#zener diode breakdown voltage
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Zener diode breakdown voltage, Zener voltage, Tuning varactor diode
BZX84C5V1 Series 350 mW 5.1 V 10 mA Surface Mount Zener Diode - SOT-23
#Diodes Incorporated#BZX84C5V1-7-F#Diodes#Zener Diodes#zener diode breakdown voltage#Zener voltage#Tuning varactor diode#Switching diode#Zener Voltage Regulator#small signal diodes#Bridge rectifier#Zener diodes#Schottky diodes#current limiting diode
1 note
·
View note
Text
Understanding Circuit Board Electronic Components: A Comprehensive Guide
In today's digital world, electronic devices have become an essential part of our daily lives. But what makes these devices tick? At the heart of every electronic device lies a circuit board—a masterpiece of tiny electronic components working together to perform complex tasks. In this article, we’ll dive deep into the fascinating world of circuit board electronic components, exploring each element’s role and how they contribute to the overall functionality of the device.
What is a Circuit Board?
A circuit board, often referred to as a PCB (Printed Circuit Board), is a flat board used to mechanically support and electrically connect various electronic components. These components work in unison to perform a specific task. Think of the circuit board as the skeleton and nervous system of an electronic device—it holds everything together and allows communication between parts.
Types of Circuit Boards
Single-sided PCB: Has one layer of conducting material.
Double-sided PCB: Contains two layers for components and connections.
Multi-layer PCB: Complex boards with multiple layers for advanced applications.
The Role of Electronic Components on a Circuit Board
Every electronic device you interact with is powered by a carefully designed circuit board filled with various components. These components might be tiny, but each one has a critical role in the operation of the device. Here's a breakdown of the most important electronic components you’ll find on a typical circuit board.
1. Resistors
Resistors are fundamental components that control the flow of electrical current. They resist the flow of electrons, hence the name "resistor." Their primary function is to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, and divide voltages in a circuit. Without resistors, circuits would allow too much current to flow, potentially damaging other components.
Types of Resistors
Fixed resistors: Have a set resistance value.
Variable resistors: Allow adjustment of the resistance.
2. Capacitors
Capacitors store and release electrical energy in a circuit. They are often compared to small rechargeable batteries that quickly charge and discharge. Capacitors help smooth out fluctuations in voltage, filter noise, and store energy for future use.
Common Uses of Capacitors
Energy storage
Signal filtering
Voltage stabilization
3. Inductors
Inductors are components that store energy in a magnetic field when electrical current flows through them. They resist changes in current and are typically used in circuits to filter signals, manage power, and store energy.
Applications of Inductors
Power supplies
Radio frequency circuits
Noise suppression in circuits
4. Diodes
A diode is like a one-way valve for electricity, allowing current to flow in only one direction. They are vital in circuits to prevent reverse currents, which can damage components.
Types of Diodes
Light-emitting diodes (LEDs): Produce light when current flows through.
Zener diodes: Regulate voltage within a circuit.
5. Transistors
The transistor is a versatile component used to amplify or switch electronic signals. In essence, transistors are like tiny switches that turn signals on and off rapidly, making them essential in modern electronics.
Types of Transistors
NPN transistors: Allow current flow when a small voltage is applied to the base.
PNP transistors: Conduct when the base is negatively charged.
How Circuit Board Components Work Together
In a circuit, each component has a specific role, and together they form a cohesive system. For example:
Capacitors and resistors may work together to filter signals or smooth out voltage fluctuations.
Transistors and diodes ensure that signals are amplified or directed properly.
Integrated circuits handle the complex tasks, processing data, and controlling the overall system.
Choosing the Right Components for Your Circuit Board
When designing or repairing a circuit board, choosing the correct components is crucial. Some factors to consider include:
Voltage requirements
Power consumption
Signal type and frequency
Physical size and compatibility
Conclusion
Circuit boards are an integral part of any electronic device. The various components on the board each play a specific role in ensuring the device functions as intended. Understanding these components, from resistors to integrated circuits, is essential for anyone working with electronics, whether you're designing a new system or troubleshooting an existing one.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Various types of diodes are used in digital cameras, each serving specific functions to enhance your photography experience.
