#Artillery Systems Market Companies
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Market Share Insights in the Artillery Systems Industry

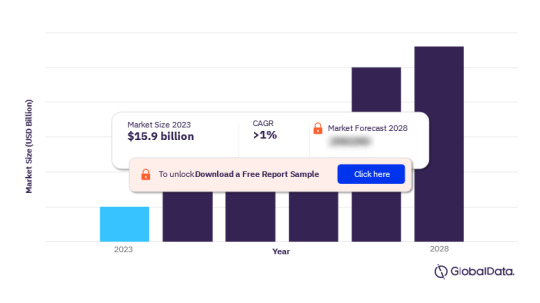
The Artillery Systems Market is projected to grow significantly, with market statistics indicating an increase from USD 11.8 Billion in 2023 to USD 16.0 Billion by 2028, representing a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 6.2% over the forecast period. This report delves into the market size, trends, industry drivers, opportunities, and challenges shaping the future of Artillery Systems Industry.
Market Overview
Artillery systems are crucial in modern warfare, providing long-range firepower and precision support. These systems play a vital role on the battlefield by delivering large-caliber projectiles to distant targets with remarkable accuracy. This capability allows forces to engage enemy positions, disrupt movements, and offer indirect fire support to friendly troops. The range and precision of artillery systems make them indispensable in combat situations, enabling engagement of targets beyond the line of sight and reducing risks to friendly forces.
Market Size and Growth
The artillery systems market, valued at USD 11.8 billion in 2023, is anticipated to reach USD 16.0 billion by 2028. Several factors, including modernization initiatives and advancements in artillery technology, drive this growth. The increasing demand for enhanced artillery systems, capable of delivering precise and long-range firepower, is a significant contributor to this market expansion.
Key Market Drivers
Advancing Artillery Capabilities for Modern Warfare
Modernization initiatives aim to upgrade existing artillery systems with the latest technologies, enhancing their effectiveness, range, accuracy, and mobility. These upgrades include digitalized fire control systems, improved targeting systems, and enhanced communication capabilities. The integration of artillery systems with modern military components, such as command and control systems, surveillance systems, and unmanned platforms, is crucial for network-centric operations.
The need to keep pace with evolving threats, technological advancements, and changing operational requirements drives these modernization efforts. Defense forces are focused on having artillery systems that can engage targets accurately and rapidly, even in complex battlefield environments. Modernization also aims to enhance the survivability of artillery units through advanced protection systems and improved mobility platforms.
Increasing Adoption of Self-Propelled Artillery
Self-propelled artillery, equipped with their propulsion systems, offers high lethality and improved maneuverability. These systems provide long-range indirect bombardment support and are essential for modern military operations. The increased demand for self-propelled artillery systems, driven by their unique capabilities, contributes significantly to the market's growth.
Get a Deeper Understanding of the Industry by Visiting: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/artillery-system-market-69844596.html
Restraints
Limited Ammunition Storage Space
One of the major restraints in the artillery systems market is the limited space for ammunition storage. Artillery systems require ample storage space for a substantial quantity of ammunition, essential for sustained operations. The constraints include:
Size and Weight Constraints: Ammunition for artillery systems is bulky and heavy, requiring dedicated storage facilities. Limited physical space can restrict the quantity of ammunition stored, impacting operational readiness.
Safety Considerations: Strict safety protocols are necessary for ammunition storage, including maintaining appropriate distances and ensuring proper ventilation and security measures.
Mobility and Logistics Challenges: Limited storage space can present logistical challenges, necessitating frequent resupply and replenishment of ammunition, which can hamper sustained operations.
Vulnerability to Attacks: Compact ammunition storage areas are vulnerable to attacks, reducing the options for dispersing ammunition and making it more susceptible to damage.
Cost Implications: Expanding storage facilities or constructing additional infrastructure to overcome space limitations can be costly.
High Costs of Artillery Systems
The development of self-propelled artillery systems involves substantial time, capital, and technical expertise. The high costs of developing advanced technologies for these systems act as a significant challenge, especially for emerging nations. The average cost of a self-propelled artillery unit is around USD 6.7 million, with costs increasing based on advanced specifications.
Opportunities
Unmanned Artillery Systems Transforming Battlefields
Unmanned artillery systems offer significant opportunities for increased battlefield adaptability. These systems can be rapidly deployed and repositioned, allowing for dynamic responses to changing operational requirements. The integration of unmanned artillery systems with other autonomous platforms, such as drones and ground robots, enhances situational awareness and collaborative engagement.
Unmanned systems reduce the logistical footprint by requiring fewer personnel and support equipment, streamlining operations and increasing operational efficiency. The development of unmanned artillery systems also drives innovation in artificial intelligence, robotics, and advanced sensors, fostering cross-sector collaboration.
Market Segmentation
This Research Report Categorizes Artillery Systems Based on Type, Range, Subsystem, and Region:
By Type:
Howitzers
Mortars
Rocket Launchers
Anti-Air Weapons
Artillery
By Subsystem:
Turrets
Engines
Fire Control Systems
Ammunition Handling Systems
Chassis
Auxiliary Systems
By Range:
Short-Range
Medium-Range
Long-Range
By Region:
North America
Europe
Asia Pacific
Rest of the World
By Howitzer Type
Medium Caliber (100 MM-155 MM): The medium caliber howitzer segment is expected to record the highest market share during the forecast period. Medium caliber howitzers provide a balance between range and lethality, achieving extended ranges and supporting operations over a wider area.
By Mortar Type
Small Caliber: Small caliber mortars are witnessing rapid growth due to their portability and lightweight design. These systems are easily transported and deployed, providing greater maneuverability for infantry units and offering close-range indirect fire support.
By Artillery Type
Coastal Artillery: Coastal artillery systems have secured the largest market share due to their high accuracy and critical role in coastal defense and maritime security. These systems deter hostile naval forces and protect strategic maritime assets and infrastructure.
Download Sample PDF Copy to Understand More: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/pdfdownloadNew.asp?id=69844596
Regional Analysis
Asia Pacific
The Asia Pacific region is expected to lead the artillery systems market in 2023. Factors contributing to this growth include:
Major Military Powers: The presence of major military powers, such as China, Japan, India, and Australia, drives the demand for advanced artillery systems.
High Military Budgets: Countries in the region have high military budgets and invest heavily in modernizing their artillery capabilities.
Technological Advancements: Rapid technological advancements and investments in artillery systems technology drive market growth in the region.
Key Market Players
Leading Companies in the artillery systems market include:
Lockheed Martin Corporation (US)
BAE Systems (UK)
Hanwha Group (South Korea)
Rheinmetall AG (Germany)
Nexter Group (France)
Norinco International Cooperation Ltd. (China)
Rostec (Russia)
General Dynamics Corporation (US)
Avibras (Brazil)
Elbit Systems (Israel)
These companies have well-equipped manufacturing facilities and strong distribution networks across North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East & Africa.
The artillery systems market is poised for significant growth, driven by modernization initiatives, advancements in technology, and increasing adoption of self-propelled and unmanned artillery systems. Despite challenges such as limited ammunition storage space and high costs, the market offers substantial opportunities for innovation and expansion. The Asia Pacific region, with its major military powers and high investments in military technology, is expected to lead the market. Key players in the industry are well-positioned to capitalize on these trends, contributing to the ongoing evolution of artillery systems in modern warfare.
About MarketsandMarkets™
MarketsandMarkets™ has been recognized as one of America's best management consulting firms by Forbes, as per their recent report.
MarketsandMarkets™ is a blue ocean alternative in growth consulting and program management, leveraging a man-machine offering to drive supernormal growth for progressive organizations in the B2B space. We have the widest lens on emerging technologies, making us proficient in co-creating supernormal growth for clients.
Earlier this year, we formally transformed into one of America's best management consulting firms as per a survey conducted by Forbes.
The B2B economy is witnessing the emergence of $25 trillion of new revenue streams that are substituting existing revenue streams in this decade alone. We work with clients on growth programs, helping them monetize this $25 trillion opportunity through our service lines - TAM Expansion, Go-to-Market (GTM) Strategy to Execution, Market Share Gain, Account Enablement, and Thought Leadership Marketing.
Built on the 'GIVE Growth' principle, we work with several Forbes Global 2000 B2B companies - helping them stay relevant in a disruptive ecosystem. Our insights and strategies are molded by our industry experts, cutting-edge AI-powered Market Intelligence Cloud, and years of research. The KnowledgeStore™ (our Market Intelligence Cloud) integrates our research, and facilitates analysis of interconnections through applications, helping clients look at the entire ecosystem and understand the revenue shifts in their industry.
To learn more, visit www.MarketsandMarkets™.com or follow us on Twitter, LinkedIn and Facebook.
Contact: Mr. Aashish Mehra MarketsandMarkets™ INC.
630 Dundee Road Suite 430 Northbrook, IL 60062 USA: +1-888-600-6441
Email: [email protected] (Image Credit: Mittler Report Verlag)
#Artillery Systems#Artillery Systems Market#Artillery Systems Industry#Global Artillery Systems Market#Artillery Systems Market Companies#Artillery Systems Market Size#Artillery Systems Market Share#Artillery Systems Market Growth#Artillery Systems Market Statistics
0 notes
Text
