#wright patterson air force base
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
On December 17, 1969, the United States Air Force closed their "Project Blue Book" investigation of Unindentified Flying Objects. (SETI, event)
#nerds yearbook#real life event#december#1969#ufo#usaf#project blue book#air force#seti#history#alien#wright patterson air force base#edward j ruppelt#sci fi#science#unidentified flying object#u2#a12
25 notes
·
View notes
Video
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
#Tags:Aerial Surveillance#Counter-Drone Strategy#Drone Sightings#facts#life#Military Testing Programs#National Defense#Plausible Deniability#Podcast#Radiation Detection Drones#straight forward#Swarm Drone Technology#truth#U.S. Military Operations#upfront#Wright-Patterson Air Force Base
0 notes
Link
The article "North American XB-70 Valkyrie — America’s Cold War Supersonic Speed Bomber" by Friedrich Seiltgen, published on The Armory Life, discusses the history and development of the North American Aviation XB-70 Valkyrie, a planned supersonic strategic bomber for the United States Air Force. Intended to replace the Boeing B-52 Stratofortress and the Convair B-58 Hustler, the Valkyrie was designed during the Cold War to fly faster and higher, evading interceptor aircraft. The program, initiated in the mid-1950s, was ultimately canceled in 1961 due to advancements in Soviet surface-to-air missile technology and the rise of cost-effective Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles (ICBMs). The article highlights the Valkyrie's ambitious design goals, including a proposed cruising speed of Mach 3 and an operational altitude of 70,000-75,000 feet. Despite the cancellation, two prototypes were built, contributing valuable data on supersonic flight, aerodynamics, and airplane propulsion. The Valkyrie program also faced a tragic incident in 1966 involving a collision with an F-104 Starfighter during a photo shoot, leading to the destruction of one prototype. The surviving XB-70 is now displayed at the National Museum of the United States Air Force.
#North American XB-70 Valkyrie#supersonic bomber#Cold War era#Mach 3 speed#strategic reconnaissance#nuclear deterrent#B-58 Hustler#B-52 Stratofortress#high-altitude flight#Wright-Patterson Air Force Base#General Electric YJ93 engines#delta wing design#aeronautical engineering#aviation history#aerodynamic heating#experimental aircraft.
0 notes
Text

4 February 1969. Final flight of the North American Aviation XB-70A-1-NA Valkyrie, 62-0001. It flew from Edwards Air Force Base, California, to Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, Ohio and the National Museum of the United States Air Force.
@ron_eisele via X
#xb 70 valkyrie#north american aviation#bomber#aircraft#usaf#sac#nuclear weapons#aviation#cold war aircraft#prototype
99 notes
·
View notes
Text
Brrrrrttt!

