#2) Economic Reforms
Text
The Livret
“Under the Old Regime, the billet de congé was a document used as an instrument of control by employers. Workers had to hand over this document to their employer in order to be hired. Holding on to this document until a job had been completed to their satisfaction, employers made sure that workers could not leave them at will. The billet was a tool of subordination, since it allowed employers to write down an assessment of their employees that would be considered by the next person to hire them. Falling into disuse during the revolutionary decade, this practice became the object of a widespread debate that led workers, but also bosses and state administrators, to agree that Old Regime rules would not be restored. When the billet de congé was reinstated as the livret ouvrier by the Napoleonic state in 1803, its function was radically transformed by the application of revolutionary principles of reciprocity and equality to labour relations, under the auspices of tribunals and local authorities. The document had thus lost its disciplinary power, and the law that re-established it was in any case largely ignored by employers and labourers alike. Prud'hommes ensured that employers could not retain the livret, even in case of conflict with their employee, and labourers no longer faced criminal charges when unilaterally leaving their bosses. Moreover, according to a frequently reprinted circular by the Minister of the Interior, Montalivet, in 1809, [employers] were expressly prohibited from making any comment about a worker’s performance or ability on the livret itself. Far from restricting it, by acting as a way to establish private contracts (in accordance with customary usages), the livret had in fact become a means to facilitate the worker’s mobility.”
— Xavier Lafrance, The Making of Capitalism in France — Class Structures, Economic Development, the State and the Formation of the French Working Class, 1750-1914, ch. 3, p. 129-130
#The Making of Capitalism in France#livret ouvrier#billet de congé#Montalivet#napoleonic era#napoleonic#first french empire#french empire#history#19th century#1800s#france#Xavier Lafrance#working class#economics#economic history#napoleon#french history#Napoleon’s reforms#reforms#napoleonic reforms#Napoleon’s reforms 2
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
#Salarjung Reforms - Part 1 | Telangana History | TOne Academy | Balakrishna#Salarjung was the ancestral title conferred to Salar Jung at the age of 13. There were some changes made during his times. They were:-#1) Administrative Reforms#2) Economic Reforms#3) Revenue Reforms#4) Law Reforms#5) Educational Reforms#6) Police Reforms#7) Currency Reforms#8) Transport Reforms#9) Other Important Reforms#salarjungReforms#salarjung#telanganahistory#toneacademy#tspsc#telanganastatepublicservicecommission#history#importantReforms#For any queries/doubts/information - we are just an email away - mail us @ [email protected]#Subscribe to : https://bit.ly/2YQOgbs#Abolition Of Zamindari Act - https://youtu.be/HUVTHaEvl-E#Seasons - https://youtu.be/FtfdJiUYVPE#Problems on Time & Work Concept – 5 Efficiency - https://youtu.be/vAFcu4jaZ9Y#Indus Valley Civilization - Society - https://youtu.be/JFo0fnVlXTk#Fundamental Rights-Protection In Respect of Conviction for Offences Part-6 - https://youtu.be/APa4KcCmGp4#Latitudes And Longitudes - https://youtu.be/rx1nYENfuoE#Problems On Time and Work - Concept-3 Leaving and Joining-Part 3 - https://youtu.be/Ud4OuneetS0#Land Administration Under Nizams - https://youtu.be/3fEvTJpbCjw#Land Reforms- Intermediaries in Telangana - https://youtu.be/f8rjm2ATrg0
0 notes
Text
How to shatter the class solidarity of the ruling class

I'm touring my new, nationally bestselling novel The Bezzle! Catch me WEDNESDAY (Apr 11) at UCLA, then Chicago (Apr 17), Torino (Apr 21) Marin County (Apr 27), Winnipeg (May 2), Calgary (May 3), Vancouver (May 4), and beyond!

Audre Lorde counsels us that "The Master's Tools Will Never Dismantle the Master's House," while MLK said "the law cannot make a man love me, but it can restrain him from lynching me." Somewhere between replacing the system and using the system lies a pragmatic – if easily derailed – course.
Lorde is telling us that a rotten system can't be redeemed by using its own chosen reform mechanisms. King's telling us that unless we live, we can't fight – so anything within the system that makes it easier for your comrades to fight on can hasten the end of the system.
Take the problems of journalism. One old model of journalism funding involved wealthy newspaper families profiting handsomely by selling local appliance store owners the right to reach the townspeople who wanted to read sports-scores. These families expressed their patrician love of their town by peeling off some of those profits to pay reporters to sit through municipal council meetings or even travel overseas and get shot at.
In retrospect, this wasn't ever going to be a stable arrangement. It relied on both the inconstant generosity of newspaper barons and the absence of a superior way to show washing-machine ads to people who might want to buy washing machines. Neither of these were good long-term bets. Not only were newspaper barons easily distracted from their sense of patrician duty (especially when their own power was called into question), but there were lots of better ways to connect buyers and sellers lurking in potentia.
All of this was grossly exacerbated by tech monopolies. Tech barons aren't smarter or more evil than newspaper barons, but they have better tools, and so now they take 51 cents out of every ad dollar and 30 cents out of ever subscriber dollar and they refuse to deliver the news to users who explicitly requested it, unless the news company pays them a bribe to "boost" their posts:
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2023/04/saving-news-big-tech
The news is important, and people sign up to make, digest, and discuss the news for many non-economic reasons, which means that the news continues to struggle along, despite all the economic impediments and the vulture capitalists and tech monopolists who fight one another for which one will get to take the biggest bite out of the press. We've got outstanding nonprofit news outlets like Propublica, journalist-owned outlets like 404 Media, and crowdfunded reporters like Molly White (and winner-take-all outlets like the New York Times).
But as Hamilton Nolan points out, "that pot of money…is only large enough to produce a small fraction of the journalism that was being produced in past generations":
https://www.hamiltonnolan.com/p/what-will-replace-advertising-revenue
For Nolan, "public funding of journalism is the only way to fix this…If we accept that journalism is not just a business or a form of entertainment but a public good, then funding it with public money makes perfect sense":
https://www.hamiltonnolan.com/p/public-funding-of-journalism-is-the
Having grown up in Canada – under the CBC – and then lived for a quarter of my life in the UK – under the BBC – I am very enthusiastic about Nolan's solution. There are obvious problems with publicly funded journalism, like the politicization of news coverage:
https://www.theguardian.com/media/2023/jan/24/panel-approving-richard-sharp-as-bbc-chair-included-tory-party-donor
And the transformation of the funding into a cheap political football:
https://www.cbc.ca/news/politics/poilievre-defund-cbc-change-law-1.6810434
But the worst version of those problems is still better than the best version of the private-equity-funded model of news production.
But Nolan notes the emergence of a new form of hedge fund news, one that is awfully promising, and also terribly fraught: Hunterbrook Media, an investigative news outlet owned by short-sellers who pay journalists to research and publish damning reports on companies they hold a short position on:
https://hntrbrk.com/
For those of you who are blissfully distant from the machinations of the financial markets, "short selling" is a wager that a company's stock price will go down. A gambler who takes a short position on a company's stock can make a lot of money if the company stumbles or fails altogether (but if the company does well, the short can suffer literally unlimited losses).
Shorts have historically paid analysts to dig into companies and uncover the sins hidden on their balance-sheets, but as Matt Levine points out, journalists work for a fraction of the price of analysts and are at least as good at uncovering dirt as MBAs are:
https://www.bloomberg.com/opinion/articles/2024-04-02/a-hedge-fund-that-s-also-a-newspaper
What's more, shorts who discover dirt on a company still need to convince journalists to publicize their findings and trigger the sell-off that makes their short position pay off. Shorts who own a muckraking journalistic operation can skip this step: they are the journalists.
