#A living computer “virus” that actually wants to help Thatcher out.
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Note
ooh in that case could we hear about thatcher or ruth :o
YEEAAA Sorry i'm just happy to be able to ramble a bit- /VLH
Thatcher. I'm thinking he's a werewolf but I haven't gotten a good idea of his design that. wouldn't just be alt au Thatcher- /VLH
Basically, he got turned on the investigation in the murray household, being attacked and bit by another werewolf, while Ruth. unfortunately died in the attack. Thatcher definitely. hates the fact that he's no longer fully human.
However, Ruth. is still around. in spirit anyway. She mainly talks through radios, but also really likes living in computers and only making herself known to Thatcher. she basically takes over the computer fully and can access anything said computer also can access. Kinda like. a sentient, less annoying and actually helpful Clippy.
Also I just finished a mock up of her design like less than an hour ago so here!
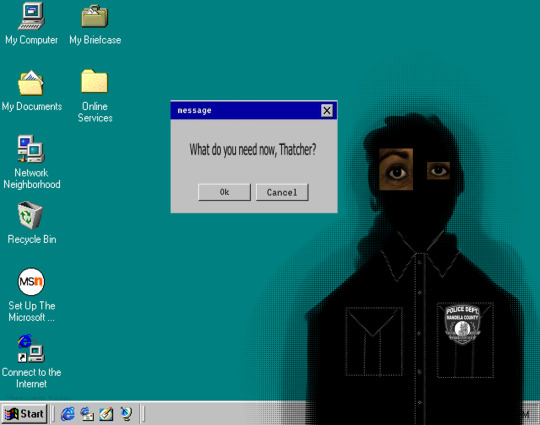
#asks are neat#tmc monster au#Virus Ruth#Monster Thatcher#Yeah. i'll tag them as that#unsettling#eye contact tw#shmorps art#Still working on Thatcher in this au but Ruth is decently developed.#A living computer “virus” that actually wants to help Thatcher out.#Oh yeah also the MCPD wants to cover up monsters existence and/or kill them#being the reason Ruth prefers to hide from them aside from Thatcher and why Thatcher doesn't want them to know HE TOO is a monster.#Thought I should. add that too-
107 notes
·
View notes
Text
If scientific discoveries and technological developments split humankind into a mass of useless humans and a small elite of upgraded superhumans, or if authority shifts altogether away from human beings into the hands of highly intelligent algorithms, then liberalism will collapse. What new religions or ideologies might fill the resulting vacuum and guide the subsequent evolution of our godlike descendants?
The new religions are unlikely to emerge from the caves of Afghanistan or from the madrasas of the Middle East. Rather, they will emerge from research laboratories. Just as socialism took over the world by promising salvation through steam and electricity, so in the coming decades new techno-religions may conquer the world by promising salvation through algorithms and genes.
Despite all the talk of radical Islam and Christian fundamentalism, the most interesting place in the world from a religious perspective is not the Islamic State or the Bible Belt, but Silicon Valley. That’s where hi-tech gurus are brewing for us brave new religions that have little to do with God, and everything to do with technology. They promise all the old prizes – happiness, peace, prosperity and even eternal life – but here on earth with the help of technology, rather than after death with the help of celestial beings.
These new techno-religions can be divided into two main types: techno-humanism and data religion. Techno-humanism agrees that Homo sapiens as we know it has run its historical course and will no longer be relevant in the future, but concludes that we should therefore use technology in order to create Homo deus – a much superior human model. Homo deus will retain some essential human features, but will also enjoy upgraded physical and mental abilities that will enable it to hold its own even against the most sophisticated non-conscious algorithms. Since intelligence is decoupling from consciousness, and since non-conscious intelligence is developing at breakneck speed, humans must actively upgrade their minds if they want to stay in the game.
Dataism says that the universe consists of data flows, and the value of any phenomenon or entity is determined by its contribution to data processing. This may strike you as some eccentric fringe notion, but in fact it has already conquered most of the scientific establishment. Dataism was born from the explosive confluence of two scientific tidal waves. In the 150 years since Charles Darwin published On the Origin of Species, the life sciences have come to see organisms as biochemical algorithms. Simultaneously, in the eight decades since Alan Turing formulated the idea of a Turing Machine, computer scientists have learned to engineer increasingly sophisticated electronic algorithms. Dataism puts the two together, pointing out that exactly the same mathematical laws apply to both biochemical and electronic algorithms. Dataism thereby collapses the barrier between animals and machines, and expects electronic algorithms to eventually decipher and outperform biochemical algorithms.
For politicians, business people and ordinary consumers, Dataism offers groundbreaking technologies and immense new powers. For scholars and intellectuals it also promises to provide the scientific holy grail that has eluded us for centuries: a single overarching theory that unifies all the scientific disciplines from literature and musicology to economics and biology. According to Dataism, King Lear and the flu virus are just two patterns of data flow that can be analysed using the same basic concepts and tools. This idea is extremely attractive. It gives all scientists a common language, builds bridges over academic rifts and easily exports insights across disciplinary borders. Musicologists, political scientists and cell biologists can finally understand each other.
