#conservation
Text
— Recent giant anteater sightings in Rio Grande do Sul state indicate the species has returned to southern Brazil, where it had been considered extinct for more than a century.
— Experts concluded that the giant anteater ventured across the border from the Iberá Park in northeastern Argentina where a rewilding project has released around 110 individuals back into the habitat.
— The sightings emphasize the importance of rewilding projects, both to restore animal populations in specific regions and help ecosystems farther afield.
— Organizations across Brazil are working to protect and maintain current giant anteater populations, including rallying for safer highways to prevent wildlife-vehicle collisions that cause local extinctions.
Playing back hours of footage from a camera trap set in Espinilho State Park in the south of Brazil in August 2023, Fábio Mazim and his team banked on possible sightings of the maned wolf or the Pantanal deer and had their fingers crossed for a glimpse of a Pampas cat (Leopardus pajeros), one of the most threatened felines in the world.
What they didn’t expect to see was an animal long presumed extinct in the region. To their surprise, the unmistakable long snout and bushy tail of a giant anteater ambled into shot.
"We shouted and cried when we saw it,” the ecologist from the nonprofit Pró-Carnívoros Institute told Mongabay. “It took a few days to grasp the importance of this record. A sighting of a giant anteater was never, ever expected.”
Last seen alive in the southwest of the Rio Grande do Sul state in 1890, the giant anteater (Myrmecophaga tridactyla) has since been spotted 11 times since August 2023, although the scientists are unsure whether it’s the same one or different individuals. However, the sightings confirm one clear fact: The giant anteater is back.
It's a huge win for the environment. Giant anteaters play an important role in their ecosystems, helping to control insect numbers, create watering holes through digging and are prey for big cats such as jaguars and pumas.
The habitat of the giant anteater stretches from Central America toward the south cone of Latin America.
Its conservation status is “vulnerable,” although it is considered extinct in several countries, including El Salvador, Guatemala and Uruguay, as well as specific regions such as the states of Rio de Janeiro, Espirito Santo, Santa Catarina and (until now) Rio Grande do Sul in Brazil and the Cordoba and Entre Rios regions in Argentina.
In the last six months, the giant anteater was spotted on camera 11 times in the Espinilho State Park in the state of Rio Grande do Sul in Brazil. It was the first time in 130 years that the species has been seen alive there.
Yet not only is it a triumph for conservationists to see these animals returning to Brazilian biomes, it’s also a surprising mark of success for a rewilding program about 150 kilometers (93 miles) away in neighboring Argentina.

Rewilding Argentina’s biomes
Iberá National Park in Corrientes province in northeastern Argentina is a 758,000-hectare (1.9 million-acre) expanse of protected land comprising a part of the Iberá wetlands with its swaths of grasslands, marshes, lagoons and forests. The region was once home to just a handful of giant anteaters after habitat loss, hunting and vehicle collisions decimated the population.
Since 2007, the NGO Rewilding Argentina, an offspring of the nonprofit Tompkins Conservation, has been reintroducing the species back to the area, most individuals being orphaned pups rescued from vehicle collisions or poaching.
So far, they have released 110 giant anteaters back into the wild. Nowadays, several generations inhabit the park, transforming it from “a place of massive defaunation to abundance,” Sebastián Di Martino, director of conservation for Rewilding Argentina, was quoted as saying in an official statement.
The project has been so successful that the giant anteaters appear to be venturing farther afield and moving to new territories beyond national borders, such as Espinilho State Park in Brazil’s Rio Grande do Sul region...
Experts now hope that a giant anteater population can reestablish itself naturally in Espinilho State Park without the need for human intervention.
“The giant anteater returning to Rio Grande do Sul shows the success of the work done in Argentina and how it’s viable, possible and important to do rewilding and fauna reintroduction projects,” Mazim said. “It is also an indication that the management of conservation units and also the agricultural areas of the ecosystems are working,” he added. “Because if large mammals are coming from one region and settling in another, it is because there is a support capacity for them. It is an indication of the health of the environment.”
-via GoodGoodGood, via May 25, 2024
#anteater#giant anteater#brazil#brasil#argentina#rewilding#conservation#conversation news#nature#biodiversity#environment#ecosystem#ecology#good news#hope
290 notes
·
View notes
Text
Straight Out of the Colonial Playbook:
The Myth of Untouched Lands
The Jewish National Fund (JNF) is an organisation with charity status all across the world. Many people know them as the people who use their little blue boxes to collect money to plant trees. They seem to be doing well to reach their goals, having planted over 250 million trees since 1901. All this seems pretty innocuous, perhaps even noble. After all, the idea of planting trees seems quite divorced from violent settler colonialism.

