#egyptian art
Text

I was working on some other tasks and somehow landed on the animal figurine side of JSTOR (don't tell my manager).
May I offer you three conspiring jerboa figurines from the Metropolitan Museum of Art?
#serious question: is this the inspo for the muad'dib in dune?#jstor#jerboa#rodent#figurines#egyptian art#the metropolitan museum of art
450 notes
·
View notes
Text
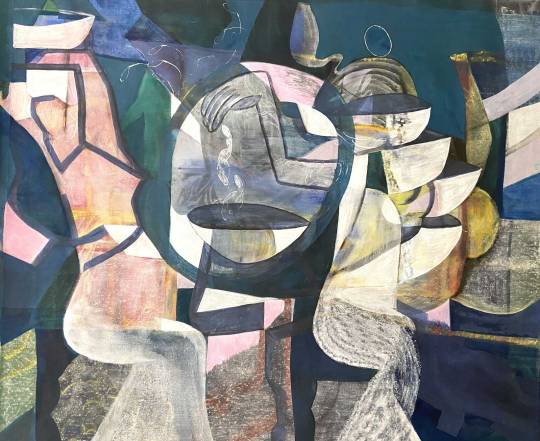
Essam Marouf (Egyptian, 1958) - EM 01 (2021)
50 notes
·
View notes
Text
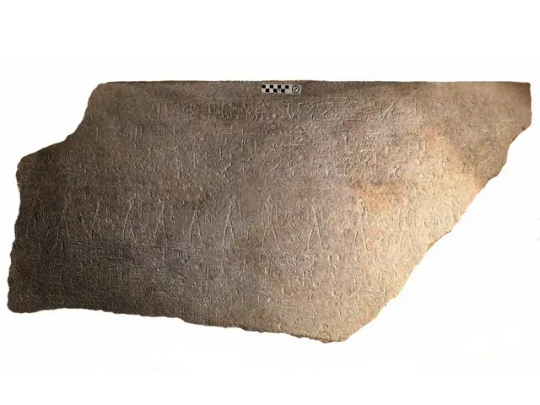

Ramses II’s Long-Lost Sarcophagus Has Finally Been Identified
An Egyptologist recently concluded that a fragment of an overlooked granite coffin bears the great pharaoh’s name.
Ramses II, a pharaoh who ruled in the 13th century B.C.E., is one of ancient Egypt’s best-known rulers. The 19th-Dynasty king expanded Egypt’s territory into modern-day Syria, fathered some 100 children and boasted one of the civilization’s most ornate coffins. But the carved granite sarcophagus built to house that coffin has never been identified—until now.
Frédéric Payraudeau, an Egyptologist at France’s Sorbonne University, recently re-examined a sarcophagus fragment found in the ancient necropolis of Abydos in 2009. At the time, experts posited that the engraved stone box had held the remains of two different people at different times, per a statement from the French National Center for Scientific Research. The second occupant was Menkheperre, a high priest who lived around 1000 B.C.E. But the first proved to be more difficult to pin down: Archaeologists only knew that they were a very high-ranking figure from the Egyptian New Kingdom, reports Live Science’s Jennifer Nalewicki.
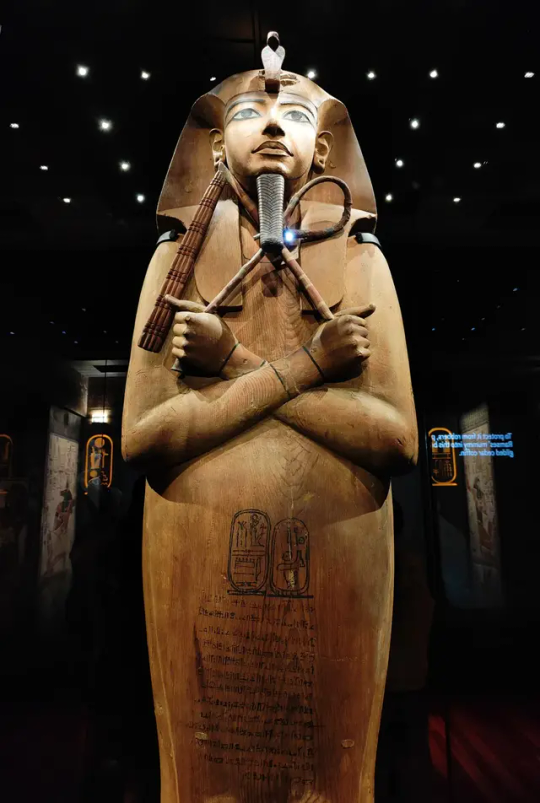

