Text
How to attract Venture Capital & Angel Investment: A business plan from an investor's perspective

1.0 Introduction - Reasons for raising capital
Fundraising for startups is quite an important step and different methods are often utilized which include Venture capital, Bank loans, Crowdfunding or Angel investors.When seeking startup funding it is critical to understand what stage of maturity your enterprise has reached. It is vital to be sure that the type and stage of funding you seek is in alignment with what funders are looking for as financing can facilitate growth but it often comes at the expense of reduced equity and corporate control.
1.1 Stages of Funding
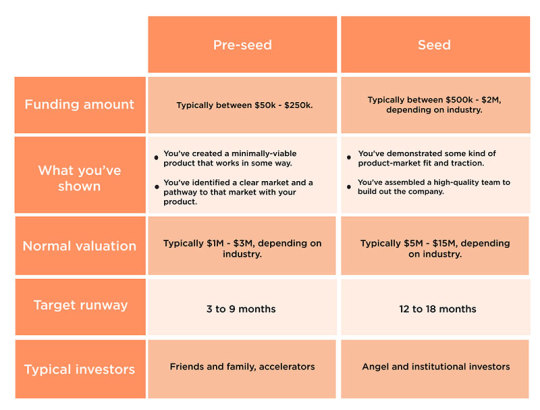
VC Pre-Seed/ Seed stage
Seed Stage capital is required to finance the early development of a new product or service.This early funding may be directed towards product development, proof-of-concept ,market research, or to cover the administrative costs of starting the enterprise. A true seed stage company has not yet established commercial operations .A startup in this phase establishes proof of concept by demonstrating a prototype(product or service) to potential customers and entices them to become sources of capital.The company’s goal in this stage is to test the market, establish the viability of the business idea, and measure interest and attractiveness to investors.
Startup stage
Financing for startups entering this phase provides funds for product development, some initial marketing and some administrative overhead.This type of financing is usually offered to recently organized companies or to those that have been in business for a short time ,but have not yet sold their product into the marketplace.Startup companies in this stage have,often times,assembled key management, prepared a proper business plan,and have conducted due diligence on the market viability of their product or service.
Early stage
Startups requiring“early”stage financing have usually been in business between 2-3years and have launched the company.The management team has been established, commercial operations have begun and funding at this stage is often required to cover cash flow requirements. Financing in this stage also strengthens capabilities in the areas of manufacturing, sales,and marketing.
Second stage capital financing facilitates the expansion of companies that are already selling products or services. At this stage a company raises additional equity capital to expand its engineering, technology platforms, sales, marketing, and manufacturing capabilities. Many companies in this stage are not yet profit-able and they often use the financing obtained in this stage to cover working capi-tal requirements, and to support organizational overhead, and inventory costs. Third Stage financing, if necessary,facilitates major expansion projects such as plant expansion,integrated marketing programs,the development of a large scale sales organization,and new product development. At this stage the company is usually a tor near breakeven or profitable.
Mezzanine Financing Phase
Mezzanine financing is a late stage form of financing for startups and is often used for major expansion of the company.This type of financing can also fund an emerging growth opportunity for the company. At this point the company may not wish to seek an additional round of equity diluting investment and may prefer the hybrid form of financing that mezzanine debt/equity financing offers.In addition, entrepreneurs may still be unable to obtain traditional bank loans at this point. Mezzanine loan investors are able to obtain a higher degree of security than an ordinary investment in equity since their rights, as debt holders, are senior to that of shareholders.
2.0 Types of funding

Angels
Once the initial start-up phase of a start-up is over, business angels often appear as the first external equity providers in the seed phase. Business angels are wealthy individuals who invest their private assets in young start-ups with great growth potential. This is done by providing venture capital in exchange for company shares. Often having been active as founders themselves or as experts in a specific industry, business angels can contribute additional expertise and an excellent network in addition to their capital and thus support the founders comprehensively. Companies that receive their first BA financing are, on average, 10.5 months old,and only just under 30% can already show sales. Once a start-up has been able to win a BA as an investor, this increases the attractiveness of the start-up for other investors as well (Denis 2004; Mitter & Kraus 2011). This signal effect is one of the most important added values offered by an angel investor, along with the contribution of one's own experience and active participation in the further development of the company. If a start-up even manages to attract several co-operating BA investors, this syndicate of co-investors, due to a wider range of non-monetary contributions, demonstrably leads to increased business performance and a higher survival rate within the next three years after the investment.
Angel Investors often provide a required round of financing to startups that are on the early stage path to profitability. In many cases,startups have overlooked the category of angel investor for their financing needs. Some academics place angel investors in the seed stage category of capital sources and others identify angel investors as filling the gap between seed stage capital and venture capital.Angel investing is in actuality,a hybrid between the two. Angel investors are often affluent people such as successful entrepreneurs, who wish to stay involved with their industry by assisting the next generation of startups. It is not just money that motivates angel investors; providing needed and valuable guidance to management of the startup is gratifying as well. Startup founders need to take a close look at their own needs and requirements before entering customized agreements with angel investors as they may find them-selves giving away more control over their companies than they really want to. Angel investors require a return on investment in the area of 20x-30x their initial investment. These investors are not interested in slow-growth or “lifestyle” busi-nesses. They are after businesses that can grow at an annual rate of 40% or more. Unlike venture capitalists (VCs), many angel investors do not calculate Internal Rates of Return (IRR) and other measures of investment performance. Angels often regard these types of calculations as too speculative. Startups can also expect a changing playing field when negotiating return expectations with angel investors
Venture Capital
The financing of angel investors is often followed by another form of external equity financing, namely venture capital (VC). Unlike business angels, VCs operate in the form of public or private investment companies that provide venture capital to start-ups. The invested sums usually comprise amounts in the millions. The primary investment targets are innovative companies with high growth potential, but which often entail a high risk . From the founder's point of view, the same applies: venture capital is attractive for start-ups with great growth ambitions and the associated high strategic uncertainty, low prospects of success, but in the case of success, strongly positive cash flows. In addition to venture capital, VCs as active investors bring their expertise and access to networks to the respective start-up as value-adding services. They also perform monitoring tasks to reduce existing information asymmetries. This active investment approach, combined with the risk taken, makes VC funds demand a higher return, which in turn leads to high capital costs compared to otherwise financed start-ups. Additionally, VC funds often require a substantial ownership share. Venture capital is a source of financing that usually follows seed stage funding and angel investor funding that is utilized in the earlier stages of the startup’s life. This type of growth financing is provided to high-potential,growth-oriented companies that require a substantial round of investment.The amounts are usually in excess of five hundred thousand dollars and up to tens of millions of dollars or more.However,it should be noted that venture capital funding can occur at any time throughout the startup’s initial phases prior to IPO.
Venture capital firms bear a high degree of risk investing in startups, including a complete loss of their investment. As such,most venture capital investments are done in a pooled for-mat,where several investors combine their investments into one large fund that invests in many different startup companies.Large pooled funds of VC firms can range anywhere in size from$25million–$1billion.The VC firm will generally take a seat on the Board of Directors of the startup and will take an active role in bringing their management experience to the company. Many VC firms specialize in certain industries such as technology, biotechnology, and health care where they bring deep industry expertise to bear. VC’s most often take equity positions in startup companies in exchange for their capital and expect annual rates of return of between 30%-50%.It should be noted, however, that rates of return in this category are subject to a wide variety of factors, not least of which has been the difficulty in raising pools of capital for venture financing over the last several years. VC’s require high rates of return because ,in many cases ,their investments in startups are highly illiquid and require anywhere from 3-7years to come to fruition through a favorable exit event such as an IPO,merger and acquisition,or a leveraged buy-out. It is critical for startups to perform their due diligence on VC firms before jumping into bed with them.

