#waste electrical and electronic equipment
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
What to do with electronic waste in Latin-America?

Around 50 million tons of e-waste are discarded each year worldwide. And only 5% of the total is recycled. The regional average reaches around 7 kg per person, per year
Have you ever imagined having gold in your possession and throwing it away? Well, this happens more than we think. For example, with those electrical or electronic devices that stopped working or that we no longer use. These artifacts are generally made of plastics and metals, such as aluminum, copper, and also the famous gold.
However, as we live in an era of consumption and disposal, when we talk about waste from these devices, known as WEEE[1], instead of looking for a new use or recycling it, we throw it away.
Clearly, both the famous planned obsolescence and the latest model fever do not help. And the ranking proposed by the World Observatory of Electronic Waste[2] estimates that what is discarded the most are cell phones, hard drives, cpus[3], disused monitors, modems, printers, cables and televisions.
And this can be dangerous. The composition of the artifacts[4] reaches 72% recyclable materials, 25% reusable materials and 3% hazardous waste (cathode ray tubes, integrated circuit boards, refrigeration gases, PCBs). "Its accumulation affects human health through exposure to toxic elements such as lead[5]," says a study by the entity.
This also describes "adverse health effects [6], ranging from birth problems, neurological development disorders, learning disabilities, DNA damage, cardiovascular and respiratory problems, skin diseases, among others and soil contamination and of the water and the air”.
For its part, the International Labour Organization (ILO) [7] states that they constitute the fastest growing waste stream in the world. And that they require special treatment for having dangerous elements. Their complexity in recycling and their cost generate an urgent need for an adequate regulatory framework since "they constitute an important problem for the environment and the health of the population."[8]
World ranking
According to the Eco House organisation[9], around 50 million tons of electronic waste are discarded each year worldwide. Among the countries most affected by electronic waste that receive more than they emit are: Ethiopia, Ghana[10], India, Singapore and Malaysia. The ILO reveals that the countries that generate the most WEEE are Brazil (35%), Mexico (20%), Colombia (8%) and Argentina (7%).
However, if the generation of WEEE is analysed in relative terms to the population of the countries, the largest producers are Chile (9.9 kg/inhab) and Uruguay (9.5 kg/inhab). "These levels are moderate even when compared to countries like the United States or Italy –22 and 17.8 kg/inhabitant/year, respectively."
Other data comes from the report Technology for climate action in Latin America, by the GSMA Association and the Inter-American Development Bank (IDB), published in June 2018[11] . There, Uruguay is registered as the country with the highest generation of electronic waste per person, with an average of 11 kg per person per year.
And the country with the lowest generation per person is Nicaragua, with an average of two kg of electronic waste. "The regional average reached around seven kg per person per year, close to the world average (estimated at six), but considerably lower than that of Europe (16 kg)," the document details. “These figures in Latin America possibly respond to the practice of reusing electronics. In the region, reused devices are often given away or sold, increasing their useful life."
Other life
The issue is that although we believe that they no longer make sense in our day to day, that does not mean that their useful life has ended. On the contrary, not only are there many ventures and projects that continue to use it, but by recycling them we are doing good for the planet[12].
The World Observatory for Electronic Waste[13] suggests that only 5% of the total are recovered or recycled. In general, 50% of unused cell phones are stored in homes and institutions due to lack of knowledge about what to do with them. What can we do from our place?[14]
Acquire electrical and electronic products that prioritize the recycling of certain parts.
Try to extend the useful life of our devices to the maximum
Avoid changing them if they still work or fixing them, while you can
And what we discard, it is advisable to bring them closer to ventures, foundations or programs that receive them to renovate or recycle them. You have to inquire in each region.
What is possible to recycle?[15]
Computers, notebooks, monitors, keyboards, mice
Decoders, modems.
Printers.
Telephone lines, cell phones.
Faxes, stereos, VCRs, DVDs and televisions, among others.
Where can I take my electronic waste? There are various initiatives in the different countries of South-America. These are some:
Argentina. Electronic waste and art
In the City of Buenos Aires, there is a place where electronic waste becomes art. Nothing is wasted. This is Esquinazo Recicla[16], a civil association that recycles electronic waste. They receive from a headset to a refrigerator. And the most wonderful thing is that the plates of LED televisions or CPUs can end up being from a Mona Lisa to a Darth Vader.
“We carry out a chain of favours. Of the equipment we recovered. For example, we donate recovered computers to social spaces,” Mariano Moreyra, founder of Esquinazo Recicla, tells América Futura.
Other places to bring Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment closer in Buenos Aires are the CABA Green Points[17], the company Qué Reciclo,[18] Gea Sustentable Fundación[19], San Isidro[20] or the Conectar Program in Ituzaingó[21], where used computers are repaired to be donated to families with members with ASD[22].
Colombia
Colombia, according to the organization Manos Verdes[23], produces 130,000 tons of electronic waste per year. “It is the fourth country with the highest production on the continent, but the first in management, disposal and recycling. This is thanks to the fact that, since 2013, the Law 1672 on Waste Management of Electrical and Electronic Equipment has been in force. This urges the companies that sell these devices to manage their recycling and provide the consumer with spaces for their collection”.
It is one of the few countries in the region with a National Policy for the comprehensive management of this waste that defines the roadmap until the year 2032. Although each country outlines its public policies, in general they are based on some international treaties and conventions. such as the Montreal Protocol[24], the Basel[25] and Stockholm[26] Conventions, and the Minamata Convention[27].
The United Nations Development Program, supported by the World Environment Fund, implemented in Colombia the project called Reduction of unintentional releases of POPs and mercury from hospital waste management, WEEE, metal scrap processing and biomass burning in 2017. As of today, there are initiatives that work in the country are RAEE Colombia SAS[28] and Ekosolv[29].
Chili
The trans-Andes nation is another of the countries that has legislation that frames WEEE. This is Law 20,920 of Extended Producer Responsibility (REP). There are some private initiatives such as Recycla[30], which recycles electronics. And Fundación Chile[31], which launched the #Renchúfate campaign[32], which works with the school community and municipalities, providing information[33] for the correct disposal of these devices.
For its part, the company Samsung launched the Recycle and Save campaign, to remove and recover all kinds of household appliances in Chile. According to the company, "each appliance will go to Degraf, a company[34] in which its components will be separated according to their composition: plastics, metals or glass".
Ecuador
In Ecuador, there is Vertmonde[35], an initiative that seeks an "Ecuador free of electronic waste with technical recycling of e-waste and circular electronics".
It is estimated that this kind of waste is the one that will increase the most in the future due to technological advances. For this reason, every time we stop using a cell phone, a computer or even a refrigerator, what is worth gold is knowing its correct disposition in order to promote the circular economy and a better future for our planet.
Source
Augustina Grasso, ¿Qué hacer con los residuos electrónicos?, in: El País, 14-08-2023, https://elpais.com/america-futura/2023-08-14/que-hacer-con-los-residuos-electronicos.html
[1] Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment
[2] https://www.itu.int/dms_pub/itu-d/opb/gen/D-GEN-E_WASTE.01-2020-PDF-S.pdf
[3] A central processing unit (CPU)—also called a central processor or main processor—is the most important processor in a given computer.