Ramses II's cedar coffin.
When Payraudeau studied the sarcophagus fragment’s inscriptions, including a previously obstructed and misidentified cartouche (an oval that typically encloses a royal name), he realized the hieroglyphs bore Ramses’ name. The scholar published his findings in the journal Revue D’Égyptologie.
Ramses’ reign lasted around 67 years, making it one of the ancient civilization’s longest. Dubbed the “builder pharaoh,” Ramses commissioned many temples throughout the region. As Payraudeau says in the statement, finding an ancient Egyptian site that isn’t marked with Ramses’ name is rare. The king even added his name to monuments built before his rule.
Ramses’ death in 1213 B.C.E. left a layered physical trail, thanks to multifaceted Egyptian entombing techniques and numerous pillagings of the Valley of the Kings, which held his and many other royal tombs. The pharaoh was buried in a gilded wooden coffin that was nested inside of an alabaster sarcophagus and a larger granite sarcophagus. Later, the coffin was stolen, the alabaster sarcophagus was shattered by looters and the granite sarcophagus—from which the fragment in question originated—was reused by Menkheperre.




As Payraudeau explains, the Valley of the Kings was plundered numerous times during ancient Egypt’s 19th Dynasty, an era of economic and social crises that led to scarcity, forcing even royals to reuse funerary objects created for their predecessors.
In 1881, Ramses’ mummy and coffin were discovered in a hiding place in the temple complex Deir el-Bahari, which housed the remains of 50 other members of the nobility, including the pharaoh’s father, Seti I, according to the Egypt Museum. Since then, the gold coffin and Ramses’ mummy have been exhibited at museums around the world. Whether the sarcophagus fragment, which is currently stored in Abydos, will one day go on display, too, remains unclear.
By Sonja Anderson.



#Ramses II’s Long-Lost Sarcophagus Has Finally Been Identified#Ramses II#sarcophagus#ancient artifacts#archeology#archeolgst#history#history news#ancient history#ancient culture#ancient civilizations#ancient egypt#egyptian history#egyptian hieroglyphs#egyptian pharaoh#egyptian mythology#egyptian gods#egyptian art
28 notes
·
View notes
Text

I know this isn't ninjago guys but I finished this 17 hour painting for my art class and I was proud of it so...enjoy.
I love Egypt fun fact about me. :)
[ID: a detailed, realistic painting of the hathor columns at the dendera temple complex in dendera, egypt. /end ID]
#my art#art#egypt#egyptian#egyptology#egyptian art#ancient egypt#antiquity#ancient art#ancient egyptian#painting#digital painting
102K notes
·
View notes
Text

Statue of Princess Takushit, c.670 BC
5K notes
·
View notes
Text
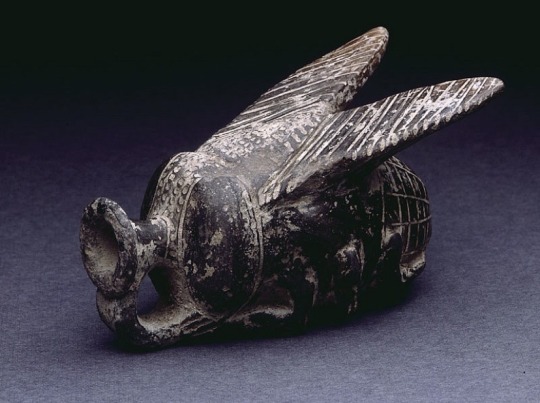

