#AWS Azure pros and cons
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Compare AWS and Azure in this comprehensive guide to determine which cloud platform best suits your business needs. Explore key features, pricing, and performance.
#AWS vs Azure comparison#cloud computing platforms#best cloud services 2024#AWS Azure pros and cons#cloud platform battle
0 notes
Text










UOC - PAC 3: Kevin Boix - Plataformas de Distribución de Contenido
Reproducción
Vimeo, tiene un reproductor de vídeo bastante simple, creado en HTML5, donde podemos ver todas las features básicas que cumplen con las necesidades del usuario, controlar el volumen, pause and play, añadir subtítulos, configuración de calidad, maximizar y minimizar, todas estas funcionabilidades están en la parte inferior, pero en la parte superior derecha, tenemos el sharing, donde permite dar control al usuario: compartir, me gusta, guardar en listas personales.
2. Plataformas
Los navegadores compatibles son los siguientes:
Chrome 60 en adelante (tiene actualizaciones automáticas)
Firefox 60 en adelante (tiene actualizaciones automáticas)
Microsoft Edge 79 en adelante (tiene actualizaciones automáticas)
Safari 11+
Sistemas operativos:
Se garantiza la funcionabilidad al 100% en los siguientes:
Windows 10 en adelante
Apple desde macOs11 (BigSur) en adelante con Safari 16 en adelante.
Dispositivos móviles y tabletas:
Android 8.0 (Oreo) en adelante
Navegador Safari con iOS12 – iPad12 en adelante
En cuanto a la aplicación móvil de vimeo:
Andorid(Nougat) versión 7.0 o superior
iOS, versión 14 o superior
*La aplicación vimeo para macOS requiere macOS12.12 (Sierra) o superior
La diferencia es que en Iphone, si el dispositivo es compatible con HDR10 y un sistema de reproducción que admita H.265 (HEVC), podrás reproducir HDR y Dolby Vision.
3. Servicios asociados
También, Vimeo proporciona una serie de herramientas de gestión empresarial, como por ejemplo asesoría para mejorar las métricas de tu contenido, soluciones de marketing y también un plan de hosting de servidores, como hace Amazon con AWS o Microsoft con Azure, sin olvidar, que también ofrece la posibilidad de realizar un pan o análisis de datos con todas las métricas para saber el engaging de tu contenido, quién y cuantas veces lo visualizan y para finalizar tienes la posibilidad de crear webinars o tener un sistema para webinars si eliges pagar la versión Premium de Vimeo para empresas
Siempre con la premisa de acelerar tu compañía hacia el éxito, captación de clientes aumentando la interacción y cualquier tipo de optimización, en pocas palabras, aprovechar todo el potencial de tu contenido.
4. Transmisión
Si prefieres retransmitir en vivo, Vimeo crea una transcodificación de tu video en la nube y RTMP para perder la mínima calidad posible y tengas flexibilidad para subir un contenido algo pesado o de mucha calidad y que el usuario final pueda reproducirlo sin problema con su ancho de banda preferido.
Para la transmisión hace uso de los siguientes protocolos:
HTTP (HYPERTEXT TRANSFER PROTOCOL)
HLS (HTTP LIVE STREAMING)
RTMP (REAL-TIME MESSAGING PROTOCOL)
HDS (HTTP DYNAMIC STREAMING)
Y los protocolos base, para la reproducción de vídeo, envío de paquetes y el transporte, son los siguientes:
Capa de comunicación o enlace: PPP, DSL, Wi-Fi, etc.
Capa de Internet: IPv4, IPv6, etc.
Capa de transporte: TCP, UDP, etc.
Capa de aplicación: HTTP, IMAP, FTP, etc
5. Almacenamiento
En este caso, Vimeo está limitado a una cuota semanal y un almacenamiento total, con los planes basic, plus y pro, te permiten más cantidad de almacenamiento o menos, esa cuota se restablece cada 7 días:
La cuota de carga semanal se concede de la siguiente manera:
Básico: 500MB/semana, limitado a 10 cargas cada 24 horas
Más: 5 GB/semana
Pro: 20 GB/semana
El almacenamiento total se concede de la siguiente manera:
Básico: 5GB
Pro Ilimitado: 3TB
Empresas: 5TB
Premium 7TB
6. Codificación
Códecs de video: H.264, Apple ProRes 422 (HQ) o H.265 (HEVC)
Velocidad de fotogramas: mantén la velocidad de fotogramas nativa y elige una velocidad de fotogramas constante
Tasa de bits: elige variable si es posible y sigue los rangos basados en la definición de tu video
Resolución: proporción de aspecto de píxeles de 1:1
Colores primarios y coeficientes de la matriz: se aceptan todos, pero recomendamos BT.2020 (Rec. 2020) o BT.709 (Rec. 709)
Características de transferencia del color: para los videos HDR, solo admitimos la función de transferencia PQ (SMPTE 284) o HLG
Profundidad de bits: 10 o superior
Tipo de escaneo: progresivo, y se recomienda desentrelazar videos
Códec de audio: AAC-LC (AAC de baja complejidad)
Velocidad de transmisión de datos: 320 kb/s
Frecuencia de muestreo: 48 kHz
7. Estadísticas
Vimeo tiene integrada (en su plan de pago) una herramienta de analíticas para conocer mejor a tu público proporciona las siguientes estadísticas:
Ubicación, edad, rango del público objetivo
Redes sociales o plataformas donde han visualizado el contenido
Monitorización de los KPY de tus vídeos, para conocer el rendimiento real de tus vídeos, la duración media de tus vídeos y cuando dejan de ser interesantes para tus usuarios.
8. Modelo de negocio
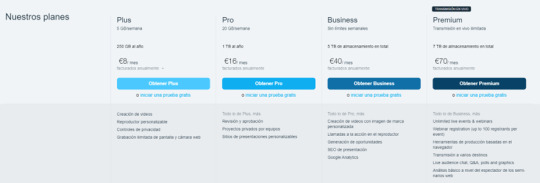
Vimeo principalmente gana a través de las subscripciones, hay cuatro opciones de membresía:
Vimeo plus
Vimeo PRO
Vimeo Business
Vimeo Premium
9. Formatos de publicidad
Vimeo es ad-free para la mayoría de los usuarios, los miembros básicos podrán visualizar publicidad en sus vídeos como sucede en otras plataformas como youtube, twitch, etc...
Si tienes un plan de pago entonces no te aparecerá publicidad.
En cuanto a la monetización de los vídeos para los creadores de contenido, Vimeo te permite (con una tarifa) crear un sitio exclusivo para tu audiencia y seguidores, donde podrás convertir tus vídeos en productos de suscripción y membresía, cursos en línea, webinars y todos estos servicios estarán monetizados para que ambos generen liquidez.
10. Investiga y define nuevos formatos
Vimeo te permite definir y crear una estrategia de marketing para que tu contenido sea lo más impactante y relevante posible.