There's a way in which this is sheer genius. Well-funded shorts who don't care about the news per se can still be motivated into funding freely available, high-quality investigative journalism about corporate malfeasance (notoriously, one of the least attractive forms of journalism for advertisers). They can pay journalists top dollar – even bid against each other for the most talented journalists – and supply them with all the tools they need to ply their trade. A short won't ever try the kind of bullshit the owners of Vice pulled, paying themselves millions while their journalists lose access to Lexisnexis or the PACER database:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/02/24/anti-posse/#when-you-absolutely-positively-dont-give-a-solitary-single-fuck
The shorts whose journalists are best equipped stand to make the most money. What's not to like?
Well, the issue here is whether the ruling class's sense of solidarity is stronger than its greed. The wealthy have historically oscillated between real solidarity (think of the ultrawealthy lobbying to support bipartisan votes for tax cuts and bailouts) and "war of all against all" (as when wealthy colonizers dragged their countries into WWI after the supply of countries to steal ran out).
After all, the reason companies engage in the scams that shorts reveal is that they are profitable. "Behind every great fortune is a great crime," and that's just great. You don't win the game when you get into heaven, you win it when you get into the Forbes Rich List.
Take monopolies: investors like the upside of backing an upstart company that gobbles up some staid industry's margins – Amazon vs publishing, say, or Uber vs taxis. But while there's a lot of upside in that move, there's also a lot of risk: most companies that set out to "disrupt" an industry sink, taking their investors' capital down with them.
Contrast that with monopolies: backing a company that merges with its rivals and buys every small company that might someday grow large is a sure thing. Shriven of "wasteful competition," a company can lower quality, raise prices, capture its regulators, screw its workers and suppliers and laugh all the way to Davos. A big enough company can ignore the complaints of those workers, customers and regulators. They're not just too big to fail. They're not just too big to jail. They're too big to care:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/04/04/teach-me-how-to-shruggie/#kagi
Would-be monopolists are stuck in a high-stakes Prisoner's Dilemma. If they cooperate, they can screw over everyone else and get unimaginably rich. But if one party defects, they can raid the monopolist's margins, short its stock, and snitch to its regulators.
It's true that there's a clear incentive for hedge-fund managers to fund investigative journalism into other hedge-fund managers' portfolio companies. But it would be even more profitable for both of those hedgies to join forces and collude to screw the rest of us over. So long as they mistrust each other, we might see some benefit from that adversarial relationship. But the point of the 0.1% is that there aren't very many of them. The Aspen Institute can rent a hall that will hold an appreciable fraction of that crowd. They buy their private jets and bespoke suits and powdered rhino horn from the same exclusive sellers. Their kids go to the same elite schools. They know each other, and they have every opportunity to get drunk together at a charity ball or a society wedding and cook up a plan to join forces.
This is the problem at the core of "mechanism design" grounded in "rational self-interest." If you try to create a system where people do the right thing because they're selfish assholes, you normalize being a selfish asshole. Eventually, the selfish assholes form a cozy little League of Selfish Assholes and turn on the rest of us.
Appeals to morality don't work on unethical people, but appeals to immorality crowds out ethics. Take the ancient split between "free software" (software that is designed to maximize the freedom of the people who use it) and "open source software" (identical to free software, but promoted as a better way to make robust code through transparency and peer review).
Over the years, open source – an appeal to your own selfish need for better code – triumphed over free software, and its appeal to the ethics of a world of "software freedom." But it turns out that while the difference between "open" and "free" was once mere semantics, it's fully possible to decouple the two. Today, we have lots of "open source": you can see the code that Google, Microsoft, Apple and Facebook uses, and even contribute your labor to it for free. But you can't actually decide how the software you write works, because it all takes a loop through Google, Microsoft, Apple or Facebook's servers, and only those trillion-dollar tech monopolists have the software freedom to determine how those servers work:
https://pluralistic.net/2020/05/04/which-side-are-you-on/#tivoization-and-beyond
That's ruling class solidarity. The Big Tech firms have hidden a myriad of sins beneath their bafflegab and balance-sheets. These (as yet) undiscovered scams constitute a "bezzle," which JK Galbraith defined as "the magic interval when a confidence trickster knows he has the money he has appropriated but the victim does not yet understand that he has lost it."
The purpose of Hunterbrook is to discover and destroy bezzles, hastening the moment of realization that the wealth we all feel in a world of seemingly orderly technology is really an illusion. Hunterbrook certainly has its pick of bezzles to choose from, because we are living in a Golden Age of the Bezzle.
Which is why I titled my new novel The Bezzle. It's a tale of high-tech finance scams, starring my two-fisted forensic accountant Marty Hench, and in this volume, Hench is called upon to unwind a predatory prison-tech scam that victimizes the most vulnerable people in America – our army of prisoners – and their families:
https://us.macmillan.com/books/9781250865878/thebezzle
The scheme I fictionalize in The Bezzle is very real. Prison-tech monopolists like Securus and Viapath bribe prison officials to abolish calls, in-person visits, mail and parcels, then they supply prisoners with "free" tablets where they pay hugely inflated rates to receive mail, speak to their families, and access ebooks, distance education and other electronic media:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/04/02/captive-customers/#guillotine-watch
But a group of activists have cornered these high-tech predators, run them to ground and driven them to the brink of extinction, and they've done it using "the master's tools" – with appeals to regulators and the finance sector itself.
Writing for The Appeal, Dana Floberg and Morgan Duckett describe the campaign they waged with Worth Rises to bankrupt the prison-tech sector:
https://theappeal.org/securus-bankruptcy-prison-telecom-industry/
Here's the headline figure: Securus is $1.8 billion in debt, and it has eight months to find a financier or it will go bust. What's more, all the creditors it might reasonably approach have rejected its overtures, and its bonds have been downrated to junk status. It's a dead duck.
Even better is how this happened. Securus's debt problems started with its acquisition, a leveraged buyout by Platinum Equity, who borrowed heavily against the firm and then looted it with bogus "management fees" that meant that the debt continued to grow, despite Securus's $700m in annual revenue from America's prisoners. Platinum was just the last in a long line of PE companies that loaded up Securus with debt and merged it with its competitors, who were also mortgaged to make profits for other private equity funds.
For years, Securus and Platinum were able to service their debt and roll it over when it came due. But after Worth Rises got NYC to pass a law making jail calls free, creditors started to back away from Securus. It's one thing for Securus to charge $18 for a local call from a prison when it's splitting the money with the city jail system. But when that $18 needs to be paid by the city, they're going to demand much lower prices. To make things worse for Securus, prison reformers got similar laws passed in San Francisco and in Connecticut.
Securus tried to outrun its problems by gobbling up one of its major rivals, Icsolutions, but Worth Rises and its coalition convinced regulators at the FCC to block the merger. Securus abandoned the deal:
https://worthrises.org/blogpost/securusmerger
Then, Worth Rises targeted Platinum Equity, going after the pension funds and other investors whose capital Platinum used to keep Securus going. The massive negative press campaign led to eight-figure disinvestments:
https://www.latimes.com/business/story/2019-09-05/la-fi-tom-gores-securus-prison-phone-mass-incarceration
Now, Securus's debt became "distressed," trading at $0.47 on the dollar. A brief, covid-fueled reprieve gave Securus a temporary lifeline, as prisoners' families were barred from in-person visits and had to pay Securus's rates to talk to their incarcerated loved ones. But after lockdown, Securus's troubles picked up right where they left off.