A kooky fly-shaped clay vessel (15th Dynasty)
With its realistic representation of a fly, it includes large eyes, wings, and legs that resemble hands
#art#lol#weird#archaeology#ancient#ancient art#egyptian art#egypt#egyptology#ancient egypt#clay#clay art#kemetic#ancient kemet#kemet
8K notes
·
View notes
Text
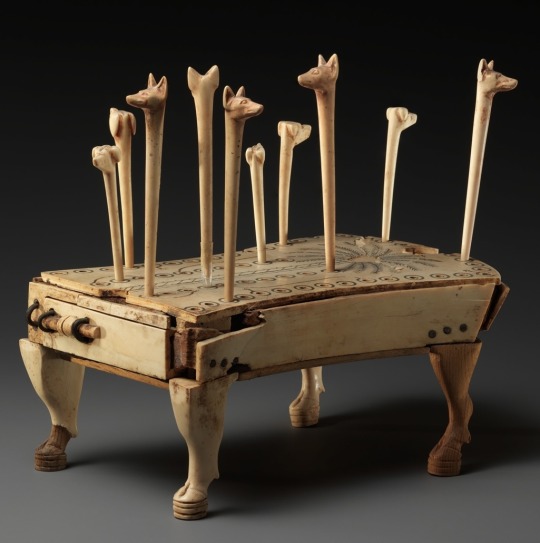
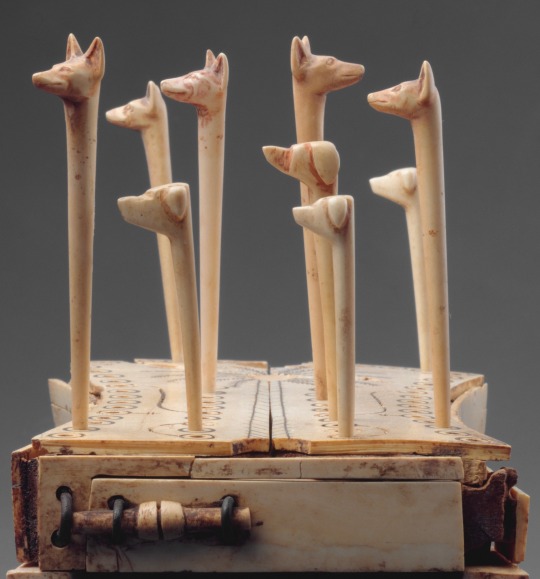


Egyptian
Game of Hounds and Jackals
Middle Kingdom, ca. 1814-1805 B.C.E.
#egyptian art#ancient egypt#ancient art#hounds and jackals#ancient history#artifact#antiquities#ancient people#ancient culture#egyptian history#egyptian culture#board games#chess#aesthetic#beauty#art history#aesthetictumblr#tumblraesthetic#tumblrpic#tumblrpictures#tumblr art#tumblrstyle#artists on tumblr#ancient artifacts
5K notes
·
View notes
Text

