Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
Web Application Penetration Testing Checklist
Web-application penetration testing, or web pen testing, is a way for a business to test its own software by mimicking cyber attacks, find and fix vulnerabilities before the software is made public. As such, it involves more than simply shaking the doors and rattling the digital windows of your company's online applications. It uses a methodological approach employing known, commonly used threat attacks and tools to test web apps for potential vulnerabilities. In the process, it can also uncover programming mistakes and faults, assess the overall vulnerability of the application, which include buffer overflow, input validation, code Execution, Bypass Authentication, SQL-Injection, CSRF, XSS etc.
Penetration Types and Testing Stages
Penetration testing can be performed at various points during application development and by various parties including developers, hosts and clients. There are two essential types of web pen testing:
l Internal: Tests are done on the enterprise's network while the app is still relatively secure and can reveal LAN vulnerabilities and susceptibility to an attack by an employee.
l External: Testing is done outside via the Internet, more closely approximating how customers — and hackers — would encounter the app once it is live.
The earlier in the software development stage that web pen testing begins, the more efficient and cost effective it will be. Fixing problems as an application is being built, rather than after it's completed and online, will save time, money and potential damage to a company's reputation.
The web pen testing process typically includes five stages:
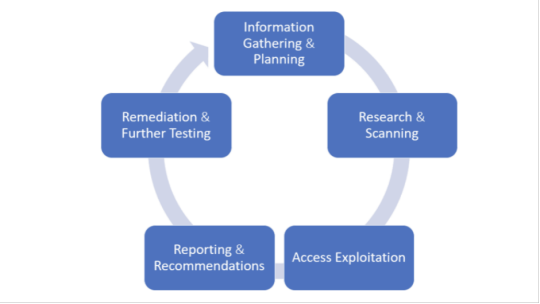
1. Information Gathering and Planning: This comprises forming goals for testing, such as what systems will be under scrutiny, and gathering further information on the systems that will be hosting the web app.
2. Research and Scanning: Before mimicking an actual attack, a lot can be learned by scanning the application's static code. This can reveal many vulnerabilities. In addition to that, a dynamic scan of the application in actual use online will reveal additional weaknesses, if it has any.
3. Access and Exploitation: Using a standard array of hacking attacks ranging from SQL injection to password cracking, this part of the test will try to exploit any vulnerabilities and use them to determine if information can be stolen from or unauthorized access can be gained to other systems.
4. Reporting and Recommendations: At this stage a thorough analysis is done to reveal the type and severity of the vulnerabilities, the kind of data that might have been exposed and whether there is a compromise in authentication and authorization.
5. Remediation and Further Testing: Before the application is launched, patches and fixes will need to be made to eliminate the detected vulnerabilities. And additional pen tests should be performed to confirm that all loopholes are closed.
Information Gathering

1. Retrieve and Analyze the robot.txt files by using a tool called GNU Wget.
2. Examine the version of the software. DB Details, the error technical component, bugs by the error codes by requesting invalid pages.
3. Implement techniques such as DNS inverse queries, DNS zone Transfers, web-based DNS Searches.
4. Perform Directory style Searching and vulnerability scanning, Probe for URLs, using tools such as NMAP and Nessus.
5. Identify the Entry point of the application using Burp Proxy, OWSAP ZAP, TemperIE, WebscarabTemper Data.
6. By using traditional Fingerprint Tool such as Nmap, Amap, perform TCP/ICMP and service Fingerprinting.
7.By Requesting Common File Extension such as.ASP,EXE, .HTML, .PHP ,Test for recognized file types/Extensions/Directories.
8. Examine the Sources code From the Accessing Pages of the Application front end.
9. Many times social media platform also helps in gathering information. Github links, DomainName search can also give more information on the target. OSINT tool is such a tool which provides lot of information on target.
Authentication Testing

1. Check if it is possible to “reuse” the session after Logout. Verify if the user session idle time.
2. Verify if any sensitive information Remain Stored in browser cache/storage.
3. Check and try to Reset the password, by social engineering crack secretive questions and guessing.
4.Verify if the “Remember my password” Mechanism is implemented by checking the HTML code of the log-in page.
5. Check if the hardware devices directly communicate and independently with authentication infrastructure using an additional communication channel.
6. Test CAPTCHA for authentication vulnerabilities.
7. Verify if any weak security questions/Answer are presented.
8. A successful SQL injection could lead to the loss of customer trust and attackers can steal PID such as phone numbers, addresses, and credit card details. Placing a web application firewall can filter out the malicious SQL queries in the traffic.
Authorization Testing