Retención y captación de clientes con más engaging
Estudios para conocer tu mercado y tus clientes
Personalizar tus mensajes y ofertas
Te permite conocer y contactar con tu público
Redes sociales para contribuir a mejorar tu imagen y conocer tus clientes
Asistencia y asesoramiento para ser lo más competitivo posible
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Cloud Migration Services vs. DIY Migration: Which Is Right for Your Business?
In today's data-driven world, businesses are rapidly shifting to the cloud to improve agility, scalability, and performance. As organizations of all sizes pursue digital transformation, the debate between leveraging cloud migration services and taking the DIY (do-it-yourself) route has intensified. Both options come with distinct benefits and challenges, making it essential for business leaders to understand which path aligns best with their goals, budget, and in-house capabilities.
This comprehensive guide breaks down the pros and cons of cloud migration services versus DIY migration, helping you make an informed decision tailored to your business needs.

What Is Cloud Migration?
Cloud migration refers to the process of moving digital assets—such as applications, data, and IT infrastructure—from on-premises servers to a cloud environment. The cloud offers significant advantages such as reduced operational costs, improved accessibility, enhanced security, and seamless scalability.
However, the complexity of migration depends on factors such as existing infrastructure, data volume, compliance requirements, and integration with other systems. This complexity leads many organizations to weigh whether they should manage the migration in-house or work with a specialized data migration services company.
Understanding Cloud Migration Services
Cloud migration services are professional services offered by third-party providers that specialize in planning, executing, and optimizing cloud migrations. These providers often have extensive experience and industry-standard tools to ensure a smooth and secure transition to the cloud.
Partnering with cloud migration services often includes:
Assessment of existing infrastructure
Selection of the right cloud platform (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, etc.)
Migration strategy and timeline planning
Data security and compliance checks
Post-migration support and optimization
Many of these providers also act as data migration consultants, offering strategic advice on architecture, performance, and cost efficiency.
What Is DIY Cloud Migration?
DIY cloud migration is when a company manages the entire migration process internally using its own IT team and resources. This approach may appeal to businesses with limited budgets, specific internal expertise, or a desire for full control over the migration process.
While DIY migration can work for some businesses, it requires careful planning, skilled personnel, and a strong understanding of both the legacy and new cloud environments.
Pros of Using Cloud Migration Services
1. Access to Expertise
One of the key advantages of working with data migration consultants is gaining access to experts who’ve handled dozens or even hundreds of migration projects. They bring best practices, foresight into potential roadblocks, and proven methods to minimize risk.
2. Faster Time-to-Value
Experienced cloud migration services can accelerate the process, minimizing downtime and avoiding common delays. This means your team can start using cloud benefits—like scalability and flexibility—much sooner.
3. Reduced Risk and Errors
Professional data migration services company teams have the tools and processes to ensure data integrity, security compliance, and minimal disruption. DIY migrations are more prone to errors, which can lead to costly setbacks or data loss.
4. Customization and Scalability
A reputable data migration services company will tailor the migration strategy based on your business goals, compliance requirements, and future scalability needs. This is especially beneficial for industries like healthcare, finance, or retail where security and regulatory compliance are paramount.
5. Ongoing Support and Optimization
Beyond migration, many cloud migration services offer post-deployment support including cost optimization, performance tuning, and system health monitoring—helping you get the most from your cloud investment.
Pros of DIY Cloud Migration
1. Lower Upfront Cost
For small businesses or startups with limited resources, handling the migration in-house may seem more cost-effective at first glance. There's no need to pay for external data migration consultants or agencies.
2. Greater Internal Control
Some organizations prefer to manage the process internally to retain full control over architecture decisions, timeline, and resource allocation.
3. Team Skill Development
Handling cloud migration in-house can serve as a learning experience for your IT team, allowing them to gain valuable cloud expertise for future projects.
Cons of Using Cloud Migration Services
1. Higher Initial Costs
Partnering with a data migration services company involves service fees that can be significant, especially for larger or more complex migrations. However, these costs often pay off in the form of efficiency and long-term performance gains.
2. Dependency on Third-Party Providers
Some companies are hesitant to rely on external partners due to data security concerns or a desire to maintain full internal control. Choosing a trustworthy cloud migration services provider is essential to mitigate this risk.
3. Potential for Overengineering
Occasionally, external data migration consultants may overcomplicate a project, recommending solutions that go beyond your actual business needs. It’s essential to ensure alignment between the service provider and your business objectives.
Cons of DIY Cloud Migration
1. Lack of Expertise
Unless your internal team includes experienced data migration consultants, DIY migration can be risky. Inadequate planning or execution may lead to downtime, performance issues, or even data breaches.
2. Longer Timeframes
Without the experience of a cloud migration services team, your business may face extended migration periods, resulting in downtime, lost productivity, or missed business opportunities.
3. Security and Compliance Challenges
Maintaining compliance with standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, or ISO 27001 is critical during migration. A data migration services company typically has the knowledge to navigate these requirements, whereas in-house teams may not.
4. Hidden Costs
Mistakes during migration—such as data loss, downtime, or misconfigurations—can lead to hidden costs that outweigh the savings of doing it yourself.
When to Choose Cloud Migration Services
Opt for cloud migration services if:
You have limited in-house cloud expertise.
You’re working with legacy systems or large-scale data.
You operate in a regulated industry and require compliance expertise.
You need the migration done quickly and with minimal risk.
You want post-migration support to optimize cloud performance.
Working with a data migration services company ensures a structured and scalable approach. They offer not just technical execution but also strategic consulting from experienced data migration consultants who align migration goals with your business outcomes.
When DIY Cloud Migration Makes Sense
Choose the DIY route if:
You have a highly skilled internal IT team with cloud experience.
Your infrastructure is relatively simple and easy to migrate.
You want to save money on professional services.
You’re migrating non-critical workloads or testing cloud environments.
Still, it’s wise to consult with data migration consultants even if you plan to handle the migration internally. A short-term engagement can help you validate your strategy, identify risks, and prepare a more efficient roadmap.
Cost Comparison: Services vs. DIY
AspectCloud Migration ServicesDIY MigrationUpfront CostHighLowLong-Term ROIHigh (due to efficiency and optimization)VariableDowntime RiskLowMedium to HighInternal Resource BurdenLowHighCustom StrategyYesLimitedCompliance ExpertiseYesDepends on internal teamPost-Migration SupportYesRequires in-house effort
Case Studies
Case Study 1: Mid-Sized Manufacturer Uses Cloud Migration Services
A mid-sized manufacturer needed to move its ERP and legacy systems to AWS. With limited cloud knowledge, they hired a data migration services company. The project was completed within 6 weeks, with zero data loss and 30% reduction in cloud costs due to optimization by data migration consultants.
Case Study 2: Startup Handles DIY Migration
A SaaS startup with strong DevOps capabilities chose a DIY approach to migrate their app infrastructure to Azure. While the team was competent, the project took longer than expected due to unforeseen issues with third-party integrations. Ultimately, they engaged data migration consultants for fine-tuning and cost control.