They targeted Platinum's founder, Tom Gores, who papered over his bloody fortune by styling himself as a philanthropist and sports-team owner. After a campaign by Worth Rises and Color of Change, Gores was kicked off the Los Angeles County Museum of Art board. When Gores tried to flip Securus to a SPAC – the same scam Trump pulled with Truth Social – the negative publicity about Securus's unsound morals and financials killed the deal:
https://twitter.com/WorthRises/status/1578034977828384769
Meanwhile, more states and cities are making prisoners' communications free, further worsening Securus's finances:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/02/14/minnesota-nice/#shitty-technology-adoption-curve
Congress passed the Martha Wright-Reed Just and Reasonable Communications Act, giving the FCC the power to regulate the price of federal prisoners' communications. Securus's debt prices tumbled further:
https://www.govtrack.us/congress/bills/117/s1541
Securus's debts were coming due: it owes $1.3b in 2024, and hundreds of millions more in 2025. Platinum has promised a $400m cash infusion, but that didn't sway S&P Global, a bond-rating agency that re-rated Securus's bonds as "CCC" (compare with "AAA"). Moody's concurred. Now, Securus is stuck selling junk-bonds:
https://www.govtrack.us/congress/bills/117/s1541
The company's creditors have given Securus an eight-month runway to find a new lender before they force it into bankruptcy. The company's debt is trading at $0.08 on the dollar.
Securus's major competitor is Viapath (prison tech is a duopoly). Viapath is also debt-burdened and desperate, thanks to a parallel campaign by Worth Rises, and has tried all of Securus's tricks, and failed:
https://pestakeholder.org/news/american-securities-fails-to-sell-prison-telecom-company-viapath/
Viapath's debts are due next year, and if Securus tanks, no one in their right mind will give Viapath a dime. They're the walking dead.
Worth Rise's brilliant guerrilla warfare against prison-tech and its private equity backers are a master class in using the master's tools to dismantle the master's house. The finance sector isn't a friend of justice or working people, but sometimes it can be used tactically against financialization itself. To paraphrase MLK, "finance can't make a corporation love you, but it can stop a corporation from destroying you."
Yes, the ruling class finds solidarity at the most unexpected moments, and yes, it's easy for appeals to greed to institutionalize greediness. But whether it's funding unbezzling journalism through short selling, or freeing prisons by brandishing their cooked balance-sheets in the faces of bond-rating agencies, there's a lot of good we can do on the way to dismantling the system.

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/04/08/money-talks/#bullshit-walks

Image:
KMJ (modified)
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Boerse_01_KMJ.jpg
CC BY-SA 3.0
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/deed.en
#pluralistic#shorts#short sellers#news#private equity#private prisons#securus#prison profiteers#the bezzle#anything that cant go on forever eventually stop#steins law#hamilton nolan#Platinum Equity#American Securities#viapath#global tellink#debt#jpay#worth rises#insurance#spacs#fcc#bond rating#moodys#the appeal#saving the news from big tech#hunterbrook media#journalism
804 notes
·
View notes
Text

https://www.washingtonpost.com/business/interactive/2024/us-sanction-countries-work/?itid=ap_jeffstein
NEW: THE STAGGERING RISE OF AMERICA'S GLOBAL ECONOMIC WARFARE (summary by author Jeff Stein from twitter)
1. ~1/3 of all nations on Earth now face some form of US sanctions. Huge increase from when mostly applied to Cuba & a handful of regimes
2. +*60%* of *all poor countries* are under US sanctions of some kind. Has become almost a reflex of US foreign policy
3. Sanctions have spawned multi-billion-dollar lobbying & influence industry, enriching former US officials who are hired by foreign countries & oligarchs
4. Sanctions have had devastating effects on innocent civilians. In Cuba, they've made critical medical supplies impossible to import. In Venezuela, they contributed to a financial collapse 3X greater than the US Great Depression. Syria faces its greatest humanitarian crisis this year after a decade civil war & sanctions.
5. Treasury staffers drafted a ~40 page plan aimed at reforming the sanctions process that was dramatically whittled down amid disagreements w/ State
6. OFAC is widely described as overwhelmed by tens of thousands of requests. WH officials have brainstormed sanctions scenarios w/ outside nonprofits
7. Biden has unleashed unprecedented volley of +6K sanctions in 2 years. Higher than even previously unprecedented rate of Trump.
“We don’t think about the collateral damage of sanctions the same way we think about the collateral damage of war ... But we should.”
763 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Expanding freedom and opportunity to millions
Over a decade ago, researchers, policymakers, journalists, and individuals and family members harmed by prisons and jails helped define American mass incarceration as one of the fundamental policy challenges of our time. In the years since, policymakers and voters in red, blue, and purple jurisdictions have advanced criminal justice reforms that safely reduced prison and jail populations, expanding freedom and opportunities to tens of millions of Americans.
After nearly forty years of uninterrupted prison population growth, our collective awareness of the costs of mass incarceration has fundamentally shifted–and our sustained efforts to turn the tide have yielded meaningful results.

Since its peak in 2009, the number of people in prison has declined by 24 percent (see figure 1). The total number of people incarcerated has dropped 21 percent since the 2008 peak of almost 2.4 million people, representing over 500,000 fewer people behind bars in 2022. Absent reforms, more than 40 million more people would have been admitted to prison and jail over this period. The number of people on probation and parole supervision has also dropped 27 percent since its peak in 2007, allowing many more people to live their lives free from onerous conditions that impede thriving and, too often, channel them back into incarceration for simple rule violations.1
"Absent reforms, more than 40 million more people would have been admitted to prison and jail over this period. [2008 to 2022]"
Make no mistake: mass incarceration and the racial and economic disparities it drives continue to shape America for the worse. The U.S. locks up more people per capita and imposes longer sentences than most other countries. Nearly 1-in-2 adults in the U.S. have an immediate family member that has been incarcerated, with lifelong, often multigenerational, consequences for family members’ health and financial stability. Yet the past decade of successful reforms demonstrate that we can and must continue to reduce incarceration. These expansions of freedom and justice–and the millions of people they have impacted–help define what is at stake as public safety has reemerged as a dominant theme in American public and political conversation.
...We have a robust body of research built over decades showing that jail stays and long prison sentences do not reduce crime rates. And fortunately, we have an extensive and expanding body of research on what does work to reduce crime and keep communities safe. The evidence is clear: our focus must be on continuing and accelerating reductions in incarceration.
Black imprisonment rate drops by nearly half
People directly impacted by incarceration and other leaders in the criminal justice reform movement have persistently called out how the unequal application of policies such as bail, sentencing, and parole (among others) drive massive racial disparities in incarceration. The concerted effort to reduce our prison population has had the most impact on the group that paid the greatest price during the rise of mass incarceration: Black people, and particularly Black men.

The Black imprisonment rate has declined by nearly 50 percent since the country’s peak imprisonment rate in 2008 (see figure 2). And between 1999 and 2019, the Black male incarceration rate dropped by 44 percent, and notable declines in Black male incarceration rates were seen in all 50 states. For Black men, the lifetime risk of incarceration declined by nearly half from 1999 to 2019—from 1 in 3 Black men imprisoned in their lifetime to 1 in 5.
While still unacceptably high, this reduction in incarceration rates means that Black men are now more likely to graduate college than go to prison, a flip from a decade ago. This change will help disrupt the cycle of incarceration and poverty for generations to come.
Expanding safety and justice together
The past decade-plus of incarceration declines were accompanied by an increase in public safety. From 2009-2022, 45 states saw reductions in crime rates, while imprisoning fewer people, with crime falling faster in states that reduced imprisonment than in states that increased it.
This is in keeping with the extensive body of research showing that incarceration is among the least effective and most expensive means to advance safety. Our extremely long sentences don’t deter or prevent crime. In fact, incarcerating people can increase the likelihood people will return to jail or prison in the future. Public safety and a more fair and just criminal system are not in conflict.
Strong and widespread support for reform
We have also seen dramatic progress on the public opinion front, with a clear understanding from voters that the criminal justice system needs more reform, not less. Recent polling shows that by a nearly 2 to 1 margin respondents prefer addressing social and economic problems over strengthening law enforcement to reduce crime. [In simpler terms: people are twice as likely to prefer non-law-enforcement solutions to crimes.]
Nearly nine-in-ten Black adults say policing, the judicial process, and the prison system need major changes for Black people to be treated fairly. Seventy percent of all voters (see figure 3) and 80 percent of Black voters believe it’s important to reduce the number of people in jail and prison. Eighty percent of all voters, including nearly three-fourths of Republican voters, support criminal justice reforms.