Now that Donald Trump is returning to a second term as U.S. president, ascertaining the true state of Russia’s war economy is more important than ever. Trump’s advisors believe that Ukraine must settle for peace by whatever means necessary “to stop the killing.” Implicit in this argument is the view that Russia has the ability to sustain the war for many years to come. On close examination of the evidence, however, the narrative that Russia has the resources to prevail if it so chooses does not hold.
The apparent resilience of the Russian economy has confounded many strategists who expected Western sanctions to paralyze Moscow’s war effort against Ukraine. Russia continues to export vast quantities of oil, gas, and other commodities—the result of sanctions evasion and loopholes deliberately designed by Western policymakers to keep Russian resources on world markets. So far, clever macroeconomic management, particularly by Russian Central Bank Governor Elvira Nabiullina, has enabled the Kremlin to keep the Russian financial system in relative health.
At first glance, the numbers look surprisingly strong. In 2023, GDP grew by 3.6 percent and is expected to rise by 3.9 percent in 2024. Unemployment has fallen from around 4.4 percent before the war to 2.4 percent in September. Moscow has expanded its armed forces and defense production, adding more than 500,000 workers to the defense industry, approximately 180,000 to the armed forces, and many thousands more to paramilitary and private military organizations. Russia has reportedly tripled its production of artillery shells to 3 million per year and is manufacturing glide bombs and drones at scale.
Despite these accomplishments, Russia’s war economy is heading toward an impasse. Signs that the official data masks severe economic strains brought on by both war and sanctions have become increasingly apparent. No matter how many workers it tries to shift to the defense industry, the Kremlin cannot expand production fast enough to replace weapons at the rate they are being lost on the battlefield. Already, about around half of all artillery shells used by Russia in Ukraine are from North Korean stocks. At some point in the second half of 2025, Russia will face severe shortages in several categories of weapons.
Perhaps foremost among Russia’s arms bottlenecks is its inability to replace large-caliber cannons. According to open-source researchers using video documentation, Russia has been losing more than 100 tanks and roughly 220 artillery pieces per month on average. Producing tank and artillery barrels requires rotary forges—massive pieces of engineering weighing 20 to 30 tons each—that can each produce only about 10 barrels a month. Russia only possesses two such forges.
In other words, Russia is losing around 320 tank and artillery cannon barrels a month and producing only 20. The Russian engineering industry lacks the skills to build rotary forges; in fact, the world market is dominated by a single Austrian company, GFM. Russia is unlikely to acquire more forges and increase its production rate, and neither North Korea nor Iran have significant stockpiles of suitable replacement barrels. Only a decision by China to provide barrels from its own stockpiles could stave off Russia’s barrel crisis.
To resupply its forces, Russia has been stripping tank and artillery barrels from the vast stockpiles it inherited from the Soviet Union. But these stockpiles have withered since the start of the war. Combining current rates of battlefield loss, recycling from stockpiles, and production, Russia looks set to run out of cannon barrels some time in 2025.
Russia is consuming other weapons, too, at rates far faster than its ability to produce them. Open-source researchers have counted the loss of at least 4,955 infantry fighting vehicles since the war’s onset, which comes out to an average of 155 per month. Russian defense contractors can produce an estimated 200 per year, or about 17 per month, to offset these losses. Likewise, even Russia’s expanded production of 3 million artillery shells per year pales in comparison to the various estimates for current consumption at the front. While those estimates are lower than the 12 million rounds Russian forces fired in 2022, they are much higher than what Russian industry can produce.
We do not know when Russia will hit the end of the road with each equipment type. But there is little the Kremlin can do little to stave off that day. With the Russian economy essentially at full employment, Russian defense companies now struggle to attract workers. To make matters worse, these companies are competing for the same personnel as the Russian armed forces, which need to recruit 30,000 fresh troops each month to replace casualties. To this end, the military is offering lavish signing bonuses and greatly increased pay. Defense producers, in turn, have had to increase wages fivefold, contributing to an inflation rate that reached 8.68 percent in October.
Paradoxically, the same factors that are converging to restrict Russia’s ability to wage war also mean that it cannot easily make peace.
Russia’s economic performance—marked by low unemployment and rising wages—is a product of military Keynesianism. In other words: Vast military expenditures, which are unsustainable in the long term, are artificially boosting employment and growth. Almost all the new jobs are related to the military and produce little of value to the civilian economy, where most sectors have great difficulty finding workers.
Defense spending has officially jumped to 7 percent of Russia’s GDP and is projected to consume more than 41 percent of the state budget next year. The true magnitude of military expenditures is significantly higher. Russia’s nearly 560,000 armed internal security troops, many of which have been deployed to occupied Ukraine, are funded outside the defense budget—as are the private military companies that have sprouted across Russia.
Paring back these massive defense expenditures, however, will inevitably produce an economic downturn. If the Kremlin draws down the armed forces to a sustainable level, large numbers of traumatized veterans and well-paid defense workers will find themselves redundant. The experience of other societies—in particular, European states after World War I—suggests that hordes of demobilized soldiers and jobless defense workers are a recipe for political instability.
The magnitude of the post-war Russian recession will be all the worse because Russia’s civilian economy—particularly small- and medium-sized firms—has shrunk due to the war. In a phenomenon familiar to economists, high defense expenditures have bid up salaries and attracted labor away from nondefense firms. The Russian Central Bank’s policy of raising interest rates, which currently stand at 21 percent, has made it much more difficult for nondefense companies to raise capital through loans. In post-war Russia, a shrunken civilian sector will not be able to absorb the soldiers and workers cast off by the military and defense sector.
Therefore, Russia’s leaders face an unenviable set of dilemmas entirely of their own making. Russia cannot continue waging the current war beyond late 2025, when it will begin running out of key weapons systems.
Concluding a peace agreement, however, poses a different set of problems, as the Kremlin needs to choose between three unpalatable options. If it draws down the armed forces and defense industries, it will spark a recession that could threaten the regime. If Russian policymakers instead maintain high levels of defense spending and a bloated peacetime military, it will asphyxiate the Russian economy, crowding out civilian industry, and stifle growth. Having experienced the Soviet Union’s decline and fall for similar economic reasons, Russian leaders will probably seek to avoid this fate.
A third option, however, is available and likely beguiling: Rather than demobilizing or bankrupting themselves, Russian leaders could instead use their military to obtain the economic resources needed to sustain it—in other words, using conquest and the threat thereof to pay for the military.
Plenty of precedents exist. In 1803, French Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte ended 14 months of peace in Europe because he could not afford to fund his military based on French revenues alone—and he also refused to demobilize it. In 1990, Iraqi leader Saddam Hussein similarly invaded oil-rich Kuwait because he could not afford to pay the million-man army that he refused to downsize. In both cases, the mirage of conquest seemed attractive for sustaining overly large defense establishments without having to pay for them.
Russia could likewise exploit its expanded military to extract rents from other states. Even though Russia is running out of key weapons systems for its all-out war on Ukraine, its forces will still be capable of punctual acts of aggression. Indeed, it’s easy to imagine how Russia might pursue such a policy.
Substantial offshore gas reserves have been discovered in the Black Sea within Ukraine’s and Georgia’s internationally recognized exclusive economic zones (EEZs). Whenever Western states are distracted by other priorities, Russia could also renew its aggression against Ukraine in order to gain control of its agricultural, gas, and rare-earth resources. Finally, Russia might use threats of force rather than actually fighting in order to coerce European states to withdraw sanctions, unfreeze Russian assets, or reopen gas and oil pipelines.
Some important lessons emerge. First, Russia’s economy cannot indefinitely sustain its war against Ukraine. Labor and production bottlenecks will condemn Russia to defeat as long as Ukraine’s allies sustain it beyond the second half of 2025. Contrary to the myth of infinite Russian resources, the Kremlin’s armies are far from unbeatable. But Russia’s defeat demands a level of Western patience and commitment that a combination of vacillating Western leaders and volatile domestic politics renders questionable.
Second, the cessation of full-scale fighting in Ukraine will not end the West’s problems with Russia. Russia’s supersized military sector incentivizes the Kremlin to use its military to extract rents from neighboring states. The alternatives—demobilizing and incurring a recession or indefinitely funding a bloated military and defense industry—pose existential threats to Putin’s regime.
However Russia ends its current war, the country’s economic realities alone will generate new forms of insecurity for Europe. Far-sighted policymakers should focus on mitigating these future threats, even as they focus on how the current round of fighting in Ukraine will end.
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
Israel records $12.5 billion in defense exports, led by drones, air defense
Abraham Accord partners account for a jump in Jerusalem's sales.
By SETH J. FRANTZMAN