[4] https://residuoselectronicosal.org/2021/03/observatorio-mundial-de-los-residuos-electronicos-2020-version-en-espanol/
[5] https://elpais.com/planeta-futuro/2023-02-10/los-ninos-invisibles-del-plomo-en-el-norte-remoto-de-chile.html
[6] https://elpais.com/mexico/2022-11-23/la-contaminacion-ambiental-el-monstruo-silencioso-que-ahoga-cada-ano-a-8000-personas-en-ciudad-de-mexico.html
[7] https://www.ilo.org/wcmsp5/groups/public/---americas/---ro-lima/---ilo-buenos_aires/documents/publication/wcms_750434.pdf
[8] Read also: https://www.tumblr.com/earaercircular/665044124448227328/what-are-the-challenges-in-the-framework-of?source=share
[9] https://ecohouse.org.ar/
[10] https://elpais.com/planeta-futuro/2023-05-11/jugarse-la-vida-en-el-gran-cementerio-electronico-de-ghana-inundado-con-la-basura-del-norte.html
[11] https://www.gsma.com/latinamerica/resources/technology-climate-action/
[12] https://elpais.com/america-futura/2023-04-16/como-reciclar-en-america-latina-sabes-donde-acaba-tu-basura.html
[13] https://residuoselectronicosal.org/2021/03/observatorio-mundial-de-los-residuos-electronicos-2020-version-en-espanol/
[14] Read also: https://www.tumblr.com/earaercircular/707326337365442560/recycling-raw-materials-from-urban-mines-are?source=share
[15] Read also: https://www.tumblr.com/earaercircular/670292335907815424/e-waste-an-ecological-bomb-how-to-get-rid-of?source=share
[16] https://www.instagram.com/esquinazorecicla/
[17] https://buenosaires.gob.ar/ciudadverde/noticias/para-acompanar-la-puesta-en-marcha-de-la-ciudad-los-puntos-verdes-ubicados-en
[18] https://www.quereciclo.com.ar/empresa.php
[19] https://geasustentable.com.ar/nosotros/
[20] https://www.idealist.org/es/ong/f54f374b07fe47248b565fc5973c1b79-asociacion-civil-comunidad-organizada-por-san-isidro-san-isidro
[21] https://www.miituzaingo.gov.ar/es/gobierno-abierto/noticias/2023-06-07/mas-de-440-alumnos-y-alumnas-de-ituzaingo-recibieron-sus
[22] Autistic Spectrum Disorder
[23] https://www.manosverdes.co/
[24] The Montreal Protocol is an international treaty designed to protect the ozone layer by phasing out the production of numerous substances that are responsible for ozone depletion. It was agreed on 16 September 1987, and entered into force on 1 January 1989.
[25] The Basel Convention on the Control of Transboundary Movements of Hazardous Wastes and Their Disposal, usually known as the Basel Convention, is an international treaty that was designed to reduce the movements of hazardous waste between nations, and specifically to prevent transfer of hazardous waste from developed to less developed countries. It does not, however, address the movement of radioactive waste.
[26] Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants is an international environmental treaty, signed on 22 May 2001 in Stockholm and effective from 17 May 2004, that aims to eliminate or restrict the production and use of persistent organic pollutants (POPs).
[27] The Minamata Convention on Mercury is an international treaty designed to protect human health and the environment from anthropogenic emissions and releases of mercury and mercury compounds. The convention is named after the Japanese city Minamata.
[28] https://www.raee.com.co/servicios/
[29] https://www.ekosolv.com/
[30] https://www.recycla.cl/
[31] https://fch.cl/iniciativa/residuos-e/
[32] https://www.facebook.com/watch/?v=1169188090336927
[33] https://fch.cl/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/Puntos-de-Recoleccio%CC%81n-Ewaste.pdf
[34] DEGRAF started its activities in 1982 in the field of recycling graphic, photographic and radiological waste. Over the years and in response to the evolution of the industry and the requirements of its customers, DEGRAF has developed new service areas, becoming a comprehensive manager of industrial waste specializing in electrical and electronic waste (WEEE), hazardous waste (RESPEL) and ferrous and non-ferrous metal waste. https://degraf.cl/nosotros/nuestra-empresa/
[35] https://www.vertmonde.com/
0 notes
Text
What is the Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) Directive? | Definition from TechTarget
What is the Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) Directive? The Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) Directive is a legislative act that the European Union adopted to address the growing amounts of e-waste that come from electrical and electronic equipment (EEE) at the end of its life. The directive aims to improve the collection, treatment and recycling processes employed…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
The phone or computer you’re reading this on may not be long for this world. Maybe you’ll drop it in water, or your dog will make a chew toy of it, or it’ll reach obsolescence. If you can’t repair it and have to discard it, the device will become e-waste, joining an alarmingly large mountain of defunct TVs, refrigerators, washing machines, cameras, routers, electric toothbrushes, headphones. This is “electrical and electronic equipment,” aka EEE—anything with a plug or battery. It’s increasingly out of control.
As economies develop and the consumerist lifestyle spreads around the world, e-waste has turned into a full-blown environmental crisis. People living in high-income countries own, on average, 109 EEE devices per capita, while those in low-income nations have just four. A new UN report finds that in 2022, humanity churned out 137 billion pounds of e-waste—more than 17 pounds for every person on Earth—and recycled less than a quarter of it.
That also represents about $62 billion worth of recoverable materials, like iron, copper, and gold, hitting e-waste landfills each year. At this pace, e-waste will grow by 33 percent by 2030, while the recycling rate could decline to 20 percent. (You can see this growth in the graph below: purple is EEE on the market, black is e-waste, and green is what gets recycled.)
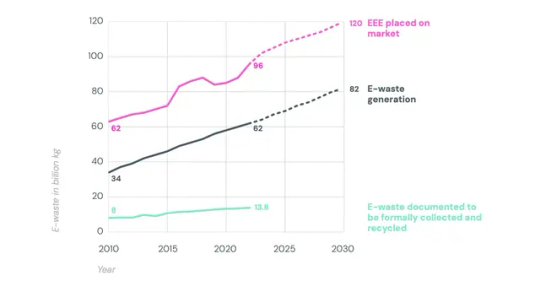
“What was really alarming to me is that the speed at which this is growing is much quicker than the speed that e-waste is properly collected and recycled,” says Kees Baldé, a senior scientific specialist at the United Nations Institute for Training and Research and lead author of the report. “We just consume way too much, and we dispose of things way too quickly. We buy things we may not even need, because it's just very cheap. And also these products are not designed to be repaired.”