ID: A large slice of watermelon. You can see the Red of the flesh, the black of the seeds, and the white and green of the rind. It is set against a light teal background, a colour that may invoke peace and calm, much like a free Palestine would.
But the two have long, intertwined histories. Just look to the National Parks of the US, used to grab land from Native Americans with the justification that they were "uninhabited". Colonisation of the Arabian peninsula was partially justified with the argument that native Arabs had degraded the environment to the point of desertification, and colonial rule was the only way they could be saved from themselves [1]. Unsurprisingly, most of the ecological damage in that region had been done by the colonialists themselves in the pursuit of resources.
The JNF isn't just some minor organisation that has unfortunate ties to questionable powers. Though they shroud themselves in the soft words of environmentalism, they currently stand as one of the primary tools of violence for Zionism.
Established in 1901 by the 5th Zionist Congress in Basel, Switzerland, they have always been an organisation with settler colonial intentions. In 1940, their leader Yosef Weitz, said “There is no way but to transfer the Arabs from [Palestine] to the neighbouring countries, to transfer all of them… not one village must be left… for this goal funds will be found." [2]. You know what happened to him after the first Nakba? He became the head of the JNF's forestry department [3].
According to their own website, they currently stand as the "single largest provider of Zionist programs in the U.S." [4]. They also own about 13% of all state lands in Israel [5]. They have been both a major driver, and unsurprisingly, benefactor from the ongoing Nakba of the Palestinian people.
So how exactly does planting trees feed into settler colonialism? The model works like this:
The Israeli government violently displaces people from their lands in the name of "self-defence".
The land becomes "uninhabited".
The JNF uses funds they have accrued from overseas donations to buy up the land.
They establish a national park in the area and begin to plant trees.
Settlers move into the surrounding regions. The JNF have a policy of not leasing land or accommodation to non-Jewish people [5].
Any remigration of indigenous people back into those lands is framed as "environmental destruction" and those people are forced out once more.
You know what's sneaky? They are using trees as bodies. They don’t have enough people to colonise all the land they've stolen, so they plant trees to occupy the spaces that human bodies cannot. They deliberately use fast growing trees like pines to aid in this pursuit [3]. Each forest acts as an occupying force, just one that uses seeds instead of bullets and trees instead of soldiers.
Most of their efforts are concentrated on Naqab (Negev in Hebrew), a region in the south of Israel mostly consisting of desert. On their website, the JNF boast of their Blueprint Negev initiative, and how it's "transformed Israel’s Negev Desert, making the Southern Israel an attractive place to live and work" [4]. Their mission statement in the Naqab includes the justification that they are providing homes, jobs and opportunities in the "empty" region [6]. One of the slogans have on their website is "Building the Negev, town by town"[6]. This is explicitly a settler colonial project, and all of it can be found on JNF website, in their own words.
And to top it all off, you guessed it, the Naqab is far from uninhabited. It was never empty land. In August 2018, 350 villagers from Umm al-Hiran were displaced to the state-regulated Bedouin township, Hura to accommodate the expansion of the Beit Yatir settlement in the Yatir forest, which was planted by the JNF [5]. In 2010, Nuri-al-Uqbi presented evidence that his ancestors had owned and lived in the lands of al-Araqib since before the Israeli occupation to the courts. In 2010, a Beersheva judge rejected the case, siding with the government's claims that his tribe had no ownership claims on the land [7]. The indigenous peoples of Palestine are constantly disenfranchised, displaced, and have very little means of winning their land back within an Apartheid legal system.