This is not only a blue state phenomenon. Recent polling in Mississippi indicates strong support across the political spectrum for bold policies that reduce incarceration. For example, according to polling from last month, 72 percent of Mississippians, including majorities from both parties, believe it is important to reduce the number of people in prison (see figure 4). Perhaps most tellingly, across the country victims of crime also support further reforms to our criminal justice system over solutions that rely on jail stays and harsh prison sentences...
We are at an inflection point: we can continue to rely on the failed mass incarceration tactics of the past, or chart a new path that takes safety seriously by continuing to reform our broken criminal justice system and strengthening families and communities."
-via FWD.us, May 15, 2024
#REFORMS HAVE ALREADY SAVED OVER 40 MILLION PEOPLE FROM ENTERING JAILS AND PRISONS#THAT ALONE IS A MASSIVE MASSIVE ACCOMPLISHMENT#never doubt that we CAN make a difference#no matter how long it takes#we are going to build a better and freer world#whether those in power want us to or not#mass incarceration#prison#prison system#racism#united states#us politics#systemic racism#incarcerated people#incarceration#criminal justice#criminal justice reform#crime rate#prison industrial complex#good news#hope
406 notes
·
View notes
Text
Mansfield Park - Henry Crawford and Fanny Price
I want to lay out how I see these characters and their relationship, because to me they seem to be set up as a deliberate contrast to Pride and Prejudice. At the tine of Henry’s first proposal, they are in a similar place to Elizabeth and Darcy at the time of Darcy’s first proposal, albeit with extremely different personalities than those characters: Fanny refuses him despite his wealth and her economic precarity because she cannot like or even respect him. However, Fanny, who is far shyer than Elizabeth, cannot lay out in direct and specific terms the foundation of her disapprobation of him.
From there, Henry sets out to win her regard in ways that very closely recall some of the events between Elizabeth and Darcy.
1) He does a great favour for a relative of hers. In his case, it is getting his uncle the admiral to have Fanny’s brother William promoted to lieutenant; in Darcy’s, it is saving the Bennets from disgrace by getting Wickham to marry Lydia. Darcy’s favour is far greater, and much more personally unpleasant for him, and he keeps it intentionally secret; he does it out of love of Elizabeth, but not to make her feel obligated. Henry’s takes only a few days of his time, its goal is get to Fanny to like him better, and he leverages it both at first and later to make her feel obliged to him.
2) He changes his manners to suit her. In Darcy’s case this means being polite rather than rude and haughty; in the case of Henry, who has always been charming and gregarious, it involves softening his manners to suit Fanny’s shy and quiet personality and engaging in more serious talk. In Darcy’s case this is a fundamental change in response to Elizabeth’s reproof; in Henry’s, it’s a simple adaptation to one person’s taste rather than another. He’s intelligent and able to engage in serious conversation when he wants to, but that’s not indicative of any fundamental change in his thinking.
3) He is polite to her family (the Prices, in Portsmouth) even when they are embarrassing.
4) He speaks with Fanny about reforms he is making on his estates to make sure his tenants are being treated fairly. These feels like a parallel to Elizabeth’s improved opinion of Darcy upon visiting Pemberley and hearing how well his servants speak of him. The difference is that Darcy has always been like that, whereas we are told early in Mansfield Park that Henry has been little on his estates during his adulthood: “To any thing like a permanence of abode, Henry Crawford had…a great dislike”. Darcy is acting in line with deep-seated principles; Henry is doing it as part of his courtship of Fanny, so he can bring it up to her and look good. He also tries to get her to counsel him to continue in this current vein, to engage her in a desire to fix/improve him, which Fanny shuts down laudably: “I advise! - you know very well what is right,” and when he reples that he always knows what is right when she tells him: “We all have a better guide in ourselves, if we would attend to it, than any other person could be.” The weakness of Henry’s motivation is seen in the ending, where he puts off a visit to his estates to set matters right there in order to flirt with the now-married Maria Rushworth.
In short, Darcy is already good in many concrete ways, and sincerely improves in the ways where he is faulty, not in order to get Elizabeth to love him but because he thinks about her criticisms, agrees with them, and wants to be better for its own sake; and he helps her family solely out of love for her and deliberately hides it. Henry changes his manner and talk as part of his courtship, but his deeper values and attitudes do not change, and everything is directed at getting Fanny to fall for him.
The second area of contrast is in what the heroines object to. Elizabeth’s aspersions on Darcy’s character, regarding his interactions with Wickham, are found to be mistaken; her legitimate objections are to his attitude and arrogance, and he amends this. Henry’s manners are impeccable and his company charming; Fanny’s objections are to his character. She sees him deliberately flirt with both her cousins at once to a degree that implies an intent to propose, and play them off against one another; she sees him make some very deliberate and mutually-understood innuendo towards Maria, signifying that she should break off her engagement and be with him instead, all with zero intention of actually proposing if she did do so; she sees him use the theatricals to continue this pursuit of Maria. And this is very usual behaviour for Henry; his sister says he has broken many hearts, and when he starts courting Fanny his goal is to make her fall in love with him and then leave her “feeling she will never be happy again”.
This is what makes me judge Henry much more harshly than his sister Mary. Mary can be selfish, but she is not malicious or cruel, and she can be kind when it doesn’t inconvenience her (and one of her better traits is that even when she is unhappy or disappointed she never takes it out on other people). In contrast, Henry’s principal diversion and entertainment for years has been deliberately making young women miserable, leading them on, getting them to reject other suitors in hopes of him, and then departing without a care, to please his own vanity. He is, in truth, doing not once but habitually, what Willoughby did to Marianne: always implying enough to seem on the edge of an engagement but never following through, and then pretending it was all nothing. It’s a casual cruelty he finds amusing as a proof of his skills. In short, he’s a deceptive playboy. Even after Maria is married, he can’t resist flirting with her, which is what leads to her disgrace and social destruction.
Even though Austen lays out an alternative scenario where Henry might have married Fanny if not for that final flirtation with Maria Rushworth, all of the above does not lead me to believe she find that scenario desirable. She’s painstakingly laid out all the contrasts with her previous novel that make this scenario a very different one from Pride and Prejudice.
In addition to Henry’s serial seductions, one of the biggest red flags is his attempt to make Fanny responsible for his character, with an attitude of ‘you’re such an angel, you can make me do whatever you want’. This gives me Tenant of Wildfell Hall vibes, where Helen’s aunt tries to warn her off thinking that an older man of the world will let himself be guided and led by a younger woman who is in his power. Fanny rejects this idea: Henry knows what is right, can make his own choice to do it, and she will not let herself be appropriated as his conscience. Henry isn’t debauched like Huntington, but if Fanny married him the chances of him feeling bored after some years - when he no longer has the thrill of the pursuit to keep him interested - and pursuing other flirtations and affairs to Fanny’s misery, seems pretty high based on his character; and he’s skilled enough at skirting the line that he could easily brush away any objections from her as “oh, it’s nothing, just being sociable.”
On top of all the faults of character - even if Henry did reform, I have trouble seeing Fanny and Henry being happy together. At the core of his personality is a need for change, for stimulus, for challenge (the latter, rather than sexual desire, is the main thing driving his string of conquests), and for company. Fanny, in contrast, very much prefers quiet and the company of a few people she is close to, and I think this is her genuine personality, not something that needs to be overcome by “bringing her out of her shell”. Henry would be bored to misery living the kind of lifestyle that Fanny is comfortable with, and Fanny would be deeply unhappy living in the social whirl and flurry of activity that Henry prefers. In contrast, Fanny and Edmund are both “me after a quiet day in: time for a quiet night in” people.
