#caves
Text
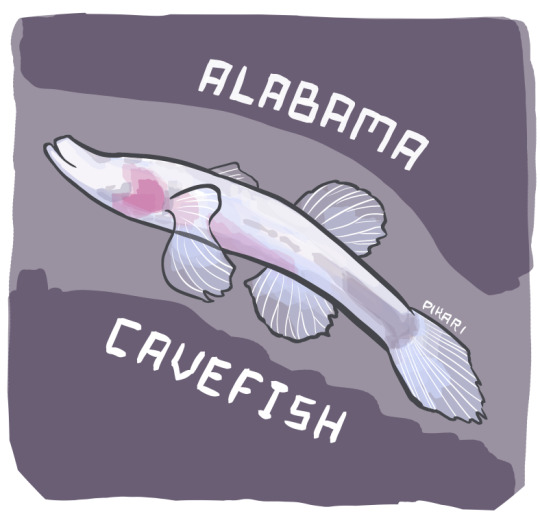

Aw, shucks. I'm too bashful to come out of this cave.
Alabama Cavefish (Speoplatyrhinus poulsoni)
Key Cave in Alabama, USA
Status: Critically Endangered
Threats: Extremely small population, groundwater pollution, dependence on the endangered Gray Bat for nutrients from its guano
#fish#fish art#cave fish#fishblr#caves#freshwater fish#conservation#endangered#north america#usa#alabama
40 notes
·
View notes
Text
Cave fish time!!
Cryptotora thamicola or the waterfall climbing cave fish are extremely rare, found in only eight caves on the border of Thailand and Myanmar. Like most cave fish they are blind and pigmentless but what makes them special is there ability to cling to walls and climb up flowing water.





#fishblr#marine biology#caves#spelunking#cave fish#caving#nature#strange#gif#fish facts#fish#fresh water
9K notes
·
View notes
Text

Cave Homes Cappadocia Turkey
#europe#turkey#history#ancient origins#archaeology#caves#ancient#tomb#stone#destert#ancient homes#ancient civilizations
1K notes
·
View notes
Photo

"A Kind of Blindness, A Kind of Sight" by Jaclyn Kolev Brown
6K notes
·
View notes
Text




#naturecore#cave#caverns#crystals#geology#caves#woodlandcore#forests#aesthetics#landscape#nature aesthetic#nature#explore#traveling#travel#plants#photography#forestcore#treecore#woodlands#scenery#green#blue green#moodboard#forest aesthetic#forest vibes
1K notes
·
View notes
Text

Texas zoo hatches brood of rare, ghostlike crayfish species
The hatchlings also mark the second-ever breeding of a blind, white, and 'cave-adapted' crayfish.
Another Texas zoo is celebrating a historic milestone in the restoration of a critically endangered species. This week, the San Antonio Zoo announced the births of 47 Oklahoma Cave Crayfish (Cambarus tartarus). Born at the zoo's Center for Conservation and Research (CCR), the crayfish are the first-ever to be hatched under the care of humans.

Known as one of the rarest crayfish species in North America, the Oklahoma Cave Crayfish is no more than three inches in length, with a white or colorless appearance, according to the Oklahoma Department of Wildlife Conservation.
The crayfish, which have no external eyes, thin pinchers and legs, are most at risk from groundwater pollution. Direct disturbance of their caves, which are limited to a single county in northeast Oklahoma, is also a critical threat.
The state has listed the species as "state endangered." However, the species is undergoing review for possible inclusion on the endangered species list by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service...
Read more: https://www.chron.com/life/wildlife/article/texas-zoo-rare-crayfish-18364707.php
#crayfish#crustacean#endangered#conservation#caves#animals#nature#science#environment#texas#north america
2K notes
·
View notes
Text