Photodiodes are essential in converting light into electrical signals, which is fundamental for image sensors. They help capture the intricate details of every shot, ensuring high-quality images.
Schottky diodes are used for their fast-switching capabilities and low forward voltage drop, contributing to the efficiency of power management in cameras. This helps in extending battery life and improving the overall performance of the device.
Zener diodes are used for voltage regulation, protecting the camera’s sensitive electronic components from voltage spikes. They ensure that the internal circuits receive stable voltage levels, which is vital for the longevity and reliability of the camera.
Using high-quality diodes ensures your cameras perform efficiently and reliably, capturing the perfect shot every time. On the other hand, low-quality diodes can lead to numerous issues. They may fail to regulate voltage properly, causing erratic performance or even damage to other sensitive components. This can result in blurry images, malfunctioning flashes, or complete camera failures, leading to dissatisfied customers and costly repairs or replacements.
By opting for high-quality diodes, you are investing in the longevity and reliability of your cameras. This choice can help prevent unexpected breakdowns and maintain your brand’s reputation for producing reliable and durable photography equipment.
the quality of diodes you choose directly impacts the performance and durability of your digital cameras. Prioritize high-quality diodes to enhance your product’s reliability and user satisfaction, avoiding the pitfalls that come with using inferior components.
At SUV System Ltd, we're committed to supplying nothing but the best diodes on the market. We've spent years honing our craft, ensuring that each component meets our rigorous standards of quality and reliability.
To get the best price in the industry, Get in touch with us today [email protected] or connect on Skype at [email protected]
You can also visit us at https://www.suvsystem.com/
#digital camera#semiconductors#diode supplier#electronic components#diodes#electronics supplier#diode#capacitors#rectifiers#tvs diode
0 notes
Text
What are the Types of Breakdowns in Zener Diode?
A special diode. Which is capable of allowing current to pass from anode to cathode. However, the most unique feature about this diode is it will allow current to flow in the reverse direction, unlike other diodes. And this is one of the main reasons, the Zener Diode is actively used in different types of semiconductors. Furthermore, the Zener Diode is also known as a Breakdown diode, mainly because it consists of a heavily doped semiconductor, which has the ability to operate in the reverse direction.
In experimental form, when the terminals connected to the diode are reversed, then the voltage flow in the diode is also reversed, which in turn will result in the effect known as Zener Effect. According to this effect, if the voltage passing in the reverse direction reaches its potential, known as the Zener Potential, then it will lead to a complete breakdown of the junctions.
Types of Breakdowns in Zener Diode
Now that we have covered basic details on how the Zener diode as voltage regulator works, and how the Zener effect is created. Let us talk about the different types of breakdowns that are commonly observed in the Zener Diode.
Zener Breakdown such as,
Zener Breakdown
Avalanche Breakdown
Avalanche Breakdown
This kind of phenomenon is observed in both normal diodes as well as Zener diodes at potentially high reverse voltage, especially when it is forward-based. However, with the passage of current through, there will be a small leak, which will flow directly through the diode during the reverse mode. Moreover, the increased voltage in the diode will cause the electrons to accelerate at high velocities.
Besides, the free electrons will continue to collide with the electrons, which in turn will increase the electric current in the diode, leading to a breakdown. However, unlike the normal diode, which will be generally destroyed, this diode is capable of handling the current spike. Apart from this, avalanche breakdowns can also be observed in Zener diodes, when the voltage applied is much greater than 6v.
Zener Breakdown
As you already know from the above sections, the Zener breakdown occurs in the Zener diodes, when the Zener effect is observed. So, in theory, when the applied reverse voltage is increased, the depletion region will expand, which causes electrons to get expelled from the band. And with the increase in the number of electrons getting expelled, the electric current will rise rapidly.
Application of Zener Diode
There are multiple applications of the Zener diode, that are actively used such as,
Zener Diode as Voltage Regulator: In order to regulate the voltage across small loads, such as a Shunt Voltage regulator.