So, with all this, why is Henry/Fanny a popular AU? Apart from fannish dislike of Edmund (which I don’t share), I think part of it is that we don’t get an open confrontation between Fanny and Henry, the way we do between Elizabeth and Darcy, where she lays out her objections to him: I saw you flirting with both my cousins at once, I saw you making them both unhappy for your own amusement, I saw you repeatedly tempting Maria to break her engagement with no intention of following through if she did, just because you liked the challenge of winning an engaged woman. And the lack of this naturally raises the question of: how would Henry react if this confrontation happened? Which provides fertile soil for AUs.
211 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hii I read Socialism with Chinese Characteristics (2022) by Roland Boer, a Chinese Marxist professor, recently, and I think it conflicts with something on your old blog. It says that there's no fundamental incompatibility between a market economy, private ownership, and socialist governance, because markets under socialism have a different character and don't lead to bourgeois class consciousness. It says that the correct move for the CPC is to address the problems caused by reform (corruption, environmental costs, labor law skirting, income inequality, etc) individually, rather than rolling the reform process back by renationalizing industries. It says that this should be done because there still needs to be a focus on improving productive capacity over increasing CPC control over anything. It says that Xi's decision to "deepen reform" shows a commitment to solving the problems of privatization without reversing the process. (If I've interpreted correctly everything the book is saying.) In the past, though, you've expressed hope for more nationalization and used proof of modern nationalizations to justify that the CPC is moving China towards communism. What are your current thoughts on this?
Heyo! I'll have reread the book to truly answer but I think there's a couple points of context that might help.
The first is that there's 2 periods of reform. The reform and opening up (GGKF) period starting in 1979, characterized by special economic zones, market reforms, and PRC integration into the imperialist lead world economy. The second period began in the 2010s around the time of Xi Jinping's presidency. This latter reform saw the PRC take a departure from GGKF policies to reinstate state control, nationalization, anti-corruption reform, and social welfare expansion including the poverty alleviation campaign. In essence, it can be described as beginning a rollback of GGKF policies. Based on what you've mentioned, the author is likely referring to the latter reform period.
Second, because the CPC is not a monolithic organization, there's differing stances within in on approaches to political-economy. The author takes a more conservative approach, that is, a slower cautious approach which primarily highlights the contradiction between the PRC's productive forces and capacity against that of its own material needs and the forces of the west. On the other hand, I would be more akin to the radical approach (though i understand the worries of the conservative approach) which advocates for more state control, social welfare reform, and advancing class struggle to primarily address the internal contradictions that were sharpened by GGKF. The CPC line falls somewhere in the middle. Since, based on their actions, have adopted policies that reflect both sides.
42 notes
·
View notes
Text
i feel like given the genre and the nature of most power fantasy books and how frankly PIDW clearly had a tongue and cheek humor to it that you find the in the genre that Shang Qinghua's biggest regret is probably making every prominent enough to have mention as a political figure character... to put it nicely an idiot.
Tell me a single shameless power fantasy where the politicians or lords have an eight of a braincell collected between their ears. Outside of Mobei-Jun and Sha Hauling i doubt these generals and lords have any real common sense half the time. They're either yes men, schemers, or too stupid to live. Sometimes all three. Imagine dealing with that?
Imagine having to deal with that? Have you ever been in project management? Have you ever had to scream as you work project management in food service especially? Ever work for a branch of government? I only have 2 coworkers in those categories and I want them dead yesterday. How do you think he feels?
I like to believe that Shang Qinghua's real form of suffering is that he is forced to forever mop up a broken economic and political system of his own making while his coworkers make him wonder how ethical it would be to murder them systematically and replace them with his own puppets or maybe if he should do active political reform and just say fuck it. I'm immortal. I can wait these bitches out.
I have time to become the autocratic dictator so i never have to deal with anyone again. Like An Ding must feel like a luxury bath for him brain in comparison. Those guys listen to him and understand logistics. And unlike lord general whatever characters would make this joke work Suckka Dic of the northwester providence or whatever man isn't insisting they spend the entire budget on a war boat for a landlocked region. An Ding is just like 'here is the monthly budget. here is the allotted broken doors fund. here is what we'll be buying for the incoming quarter for supplies. Here are allotted variables for changes we can expect. invest in these stocks. cool we're done.'
it's just funny you know
#svsss#scumbag system#svsss shitpost#shang qinghua#meta#scum villain#scum villian self saving system#svsss sqh#sqh#scumbag self saving system#moshang
206 notes
·
View notes
Text
I think there are three large classes of socialist concern, which are not reducible to each other and which require different types of solutions. I would describe them as follows:
Distributional concerns — Markets tend towards inequality, and thus even in times of abundance fail to allocate resources to people who need them.
Concerns over autonomy — Private control of resources, especially when it is highly concentrated, comes at the cost of the autonomy of those who don't control the resources. As a significant special case of this, private control of the means of production deprives workers of autonomy over their own work, which constitutes most of their waking lives. Concentration of property in the hands of the few leaves most people with no choice but to sell their labor, turning them into workers deprived of autonomy in the above sense.
Humanistic concerns — Markets optimize for specific outcomes and, furthermore, the desirable properties of market economies are predicated on the existence of firms which optimize for profit. In both cases these optimization procedures are premature; they do not factor in the full human condition and thus come at the cost of many things which people find desirable.
In my view, a successful socialist program must at least attempt to address all three of these concerns. Often when debating other socialists, I feel that they err by focusing on some of these concerns to the exclusion of the others.
I have listed these concerns in order of how difficult I believe them to be to solve. Concern (1) can, in fact, be solved relatively easily even within a liberal economic system, by implementing massive redistributive taxes that equalize wealth. I want to stress that this proposal is still radical by the standards of any nation on earth today, but a solution is easy to imagine. And all these problems are interrelated; solving (1), for instance, would go a long way towards remedying (2).
Concern (2) can also, I think, be solved or at least greatly mitigated under a market framework, though not a classical liberal one. Replacing private firms wholesale with worker co-ops would go along way towards addressing (2), and in combination with the above solution for (1) provides I think the easiest to conceptualize vision of what a workable socialist (socialist enough) economy might look like.
Concern (3) is by far the hardest to address—it is in essence just the alignment problem as applied to economic systems. Suffice it to say, the problem remains open.
A common theme I see in debates between certain (usually more liberal-leaning) practically-minded socialists and certain (usually more radical) utopian-minded socialists is that the practical socialist will propose some solution that aims to address (1) and (2), and the more utopian-minded socialist will respond with vague and often not particularly coherent accusations of insufficient radicalism. The practical socialist will often then reply by dismissing the utopian's criticisms as nothing but hot air, as unserious radical posturing. But I think this represents an unfortunate misunderstanding. That utopian is often pointing at something real, even if it is articulated in a way that offends more pragmatic sensibilities. Concern (3) touches on every part of human life, I think it's fair to say, and though the habit of incoherently blaming everything that goes wrong on capitalism is not that useful, it doesn't point at nothing.
The alignment problem is not solved in the general case, but there are things we can change about a system to try and make it more aligned with specific, known goals. So the job of a good socialist (or really, anyone interested in any kind of political reform) should then be to listen to the ways in which people are dissatisfied with their lives, even when articulated poorly, and try to accrue an understanding of the most recurrent and significant ways in which the present system fails to satisfy people. Then you can look for specific tweaks that will more readily accommodate the things people in fact seem to want. But crucially, this task in empirical—you cannot come upon the most desirable tweaks rationally. It's also empirical in a way that is difficult to approach with any kind of scientific rigor. You have to listen to people, and try to understand them on their own terms. You have to try to understand where people are coming from even if they phrase things in a way that you very much dislike, a way that irritates you or makes you feel threatened.
As I've said before, "listen to marginalized voices" is oft-misused, but not actually incorrect as a description of the practical obligations of anyone who wants to consider themself a leftist.
