#vcenter server 7 installation
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Dell VxRail Deploy Exam (D-VXR-DY-01) Prep Guide & Practice Exam
The D-VXR-DY-01 Dell VxRail Deploy Version 2 exam is a qualifying exam for the Dell VxRail Deploy v2 Certification, designed to assess your knowledge of implementing and managing a VxRail cluster. This exam covers various topics, from solution planning to hardware and software installation, and troubleshooting, making it essential for IT professionals working with VxRail solutions.
In this blog post, we’ll dive into the key aspects of the exam, explore its structure, and share the best tips for preparing, including how to make use of the D-VXR-DY-01 practice exam from Cert007 for optimal study results.
Dell VxRail Deploy Version 2 Exam Overview
The Dell VxRail Deploy v2 Certification exam tests your ability to implement a basic VxRail cluster, including hardware installation, environment validation, software implementation, and post-deployment tasks. The exam is split into two parts:
Part 1: 90 minutes
Part 2: 30 minutes
To pass the exam, you need to meet the passing score requirements for both parts.
Understand Key Exam Topics
The following topics are essential for the D-VXR-DY-01 Dell VxRail Deploy Version 2 exam:
1. VxRail Physical Components (4%)
Understanding VxRail cluster architecture
Knowing rack requirements for VxRail clusters
2. VxRail Deployment Planning (12%)
vCenter server and its role in deployment
Networking components and vSphere Distributed Switches
DNS options, node discovery, and vSAN settings
3. Using VxRail Configuration Tools (4%)
Creating and reviewing VxRail projects and configurations
4. VxRail Hardware Installation and Initialization (8%)
Procedures for installing and cabling VxRail hardware
Configuring VxRail node iDRAC and system time settings
5. VxRail Network Environment Requirements and Initialization (8%)
Configuring and validating VxRail network settings manually
6. Deploying the VxRail Cluster (24%)
Initializing VxRail clusters with VxRail or customer-managed vCenter Server
vSAN ESA (vSAN Express Storage Architecture) setup
7. VxRail Post-Deployment Procedures (18%)
Performing post-installation validation
Configuring vSAN settings and native backups
8. VxRail Cluster Upgrade and Expansion (10%)
Understanding upgrade requirements and scale-out processes
9. VxRail Troubleshooting (6%)
Collecting logs and troubleshooting using VxRail and vSAN tools
10. VxRail REST API (6%)
Using VxRail REST APIs to automate tasks and troubleshoot issues
Study Tips for D-VXR-DY-01 Dell VxRail Deploy Exam
Preparing for the D-VXR-DY-01 exam requires a solid understanding of the VxRail system, hardware installation, networking, and troubleshooting. To maximize your chances of success, follow these steps:
Understand the Core Topics: Focus on the key areas of the exam, including deployment planning, hardware installation, and post-deployment procedures. Review Dell’s official documentation and guides related to VxRail clusters.
Hands-On Experience: Practical experience with VxRail components, vCenter Server, and networking setups is crucial. Try to work on a live or simulated VxRail environment to get familiar with the installation and configuration processes.
Use VxRail Tools: Gain proficiency with tools like the VxRail Configuration Portal and REST API. Understanding how to troubleshoot common issues using logs and vSAN tools will be particularly useful for the troubleshooting section.
Practice Exams: One of the best ways to prepare for the exam is by using D-VXR-DY-01 practice exams from Cert007. These practice exams closely simulate the real exam experience, helping you assess your readiness and pinpoint areas that need more study.
Review Study Materials: Cert007 offers comprehensive and up-to-date study materials specifically designed for the Dell VxRail Deploy v2 exam. These materials cover every exam topic in detail and provide insights into common issues and troubleshooting strategies.
Final Thoughts
The D-VXR-DY-01 Dell VxRail Deploy Version 2 Certification is an essential step for professionals looking to demonstrate their expertise in deploying and managing Dell VxRail clusters. By focusing on key exam topics, gaining hands-on experience, and leveraging practice exams from Cert007, you can confidently prepare for and pass the exam.
Invest in quality study materials and practice exams to ensure you're well-prepared for this important certification. Good luck on your journey to becoming Dell VxRail Deploy certified!