The JNF are using strategies employed by colonial powers in the past to violently seize land from native peoples. Acting under the guise of environmentalism "launders" the colonisation, adding extra steps in between the expulsion of people from their homes and the eventual settlement of that land by colonists, with the added bonus of making the JNF look very good. And you know what? Their reforestation schemes suck. Fast growing, new growth forests in the DESERT are not a substitute for old growth forests, not to mention the enormous amount of water they must be using to keep these forests as, well, forests.
What boils my blood the most is that you can see them honouring their colonial inspirations and sponsors in how they name their parks. Britannia park in the Hebron district obviously takes its name from Britain, a country instrumental in the establishment of the Israeli state and the Nakba that has ensued. Fittingly, it sits upon the ruins of seven Palestinian villages, destroyed by Israel during the first Nakba [8].
And this isn't just stuff that has happened in the past, but is happening right now. JNF UK is currently receiving donations to plant a memorial forest "to commemorate those who were brutally murdered on October 7." For £100, you can plant one tree. For £250, you can contribute to an outdoor seating area for group events. For £36, you can pay for an irrigation system that will provide enough water for one tree for four years [9]. Doesn't it make you angry? 36,000+ Palestinians have been murdered, and the JNF are collecting money to water trees on their graves.
I hate it when scientists stay neutral. We and our work are not divorced from the world around us. Conservation means nothing if it comes at the cost of human lives; it means nothing if it is used to veil the atrocities of colonialism and apartheid. It is our duty as conservationists, and as human beings to hear those whose voices carry cries for help, and answer the call. Do not be won over by the siren song of green colonialism.
Free Palestine. May all empires fall.
Bibliography
[1] Skandrani, Z., Decolonizing ecological research. Journal of Environmental Studies and Sciences, 2018. 8(3): p. 368-370.
[2] Stop the JNF, The JNF, Apartheid and Settler Colonialism. (Spring 2024). https://www.stopthejnf.org/the-jnf-apartheid-and-settler-colonialism-spring-2024/
[3] Stop the JNF, Tower and Stockades, Forests and Jim Crow Vetting Commitees. https://www.stopthejnf.org/jnfs-sordid-history-tower-and-stockades-forests-and-jim-crow-vetting-committees-by-jonathan-cook/
[4] Jewish National Fund, We are JNF. https://www.jnf.org/menu-3/about-jnf
[5] Amnesty International, ISRAEL: APARTHEID IN ACTION. Amnesty international: submission to the 43rd session of the UPR working group, 9 May 2023.
[6] Jewish National Fund UK, Homepage, https://www.jnf.co.uk/
[7] Jonathan Cook, Bedouins defiant despite Israel eviction plan. https://www.jonathan-cook.net/2014-06-14/bedouins-defiant-despite-israel-eviction-plan/
[8] Palestine Land Society, Britannia Park - Burial and Treachery. https://www.plands.org/en/articles-speeches/articles/2022/britannia-park-burial-and-treachery
[9] Jewish National Fund UK, Green Sunday 2024 – Memorial Forest. https://israelunderattack.jnf.co.uk/projects/green-sunday-2024-memorial-forest/
221 notes
·
View notes
Text
Everyone is talking about axolotls, but what exactly are these fascinating animals, and how do we care for them? This week on Aquarium of the Podcific, we are joined by Animal Care Specialist America Sahagun who cares for our axolotl squad at the Aquarium to discuss these “water dogs.” We also discuss our newest exhibit, FROGS: Facing a Changing World, which is open now!
Visit pacific.to/podcific to listen, or search “Aquarium of the Podcific” in your favorite podcast app. 🎧
#aquarium of the pacific#conservation#baby animals#animal care#axolotls#axolotl#podcast#aquarium of the podcific
113 notes
·
View notes
Text
#conservation#country music#rinharu#preschoolers#the wolf among us#rose mcgowan#choi san#lady gaga#submit to be featured!#wallpaper#bowser#deadpool
125 notes
·
View notes
Text
Im fucking sobbing looking at the new black footed cat at Utah's Hogle zoo
Shes just a fucking baby
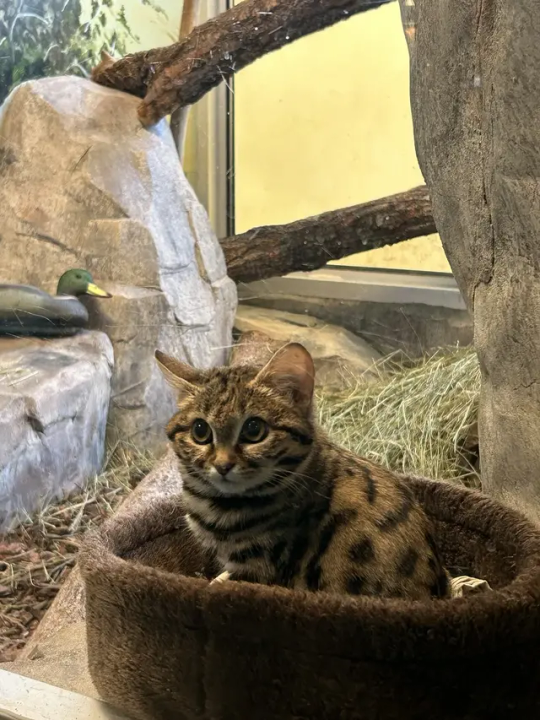
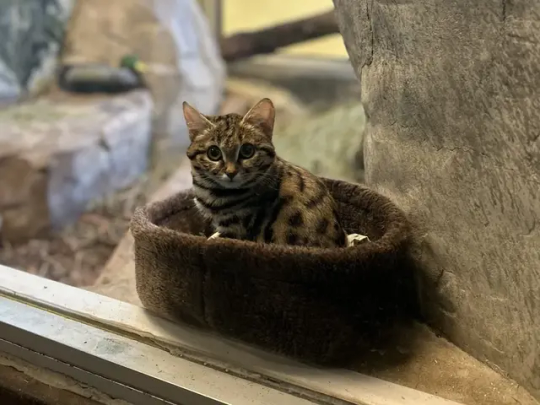