Hybrid Approaches: Best of Both Worlds?
Some businesses combine both approaches. They handle the less complex aspects of migration in-house but rely on cloud migration services for critical phases like data security or compliance validation.
This hybrid model works particularly well for:
Businesses with budget constraints but complex needs.
Companies using multi-cloud or hybrid cloud environments.
Organizations with strong IT teams that still need expert oversight.
Engaging a data migration services company on a consultative basis can bridge gaps without taking over the entire project. Even short-term involvement from data migration consultants can prevent costly mistakes.
Key Questions to Ask Before Deciding
How complex is your current IT environment?
Do you have experienced in-house cloud professionals?
What is your timeline for migration?
Are you bound by strict compliance requirements?
What is your budget for the project?
Do you need ongoing support after migration?
Are your systems mission-critical or experimental?
Final Thoughts: Which Is Right for You?
There’s no one-size-fits-all answer when it comes to cloud migration. If you value speed, efficiency, compliance, and reduced risk, cloud migration services may be the better path. A reputable data migration services company can provide not just technical implementation but also strategic insights from experienced data migration consultants.
On the other hand, if you have a capable IT team, limited scope, or are simply experimenting with cloud environments, DIY migration might make sense—at least for your first phase.
Either way, understanding the scope and risks upfront is essential. And for many organizations, the smartest move might be a hybrid model: Do what you can internally and bring in data migration consultants to guide and validate critical stages.
0 notes
Text

🚀 Azure vs. AWS vs. Google Cloud: Which Managed Service is Right for You? 🌐 Choosing the right cloud provider can make or break your business efficiency. From scalability to security, we break down the pros and cons of each platform. Don’t make a blind choice—read our in-depth comparison to find the best fit for your business! 💡
0 notes
Text
Hosting Options for Full Stack Applications: AWS, Azure, and Heroku

Introduction
When deploying a full-stack application, choosing the right hosting provider is crucial. AWS, Azure, and Heroku offer different hosting solutions tailored to various needs. This guide compares these platforms to help you decide which one is best for your project.
1. Key Considerations for Hosting
Before selecting a hosting provider, consider: ✅ Scalability — Can the platform handle growth? ✅ Ease of Deployment — How simple is it to deploy and manage apps? ✅ Cost — What is the pricing structure? ✅ Integration — Does it support your technology stack? ✅ Performance & Security — Does it offer global availability and robust security?
2. AWS (Amazon Web Services)
Overview
AWS is a cloud computing giant that offers extensive services for hosting and managing applications.
Key Hosting Services
🚀 EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud) — Virtual servers for hosting web apps 🚀 Elastic Beanstalk — PaaS for easy deployment 🚀 AWS Lambda — Serverless computing 🚀 RDS (Relational Database Service) — Managed databases (MySQL, PostgreSQL, etc.) 🚀 S3 (Simple Storage Service) — File storage for web apps
Pros & Cons
✔️ Highly scalable and flexible ✔️ Pay-as-you-go pricing ✔️ Integration with DevOps tools ❌ Can be complex for beginners ❌ Requires manual configuration
Best For: Large-scale applications, enterprises, and DevOps teams.
3. Azure (Microsoft Azure)
Overview
Azure provides cloud services with seamless integration for Microsoft-based applications.
Key Hosting Services
🚀 Azure Virtual Machines — Virtual servers for custom setups 🚀 Azure App Service — PaaS for easy app deployment 🚀 Azure Functions — Serverless computing 🚀 Azure SQL Database — Managed database solutions 🚀 Azure Blob Storage — Cloud storage for apps
Pros & Cons
✔️ Strong integration with Microsoft tools (e.g., VS Code, .NET) ✔️ High availability with global data centers ✔️ Enterprise-grade security ❌ Can be expensive for small projects ❌ Learning curve for advanced features
Best For: Enterprise applications, .NET-based applications, and Microsoft-centric teams.
4. Heroku
Overview
Heroku is a developer-friendly PaaS that simplifies app deployment and management.
Key Hosting Features
🚀 Heroku Dynos — Containers that run applications 🚀 Heroku Postgres — Managed PostgreSQL databases 🚀 Heroku Redis — In-memory caching 🚀 Add-ons Marketplace — Extensions for monitoring, security, and more
Pros & Cons
✔️ Easy to use and deploy applications ✔️ Managed infrastructure (scaling, security, monitoring) ✔️ Free tier available for small projects ❌ Limited customization compared to AWS & Azure ❌ Can get expensive for large-scale apps
Best For: Startups, small-to-medium applications, and developers looking for quick deployment.
5. Comparison Table
FeatureAWSAzureHerokuScalabilityHighHighMediumEase of UseComplexModerateEasyPricingPay-as-you-goPay-as-you-goFixed plansBest ForLarge-scale apps, enterprisesEnterprise apps, Microsoft usersStartups, small appsDeploymentManual setup, automated pipelinesIntegrated DevOpsOne-click deploy
6. Choosing the Right Hosting Provider
✅ Choose AWS for large-scale, high-performance applications.
✅ Choose Azure for Microsoft-centric projects.
✅ Choose Heroku for quick, hassle-free deployments.
WEBSITE: https://www.ficusoft.in/full-stack-developer-course-in-chennai/
0 notes
Text
Efficient GPU Management for AI Startups: Exploring the Best Strategies
The rise of AI-driven innovation has made GPUs essential for startups and small businesses. However, efficiently managing GPU resources remains a challenge, particularly with limited budgets, fluctuating workloads, and the need for cutting-edge hardware for R&D and deployment.
Understanding the GPU Challenge for Startups
AI workloads—especially large-scale training and inference—require high-performance GPUs like NVIDIA A100 and H100. While these GPUs deliver exceptional computing power, they also present unique challenges:
High Costs – Premium GPUs are expensive, whether rented via the cloud or purchased outright.
Availability Issues – In-demand GPUs may be limited on cloud platforms, delaying time-sensitive projects.
Dynamic Needs – Startups often experience fluctuating GPU demands, from intensive R&D phases to stable inference workloads.
To optimize costs, performance, and flexibility, startups must carefully evaluate their options. This article explores key GPU management strategies, including cloud services, physical ownership, rentals, and hybrid infrastructures—highlighting their pros, cons, and best use cases.
1. Cloud GPU Services
Cloud GPU services from AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure offer on-demand access to GPUs with flexible pricing models such as pay-as-you-go and reserved instances.
✅ Pros:
✔ Scalability – Easily scale resources up or down based on demand. ✔ No Upfront Costs – Avoid capital expenditures and pay only for usage. ✔ Access to Advanced GPUs – Frequent updates include the latest models like NVIDIA A100 and H100. ✔ Managed Infrastructure – No need for maintenance, cooling, or power management. ✔ Global Reach – Deploy workloads in multiple regions with ease.