Clipping Circuits: To limit the parts of one or both cycles in the AC Waveform, modified clipping circuits are used.
Over-Voltage Protection: So, as you know the Zener diode has the ability to resist the breakdown due to a short circuit, due to rising voltage in the said circuit.
The above article would help you understand all about the working of Zener Diode, in more detail with the diagram. So, if you have trouble understanding any other complex topics, in the subject. Then it would be a good option for you to enroll in the Online Interactive Classes offered by the Tutoroot platform. Mainly because the students will get access to the best study guides, expert staff, constant online revisions, doubt clearing sessions, and much more.
0 notes
Text
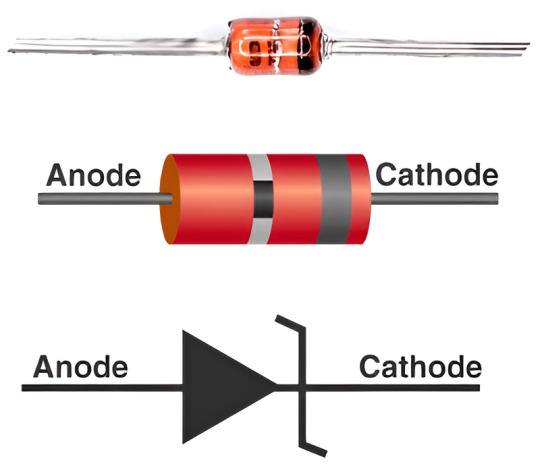
Zener Diode is the diode which lets current flow in both the directions i.e. from anode to cathode and cathode to anode. It does not breakdown in reverse direction unlike normal diodes and thereby it operates reliably in devices. They are used to regulate stabilized power supplies, provide low power supplies from high voltages and protect the circuit from high voltages.
0 notes
Text
Standard Resistor, Resistance Standard, Manufacturer, India
Standard Resistor, Resistance Standard, Testing Equipments, Calibration Standards, Testing Equipments, Measuring Instruments, Manufacturer, Supplier, Exporter, Pune, Maharashtra, India.
Resistance Standard, Calibration Standard, Calibration Standards, Multi Function Calibrator, Multi Function Calibrators, Three Phase Power Meter Calibrator, Three Phase Power Meter Calibrators, Three Phase Energy Meter Calibrator, Three Phase Energy Meter Calibrators, Testing Equipment, Testing Equipments, Single Phase Energy Meter Calibrator, Single Phase Energy Meter Calibrators, Tachometer Calibrator, Tachometer Calibrators, Non Contact Type Tachometer Calibrator, Non Contact Type Tachometer Calibrators, mV Calibrator, mV Calibrators, mA Calibrator, mA Calibrators, RTD Calibrator, RTD Calibrators, Decade Resistance Box, Decade Boxes or Decade RLC Boxes, Precision Decade Resistance Box, Precision Decade Boxes or Decade RLC Boxes, High Resistance Jig, High Resistance Jigs, Low Resistance jig, Low Resistance jigs, Decade Inductance Box, Decade Inductance Boxes, Inductance Decade Box, Inductance Decade Boxes, Voltage Measurement Probe, High Voltage Measurement Probe, AC High Voltage Measurement Probe, AC High Voltage Measurement Probe, DC Low Current Source, DC Low Current Sources, Linear Transmitter Simulator, Linear Transmitter Simulators, Standard Resistor, Testing Equipment, Testing Equipments, High Voltage Breakdown Tester, Breakdown Voltage Tester, Breakdown Voltage Testers, High Voltage Breakdown Tester, Insulation Resistance Tester, Electronic Load, Electronic Loads, DC Electronic Load, DC Electronic Loads, Ground Bond Tester, Ground Bond Testers, Ground Continuity Bond Tester, Fixed Resistance Box, Decade Resistance Box With Fixed Resistors, Secondary Injection Kit, Transistor Tester, Zener Diode Tester, Digital Variac, Digital Variacs, Measuring Instrument, Measuring Instruments, Digital Resistance Meter, Digital Resistance Meters, Digital 4 wire Resistance Meter, Time Interval Meter, Time Interval Meters, Digital Panel Meter, Digital Panel Meters, DC Power Supply, DC Regulated Power Supply, Dual DC Regulated Power Supply, High Current Power Supply, High Current DC Power Supply, High Voltage Power Supply, High Voltage DC Power Supply, Variable Current Source with Variable Frequency, Variable Voltage Source with Variable Frequency, Variable Current Variable Frequency Source, Variable Voltage Variable Frequency Source, Bipolar Power Supply, Cell Booster, Cell Boosters, AC High Current Source, DC High Current Source, Manufacturer, Supplier, Exporter, Pune, Maharashtra, India.