A model by Israeli Aerospace Industries at Sea Air Space 2023 shows an uncrewed system coming in for a landing on a ship. (Aaron Mehta / Breaking Defense)
JERUSALEM — Israel’s defense exports reached a record high of $12.5 billion in 2022, according to the Israeli Ministry of Defense, led by keen global interest in drones and air defense systems.
An MoD report released today also noted continued growth in a new, big market for Israeli tech: Abraham Accords countries in the Gulf that bought approximately $3 billion-worth of defense platforms. This means that since the peace deals were signed in 2020, sales to countries that Israel has new ties with are now almost as high as all of Israel’s $3.6 billion in sales back in 2005.
Overall “Israeli defense exports have doubled in less than a decade and increased by fifty percent in three years,” the Ministry said. Israel has been a leader in drone exports for decades, owing to the fact the country was a pioneer in UAVs in the 1980s and also a leading developer of loitering munitions.
RELATED: Latest tests of Israel’s maritime Iron Dome take aim at ‘future’ threats
Even with competition from China, Turkey and other drone manufacturers, the Israeli report says around one quarter of the agreements signed in 2022 were for UAVs and drones. Israel’s three large defense companies — Elbit Systems, Rafael Advanced Defense Systems and Israel Aerospace Industries — all play a role in the UAV and counter-UAV market. Elbit makes the large Hermes 900 drone, and IAI sells the Heron line of drones. Rafael is a part owner of Aeronautics with makes the Orbiter line.
“The remarkable data unveiled by the Israeli defense establishment, reaching new heights in defense exports, showcases the State of Israel’s strength and excellent technological capabilities. Through the creativity and innovation of both the Israeli defense establishment and the Ministry of Defense, we not only outpace our adversaries but also sustain our qualitative edge,” said Minister of Defense, Yoav Gallant.
Israel has approximately 120 defense companies, including many smaller companies that focus on unique technologies, such as radars, or sights for rifles and C-UAS systems. Israel’s defense sales are led in some cases by government-to-government deals, such as the May deal between Israeli and Dutch ministries of defense for $305 million-worth of Elbit-made PULS Rocket Artillery Systems.
Read More: Breaking Defense
8 notes
·
View notes
Text

How would a free market or socialist economy work? They sound nice but we don't have either in my country, the USA.
The government's fate is tied to the health of the economy, regardless of what kind of ism you prefer.
Liberalism, capitalism, socialism, communism, whatever, it needs an efficient clean energy economy or it will explode and collapse, sooner or later.
Wouldn't we need to have a system of charging biobatteries with clean energy instead of using petrofascist infrastructure to truly call ourselves free market or socialist?
Has liberalism itself failed in the struggle against electricity monopolies and petrofascism?
Yes and, to speak to the original comment, I'm agreed that criminal justice should be rehabilitative not punative, yet that is already the doctrine in the USA, but not the practice de facto. We need a more nuanced convo about police accountability and a reminder that the US penal system is vastly corrupt if those questions are getting asked...here's a question, aren't we going to need fossil fuel to make the casings for our organic batteries? Nope, because:
Fun fact, plastic can be made from hemp instead of fossil fuels!

All our economies will flourish with abundant solar and wind charging organic, compostable batteries. We would leave the petrofascists to apply for unemployment insurance benefits. Fine by me, I'm glad that safety net is there for them, remember that when those petrofascists will complain we are killing them and their industry, yet that's what they did to our industry 1900-1920, killing electric rail and monopolizing energy storage.
Consider that our energy is literally monopolized, and how absurd that is, and how profound that is.
Our local electric monopoly bill is due soon, better pay their demands and not ask questions, god forbid we would have a choice for our electricity.
Free markets? What are those? Sounds nice.
The struggle for socialism vs liberalism is a philosophical discussion while we have neither, and our energy is literally being monopolized by fascists.
Lemme jostle some matrix plugs in some brains out there, the electric company monopolizes our energy.
This is a profound insult worthy of revolt, and that revolt would receive landslide public approval yet it would be met with gunpoint by the vastly outnumbered petrofascist skeletor seal-team-6.
Welcome to the borderlands, where sugar biobatteries are 10x as efficient as lithium ion, and we can charge those batteries with abundant wind and solar distrubuted out in key urban and suburban places with existing foundations, but we're stuck buying monopolized electricity, reading blogs by Warren Buffet and Bill Gates thinking they're the "good" billionaires, we're stuck buying monopolized gas, and EVs made with batteries of lithium ion which is inferior for not only being 10x weaker physically than sugar batteries, but also much more harmful to the environment.
Here lies the extent of the waters of western liberalism, that the United States of America was founded on, this is the far-frontier beach of the edge of that unfinished American Revolution, this is where the boats floated to, on this beach we stand on a continent of western authoritarianism and petro-fascism, time to fill that gas tank at one of 4 suppliers or you can't go to work, and then pay the electric monopoly bill without receiving equity or voting power because de facto it's illegal to build clean infrastructure on this continent, this is the center of the front line of our battle, this is how the economy can work and you can call that gov't whatever children's philosophy vocab -ism you like it lives or dies with the health of its energy economy, both in the revolutionary struggle as their tanks run out of gas on the battle field and ours escape with clean energy before the mega artillery rains down like a monsoon; and this is how we thrive in the peacetime economy after; this is how to actually win the struggle against petrofascism by charging hard here and never stopping...
I know the names of my ancestors who fought in the American revolution but it's still not finished
Hey bro/ster I'm super sorry to have to be the one to break this to you, but uh sometimes being a socialist means, you know, putting your dreams of terrorism down for a minute and talking about public policy and how your proposed form of government would like, uhhhhh................ work.
#solarpunk manifestos to critique#solarpunk manifestos to emblazon via moss graffiti#lol#thothy#revolutionary solarpunks
31K notes
·
View notes
Text
General Dynamics Land Systems Competitors: A Competitive Landscape in Defense and Combat Vehicles
General Dynamics Land Systems (GDLS) is a major player in the global defense industry, renowned for its design and manufacture of combat vehicles, including the iconic M1 Abrams tank. As a key segment of General Dynamics Corporation, GDLS operates in a competitive environment with several formidable rivals specializing in defense technology, combat systems, and vehicle production.
Here’s an analysis of the key competitors challenging GDLS in the global defense market.
1. BAE Systems
Headquarters: Farnborough, United Kingdom
BAE Systems is a leading defense contractor and one of GDLS’s top competitors. It specializes in producing armored vehicles, artillery systems, and military support vehicles. Notable offerings include the CV90 infantry fighting vehicle and the M109 self-propelled howitzer.
BAE Systems distinguishes itself with a strong focus on innovation and modularity, enabling customization for various military needs. The company's global reach and partnerships with governments worldwide have solidified its position as a direct rival to GDLS in the armored vehicle market.
2. Rheinmetall Defence
Headquarters: Düsseldorf, Germany
Rheinmetall is a prominent European defense contractor with expertise in military vehicles and weapon systems. Its flagship products, such as the Lynx infantry fighting vehicle and the Leopard tank (produced in partnership with Krauss-Maffei Wegmann), make it a significant competitor to GDLS.
Rheinmetall's strong engineering capabilities and focus on advanced technologies, such as active protection systems and autonomous vehicle solutions, position it as a formidable rival in the combat vehicle segment.
3. Oshkosh Defense
Headquarters: Oshkosh, Wisconsin, USA
Oshkosh Defense specializes in tactical wheeled vehicles for military applications, including the Joint Light Tactical Vehicle (JLTV), which is a direct competitor to GDLS’s lighter combat vehicle offerings.
Oshkosh is known for its durability-focused designs and proprietary technologies like TAK-4® independent suspension systems. Its expertise in lightweight and highly mobile platforms gives it an edge in areas where agility and speed are critical.
4. Krauss-Maffei Wegmann (KMW)
Headquarters: Munich, Germany
KMW, often working in collaboration with Rheinmetall, is a leader in producing heavy military vehicles such as tanks and self-propelled artillery. The Leopard 2 tank, one of the most advanced main battle tanks globally, competes directly with GDLS’s M1 Abrams.
KMW's focus on integrating cutting-edge technologies, including advanced optics and fire-control systems, makes it a preferred supplier for many European nations.
5. Lockheed Martin
Headquarters: Bethesda, Maryland, USA
Although primarily known for its aerospace capabilities, Lockheed Martin competes with GDLS in specific land systems through programs like its modernized ground combat vehicles and unmanned ground systems.
Lockheed Martin leverages its expertise in integrated systems and defense electronics to provide versatile land platforms. Its ability to integrate advanced sensors and AI technologies into combat vehicles positions it as a competitor in areas where GDLS is also innovating.
6. Leonardo S.p.A.
Headquarters: Rome, Italy
Leonardo is a global defense company offering a range of land vehicles, including armored personnel carriers and infantry fighting vehicles. Its Freccia and Centauro vehicles are widely used in Europe and other regions, competing with GDLS’s mid-range combat platforms.
Leonardo's focus on collaboration and its ability to provide end-to-end solutions, including weapon systems and electronic warfare technologies, make it a noteworthy competitor in the land systems market.
7. Hyundai Rotem
Headquarters: Seoul, South Korea
Hyundai Rotem is a growing competitor in the armored vehicle market, particularly in Asia. Its K2 Black Panther main battle tank is a rival to GDLS’s M1 Abrams and has garnered attention for its advanced mobility and protection features.
Hyundai Rotem’s focus on innovation and its growing exports to global markets make it a rising competitor to watch in the combat vehicle sector.
Conclusion
The competitive landscape for General Dynamics Land Systems is marked by the presence of well-established global players with distinct strengths. While GDLS remains a leader with its proven platforms like the M1 Abrams and Stryker vehicles, rivals such as BAE Systems, Rheinmetall, and Oshkosh Defense continue to challenge its dominance through innovation, regional influence, and tailored offerings.
As the defense industry evolves, GDLS must continue to focus on technological advancements, strategic partnerships, and cost-effective solutions to maintain its competitive edge in the global market.
0 notes
Text