❌ Cons:
✖ High Long-Term Costs – Usage-based billing can become expensive for continuous workloads. ✖ Availability Constraints – Popular GPUs may be out of stock during peak demand. ✖ Data Transfer Costs – Moving large datasets in and out of the cloud can be costly. ✖ Vendor Lock-in – Dependency on a single provider limits flexibility.
🔹 Best Use Cases:
Early-stage startups with fluctuating GPU needs.
Short-term R&D projects and proof-of-concept testing.
Workloads requiring rapid scaling or multi-region deployment.
2. Owning Physical GPU Servers
Owning physical GPU servers means purchasing GPUs and supporting hardware, either on-premises or collocated in a data center.
✅ Pros:
✔ Lower Long-Term Costs – Once purchased, ongoing costs are limited to power, maintenance, and hosting fees. ✔ Full Control – Customize hardware configurations and ensure access to specific GPUs. ✔ Resale Value – GPUs retain significant resale value (Sell GPUs), allowing you to recover investment costs when upgrading. ✔ Purchasing Flexibility – Buy GPUs at competitive prices, including through refurbished hardware vendors. ✔ Predictable Expenses – Fixed hardware costs eliminate unpredictable cloud billing. ✔ Guaranteed Availability – Avoid cloud shortages and ensure access to required GPUs.
❌ Cons:
✖ High Upfront Costs – Buying high-performance GPUs like NVIDIA A100 or H100 requires a significant investment. ✖ Complex Maintenance – Managing hardware failures and upgrades requires technical expertise. ✖ Limited Scalability – Expanding capacity requires additional hardware purchases.
🔹 Best Use Cases:
Startups with stable, predictable workloads that need dedicated resources.
Companies conducting large-scale AI training or handling sensitive data.
Organizations seeking long-term cost savings and reduced dependency on cloud providers.
3. Renting Physical GPU Servers
Renting physical GPU servers provides access to high-performance hardware without the need for direct ownership. These servers are often hosted in data centers and offered by third-party providers.
✅ Pros:
✔ Lower Upfront Costs – Avoid large capital investments and opt for periodic rental fees. ✔ Bare-Metal Performance – Gain full access to physical GPUs without virtualization overhead. ✔ Flexibility – Upgrade or switch GPU models more easily compared to ownership. ✔ No Depreciation Risks – Avoid concerns over GPU obsolescence.
❌ Cons:
✖ Rental Premiums – Long-term rental fees can exceed the cost of purchasing hardware. ✖ Operational Complexity – Requires coordination with data center providers for management. ✖ Availability Constraints – Supply shortages may affect access to cutting-edge GPUs.
🔹 Best Use Cases:
Mid-stage startups needing temporary GPU access for specific projects.
Companies transitioning away from cloud dependency but not ready for full ownership.
Organizations with fluctuating GPU workloads looking for cost-effective solutions.
4. Hybrid Infrastructure
Hybrid infrastructure combines owned or rented GPUs with cloud GPU services, ensuring cost efficiency, scalability, and reliable performance.
What is a Hybrid GPU Infrastructure?
A hybrid model integrates: 1️⃣ Owned or Rented GPUs – Dedicated resources for R&D and long-term workloads. 2️⃣ Cloud GPU Services – Scalable, on-demand resources for overflow, production, and deployment.
How Hybrid Infrastructure Benefits Startups
✅ Ensures Control in R&D – Dedicated hardware guarantees access to required GPUs. ✅ Leverages Cloud for Production – Use cloud resources for global scaling and short-term spikes. ✅ Optimizes Costs – Aligns workloads with the most cost-effective resource. ✅ Reduces Risk – Minimizes reliance on a single provider, preventing vendor lock-in.
Expanded Hybrid Workflow for AI Startups
1️⃣ R&D Stage: Use physical GPUs for experimentation and colocate them in data centers. 2️⃣ Model Stabilization: Transition workloads to the cloud for flexible testing. 3️⃣ Deployment & Production: Reserve cloud instances for stable inference and global scaling. 4️⃣ Overflow Management: Use a hybrid approach to scale workloads efficiently.
Conclusion
Efficient GPU resource management is crucial for AI startups balancing innovation with cost efficiency.
Cloud GPUs offer flexibility but become expensive for long-term use.
Owning GPUs provides control and cost savings but requires infrastructure management.
Renting GPUs is a middle-ground solution, offering flexibility without ownership risks.
Hybrid infrastructure combines the best of both, enabling startups to scale cost-effectively.
Platforms like BuySellRam.com help startups optimize their hardware investments by providing cost-effective solutions for buying and selling GPUs, ensuring they stay competitive in the evolving AI landscape.
The original article is here: How to manage GPU resource?
#GPUManagement #GPUsForAI #AIGPU #TechInfrastructure #HighPerformanceComputing #CloudComputing #AIHardware #Tech
#GPU Management#GPUs for AI#AI GPU#High Performance Computing#cloud computing#ai hardware#technology
0 notes
Text
AWS, Azure, and GCP: Pros and Cons for Developers
AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) are the leading cloud service providers. Each offers unique advantages and has certain limitations. Here's a breakdown of their pros and cons for developers:
1. AWS (Amazon Web Services)
Pros:
Mature Ecosystem: AWS has the largest number of services and the most mature ecosystem, providing solutions for almost any need.
Global Reach: AWS offers the widest global infrastructure with more data centers worldwide.
Developer Tools: A comprehensive suite of tools like AWS Lambda, CloudFormation, and CodePipeline for automation and CI/CD.
Extensive Documentation and Community: A vast array of tutorials, official docs, and a large community for support.
Rich Marketplace: Offers pre-configured machine images and services via its AWS Marketplace.
Cons:
Complex Pricing: AWS pricing models can be difficult to understand and may result in unexpected costs.
Overwhelming Options: The large number of services can be overwhelming for beginners.
Learning Curve: The platform’s depth and complexity make it challenging to master.
2. Azure (Microsoft Azure)
Pros:
Integration with Microsoft Tools: Seamless integration with Microsoft products like Office 365, Active Directory, and Windows Server.
Hybrid Cloud Solutions: Strong support for hybrid cloud environments, making it easier for businesses to transition to the cloud.
Enterprise Focus: Designed with enterprise developers in mind, offering great solutions for large organizations.
DevOps Integration: Built-in tools like Azure DevOps for CI/CD pipelines and project management.
Ease of Use: A more user-friendly portal and dashboard compared to AWS.
Cons:
Global Coverage: Slightly fewer regions compared to AWS, though expanding rapidly.
Linux Compatibility: Historically more Windows-oriented, though this is improving.
Documentation and Community: Smaller developer community compared to AWS, leading to fewer third-party resources.
3. GCP (Google Cloud Platform)
Pros:
AI/ML Capabilities: Industry-leading tools for artificial intelligence and machine learning, like TensorFlow and BigQuery.
Pricing Transparency: Simpler and often more affordable pricing structure compared to AWS and Azure.
Network Performance: Superior network infrastructure due to Google’s investments in fiber optic cables.
Developer-Friendly Tools: Focused on modern app development with Kubernetes (invented by Google) and serverless options.