Baby with a 60% successful kill rate
#wrenfea.article#theres a video in the article#her name is gaia and shes 8 months#shes part of the AZA breeding program#i now have a reason to visit utah#leetle baby gorl#black footed cat#conservation news#conservation#zoos#animals#also the highest successful kill percentage for big cats is like. 25%#so 60% is fucking crazy
51K notes
·
View notes
Text

WELCOME BACK YELLOW-CRESTED HELMETSHRIKE!!!
25K notes
·
View notes
Text

9K notes
·
View notes
Text
Yo this rules and is genuinely uplifting
16K notes
·
View notes
Text
Golf Courses ARE Being Converted
The Solarpunk "fantasy" that so many of us tout as a dream vision, converting golf courses into ecological wonderlands, is being implemented across the USA according to this NYT article!
The article covers courses in Michigan, Pennsylvania, California, Colorado, and New York that are being bought and turned into habitat and hiking trails.

The article goes more into detail about how sand traps are being turned into sand boxes for kids, endangered local species are being planted, rocks for owl habitat are being installed, and that as these courses become wilder, they are creating more areas for biodiversity to thrive.
Most of the courses in transition are being bought by Local Land Trusts. Apparently the supply of golf courses in the USA is way over the demand, and many have been shut down since the early 2000s. While many are bought up and paved over, land Trusts have been able to buy several and turn them into what the communities want: public areas for people and wildlife. It does make a point to say that not every hold course location lends itself well to habitat for animals (but that doesn't mean it wouldn't make great housing!)