202 notes
·
View notes
Text
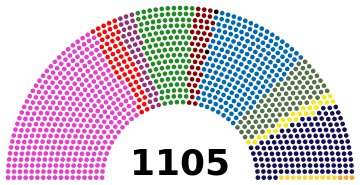
By 9 ABY, the New Republic had liberated Coruscant, the Galactic capital, and established its government there. After leading the Rebellion and then the Republic through the heady days of the Galactic Civil War, Mon Mothma stepped down as Chancellor, leaving behind a Senate divided into four major power blocs.

THE ORGANA BLOC
Progressive People's Party (center-left, 364 seats): The majority successor to the original Progressive Party which acted as the Rebellion's political wing in the Republic and Imperial Senates, the PPP is majority social democratic and socially progressive. As it carries the Progressive Party's reputation of being the "party of the Rebellion" and the standard-bearer of Mothmism, the PPP enjoys widespread popularity and is the largest party in the Senate, despite surging poll numbers for the opposition after a half-decade of PPP governance. Led by Leia Organa of Coruscant.
Liberal Party (center, 56 seats): Socially liberal and fiscally moderate, the Liberal Party is one of the few parties to survive from the time of the Old Republic in its current form. The Progressive Party was originally a splinter faction from the Liberals, and they affiliate with its successor the PPP in the government coalition. Led by Rees Vera of Mikkia.
Federalist Party (center-left, 39 seats): A social liberal party which advocates for increased decentralization of the New Republic and the establishment of devolved regional governments. Led by Boona Kalan of Taris.

THE IBLIS BLOC
People's Union Party (far left, 122 seats): A socialist party which advocates for the restructuring of Galactic society on a free and equal basis, the transfer of the means of production into the hands of the working class, and the development of a socialist mode of production. In practical terms, the party is democratic socialist and draws strong support from industrial worlds and unions. Local parties such as the Communist Party of Corellia and the Gran Socialist Union are affiliates of the PUP. Led by Garm Bel Iblis of Corellia.
Reform Party (left, 44 seats): A democratic socialist party which argues for a fundamental restructuring of the New Republic into a "Federation of Free Alliances." A successor to the original Reform Party in the Old Republic. Led by Cal Omas of New Alderaan.
Libertarian Party (far left, 2 seats): A loose affiliation of anarchists. Collective leadership.

THE FEY'LYA BLOC
Progressive Conservative Party (center right, 201 seats): A liberal conservative party which is hawkish on military matters and foreign affairs. Generally socially conservative with more liberal factions while remaining economically liberal. The minority splinter of the original Progressive Party. Led by Borsk Fey'lya of Bothawui.
Constitutionalist Party (center, 89 seats): A centrist party, and a revival of the Old Republic party of the same name. Advocates of a return to the structure of the Old Republic as it existed in the High Republic and Republic Classic eras, before what they see as its distortion under Palpatine. The text of the Ruusan Reformations serves as their guiding charter. Led by Waltyr Valorum of Hosnian Prime.
Free Hyperlanes Party (center right, 24 seats): A classical liberal party, economically hypercapitalist and disdainful of government intervention in the market, and supportive of corporations. Socially libertarian. Led by Udo Mopot of Giju.

THE MOTHMA BLOC
Galactic Unity Party (far right, 151 seats): A far right, traditionalist party which advocates for ultraconservative social policies and an immediate cessation of hostilities against the Imperial remnants, arguing that the war was won when the Core was liberated. Often accused of Imperial sympathies and of being a continuation of the Galactic Integralist Party, the state party under the Empire; several GIP Senators have reentered politics under the GUP banner. Led by Leida Mothma of Chandrila, the daughter of former Chancellor Mon Mothma, who does not share her mother's politics.
Core Alliance (right, 10 seats): A coalition of wealthy and influential Core worlds, whose priority is securing and expanding the privileges traditionally afforded them. Led by Jonas Piven of Alsakan.
Anti-Jedi Party (far right, 3 seats): One of the few parties to exist in its current form since the time of the Old Republic. Far right and conspiratorial, it gained some popularity after the Clone Wars due to a conspiracy theory spread by its leader about Emperor Sheev Palpatine being a secret Jedi who had worked with the Jedi Council to seize power, only to then betray his fellow Jedi in order to consolidate power around himself. Currently opposes the nascent New Jedi Order and has taken credit for Luke Skywalker having declined to base it on Coruscant. led by Alyx J'onzz of Tekaris.
270 notes
·
View notes
Text
Exclusive interview with Wang Yibo: Maintain a sincere heart丨"War of Faith" hits the airwaves

Since its launch on CCTV 8 in late March, the contemporary youth growth drama "War of Faith", directed by Yao Xiaofeng and written by Weng Liangping, starring Wang Yibo, Li Qin, Wang Yang and others, has been performing well in recent days. The show topped the CVB prime-time ratings the day after it aired. The real-time ratings of Kuyun peaked at 2, and the popularity on iQiyi exceeded 9,600. The ratings are both good. The male protagonist Wei Ruolai, played by young actor Wang Yibo, is also loved by the audience for his smart, intelligent and righteous character.
"He is very passionate, has a sense of justice, is persistent and brave in his work. Even when facing the dark social reality, Wei Ruolai still maintains a sincere heart and wants to change the social status quo through his own efforts." Wang Yibo accepted the Liberation Daily Exclusive interview with a reporter from Shangguan News, explaining what "Wei Ruolai" is in his eyes.
At the beginning of the TV series, there is an assassination, a rescue, and a stock market game. The plot advances on multiple parallel lines, but they contain inextricable connections. "War of Faith" is set in Shanghai in the 1930s. It adopts a novel narrative incision and starts from the perspective of the financial industry. It embeds the storyline on the real historical picture of Shanghai and depicts Shanghai from 1929 to 1934. A scene filled with smoke and silent struggle. This makes the social turmoil in a specific historical period and the intrigue on the financial front in the play cleverly form an intertextuality.
From the character setting point of view, Wei Ruolai is a character with obvious growth meaning. In the complicated political, economic and social environment of Shanghai at that time, Wei Ruolai, as a young man who bravely came to Shanghai from the Jiangxi countryside, rented in Qibao Street, a mixed and dilapidated place. His initial wish was just to be admitted to the Central Bank and have a good job. income. Wang Yibo revealed that what impressed him about the role of Wei Ruolai was his charisma. This ideal and belief in taking family and country as one's own responsibility, as well as the unique passionate feelings of young people, are the character traits that Wang Yibo admires.
As a young man from a poor family who left his hometown to work in Shanghai, Wei Ruolai showed great personal talent in the financial field. Whether he is helping his neighbor Aunt Zhou on Qibao Street to trade stocks, or being fearless in the face of fire during the central bank exam, the character's agility and human touch are all reflected. When Wei Ruolai got up early to rush to the central bank for an interview, her pair of torn socks, her leather shoes that "gathered dust" under the bed, and her slightly messy hairstyle in the mirror all gave the scenes in the play a sense of life.
In Wang Yibo's view, Wei Ruolai was just like the young people of that era. Although he initially regarded his career as a job that could earn more money to support his family, he had his own ideals and ambitions in his heart. This can be seen from his bent on joining the central bank. "In the context of the times, he was eager to create value through his own efforts on the best financial platform, improve people's livelihood, and make society better."
"War of Faith" adopts a two-line parallel narrative structure. One line is a financial war without gunpowder, and the other is a thrilling spy war drama. In the workplace where the central bank is the stage, the new senior adviser Shen Tunan (played by Wang Yang) plays the role of Wei Ruolai's master and becomes his guide on the career path. Shen Tunan is both good and evil, and he wants to promote Shanghai's financial reform, and he does not hesitate to take risks with his own life. Shen Tunan's sister Shen Jinzhen (played by Li Qin) and Wei Ruolai's brother Wei Ruochuan are both underground members of the Communist Party of China. In the dark current situation, they disregard their personal lives for the cause of the party. Therefore, these important characters surrounding Wei Ruolai constituted his dilemma in social situation, and also laid the foundation for Wei Ruolai and Shen Tunan to part ways.