Open Source Commitment: Strong emphasis on open-source technologies and tools.
Cons:
Fewer Services: While sufficient for most needs, GCP has fewer services compared to AWS and Azure.
Smaller Ecosystem: A smaller marketplace and community than AWS or Azure.
Enterprise Adoption: Less enterprise penetration compared to AWS and Azure, meaning fewer integrations for legacy systems.
Summary
Choose AWS if you need a vast array of services, global reach, and scalability. Ideal for mature projects and enterprises.
Choose Azure if you are already in the Microsoft ecosystem or need strong hybrid solutions. Great for enterprises.
Choose GCP if you're focused on AI/ML, cost efficiency, or modern app development. Ideal for startups and innovative projects.
Let me know if you'd like further insights or guidance!
0 notes
Text
Facing Challenges to choose the right cloud platform to drive your business forward?
The battle of the clouds! AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud – which one truly fits your business needs? 🏆 Don’t let confusion hold you back from scaling! Our detailed comparison breaks down the pros, cons, and key features of each platform so you can make an informed decision for your cloud journey. Unlock the power of the right cloud today!
👉 Explore now: AWS vs Azure vs Google Cloud
#CloudComputing#AWS#Azure#GoogleCloud#CloudComparison#BusinessGrowth#CloudSolutions#TechInnovation#CloudServices#TechDecisions#CloudTech#CloudDevelopment#BusinessSolutions#SaaS#HiddenBrains
0 notes
Text
Cloud vs On-Prem Data Warehouse: Making the Right Choice for Your Business
In today's data-driven world, businesses face a critical decision when it comes to choosing the right data warehouse solution. The debate between cloud and on-premise data warehouses has been ongoing, with each option offering distinct advantages and challenges. This article will delve into the practical differences between cloud and on-premise data warehouses, offering real-world examples and data-driven insights to help you make an informed decision.

What is a Cloud Data Warehouse?
A cloud data warehouse is a scalable and flexible data storage solution hosted on cloud platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, or Microsoft Azure. Unlike traditional on-premise data warehouses, cloud data warehouses eliminate the need for physical infrastructure, offering businesses the ability to store and manage data with ease and efficiency.
On-Premise Data Warehouse: A Legacy Approach
An on-premise data warehouse is a traditional data storage solution where the data is hosted on local servers within a company's own data center. This model offers complete control over the data and the infrastructure but comes with significant upfront costs and ongoing maintenance requirements.
Key Differences Between Cloud and On-Premise Data Warehouses
1. Cost Efficiency
Cloud Data Warehouse:
Pros: The pay-as-you-go model allows businesses to scale resources up or down based on demand, reducing unnecessary costs. There is no need for significant capital investment in hardware or software.
Cons: Long-term costs can add up if not managed properly, especially with increasing data volumes and computational needs.
On-Premise Data Warehouse:
Pros: Once the initial investment is made, ongoing costs can be more predictable. No recurring subscription fees.
Cons: High upfront costs for hardware, software, and skilled IT personnel. Ongoing maintenance, power, and cooling expenses add to the total cost of ownership (TCO).
2. Scalability
Cloud Data Warehouse:
Pros: Cloud solutions offer almost infinite scalability. Businesses can adjust their storage and processing power according to their needs without physical limitations.
Cons: Rapid scaling can lead to unexpectedly high costs if usage is not carefully monitored.
On-Premise Data Warehouse:
Pros: Customizable to specific business needs. Scaling is possible but requires additional hardware and can be time-consuming.
Cons: Scaling is limited by the physical infrastructure, often requiring significant time and financial investment.
3. Performance
Cloud Data Warehouse:
Pros: Advanced cloud architectures are optimized for performance, offering faster query processing and better data handling capabilities.
Cons: Performance can be affected by network latency and bandwidth limitations.
On-Premise Data Warehouse:
Pros: Performance is highly controlled, with low latency since data is processed on-site.
Cons: Performance improvements require hardware upgrades, which can be costly and time-consuming.
4. Security and Compliance
Cloud Data Warehouse:
Pros: Leading cloud providers offer robust security features, including encryption, access controls, and compliance with industry standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC 2.
Cons: Data security in the cloud is a shared responsibility. Organizations must ensure that they implement proper security measures on their end.
On-Premise Data Warehouse:
Pros: Complete control over security policies and compliance with regulatory requirements. Data remains within the company's own environment.
Cons: Higher responsibility for maintaining security, requiring dedicated IT staff and resources.
Live Examples: Cloud vs On-Premise in Action
Cloud Data Warehouse: Netflix
Netflix is a prime example of a company leveraging cloud data warehouses to manage its massive data volumes. By using AWS Redshift, Netflix can analyze petabytes of data in real-time, optimizing its recommendation algorithms and improving user experience. The scalability and performance of cloud data warehouses allow Netflix to handle peak loads, such as during new content releases, without compromising speed or reliability.
On-Premise Data Warehouse: Bank of America
Bank of America relies on an on-premise data warehouse to maintain full control over its sensitive financial data. By keeping data in-house, the bank ensures that all security and compliance requirements are met without relying on external cloud providers. While the costs and complexity of managing an on-premise solution are higher, the bank prioritizes control and security over the flexibility offered by cloud solutions.
Data-Driven Insights: Market Trends and Future Outlook
Market Growth: According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global cloud data warehouse market is expected to grow from $4.7 billion in 2021 to $12.9 billion by 2026, at a CAGR of 23.8%. This growth is driven by the increasing adoption of cloud technologies, the need for real-time analytics, and the flexibility offered by cloud solutions.
Hybrid Approaches: Many organizations are adopting hybrid models, combining both cloud and on-premise data warehouses to balance the benefits of both. For instance, sensitive data may be stored on-premise, while less critical data is managed in the cloud.
AI and Machine Learning Integration: Cloud data warehouses are increasingly integrating AI and machine learning tools to enhance data processing capabilities. This trend is expected to accelerate, with cloud providers offering more advanced analytics and automation features.
Making the Right Choice: Key Considerations
Business Needs: Assess your organization’s specific needs, including data volume, security requirements, budget, and long-term goals.
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider both the short-term and long-term costs associated with each solution, including maintenance, upgrades, and scalability.
Security and Compliance: Ensure that your chosen solution meets all regulatory requirements and provides the necessary security features to protect your data.
Scalability and Performance: Evaluate the scalability and performance needs of your organization, and choose a solution that can grow with your business.
Conclusion
Choosing between a cloud and an on-premise data warehouse is a decision that requires careful consideration of various factors, including cost, scalability, performance, and security. While cloud data warehouses offer flexibility, scalability, and advanced analytics, on-premise solutions provide greater control and security. By understanding your organization’s unique needs and long-term goals, you can make an informed decision that will support your data management strategy for years to come.