0 notes
Text
rerecorded this because I was dissatisfied with my previous video
anyway, tldr: (vintage) power supply died probably due to a shorted zener diode (NEC RD16A), couldn't find any of the exact model of diode online, but can find information on it, so I'm debating whether I should replace it with another diode with equivalent breakdown voltage (15.8v) or not as I don't really know how the circuit works too well.
6 notes
·
View notes
Link
Zener diodes are a special kind of diode which permits current to flow in the forward direction. What makes them different from other diodes is that Zener diodes will also allow current to flow in the reverse direction when the voltage is above a certain value. This breakdown voltage is known as the Zener voltage.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Understanding Circuit Board Electronic Components: A Comprehensive Guide
In today's digital world, electronic devices have become an essential part of our daily lives. But what makes these devices tick? At the heart of every electronic device lies a circuit board—a masterpiece of tiny electronic components working together to perform complex tasks. In this article, we’ll dive deep into the fascinating world of circuit board electronic components, exploring each element’s role and how they contribute to the overall functionality of the device.
What is a Circuit Board?
A circuit board, often referred to as a PCB (Printed Circuit Board), is a flat board used to mechanically support and electrically connect various electronic components. These components work in unison to perform a specific task. Think of the circuit board as the skeleton and nervous system of an electronic device—it holds everything together and allows communication between parts.
Types of Circuit Boards
Single-sided PCB: Has one layer of conducting material.
Double-sided PCB: Contains two layers for components and connections.
Multi-layer PCB: Complex boards with multiple layers for advanced applications.
The Role of Electronic Components on a Circuit Board
Every electronic device you interact with is powered by a carefully designed circuit board filled with various components. These components might be tiny, but each one has a critical role in the operation of the device. Here's a breakdown of the most important electronic components you’ll find on a typical circuit board.
1. Resistors
Resistors are fundamental components that control the flow of electrical current. They resist the flow of electrons, hence the name "resistor." Their primary function is to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, and divide voltages in a circuit. Without resistors, circuits would allow too much current to flow, potentially damaging other components.
Types of Resistors
Fixed resistors: Have a set resistance value.
Variable resistors: Allow adjustment of the resistance.
2. Capacitors
Capacitors store and release electrical energy in a circuit. They are often compared to small rechargeable batteries that quickly charge and discharge. Capacitors help smooth out fluctuations in voltage, filter noise, and store energy for future use.
Common Uses of Capacitors
Energy storage
Signal filtering
Voltage stabilization
3. Inductors
Inductors are components that store energy in a magnetic field when electrical current flows through them. They resist changes in current and are typically used in circuits to filter signals, manage power, and store energy.
Applications of Inductors
Power supplies
Radio frequency circuits
Noise suppression in circuits
4. Diodes
A diode is like a one-way valve for electricity, allowing current to flow in only one direction. They are vital in circuits to prevent reverse currents, which can damage components.
Types of Diodes
Light-emitting diodes (LEDs): Produce light when current flows through.
Zener diodes: Regulate voltage within a circuit.
5. Transistors
The transistor is a versatile component used to amplify or switch electronic signals. In essence, transistors are like tiny switches that turn signals on and off rapidly, making them essential in modern electronics.
Types of Transistors
NPN transistors: Allow current flow when a small voltage is applied to the base.
PNP transistors: Conduct when the base is negatively charged.