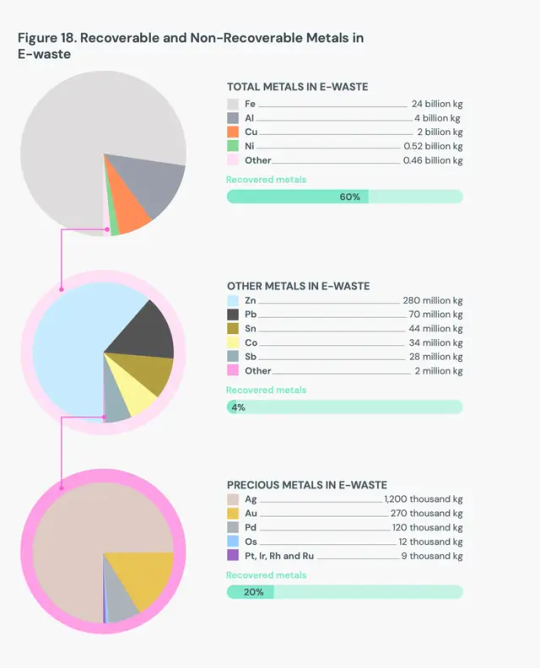
Humanity has to quickly bump up those recycling rates, the report stresses. In the first pie chart below, you can see the significant amount of metals we could be saving, mostly iron (chemical symbol Fe, in light gray), along with aluminum (Al, in dark gray), copper (Cu), and nickel (Ni). Other EEE metals include zinc, tin, and antimony. Overall, the report found that in 2022, generated e-waste contained 68 billion pounds of metal.
E-waste is a complex thing to break down: A washing machine is made of totally different components than a TV. And even for product categories, not only do different brands use different manufacturing processes, but even different models within those brands vary significantly. A new washing machine has way more sensors and other electronics than one built 30 years ago.
Complicating matters even further, e-waste can contain hazardous materials, like cobalt, flame retardants, and lead. The report found that each year, improperly processed e-waste releases more than 125,000 pounds of mercury alone, imperiling the health of humans and other animals. “Electronic waste is an extremely complex waste stream,” says Vanessa Gray, head of the Environment and Emergency Telecommunications Division at the UN’s International Telecommunication Union and an author of the report. “You have a lot of value in electronic waste, but you also have a lot of toxic materials that are dangerous to the environment.”
That makes recycling e-waste a dangerous occupation. In low- and middle-income countries, informal e-waste recyclers might go door-to-door collecting the stuff. To extract valuable metals, they melt down components without proper safety equipment, poisoning themselves and the environment. The new report notes that in total, 7.3 billion pounds of e-waste is shipped uncontrolled globally, meaning its ultimate management is unknown and likely not done in an environmentally friendly way. Of that, high-income countries shipped 1.8 billion pounds to low- and middle-income countries in 2022, swamping them with dangerous materials.
High-income countries have some of this informal recycling, but they also have formal facilities where e-waste is sorted and safely broken down. Europe, for example, has fairly high formal e-waste recycling rates, at about 43 percent. But globally, recycling is happening nowhere near enough to keep up with the year-over-year growth of the waste. Instead of properly mining EEE for metals, humanity keeps mining more ore out of the ground.
Still, the report found that even the small amount of e-waste that currently gets recycled avoided the mining of 2 trillion pounds of ore for virgin metal in 2022. (It takes a lot of ore to produce a little bit of metal.) The more metals we can recycle from e-waste, the less mining we’ll need to support the proliferation of gadgets. That would in turn avoid the greenhouse gases from such mining operations, plus losses of biodiversity.
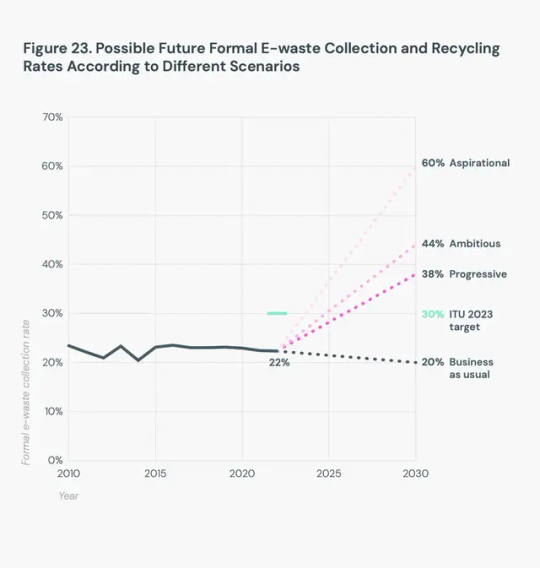
The complexity of e-waste, though, makes it expensive to process. As the chart above shows, even an ambitious scenario of a formal e-waste collection rate in 2030 is 44 percent. “There is no business case for companies to just collect e-waste and to make a profit out of this in a sustainable manner,” says Baldé. “They can only survive if there is legislation in place which is also compensating them.”
The report notes that 81 countries have e-waste policies on the books, and of those, 67 have provisions regarding extended producer responsibility, or EPR. This involves fees paid by manufacturers of EEE that would go toward e-waste management.
Of course, people could also stop throwing so many devices away in the first place, something right-to-repair advocates have spent years fighting for. Batteries, for instance, lose capacity after a certain number of charge cycles. If a phone can’t hold a charge all day anymore, customers should be able to swap in a new battery. “Manufacturers shouldn't be able to put artificial limitations on that ability,” says Elizabeth Chamberlain, director of sustainability at iFixit, which provides repair guides and tools. That includes limiting access to parts and documentation. “Repair is a harm-reduction strategy. It's not the be-all-end-all solution, but it's one of many things we need to do as a global society to slow down the rate at which we're demanding things of the planet.”
At the core of the e-waste crisis is the demand: A growing human population needs phones to communicate and fridges to keep food safe and heat pumps to stay comfortable indoors. So first and foremost we need high-quality products that don’t immediately break down, but also the right to repair when they do. And what absolutely can’t be fixed needs to move through a safe, robust e-waste recycling system. “We are consuming so much,” says Baldé, “we cannot really recycle our way out of the problem.”
26 notes
·
View notes
Text
Why I decided to publish fanfiction "on demand"
A lot of noise going on in AO3 among my readers about my decision not to keep uploading content into AO3 unless there are readers asking for it, effectively publishing "on demand". Basically I keep writing (try to stop me) and I have for years, consistently, daily, but I no longer upload fanfics online, unless they're very requested, with very few exceptions. And I have also removed some fanfics from the online world. Even if some readers get pretty nasty about it all.
It's all for the same reasons:
Environmental impact:
1. Data centres, which host much of the online content, account for approximately 1-2% of global electricity usage, consuming an estimated 200-250 TWh of electricity per year. 2. According to the University of Massachusetts Lowell, the carbon footprint of the internet is estimated to be around 3.7% of global greenhouse gas emissions.
3. The production of electronic devices used in the digital infrastructure, such as servers, routers, and smartphones, generates about 50 million tons of e-waste annually, with only 20% being recycled properly. 4. The lifespan of some data centre equipment can be as short as 3-5 years, leading to a rapid turnover and accumulation of e-waste.
5. Data centres are estimated to consume approximately 200 million cubic meters of water per year globally, equivalent to the water usage of a small city. Some studies suggest that the water footprint of the internet could be as high as 15 litres per gigabyte of data transferred.