𝐓𝐡𝐫𝐞𝐞 𝐈𝐧𝐝𝐢𝐚𝐧 𝐜𝐨𝐦𝐩𝐚𝐧𝐢𝐞𝐬—Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (Rank 43), Bharat Electronics Limited (Rank 67), and Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Ltd (Rank 94)—secured spots in SIPRI’s Top 100 global arms producers.
Their combined revenues rose 5.8% to $6.74 billion (₹56,769 crore) in 2023. Globally, US companies dominated with $317 billion in revenues, followed by China ($103 billion) and Russia ($25.5 billion). Rising arms sales are fueled by conflicts in Gaza and Ukraine, East Asian tensions, and global rearmament efforts.
India’s key defense exports include BrahMos missiles, Dornier-228 aircraft, artillery systems, and advanced electronic equipment, showcasing its growing capabilities in the global defense market.
#general knowledge#affairsmastery#generalknowledge#current events#current news#upscaspirants#upsc#upsc2024#generalknowledgeindia#breaking news#india news#world news#news#public news#technology#us military#upscpreparation#upsc2025#upsccoaching#iaspreparation#ias#civil service#aeronautica militare#defense#military#missile#armedforces#gaza#ukraine#russo ukrainian war
1 note
·
View note
Text
The Artillery Systems Industry: Trends, Challenges, and Market Insights
The artillery systems industry is a vital segment of the defense sector, focusing on the development and production of artillery weapons and supporting systems. This market has evolved significantly in response to geopolitical dynamics, technological advancements, and changing warfare strategies. In this blog, we will explore the current state of the artillery systems market, emerging trends, challenges, and prospects.
Overview of the Artillery Systems Market
The Artillery Systems Market is projected to be valued at approximately USD 8.84 billion in 2024, with expectations to grow to USD 12.54 billion by 2029. This growth represents a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.24% over the forecast period from 2024 to 2029.
The global artillery systems market has seen substantial growth in recent years, driven by increased military spending and modernization programs across various nations. According to market research, the industry is projected to grow at a CAGR of around 3-5% over the next decade. This growth is fueled by:
Rising Geopolitical Tensions: Ongoing conflicts and regional disputes have prompted countries to enhance their military capabilities, leading to higher demand for artillery systems.
Modernization of Armed Forces: Many nations are investing in upgrading their existing artillery systems to improve accuracy, range, and firepower.
Key Trends Shaping the Market
Technological Advancements: Innovations such as precision-guided munitions (PGMs), automated artillery systems, and advanced targeting systems are transforming traditional artillery into highly efficient and lethal platforms.
Integration of Smart Technology: The incorporation of smart technology, including artificial intelligence and data analytics, enhances decision-making capabilities and operational efficiency in artillery operations.
Focus on Mobility and Versatility: Modern warfare emphasizes rapid deployment and adaptability. As a result, manufacturers are developing lighter, more mobile artillery systems that can be easily transported and deployed in various terrains.
Increased Defense Budgets: Countries are allocating larger portions of their budgets to defense, particularly in regions like Asia-Pacific and Eastern Europe, where security concerns are mounting.
Collaboration and Partnerships: Defense contractors are increasingly collaborating with technology firms and research institutions to leverage expertise and develop next-generation artillery systems.
Challenges Facing the Industry
Despite its growth potential, the artillery systems market faces several challenges:
Regulatory and Compliance Issues: The defense industry is heavily regulated, and compliance with international arms control agreements can complicate operations and expansion.
High Research and Development Costs: The need for continuous innovation and the high costs associated with R&D can strain budgets, particularly for smaller manufacturers.
Geopolitical Risks: Changing political landscapes can impact defense contracts and international cooperation, leading to uncertainties in market stability.
Supply Chain Disruptions: Recent global events have highlighted vulnerabilities in supply chains, affecting the timely delivery of components and materials essential for artillery production.
Future Outlook
The future of the artillery systems industry appears promising, driven by ongoing advancements in technology and increasing defense investments. Key areas to watch include:
Expansion of Product Offerings: Companies are likely to diversify their product lines, offering integrated systems that combine artillery with unmanned platforms and other advanced technologies.
Emerging Markets: Countries in regions like Asia, Africa, and Latin America are expected to invest in artillery systems, providing growth opportunities for manufacturers.
Sustainability Initiatives: As global attention shifts toward sustainability, the industry may explore eco-friendly production methods and the development of greener munitions.
Conclusion
The artillery systems market is poised for significant growth, shaped by technological advancements and evolving military needs. As geopolitical tensions continue to influence defense strategies, companies in this sector must navigate challenges while seizing opportunities for innovation and collaboration. By staying ahead of market trends and embracing new technologies, manufacturers can thrive in this dynamic industry and contribute to the future of modern warfare.
For a detailed overview and more insights, you can refer to the full market research report by Mordor Intelligence https://www.mordorintelligence.com/industry-reports/artillery-systems-market
#artillery systems market#artillery systems market size#artillery systems market share#artillery systems market trends#artillery systems market report
0 notes
Text
Laser Warning Receiver Market – Latest Scenario Report And Forecast 2024-2033 | Global Insight Services
“Global Insight Services company has recently revised its global market reports, now incorporating the most current data for 2024 along with projections extending up to 2033.
Market Definition
A Laser Warning Receiver (LWR) is a device used to detect and alert a user to the presence of laser beams in a given area. The LWR is typically designed to detect laser beams in the visible, near-infrared, and mid-infrared spectrum. These devices are used in a variety of applications, including military, law enforcement, and industrial settings.
Market Dynamics
The LWR typically consists of a receiver unit, which contains a set of optics and sensors to detect the laser beam. In order to detect the laser beam, the optics focus the beam onto the sensors, which then convert the energy of the beam into an electrical signal. This signal is then sent to the receiver unit, which then alerts the user to the presence of the laser beam.
The LWR is designed to detect laser beams in the visible, near-infrared, and mid-infrared spectrum. This range of detection allows the LWR to detect a wide variety of laser devices, including laser pointers, laser rangefinders, laser illuminators, and laser target designators.
The LWR can be used in a variety of applications, including military, law enforcement, and industrial settings. In the military, the LWR can be used to detect laser designators used by the enemy to mark targets for artillery and air strikes. In law enforcement, the LWR can be used to detect laser pointers used to distract drivers. In industrial settings, the LWR can be used to detect laser beams used to measure distances, as well as to detect laser beams used for welding and cutting.
To Know More@ https://www.globalinsightservices.com/reports/laser-warning-receiver-market/?utm_id=1042
Key Trends
Laser Warning Receiver (LWR) technology has been steadily advancing in recent years, with new developments and improvements being made to ensure that the technology remains reliable and effective. This article will explore some of the key trends in LWR technology and explain their implications for the industry.
One of the key trends in LWR technology is the development of sophisticated algorithms and software that can detect and identify laser threats from a wide range of angles and distances. This is important because it allows LWRs to detect threats that may be invisible to the naked eye. The algorithms and software also allow for the detection of multiple threats at once, giving the user more time to react and take appropriate action.
Another key trend is the use of advanced sensors. These sensors are designed to detect a wide range of laser wavelengths and intensities, allowing them to accurately identify laser threats. Some of the most advanced sensors can even differentiate between different types of laser threats, such as lasers used for targeting or surveillance. This helps to ensure that the user is able to respond to threats in an appropriate manner.
A third trend in LWR technology is the development of automated systems. These systems are designed to automatically detect and identify laser threats, allowing the user to take appropriate action without having to manually scan for threats. This can be especially useful in situations where manual scanning is not feasible due to time constraints.
Finally, the development of more compact and lightweight LWRs is another key trend. This is important because it allows the user to carry the LWR more easily and in more places. It also reduces the size and weight of the LWR, making it easier to install and use.
Key Drivers
The Laser Warning Receiver market is driven by a number of factors, including the need for improved security, the development of new technologies, and the rising demand for advanced defense systems.
Security: Security threats have become increasingly sophisticated and the need for advanced detection systems has grown in response to this. Laser warning receivers act as an early warning system that can detect the presence of laser weapons used by adversaries. This allows for a timely response and increased safety for personnel.
New Technologies: Advances in technology have enabled the development of sophisticated laser warning receivers. These systems are able to detect not only the presence of laser weapons, but also the direction of the source. This allows for a more accurate response and better protection.
Rising Demand: The rising demand for advanced defense systems has created an increase in demand for laser warning receivers. This is due to the need for improved security and the development of new technologies.
Cost: Laser warning receivers are becoming increasingly cost-effective, allowing for more widespread use. This is due to the development of new technologies and the increasing availability of components.
Request Sample@ https://www.globalinsightservices.com/request-sample/GIS26324/?utm_id=1042
Integration: Laser warning receivers are becoming increasingly easy to integrate into existing defense systems. This is due to the development of new technologies and the increasing availability of components.
Reliability: The reliability of laser warning receivers has increased over time, allowing for a more reliable response. This is due to the development of new technologies and the increasing availability of components.
These are the key drivers of the Laser Warning Receiver market. The need for improved security, the development of new technologies, the rising demand for advanced defense systems, the cost-effectiveness of the systems, the ease of integration, and the increased reliability of the systems have all contributed to the growth of the market.
Research Objectives
Estimates and forecast the overall market size for the total market, across product, service type, type, end-user, and region
Detailed information and key takeaways on qualitative and quantitative trends, dynamics, business framework, competitive landscape, and company profiling
Identify factors influencing market growth and challenges, opportunities, drivers and restraints
Identify factors that could limit company participation in identified international markets to help properly calibrate market share expectations and growth rates
Trace and evaluate key development strategies like acquisitions, product launches, mergers, collaborations, business expansions, agreements, partnerships, and R&D activities
Thoroughly analyze smaller market segments strategically, focusing on their potential, individual patterns of growth, and impact on the overall market
To thoroughly outline the competitive landscape within the market, including an assessment of business and corporate strategies, aimed at monitoring and dissecting competitive advancements.
Identify the primary market participants, based on their business objectives, regional footprint, product offerings, and strategic initiatives
Request Customization@ https://www.globalinsightservices.com/request-customization/GIS26324/?utm_id=1042
Market Segmentation
The market can be segmented by type, application, and region. By type, the market can be divided into Beam Riding Detection, Laser Range Finder, and Laser Target Designator. By Application, the market can be divided into Ground Force, Maritime Force, and Air Force. By region, the market is divided into North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and the Rest of the World.
Key Players
The market includes players such as ASELSAN A.S. (Turkey), BAE Systems (United Kingdom), Elbit Systems Ltd. (Israel), Ferranti Technologies (United Kingdom), HENSOLDT AG (Germany), Leonardo S.p.A. (Italy), METRODAT s.r.o.(Czech Republic), PCO S.A. (Poland), Saab AB (Sweden), and Thales Group (France).
Buy your copy here@ https://www.globalinsightservices.com/checkout/single_user/GIS26324/?utm_id=1042
Research Scope
Scope – Highlights, Trends, Insights. Attractiveness, Forecast
Market Sizing – Product Type, End User, Offering Type, Technology, Region, Country, Others
Market Dynamics – Market Segmentation, Demand and Supply, Bargaining Power of Buyers and Sellers, Drivers, Restraints, Opportunities, Threat Analysis, Impact Analysis, Porters 5 Forces, Ansoff Analysis, Supply Chain
Business Framework – Case Studies, Regulatory Landscape, Pricing, Policies and Regulations, New Product Launches. M&As, Recent Developments
Competitive Landscape – Market Share Analysis, Market Leaders, Emerging Players, Vendor Benchmarking, Developmental Strategy Benchmarking, PESTLE Analysis, Value Chain Analysis
Company Profiles – Overview, Business Segments, Business Performance, Product Offering, Key Developmental Strategies, SWOT Analysis.
With Global Insight Services, you receive:
10-year forecast to help you make strategic decisions
In-depth segmentation which can be customized as per your requirements
Free consultation with lead analyst of the report
Infographic excel data pack, easy to analyze big data
Robust and transparent research methodology
Unmatched data quality and after sales service
Contact Us:
Global Insight Services LLC 16192, Coastal Highway, Lewes DE 19958 E-mail: [email protected] Phone: +1-833-761-1700 Website: https://www.globalinsightservices.com/
About Global Insight Services:
Global Insight Services (GIS) is a leading multi-industry market research firm headquartered in Delaware, US. We are committed to providing our clients with highest quality data, analysis, and tools to meet all their market research needs. With GIS, you can be assured of the quality of the deliverables, robust & transparent research methodology, and superior service.
0 notes
Text