Mummy portrait (wax encaustic on sycamore wood) of a girl, from the Fayum region of Egypt. Artist unknown; ca. 120-150 CE (reign of Hadrian or Antoninus Pius). Now in the Liebieghaus, Frankfurt am Main, Germany. Photo credit: Carole Raddato.
#history#ancient history#Ancient Egypt#Roman Empire#Roman Egypt#art#art history#ancient art#Roman art#Egyptian art#Romano-Egyptian art#mummy portrait#encaustic painting#Liebieghaus
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
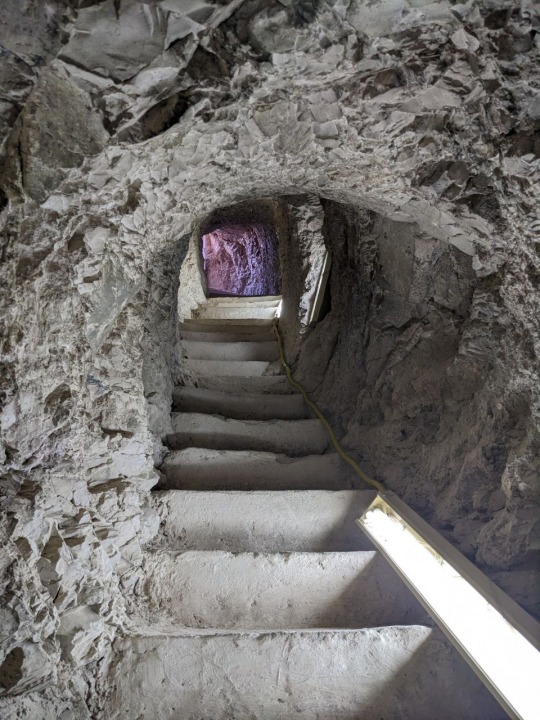
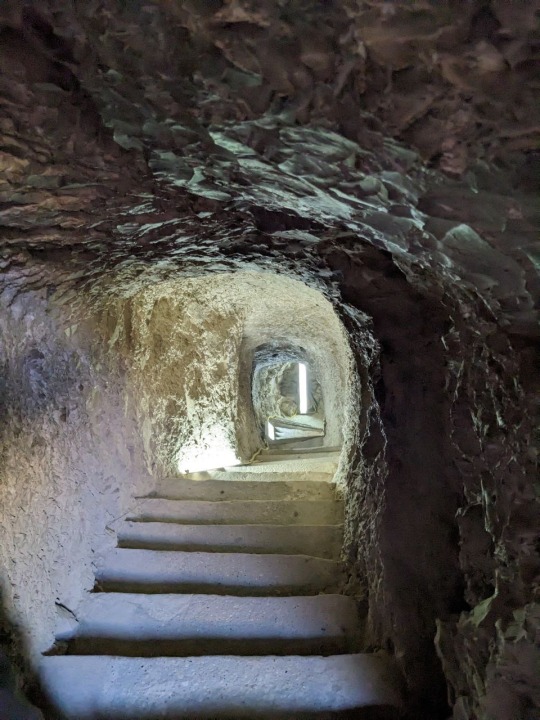
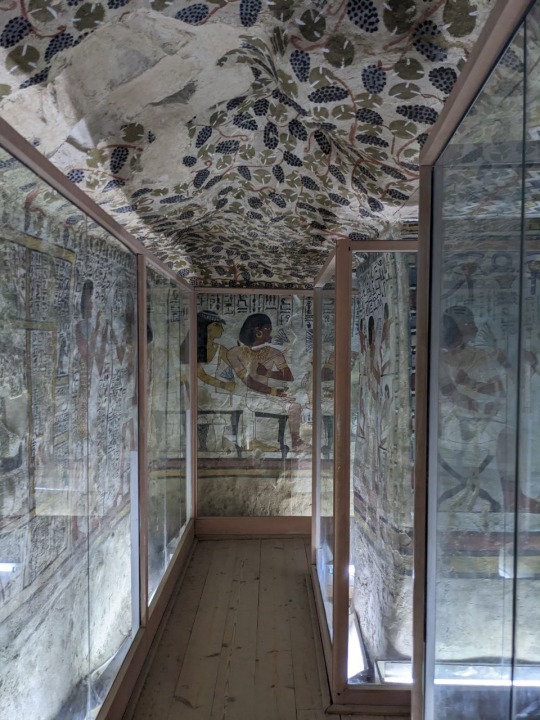
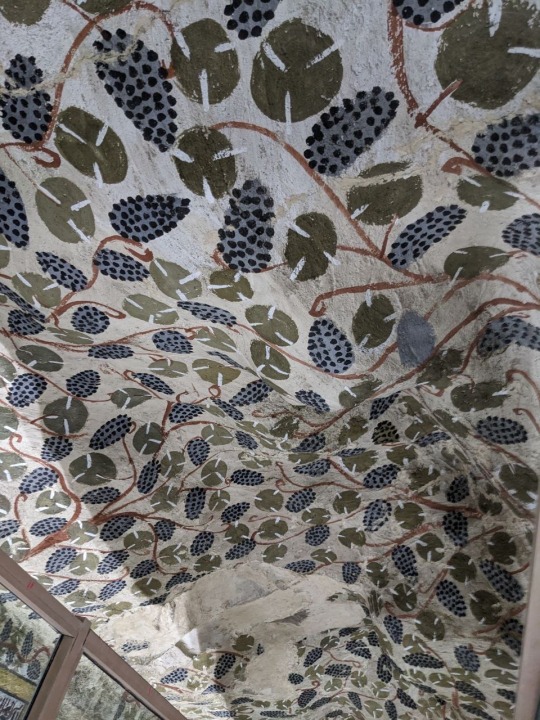
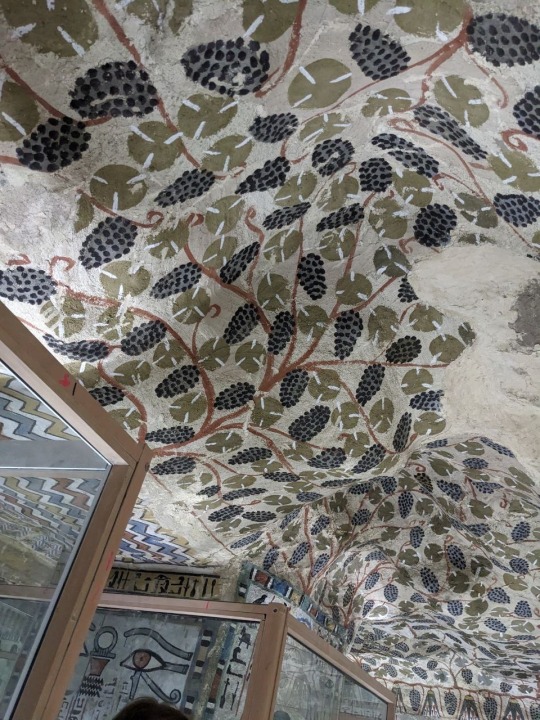
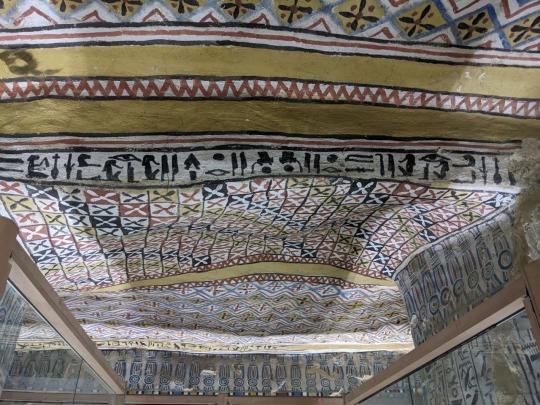
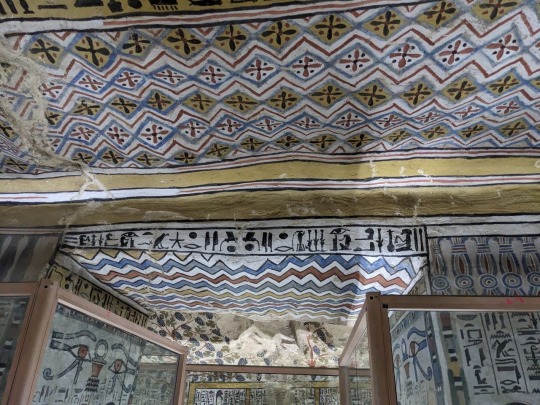