2. Time wasting: For me, writing is something I love doing. I absolutely love it, and I do it relentlessly, day after day, full stories. It took time to upload each story into the website, as you have to select the right chapter, copy, paste, add all warnings, add all necessary notes, fix any formatting issues, and so on, one chapter at a time. It's sometimes taken me over an hour to upload all of my stories, sometimes longer. But it was worth it when I saw the glee in the readers. But in the last few years, it isn't so pleasant. I am now a grown up adult with a whole life of my own, which makes it harder to find the hour/s to upload content.
3. Lack of response/engagement: And I go through all that just for what? nasty comments, or complete silence. It feels like nobody's reading, and so logically, I think, well if nobody's reading that's fine, time's change, I'm not hurt nor offended, but if nobody reads then uploading fanfics into the internet is an effective waste of my time that perhaps I could afford in the 2010s, but not any more. I've got far too many things to do. And since I'm still going to write the story and love that, I don't feel any need to post it, because I don't get any compensation from posting it.
Sometimes I even get grief for whatever I post, so what's the point?
#fanfiction#fanfic#hjellacott#cormoran strike#robin ellacott#ao3#archive of our own#archive of our own 3#writer#writing#computers#environment#environmental footprint#writers#literature#Earth
6 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Enhancing thermoelectricity with guided impurity position control
Thermoelectric materials, substances that convert temperature difference into electricity, find a multitude of applications involving the conversion of waste heat into useful electrical energy. However, they often need to rely on heavy rare earth elements for efficient thermoelectric conversion.
This, unfortunately, makes them expensive and environmentally hazardous. In recent years, conjugated polymer-based material has received attention as an environmentally benign alternative to the conventional rare earth metal-based thermoelectric materials.
Owing to their high charge carrier mobility in the amorphous state, IDT-containing conductive polymers have the potential to reduce thermal conductivity while keeping their electronic conductivity intact. Unfortunately, these polymers suffer from low electronic conductivity, limiting our ability to synthesize high-performance thermoelectric materials from IDT-based polymers.
A team of researchers led by Prof. Sukwon Hong Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology in Korea have now found a solution to the problem. Equipped with their understanding of plausible reasons for the observed low conductivity, the team designed a novel strategy for developing an IDT-based polymer with improved thermoelectric performance based on dopant (impurity) position controlling within an acetal-functionalized IDT (IDTa) polymer. Their study was made available in Chemistry of Materials.
Read more.
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Value and Sustainability of Refurbished Laptops

In a world where technology is developing quickly, finding the right balance between performance and cost is crucial. Buying used laptops is one option that is becoming more and more common. But what does the term "refurbished" really mean, and how does it impact computer usage?
What Refurbished Computers Involve
Used laptops that have been meticulously restored to nearly new condition are called refurbished laptops. This calls for routine component testing, inspection, and replacement in order to maintain optimal functionality.
The following are some benefits of choosing refurbished computers: Refurbished laptops are typically significantly less expensive than new ones in terms of price.
Environmental Impact: Choosing a reconditioned laptop will help reduce the quantity of electronic waste that ends up in the environment.
Understanding the Renovation Process
Overview of Renovation
When the laptop is being refurbished, every part is carefully examined and checked. Any broken parts are located and replaced to ensure that the device meets quality standards.
Quality Assurance Metrics
Diagnostic testing: Comprehensive testing to identify any issues.
Component Replacement: Changing or improving current components to make sure they meet performance standards.
Changing Out Components
Used laptops are regularly upgraded with faster CPUs and more RAM, exceeding the original specifications in terms of performance.
Crucial Features to Consider When Buying a Refurbished Laptop
dependable suppliers
Make sure the suppliers you choose are trustworthy and have a good track record of offering high-quality reconditioned computers.
Return and warranty guidelines
Warranty Coverage: To provide protection against flaws, look for a warranty period.
Return Policies: Be aware of the conditions under which you can return a reconditioned laptop.
Comparison of Specifications
To determine whether a refurbished laptop is worth the money, compare its characteristics to those of new models.
Popular Models of Refurbished Laptops
Refurbished Dell Laptops
Explore the range of refurbished Dell laptops known for their reliability and performance.
Laptops Refurbished by HP
Explore the alternatives in the lineup of refurbished HP laptops that combine functionality and style.
Refurbished Laptops by Lenovo
Lenovo provides a wide selection of reconditioned laptops to meet various user requirements.
Savings and Value for Money: A Comparison of Prices for New Laptops
To determine the savings, compare the cost of refurbished laptops with those of new laptops.
Both affordability and performance
Refurbished laptops are a sensible option for customers on a tight budget since they frequently offer superior performance at a small fraction of the price of new equipment.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Cutting Down on E-Waste
Choosing a refurbished laptop helps lessen the impact that electrical waste from abandoned gadgets has on the environment.
Eco-Friendly Renovation Techniques
Find out what environmentally friendly methods refurbishing firms use to reduce their carbon footprint.
Reviews & Testimonials from Customers
Actual Refurbished Laptop User Experiences
Learn from consumers who have bought and utilized refurbished computers, emphasizing their own experiences.
Both positive and negative comments
Examine the advantages and disadvantages of reconditioned laptops based on user feedback.
Advice on How to Take Care of and Handle Refurbished Laptops Properly
To guarantee life and peak performance, maintain your reconditioned laptop according to recommended guidelines.
Security precautions and software updates
To safeguard your refurbished equipment, be cautious and update your software frequently. You should also put security measures in place.
In India, Refurbished Laptops Are Available
Expanding Pattern in India
Examine the growing demand for reconditioned laptops in the Indian market.
Best Selling Items and Brands
Find out which companies and top sellers in India are selling reconditioned laptops.
Obstacles and misunderstandings
Typical Untruths Regarding Refurbished Laptops
Examine and dispel popular misunderstandings about buying reconditioned laptops.
Resolving Customer Issues
Address the typical worries that customers might have when thinking about purchasing a reconditioned laptop.
Future Trends in the Refurbished Laptop Industry
Technological Advancements
Explore the anticipated technological advancements in the refurbishing process.
Market Forecasts
Analyze market forecasts for the expansion and development of reconditioned laptops.
Summary of the Benefits of Refurbished Laptops
List the main benefits of selecting reconditioned computers, highlighting their affordability and durability.
Encouragement of Knowledgeable Buying
Emphasize the advantages and debunk any misconceptions to help readers make well-informed judgments when thinking about purchasing a used laptop. Visit our site for more products at Retechie.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
THE BEST SELECTION OF USED MOBILE PHONES IN THE UK

Refurbished Phones from Big Phone Store Save Money and the Environment
It is costly to keep up with smartphone trends. Refurbished phones fit that criterion while being affordable and environmentally friendly. Refurbished phones are repaired, cleaned, and tested before being sold again after being traded in, sold to a shop, or returned. Customers can obtain a premium phone at a moderate cost while reducing power waste with this environmentally friendly strategy.
Why Should You Buy Second Hand Phones?
Refurbished phones provide more than just cost reductions. Every year, billions of electrical devices harm the environment. The Big Phone Store's expertly repaired phones mitigate this effect. By reusing completely recovered phones, we can all help to decrease electronic waste. Reconditioned equipment may also be less expensive than new equipment.