1. Test the Role and Privilege Manipulation to Access the Resources.
2.Test For Path Traversal by Performing input Vector Enumeration and analyze the input validation functions presented in the web application.
3.Test for cookie and parameter Tempering using web spider tools.
4. Test for HTTP Request Tempering and check whether to gain illegal access to reserved resources.
Configuration Management Testing

1. Check file directory , File Enumeration review server and application Documentation. check the application admin interfaces.
2. Analyze the Web server banner and Performing network scanning.
3. Verify the presence of old Documentation and Backup and referenced files such as source codes, passwords, installation paths.
4.Verify the ports associated with the SSL/TLS services using NMAP and NESSUS.
5.Review OPTIONS HTTP method using Netcat and Telnet.
6. Test for HTTP methods and XST for credentials of legitimate users.
7. Perform application configuration management test to review the information of the source code, log files and default Error Codes.
Session Management Testing
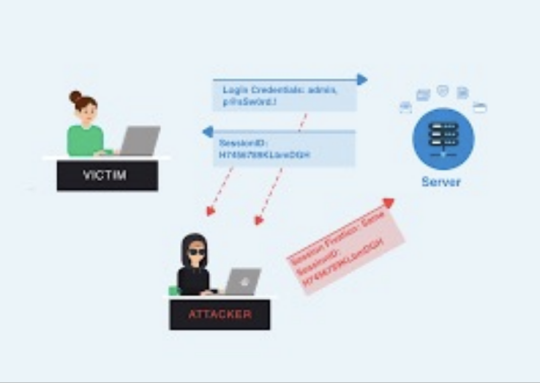
1. Check the URL’s in the Restricted area to Test for CSRF (Cross Site Request Forgery).
2.Test for Exposed Session variables by inspecting Encryption and reuse of session token, Proxies and caching.
3. Collect a sufficient number of cookie samples and analyze the cookie sample algorithm and forge a valid Cookie in order to perform an Attack.
4. Test the cookie attribute using intercept proxies such as Burp Proxy, OWASP ZAP, or traffic intercept proxies such as Temper Data.
5. Test the session Fixation, to avoid seal user session.(session Hijacking )
Data Validation Testing
1. Performing Sources code Analyze for javascript Coding Errors.
2. Perform Union Query SQL injection testing, standard SQL injection Testing, blind SQL query Testing, using tools such as sqlninja, sqldumper, sql power injector .etc.
3. Analyze the HTML Code, Test for stored XSS, leverage stored XSS, using tools such as XSS proxy, Backframe, Burp Proxy, OWASP, ZAP, XSS Assistant.
4. Perform LDAP injection testing for sensitive information about users and hosts.
5. Perform IMAP/SMTP injection Testing for Access the Backend Mail server.
6.Perform XPATH Injection Testing for Accessing the confidential information
7. Perform XML injection testing to know information about XML Structure.
8. Perform Code injection testing to identify input validation Error.
9. Perform Buffer Overflow testing for Stack and heap memory information and application control flow.
10. Test for HTTP Splitting and smuggling for cookies and HTTP redirect information.
Denial of Service Testing

1. Send Large number of Requests that perform database operations and observe any Slowdown and Error Messages. A continuous ping command also will serve the purpose. A script to open browsers in loop for indefinite no will also help in mimicking DDOS attack scenario.
2.Perform manual source code analysis and submit a range of input varying lengths to the applications
3.Test for SQL wildcard attacks for application information testing. Enterprise Networks should choose the best DDoS Attack prevention services to ensure the DDoS attack protection and prevent their network
4. Test for User specifies object allocation whether a maximum number of object that application can handle.
5. Enter Extreme Large number of the input field used by the application as a Loop counter. Protect website from future attacks Also Check your Companies DDOS Attack Downtime Cost.
6. Use a script to automatically submit an extremely long value for the server can be logged the request.
Conclusion:
Web applications present a unique and potentially vulnerable target for cyber criminals. The goal of most web apps is to make services, products accessible for customers and employees. But it's definitely critical that web applications must not make it easier for criminals to break into systems. So, making proper plan on information gathered, execute it on multiple iterations will reduce the vulnerabilities and risk to a greater extent.
1 note
·
View note