In the process, Dataism inverts the traditional pyramid of learning. Hitherto, data was seen as only the first step in a long chain of intellectual activity. Humans were supposed to distil data into information, information into knowledge, and knowledge into wisdom. However, Dataists believe that humans can no longer cope with the immense flows of data, hence they cannot distil data into information, let alone into knowledge or wisdom. The work of processing data should therefore be entrusted to electronic algorithms, whose capacity far exceeds that of the human brain. In practice, this means that Dataists are sceptical about human knowledge and wisdom, and prefer to put their trust in Big Data and computer algorithms.
Dataism is most firmly entrenched in its two mother disciplines: computer science and biology. Of the two, biology is the more important. It was the biological embracement of Dataism that turned a limited breakthrough in computer science into a world-shattering cataclysm that may completely transform the very nature of life. You may not agree with the idea that organisms are algorithms, and that giraffes, tomatoes and human beings are just different methods for processing data. But you should know that this is current scientific dogma, and that it is changing our world beyond recognition.
Not only individual organisms are seen today as data-processing systems, but also entire societies such as beehives, bacteria colonies, forests and human cities. Economists increasingly interpret the economy, too, as a data-processing system. Laypeople believe that the economy consists of peasants growing wheat, workers manufacturing clothes, and customers buying bread and underpants. Yet experts see the economy as a mechanism for gathering data about desires and abilities, and turning this data into decisions.
According to this view, free-market capitalism and state-controlled communism aren’t competing ideologies, ethical creeds or political institutions. At bottom, they are competing data-processing systems. Capitalism uses distributed processing, whereas communism relies on centralised processing.
Capitalism did not defeat communism because capitalism was more ethical, because individual liberties are sacred or because God was angry with the heathen communists. Rather, capitalism won the Cold War because distributed data processing works better than centralised data processing, at least in periods of accelerating technological changes. The central committee of the Communist Party just could not deal with the rapidly changing world of the late twentieth century. When all data is accumulated in one secret bunker, and all important decisions are taken by a group of elderly apparatchiks, you can produce nuclear bombs by the cartload, but you won’t get an Apple or a Wikipedia.
There is a story (probably apocryphal, like most good stories) that when Mikhail Gorbachev tried to resuscitate the moribund Soviet economy, he sent one of his chief aids to London to find out what Thatcherism was all about, and how a capitalist system actually functioned. The hosts took their Soviet visitor on a tour of the City, of the London stock exchange and of the London School of Economics, where he had lengthy talks with bank managers, entrepreneurs and professors. After a few hours, the Soviet expert burst out: ‘Just one moment, please. Forget about all these complicated economic theories. We have been going back and forth across London for a whole day now, and there’s one thing I cannot understand. Back in Moscow, our finest minds are working on the bread supply system, and yet there are such long queues in every bakery and grocery store. Here in London live millions of people, and we have passed today in front of many shops and supermarkets, yet I haven’t seen a single bread queue. Please take me to meet the person in charge of supplying bread to London. I must learn his secret.’ The hosts scratched their heads, thought for a moment, and said: ‘Nobody is in charge of supplying bread to London.’
That’s the capitalist secret of success. No central processing unit monopolises all the data on the London bread supply. The information flows freely between millions of consumers and producers, bakers and tycoons, farmers and scientists. Market forces determine the price of bread, the number of loaves baked each day and the research-and-development priorities. If market forces make the wrong decision, they soon correct themselves, or so capitalists believe. For our current purposes, it doesn’t matter whether the theory is correct. The crucial thing is that the theory understands economics in terms of data processing.
[…] Dataism naturally has its critics and heretics. As we saw in Chapter 3, it’s doubtful whether life can really be reduced to data flows. In particular, at present we have no idea how or why data flows could produce consciousness and subjective experiences. Maybe we’ll have a good explanation in twenty years. But maybe we’ll discover that organisms aren’t algorithms after all.
It is equally doubtful whether life boils down to decision-making. Under Dataist influence, both the life sciences and the social sciences have become obsessed with decision-making processes, as if that’s all there is to life. But is it so? Sensations, emotions and thoughts certainly play an important part in making decisions, but is that their sole meaning? Dataism gains a better and better understanding of decision-making processes, but it might be adopting an increasingly skewed view of life.
[…] Of course, even if Dataism is wrong and organisms aren’t just algorithms, it won’t necessarily prevent Dataism from taking over the world. Many previous religions gained enormous popularity and power despite their factual mistakes. If Christianity and communism could do it, why not Dataism? Dataism has especially good prospects, because it is currently spreading across all scientific disciplines. A unified scientific paradigm may easily become an unassailable dogma. It is very difficult to contest a scientific paradigm, but up till now, no single paradigm was adopted by the entire scientific establishment. Hence scholars in one field could always import heretical views from outside. But if everyone from musicologists to biologists uses the same Dataist paradigm, interdisciplinary excursions will serve only to strengthen the paradigm further. Consequently even if the paradigm is flawed, it would be extremely difficult to resist it.
- Yuval Noah Harari, The Data Religion in Homo Deus: A Brief History of Tomorrow
7 notes
·
View notes