Quality is guaranteed by The Big Phone Store UK
Do you have reservations about used phones? All refurbished phones at The Big Phone Store are subjected to a 90-point inspection to ensure they function as well as new phones. Cosmetic states include "Like New" for perfect and "Good" for moderate wear. Every item, regardless of appearance, comes with a 12-month warranty, comprehensive testing, and a commitment to customer satisfaction.
What makes Big Phone Store the ideal option for you?
In the United Kingdom, The Big Phone Store sells refurbished phones. We value dependability and quality and provide numerous cost-effective options. Apple, Samsung, Google, Sony, Motorola, Honour, Oppo, and Huawei refurbished phones are available. The Big Phone Store offers unrivalled affordability, quality, and environmental responsibility, with a 12-month guarantee, free UK shipping on orders over £30.00, and a commitment to sustainability.
Explore The Big Phone Store's refurbished phones to save money and find eco-friendly options. https://www.thebigphonestore.co.uk/refurbished-phones.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Greenway Metals Sydney: The Prime Destination for Copper Recycling Excellence
Greenway Metals Sydney has emerged as a beacon of excellence in the recycling industry, particularly when it comes to copper recycling. With a commitment to advanced technology, environmental responsibility, and community engagement, Greenway Metals Sydney has positioned itself as the go-to destination for efficient and eco-friendly copper recycling solutions.
State-of-the-Art Copper Recycling Technology
Greenway Metals Sydney boasts cutting-edge technology designed specifically for the efficient and effective recycling of copper. Their state-of-the-art facilities and machinery are equipped to handle various sources of copper waste, including industrial scrap, electrical components, and construction materials. This technological prowess ensures that copper recycling is not only environmentally responsible but also maximally resource-efficient.
Environmental Stewardship and Sustainability
At the heart of Greenway Metals Sydney's mission is a commitment to environmental stewardship and sustainability. Copper extraction from raw materials can be an energy-intensive and environmentally harmful process. By prioritizing copper recycling, Greenway Metals Sydney contributes to a significant reduction in energy consumption, greenhouse gas emissions, and the overall environmental impact associated with copper production.
Community Involvement and Education
Greenway Metals Sydney actively engages with the local community to promote the importance of copper recycling. Through educational programs, workshops, and outreach initiatives, they empower individuals and businesses with the knowledge needed to make environmentally conscious decisions. By fostering a sense of responsibility within the community, Greenway Metals Sydney extends the impact of their recycling efforts beyond their facilities.
Comprehensive Copper Recycling Services
Greenway Metals Sydney offers a comprehensive range of copper recycling services, catering to the diverse needs of industries such as construction, electronics, and manufacturing. From processing industrial copper scrap to recycling discarded electrical wiring, Greenway Metals Sydney provides a one-stop solution for copper recycling, simplifying the process for businesses and individuals alike.
Competitive Pricing and Economic Benefits
Copper recycling at Greenway Metals Sydney not only contributes to environmental conservation but also offers economic benefits. The competitive pricing structure for copper scrap encourages businesses and individuals to choose recycling over disposal. This financial incentive fosters a circular economy, where copper is recycled and reintegrated into the manufacturing process, reducing the need for new raw materials.
Zero-Waste Philosophy
Greenway Metals Sydney adheres to a zero-waste philosophy, striving to minimize waste at every stage of the copper recycling process. By implementing efficient waste management practices, they not only reduce the environmental impact of their operations but also set a standard for sustainable business practices in the recycling industry.
Quality Assurance for Recycled Copper
Maintaining high-quality standards is a priority for Greenway Metals Sydney. Rigorous quality control measures are in place to ensure that the recycled copper they produce meets industry specifications. This commitment to quality makes Greenway Metals Sydney a trusted supplier of recycled copper for various manufacturing processes.
Regulatory Compliance and Responsible Practices
Greenway Metals Sydney operates in full compliance with local and national regulations governing recycling and environmental protection. Their commitment to responsible practices ensures that their copper recycling operations are not only environmentally sound but also aligned with legal requirements.
Innovation in Copper Recycling
Greenway Metals Sydney fosters a culture of innovation, continually exploring new technologies and methodologies to enhance the efficiency of copper recycling. By staying at the forefront of industry advancements, they position themselves as leaders in sustainable metal recycling practices.
Convenience and Accessibility
To encourage widespread participation in copper recycling, Greenway Metals Sydney prioritizes convenience and accessibility. They provide easily accessible drop-off points and efficient collection services, making it convenient for businesses and individuals to contribute to copper recycling efforts.
Conclusion
Greenway Metals Sydney stands as a beacon in the realm of copper recycling, offering not just a service but a commitment to environmental stewardship, technological innovation, and community engagement. By choosing Greenway Metals Sydney for copper recycling needs, businesses and individuals are actively contributing to a sustainable future while enjoying economic advantages. As the demand for responsible metal recycling continues to grow, Greenway Metals Sydney remains at the forefront, providing exemplary solutions for a greener and more sustainable world.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Environmentally friendly artist pleadge
As artists, we have the unique ability to capture the beauty of the world around us, and it is our responsibility to ensure that we are doing our part to protect and preserve our environment. Embracing sustainability not only benefits the planet but also enables us to build a stronger and more ethical business. In this blog post, I pledge to be an environmentally friendly artist business owner and share some actionable steps that we can all take to reduce our ecological footprint.
Use eco-friendly materials: One of the simplest ways to become more environmentally conscious is to transition to using eco-friendly art supplies. Look for products that are made from recycled or sustainably sourced materials, such as paints, papers, and canvases. Additionally, opt for water-based paints that emit fewer harmful chemicals and reduce air pollution.
Reduce waste: Artistic inspiration can sometimes lead to excessive consumption. However, being mindful of waste can make a significant difference. When possible, try to reuse or repurpose materials, such as old canvases or paintbrushes. Use scrap papers or upcycled cardboard for sketches or preliminary work. By finding creative solutions for waste reduction, we can actively contribute to minimizing our environmental impact.
Opt for sustainable packaging: Packaging materials, such as bubble wrap and Styrofoam, are harmful to the environment. Transitioning to sustainable packaging alternatives, like biodegradable and recyclable options, is an essential step in reducing waste. Additionally, consider using eco-friendly shipping options that offset carbon emissions.
Conserve energy: Operating our art studios and workspaces efficiently helps conserve energy and reduce our carbon footprint. Take advantage of natural light as much as possible and use energy-efficient lighting, such as LED bulbs. Turn off equipment and electronics when not in use and invest in energy-efficient appliances to minimize electricity consumption. Conserving energy not only helps the environment but also reduces your utility bills.
Offset carbon emissions: Despite our best intentions, it is challenging to completely eliminate our carbon emissions. One way to minimize our impact is by purchasing carbon offset credits. These credits fund projects that reduce greenhouse gas emissions, ultimately balancing out our own emissions. Supporting such initiatives allows us to take responsibility for our carbon footprint and support a greener future.