When you design a gun with wings... 😎
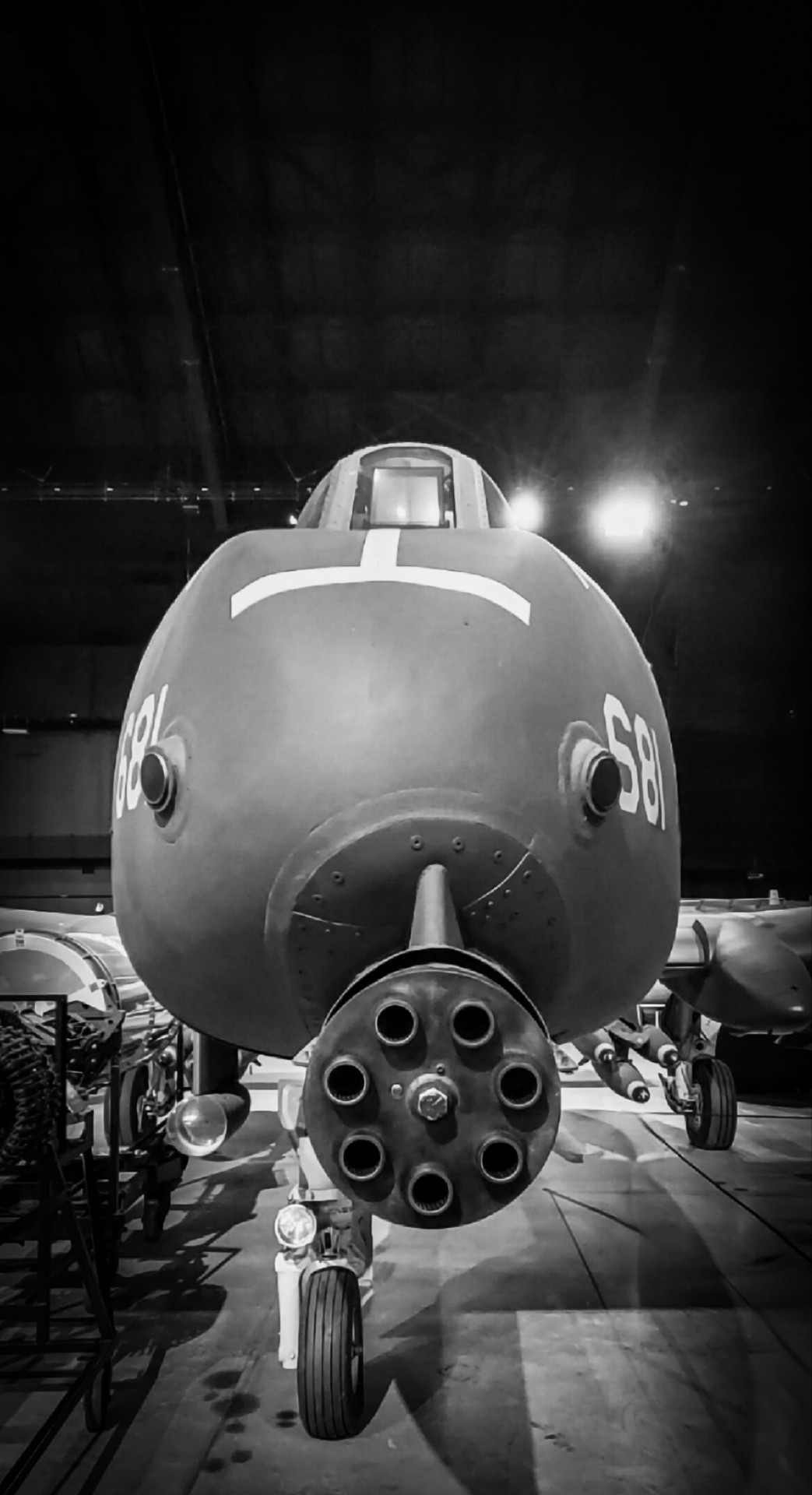

Fairchild Republic A-10A Thunderbolt that served in Operation Desert Storm, 1991. U.S. Air Force Museum, Wright Patterson Air Force Base, Dayton, Ohio. June 11, 2021.
By @aviationgeek71
#avgeek#aviation#aviation history#a 10 warthog#a10#my photography#my writing#original photography#my photo
101 notes
·
View notes
Video
Rockwell HiMAT Research Aircraft by NASA on The Commons Via Flickr: This HiMAT (Highly Maneuverable Aircraft Technology) subscale research vehicle, seen here after a research flight, was one of two flown by the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center (now Armstrong Flight Research Center), Edwards, California, from mid 1979 to January 1983. The maiden flight of the HiMAT project was on July 27, 1979. The aircraft demonstrated advanced fighter technologies that have been used in the development of many modern high performance military aircraft. HiMAT research at Dryden was conducted jointly by NASA and the Air Force Flight Dynamics Laboratory, Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, Ohio. Because the two planes were controlled from a ground station, experimental technologies and high-risk maneuverability tests could be employed without endangering pilots. The aircraft were flown 26 times during the three-and-a-half-year history of the program. The HiMAT project represented a shift in focus by researchers at Dryden. Through the Vietnam era, the crux of fighter research had been speed. In the 1970s, driven by a national energy crisis, new digital technology, and a changing combat environment, researchers sought to develop efficient research models for experiments into the extremes of fighter maneuverability. As a result, the quest for speed, long considered the key component of successful air combat, became secondary. NASA Media Usage Guidelines Credit: NASA Image Number: EC79-12055 Date: January 3, 1980
#HiMAT#maneuverability#Armstrong Flight Research Center#Dryden Flight Research Center#Rockwell#Rockwell International#flickr#Mecha#Aircraft#Real-World Mecha
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
Pink airplanes ???
In another post we were talking about pink airplanes. Did you know that, once upon a time, THIS famous airplane...