#Cloud Data Warehouse#On Premise Data Warehouse#Data Storage#Data Management#Cloud Computing#Enterprise Data#Hybrid Cloud#Data Analytics#Data Security#Digital Transformation#Data Infrastructure#Business Intelligence
0 notes
Text
How to Choose the Best Full Stack Developer Course
In today's rapidly evolving tech landscape, becoming a full-stack developer can open doors to numerous career opportunities. A full-stack development training program is essential in acquiring the skills to build both front-end and back-end applications. However, choosing the right one can be daunting, given the many courses available. This guide will help you select the best Full Stack Developer course for your needs.
Define Your Goals and Learning Objectives
Before exploring course options, it’s crucial to clarify your goals. Are you looking to switch careers, enhance your skill set, or explore a new hobby? Comprehending your objectives will help you identify the course that aligns with your aspirations. For instance, if you aim to secure a job as a full-stack developer, look for courses that offer comprehensive training and job placement assistance.
Consider Your Current Skill Level
Assess your knowledge and experience in web development with training programs ranging from beginner to advanced levels. If you are new to coding, opt for a beginner-friendly course that covers the basics of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript before delving into more complex topics. Conversely, if you have some experience, an advanced course focusing on modern frameworks and tools might be more suitable.
Course Curriculum
A well-structured curriculum is the backbone of any effective training program. Ensure the training covers the following key areas:
Front-End Development: HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and popular frameworks like React or Angular.
Back-End Development: Server-side languages like Node.js, Express.js, Python, or Ruby on Rails.
Databases: SQL (MySQL, PostgreSQL) and NoSQL (MongoDB) databases.
Version Control: Git and GitHub.
Deployment: Understanding cloud services like AWS, Heroku, or Azure.
Security: Basic principles of web security and best practices.
Check if the course offers hands-on projects and real-world applications, as practical experience is crucial for mastering full-stack development.
Learning Format: Online vs. In-Person
Which do you prefer: online or in-person learning? Each format has its pros and cons:
Online Courses: Offer flexibility, allowing you to learn at your own pace and schedule. They are often more affordable and accessible from anywhere. However, they require self-discipline and motivation.
In-person courses: These provide a structured learning environment with direct interaction with instructors and peers. They can be more engaging and offer immediate feedback but are less flexible and often more expensive.
Instructor Expertise
The quality of instruction can largely impact your learning experience. Research the instructors' backgrounds to check if they have relevant industry experience and expertise in full-stack development. Look for courses taught by professionals in reputable companies or with significant teaching experience.
Reviews and Testimonials
Student reviews and testimonials are invaluable resources for gauging the effectiveness of a course. Look for feedback on Course Report, SwitchUp, or social media groups. Pay attention to comments about the curriculum, teaching style, support, and overall satisfaction. High ratings and positive feedback from past students are good indicators of a quality course.
Job Placement Assistance
If you want to land a job after completing the course, consider programs offering job placement assistance. Many reputable courses provide career services, including resume reviews, interview preparation, and connections to hiring partners. Some even boast impressive job placement rates, which can give you confidence in their ability to help you transition into a full-stack development role.
Cost and Financial Aid
A Full Stack Developer course can range from free to several thousand dollars. While choosing the most affordable option is compelling, remember that quality education is an investment in your future. Consider the value you’re getting for the price. Some courses offer financial aid, scholarships, or instalment plans to make payments more manageable. Research these options to find a course that fits your budget without compromising quality.
Flexibility and Time Commitment
Evaluate the time commitment the course requires and whether it fits into your schedule. Some courses are intensive bootcamps designed to be completed in a few months, while others are more flexible, allowing you to study part-time over a longer period. Choose a course format that aligns with your availability and learning pace.
Accreditation and Certification
While not always necessary, accredited courses or those offering recognised certifications can add value to your resume. Certifications from reputable institutions or tech giants like Google, Microsoft, or Amazon can enhance your credibility and job prospects.
Conclusion
Choosing the best Full Stack Developer course involves careful consideration of your goals, current skills, learning preferences, and the course offerings. By thoroughly researching and evaluating your options based on curriculum, instructor expertise, reviews, job placement assistance, cost, and flexibility, you can find a course that meets your skilling needs and sets you on the road to becoming a successful full-stack developer. Remember, the right course is about acquiring knowledge and gaining the practical experience and support necessary to thrive in the tech industry.
0 notes
Text
Check out our blog on Comparing AWS vs Azure vs GCP: Which Cloud Platform Should You Choose?
1 note
·
View note
Text

🚀 Azure vs. AWS vs. Google Cloud: Which Managed Service is Right for You? 🌐 Choosing the right cloud provider can make or break your business efficiency. From scalability to security, we break down the pros and cons of each platform. Don’t make a blind choice—read our in-depth comparison to find the best fit for your business! 💡
0 notes
Text
How to Deploy Your Full Stack Application: A Beginner’s Guide
Deploying a full stack application involves setting up your frontend, backend, and database on a live server so users can access it over the internet. This guide covers deployment strategies, hosting services, and best practices.
1. Choosing a Deployment Platform
Popular options include:
Cloud Platforms: AWS, Google Cloud, Azure
PaaS Providers: Heroku, Vercel, Netlify
Containerized Deployment: Docker, Kubernetes
Traditional Hosting: VPS (DigitalOcean, Linode)
2. Deploying the Backend
Option 1: Deploy with a Cloud Server (e.g., AWS EC2, DigitalOcean)
Set Up a Virtual Machine (VM)
bash
ssh user@your-server-ip
Install Dependencies
Node.js (sudo apt install nodejs npm)
Python (sudo apt install python3-pip)
Database (MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB)
Run the Server
bash
nohup node server.js & # For Node.js apps gunicorn app:app --daemon # For Python Flask/Django apps
Option 2: Serverless Deployment (AWS Lambda, Firebase Functions)
Pros: No server maintenance, auto-scaling
Cons: Limited control over infrastructure
3. Deploying the Frontend
Option 1: Static Site Hosting (Vercel, Netlify, GitHub Pages)
Push Code to GitHub
Connect GitHub Repo to Netlify/Vercel
Set Build Command (e.g., npm run build)
Deploy and Get Live URL
Option 2: Deploy with Nginx on a Cloud Server
Install Nginx
bash
sudo apt install nginx
Configure Nginx for React/Vue/Angular
nginx
server { listen 80; root /var/www/html; index index.html; location / { try_files $uri /index.html; } }
Restart Nginx
bash
sudo systemctl restart nginx
4. Connecting Frontend and Backend
Use CORS middleware to allow cross-origin requests
Set up reverse proxy with Nginx
Secure API with authentication tokens (JWT, OAuth)
5. Database Setup
Cloud Databases: AWS RDS, Firebase, MongoDB Atlas
Self-Hosted Databases: PostgreSQL, MySQL on a VPS
bash# Example: Run PostgreSQL on DigitalOcean sudo apt install postgresql sudo systemctl start postgresql
6. Security & Optimization
✅ SSL Certificate: Secure site with HTTPS (Let’s Encrypt) ✅ Load Balancing: Use AWS ALB, Nginx reverse proxy ✅ Scaling: Auto-scale with Kubernetes or cloud functions ✅ Logging & Monitoring: Use Datadog, New Relic, AWS CloudWatch
7. CI/CD for Automated Deployment
GitHub Actions: Automate builds and deployment
Jenkins/GitLab CI/CD: Custom pipelines for complex deployments
Docker & Kubernetes: Containerized deployment for scalability
Final Thoughts
Deploying a full stack app requires setting up hosting, configuring the backend, deploying the frontend, and securing the application.