White Cave Velvet Worm (Peripatopsis alba), family Peripatopsidae, endemic to 2 cave systems in South Africa
Live bearing (viviparous).
Vulnerable, rare.
photograph by Rodrigo Ferreira
720 notes
·
View notes
Text
Wet Beast Wednesday: cave fish
Prepare for a deep dive today. Not because I'm going to be more in-depth than usual, but because we're talking about caves. Which are deep. In the ground.... Yeah, you get it. Today is going to be a bit different from my normal WBW posts. Instead of going in depth on a particular species or group of related species I'm going to discuss common adaptations fish evolve to live permanently in caves and then go over a few species I find interesting. Let's get spelunking.
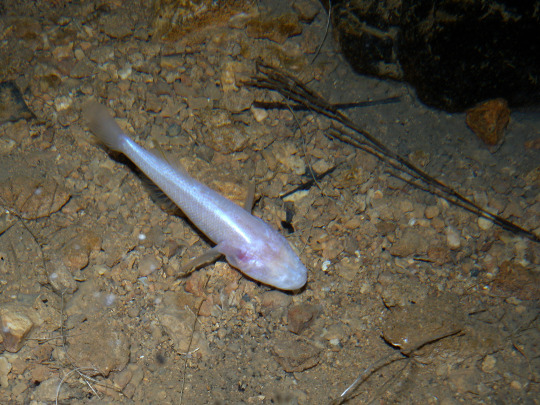

(Image: Typhleotris madagascariensis, a typical cave fish. It is a small fish with an entirely white body and smooth skin where the eyes would be on a normal fish. It is resting on rocky sediment. End ID)
Caves are not an easy place to live. There's no light, limited food, often low oxygen levels, and the threat of collapse or rockfall. Cave-swelling animals (collectively called troglofauna) need a number of special adaptations to survive and there is little room for error. Troglofauna that are strictly aquatic are called stygofauna. Troglofauna and stygofauna can be divided into three groups based on their life history. Troglophiles and stygophiles complete part of their life cycle in caves and part outside of them. A classic example of this is the many species of bat who seasonally inhabit caves to give birth and mate. Trogloxenes and stygoxenes are animals who will visit caves, but do not require time in caves to complete their life cycle. An example trogloxene would be a bear who takes shelter in a cave during winter. Finally, troglobites and stygobites live their entire lives in caves and never leave. The fish I discuss today are stygobites. Because troglobites and stygobites generally will die outside of their caves, they have very little opportunity to disperse. As such, many cave fish species are found only in a single cave or cave system and are entirely dependent on the health of their homes to survive.

(Image: two cave catfish sitting next to each other on a rock. They are white with elongated anal and rear dorsal fins, and no eyes. End ID)
Many cave-dwelling animals develop a set of common adaptations called troglomorphism. Cave water is often high in minerals but low in oxygen and food content. To survive, the fauna develop very slow metabolisms, allowing them to last a long time on limited resources while slowing down movement and other active systems and increasing age. These species are also typically smaller than their epigean (above-ground) relatives, further reducing their energy requirements. Slowed metabolism results in comparatively slow development. Cave species take much longer to mature and reproduce then related epigean species. Many species further decrease their energy consumption by moving as little as possible. Many species of cave fish are able to last long periods of time between meals without negative impacts to their health. They will binge eat whatever they can find and then subsist on fat stores while food is scarce. One test in captivity showed that a Phreatobius cisternarum (cave catfish) could go a while year between meals and stay healthy. Cave species are usually opportunistic generalists as they can't afford to pass up resources. Much of their food will originate outside of the cave, either directly or indirectly. Water flow into caves brings in algae, bacteria, plankton, and other food sources. Other more indirect methods of introducing include bat feces. While the fish may not eat the feces directly, other species may do so and potentially become prey to the cave fish. The feces also introduces nutrients from outside the cave that encourages the growth of other food sources like bacteria, fungi, and planktonic animals.