2.2 A Business Plan
A Business Plan is a document in which a business opportunity, or a business already under way, is identified, described and analyzed, examining its technical, economic and financial feasibility. The Plan develops all of the procedures and strategies necessary in order to convert the business opportunity into an actual business project
A business plan, in principle, can be seen as a document that commercial-izes your business idea as a whole towards potential investors and stake-holders. A business plan is successful if you succeed in conveying to the reader the most significant opportunities and growth capacities of your company realistically. A business plan should justify and describe your business idea and further business development in a clear and adequate manner. It should not merely aim at emphasizing the strengths of the company, but rather at presenting a realistic portrait of its problems, risks and obstacles. In addition to this, appropriate solutions should be proposed and discussed in detail. A business plan can be used for specific purposes. One target might be to obtain new means of investment for the development of a product or the marketing of a new product.
2.3 Aspects of an attractive business plan from an investors perspective
Financial performance
It is vital to prove to potential investors that the company has excellent financial performance. Venture capitalists will look for a potential of high returns and a clear exit opportunity. Investors will wonder if the company shows signs of growth and if it has plans such as issuing shares or borrowing money to stimulate growth
Background and experience in the industry
Investors don’t want entrepreneurs to make mistakes on their dime. Investors look for experienced entrepreneurs and management teams with a track record of high performance and leadership in the company’s industry or in prior ventures. Most investors will research your business experience and your background in the industry. Passion and commitment should be evident to inspire confidence in investors and stakeholders.
The product or services need to be unique. It is vital to prove to investors, with concrete evidence, that the market potential is big enough to make investing worthwhile.Venture capitalists are influenced by product characteristics such as proprietary features and competitive advantage. Also, investors look for features that distinguish the startup from potential competitors and give them some sort of advantage, such as intellectual property protection, exclusive licenses and exclusive marketing and distribution relationships.
Effective business model
The startup will start to display its strategic value as soon as it begins to generate profits. It is important to prove that the business model that is currently being used will help the company become more profitable.Different types of investors seek different attributes from a business plan. It’s important to customize the business plan and pitch to each investor. For example, venture capital fund managers and angel investors tend to put more emphasis on both market and finance issues, so those are areas that a startup should focus on when approaching these types of investors.
Large market size
Angel investors typically invest in solutions that address major problems for significantly large target markets. On the other hand, venture capitalists look at market characteristics such as significant growth and limited competition when investing.The larger and more stable customer base that your brand has, the stronger competitive advantage a startup will have when pitching to investors. A larger and more stable customer base will serve as proof that the company has a great impact on its target market.Investors look for companies that can grow quickly and manage this high growth scale. Investors must see that the company can generate significant profits beyond the initial product idea with adequate financial projections and a plan to include multiple sources of revenue.
References
Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences. (2003). Strategies for attracting angel investors. Journal of Commercial Biotechnology, 9(January 2003), 8. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/233551418_Strategies_for_attracting_angel_investors
Università degli Studi del Sannio. (2014). The New Ways to Raise Capital: An Exploratory Study of Crowdfunding. nternational Journal of Financial Research, 5(April 2014), 10. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/273985092_The_New_Ways_to_Raise_Capital_An_Exploratory_Study_of_Crowdfunding
University of Glasgow. (2004). What do Investors Look for in a Business Plan?: A Comparison of the Investment Criteria of Bankers, Venture Capitalists and Business Angels. International Small Business Journal, 22(June 2004), 10. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/247738793_What_do_Investors_Look_for_in_a_Business_Plan_A_Comparison_of_the_Investment_Criteria_of_Bankers_Venture_Capitalists_and_Business_Angels
0 notes