Wang Yibo feels that Shen Tunan plays an important role in Wei Ruolai's professional and personal growth. "Wei Ruolai, who had just entered the workplace and had no work experience, just rushed forward with momentum and persistence. Therefore, he admired Shen Tunan very much and once regarded him as the direction of his life's efforts. The two of them also learned from each other in the process of getting along."
But as Wei Ruolai received more and more attention, the corruption within the Kuomintang was exposed in front of him. Inspired by the people around him, Wei Ruolai and Shen Tunan eventually embarked on completely different paths of faith. "After experiencing a series of changes such as investigating the counterfeit currency case and treasury bills, he witnessed the darkness and corruption of the current situation, and realized that he needed to change the status quo of the country and fight for the people. Therefore, the sense of opposition between his master and his faith made him once I lost confidence in Shen Tunan, who was once a like-minded person, and eventually embarked on a different path of faith, but Shen Tunan has always been Wei Ruolai's guide"
Director Yao Xiaofeng once said in an interview that he chose Wang Yibo to play the role because he saw many similarities between the two. "I saw something in Wang Yibo. I felt that this story should be filmed as a small character who came to a big city to develop, and then accidentally got involved in a bloody storm and fell into a battle between two forces that were beyond his power. , let him hesitate, let him make a choice."
In one scene, his brother Wei Ruochuan was betrayed by his companions. After searching for Wei Ruolai in Shanghai, he eventually died due to excessive blood loss. In this scene, Wang Yibo performed Wei Ruolai's pain and fear. After his brother died, Wei Ruolai had no time to grieve and buried his brother in pain overnight. "In such a terrifying period, if you have a Communist brother, you have to be screened, and the first thing you will definitely bring is fear. I was very impressed by Wang Yibo in this scene, and the whole audience applauded (after filming)." Yao Xiaofeng said. In Wang Yibo's eyes, Yao Xiaofeng is a director who pays great attention to details. "He is more of a good guide to the actors in terms of performance. He will let me use my own real experiences and feelings to understand the character's current emotions, allowing the actors to perform the performance more closely to life."
In real life, Wang Yibo likes racing. When a reporter asked which scene in "War of Faith" was the most fun, his answer was a bit unexpected but reasonable. "The most fun thing was riding a motorcycle from that era." As for what themes or roles he wants to challenge in the future, his answer is also very open, "I want to try them all, and have a sense of freshness."
#AAAAHHHH YASSS THANK YOU FOR THE INTERVIEW!#wang yibo#wei ruolai#war of faith#accio victuuri translation
50 notes
·
View notes
Note
In a world where Robb Stark wins his war and manages to consolidate his realm, with the 7K being no more, lets assume he also annexes the northern crownlands too, what kind of council or burocracy would he establish to govern and how much of your economic development plans could he reasonably carry out in his lifetime and how could he unify his 2 realms economy into a cohesive unit?
In a Stark victory scenario, I think annexing the northern Crownlands would be an overstretch and something of a distraction from more important tasks (like bringing the Iron Islands and the Vale into his sphere of influence so that he can govern a geographically, economically, and politically coherent kingdom/coalition of northern Westeros).
To quote King Robb:
"Duskendale, on the narrow sea? Why would they go to Duskendale?" He'd shook his head, bewildered. "A third of my foot, lost for Duskendale?"
What matters in a brand-new Kingdom of the North is things like whether Gulltown accepts silver coins minted in White Harbor with Robb's face on them as valid payment for debts and taxes, or whether the Ironborn agree to keep their reaving south of Ironman's Bay, or whether the Stark navy can keep the Trident open all the way to the Bay of Crabs so that the Riverlands can keep trading directly with Braavos.
I did some back-reading through various economic development posts to see what I'd said in the past about the tricky scenario of how one balances the interests of multiple kingdoms in pursuing economic development. One of the things I'm noticing is that there are some reforms where there is real issues with competition/duplication of efforts (a Kingdom of the North can probably only support one Bank, one canal scheme, one sub-treasury system, one purchasing/marketing cooperative, etc.), some reforms where individual kingdoms can pursue their own goals but where there would be an issue about how the king balances the rewards he's doling out between the kingdoms (do you put your marginal dragon into winter schools and greenhouses for the North or church schools for the Riverlands or roads for the Vale?), and some where every kingdom can pitch in in a common effort (if there's going to be one sub-treasury plan, you're going to need a network of granaries along waterways from the Last River down to the Trident, the same information about how to improve agricultural productivity can be shared between the North, the Riverlands, and the Vale basically for free, etc).
That being said, one of the major political challenges of the Kingdom of the North was always going to be how you balance the interests of the component kingdoms and make everyone feel like the central government is giving them a fair deal and being attentive to their interests - and as you say, forging them into a cohesive economy would go a long way into doing that. So for example, one priority should be in working out reciprocity in trade between the newly-chartered cities. It certainly helps that a bunch of them (White Harbor, Gulltown, Maidenpool, Lord Harroway's Town, Saltpans) are along the same coast of the Narrow Sea or just upriver from the Narrow Sea, which makes close trade links more likely. However, you're going to want to make formal legal arrangements that, when it comes to port fees and staple fees and warehousing fees and the like, all of the North's cities agree to set them as low as possible for other Northern cities (if not an outright zollverein), and that burgher rights are transferrable between cities and that city ordinances will be honored by other cities, and so on.
In terms of "council or burocracy would he establish to govern," Robb was already taking a decent first step to bolster Lord Paramount Edmure Tully by appointing Brynden the Blackfish as Warden of the Southern Marches.
As I've written before, issuing city charters would be a crucial element of governing the Riverlands effectively. Giving Maidenpool, Lord Harroway's Town, Stoney Sept, Fairmarket, and Seagard a combination of economic and political self-governance would paradoxically allow King Robb to project royal authority more effectively - especially when it comes to generating revenue and manpower and enforcement of economic regulations.
#asoiaf#asoiaf meta#westerosi economic development#war of five kings#kingdom of the north#the north#the riverlands#the vale#iron islands#robb stark
131 notes
·
View notes
Text
By David Chang and Deanna Durante
On Nov. 27, 2023, at 9:33 a.m., the officer responded to the 500 block of Manor Road in Wynnewood for a report of a theft. The homeowner, Stephen Chopnick, told the officer he noticed someone had stolen his two “We Stand With Israel” signs from his front yard and he had last seen them four days earlier. Investigators later determined those two signs were the same signs that were found inside Chilton’s vehicle, according to the criminal complaint.
The officer then met with a woman who lived nearby. The woman showed the officer home surveillance video that captured Chilton’s Honda CRV driving past her home around the same time as the theft, investigators said.
That same day, the officer met with the executive director of the Main Line Reform Temple. She told the officer a security company that monitors the temple informed her that several pro-Israel signs had been stolen from the property. She later identified the stolen signs as the same ones that were found inside Chilton’s vehicle, according to the criminal complaint.
Chilton, Prickett and Penn were all arrested in connection to the incident.
Chilton is charged with conspiracy – theft by unlawful taking – movable property, conspiracy – criminal trespass, driving an unregistered vehicle, notice of change of name or address, failure to carry a license and receiving stolen property. Her case was moved to county court and is currently in the pretrial stage.
Prickett and Penn are both charged with theft by unlawful taking – movable property, receiving stolen property and criminal trespassing.
During an interview with NBC10 on Tuesday, July 2, 2024, Chopnick told NBC10 he had replaced the stolen signs with new ones that also support Israel.
“I wouldn’t take a sign down. I’ve certainly seen signs that I don’t agree with,” Chopnick said. “I assumed it was somebody who took a different view of the issues in the Middle East than I do.”
Chilton is a professor at the Dornsife School of Public Health at Drexel University in Philadelphia. She is also the director of Dornsife’s Center for Hunger-Free Communities, a research and advocacy center that focuses on developing solutions for hunger and economic insecurity. She also founded Witnesses to Hunger, a research and advocacy project that partners with experts on mothers and caregivers of young children who have experienced hunger and poverty.