the North American Aviation X-15 hypersonic research aircraft, was pink?
It was. I kid you not.

That's it. Really.
In order to go higher/faster and to protect the skin from extreme aerodynamic heating, the airframe was coated with Martin MA-25S ablative heat shield material. The most badass rocket airplane ever built was now PINK!
Now a perhaps-apocryphal account had it that one of the pilots refused to fly a pink airplane. True or not, that wasn't the plan anyway. The pink surface was prone to damage from spilled fuel, so it was given several coats of a white silicone to serve as a wear layer.

With the pink ablator discreetly hidden under the white outer coat, the X-15A-2 went on to reach its fastest speed ever of 4,520 mph (Mach 6.7). The special coating really didn't help and actually exacerbated damage caused by aerodynamic heating, and the aircraft came within minutes of breaking up from the damage. After repairs it was grounded and never flew again. Today, you can see it (minus the pink/white shell) at the U.S. Air Force Museum at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base in Ohio.
75 notes
·
View notes
Text
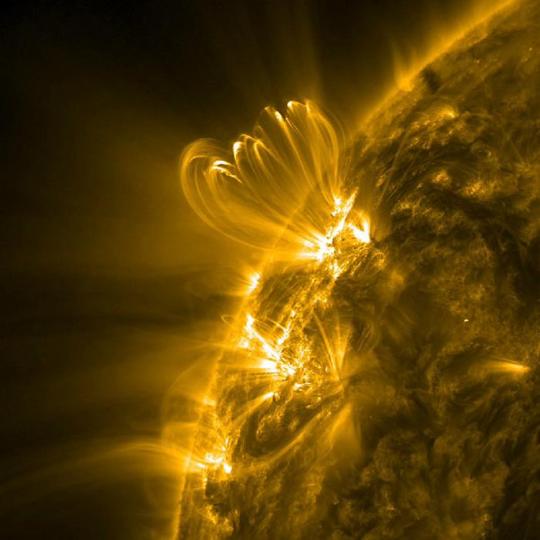