So lets be excited by the fact that people we don't even know about are working on the solutions we love to see! Turning a private space that needs thousands of gallons of water and fertilizer into an ecologically oriented public space is the future I want to see! I can say when I used to work in water conservation, we were getting a lot of clients that were golf courses that were interested in cutting their resource input, and they ended up planting a lot of natives! So even the golf courses that still operate could be making an effort.
So what I'd encourage you to do is see if there's any land or community trusts in your area, and see if you can get involved! Maybe even look into how to start one in your community! Through land trusts it's not always golf course conversions, but community gardens, solar fields, disaster adaptation, or low cost housing! (Here's a link to the first locator I found, but that doesn't mean if something isn't on here it doesn't exist in your area, do some digging!)
#solarpunk#sustainability#climate change#gardening#activism#hope#climate justice#news#new york times#golf courses#habitat#conservation
14K notes
·
View notes
Photo

I’ve seen a few ~aesthetic~ photos of rock stacks in rivers recently and this is just a reminder that you are destroying habitat when you move rocks around in rivers and streams.
In addition to dragonfly nymphs, rocky river beds are home to lots of other larval invertebrates like damselflies, mayflies, water beetles, caddisflies, stoneflies, and a bunch of dipterans. Not to mention lots of fish and amphibians!
Plus large scale rock stacking can change the flow of a stream and lead to increased erosion.
Anyway dragonfly for admiration:

Calico pennant by nbdragonflyguy
39K notes
·
View notes
Text
"In one of Africa’s last great wildernesses, a remarkable thing has happened—the scimitar-horned oryx, once declared extinct in the wild, is now classified only as endangered.
It’s the first time the International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN), the world’s largest conservation organization, has ever moved a species on its Red List from ‘Extinct in the Wild’ to ‘Endangered.’
The recovery was down to the conservation work of zoos around the world, but also from game breeders in the Texas hill country, who kept the oryx alive while the governments of Abu Dhabi and Chad worked together on a reintroduction program.
Chad... ranks second-lowest on the UN Development Index. Nevertheless, it is within this North African country that can be found the Ouadi Rimé-Ouadi Achim Faunal Reserve, a piece of protected desert and savannah the size of Scotland—around 30,000 square miles, or 10 times the size of Yellowstone.
At a workshop in Chad’s capital of N’Djamena, in 2012, Environment Abu Dhabi, the government of Chad, the Sahara Conservation Fund, and the Zoological Society of London, all secured the support of local landowners and nomadic herders for the reintroduction of the scimitar-horned oryx to the reserve.
Environment Abu Dhabi started the project, assembling captive animals from zoos and private collections the world over to ensure genetic diversity. In March 2016, the first 21 animals from this “world herd” were released over time into a fenced-off part of the reserve where they could acclimatize. Ranging over 30 miles, one female gave birth—the first oryx born into its once-native habitat in over three decades.
In late January 2017, 14 more animals were flown to the reserve in Chad from Abu Dhabi.
In 2022, the rewilded species was officially assessed by the IUCN’s Red List, and determined them to be just ‘Endangered,’ and not ‘Critically Endangered,’ with a population of between 140 and 160 individuals that was increasing, not decreasing.
It’s a tremendous achievement of international scientific and governmental collaboration and a sign that zoological efforts to breed endangered and even extinct animals in captivity can truly work if suitable habitat remains for them to return to."
-via Good News Network, December 13, 2023
#chad#abu dhabi#north africa#rewilding#endangered species#conservation#zoology#conservation biology#oryx#good news#hope#texas#big game#animals#endangered#environmentalism#environmental science#zoo#zoos#zoo animals
24K notes
·
View notes
Text
If you aren't following the news here in the Pacific Northwest, this is a very, very big deal. Our native salmon numbers have been plummeting over the past century and change. First it was due to overfishing by commercial canneries, then the dams went in and slowed the rivers down and blocked the salmons' migratory paths. More recently climate change is warming the water even more than the slower river flows have, and salmon can easily die of overheating in temperatures we would consider comfortable.
Removing the dams will allow the Klamath River and its tributaries to return to their natural states, making them more hospitable to salmon and other native wildlife (the reservoirs created by the dams were full of non-native fish stocked there over the years.) Not only will this help the salmon thrive, but it makes the entire ecosystem in the region more resilient. The nutrients that salmon bring back from their years in the ocean, stored within their flesh and bones, works its way through the surrounding forest and can be traced in plants several miles from the river.
This is also a victory for the Yurok, Karuk, and other indigenous people who have relied on the Klamath for many generations. The salmon aren't just a crucial source of food, but also deeply ingrained in indigenous cultures. It's a small step toward righting one of the many wrongs that indigenous people in the Americas have suffered for centuries.
#salmon#dam removal#fish#animals#wildlife#dams#Klamath River#Klamath dams#restoration ecology#indigenous rights#Yurok Tribe#Karuk Tribe#nature#ecology#environment#conservation#PNW#Pacific Northwest
15K notes
·
View notes
Text
It *is* a problem that charismatic species are often focused on for conservation at the expense of less charismatic but important species, but threatened species that are the subject of a lot of public outreach and education are also typically strategically selected.
I suspect that monarch butterflies are an example of this. Milkweed is a highly valuable plant for pollinators and a host plant for like. 400+ insect species. Getting people to plant it to save monarchs is funny because you're essentially finessing people into saving a ton of other insects that they wouldn't ordinarily care about
49K notes
·
View notes
Text

