Aeliya marine is global supplier of used & new equipment required for industrial & marine automation. Free & Fast Shipping all over the globe Visit: https://aeliyamarine.net
Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
High-Quality Recorder
Discover the perfect recorder for all your audio needs. Whether it's for music, lectures, or personal notes, our recorders deliver crystal-clear sound quality and easy-to-use features. Explore now!
0 notes
Text
High-Quality Recorder | Capture Audio with Precision
Discover the perfect recorder for all your audio needs. Whether it's for music, lectures, or personal notes, our recorders deliver crystal-clear sound quality and easy-to-use features. Explore now!
0 notes
Text
Understanding I/O Modules: Functions and Applications
Explore I/O modules, their roles in automation systems, and how they streamline data transfer between devices and controllers.
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
Understanding Controllers: Role, Types, and Importance
Learn about controllers, their role in automation, regulation, and optimization in various systems, from industrial machines to smart homes and beyond.
0 notes
Text
Explore Reliable Capacitors for Efficient Power Management
Discover high-quality capacitors for various applications, ensuring reliable performance and efficiency in your electrical and electronic systems.
0 notes
Text
Siemens S5-100U Cpu 102 Module
The Siemens S5-100U CPU 102 Module is a compact and reliable processor unit designed for small automation tasks, offering efficient control and integration within the S5 PLC system.

0 notes
Text
0-366 T M-1 Pressure Meter 250v The 0-366 T M-1 Pressure Meter 250v is an electronic device used to accurately measure pressure within a specific range. It has a wide range of applications in various industries and scientific fields.
0 notes
Text
Relays in Automation: Electromechanical Solutions for Complex Control Tasks
In the realm of industrial and marine automation, reliability, precision, and efficiency are paramount. Complex control tasks demand sophisticated solutions, and one such crucial component that plays a pivotal role in achieving these goals is the relay. Relays have been a cornerstone of automation for decades, offering a dependable bridge between the digital and physical worlds. This blog post delves into the world of relays, their essential functions, applications, and why you should consider them for your automation needs.
The Heart of Automation
Relays are the essential building blocks of automation, serving as electromechanical switches that enable the control of high-power electrical circuits with low-power signals. These devices have been the cornerstone of industrial automation for decades, providing a reliable means of controlling complex systems with precision. They operate based on a simple yet ingenious principle: the conversion of an electrical signal into a mechanical action.
A relay consists of a coil and a set of contacts. When an electrical current flows through the coil, it generates a magnetic field that either attracts or repels a movable contact. This action opens or closes the circuit connected to the relay's contacts. In essence, a relay serves as an intermediary, allowing a small control signal to exert control over a much larger electrical load. This capability makes relays indispensable for applications where precision control and isolation of electrical circuits are critical.
The Role of Relays in Industrial Automation
Industrial automation encompasses a vast array of applications, from manufacturing and processing to robotics and quality control. In this context, relays play a pivotal role in ensuring the smooth operation of machinery and systems. One of their primary functions is to provide electrical isolation, safeguarding sensitive control circuits from high-voltage or high-current environments. This isolation helps prevent electrical interference and enhances the overall reliability of the system.
Moreover, relays offer precise control over the timing and sequencing of operations, making them ideal for applications that require synchronization. For instance, in a production line, relays can coordinate the activation of different components and ensure that they work together seamlessly. This level of control is crucial in achieving efficiency and consistency in industrial processes.

Types of Relays and Their Applications
Relays come in various types, each tailored to specific applications. Some of the most common types include:
Electromagnetic Relays: These relays use an electromagnetic coil to control the switching action. They are widely used in industrial automation for applications like motor control, lighting control, and safety interlocks.
Solid-State Relays: Unlike electromagnetic relays, solid-state relays use semiconductor components to switch electrical circuits. They are preferred for applications requiring fast switching, high reliability, and long service life.
Time Delay Relays: These relays introduce a time delay between the actuation of the coil and the switching action. They are indispensable for applications such as time-based control and motor soft-start circuits.
Latching Relays: Latching relays maintain their state even after the control signal is removed. They are suitable for applications where power consumption is a concern, as they don't require a continuous control signal.
The choice of relay type depends on the specific requirements of the automation task at hand. For instance, solid-state relays are often used in high-speed automation, while electromagnetic relays are preferred in applications requiring high current switching.