(Image: Amblyopsis hoosieri, the hoosier cave fish. It is a very simplistic fish with no eyes or scales. End ID)
Life in a cave comes with a different sensory requirement. The complete lack of light makes vision useless. You don't know dark until you've seen cave dark. Fun fact: caves are so dark that sighted people can start hallucinating in them because our brains aren't evolved to handle zero visual stimulus and will start making stuff up to fill that gap. As a result of the utter darkness, many species of cave fish are blind. They either evolve to completely lose their eyes or have the eyes considerably reduced in size and function. Eyes take up a lot of energy to maintain and in caves, there is a lot of selective pressure to get rid of organs that aren't useful there. Despite the blindness, many species retain some form of photosensitivity and will flee from light. Cave species also often lack skin pigmentation. Skin pigment has two primary uses. It protects the skin from ultraviolet light in sunlight, and provides skin coloration that can be used for camouflage, displays, warnings, and so on. In an environment where there is no ultraviolet light and everyone is blind, skin pigment serves no real purpose and is lost. As a result, most cave species are white or translucent. The lack of pigment may be a reason so many species remain photosensitive. Without pigment, they would be highly susceptible to sunburn or skin cancer from ultraviolet light. Caves also have a sound dampening effect that makes hearing less valuable. Reduced eyes and pigmentation is also seen in deep sea fish that live too deep for light to reach. Even those species still use visual curs more than cave fish due to the abundance of bioluminescence in the deep ocean.

(Image: Sinocyclocheilus longicornus, a recently discovered species. It is a fish with translucent skin, revealing the skeleton. It has a long shout with two pairs of barbels. Emerging from the upper back is a horn-like protrusion. End ID)
With vision off the table, cave fish rely on other senses. chemoreception through taste and smell are strongly selected for as traits that can direct cave animals toward food or away from threats. Another sensory system fish have is the lateral line. The Lateral line is an organ system found on each side of a fish where modified skin cells called hair cells detect motion in the water. The lateral line allows fish to sense movement in the water around them, informing them of water flow and the movement of food and threats. Cave fish typically have a well-developed lateral line system that compensates for the lack of vision. Many fish perform displays for various reasons, such as attracting mates. These displays are typically visual, but in cave fish, that isn't an option. Instead, their displays are more focused on moving the water in ways that can be detected by lateral lines. Some species of cave fish maintain additional sensory abilities from their epigean ancestors. An example of this are cave catfish, who retain the barbels and electroreception common to their kind.
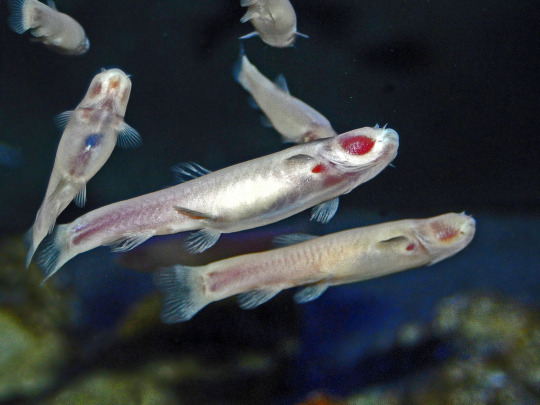

(Image: six Phreatichthys andruzzii. They are long, eyeless, white fish. The blood-filled gills are visible through its translucent skin, seen as a large red patch on the head. End ID)
Before moving on to specific species, it should be noted that cave fish is not a taxonomic category. Cave fish come from many different lines of descent and independently evolved similar adaptations to cave conditions. These similar adaptations are seen in most cave fauna, not just fish, and are collectively called troglomorphism. There are about 300 species of cavefish known to science.
Ophisternon candidum, or the blind cave eel, lives in north Australian caves that are connected to the ocean. Because these caves intake salt water, the pools and streams within them can become very salty, resulting in the eels developing a tolerance to a high range of salinity. They are rare, having been spotted under 40 times since 1959, and thus little is known of their lifestyle. We do know they burrow into sediment and secrete mucus to keep those burrows stable. Males seem to build burrows to woo females. They have been bred in captivity for use un laboratories. At up to 40 cm long, they are huge for cave fish and used to hold the record for the largest species known until another species was found that's even bigger.

(Image: an eel with translucent, pink skin, no eyes, and ribs visible through the skin. It looks somewhat like an earthworm. End ID)
The actual largest known cave fish is Neolissochilus pnar, which gets up to 40 cm while being more massive than the eel. They are found in a single cave system 100 meters underground in India. The primary food source in the cave appears to be debris from the nearby forest that is washed into the cave during seasonal flooding. The fish may have been known to locals well before it was scientifically described, as there are stories of white cave fish going back over a century in the region.