#green memes for ecological fiends#zoology#ecology#bird#hawks#environmental science#biodiversity#conservation biology#conservation#wildlife
28K notes
·
View notes
Text


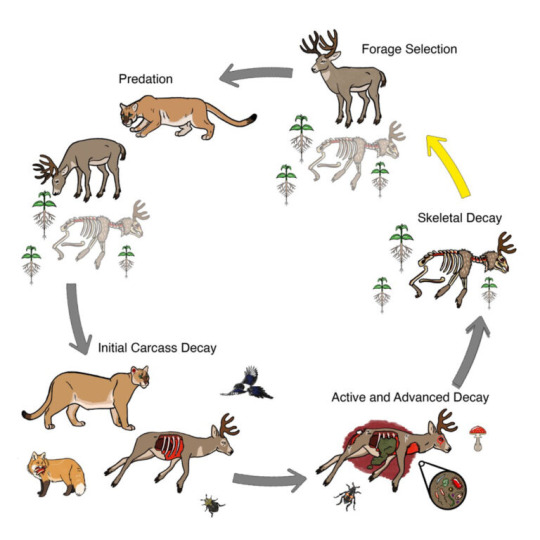

the mountain lions are unwittingly practicing witchcraft to improve their hunting chances and leaving patches of terra preta behind
21K notes
·
View notes
Text
EEEEEEEE EEEEEEEEE EEEEEEE

That's right! It's International Bat Appreciation Day! We share our planet with over 1400 species of bat, making the second most abundant mammal order, and they perform a wide variety of ecological roles, from dispersing seeds to pollinating flowers to eating thousands of insects in a single night! Over 200 bat species are listed as Threatened by the International Union for the Conservation of Nature--that is over 14 percent of all bats!
YOU can help endangered bats today by donating to Pennsylvania Bat Rescue at this link. This PA-based organization rehabilitates sick or injured bats and helps educate people like you and me in how we can create more bat-friendly environments.
If you want to learn about particularly-cool bat species native to New Zealand, check out this Consider Nature article on the Pekapeka, the bat that walks:
For the rest of the day, Consider Nature will be bat-bombing Tumblr with some of our favorite bat species to share them with the world!
Alt text: a small brown bat stretching its wings with the kind of fabulous flourish that would impress Ryan Evans.
#animals#nature#science#biology#wildlife#conservation#environment#bats#international bat appreciation day#batbombing
4K notes
·
View notes