Underground Bunker Construction Market size to expand at a CAGR of 9.85% reaching a value of USD 36.66 billion by 2030. The Global Underground Bunker Construction Market is propelled by the growing global uncertainties, geopolitical conflicts, and a heightened emphasis on emergency preparedness. Governments, companies, and individuals are increasingly building or upgrading bunkers to safeguard against threats like natural disasters and man-made crises. Technological advances in construction materials, ventilation, and sustainable energy are expected to drive the future of this market. Additionally, smart technologies such as sophisticated security systems and advanced communication networks are becoming more common in bunker design. With growing concerns about climate change, there's a shift towards eco-friendly and energy-efficient shelter designs. Although the market is expanding worldwide, it faces challenges such as regulatory compliance, cost management, and public awareness. In summary, the market for underground bunkers and shelters is set to grow, with a focus on innovation, sustainability, and comprehensive emergency preparedness.
Impact of Escalating Geopolitical Tensions on Global Underground Bunker Construction Market
Escalating geopolitical tensions are presenting significant challenges while also driving demand in the Global Underground Bunker Construction Market. With increasing concerns about national security, nuclear threats, and societal instability, both governments and private entities are investing in underground bunkers as a means of protection. These robust structures are designed to withstand a range of disasters, offering secure shelter and storage for those seeking safety. The demand comes from public and private sectors alike, with individuals, corporations, and governments seeking to mitigate risks from conflicts and natural disasters. For instance, Ukraine's Kryvyi Rih, where workers at a steel plant are shifting from mining equipment production to building metal bunkers for front-line troops. This repurposing, prompted by Russia's ongoing invasion, highlights the urgent need for safety and preparedness in conflict zones. The bunkers, constructed from nearly two tons of steel and designed to be buried underground, can withstand heavy artillery and provide accommodations for up to six soldiers. With features like wooden beds, storage space, and stoves, they serve as practical shelters. Metinvest's initiative uses Soviet-era designs, reinforcing the influence of geopolitical conflicts on the bunker market. This shift towards bunker construction indicates a broader trend toward security and resilience, driven by growing global instability.
Sample Request @ https://www.blueweaveconsulting.com/report/underground-bunker-construction-market/report-sample
0 notes
Text
Military Ground Vehicle Propulsion System | Key Market Insights

