#visitFrenchGuiana
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
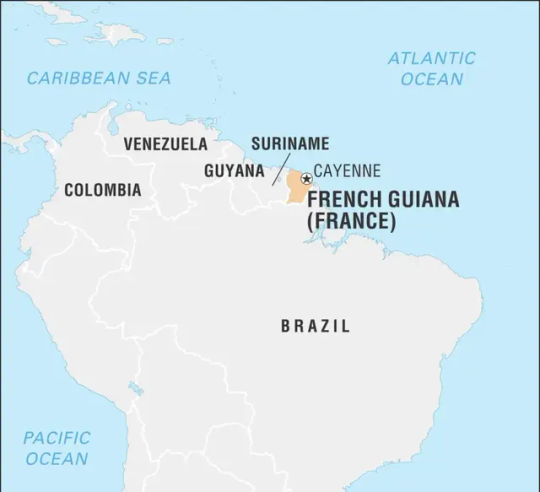
French Guiana

French Guiana is a department of France situated in South America, bordering Brazil, Suriname, and the Atlantic Ocean. It is an overseas region of France and is the only non-independent territory on the South American continent. It covers an area of 83,534 square kilometers and is home to around 296,711 people. French Guiana's capital city is Cayenne. The region is known for its dense Amazonian rainforest, tepuis (table-top mountains), and rivers, with the Maroni and Oyapock rivers forming borders with neighboring countries. The Amazon rainforest covers almost all of the region's land, making it an important biodiversity hotspot. The official language is French, and the Euro is the official currency used in the region. While French Guiana's economy is largely dependent on the French government, fishing and gold mining are vital contributors to the region's economy. The Guiana Space Centre, one of the world's most significant spaceports, is also located in French Guiana and is operated by the French government. French Guiana's climate is tropical, with high levels of humidity and temperatures ranging between 26°C and 32°C on average. The rainy season typically falls between December and July, while the dry season lasts from August through November. While French Guiana is a part of France, it is still quite unique, and there are significant differences between the department and the rest of the country. Unlike mainland France, the department is situated within South America and boasts a unique blend of cultures and traditions. The region is also home to a diverse population of ethnic groups, including Creoles, Amerindians, and Maroons. French Guiana's culture is a fusion of various traditions influenced by its history and the different immigrant groups that have settled in the region over the years. The department is an excellent place for ecotourism, featuring many natural landmarks and animal species. Along with national parks, a popular attraction in French Guiana is the Guiana Space Centre, which attracts many international visitors due to the many rocket launches that take place at the spaceport. Despite its small size, French Guiana's unique blend of culture, natural beauty, and scientific advancements make it a fascinating region to explore and learn about.
Etymology
French Guiana, also known as Guiana, is a French overseas region located on the northeast coast of South America. The name "Guiana" comes from an Amerindian language, meaning "Land of Many Waters." The name is fitting as the region is home to numerous rivers and waterways, including the Amazon and its tributaries. The term "French Guiana" was first used by the French when they laid claim to the region in the 17th century. The name was given to distinguish it from the neighboring territories of British Guiana (now Guyana) and Dutch Guiana (now Suriname). French Guiana's name reflects its complex history and cultural heritage. The region has been home to various indigenous peoples for thousands of years before being colonized by the French and becoming a part of the larger French colonial empire in the 19th century. The region is also known for its rich biodiversity and unique flora and fauna. Today, French Guiana is an important center for space exploration and research, with the Guiana Space Centre being located in Kourou. The name French Guiana reflects the region's ties to France and its contributions to science and technology.
History
French Guiana has a rich history stretching back to pre-Columbian times. The indigenous Amerindian tribes, including the Kalina, Wayampi, and Arawak, were the first inhabitants of the region. However, during the 17th century, European explorers began arriving in the area, and French traders established settlements along the coast. In 1664, French Guiana officially became a French colony, and the region was used primarily as a penal colony throughout the 18th and 19th centuries. Thousands of prisoners were sent from France to work on plantations and in gold mines. Conditions were harsh, and many prisoners perished due to disease and mistreatment. In the late 19th century, French Guiana underwent significant changes, and it became a center for scientific research. The French government funded numerous expeditions to study the region's flora, fauna, and geology. Some of the most notable expeditions were led by naturalist Alfred Wallace and geologist Charles Darwin. During World War II, French Guiana played an essential role in the allied war effort. The United States government constructed a military base in the region, and troops were stationed there to protect against Nazi submarines. In the 1960s, French Guiana began a new phase of development, and the focus shifted to space exploration. The European Space Agency built the Guiana Space Centre in Kourou, which is the world's busiest satellite launch site. The center is responsible for launching satellites for both European and American clients. Despite its intriguing past, French Guiana is a territory that is often overlooked in discussions of South American history. This region's history is complex and multilayered, and it's worth exploring for those interested in colonialism, indigenous cultures, and scientific exploration. Geology The unique and rugged landscape of French Guiana owes much to its geological history. The region is characterized by rocky plateaus, rolling hills, and dense forests, all of which are the result of millions of years of tectonic activity, erosion, and deposition. French Guiana lies on the northern edge of the Amazonian Craton, a stable and ancient geological region that forms the foundation of much of South America. However, the region is not entirely stable. The Guiana Shield, an area of ancient rock that extends across much of northern South America, was formed billions of years ago by volcanic activity and has been subject to tectonic uplift and folding. The landscape of French Guiana has been shaped by the slow wearing away of the Guiana Shield, which has exposed a variety of rock formations, including sandstone, shale, and limestone. The region is also rich in mineral resources, including gold, bauxite, and diamonds. The most prominent feature of the landscape, however, is the Amazon Rainforest, which covers more than 90% of French Guiana. The dense vegetation is the result of a combination of weather patterns, soil conditions, and a wet and humid climate. The region's geological heritage also plays a crucial role in shaping the biodiversity of the area. The unique combination of rock formations, soils, and climate has led to the evolution of a vast array of plant and animal species, many of which are found nowhere else on Earth. French Guiana is also home to several geological formations of unique interest to scientists and