How Circuit Board Components Work Together
In a circuit, each component has a specific role, and together they form a cohesive system. For example:
Capacitors and resistors may work together to filter signals or smooth out voltage fluctuations.
Transistors and diodes ensure that signals are amplified or directed properly.
Integrated circuits handle the complex tasks, processing data, and controlling the overall system.
Choosing the Right Components for Your Circuit Board
When designing or repairing a circuit board, choosing the correct components is crucial. Some factors to consider include:
Voltage requirements
Power consumption
Signal type and frequency
Physical size and compatibility
Conclusion
Circuit boards are an integral part of any electronic device. The various components on the board each play a specific role in ensuring the device functions as intended. Understanding these components, from resistors to integrated circuits, is essential for anyone working with electronics, whether you're designing a new system or troubleshooting an existing one.
1 note
·
View note
Link
Zener diodes are a special kind of diode which permits current to flow in the forward direction. What makes them different from other diodes is that Zener diodes will also allow current to flow in the reverse direction when the voltage is above a certain value. This breakdown voltage is known as the Zener voltage.
1 note
·
View note
Text
The Role of Diodes in Enhancing Your Digital Photography Experience
Various types of diodes are used in digital cameras, each serving specific functions to enhance your photography experience.
Photodiodes are essential in converting light into electrical signals, which is fundamental for image sensors. They help capture the intricate details of every shot, ensuring high-quality images.
Schottky diodes are used for their fast-switching capabilities and low forward voltage drop, contributing to the efficiency of power management in cameras. This helps in extending battery life and improving the overall performance of the device.
Zener diodes are used for voltage regulation, protecting the camera’s sensitive electronic components from voltage spikes. They ensure that the internal circuits receive stable voltage levels, which is vital for the longevity and reliability of the camera.
Using high-quality diodes ensures your cameras perform efficiently and reliably, capturing the perfect shot every time. On the other hand, low-quality diodes can lead to numerous issues. They may fail to regulate voltage properly, causing erratic performance or even damage to other sensitive components. This can result in blurry images, malfunctioning flashes, or complete camera failures, leading to dissatisfied customers and costly repairs or replacements.
By opting for high-quality diodes, you are investing in the longevity and reliability of your cameras. This choice can help prevent unexpected breakdowns and maintain your brand’s reputation for producing reliable and durable photography equipment.
the quality of diodes you choose directly impacts the performance and durability of your digital cameras. Prioritize high-quality diodes to enhance your product’s reliability and user satisfaction, avoiding the pitfalls that come with using inferior components.
At SUV System Ltd, we're committed to supplying nothing but the best diodes on the market. We've spent years honing our craft, ensuring that each component meets our rigorous standards of quality and reliability.
To get the best price in the industry, Get in touch with us today [email protected] or connect on Skype at [email protected]
You can also visit us at https://www.suvsystem.com/
0 notes
Text
What are the Types of Breakdowns in Zener Diode?
A special diode. Which is capable of allowing current to pass from anode to cathode. However, the most unique feature about this diode is it will allow current to flow in the reverse direction, unlike other diodes. And this is one of the main reasons, the Zener Diode is actively used in different types of semiconductors. Furthermore, the Zener Diode is also known as a Breakdown diode, mainly because it consists of a heavily doped semiconductor, which has the ability to operate in the reverse direction.
In experimental form, when the terminals connected to the diode are reversed, then the voltage flow in the diode is also reversed, which in turn will result in the effect known as Zener Effect. According to this effect, if the voltage passing in the reverse direction reaches its potential, known as the Zener Potential, then it will lead to a complete breakdown of the junctions.
Types of Breakdowns in Zener Diode
Now that we have covered basic details on how the Zener diode as voltage regulator works, and how the Zener effect is created. Let us talk about the different types of breakdowns that are commonly observed in the Zener Diode.
Zener Breakdown such as,
Zener Breakdown
Avalanche Breakdown
Avalanche Breakdown
This kind of phenomenon is observed in both normal diodes as well as Zener diodes at potentially high reverse voltage, especially when it is forward-based. However, with the passage of current through, there will be a small leak, which will flow directly through the diode during the reverse mode. Moreover, the increased voltage in the diode will cause the electrons to accelerate at high velocities.