As per Triton Market Research, the Global Military Ground Vehicle Propulsion System Market report is segmented by Vehicle Type (Fighting Vehicles, Combat Tanks, Self-Propelled Artillery, Small UGV Robots), Technology (Conventional Propulsion System, Electric Propulsion System, Hybrid Propulsion System, Plug-In Hybrid Electric Propulsion System), Application (Mining, Explosive Ordnance Disposal (EOD), Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance (ISR), Logistics and Support, Combat Support, Other Applications), and Regional Outlook (Asia-Pacific, Europe, North America, Middle East and Africa, Latin America).
The report highlights the Market Summary, Industry Outlook, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Market Attractiveness Index, Regulatory Framework, Key Market Strategies, Market Drivers, Challenges, Opportunities, Competitive Landscape, Research Methodology and scope, Global Market Size, Forecasts & Analysis (2024-2032).
According to Triton’s research report, the global market for military ground vehicle propulsion system is expected to progress with a CAGR of 5.25% in revenue over the forecasting period 2024-2032.
Military ground vehicle propulsion systems are important components that generate the required power to propel tactical and armored military vehicles. These systems impact the agility, mobility, and overall performance of military ground vehicles in harsh operational surroundings.
Amidst rising geopolitical tensions, an increasing need for modern warfare techniques and technological advancements in electric and hybrid propulsion systems drive the growth of the studied market. Moreover, improving fuel efficiency to reduce the environmental impact and integrating AI to enhance the autonomous operations of military ground vehicles together influence the market progress.
However, the acquisition and development costs regarding advanced propulsion technologies obstruct the market growth. The biggest obstacle for manufacturers is the need for standardization across versatile military platforms, stringent regulations, and export limitations on defense technologies also hampers the expansion of the military ground vehicle propulsion system market.
In spite of these challenges, there is an increasing demand for electric and hybrid propulsion systems, which creates opportunities for the market players. As the military forces prioritize unmanned ground vehicles, there is a need to develop propulsion systems with highly advanced automation.
The major competitive companies in the studied market are Bae Systems, L3harris Technologies Inc, Cummins Inc, Caterpillar Inc, Oshkosh Corporation, Rheinmetall AG, Epsilor-Electric Fuel Ltd, General Dynamics, Northrop Grumman Corporation, Daimler AG, Israel Aerospace Industries Ltd, Lockheed Martin Corporation, General Motors Company, and Qinetiq Group.
Additionally, the need for developing strategic partnerships and improving defense forces provide new avenues for emerging market players to diversify their products. Similarly, tapping into regional markets can be another competitive edge for the stakeholders.
#MILITARY GROUND VEHICLE#PROPULSION SYSTEM#Aerospace & Defense#triton market research#market research reports
0 notes
Text
KNDS France Proposes Assembly of Caesar Self-propelled Howitzer in Malaysia
KNDS France, the main provider of artillery systems for Malaysia and a strategic industrial partner for the Malaysian defence industry. The achievement of industrial partnership initiated in 2018 with the assembly and delivery of 18 units of 105mm LG 1 MKIII 105 mm towed howitzers to the Malaysian Army reflects their mutual commitment to enhancing the nation's defense capabilities but also signifies the excellence of local skills in the defense industry. In a pro-active action, both companies will also address selected export markets for the 105mm LG1 MKIII, creating additional value to the Malaysian eco-system. KNDS France, together with Malaysian company Advanced Defense Systems (ADS), commit to expand their partnership at an upper level in addressing the 155mm CAESAR self-propelled howitzer to be assembled and integrated in the industrial facilities of ADSSB in Segamat, State of Johor. The installation of the CAESAR not only provides additional strength to the Malaysian Army but also contributes to the local economy by creating job opportunities and enhancing expertise in the field of armaments. KNDS and ADSSB are committed to continuing its efforts to advance Malaysia's defense industry and support national security initiatives.
KNDS France, the main provider of artillery systems for Malaysia and a strategic industrial partner for the Malaysian defence industry. The achievement of industrial partnership initiated in 2018 with the assembly and delivery of 18 units of 105mm LG 1 MKIII 105 mm towed howitzers to the Malaysian Army reflects their mutual commitment to enhancing the nation’s defense capabilities but also…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
1. Trying to separate Musk from his companies is a fool's errand. Starship wouldn't be being built if not for Musk. It fills no extant niche in the space launch market.
2. Starship will likely never go to Mars. Musk is a marketing expert, so he says it will. But getting the entire ship to Mars requires at least a few refueling flights - probably at least 8. That's insane. Falcon Heavy and SLS can throw at bare minimum 10 and 18 tons to Mars in a single launch respectively. That's while weighing 30 and 50 as much as a single starship-super heavy.
3. Starship was not ready for flight. Sure, something might go wrong and the flight might not make it to orbit. But losing 8 of 33 engines during ascent indicates something was wrong. Failing to separate stages indicates something was wrong. Having the flight termination system fail to destroy the vehicle when activated is a huge problem. Utterly destroying your launchpad is as well. SpaceX knows how to do all of these things. Musk pushed for the launch either because he didn't care or because he needed something to distract from all of his other bad press.
4. The launch pad thing. There are five other historical or current launch vehicles in this class flown by two different countries, four of which were successful programs - humanity knows how to build launch pads to handle them. But pads 39A and 39B, used to launch Saturn V, Space Shuttle, and SLS, were expensive in both time and money. I can only imagine the pads used for N-1 and Energia were similarly expensive.
5. What is starship actually for, if not Mars? Starlink. V1.5 satellites launched on Falcon weigh about 300kg for 50-55 per Launch. V2 meant for starship? 1250kg. They've launched 21 on a Falcon 9, but they could probably fit over 120 on starship assuming they have the payload volume. Why is this important? So they can get as many satellites in orbit before mega constellations are (rightfully) outlawed.
6. I'm not done with the flight termination system thing. This is what we as a society have agreed on is the thing keeping your space rocket from becoming an artillery shell when things go wrong. If your rocket goes off course, it's what keeps debris from landing outside of the corridor cleared for the launch. And Musk's rocket fell for nearly a full minute after the FTS fired before it lost structural integrity and broke up. That's not okay. If you need proof that SpaceX knows how to FTS, go watch the Crew Dragon in flight abort test.
P.S. Euphemisms like "Rapid Unplanned Disassembly" have been in the space lexicon for much longer than Musk. It was popularized in modern times by Kerbal Space Program, and were mostly used as a tongue in cheek way to acknowledge you done fucked up. I despise Musk fans using it to minimize SpaceX's responsibility for their failures.

this is maybe the funniest thing to happen, ever. thank you spacex for once again pushing the boundaries of trashy scifi
27K notes
·
View notes
Text
Key Players in the Turkey Defense Market: Domestic Manufacturers and International Partnerships
In the Turkey defense market, there are both domestic manufacturers and international partnerships that play significant roles in shaping the industry.
Buy the full report to gain more information about the Turkey defense market forecast, download a free report sample
Here are key players in both categories:
Domestic Manufacturers:
ASELSAN: ASELSAN is Turkey's largest defense electronics company, specializing in the development, production, and integration of advanced military systems and technologies. ASELSAN manufactures a wide range of products, including communication systems, radar systems, electronic warfare systems, electro-optical systems, and weapon systems.
TAI (Turkish Aerospace Industries): TAI is Turkey's leading aerospace and defense company, involved in the design, development, production, and support of military and commercial aerospace platforms and systems. TAI manufactures aircraft, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), satellites, and aerospace components.
FNSS Defense Systems: FNSS Defense Systems is a joint venture between Turkey's Nurol Holding and BAE Systems, specializing in the design, development, and production of armored combat vehicles and weapon systems. FNSS manufactures a range of armored vehicles, including wheeled and tracked armored personnel carriers and infantry fighting vehicles.
BMC (BMC Otomotiv Sanayi ve Ticaret A.Ş.): BMC is a Turkish automotive and defense company, involved in the production of tactical wheeled vehicles, including armored personnel carriers, tactical trucks, and military land vehicles. BMC manufactures vehicles for military and security forces, as well as commercial markets.
Roketsan: Roketsan is Turkey's leading missile and rocket manufacturer, specializing in the design, development, and production of guided missiles, rockets, and munitions for air, land, and sea-based platforms. Roketsan's product portfolio includes anti-tank missiles, air defense systems, artillery rockets, and precision-guided munitions.
International Partnerships:
Lockheed Martin: Lockheed Martin is a major U.S. defense contractor that collaborates with Turkish defense companies on various defense projects, including the production of F-16 fighter jets and the development of missile defense systems.
Airbus: Airbus collaborates with Turkish Aerospace Industries (TAI) on the production of Airbus A400M military transport aircraft. TAI manufactures fuselage sections, landing gear components, and other structural parts for the A400M aircraft.
MBDA: MBDA is a European missile manufacturer that collaborates with Turkish defense companies on missile defense projects. MBDA has been involved in joint development programs with Turkey's Roketsan, including the SOM (Standoff Missile) cruise missile program.
Leonardo: Leonardo, an Italian aerospace and defense company, collaborates with Turkish defense companies on various defense projects, including the production of helicopters and unmanned aerial systems (UAS).
Thales: Thales, a French multinational company, collaborates with Turkish defense companies on the development and production of defense electronics, communication systems, and naval systems.
These are just a few examples of key players in the Turkey defense market, both domestic manufacturers and international partners. Collaborations and partnerships between domestic and international companies contribute to the development, production, and export of advanced defense systems and technologies, enhancing Turkey's defense capabilities and promoting defense industry cooperation.
0 notes
Text
Bomb Jammer, Global Market Size Forecast, Top 10 Players Rank and Market Share
Bomb Jammer Market Summary
According to the new market research report “Global Bomb Jammer Market Report 2023-2029”, published by QYResearch, the global Bomb Jammer market size is projected to reach USD 162.9 million by 2029, at a CAGR of 4.6% during the forecast period.