Ceiling and imagery of the Tomb of the Vineyards, burial of Sennefer, Mayor of the Southern City, Thebes, during the 18th dynasty of Egypt.
Photos taken by me, August 2023
It’s hard to tell which way is up and down when walking through the tunnel leading from the surface into the tomb. Before entering the main chamber there is a small antechamber whose ceiling is quite low, and then a shallow arch which leads to the main room depicted in the above photographs. Both chambers contain a good deal of paintings, however the main chamber holds the most numerous and well preserved paintings, of course. Besides the ceiling, everything is encased in glass.
#ancient egypt#egyptian mythology#egyptian hieroglyphs#egyptian art#ancient history#egyptian gods#egyptology#hieroglyphs#archaeology#egyptian history#egypt
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
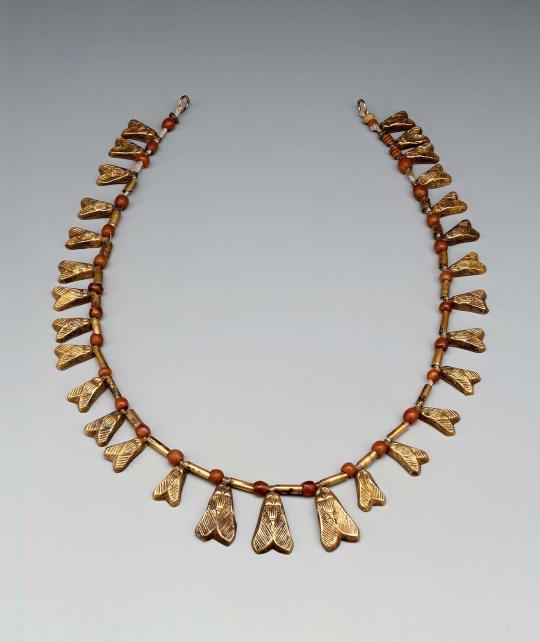

