him that he could take it over her dead body. She wore her award every day until her death. In 1880 Alvah Walker passed, leaving Mary his farm. Mary spent the rest of her life there, traveling between New York and Washington DC, lecturing and agitating for change. In 1919 she had a fall on the steps of the US Capitol, and died shortly after. After her death, her family crusaded tirelessly to have her Medal of Honor restored. In 1977, they were successful, and Mary's medal was officially restored to her by President Jimmy Carter. Today, it is on display in the Pentagon.
#history#civil war#american civil war#united states#united states history#mary edwards walker#mary walker#dr. mary walker#suffragette
33 notes
·
View notes
Text
Events 5.13 (before 1955)
1373 – Julian of Norwich has visions of Jesus while suffering from a life-threatening illness, visions which are later described and interpreted in her book Revelations of Divine Love. 1501 – Amerigo Vespucci, this time under Portuguese flag, set sail for western lands. 1568 – Mary Queen of Scots is defeated at the Battle of Langside, part of the civil war between Queen Mary and the supporters of her son, James VI. 1612 – Sword duel between Miyamoto Musashi and Sasaki Kojiro on the shores of Ganryū Island. Kojiro dies at the end. 1619 – Dutch statesman Johan van Oldenbarnevelt is executed in The Hague after being convicted of treason. 1654 – A Venetian fleet under Admiral Cort Adeler breaks through a line of galleys and defeats the Turkish navy. 1779 – War of the Bavarian Succession: Russian and French mediators at the Congress of Teschen negotiate an end to the war. In the agreement Austria receives the part of its territory that was taken from it (the Innviertel). 1780 – The Cumberland Compact is signed by leaders of the settlers in the Cumberland River area of what would become the U.S. state of Tennessee, providing for democratic government and a formal system of justice. 1804 – Forces sent by Yusuf Karamanli of Tripoli to retake Derna from the Americans attack the city. 1830 – Ecuador gains its independence from Gran Colombia. 1846 – Mexican–American War: The United States declares war on the Federal Republic of Mexico following a dispute over the American annexation of the Republic of Texas and a Mexican military incursion. 1861 – American Civil War: Queen Victoria of the United Kingdom issues a "proclamation of neutrality" which recognizes the Confederacy as having belligerent rights. 1861 – The Great Comet of 1861 is discovered by John Tebbutt of Windsor, New South Wales, Australia. 1861 – Pakistan's (then a part of British India) first railway line opens, from Karachi to Kotri. 1862 – The USS Planter, a steamer and gunship, steals through Confederate lines and is passed to the Union, by a southern slave, Robert Smalls, who later was officially appointed as captain, becoming the first black man to command a United States ship. 1888 – With the passage of the Lei Áurea ("Golden Law"), the Empire of Brazil abolishes slavery. 1909 – The first edition of the Giro d'Italia, a long-distance multiple-stage bicycle race, began in Milan; the Italian cyclist Luigi Ganna was the eventual winner. 1912 – The Royal Flying Corps, the forerunner of the Royal Air Force, is established in the United Kingdom. 1917 – Three children report the first apparition of Our Lady of Fátima in Fátima, Portugal. 1940 – World War II: Germany's conquest of France begins, as the German army crosses the Meuse. Winston Churchill makes his "blood, toil, tears, and sweat" speech to the House of Commons. 1941 – World War II: Yugoslav royal colonel Dragoljub Mihailović starts fighting against German occupation troops, beginning the Serbian resistance. 1943 – World War II: Operations Vulcan and Strike force the surrender of the last Axis troops in Tunisia. 1945 – World War II: Yevgeny Khaldei's photograph Raising a Flag over the Reichstag is published in Ogonyok magazine. 1948 – Arab–Israeli War: The Kfar Etzion massacre occurs, a day prior to the Israeli Declaration of Independence. 1950 – The inaugural Formula One World Championship race takes place at Silverstone Circuit. The race was won by Giuseppe Farina, who would go on to become the inaugural champion that year. 1951 – The 400th anniversary of the founding of the National University of San Marcos is commemorated by the opening of the first large-capacity stadium in Peru. 1952 – The Rajya Sabha, the upper house of the Parliament of India, holds its first sitting. 1954 – The anti-National Service Riots, by Chinese middle school students in Singapore, take place.
2 notes
·
View notes
Photo
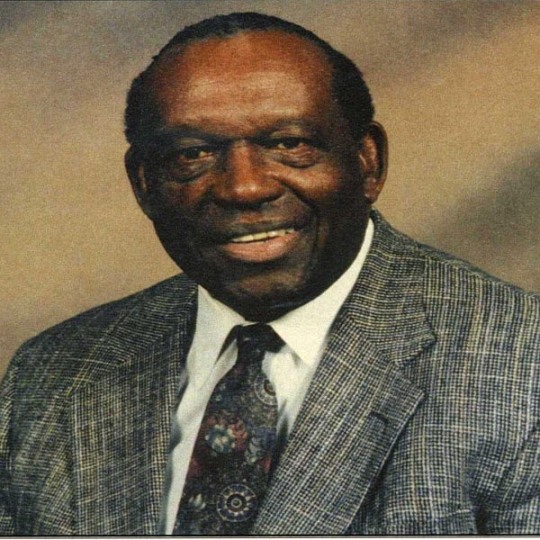

Charles Douglas Langford (December 9, 1922 – February 11, 2007) was an Alabama state senator who represented Rosa Parks in the famous civil rights case of the 1960s. He served in the Alabama Legislature as a State Representative, in District 77, Montgomery County, from 1976 to 1983, and as a State Senator, in District 26, Montgomery County, from 1983 to 2002. He was the sixth child of Nathan G. and Lucy Brown Langford. He was one of two African American lawyers in Montgomery at this time. He completed two years at Tuskegee Institute before being drafted into the Army during WWII, where he served overseas as a truck driver in the European Theater Operation. He had an honorable discharge from the Army in 1946. He earned his JD at The Catholic University of America. He had earned his BA at Tennessee State University. He was a partner in the law firm of Gray, Langford, Sapp, McGowan, Gray, and Nathanson. He helped end the flying of a Confederate battle flag from the dome of the State Capitol in Montgomery. In 1964 he represented Arlam Carr in a lawsuit against Montgomery's Board of Education that led to the desegregation of the city's public schools. In 1953, he was admitted to the Alabama State Bar, and opened his law office on Monroe Street in Montgomery. He stayed in Montgomery and continued to represent local African-Americans in civil rights cases. He served five terms in the Senate before retiring in 2002. #africanhistory365 #africanexcellence #alphaphialpha https://www.instagram.com/p/Cl_OvkIrygH/?igshid=NGJjMDIxMWI=
7 notes
·
View notes