Cloud platforms like AWS, Heroku, and Vercel simplify the process, while advanced setups use Kubernetes and Docker for scalability.
WEBSITE: https://www.ficusoft.in/full-stack-developer-course-in-chennai/
0 notes
Text
Buy Amazon AWS Accounts
Buy Amazon AWS Accounts Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a cloud computing platform that provides users with a variety of services including computing, storage, database, analytics, application services, and more. AWS is one of the most popular cloud platforms and is used by many businesses around the world. To use AWS services, you need to have an account. Buying an Amazon AWS account can be a great way to access all of the features and benefits offered by this powerful platform.
Buy AWS Accounts
In this article, we’ll discuss what Amazon AWS accounts are and how they can benefit you. We’ll also cover how to buy AWS account, different types of accounts available, best practices for buying an account, pros and cons of using them, security considerations when buying an account, tips for choosing the right one for your needs, common mistakes to avoid when purchasing an account, FAQs about Buy Amazon AWS Accounts and alternatives to buying one.
About Amazon AWS Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a cloud computing platform offered by Amazon.com. It provides a wide range of services, including computing power, storage, database management, and content delivery, among others. AWS is used by individuals and organizations of all sizes, from small startups to large enterprises, to run their applications and store their data in the cloud. So Buy Amazon AWS Accounts From Our Digitalac.net.
Buy AWS Accounts
AWS offers a pay-as-you-go model, which means users only pay for the resources they use, without any upfront costs or long-term commitments. This makes it cost-effective for businesses of all sizes, as they can scale up or down their resources as needed. AWS also provides a wide range of tools and services to help developers and IT professionals manage their applications and infrastructure in the cloud, such as AWS Elastic Beanstalk, AWS Lambda, and AWS Cloud Formation.
Overall, AWS is a highly scalable, secure, and reliable platform that enables businesses to run their applications and store their data in the cloud with ease.
Buy AWS Accounts AWS is a cloud computing platform that enables individuals and businesses to run their applications and store their data in the cloud.
With an AWS account, users can access a wide range of services, including computing power, storage, database management, content delivery, and more. AWS offers a pay-as-you-go model, which means users only pay for the resources they use, without any upfront costs or long-term commitments.
Buy Amazon AWS Accounts
Check Our More Products: Buy Google Cloud Accounts, Buy Digital Ocean Accounts, Buy Azure Accounts
An AWS account also provides users with tools and services to help manage their applications and infrastructure in the cloud, such as AWS Elastic Beanstalk, AWS Lambda, and AWS CloudFormation. AWS has a global infrastructure with data centers located in multiple regions around the world, enabling users to deploy their applications closer to their users and optimize their performance. So Buy AWS Accounts right now.
Benefits of Buying Amazon AWS Accounts There are many benefits associated with buying an Amazon AWS account. First and foremost is the access it provides you to all of the features available on the platform. With an account, you can take advantage of everything from computing power and storage space to application services such as machine learning algorithms or analytics tools.
Buy Amazon AWS Accounts
Another benefit is that it allows you to scale up or down depending on your needs at any given time without purchasing additional hardware or software licenses. This makes it easy for businesses to manage their resources efficiently while still being able to access all the features they need. Additionally, because it’s a cloud-based platform there’s no need for physical infrastructure which reduces costs associated with maintenance and upgrades as well as energy consumption overall.
Finally, having an Amazon AWS account gives you access to 24/7 technical support which can be invaluable in case something goes wrong or if you just need help understanding how something works on the platform. So decisively buy Amazon AWS account from us today!
How to Buy an AWS Account Buying an Amazon AWS account is a relatively simple process but there are some things you should consider before doing so. The first step is deciding which type of account best suits your needs – there are several different types available such as free tier accounts or pay-as-you-go plans depending on your budget and usage requirements. Once you’ve decided which type is best for you then all that’s left is to create your user profile on the website with some basic information such as name and address before entering payment details to complete the purchase process.
Different Types of Amazon AWS Accounts When it comes to buy Amazon AWS account there are several different types available depending on your usage requirements and budget constraints:
– Free Tier: This type of plan offers limited access but can be a great option if you’re just getting started with using the platform or don’t have much experience yet;
– Pay-As-You-Go: This type allows users to pay only for what they use each month which makes it perfect for those who don’t want any long-term commitments;
– Reserved Instances: These offer significant discounts compared to pay-as-you-go plans but require upfront payments;
– Spot Instances: These allow users to bid on unused capacity at lower prices than reserved instances;
– Dedicated Hosts: These are physical servers dedicated solely for use by one customer;
– Dedicated Instances: These offer dedicated computing resources within a shared environment;
– On-Demand Instances: These provide instant access without any long-term commitments;
– Savings Plans: These provide discounts based on predetermined usage levels over time;
– Enterprise Support Plans: These offer premium support options tailored specifically for larger organizations with complex IT environments;
– CloudFormation Templates: These allow users to create custom templates that automate resource provisioning across multiple regions;
– CloudFront Distributions: These provide low latency content delivery networks optimized for streaming media content worldwide;
About Aws Credit Account AWS credit account is a type of account that provides credit or funds to individuals or organizations to use AWS services. AWS credits can be used to pay for AWS services, such as EC2 instances, S3 storage, and other AWS products. AWS offers credits for various purposes, such as promotional campaigns, events, training, or research.
best aws accounts
AWS credits are typically distributed as codes that can be redeemed on an AWS account. Once the code is redeemed, the credit will be automatically applied to the AWS account and can be used to pay for eligible AWS services. AWS credits are non-transferable and non-refundable, and their usage is subject to the AWS terms and conditions.
AWS credit accounts can be a valuable tool for individuals and organizations to test and experiment with AWS services without incurring upfront costs. They can also be used to reduce the overall cost of using AWS services, especially for educational or research purposes. It’s recommended that individuals and organizations consult AWS documentation and support for guidance on using AWS credits and optimizing their usage.
Aws Accounts For Sale That being said, AWS offers a wide range of instance types that vary in terms of CPU, memory, storage, and network capacity, as well as pricing. The price of an AWS instance depends on factors such as the instance type, region, usage, and additional services or features.
Buy verified AWS Accounts
To find the best price for an AWS instance, it’s recommended that individuals and businesses use the AWS Pricing Calculator, which allows users to estimate the cost of AWS services based on their usage and configuration. It’s also recommended to explore AWS cost optimization resources, such as AWS Trusted Advisor, to help reduce costs and optimize spending.