0 notes
Text
Remote Access and Monitoring: Taking Advantage of Networked PLCs
In today’s rapidly evolving industrial landscape, efficiency is key to staying competitive. Industrial automation has been a game-changer, and at the heart of this revolution are Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs). These versatile devices have become indispensable in controlling machinery and processes, but their full potential is only realized when combined with remote access and monitoring…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
New developments in circuit breaker technology
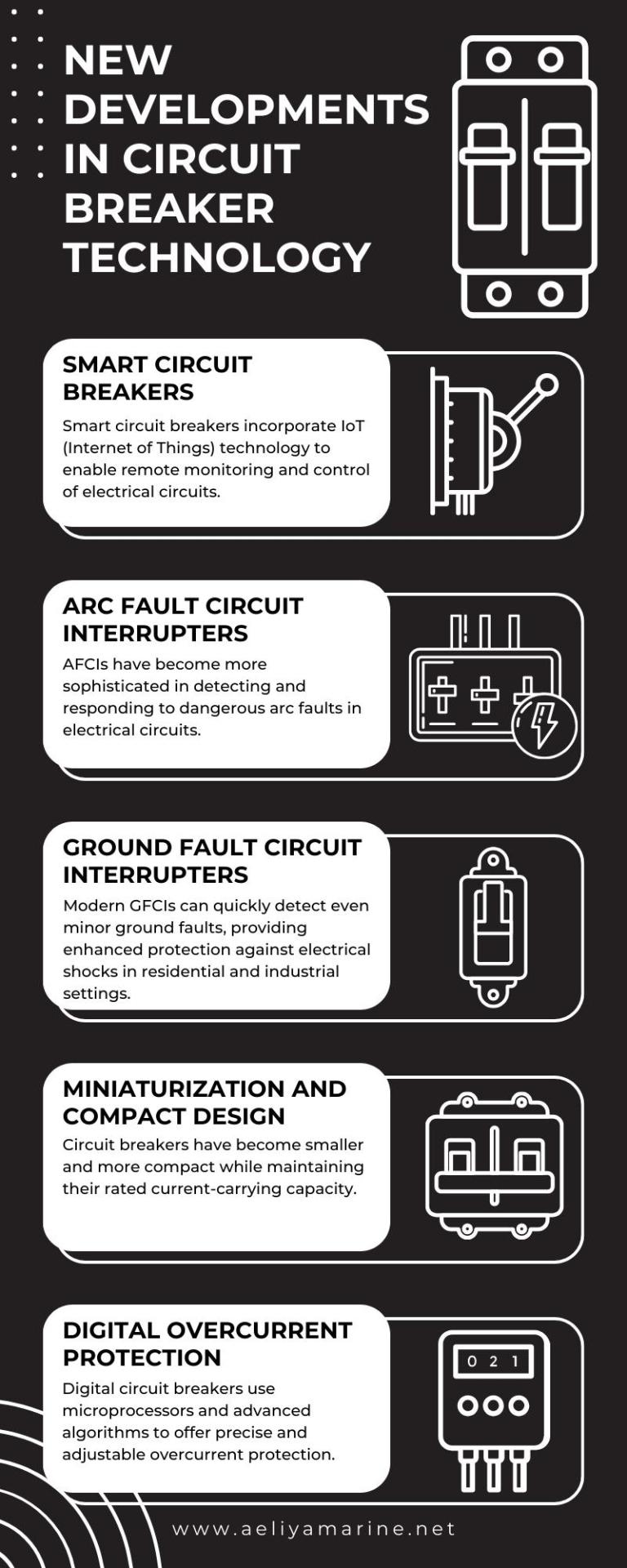
Recent breakthroughs in circuit breaker technology have ushered in a new era of electrical safety and efficiency. Innovations include smart circuit breakers with remote control capabilities, advanced arc fault and ground fault protection, miniaturized designs for space-saving solutions, digital overcurrent protection for precision, and energy management features for improved efficiency. These developments enhance the reliability and intelligence of electrical systems, making them safer, more responsive, and better equipped for the demands of modern living and industry.