Necklace of fly beads, Egyptian, New Kingdom, Dynasty 18, 1550–1295 B.C., part of the MFA Boston collection
Fly ornament necklaces, occasionally presented to courageous soldiers, may have been worn as talismans to ward off insects.
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
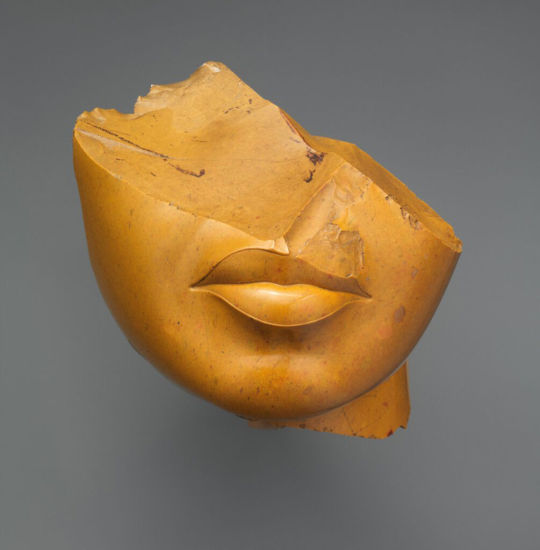

Unknown, Egyptian. Fragment of a queen's face. c. 1353-1336 BCE
339 notes
·
View notes
Text

Essam Marouf (Egyptian, 1958) - Untitled (2010)
816 notes
·
View notes
Text
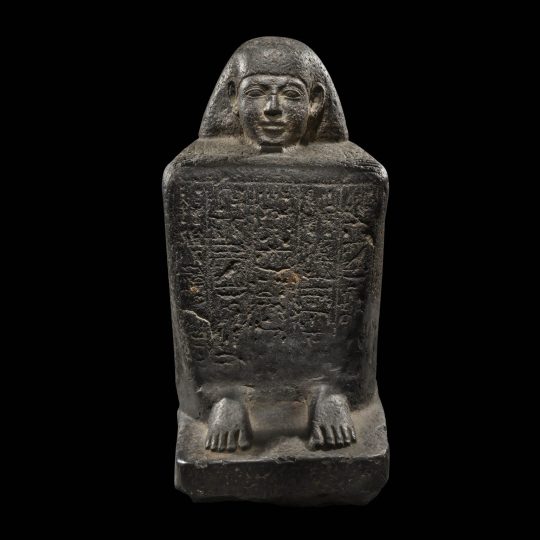
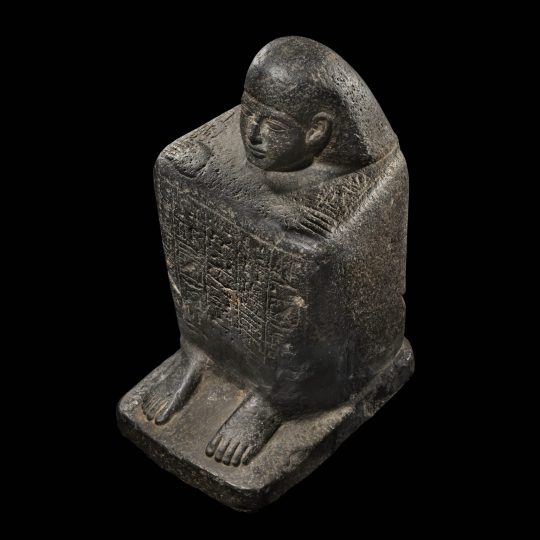