#drexel university#drexel university professor#stephen chopnick#mariana chilton#sarah prickett#sam penn#main line reform temple#philadelphia
28 notes
·
View notes
Text
29 Menachem Av 5784 (1-2 September 2024)
The 29th of Av 5556 brought Jewish emancipation to the Netherlands, the second European nation to grant its Jewish residents fully equal rights with other citizens. Jewish emancipation was at the heart of the shift towards the enlightenment model of secular nation states where all citizens would be equal under the law and away from European feudalism. The Netherlands had permitted Jewish settlement early following its independence from the Spanish monarchy, and Dutch official religious toleration had soon expanded to permit private Jewish worship and to allow Jewish residents nearly unfettered economic activity, but Jews were still prohibited from taking office in government or serving in the military or public guard, and were subjected to the humiliating practice of oath more judaico when offering testimony in civil courts.
All of that was rooted in a concept of the state in which the Calvinist Dutch establishment held control of society and magnanimously extended limited rights to other groups. While Jewish residents received more rights in the Netherlands than they would have had almost anywhere else in Europe, they still had less than other Dutch citizens, including Christian denominations other than the official Dutch Reformed Church.
The European enlightenment however carried with it a different model, in which the state would equally represent all citizens rather than being in the hands of a specific group which could choose how to treat all others. The transition from one paradigm to another did not take place without conflict. In the Netherlands, the autocratic control exercised by the House of Orange with the backing of the merchant elite was challenged by revolutionary reformers who wished to remake society upon these new lines of equality. After a period of persecution and failure, they succeeded in driving out William V in 5555 and establishing the Batavian Republic. The following year, the newly established National Convention declared
"No Jew shall be excluded from rights or advantages which are associated with citizenship in the Batavian Republic, and which he may desire to enjoy.
Amsterdam immediately appointed two Jewish officeholders to exercise these newly established rights. Moses Moresco, a Sephardi Jew, was appointed to the city council, and Moses Asher, an Ashkenazi Jew, was appointed to the city’s court of Justice. Soon, Jewish regiments were also organized in the revolutionary army seeking to defend the new republic from Prussians, Austrians, and English, who wished to restore the prior status quo.
The following decades brought significant turmoil to Europe via the Napoleonic Wars and the eventual conservative settlement which restored many of the overturned monarchies of the continent. But in the Netherlands and throughout much of the rest of the continent, the revolutionary change to Jewish legal status persisted. Emancipation was a settled reality, and Jewish life would also be changed significantly over the coming century to adjust to this shift.
#jewish calendar#hebrew calendar#judaism#jewish#jumblr#sephardi history#ashkenazi history#jewish emancipation#removal of legal barriers#equality before the law#Menachem Av#29 Menachem Av#🌑
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
Im honestly so excited to see the political repercussions for the NCR. I honestly think losing Shady Sands might be a positive for them.
When we run into them in New Vegas they’re corrupt and trapped in a cold guerrilla war. Tandy’s reforms against monopolies have been removed, and military appointments are based off of political connections, not skill.
With Caesar right there, the NCR has to maintain a presence, but its passive. There is neither the political will or need to cross the Colorado river and actually fight with Caesar, allowing him to pick the terms of the war. His terrorist campaigns at Nipton is a perfect example of this - that town should be under the NCR but they could do NOTHING to atop it and its people being burnt. They also cant stop the Powder Gangers.
The NCR is demoralized, a repletion of the exact same pre-war system that lead to Nuclear Fire. Shady Sands is five years into its decline at this point and everyone knows it.
And then Caesar dies of a brain tumor, and the Legion collapses into infighting and civil war. The NCR can relax, try to deal with Mr House formally - then their capitol has its reactor overloaded and destroyed.
Imagine the confusion and chaos there would be if the majority of the executive, legislative and judicial government just got exploded
Who’s in charge, what happens next? Who did this? It would be a Mad house
Thankfully, Mr Bishop - illegitamet son of the Chosen One and Leslie Anne Bishop - is only 38 years old when the Second Battle of Hoover Dam and destruction of Shady Sands occurs. Why are we thankful?
Because he’s a maverick. He knows the wastes like the back of his hand, he’s different from the other Bishops and far more dangerous. MB took over the family when he was just 13, and since then he has lead the family to vast amounts of power. He used the pre-existing connection between the Bishops and the NCR his father founded, as well as their insane amount of capital leading to this ending in Fallout 2 and confirmed canon by Bruce Isaacs in New Vegas, “in the decades following the alliance, several bishops rose to political power”
Right now, since we know that MB wont die until he’s 73 and right now he’s 54, he’s out there. He’s probably the leading political authority in the NCR right now - the Bishops are the NCR’s favorite black ops group. Anything the NCR needs done quietly and off the books, the Bishops can handle. And now that the main government is gone, I think that power is going straight to MB. He’s the only one who can take back control of the NCR in this chaos.
I think the NCR was forced into a bad deal by House after Shady Sands was gone which is honestly pretty positive given his plans longterm. House needs the NCR successful, but he wants his own territory. MB will make the same deal his alleged father helped broker with Vault City giving it quasi independence.
This gives the Government time to recapture itself. They sent a party to continue their cold fusion project near the ruins, but by and large the NCR has left it alone - they surround the territory on all sides, its not like they’re in danger of losing it. On a map, it would still be NCR territory, ya feel? The capital is moved to the Hub, the primary economic powerhouse in Southern California, and the democracy gets going again
#fallout prime#fallout tv series#fallout spoilers#fallout show#fallout 2#fallout nv#fallout new vegas#ncr#new california republic
32 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Communist Manifesto - Part 17
[ ◁ First | ◃Prev | Table of Contents | Next ▹ ]
2. Conservative or Bourgeois Socialism
A part of the bourgeoisie is desirous of redressing social grievances in order to secure the continued existence of bourgeois society.
To this section belong economists, philanthropists, humanitarians, improvers of the condition of the working class, organisers of charity, members of societies for the prevention of cruelty to animals, temperance fanatics, hole-and-corner reformers of every imaginable kind. This form of socialism has, moreover, been worked out into complete systems.
We may cite Proudhon’s Philosophie de la Misère as an example of this form.
The Socialistic bourgeois want all the advantages of modern social conditions without the struggles and dangers necessarily resulting therefrom. They desire the existing state of society, minus its revolutionary and disintegrating elements. They wish for a bourgeoisie without a proletariat. The bourgeoisie naturally conceives the world in which it is supreme to be the best; and bourgeois Socialism develops this comfortable conception into various more or less complete systems. In requiring the proletariat to carry out such a system, and thereby to march straightway into the social New Jerusalem, it but requires in reality, that the proletariat should remain within the bounds of existing society, but should cast away all its hateful ideas concerning the bourgeoisie.
A second, and more practical, but less systematic, form of this Socialism sought to depreciate every revolutionary movement in the eyes of the working class by showing that no mere political reform, but only a change in the material conditions of existence, in economical relations, could be of any advantage to them. By changes in the material conditions of existence, this form of Socialism, however, by no means understands abolition of the bourgeois relations of production, an abolition that can be affected only by a revolution, but administrative reforms, based on the continued existence of these relations; reforms, therefore, that in no respect affect the relations between capital and labour, but, at the best, lessen the cost, and simplify the administrative work, of bourgeois government.
Bourgeois Socialism attains adequate expression when, and only when, it becomes a mere figure of speech.
Free trade: for the benefit of the working class. Protective duties: for the benefit of the working class. Prison Reform: for the benefit of the working class. This is the last word and the only seriously meant word of bourgeois socialism.
It is summed up in the phrase: the bourgeois is a bourgeois – for the benefit of the working class.
[ ◁ First | ◃Prev | Table of Contents | Next ▹ ]
35 notes
·
View notes