(Image: a small fish with no eyes, white skin, and a long snout with barbels on it)
The Alabama cave fish (Speoplatyrhinus poulsoni) may be the rarest species of freshwater fish in the world. They live exclusively in key cave, Alabama, USA and no more than 10 have ever been seen at a time. The population is estimated to be under 100, below the generally accepted minimum viable population for a species of 200. Fittingly enough, this means a species only found in Alabama may be severely inbred. They are believed to be triggered to mate by seasonal flooding and may be mouth brooders. Climate change-caused changes to flooding and toxins leaking into the groundwater from sewers are currently threatening them with extinction.

(Image: a long, white, eyeless fish with an elongated snout. Its skeleton is visible through its skin. End ID)
Typhliasina pearsei, the Mexican blind brotula or dama blanca ciega (blind white lady), lives in the cenotes of the Yucatán peninsula. Cenotes are sinkholes filled with groundwater and the ones in the Yucatán are often connected by underground caves, rivers, and aquifers. The fish are apex predators who eat shrimp and mysids and are known to coexist with other cave fish in part of their range. As with other brotulas, they are a rare example of a bony fish that gives live birth. Because of how interconnected and numerous the cenotes are, this species has one of the largest distributions of all cave fish.

(Image: an eyeless white fish with a long tail and elongated rear dorsal and anal fins. It is next to an orange rock. End ID)
Cryptotora thamicola, the cave angel fish or waterfall climbing cave fish, is the adrenaline junkie of the cave fish world. Most cave fish live in slow-moving or still water, but this daredevil lives in rapids. But just living in rapids isn't extreme enough, these guys climb waterfalls. Their large fins with hooked fin rays let them cling onto the rocks while facing into the current. They then allow food to flow right into their mouths. Unlike other walking fish, the waterfall climbers have a well-developed pelvic girdle and walk in a style very similar to tetrapods, with front and back fins alternating strides. This has made them very interesting to evolutionary biologists studying the transition from fish to tetrapods.
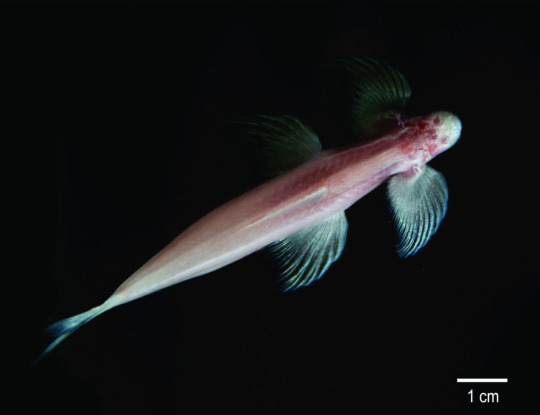

(Image: a typical cave fish with very large pectoral and pelvic fins. End ID)
The Mexican tetra (Astyanax mexicanus) is an example of a handful of fish species that have a cave form and a non-cave form. Most Mexican tetras are perfectly ordinary tetras, but one population has adapted to cave living and has developed trogomorphic traits. The cave from lack pigment, has tastebuds on its head, lacks eyes, and can store more body fat. While you would expect such radical physiological differences to mean the two populations are different species, they aren't. The two populations are fully capable of producing fertile offspring and do so in the wild. If you've ever seen a cave fish in person, there's a good chance it was one of these as the cave form has entered the pet trade and they do very well in captivity, making them the most studied cave fish.

(Image: the non-cave and cave forms of the Mexican tetra seen next to each other for comparison. The non-cave form is a fairly typical silvery-green fish. The cave form is slightly more robust, white, and eyeless. End ID)
Because most cave fish are found only in a singe cave or cave system, they are fully dependent on the health of that cave. Caves tend to be very stable environments, which results in the inhabitants being pretty bad at adapting to change. Changes in water flow, introduction of new species, and pollutants can seriously harm or wipe out whole species. Many species of cave fish are rated as endangered or critically endangered based on their low populations and vulnerability to change.
#wet beast wednesday#I went into this thinking it would be quick and easy to write.#and now it's 6 hours later#cave fish#cave animals#troglofauna#cave#caves#fish#fishblr#fishposting#aquatic life#aquatic biology#biology#zoology#ecology#animal facts#evolution#informative#image described#educational#speleobiology
511 notes
·
View notes
Text