0 notes
Text
New Post has been published on
New Post has been published on https://www.tayfundeger.com/vcenter-server-7-kurulumu.html
vCenter Server 7 Kurulumu
Merhaba,
vCenter Server 7 Kurulumu isimli bu yazımda sizlere yeni release olan vCenter Server 7 kurulumu ve konfigurasyonu hakkında bilgi vereceğim. vCenter Server 7 ile birlikte artık Windows vCenter Server kullanmadığımızı yazımın başında belirtmek isterim.
vCenter Server 7 ve yenilikleri ile ilgili bu makalemde bilgi vermeyeceğim. Bu sadece kurulum makalesidir. Eğer yenilikleri merak ediyorsanız aşağıdaki makalemi incelemenizi rica ediyorum.
vCenter Server 7 Yenilikleri
vCenter Server 7 kurulumuna başlamadan şunlara dikat etmenizi tavsiye ediyorum. Windows vCenter Server artık end of support duruma geldiği için kuruluma yanlızca vCenter Server Appliance ile yapıyoruz. vCenter Server Appliance, sadece ESXi üzerine kurulabilir ve ESXi harici bir yere asla kurulamaz. Bundan dolayı gereksinimlere çok dikkat etmeniz gerekiyor.
vCenter Server 7 versiyonunu ESXi 6.5 ve sonraki sürümlerine kurabilirsiniz. vCenter Server 7 kurulumuna başlamadan, vCenter Server 7 kurulumunda kullanacağınız hostname ve IP adresini DNS üzerinde oluşturmalısınız. Yani host A kayıtlarının tanımlanması gerekir. DNS üzerinde gerekli kayıtları oluştururken reverse kayıtlarını yapmayı lütfen unutmayın. vCenter Server 7 kurulumlarının bir çoğu DNS hatalarından dolayı fail oluyor. Bundan dolayı DNS üzerindeki konfigurasyonunuzu düzgün bir şekilde yapmalısınız. vCenter Server 7 doğrudan bir sunucu üzerine kurulmadığı için Windows gibi bir işletim sisteminden deployment’ı başlatmanız gerekiyor. vCenter Server 7 ‘nin kurulumunun başlatılacağı Windows sunucununda ESXi ve vCenter ‘da kullandığınız/kullanacağınız IP’leri çözdüğünden emin olmalısınız.
Sistem gereksinimleri:
vCenter Server 7 deploy etmeye başladığınızda ortamda barınacak virtual machine ve ESXi host sayısına göre vCenter Server ‘in CPU ve Memory konfigurasyonu değişkenlik gösterebilir.
Aşağıda, vCenter Server ‘in ESXi host ve virtual machine sayısına göre belirleyeceğiniz CPU ve Memory seçenekleri gösterilmektedir.
Number of vCPUs Memory Tiny environment (up to 10 hosts or 100 virtual machines) 2 12 GB Small environment (up to 100 hosts or 1,000 virtual machines) 4 19 GB Medium environment (up to 400 hosts or 4,000 virtual machine) 8 28 GB Large environment (up to 1,000 hosts or 10,000 virtual machines) 16 37 GB X-Large environment (up to 2,000 hosts or 35,000 virtual machines) 24 56 GB
Aynı şekilde vCenter Server ‘in içerisinde barındıracağınız ESXi host ve virtual machine sayısına göre vCenter Server ‘in storage gereksinimleri değişmektedir.
Default Storage Size Large Storage Size X-Large Storage Size Tiny environment (up to 10 hosts or 100 virtual machines) 415 GB 1490 GB 3245 GB Small environment (up to 100 hosts or 1,000 virtual machines) 480 GB 1535 GB 3295 GB Medium environment (up to 400 hosts or 4,000 virtual machine) 700 GB 1700 GB 3460 GB Large environment (up to 1,000 hosts or 10,000 virtual machines) 1065 GB 1765 GB 3525 GB X-Large environment (up to 2,000 hosts or 35,000 virtual machines) 1805 GB 1905 GB 3665 GB
Yukarıda ESXi host ve virtual machine sayısına vCenter Server 7 storage gereksinimini görebilirsiniz.