NASA Solar Observatory sees coronal loops flicker before big flares
Using NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory, scientists have identified flickering loops in the solar atmosphere that seem to signal when the Sun is about to unleash a large solar flare.
For decades, scientists have tried in vain to accurately predict solar flares — intense bursts of light on the Sun that can send a flurry of charged particles into the solar system. Now, using NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory, one team has identified flickering loops in the solar atmosphere, or corona, that seem to signal when the Sun is about to unleash a large flare.
These warning signs could help NASA and other stakeholders protect astronauts as well as technology both in space and on the ground from hazardous space weather.
Led by heliophysicist Emily Mason of Predictive Sciences Inc. in San Diego, California, the team studied arch-like structures called coronal loops along the edge of the Sun. Coronal loops rise from magnetically driven active regions on the Sun, where solar flares also originate.
The team looked at coronal loops near 50 strong solar flares, analyzing how their brightness in extreme ultraviolet light varied in the hours before a flare compared to loops above non-flaring regions. Like flashing warning lights, the loops above flaring regions varied much more than those above non-flaring regions.
“We found that some of the extreme ultraviolet light above active regions flickers erratically for a few hours before a solar flare,” Mason explained. “The results are really important for understanding flares and may improve our ability to predict dangerous space weather.”
Published in the Astrophysical Journal Letters in December 2024 and presented on Jan. 15, 2025, at a press conference during the 245th meeting of the American Astronomical Society, the results also hint that the flickering reaches a peak earlier for stronger flares. However, the team says more observations are needed to confirm this link.
Other researchers have tried to predict solar flares by examining magnetic fields on the Sun, or by looking for consistent trends in other coronal loop features. However, Mason and her colleagues believe that measuring the brightness variations in coronal loops could provide more precise warnings than those methods — signaling oncoming flares 2 to 6 hours ahead of time with 60 to 80 percent accuracy.
“A lot of the predictive schemes that have been developed are still predicting the likelihood of flares in a given time period and not necessarily exact timing,” said team member Seth Garland of the Air Force Institute of Technology at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base in Ohio.
“The Sun’s corona is a dynamic environment, and each solar flare is like a snowflake — every single flare is unique,” said team member Kara Kniezewski, a graduate student at the Air Force Institute of Technology and lead author of the paper. “We find that searching for periods of ‘chaotic’ behavior in the coronal loop emission, rather than specific trends, provide a much more consistent metric and may also correlate with how strong a flare will be.”
The scientists hope their findings about coronal loops can eventually be used to help keep astronauts, spacecraft, electrical grids, and other assets safe from the harmful radiation that accompanies solar flares. For example, an automated system could look for brightness changes in coronal loops in real-time images from the Solar Dynamics Observatory and issue alerts.
“Previous work by other researchers reports some interesting prediction metrics,” said co-author Vadim Uritsky of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, and the Catholic University of Washington in D.C. “We could build on this and come up with a well-tested and, ideally, simpler indicator ready for the leap from research to operations.”
IMAGE: NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory captured this image of coronal loops above an active region on the Sun in mid-January 2012. The image was taken in the 171 angstrom wavelength of extreme ultraviolet light. Credit NASA/Solar Dynamics Observatory
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
By Greg Hunter January 8, 2025
The results of the third annual “2024 Worldwide Embalmer Blood Clot Survey” are out, and the findings are both gruesome and scary. Retired Airforce Major Tom Haviland has been doing this survey ever since he was fired from his job at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base in 2021 for NOT taking the CV19 bioweapon vax. Haviland is the only one in the world doing a survey of embalmers from around the world to reveal the “unusual phenomenon of large, grotesque ‘white fibrous clots’ in the veins and arteries of corpses.” Haviland got the idea to start the survey of embalmers after seeing the movie “Died Suddenly.” Haviland explains, “About half the movie is about six or seven embalmers that started to find these white fibrous clots in the corpses they were embalming. . . . At the 13-minute mark, an amazing statement is made. An embalmer from Indiana, Wallace Hooker, was lecturing at an Ohio embalmer’s conference in Columbus, Ohio, on the 26th of October in 2022. He was lecturing to a room of about 100 embalmers. He showed them photographs of the white fibrous clots he had been pulling out of his corpses for the last year or so, and he asked by a show of hands how many of you are seeing these white fibrous clots? He said almost the entire room of 100 embalmers raised their hands and said yes. He then asked when did you start seeing them? They all said about six months after the Covid vaccines rolled out.”
So, Haviland started his own worldwide survey of embalmers three years ago. In his latest 2024 survey of embalmers from around the world, “white fibrous clots appeared in a weighted average of 27.5% of corpses.” Also, in the 2024 survey of embalmers, 83% are seeing these long fibrous clots. Haviland says this year’s 2024 survey shows the trend is increasing and not decreasing. Haviland says, “This is a phenomenon that the embalmers never saw before 2020. Prior to 2020, they only saw two types of clots. One is called ‘grape jelly’ clots, and they look like dark grape jelly. They dissolve easily in your hand like grape jelly does. There is also something called ‘chicken fat’ clots that are much smaller, yellow and tear very easily. They are much different than these large, long white fibrous clots. They can grow up to two feet long, and they are tough, rubbery and elastic. Embalmers in my survey have never seen these before. They are very, very unusual.”
7 notes
·
View notes
Text