Besides, the free electrons will continue to collide with the electrons, which in turn will increase the electric current in the diode, leading to a breakdown. However, unlike the normal diode, which will be generally destroyed, this diode is capable of handling the current spike. Apart from this, avalanche breakdowns can also be observed in Zener diodes, when the voltage applied is much greater than 6v.
Zener Breakdown
As you already know from the above sections, the Zener breakdown occurs in the Zener diodes, when the Zener effect is observed. So, in theory, when the applied reverse voltage is increased, the depletion region will expand, which causes electrons to get expelled from the band. And with the increase in the number of electrons getting expelled, the electric current will rise rapidly.
Application of Zener Diode
There are multiple applications of the Zener diode, that are actively used such as,
Zener Diode as Voltage Regulator: In order to regulate the voltage across small loads, such as a Shunt Voltage regulator.
Clipping Circuits: To limit the parts of one or both cycles in the AC Waveform, modified clipping circuits are used.
Over-Voltage Protection: So, as you know the Zener diode has the ability to resist the breakdown due to a short circuit, due to rising voltage in the said circuit.
The above article would help you understand all about the working of Zener Diode, in more detail with the diagram. So, if you have trouble understanding any other complex topics, in the subject. Then it would be a good option for you to enroll in the Online Interactive Classes offered by the Tutoroot platform. Mainly because the students will get access to the best study guides, expert staff, constant online revisions, doubt clearing sessions, and much more.
0 notes
Link
Zener diodes are a special kind of diode which permits current to flow in the forward direction. What makes them different from other diodes is that Zener diodes will also allow current to flow in the reverse direction when the voltage is above a certain value. This breakdown voltage is known as the Zener voltage.
1 note
·
View note
Link
Zener diodes are a special kind of diode which permits current to flow in the forward direction. What makes them different from other diodes is that Zener diodes will also allow current to flow in the reverse direction when the voltage is above a certain value. This breakdown voltage is known as the Zener voltage.
1 note
·
View note
Text
What is the Best Strategy to Prepare EDC for GATE Exam?
Hi guys today I’ll be sharing my strategy for how to prepare for Electronic Devices and Circuits for GATE . It’s one of the easiest subject from GATE point of view the only hard part is to memorize all the formulae from various topics apart from that it’s the least time consuming subject in respect to the weightage it shows in GATE exam preparation . EDC cousrse basically provides you with understanding of device physics which also forms a base for various circuit analysis and design courses.
In recent year level of question as well as the weightage of EDC in GATE exam has increased,from last 4 year anlaysis the minimum weightage seen for this subject was 6 and maximum was 12 in 2018 and 2017 it was one of the highest weighted subject and most of the toppers scored full marks in this subject .
Good knowledege of this subject can also help you after GATE in interviews of various IIT’s and PSU .If someone is looking forward to do specialization in Microelectronics this is one of the core subjects of this field ,where you will further learn in depth about device physics and after masters you can start your carrer as device engineer , a good device engineer are very higly paid.
GATE SYLLABUS
Here I have mentioned the GATE syllabus and i have divide it in parts and in next section i’ll pick out each part and discuss what to prepare and important topics for GATE
Semiconductor Physics:
Energy bands in intrinsic and extrinsic silicon, Carrier transport: diffusion current, drift current, mobility and resistivity, Generation and recombination of carriers ,Poisson and continuity equations.
Diodes
P-N junction, Zener diode.
Transistors
BJT, MOS capacitor, MOSFET .
Photovoltaic devices
LED, photo diode and solar cell .
Integrated circuit fabrication process:
oxidation, diffusion, ion implantation, photolithography and twin-tub CMOS process.
SYLLABUS DESCRIPTION AND PREPRATION STRATERGY
I would recommend you to give around 10 to 13 days for EDC in which you’ll have to cover theory, previous year GATE paper questions and solve some extra material for question practice . First of all, before starting this topic all of you should have basic idea about semiconductor, metals, and insulators, how are they classified, band model and bond model, direct and indirect band gap materials.