tourists alike. One of the most stunning is the Devil's Island, an infamous former penal colony that sits atop a rocky outcrop on the northeast coast of the region. The island is the site of several unusual geological features, including rugged cliffs, sea caves, and a stunning natural arch. the landforms and geology of French Guiana are as exciting and unique as the flora and fauna that call this region home. Whether you're a geology enthusiast or just an appreciator of natural beauty, this South American gem offers something for everyone. Geography French Guiana is the smallest region of France, located in the northeastern coast of South America. It is bordered by Suriname to the west, Brazil to the east and south, and the Atlantic Ocean to the north. The region's geography mainly comprises of low-lying coastal plains and the Guiana Highlands, a mountain range in the southern part of the region. The coastal plains occupy most of the region's area and are covered with mangrove swamps, marshlands, and savannas. These marshlands are home to various waterbirds, such as herons, egrets, and flamingos. The savannas are a mix of grasslands, scrub bushes, and small forests, and are inhabited by various bird species and capybaras. The Guiana Highlands, on the other hand, are part of the old Guiana Shield and are mainly composed of granite and crystalline rocks. The highest peak in the region, Montagne des Chevaux at 845 meters, is located in this mountain range. The Guiana Highlands are covered in lush rainforests and are home to various plant and animal species endemic to the region. The region is also home to many rivers, with the Maroni river acting as the natural boundary between French Guiana and Suriname. Other major rivers include the Oyapock, Sinnamary, and Approuague. These rivers are home to various species of fish, including piranhas, and are crucial to the region's fishing industry. French Guiana also has a few offshore islands, including the Salvation Islands, an archipelago famous for its historical use as a penal colony. The largest of these islands, Devil's Island, is now a tourist attraction and is known for its beautiful beaches. French Guiana's diverse geography plays a vital role in the region's economy and ecosystem. The region's coastal plains, highlands, rivers, and islands are home to various plant and animal species and provide various resources to the region's residents. Ecology One of the most fascinating aspects of French Guiana is its diverse environmental ecosystem. Located in South America, the region features an array of wetlands, rainforests, and savannas that are home to a variety of unique species. The Amazon rainforest covers a significant portion of French Guiana, accounting for about 90 percent of the total area. This vast expanse of greenery is home to several endangered species of plants and animals, which makes it an essential area of global significance. The region's wetlands and savannas, on the other hand, feature a wide range of animals such as capybaras, sloths, tapirs, and caimans. The coastal areas of French Guiana are mainly covered by mangroves. These forests are essential in protecting the coastline from storms and flooding. Mangroves are also home to several species of birds that are integral to the area's ecological balance. With over 4,000 recorded species of plants and animals, French Guiana boasts an immensely diverse ecological system. The region's most iconic wildlife is the giant sea turtle, which nests in large numbers on the beaches near Mana and Awala-Yalimapo. French Guiana also has the largest number of primate species in the world, with over 13 different species living in the region. The country’s rivers, such as the Maroni, which borders Suriname, is home to several species of fish, including the popular Piranha. The Amazon, Oyapock, and Approuague rivers all contribute to the overall diversity of the region's aquatic ecosystem. Despite the impressive diversity of species and natural resources, French Guiana faces environmental challenges, including deforestation, air pollution, and improper waste disposal, which can harm the population and contribute to the disruption of the ecological balance. Efforts have been made to address these issues, and the region has implemented several conservation measures and policies that have helped protect indigenous species and ecosystems. French Guiana's ecological system is a beautiful and unique aspect of the region. The lush rainforests, wetlands, mangroves, and savannas provide a home for a diverse array of species, making it a vital area of global environmental significance. The challenges faced in ensuring the region's ecological balance underscores the importance of continued efforts to protect and preserve the region's natural habitats. Biodiversity Biodiversity in French Guiana is a topic of great interest due to the abundance of unique flora and fauna found in the region. The tropical rainforests, savannas, and wetlands allow for a wide variety of species to thrive. French Guiana is known to have one of the highest levels of biodiversity in the world. The region is home to over 6,000 plant species, many of which are endemic to the area, meaning they can only be found in French Guiana. The forests are made up of different types of trees, including mahogany, greenheart, and cedar. there are over 500 species of birds in French Guiana, including the harpy eagle and toucan. French Guiana is also home to numerous species of mammals, including jaguars, tapirs, sloths, and anteaters. The region’s rivers and wetlands provide habitats for caimans, piranhas, and otters. French Guiana’s coastal waters are known for their diverse marine life, including coral reefs, sea turtles, and dolphins. One of the most unique species found in French Guiana is the Guiana Crested Eagle, which is one of the rarest birds of prey in the world. This bird was thought to be extinct until it was rediscovered in the 21st century in the forests of French Guiana. Another notable species is the giant otter, which can grow up to 6 feet long and is known for its playful behavior in the water. In order to protect the biodiversity of French Guiana, the government has established protected areas and national parks throughout the region. These areas are designed to preserve the natural habitats of the flora and fauna, while also allowing visitors to experience the beauty of the region. The Kaw-Roura Nature Reserve, for example, is one such area that is home to a wide variety of bird species and other wildlife. French Guiana's biodiversity is not only important for the region, but for the world as a whole. The unique species found in the region can provide valuable information for scientific research and can also be used for medicinal purposes. It's important to continue to protect and preserve the biodiversity of French Guiana for future generations to enjoy and learn from.