Figure. Global Bomb Jammer Market Size (US$ Million), 2018-2029

Based on or includes research from QYResearch: Global Bomb Jammer Market Report 2023-2029.
Market Drivers:
Driver 1: With the constant development and utilization of IEDs by terrorists and rebels across the world, counter IED Jammer solutions and products are indeed in demand.
Driver 2: Rapid development of jamming technology, such as Active Jamming, Reactive Jamming (RJ), Hybrid Jamming etc.
Driver 3: Army and government pay more attention to defend soldiers and VIP convoys from the dangers of roadside bombs. Also the restrictions on military market access have been greatly relaxed in some countries, and more and more enterprises have obtained the qualification for scientific research and production of military equipment.
Restraint:
Restraint 1: More private companies are restricted by the threshold of military market access and are unable to enter the field of national defense science and industry.
Restraint 2: Most civilian scientific and technological institutions or enterprises dare not undertake military R & D tasks rashly, which objectively limits their enthusiasm to enter the military market.
Restraint 3: High technical barriers to products. Also the vast majority of downstream customers are military and government.
Opportunity:
Improvised Explosive Devices (IEDs) continue to be the weapon of choice for adversary networks and this phenomenon is likely to continue for decades, either with the IED as the only threat or combined with others within a hybrid complex scenario. IEDs are fabricated in an improvised manner and designed to destroy property or incapacitate people and vehicles. The design of IEDs and the trigger systems used range from the ‘simple’ to the technologically developed. The production costs in general are low, and the components used include not only military ammunition like mines or artillery shells, but also commercially available substances and that can be combined to produce the so-called home-made explosives. Although already used for many decades in military and civil conflicts worldwide, the combination of its ease of use with its mediatic impact, will likely make IEDs an enduring threat to remain. The cumulative campaign effect of the use of IED remains capable of producing an asymmetric advantage for terrorists, insurgent/resistance movements and rogue elements, even against technologically superior conventional forces.
With the threat of global insecurity still exists, RCIEDs continue to be the weapon of choice for adversaries, the need of Counter-IED equipment (including Bomb Jammer) will still increase.
Many countries have been working on Counter-IED, fostering the capability development in identified shortfalls, as well as carefully considering its adequate integration into the Counter-IED overarching framework, covering the full range of enabler capabilities to achieve the desired end state: the mitigation of IEDs in the battlefield.
Also many players specializing in EW systems, Their comprehensive approach for remotely preventing detonation of IED, is based on full coverage Counter IED (C-IED) jamming systems in multiple configurations, suited to the ever-changing operational environment & needs.
It is expected that the jamming technology will continue to upgrade in the future
Be it for military or civilian reasons, defending soldiers and VIP convoys from the dangers of roadside bombs, or Improvised Explosive Devices (IEDs) has significantly become a top-priority and an operational challenge. As a result, with the constant development and utilization of IEDs by terrorists and rebels across the world, counter IED Jammer Solutions are indeed in demand by friendly forces both military and paramilitary. Many manufacturers have provided a valuable range of IED jammers, supplied in exclusively tailorized vehicles, Portable Briefcase, Manpack and in Static variations as well.
The Bomb Jammer solutions are tailored for to fit different operational scenarios and mission types.
Figure. Bomb Jammer, Global Market Size, The Top Five Players Hold 65% of Overall Market

Based on or includes research from QYResearch: Global Bomb Jammer Market Report 2023-2029.
This report profiles key players of Bomb Jammer such as Dynamite Global Strategies, SESP, HSS Development
In 2022, the global top five Bomb Jammer players account for 65% of market share in terms of revenue. Above figure shows the key players ranked by revenue in Bomb Jammer.
Figure. Bomb Jammer, Global Market Size, Split by Product Segment


Based on or includes research from QYResearch: Global Bomb Jammer Market Report 2023-2029.
In terms of product type, Stationary Bomb Jammer is the largest segment, hold a share of 56%.
Figure. Bomb Jammer, Global Market Size, Split by Application Segment


Based on or includes research from QYResearch: Global Bomb Jammer Market Report 2023-2029.
In terms of product application, Government is the largest application, hold a share of 63%.
Figure. Bomb Jammer, Global Market Size, Split by Region


Based on or includes research from QYResearch: Global Bomb Jammer Market Report 2023-2029.
About The Authors
Wangzhuang - Lead Author
Email: [email protected]
John is a technology & market senior analyst specializing in semiconductor devices, materials, and equipment. Wang has 3 years’ experience in semiconductor and focuses on Chemicals, consumer goods, food and beverages, machinery and equipment, software and business services, etc. He is engaged in the development of technology and market reports and is also involved in custom projects.
About QYResearch
QYResearch founded in California, USA in 2007.It is a leading global market research and consulting company. With over 16 years’ experience and professional research team in various cities over the world QY Research focuses on management consulting, database and seminar services, IPO consulting, industry chain research and customized research to help our clients in providing non-linear revenue model and make them successful. We are globally recognized for our expansive portfolio of services, good corporate citizenship, and our strong commitment to sustainability. Up to now, we have cooperated with more than 60,000 clients across five continents. Let’s work closely with you and build a bold and better future.
QYResearch is a world-renowned large-scale consulting company. The industry covers various high-tech industry chain market segments, spanning the semiconductor industry chain (semiconductor equipment and parts, semiconductor materials, ICs, Foundry, packaging and testing, discrete devices, sensors, optoelectronic devices), photovoltaic industry chain (equipment, cells, modules, auxiliary material brackets, inverters, power station terminals), new energy automobile industry chain (batteries and materials, auto parts, batteries, motors, electronic control, automotive semiconductors, etc.), communication industry chain (communication system equipment, terminal equipment, electronic components, RF front-end, optical modules, 4G/5G/6G, broadband, IoT, digital economy, AI), advanced materials industry Chain (metal materials, polymer materials, ceramic materials, nano materials, etc.), machinery manufacturing industry chain (CNC machine tools, construction machinery, electrical machinery, 3C automation, industrial robots, lasers, industrial control, drones), food, beverages and pharmaceuticals, medical equipment, agriculture, etc.
0 notes
Text
Anti-Drone Companies - RTX (US) and Lockheed Martin Corporation (US) are the Key Players
The global anti-drone market was valued at USD 1.2 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach USD 5.2 billion by 2028; it is expected to register a CAGR of 26.6% during the forecast period. Increasing government spending on counter-drone technologies and rising incidence of critical infrastructure security breaches by unauthorized drones are attributed to the ever-increasing demand for anti-drone systems.
Major Anti-Drone companies include:
RTX (US),
Lockheed Martin Corporation (US),
Leonardo S.p.A. (Italy),
Thales (France),
IAI (Israel),
Rafael Advanced Defense Systems Ltd. (Israel),
Blighter Surveillance Systems Limited (UK),
DroneShield Ltd (Australia),
Dedrone (US),
Accipiter Radar (Canada),
Boeing (US),
Moog Inc. (US),
HENSOLDT (Germany),
ApolloShield (US),
Saab (Sweden),
Northrop Grumman (US),
MBDA (Germany),
ASELSAN A.S. (Turkey),
DeTect, Inc. (US),
Battelle Memorial Institute (US), ART (Spain), Drone Defence (UK), Drone Major (England), SkySafe (US), BlueHalo (US), Fortem Technologies (US), D-Fend Solutions AD Ltd. (Israel), and CERBAIR (France) are some of the key players in the anti-drone market.
RTX
The Raytheon Missiles & Defense segment functions as a primary contractor or key subcontractor for multiple projects within the US Department of Defense, encompassing branches, such as the US Navy, US Army, Missile Defense Agency, US Air Force, and various international governments. Raytheon Australia, Speed Queen (US), Blue Canyon Technologies (US), Pratt & Whitney (US), and Microtecnica (Brazil) are its subsidiaries. It has a presence in over 30 countries, including the US, the UK, Australia, Saudi Arabia, and the UAE.
Lockheed Martin Corporation
Lockheed Martin Corporation operates as a global security and aerospace company engaged in researching, designing, developing, manufacturing, and integrating technologies, systems, products, and services. The company operates through the following business segments: Aeronautics, Missiles and Fire Control (MFC), Rotary and Mission Systems (RMS), and Space.
This segment is dedicated to activities, such as air and missile defense systems, tactical missiles, air-to-ground precision strike weapons, logistics, fire control systems, mission operations support, engineering support, integration services, manned and unmanned ground vehicles, and energy management solutions.
Leonardo S.p.A.
Leonardo S.p.A. operates in the aerospace, defense, and security sectors. The company operates through six reportable segments: Helicopters, Defence Electronics and Security, Aircraft, Aerostructures, Space and Other Activities. The Helicopters segment designs commercial and military rotorcrafts. The Helicopters segment manufactures complete tactical airlifters, combat aircraft, and unmanned air vehicles for civil and military applications. Under this segment, it specializes in designing rotorcrafts for commercial and military purposes. The Defence, Electronics & Security segment is engaged in information management, sensors, and systems integration businesses and delivers systems for critical missions, military sustainment requirements, and homeland security. It also provides combat support systems and services; unmanned, automation and electronic systems; missile systems; sensors, radars, and communications for airborne, land, naval, and underwater applications; artillery, power, and propulsion systems; weapon systems; torpedoes; and armored vehicles.
Leonardo DRS, a wholly owned subsidiary of Leonardo S.p.A., offers counter UAS systems and solutions through the Defence, Electronics & Security segment. This segment is involved in activities, such as information management, sensor technology, and system integration. It also delivers systems crucial for critical missions, military sustainability, and homeland security. It produces missile systems, torpedoes, naval artilleries, and armored vehicles.
Thales
Thales is a holding company that manufactures and sells electronic equipment and systems for the aeronautics, naval, and defense sectors. The company was formed in 1968 and is headquartered in Paris, France. Compagnie Francaise Thomson-Houston (CFTH) was founded in 1893, and in 1919, its name was changed to Compagnie General de Telegraphie Sansfil (CSF). Furthermore, the merger between CSF and Thomson-Brandt led to the formation of Thomson-CSF in 1968, and in 2000, the company changed its name to Thales.
Thales is a global technology leader in the aerospace, transport, aerospace & defense, digital identity, and security markets. The company produces, promotes, and distributes electronic equipment and systems within the aeronautics, naval, and defense sectors. It operates through the following segments: Defense and Security, Digital Identity and Security, Aerospace, and Others.
0 notes
Text
Why is the center not working anymore?