1). SEMICONDUCTOR PHYSICS (2-3 days)
This topic is some what between easy and moderate level ,but very important as it forms the basics for your further topics . Most of the parts are easy but few parts which are tricky and from which you can expect good level of questions are –
Enerdy band digram.
Carrier transport.
Graded impurity distribution.
Carrier generation and recombination.
This topic deals with semiconductor physics(particularly silicon) basically to study about properties of the semiconductor.
Silicon crystal structure ,no of valence electron ,Energy band gap etc. Graph related question can be sometime tricky so one should have good understanding of theory to answer those.
In intrinsic semiconductor study about its eletrical property like conductivity and it’s variation with temperature then mobility variation with temperature , velocity saturation at high electric field and understand graph of µ vs T and σ vs T Vd (drift velocity)vs E.
Then calculation position of intrinsic fermi level , calculation of electrons n and hole concentration p ,calculation of intrinsic concentration,mass action law ,charge neutrality, graph of ni vs T and ln(σ ) vs 1/T Once your’e done with intrinsic semiconductor Physic slightly modifies for extrinsic semicoductor calculation ,extra parts that you should know is compensated doping , non degenartive and degenerative semiconductor,variation in nature of semiconductor with temperature.
in carrier transport you should learn about drift and diffusion current density and their expression for n type and p type ,diffusion constant and mobility, life time of carrier, diffusion length ,Einstein relation.
Graded impurity distribution is very important topic in this you shoul learn about non uniform doping ,relation between doping profile and Electric field ,plot of electric field for different doping profile ,current density at equilibrium,good level numerical and graphical question can be framed from it.
Hall effect mechanism , hall coefficient for n type p type and intrinsic semiconductor,hall voltage and it’s application are important, formula based question can be asked from this.
Enerdy band digram is one of the most important and hard topic in EDC if you don’t understand it future topics can be really difficult for you as it forms the base for understanding other devices ,you should learn variation of energy band with applied voltage ,calculation of electric field from slope of band digram and fermi level variation for equilibrium case (also for non -equilibrium but not in detail).
In Carrier generation and recombination process you should learn about phonon(thermal) geneneration and photo(light) generation, expression for excess charge carrier due to light excitation and net recombination rate at steady state.
Poisson and continuity equation is same as in EMT you should learn about Minority carrier continuity equation this equation helps you to sove various problem on steady state injenction in semiconductor due to different excitation.
After learning this topics you can easily analyze physics of any device .
2). Diodes (2 days)
In diode Band Digrams can be difficulty to understand and calculation of Diode parameter like depletion width ,junction potential.
As a pre requisite you should have a good understanding of electrostatic which you can cover from EMT.
In GATE most question are asked from Step graded pn junction so you should know how to plot charge density profile for step graded pn juction and to derive plot for Electric field from it and Potential plot from Electric field and your Energy band diagram is just an inversion of your potential plot.
Charge density →Electric field →Potential plot →Energy band diagram
you should should be very clear about how to draw plot for all these not only for step graded but for any profile and to derive the above parameter.
In last few years many questions are asked from Juction law in diode and flow of charge carrier through drift and diffusion which can confuse you
Diode capcitance in reverse and forward bais for abrupt and linear junction are also important and break down mechanism in diode and there relation with doping concentration and temperature.
Transient in diode can be a hard part some time syou can expect good question from diode switching.
You should also give some time to schottky diode ,One sided pn junction and understand metal semiconductor junction this helps you to study MOS capcacitor
3).Transistor ( 3 days )
BJT (half day)
This is very small and easy topic in EDC as most of the theory you cover in Anlaog circuits some extra things that you might find difficult can be Band digrams in equilibrium and diiferent baising region.
You should study Early effect and it effect on various parameter and punch through then you should cover breakdown in BJT in different junction and relation between breakdown Vceo and Vcbo.
You should also cover topic like minority carrier distribution in different operating region , BJT time delay factor and its cut off frequency, Ebers Moll model.