1961 Ford Gyron Concept Car
The Ford Gyron was a futuristic two-wheeled gyrocar first shown to the world in 1961 at the Detroit Motor Show and designed by Syd Mead and McKinley Thompson. Like a motorcycle, one wheel was at the front and the other at the rear, and gyroscopes stabilized the car. The vehicle's two occupants were seated side by side, and when the vehicle was stationary, two small legs appeared from the sides to support it. The vehicle was created for research and marketing purposes, with no intention of putting it into production.
The gyroscopic system was based on Louis Brennan's theories and designed by Alex Tremulis, who started his career with the U.S. Air Force. In 1948, Tremulis worked at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base on the concept of Military Flying Saucers. He then became the chief designer for the ill-fated Tucker automobile before joining Ford. He was also involved with the Tuscan gyroscopic motorcycles and the Gyronaught XUI gyroscopic car.
The original fiberglass concept was destroyed in the Ford Rotunda fire of 1962. Only the studio model remains today, it was sold at an auction in December 2012 for $40,000. A second model was recently discovered in the collection of the Petersen Automotive Museum in Los Angeles and displayed as part of the 2024 exhibition, "Eyes on the Road." [Source: Wikipedia]
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
This supposed true story includes an interstellar alien police force named AFFA from 1959.
From the essay:
People have been interested in extraterrestrial life for a long time, which has led to many studies and theories. Navy Intelligence asked Robert Friend, acting as chief of the Aerial Phenomena Division at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base in Ohio, to investigate a mysterious finding on July 6, 1959. This essay examines what transpired during Friend’s investigation, the significance of the purported alien contact, and how this case aligns with the broader context of UFO research and other comparable cases.
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
instagram
Can you imagine making a decision that’s going to kill 70 to 80,000 innocent people to end a war ?
Can you imagine being one of those people killed ?
Apparently this was long before they could do strategic targeting of a government’s headquarters.
When I visited Wright Patterson Air Force Base in Dayton, Ohio, I did see the plane that dropped the second smaller bomb. 💣
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

Celebrating 60 Years of the XB-70 Valkyrie Mach 3 Super Bomber
September 16, 2024 Military Aviation
XB-70 60th anniversary
The lone XB-70 Valkyrie is photographed as it is moved to a new building at the Museum of the United States Air Force located at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, Ohio, on Oct. 27, 2015. Beginning in the late 1950s and continuing through the mid-1960s, tests were conducted at Arnold Air Force Base, Tenn., headquarters of Arnold Engineering Development Complex, in support of the XB-70 program. The now-retired aircraft made its first flight on Sept. 21, 1964. (U.S. Air Force photo by Will Haas)
The experimental legacy of the iconic XB-70 Valkyrie, which made its first flight on Sept. 21, 1964.
An article published on the U.S. Air Force website commemorates the 60th anniversary of the first flight of the legendary XB-70 Valkyrie, a supersonic bomber that captured the imagination of aviation enthusiasts and engineers alike. Known for its sleek and futuristic design, the XB-70 remains a symbol of the experimental and ambitious spirit of Cold War-era aircraft development. Despite only two prototypes ever being built, the aircraft has left an indelible mark on military aviation history.
The XB-70 Valkyrie was originally conceived in the 1950s as a high-speed, high-altitude bomber for the U.S. Air Force Strategic Air Command. At a time when technological advancements were rapidly accelerating, the U.S. Air Force sought a bomber capable of flying faster and higher than the B-52 Stratofortress, its workhorse of the era (as well as the backbone of the strategic bomber fleet today and for some more decades in the future…).
With a planned cruise speed of Mach 3 and an operating altitude of 70,000 feet, the XB-70 promised to outpace and outmaneuver Soviet defenses, which were a growing concern during the Cold War.
One of the most remarkable features of the XB-70 was its ability to “ride” its own shockwave, a design innovation that allowed it to maintain stability and performance at supersonic speeds. The Valkyrie’s iconic delta wing, combined with six powerful jet engines, gave it an exotic and striking appearance, making it one of the most visually distinctive aircraft ever built. Its outer wing panels were hinged, allowing them to be lowered during flight to optimize the aerodynamic performance at high speeds.