As artists, we have a unique platform to bring awareness to the environmental issues that our planet faces. By taking the pledge to become an environmentally friendly artist business owner, we can inspire others to join us on this transformative journey. Let's embrace sustainability, adopt eco-friendly practices throughout our artistic process, and play our part in creating a greener future, one masterpiece at a time.
3 notes
·
View notes
Note
Solar Charge/Photovoltaic item supoort? super moves? evolution?
With "Solar Charge", most of the evolutions would boil down to the user learning how to be more efficient with their energy. Things like letting them take in more sunlight at a time, holding it for longer periods, and needing less sunlight to use the electricity. One of the bigger jumps would be the user having better control over the electricity they could make, though not increasing its power as much. Things like channeling it through their finger tips to strike multiple people at once, charging it up into a ball to charge or overload something without touching it, or lighting up their body to greater extents to blind someone. As for super moves, it would come down to different flavors of blasting people with electricity. Things like shocking multiple people at a time, releasing a powerful lighting bolt at a single enemy, unleashing it all in the form of an area of effect attack, some kind of large pulse to knock out electronics, or again, blinding people with their lights to leave them out.
As for any kind of costume, there really isn't much the user could have since they need to have sunlight touching their body. Perhaps if they wore something tight and light enough to absorb it through the layers, preferably black to better absorb sunlight. Now, there is a lot of potential in support equipment. One of the big parts of the Quirk is the user charging up objects with electricity. Maybe they could have a tool to better handle and focus their electricity, able to shortcut their way to control discharge. However, I think that there could be a better option. They could have a set of whip-like tools that resemble wires. Not only could this let them charge their electricity through it to attack people with less of their charge wasted, but safely spread out their charge to other electronics. They could have smaller wires across their body they could attach to multiple devices, such as powering various tools in a disaster situation like lights. Maybe the user could specialize as a recuse hero and get a truck full of electric equipment that would be good in a disaster zone and act as a living generator for it all.
9 notes
·
View notes
Photo
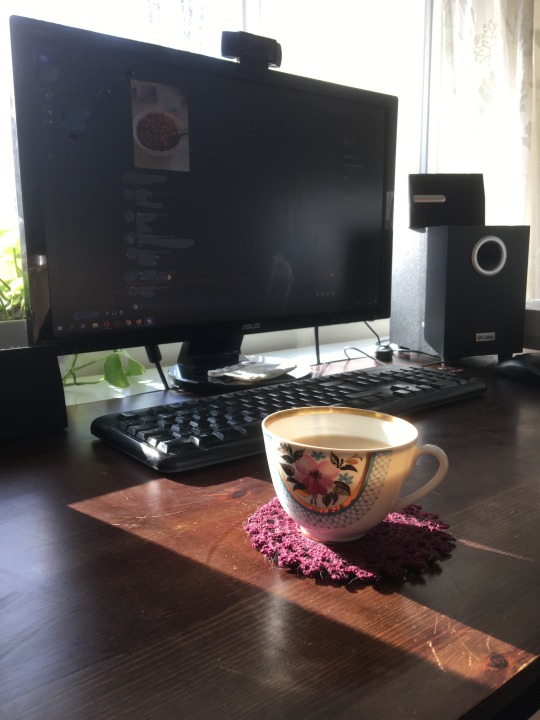


My Gamer Aesthetic
I really can’t see myself ever getting sparkly LEDs or pleather accessories etc for my gaming or work spaces.
The speakers are a bit end-of-their-life, maybe. They’re from 2002. A cat terrorist destroyed their little legs, which I superglued back into shape again and again, until they just now can’t stay up anymore, because they’ve been shattered into too many pieces. I hate throwing away things that still technically work, but these 20-year-old little fellas have also lost their ability to make sounds with reasonable reliability. I’m getting recycled speakers this weekend though, and these old ones are headed for Finnish Electricity and Electronics recycling cycle next week (if you’re in Finland, check out SER-kierrätys.) Electronics contain a lot of precious metals that are dug up from earth, and our planet has finite resources, so it’s important to get all the materials back into production cycles. Here’s a quote from Finnish recycling website (on the Finnish version of this page they say they can recycle up to 99 % of the parts of electric and electronic waste.)
What happens to the collected devices?
It is important to deliver the waste electrical and electronic equipment to recycling, so that they do not end up burdening the environment!
The collected devices are primarily processed in Finland. In recycling, raw materials and other materials are released from old appliances to be used in industry. These materials are used in the manufacture of new products.
Dangerous and harmful materials are also collected from old appliances to be processed separately. This way, the harmful agents do not end up to the environment. Some of the undamaged devices returned to the recycling find their way to reuse after inspection.
The tea cup and the little table with the controllers are from a second hand shop as well, as is the little table cloth on it. I rarely need to buy anything new these days, Helsinki area second hand stores and reuse centres are piled high with perfectly good household items (and indeed I’m going on a crusade to find a new controller for my PS3. The old controller was destroyed by a cat.)
The small table cloth is fairly new, I got it on an unexpected adventure to Hyvinkää where I went on a fun day trip (go see the town museum if you can, there’s a really fun art exhibition there right now!) My inner textile nerd can tell with some authority that the style of decoration on the cloth is an old fashioned technique called “bottom sewing” in Finnish (can’t really say what it would be in English) and it’s usually combined with drawnwork embroidery. It was made popular by the fact that it didn’t require other materials besides the fabric it was made on, so it was cheap. These are quite rare to see nowadays, probably because the work is difficult-ish (I tried some myself with a 1950s guide book), but the payoff isn’t as fabulous or effective as even the plainest cross stitch embroidery, or bobbin lace. My strange little example is more beautiful still because the cloth has been woven with two different colours of flax, which gives a nuanced impression of colouring for the rows of the little holes.
So this has been your random bit of news about antiquated arts and crafts!
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
What Are the Different Engineering Disciplines Available in Engineering Programs in Canada?
Engineering is a broad and dynamic field, offering a wide range of disciplines for students to explore. Engineering programs in Canada cater to various interests and career paths, allowing students to specialize in different branches of engineering. Each discipline has its own set of challenges, opportunities, and applications. Here's a look at the key engineering disciplines available in engineering programs in Canada.
1. Civil Engineering: Civil engineering, a time-honored and highly adaptable field, focuses on designing, constructing, and managing essential infrastructure, including roads, bridges, buildings, and water supply systems. This discipline focuses on the planning and construction of both urban and rural infrastructure, with an emphasis on sustainability and safety. Students of civil engineering programs in Canada will study subjects like structural analysis, transportation engineering, and geotechnical engineering.
2. Mechanical Engineering: Mechanical engineering is a broad field that involves the design, analysis, and manufacturing of machines and mechanical systems. It is one of the most diverse branches of engineering, with applications in industries ranging from automotive to aerospace. Mechanical engineers are responsible for creating everything from consumer products to advanced machinery. Engineering programs in Canada in this field cover topics such as thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, and materials science.
3. Electrical Engineering: Electrical engineering focuses on the design and development of electrical systems, devices, and equipment. Electrical engineers work on a variety of systems, including power generation, telecommunications, and electronics. Students in electrical engineering programs in Canada will study circuits, signal processing, and control systems, with an emphasis on innovation and technology.