Best Practices for Buy Amazon AWS Account When purchasing an Amazon Web Services (AWS) Account certain best practices should be followed in order to ensure maximum efficiency while using this powerful cloud computing platform:
1) Determine Your Needs Beforehand – Before making any decisions about which type of plan would be best suited for your needs make sure that you have taken into consideration factors such as what kind of applications will be used most often as well as expected usage levels over time so that you can choose accordingly;
2) Research Different Options – There are various types of plans available so make sure that you research each option thoroughly before making any decisions in order ensure maximum efficiency based on your specific usage requirements;
3) Make Use Of Discounts & Special Offers – If applicable take advantage of any discounts or special offers available at the time in order to get more bang for your buck when purchasing a plan from Amazon Web Services (AWS);
4) Monitor Usage Levels & Adjust Accordingly – Be sure to keep track of how much resources are being used over time so that adjustments can be made accordingly if needed in order to maximize efficiency while keeping costs down at the same time;
5) Utilize Automation Tools – Utilizing automation tools provided by third-party vendors such as Chef or Puppet can help streamline processes related to resource provisioning thus saving both time and money in the long run;
6) Leverage Support Resources Available – Making use of support resources available through official documentation tutorials blogs forums etc can help better understand how to utilize various features offered through this powerful cloud computing platform thus ensuring maximum efficiency while using the same.;
7) Take Advantage Of Free Trials – Many vendors offer free trials either through their websites or through third-party providers like Microsoft Azure so make sure to take advantage of these when possible to order and test out various features before committing anything financially.;
8) Consider Long-Term Commitments Carefully – When considering longer-term commitments like Reserved Instances make sure to look into details carefully terms conditions etc before signing anything ensure know exactly what you are getting into and avoid potential issues down the road.;
9) Monitor Costs Regularly – Lastly always monitor costs regularly to ensure staying within budget limits set forth before beginning the project thus avoiding unnecessary expenses.;
Best Aws Accounts AWS offers a wide range of accounts and services that cater to different needs and requirements, such as compute, storage, database, networking, security, and more. Some of the popular AWS accounts and services are:
Amazon EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud) for scalable computing capacity Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service) for scalable and durable object storage Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service) for managed relational databases Amazon VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) for isolated virtual networks Amazon Glacier for low-cost data archiving and backup Amazon Elastic Load Balancing for distributing incoming traffic across multiple instances Amazon Route 53 for scalable and reliable DNS (Domain Name System) routing Amazon CloudFront for delivering content and applications securely and fast globally Amazon Elasticsearch Service for scalable search and analytics The choice of the best AWS account depends on factors such as the workload type, processing power, memory and storage requirements, and budget. It’s recommended that individuals and businesses consult AWS documentation and support for guidance in choosing the right AWS accounts and services for their needs. So Buy verified AWS Accounts right now.
Final Comment To AWS Account To add to my previous comment, it’s worth noting that AWS has a global infrastructure with data centers located in multiple regions around the world. This enables businesses to deploy their applications closer to their users, resulting in lower latency and better performance.
aws accounts for sale
In addition, AWS offers a wide range of security features and compliance certifications, including encryption, network isolation, and access controls, to help businesses meet their security and compliance requirements.
Overall, AWS is a powerful cloud computing platform that provides businesses with the tools and services they need to run their applications and store their data in the cloud with ease, scalability, and security.
1 note
·
View note
Text
The Public vs Private Cloud Debate for Medical Imaging Data
Should healthcare organizations store medical imaging data in public or private clouds?
This question generates heated debate. Each option has distinct pros and cons that must be weighed given regulatory compliance, cost, and other factors.
This article explores key considerations to help providers pick the right cloud environment for their needs.
As medical imaging data continues its migration to the cloud, healthcare organizations face a pivotal decision - public or private deployment?
Choosing the optimal environment given organizational needs and constraints is crucial. The wrong pick can hinder care, inflate expenses, and put sensitive data at risk.
Public Cloud Benefits
Public clouds offer services over the open internet. Providers like AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure operate the infrastructure and lease it to customers. The public model offers advantages including:
Cost Savings
No capital expenditure on hardware and data centers
Pay only for services used based on consumption
Scale seamlessly up and down as needs change
Flexibility
Add and remove services on demand with no long-term contracts
Leverage unlimited on-demand computing resources
Deploy globally in minutes
Top-Tier Security
Physical security via global data centers
Built-in DDoS mitigation, firewalls, and intrusion detection
Automatic patching and upgrades
Innovation Pace
Constant introduction of new capabilities
Access to bleeding-edge services like AI and analytics
Future-proofed infrastructure
For many healthcare organizations, these benefits make public cloud infrastructure an appealing choice over managing their own private data centers.
Private Cloud Benefits
Private clouds provide dedicated infrastructure for a single organization. They offer:
Customization
Configure to meet unique needs
Integrate with existing systems and workflows
Control update cadence and system settings
Security
Isolation from other tenants
Set internal security protocols and auditing
Keep data within organization firewalls
Compliance
Meet regulations like HIPAA with configured controls
Limit data access to internal staff
Dictate geographic data location
Ownership
Retain infrastructure control
Avoid vendor lock-in
Set policies and procedures freely
For organizations hesitant to relinquish control to public vendors, private clouds allow them to retain oversight of data and systems.

Key Considerations
With the pros and cons in mind, how should healthcare providers approach the public versus private decision? Key factors to consider include:
Compliance Requirements
HIPAA regulations apply regardless of environment. However, private clouds simplify some aspects of compliance like HIPAA-mandated audits and access controls. Public clouds obligate you to validate vendor controls.
Security Maturity
Public cloud security requires trusting vendor capabilities. Private clouds let you dictate controls but require internal security expertise. Consider your team’s skills before leaning public.
Hybrid Approach
Hybrid models combining public and private resources provide a middle ground. Sensitive data can reside in private infrastructure while public resources handle other workloads.
Cost Tradeoffs
Public clouds promote OpEx spending versus private cloud CapEx. But bandwidth and service fees can make public options less economical depending on data volumes. Model costs carefully.
Future Planning
Private clouds provide more predictability for capacity needs given their fixed resources. Public clouds readily scale but require planning to control costs.
Data Gravity
Once data is ingested into a particular cloud, it becomes more difficult to move due to complexity and costs. Choose wisely from the start.
There is no universal answer regarding public versus private deployment for medical imaging data. Organizations must carefully weigh the critical considerations above and match them to their specific requirements and constraints.
Architecting a Hybrid Solution
For many healthcare providers, a hybrid approach reaps the most benefits. Critical imaging data remains under internal control while public cloud resources handle other workloads. There are two primary options for structuring hybrid deployments:
Cloud Bursting - Augment private infrastructure with public cloud services when demand spikes occur. This avoids overprovisioning private data centers for peak capacity needs.
Cloud Offloading - Maintain mission-critical workloads internally while shifting other services to the public cloud. For example, put revenue cycle management applications in the public cloud but keep imaging data private.
0 notes