The XB-70 looks like an alien spacecraft from this angle. (Image credit: USAF)
The article highlights the crucial role played by Arnold Engineering Development Complex (AEDC) in the development of the XB-70.
The testing of the Valkyrie’s engines, aerodynamics, and other key components began at Arnold Air Force Base in the late 1950s, well before the first prototype took shape. The AEDC’s facilities were instrumental in pushing the boundaries of what was possible in aviation at the time. One of the earliest tests involved the air-breathing engine nozzles proposed for the XB-70 in March 1958. This was followed by extensive wind tunnel testing of scale models of the Valkyrie, where the aerodynamic characteristics of bombs dropped from the aircraft were also studied.
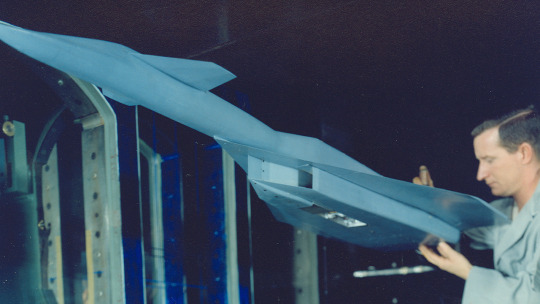
A technician makes adjustments to a scale model of the XB-70 Valkyrie before aerodynamic characteristics related to the aircraft are evaluated in Tunnel A of the von Kármán Gas Dynamics Facility at Arnold Air Force Base, Tenn., headquarters of Arnold Engineering Development Complex, in 1959. Beginning in the late 1950s and continuing through the mid-1960s, tests were conducted at Arnold Air Force Base, Tenn., headquarters of Arnold Engineering Development Complex, in support of the XB-70 program. Only two Valkyries were built, with only one of the pair remaining. The now-retired aircraft made its first flight on Sept. 21, 1964. (U.S. Air Force photo)
Development continued into the early 1960s, with the YJ93 turbojet engines, designed specifically for the XB-70, undergoing rigorous testing at AEDC. These engines were critical to the Valkyrie’s ability to reach and maintain supersonic speeds. However, in 1961, before the first prototype was even completed, the bomber program was canceled due to budget constraints and concerns over the bomber’s vulnerability to Soviet surface-to-air missiles, which had rapidly advanced in capability.
Although the XB-70 bomber program was terminated, the Valkyrie found new life as a research aircraft.

Three drag chutes were needed to slow down the landing roll of the XB-70. (Image credit: Reddit edit The Aviationist)
The U.S. Air Force recognized the potential of the aircraft to serve in aerodynamics and propulsion research, particularly in the study of large supersonic aircraft. Consequently, two XB-70 prototypes were completed, and testing continued, including at AEDC, where a scale version of the XB-70 inlet, paired with a full-scale YJ93 engine, was tested in August 1962.
XB-70A number 1 (62-001) made its first flight from Palmdale to Edwards Air Force Base, CA, on Sept. 21, 1964. The second XB-70A (62-207) made its first flight on Jul. 17, 1965. The latter differed from the first prototype for being built with an added 5 degrees of dihedral on the wings as suggested by the NASA Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, CA, wind-tunnel studies.