4. Software Engineering: Software engineering integrates concepts from computer science and engineering to create effective software solutions. Software engineers design and build applications, operating systems, and network systems. The field has grown rapidly with the rise of technology, and software engineers are in high demand. Canadian programs in this field focus on programming languages, algorithms, database management, and software development practices.
5. Chemical Engineering: Chemical engineering involves the design and operation of processes that convert raw materials into valuable products, such as fuels, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals. Chemical engineers apply principles of chemistry, biology, physics, and mathematics to optimize industrial processes. In Canada, students studying chemical engineering will focus on process design, thermodynamics, and reaction engineering.
6. Environmental Engineering: Environmental engineering is dedicated to creating solutions for addressing environmental challenges. Engineers in this field work on issues such as water and air pollution, waste management, and renewable energy. This discipline plays a crucial role in sustainability efforts and addressing climate change. Environmental engineering programs in Canada include courses in environmental chemistry, hydrology, and environmental policy.
7. Aerospace Engineering: Aerospace engineering is concerned with the design and development of aircraft and spacecraft. Engineers in this field work on cutting-edge technologies in aviation and space exploration. Students in aerospace engineering programs in Canada will study aerodynamics, propulsion, avionics, and space systems.
8. Biomedical Engineering: Biomedical engineering combines engineering principles with medical and biological sciences to design and develop medical devices, diagnostic equipment, and treatment technologies. This interdisciplinary field plays a key role in improving healthcare and patient outcomes. Biomedical engineering programs in Canada prepare students for careers in medical device development, rehabilitation engineering, and tissue engineering.
These are just a few of the many engineering disciplines available in engineering programs in Canada. The diversity of fields means that students can pursue a career in a variety of industries, from construction to healthcare, technology, and beyond.
0 notes
Text
MM Precision Machining: Achieve Exceptional Accuracy with Advanced CNC Techniques
Precision in modern manufacturing is of utmost importance. MM Precision Machining stands as an indispensable service in industries that demand exacting standards such as aerospace, automotive, electronics and medical devices. Shenzhen Yixin Precision stands out as a premier CNC Machining provider by consistently delivering components with pinpoint precision that meet even the strictest specifications.
Understanding MM Precision Machining
MM precision machining refers to manufacturing parts with tolerances measured in millimeters or micrometers, using computer numerical control (CNC) technology for consistent and accurate components. High-precision CNC machines combined with skilled operators and modern software ensure every part meets exacting standards while decreasing waste and improving efficiency.

Precision Machining Offers Multiple Advantages
Precision machining brings several crucial benefits:
1. Increased Product Performance: Precise tolerances ensure components fit and function seamlessly within complex assemblies for increased product reliability.
2. Cost Efficiency: Precision reduces rework and material waste, leading to lower production costs overall.
3. Quality Assurance:Industries such as medical and aerospace require precise specifications for safety and performance - something MM precision machining meets with ease.
Applications of MM Precision Machining
Many industries rely on precision machining for their operations:
Aerospace: Aircraft components require extremely tight tolerances to ensure safety and performance.
Automotive: High-precision components contribute to the reliability and efficiency of engines and transmission systems, while Medical Devices must meet stringent quality standards to guarantee patient safety.
Electronics: Miniaturized components in smartphones and computers rely on precision machining for proper functionality.
Key Technologies in MM Precision Machining
1. 5-Axis CNC Machining: Provides access to complex geometries without multiple setups being necessary.
2. EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining): This technique excels when dealing with intricate shapes or hard materials.
3. CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machines): These precision measuring devices ensure parts meet specifications through extensive quality control measures.

Consider These Factors When Selecting an MM Precision Machining Partner
When selecting an MM precision machining provider, keep the following in mind. These include experience and expertise: Look for companies that can demonstrate experience within your industry.
Advanced Equipment: Be sure your prospective supplier utilizes cutting-edge CNC machines and inspection tools, along with quality certifications such as ISO 9001. These indicate adherence to international quality standards.

Shenzhen Yixin Precision brings cutting-edge technology and industry expertise together to produce components that exceed client expectations. Our commitment to quality and precision has earned us global trust from clients around the globe.
0 notes
Text
The Evolution and Importance of Industrial SMPS and Power Converters in Modern Industries
What are Industrial SMPS and Power Converters?
Industrial SMPS, or Switch Mode Power Supplies, are power supply units designed to provide a regulated output voltage or current by switching the power on and off at high frequencies. Unlike traditional power supplies, Industrial Smps are more efficient, compact, and versatile, making them ideal for industrial applications where space and energy efficiency are paramount.
On the other hand, power converters are devices that convert electrical energy from one form to another. These can include converting AC (alternating current) to DC (direct current), DC to AC, or even altering voltage levels. Power converters are indispensable in applications ranging from renewable energy systems to electric vehicles.
The Role of Industrial SMPS in Modern Industries
Industrial SMPS are vital in ensuring stable power delivery in environments with varying voltage conditions. They are widely used in:
Automation Systems: Factories with robotic assembly lines rely heavily on SMPS to maintain consistent energy supply for precise operations.
Telecommunication Equipment: Stable power is crucial for uninterrupted communication, and Industrial SMPS provide the reliability needed for such systems.
Medical Devices: In the healthcare sector, SMPS are used in imaging devices, patient monitoring systems, and diagnostic machines, where power stability is critical.
Industrial SMPS not only enhance energy efficiency but also contribute to reducing operational costs. Their ability to operate over a wide input voltage range makes them ideal for use in industries with fluctuating power supplies.
Applications of Power Converters
Power converters play an equally significant role in industries. Their applications include:
Renewable Energy Systems: Solar panels and wind turbines use power converters to convert generated power into usable electricity for grids or storage systems.
Electric Vehicles (EVs): In EVs, power converters are used to manage energy between batteries and motors, optimizing performance and extending battery life.
Consumer Electronics: Power converters are integral in gadgets like laptops, smartphones, and home appliances for efficient power management.
Innovations Driving the Future
Recent advancements in Industrial SMPS and power converters are paving the way for smarter and more efficient systems. Innovations such as gallium nitride (GaN) and silicon carbide (SiC) semiconductors are making these devices more compact and energy-efficient. Furthermore, the integration of IoT in power systems allows real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, enhancing operational efficiency.
Why Industries Must Adopt Advanced Power Solutions
With rising energy demands and a growing emphasis on sustainability, adopting advanced power solutions like Industrial SMPS and Power Converters is no longer optional. They enable industries to achieve higher efficiency, reduce energy waste, and meet environmental standards. Additionally, their reliability ensures minimal downtime, which is crucial in sectors like manufacturing and healthcare.
In conclusion, Industrial SMPS and Power Converters are not just tools but essential pillars that uphold the functionality and progress of modern industries. Their continuous evolution signifies a promising future where industries can thrive with smarter, more sustainable power solutions. Embracing these technologies is key to staying competitive in an ever-changing industrial landscape.