Grjótagjá Cave, Iceland by Sergio Thor Miernik
724 notes
·
View notes
Text



Running through the Caves and avoiding the arrows
#did it in my first try without getting hit#Lara Croft#Tomb Raider#Tomb Raider Remastered#My Gif#gaming#gamingedit#gamingladies#tredit#tombraideredit#Peru#Caves#dailygaming#laracroftedit
744 notes
·
View notes
Text

Cueva de Arpea, Spain. A neat cave in the hinge of an anticline. (credit: Ángel M. Felicísimo)
2K notes
·
View notes
Photo
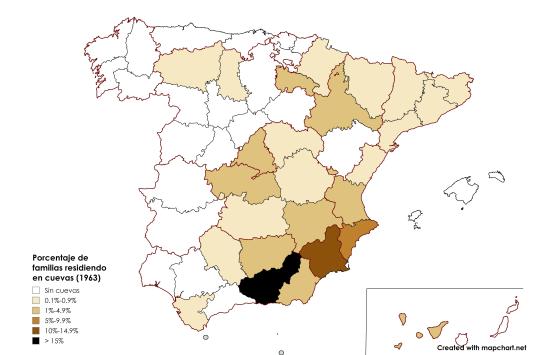
Percentage of Spanish population residing in caves, 1963.
415 notes
·
View notes
Text




Onondaga
📷: @sjscoyote , 2010
📍: Onondaga Cave State Park, Missouri
#caves#photography#nature photography#spelunking#cave photography#missouri#onondaga cave#geology#photography is art#photographers on tumblr
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
📍Alaska, USA 🇺🇸
#video#river#alaska#alasca#usa#eua#lake#lago#rio#under water#water#stones#rocks#paraiso#nature#paradise#natureza#view#caves#cavernas#waterfall#queda d'água
689 notes
·
View notes
Text
Rationally, I know that an elevated rate of mysterious disappearances tends to correlate geographically with large cave systems because caves are absurdly dangerous all by themselves and people won’t stop trying to prove otherwise, and if you fuck up while caving they usually never find the body, but in my heart I know it’s because there’s Things™ down there.
5K notes
·
View notes
Text
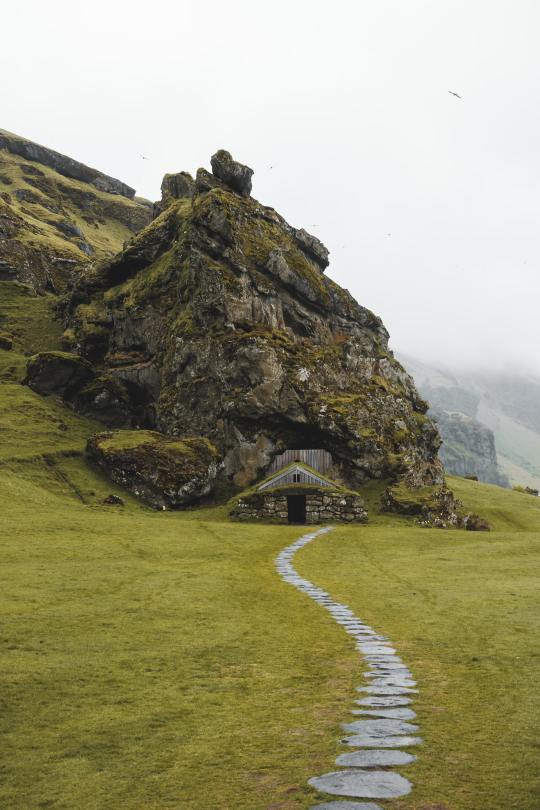

Rutshellir Cave, Iceland (by Job Savelsberg)
See more of Iceland.
#rutshellir#cave#caves#iceland#icelandic#europe#travel#wanderlust#explore#hut#viking history#vikings#viking house#historic architecture#architecture#old building#li_destinations#mountain#mountains#countryside
3K notes
·
View notes