North American XB-70A Valkyrie on the taxiway with a cherry picker. Photo taken Sept. 21, 1964, the day of the first flight. Note: the left main landing gear brakes locked during the landing causing two tires to blow. (U.S. Air Force photo)
While the 62-001 made only one flight above Mach 3, because of poor directional stability experienced past Mach 2.5, the second XB-70, achieved Mach 3 for the first time on Jan. 3, 1966 and successfully completed a total of nine Mach 3 flights by June on the same year.
However, the Valkyrie program suffered a devastating setback in June 1966 when the second prototype was destroyed in a midair collision with an F-104N Starfighter during a photoshoot. This tragic accident resulted in the loss of key personnel and diminished the future prospects of the Valkyrie.

North American XB-70A Valkyrie just after collision. Note the F-104 is at the forward edge of the fireball and most of both XB-70A vertical stabilizers are gone. (U.S. Air Force photo)
Despite this setback, the remaining XB-70 continued to serve as a valuable research platform. In 1967, the U.S. Air Force transferred the aircraft to NASA, where it was used in support of the National Supersonic Transport (SST) program. NASA employed the XB-70 to investigate supersonic flight operations, but the SST program was eventually canceled in 1971, marking the end of America’s efforts to develop a commercial supersonic airliner.
The XB-70 Valkyrie’s final flight took place on Feb. 4, 1969, when it was flown to Wright-Patterson Air Force Base in Ohio. There, the aircraft was placed on display at what is now the National Museum of the United States Air Force, where it remains a testament to the audacious engineering and design of its era.

A view of the six massive afterburners on the XB-70 Valkyrie as the aircraft is towed out of its display hangar temporarily for museum maintenance. (Photo: National Museum of the U.S. Air Force via YouTube)
Though only two XB-70s were ever built, their legacy endures: the aircraft’s pioneering advancements in aerodynamics, engine performance, and high-speed flight helped shape the future of supersonic aviation.
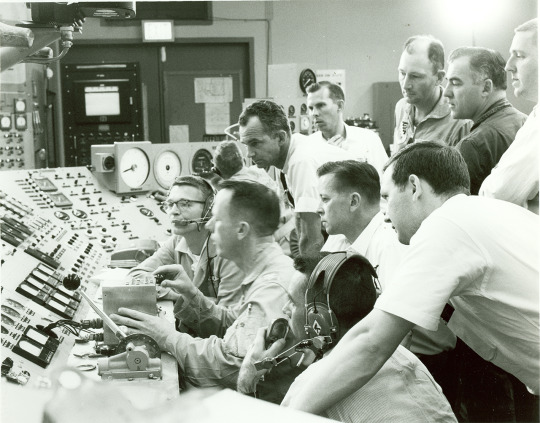

Pilots who were to perform the first test flights for the XB-70 Valkyrie operate the YJ93 engine, the powerplant of the XB-70, while the engine is tested under simulated flight conditions in May 1964 in the Rocket Test Facility at Arnold Air Force Base, Tenn., headquarters of Arnold Engineering Development Complex. This was done to help the pilots familiarize themselves with the performance characteristics of the engine prior to the first XB-70 flight, which occurred on Sept. 21, 1964. Beginning in the late 1950s and continuing through the mid-1960s, tests were conducted at Arnold AFB in support of the XB-70 program. Only two Valkyries were built, with only one of the pair remaining. (U.S. Air Force photo)
The first prototype made a total of 83 flights, amassing 160 hours and 16 minutes of flight time, while the second prototype completed 46 flights, totaling 92 hours and 22 minutes.
The XB-70 Valkyrie, with its daring design and groundbreaking capabilities, continues to captivate aviation enthusiasts and engineers. Its story, though short-lived in terms of operational use, highlights the relentless pursuit of innovation that defines the U.S. Air Force and its engineering partners. Sixty years after its first flight, the Valkyrie remains an iconic symbol of the bold ambitions of Cold War-era aviation.

