Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
What is Virtualization-Based Security for Windows Guest Operating Systems
Virtualization-Based Security (VBS) for Windows guest operating systems is a security feature that uses hardware virtualization to create and isolate a secure region of memory from the normal operating system. This helps protect the system from a variety of threats and attacks by ensuring that sensitive data and processes are isolated from potential malicious software running on the main…
View On WordPress
1 note
·
View note
Text
Export DRS (Distributed Resource Scheduler) rules from a vCenter server using PowerCLI-How to?
To export DRS (Distributed Resource Scheduler) rules from a vCenter server using PowerCLI, you can use the following script. This script will connect to your vCenter server, retrieve the DRS rules for each cluster, and export them to a CSV file. Install VMware PowerCLI if you haven’t already: Install-Module -Name VMware.PowerCLI -Scope CurrentUser 2. Run the following PowerCLI script: #…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
vSphere virtual disk transport modes (VADP) for VM backup
Virtual Disk Transport Methods (VADP) offers interfaces for integration of storage-aware applications, including backup, with efficient access to storage clusters. Backup vendors may use different transport methods, which provide efficient I/O methods to maximize backup performance and flexible deployment options. VADP supports four access methods: •SAN •SCSI HotAdd •NBD (network block…
View On WordPress
#backup#Hot Add#Local file access#NBDSSL#SAN#transport modes#VADP#vm backup#VMware#vSphere#vsphere 7#vSphere 8
0 notes
Text
How VM DRS score is calculated?
VM DRS (Virtual Machine Distributed Resource Scheduler) is a feature in VMware vSphere that helps optimize resource utilization in a cluster of ESXi hosts by automatically balancing virtual machine (VM) workloads. The VM DRS score is a key component of this feature, as it helps determine which hosts are the best candidates for running specific VMs. Here’s how the VM DRS score is calculated: 1.…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Guide to ESXTOP
ESXTOP is a powerful command-line tool in VMware ESXi that provides real-time monitoring and performance analysis of your virtual infrastructure. It offers insights into various aspects of your ESXi host and its virtual machines. The tool is available either on the ESXi host local Shell, esxtop or from remote systems, resxtop. ESXTOP Keys: ESXTOP is navigated using various keys. Here are the…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Bidirectional forwarding detection or BFD, in NSX-T (aka NSX 4.x onwards)
In VMware NSX-T (NSX Data Center), BFD stands for “Bidirectional Forwarding Detection.” BFD is a network protocol used to detect and quickly respond to failures in the forwarding path between network devices, such as routers or switches. It is designed to provide rapid failure detection and minimal downtime by quickly detecting link or path failures and notifying the network devices to take…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Service Router vs Distributed Router in NSX-T (aka NSX 4.x)
In VMware NSX-T, both Service Router (SR) and Distributed Router (DR) are integral components of the networking architecture that play distinct roles in providing routing and connectivity within the virtualized network environment. Let’s delve into the differences between these two router types: Service Router (SR): Role: The Service Router is a centralized routing component that provides…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Resource Grouping in vROps: Tags, Application Groups, and Custom Groups - Finding the Perfect Fit for Your IT Operations!