About four or five years ago, Zhongtai suddenly became popular in the corporate world. At that time, people felt that this was an advanced system, which was tall and capable of concentrating efforts to accomplish big things.
Only two years ago, due to some chance, I saw some scenes, and my mind changed.
Scene 1 was at a meeting. Students HE Tuber from the business line stood up and angrily accused the "backpackers" sent by the R&D department. They were "in Cao camp and in Han Dynasty" and did not understand the needs of the business at all.
Scenario 2 was also a meeting. The business boss spoke eloquently and even said he was excited. However, the boss responsible for growth also sat at the conference table, and he remained unmoved for almost the entire process.
At that time, I felt that China and Taiwan might not work very well.
Sure enough, starting in 2023, those companies that took the lead in building the middle platform suddenly began to dismantle the middle platform. Now, I am afraid that some companies that have learned to build a middle platform are still in a mess, wondering whether they should continue to do so.
Let me tell you, in fact, everyone did not understand the meaning of Zhongtai from the beginning. This organizational form is not originally designed to improve efficiency. It is the power structure that enterprises need at a special stage.
First of all, the middle platform cannot reduce costs and increase efficiency for enterprises.
Although it is theoretically possible, in ecological enterprises, merging the same functional departments in different business lines with similar items does seem to avoid reinventing the wheel. For example, the same group of R&D personnel can perform development work for business lines at different stages, or departments that spend money such as growth and marketing public relations can concentrate their budgets and put them in a unified way to obtain lower prices.
But for companies in a fully competitive market, the efficiency shortcomings of the middle office are obvious, because it will cause the decision-making chain to be not only too long, but also complicated. Ultimately, people who hear the sound of artillery fire may not be able to call for fire support, or artillery fire cannot be deployed in time at critical moments of competition.
To give a simple example, in many companies, the growth department often gets a very large budget. But when the growth department is taken out and becomes a middle-office organization, one department will actually be responsible for the growth of multiple business lines. At this time, the first task of the growth department becomes to share the cake.
How much money should be spent on each business line and how to formulate a growth strategy are very technical tasks for the boss of the growth department.
Of course, the business boss hopes to give him as much support as possible. In fact, for the business, the most efficient way is to integrate all functions into one reporting line. Everyone in this chain is doing When making decisions, only one factor needs to be considered, which is whether it is beneficial to the business line. But if some functions are withdrawn, another situation will arise - an increase in internal transaction costs, because everyone no longer sits on the same bench.
So the business boss will go and communicate with the growth boss. But the reality is that there is no reporting relationship between them, and there is no question of who listens to whom. Everything has to be discussed, or decided by higher-level people on the reporting line.
Over the years, everyone has always discussed what good management is. In the final analysis, management that is in line with human nature is good management. And what is human nature? Individualism is part of human nature. Why so many companies have trust and cooperation as their values? In essence, it’s because in a huge organization, trust and cooperation are very difficult. You need to shout all the time and every month to penetrate into the blood of the organization.
Personally, I have doubts about many fashionable concepts and tools, including middle-office organizations and OKR. The concept of OKR sounds very good. Through top-down decomposition, a company can all aim at the goals of the top decision-makers, forming a pyramid structure in which strategy and execution are aligned.
If executed well, OKR can theoretically ensure a company's strategic focus and create synergy. However, realizing this scenario requires a prerequisite, that is, the top decision-maker will expose his true inner goals. This alone will probably stump 90% of Chinese bosses.
Because there is a deep shadow of Wang Yangming in Chinese business culture. Wang Yangming talked about the inner sage and the outer king, which means that the inner and outer parts of a person do not have to be unified. Of course, many bosses are actually the inner king and the outer sage. So which one should show the king's side or the saint's side? you guess.
The same goes for the middle office. When you think it requires execution efficiency from the organization, the result is not always the case because it puts people in different positions. But if the top level wants decision-making efficiency from the organization, then the middle office is a good choice.
Because the middle platform can help power achieve penetration.
If you pay a little more attention, you will find that the establishment of middle-level organizations often coincides with the transfer of power in the company.
Take JD.com for example. In 2018, Liu Qiangdong phased out of the business. He needed to give more authority to the management of the three major business lines at the time.
Especially for Jingdong Retail Group, Xu Lei was picked to become the CEO of this business unit that accounted for 95% of the group's revenue. As a professional manager, it should be said that there is a lot of pressure to become the successor of a company founder. In an interview a few years ago, Xu Lei told me that in the five months after he was promoted to the rotating CEO of JD.com, he did not issue any policy guidelines or administrative orders. "Although I know all the problems," he spent more time observing.
In the development of a company, it needs to have a consensus, including a consensus on values, a consensus on strategy, and a consensus on power. In layman's terms, it's who has the final say. The founder does not need to worry about this, because he is the natural consensus of the organization, "He is the boss."
But when professional managers take over the authority, they need to establish a system within the scope of authorization to allow the organization to reach a consensus. In a nutshell: founders have property rights, maximum voting rights, and Charisma-type reputation, and they can fight wherever they want; while professional managers only have authorization and rely more on the system.
Also in this year, JD.com began to establish a middle office. The supply chain units in technology and business were decoupled and became a middle office organization. The front office organization was a business scenario. The two parties were constantly recoupled and worked together to move forward. Since it is coupled, some external force is needed as support.
Of course, JD.com’s middle-end design is still relatively personalized. Generally speaking, the middle-end design of most companies is the technical middle-end and organizational middle-end, that is, the middle-end design of finance, human resources and R&D departments. The reason for this is also very simple. Whether it is a company or a business unit, the three core elements are always people, money and materials. People and money are easy to understand, while things refer to the means of production. For Internet companies, their core production material is software, and the R&D department ensures the implementation and iteration of this production material.
Therefore, when the finance, human resources and R&D departments are centralized, the business units are actually more focused on execution. If he needs to expand his business, he needs to seek budget, headcount and R&D support from the middle office. In addition to good popularity, what business bosses need most is support from the CEO.
In other words, the middle office takes advantage of the egoism in human nature, which will lead to an increase in internal transaction costs and an increase in friction within the organization. This friction will of course cause some energy dissipation, but it will also cause the entire The organization moves closer to the center, and decision-making power is centralized upward.
This is why, when Liu Qiangdong returned to the business, JD.com began to dismantle Zhongtai again. Because the founder is the consensus of a company, he no longer has to use bureaucracy to pay more friction costs to manage the river of power within the company.
0 notes