Jaguars Climate French Guiana has a tropical equatorial climate, characterized by high humidity and frequent rainfall throughout the year. The annual temperature typically ranges between 75-90°F (24-32°C), with minimal variation during the seasons. However, the region experiences two distinct seasons - a rainy season from December to July and a dry season from August to November. During the rainy season, the rainfall ranges from heavy to moderate, and the region experiences thunderstorms and gusty winds. On the other hand, the dry season is characterized by a relatively low amount of rainfall, and often, the region experiences forest fires and drought. Furthermore, French Guiana is on the path of the South Atlantic High, which brings in variable winds across the region. These can range from light breezes to strong gusts, causing an increase in humidity levels and rain showers. Due to the region's location near the equator, the length of daylight hours remains fairly constant throughout the year, with 12 hours of daylight and 12 hours of darkness. However, during the rainy season, cloud cover can limit the amount of sunshine, and visibility can be reduced, which can affect outdoor activities. If you plan to visit French Guiana, it is recommended to check the weather forecast beforehand and pack accordingly. Light, breathable clothing is ideal as temperatures can be high, and it is also recommended to carry a jacket or raincoat in case of an unexpected shower. Mosquito repellent is also a must-have item due to the high prevalence of mosquitoes in the region, particularly during the rainy season. French Guiana experiences a rainy and dry season, which brings in variations in climate and weather patterns. Humidity, rainfall, and temperature levels remain relatively constant throughout the year, with an equatorial tropical climate prevalent in the region. Visitors should be mindful of these weather patterns and prepare accordingly, ensuring that they take the necessary measures to make their stay in French Guiana a comfortable and enjoyable experience. Environmental Issues French Guiana faces various environmental challenges that affect the biodiversity and natural habitat of the region. One of the significant challenges in the region is illegal gold mining. The gold mining process involves deforestation, which disrupts the ecological system and destroys the habitats of wildlife. It also leads to soil erosion, which alters the land structure and causes water pollution, damaging aquatic animals. Another environmental issue is the use of pesticides and fertilizers in agriculture. The chemicals used in farming are harmful to the environment, particularly to aquatic animals and birds. Pesticides and fertilizers run off into nearby water sources, causing water pollution and harming aquatic plants and animals. the chemicals can accumulate in the soil, making it unsuitable for agriculture over time. Deforestation due to logging and farming is also a significant environmental issue in French Guiana. The forest serves as a habitat for a wide range of species, and the loss of trees reduces biodiversity. Illegal logging causes income loss for the government and its people, damaging the economy and affecting the livelihood of the populace. Climate change is another environmental challenge in the region. The increasing global temperature has led to rising sea levels, more severe weather conditions, and an increased frequency of natural disasters. Changes in weather patterns have affected agriculture in the region, leading to a decline in yields. To address these environmental challenges, the local government has implemented measures to protect the environment. The government enforces laws that regulate and restrict illegal mining activities, logging, and the use of chemicals in farming. The government also promotes sustainable agriculture practices, such as agroforestry, to preserve the biodiversity of the region. French Guiana faces environmental issues that affect the natural habitat and its people. The government has put measures in place to reduce the harmful impact of human activities on the environment and promote sustainable practices. It is important to continue implementing strategies that support the preservation of the region's ecosystem to ensure a healthy and stable future for the region.
Politics
French Guiana is an overseas department of France and has been since 1946. As such, it shares the same political structures and governance as the rest of France. The President of France has an elected prefect who represents him in French Guiana, acting as the highest authority of the region. The prefect is assisted by a number of other officials, such as the Sub-Prefects and the Mayors of the different cities in the region. French Guiana sends two representatives to the French National Assembly and one senator to the French Senate to represent them on the national level. The French Guianese also have the right to vote in national French elections and referendums, making them fully integrated into the political system of France. However, despite being a part of France, French Guiana has its own regional council that is responsible for managing the region's budget, infrastructure, and other local affairs. Read the full article
0 notes