XB-70 Night Take-off. (Photo via Air Force Materiel Command History Office)
About David Cenciotti
David Cenciotti is a journalist based in Rome, Italy. He is the Founder and Editor of “The Aviationist”, one of the world’s most famous and read military aviation blogs. Since 1996, he has written for major worldwide magazines, including Air Forces Monthly, Combat Aircraft, and many others, covering aviation, defense, war, industry, intelligence, crime and cyberwar. He has reported from the U.S., Europe, Australia and Syria, and flown several combat planes with different air forces. He is a former 2nd Lt. of the Italian Air Force, a private pilot and a graduate in Computer Engineering. He has written five books and contributed to many more ones.
@TheAviationist.com
118 notes
·
View notes
Text






NASA DC-8-700 N817NA and the Gulfstream 5 N95NA landing at Wright Patterson Air Force Base Dayton Ohio
Camera info: Nikon d5500, 70mm, f/5.6, iso 350
August 4th 2023
#ohio#daytonohio#air force#nasa#jet#airliner#private jet#aviation#planes#aircraft#photography#aviation photography
54 notes
·
View notes
Text

The Amps - Maxwell's, Hoboken, New Jersey, July 1, 1995
I was watching this recent video of the Breeders in Big Sur a couple weeks back — and however great it is (it's great!), it got me thinking about the Amps, the one-and-done mid-90s Kim Deal project. Kind of a weird moment for Kim. She had climbed to the top of the Alternative Nation after the release of Last Splash, opening for Nirvana, playing Lollapalooza, hitting the late-night talk shows, etc. But by 1995, she was blowing it all up and starting again. Kinda. Here's the rundown from a very 1990s Spin magazine cover story written by Charles Aaron way back when. Those were different times, kids!
Kind of sweet, kind of pathetic. That’s how Deal has viewed her life following Last Splash‘s surprising success, propelled by the Top 40 single “Cannonball,” one of the most unlikely mosh notes ever penned. What was meant to be a well-deserved rest for the band after opening Nirvana’s last national tour, headlining gigs with Luscious Jackson, and joining Lollapalooza during the summer of ’94, became a boring winter exile for Kim in her childhood home of Huber Heights, the planned community outside Dayton that thrived in the ’50s with the opening of Wright Patterson Air Force Base, where Kim’s dad worked as a physicist. Instead of catching up on laundry and bad TV, she learned to play drums, patched together a batch of songs, and agreed to help produce the next album by her drinking buddies Guided By Voices (of which her fiance and SPIN Senior Contributing Writer Jim Greer is now a member).
Meanwhile, the other Breeders were plenty busy. Jim Macpherson finally spent some time with his kids and renovated a new house. Bassist Josephine Wiggs fell in love (with Luscious Jackson drummer Kate Schellenbach) and out of the closet (courtesy of a November ’94 Advocate story titled “Luscious Lesbians”), eventually moving from London to New York to be near Schellenbach. Kelley Deal made the most publicized move, out of Kim’s place and into a nearby house where she was arrested in November for receiving an Emery Worldwide package containing heroin. Her trial is set for July. Considering the circumstances, Kim’s desire to record a solo album made more than a little sense, for everybody concerned.
Pacer, that "solo record," hit shelves in the fall of '95 and — compared to Last Splash, anyway — was fairly low-profile. But it's a killer album, and somewhat forgotten these days, I think? If Kim had just called it a Breeders record, people might be more aware, I don't know. Anyway! The Amps toured a bit in '95 (I saw 'em open for Sonic Youth that October), and here's a nice audience tape of the band at Maxwell's that summer, playing a bunch from their then-unreleased debut, alongside a rambunctious closing cover of the Tasties' "Like A Briar." Take a trip down to Tipp City ...
18 notes
·
View notes