In the world of IT operations, the ability to monitor and manage infrastructure resources efficiently is critical. With vRealize Operations (vROps), IT teams can use various methods to organize resources, such as Tags, Application Groups, and Custom Groups. Each of these grouping methods offers unique features and benefits, making them ideal for different scenarios. In this article, we will…
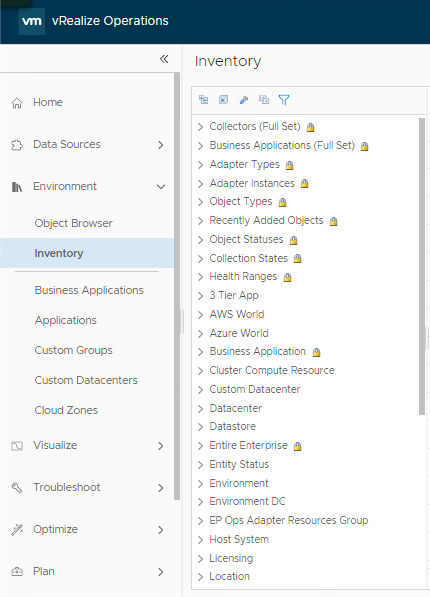
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Efficient vROps Tag Assignment with PowerCLI: Streamline Your Workflows
VMware’s vRealize Operations (vROps) is a comprehensive operations management platform that provides monitoring and management capabilities for your virtualized infrastructure. One of the ways to manage resources in vROps is by assigning tags to them, which allows you to group resources and perform monitoring and management operations more efficiently. While vROps provides its own REST API,…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Automating vROps Tagging with Python: Simplify Your Resource Management using Python
In today’s fast-paced digital world, automation is key to improving productivity and efficiency. One area where automation can be particularly useful is in managing resources in vRealize Operations (vROps), VMware’s comprehensive operations management platform. With its powerful API and extensive Python libraries, it’s possible to create Python scripts to interact with vROps, automate tasks, and…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
YAML: Your Ultimate Guide to Understanding the Basics
YAML, which stands for “YAML Ain’t Markup Language”, is a human-readable data serialization format that is commonly used for configuration files and data exchange between different programming languages. It is a popular choice for its simplicity, readability, and flexibility compared to other data serialization formats such as XML and JSON. YAML is designed to be minimal and easy to learn, with…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
VMware vSphere 7 DRS and its best practices.
vSphere Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS) is a feature of VMware’s vSphere virtualization platform that automatically balances computing workloads across multiple servers in a data center to optimize resource utilization and minimize downtime. It monitors the resource usage of virtual machines and dynamically adjusts the distribution of workloads to meet the resource demands of each virtual…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
VMware vSphere 8: What's New?
VMware vSphere 8: Intro: What's new?
Image: VMware vSphere 8, the latest version of VMware’s virtualization platform, introduces several new features and improvements to help organizations modernize their IT infrastructure and meet the demands of a rapidly changing business environment. Some of the key new features in vSphere 8 include: Native Kubernetes Support: vSphere 8 includes a built-in Kubernetes environment, known as…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
vSphere 7 lifecycle manager
vSphere 7 lifecycle manager
vSphere 7 Lifecycle Manager is a new feature introduced in vSphere 7 that provides a centralized, automated and simplified way to manage and upgrade the lifecycle of vSphere infrastructure components such as vCenter Server, ESXi hosts, and NSX-T. With vSphere 7 Lifecycle Manager, you can upgrade your vSphere environment to the latest version in a streamlined and automated way, reducing the risk…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
VMware vSAN 8
Image: VMware VMware vSAN 8 is a software-defined storage solution that is integrated with the VMware vSphere virtualization platform. It provides a distributed storage solution for virtual machines that run on vSphere hosts. Key features of vSAN 8 include: Policy-based storage management: administrators can define storage policies that specify the level of availability, performance, and…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
PowerCLI script to list datastore space utilization
Here is a PowerCLI script that lists the datastore space utilization: Connect to vCenter server Connect-VIServer -Server -User -Password Get all the datastores in vCenter $datastores = Get-Datastore Loop through each datastore foreach ($datastore in $datastores) {# Get the capacity and free space of the datastore$capacity = $datastore.CapacityGB$freeSpace = $datastore.FreeSpaceGB
#…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
PowerShell script to list VMs on ESXi host.
Here is a PowerShell script to list the virtual machines (VMs) on an ESXi host:
# Connect to the ESXi host
Connect-VIServer -Server <ESXi_host_name>
# Get a list of all VMs on the ESXi host
$VMs = Get-VM
# Loop through each VM and display its name and power state
foreach ($VM in $VMs)
{
Write-Host "Name: $($VM.Name), Power State: $($VM.PowerState)"
}
# Disconnect from the ESXi…
View On WordPress
0 notes