MOS CAPACITOR(2 days)
This is one of the most important topic in EDC it’s basically like studying OPAM in Analog ckt. This topics will require time to understand and many tricky questionss can be asked from this topic . Most of the students finds it very difficult to learn. First you should start with basic working of MOS capacitor in all three regime accumulation , depletion, and inversion and then you should study it’s band diagram in all the three region then you should start with C-V curve of MOS in this you should know the concept of surface potential , flat band voltage and threshold voltage. For studying flatband voltage Vfb you should understand the concept of workfunction for metal and semiconductor then you should study about trapped oxide charges and finally the complete expression for Vfb in term of bothFor threshold voltage Vt you should study the expression for depletion charge , surface potential at Vt. Depletion width in the semiconductor is calculated by doing one sided pn juction calculation. You should also study the calculation of inversion layer charge density. Then you should learn expression for capacitance in a different region (Cox , Cdep and Cinv) and in the inversion region, you should analyze both LFCV and HFCV curve. Finally you should study fixed oxide and interface traps charge and their effect on the C-V curve.
MOSFET (half day )
Again most of the MOSFET theory you cover in analog but prior to MOSFET, you study MOS capacitor which forms the base for MOSFET .
You should study various short channel effect in MOSFET which cause variation in its parameter and you should study variation in threshold voltage with variation in a parameter like length , oxide thickness , substrate doping etc.
You should study all the operating region of MOSFET and solve a problem related to finding operation region of different MOSFET in ckt and graph as well the expression of gm with respect to Vgs , Id .
4) PHOTOVOLTAIC DEVICES (1 DAY)
LED
very easy and can be covered in no time, you should study about direct bandgap semiconductor and reaction between Eg and λ relation between material bandgap and cut in voltage and parameter like extraction efficiency , internal radiative efficiency and external efficiency.
PHOTODIODE
In this you should learn about it’s working , operation region and parameter like photo current, dark current, Respositivity and expression for sensitivity and quantum effiency
SOLAR CELL
It’s is the most important photovoltaic device with respect to GATE and can be some times hard for some students to learn , you learn it’s working and it’s I-V graph basically there are 4 parameter you should know Voc, Isc, Conversion efficiency and fill factor.
5)Integrated circuit fabrication process(half day)
these topics are very easy but most students don’t find proper material to study these topic .
oxidation – study about wet and dry oxidation basically how much temprature is required and quality of oxide produce
diffusion and ion implantation- both are used for the same purpose but study what is their specific application and temperature require to perform both and concept of annealing
photolithography – In this you should cover topic likemasking, Photoresist , etching.
twin-tub CMOS process – you should study all the steps required and in order for fabriaction.
This topic might come for one marks you can refer any device book for these process.
BOOKS TO BE USED
1). SEMICONDUCTOR PHYSICS and DEVICES 4e – DONALD A NEAMEN
DHRUBES BISWAS
This book is one of the best book for EDC it’s little hard to understand but once you’ll study this completely I can assure you that you won’t be losing any marks in EDC it cover every topic except fabrication process,many of it’s excersice question are directly given in GATE exam one should definetly refer this book for good understanding of EDC . DIODE, TRANSISTOR, PHOTOVOLTAIC DEVICES can be directly referred from this book GATE related every aspect is covered.
2). SOLID STATE ELECTRONIC DEVICES – BEN G STREETMAN
This book is also a really good book some what easier to understand and cover most of the syllabus for EDC in the gate.
REFERENCE MATERIAL: for refrence, you can use nptel , PDF are availabel for devices courses with really good content
1 note
·
View note
Text
The transient Voltage Suppression diode, popularly known as the TVS diode in the industrial world, is a Zener diode. It uses the characteristics in the breakdown region of the code. The diode’s use includes making reference voltage circuits through the characteristics of a voltage to remain constant, irrespective of the current flowing. TVS diodes protect sensitive components like semiconductors. Read More at:https://www.millenniumsemi.com/products/tvs-diode
#electronic components distributor in india#electronic components distributor#bldc controller#igbt power modules#sic mosfet
0 notes