0 notes
Text
Getting the Most Out of Your Industrial Indicators
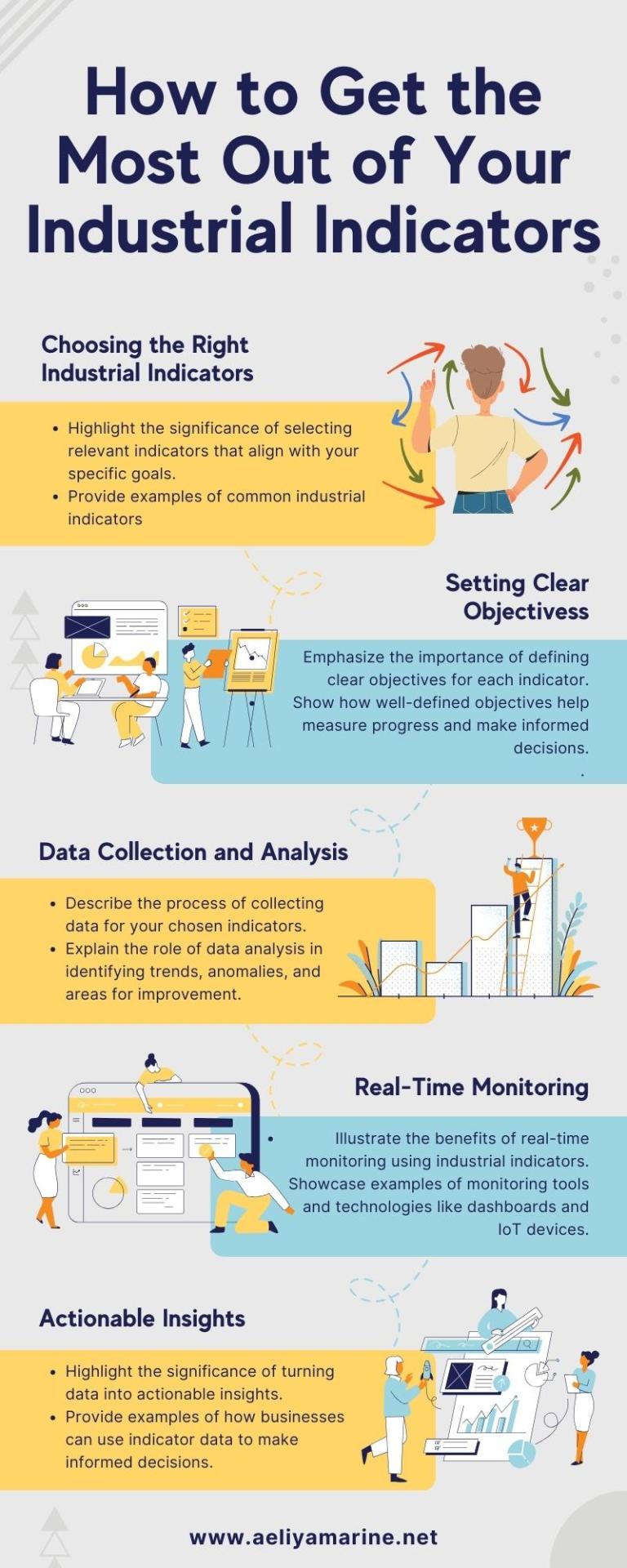
Explore the journey towards operational excellence through the informative infographic, 'Unlocking the Full Potential of Industrial Indicators.' This resource guides individuals in selecting, monitoring, and effectively utilizing industrial indicators. It empowers users to leverage data-driven insights, establish clear objectives, and continually refine processes for optimized performance and successful achievement of business objectives.
0 notes
Text
How Automation Increases Workplace Productivity and Safety

Fewer delays: Robots eliminate delays caused by human error or injury by performing many repetitive and strenuous jobs in material handling applications or on the production floor. Robots don't get bored or distracted while working, so consistent performance can be expected. This also means fewer wasted resources due to mistakes.
More data: With automated systems, it's easier for managers to calculate exactly how productive their facilities are. Rather than relying solely on what they see, managers can receive detailed metrics automatically from their equipment. This actionable information can be used to make adjustments and rework processes.
Enhanced management: Because robotic systems handle most tasks without intensive supervision, managers don't need to spend as much time micromanaging. This lets them focus on other aspects of their jobs, such as mentoring employees and guiding their professional development.
Accident prevention: Self-driving forklifts and other automated machinery deployed in manufacturing or material-handling applications prevent incidents caused by human operators' mistakes. They lessen the odds that injuries will occur due to mishandling or misuse of heavy equipment. Without having to do much heavy lifting on their own, workers also are at lower risk of being hurt or putting excess stress on their bodies.
0 notes
Text
The Fourth Industrial Revolution

The First Industrial Revolution was marked by the introduction of steam and water powered machines, which led to the mechanization of production. The Second Industrial Revolution was driven by electricity, gas, and oil, and it saw the introduction of new technologies such as cars, telephones, and telegraphs. The Third Industrial Revolution, also known as the Digital Revolution, was marked by the introduction of computers and robots, which transformed manufacturing.
The Fourth Industrial Revolution is still in its early stages, but it has the potential to revolutionize every aspect of our lives. It is already having a major impact on industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, and transportation. As these technologies continue to develop, they will likely have a profound impact on the global economy and society as a whole.
0 notes