Egyptian Basalt Block Statue
Egyptian · Late Period, Dynasty 26, ca. 664-525 B.C.
#Egyptian Basalt Block Statue#Late Period#Dynasty 26#ca. 664-525 B.C.#statue#ancient artifacts#archeology#archeolgst#history#history news#ancient history#ancient culture#ancient civilizations#ancient egypt#egyptian history#egyptian art
506 notes
·
View notes
Text









#black community#original photographers#black people#artwork#graphic design#black art#black power#black history#black culture#black family#black woman#black panther#black men#black history month#black knowledge#black love#blacklivesmatter#black representation#black relationships#black children#black king#black queen#black africans#africa fashion#egypt nt#egyptian art#african art
294 notes
·
View notes
Text
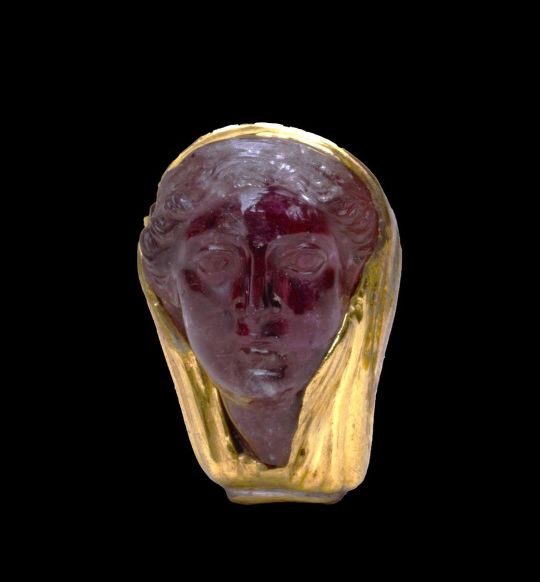
Methyst head wrapped in gold, of Arsinoë II, Queen of Ptolemaic Egypt, c. 300 B.C
335 notes
·
View notes
Text
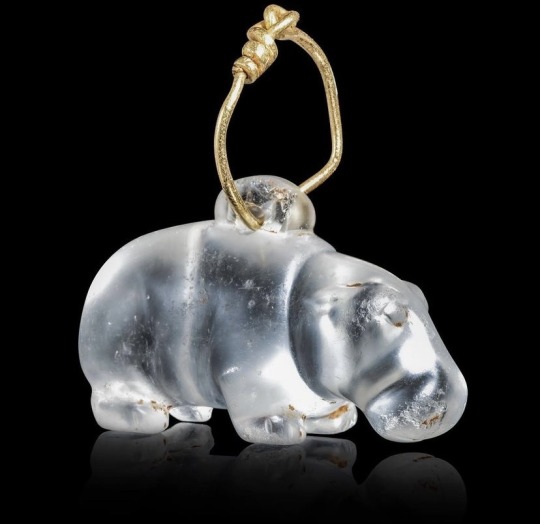

An Egyptian rock crystal of a chonky hinpopotamus amulet
(Middle Kingdom, ca. 2050-1650 BCE)
Amulets were worn by ancient Egyptians for their protective and regenative properties. Used in both in daily life and during funerary rites, amulets represented animals, deities, symbols or objects thought to possess the magical powers of warding off evil spirits.
As animals were popular representations, the hippopotamus was known for its apotropaic (e.g. ability to avert bad luck) qualities and was associated with rebirth.
#art#archaeology#sculpture#ancient#ancient art#ancient egypt#amulet#hippopotamus#apotropaic#egyptian art#egyptology#kemetic#ancient kemet#rock crystal#geology#ancient jewelry#jewelry
3K notes
·
View notes