0 notes
Text
Aluminum to Copper Brazing Flux Cored Wires—Shop Now: 8851310039
Brazing is a critical process in various industrial applications where joining dissimilar metals like aluminum and copper is required. Aluminum to Copper Brazing Flux Cored Wires are innovative solutions designed to simplify the brazing process while ensuring strong, durable, and reliable joints. These wires are particularly valuable in industries such as HVAC, automotive, aerospace, and electrical engineering, where lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and conductive materials are paramount.

What are the Brazing Flux-Cored Wires?
Brazing Flux Cored Wires are specialized brazing wires with a core filled with flux material. Flux is essential in the brazing process because it helps remove oxides, prevents oxidation, and promotes wetting by allowing the filler material to flow smoothly over the surfaces being joined. This eliminates the need for separate flux application, reducing process complexity and improving efficiency.
In the context of aluminum-to-copper brazing, the flux inside the cored wire is carefully formulated to handle the unique challenges posed by these metals. Aluminum forms a stable and hard-to-remove oxide layer, while copper's high thermal conductivity can make achieving uniform heating difficult. Flux-cored wires address these issues effectively, ensuring a seamless and reliable bond.
Advantages of Aluminum to Copper Brazing Flux-Cored Wires
Until now, the flux-cored braze wires by Shop Castron Electrode provide the following advantages:
Simplified Brazing Process: The integration of flux into the wire eliminates the need for a separate flux application step. This reduces preparation time, minimizes potential errors, and ensures consistent application across joints.
Superior Joint Strength: The filler material in flux-cored wires is engineered to create robust bonds between aluminum and copper, even under thermal and mechanical stress. These joints are suitable for high-performance applications.
Enhanced Corrosion Resistance: Brazed joints using flux-cored wires are less prone to corrosion, making them ideal for applications in humid or chemically aggressive environments, such as HVAC systems and marine equipment.
Optimized Thermal and Electrical Conductivity: Copper is known for its excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, while aluminum is valued for being lightweight. Flux-cored wires facilitate efficient bonding without compromising these critical properties.
Cost-Effectiveness: The streamlined brazing process reduces labor costs and waste, making flux-cored wires a cost-effective choice for mass production or repair applications.
Key Applications
HVAC Systems: Joining aluminum and copper components in heat exchangers and refrigerant circuits.
Automotive Industry: Brazing aluminum radiators and copper piping in thermal management systems.
Aerospace: Fabricating lightweight yet strong connections in airframes and electrical systems.
Electrical Engineering: Creating high-conductivity connections in power systems and electronics.
Best Practices for Use
To achieve optimal results with aluminum-to-copper brazing flux-cored wires, the following practices are recommended:
Surface Preparation: Ensure the surfaces to be joined are clean and free from grease, dirt, or heavy oxides.
Heating Technique: Use controlled and even heating, avoiding overheating, which can damage the metals or filler.
Wire Handling: Store the wires in a dry environment to prevent moisture absorption, which could impact the flux’s performance.
Conclusion
Aluminum to copper brazing flux-cored wires represent a significant advancement in metallurgical joining technologies. By simplifying the brazing process and delivering reliable, high-strength joints, these wires empower industries to achieve better performance and efficiency. Whether in critical HVAC systems or sophisticated aerospace applications, they ensure durability, conductivity, and corrosion resistance, making them an indispensable tool in modern manufacturing and repair processes. For further details, visit https://shop.castonelectrode.in/2024/07/26/copper-brazing-flux/
0 notes
Text
Dry Ice Blasting in Malaysia: A Revolutionary Cleaning Technology
In recent years, industrial cleaning in Malaysia has witnessed a major shift towards more efficient and environmentally friendly methods. Among these, dry ice blasting has emerged as a cutting-edge solution for cleaning machinery, equipment, and surfaces across a variety of sectors. This non-abrasive and non-toxic cleaning technique is gaining popularity due to its effectiveness and sustainability.
What is Dry Ice Blasting?
Dry ice blasting, also known as CO2 blasting, involves using compressed air to propel small pellets of dry ice (solid carbon dioxide) at high speeds towards the surface being cleaned. Upon impact, the dry ice rapidly sublimates (turns directly from a solid to a gas), creating a micro-explosion that dislodges contaminants such as dirt, grease, paint, and mold from surfaces. This process is highly effective and does not leave any residue, as the dry ice simply evaporates.
This method is especially beneficial in Malaysia, where industries such as manufacturing, food processing, automotive, and electronics face significant challenges with regular cleaning maintenance. Unlike traditional cleaning methods that use harsh chemicals or abrasive techniques, dry ice blasting in Malaysia is a safer, more efficient, and environmentally friendly option.
Advantages of Dry Ice Cleaning Solutions
There are numerous advantages to choosing dry ice cleaning over conventional methods:
Non-Abrasive: Unlike sandblasting or other abrasive cleaning techniques, dry ice blasting does not damage the surface being cleaned. It is gentle yet effective, making it ideal for delicate equipment and machinery.
Environmentally Friendly: Dry ice blasting is a sustainable cleaning solution as it doesn’t produce harmful chemicals or waste. Since the dry ice evaporates into gas, it leaves no secondary waste or residue.
Minimal Downtime: Traditional cleaning often involves lengthy disassembly of equipment. With dry ice blasting, maintenance time is significantly reduced, allowing businesses to get back to production faster.
Cost-Effective: While the initial setup of dry ice blasting equipment can be an investment, the long-term savings come from reduced downtime, less waste disposal, and fewer chemical cleaning agents.
No Water Usage: In many industries, water is a scarce and expensive resource. Dry Ice Blasting Malaysia Dry ice cleaning eliminates the need for water, helping businesses conserve this valuable resource and minimize water waste.
Applications of Dry Ice Blasting in Malaysia
Dry ice blasting has a wide range of applications across various sectors in Malaysia:
Food Industry: In food processing, cleanliness is a priority. Dry ice blasting is particularly effective in cleaning conveyor belts, molds, and ovens without leaving any residue that could contaminate food products.
Electronics and Automotive: For electronics manufacturers and automotive maintenance, dry ice blasting offers a precise and safe cleaning method for sensitive parts like circuit boards, engines, and electrical components.
Mold Remediation: For industries facing mold and mildew issues, particularly in humid environments like Malaysia, dry ice cleaning provides a quick and effective solution without the need for chemicals.
Industrial Equipment: Heavy machinery, such as turbines, engines, and compressors, requires frequent cleaning to maintain performance. Dry ice blasting effectively removes contaminants while preventing wear and tear on the equipment.
Why Choose Dry Ice Blasting in Malaysia?
Malaysia’s humid climate and rapid industrial development present unique challenges for businesses in maintaining cleanliness and efficiency. Traditional cleaning methods often fall short, either damaging expensive equipment or leaving harmful residues. Dry Ice Blasting Malaysia provides a unique solution to these challenges. It helps companies maintain high standards of cleanliness, reduce maintenance costs, and comply with environmental regulations. The growing demand for dry ice cleaning solutions reflects a shift toward sustainability and better operational efficiency.
Furthermore, businesses in Malaysia can benefit from local suppliers and service providers offering dry ice blasting services. This ensures that companies can access expert cleaning services and the latest technology without delays.
1 note
·
View note