Software Gereksinimleri:
vCenter Server 7 ‘nin bir ESXi üzerinde çalışması gerekiyor. Fiziksel sunucu üzerine kurulum yapamıyorsunuz. vCenter Server 7’nin bulunacağı ESXi host’un versiyonu 6.5 ve sonrası sürümlere sahip olmalıdır. Aynı şekilde Deployment’ını yapacağınız vCenter Server ‘in yine bir vCenter Server içerisinde çalıştırmayı düşünüyorsanız bu vCenter Server’ında 6.5 ve sonrası versiyonlara sahip olması gerekiyor. vCenter Server Appliance’i kurarken GUI veya CLI installer‘i kullanarak kurulumu gerçekleştirebilirsiniz.
Port Gereksinimleri:
vCenter Server 7 tarafından, yönetilen her ESXi host’a veri gönderebilmeli, vSphere Web Client ve Platform Services Controller hizmetlerinden veri alabilmelidir. ESXi host’lar arasında migration ve provisioning gibi işlemleri yapabilmek için, source ve destination ESXi host’larının birbirlerinden veri alabilmesi gerekir.
Bir port kullanımdaysa veya blacklist’e alınmışsa, vCenter Server installar bir hata mesajı görüntüler. Kuruluma devam etmek için başka bir port numarası kullanmalısınız. Sadece internel iletişim için kullanılan portlar vardır.
VMware, iletişim için belirlenmiş portları kullanır. Ayrıca, ESXi host’lar, vCenter Server’dan veri için belirlenmiş portları izler. Bu öğelerin herhangi biri arasında yerleşik bir güvenlik duvarı varsa, vCenter Server yükleme veya yükseltme işlemi sırasında bağlantı noktalarını açar. Özel güvenlik duvarları için, gereken bağlantı noktalarını el ile açmanız gerekir. Yönetilen iki ESXi host arasında bir güvenlik duvarınız varsa ve migration veya clone gibi operasyonları gerçekleştrirmek istiyorsanız, port’ların açık olduğundan emin olmanız gerekiyor. Portlar ile ilgili gereksinimlere buradan erişebilirsiniz.
DNS Gereksinimleri:
vCenter Server 7 kurmadan önce DNS sunucusu üzerinde gerekli tanımları yapmanız gerekmektedir. vCenter Server 7 kurarken sabit bir IP adresi ve FQDN belirtmeniz gerekiyor. Belirtmiş olduğunuz FQDN ve IP adresinin DNS sunucusu üzerinde tanımlı olduğundan emin olmalısınız. Eğer DNS tanımlarınız doğru değilse vCenter Server ‘in 2. aşamasında yani Stage 2 ‘de fail alırsınız. Web Client’a erişemediği için kurulum fail eder. DNS üzerinde yapacağınız tanımlarda PTR kayıtlarınında oluşturulması gerekir. DNS üzerindeki tüm tanımları doğru bir şekilde yaptıysanız nslookup komutu ile IP adresi’nin FQDN’i döndürdüğünü görebilirsiniz.
Browser Support:
Tarayıcınızın vSphere Web Client’i desteklediğinden emin olun. VMware, vSphere Client için aşağıdaki Guest OS tarayıcı sürümlerini test etmiş ve desteklemiştir. En iyi performans için Google Chrome’u kullanın.
Windows 32-bit and 64-bit
Microsoft Edge version 38 and later.
Microsoft Internet Explorer version 11.0.96 and later.
Mozilla Firefox version 45 and later.
Google Chrome version 50 and later.
Safari 5.1 and later.
Mac OS
Mozilla Firefox version 45 and later.
Google Chrome version 50 and later.
Safari 5.1 and later.
vCenter Server 7 Kurulumuna başlıyoruz. İlk olarak aşağıdaki linkten vCenter Server 7 download ediyoruz.
https://my.vmware.com/web/vmware/details?downloadGroup=VC700&productId=974&rPId=44114
vCenter Server 7 Kurulumu
Daha öncede belirttiğim gibi artık sadece vCenter Server Appliance bulunuyor ve Windows vCenter Server kullanılmıyor. Bundan dolayı Windows vCenter Server üzerine kurulum yapmayacağız.
vCenter Server 7 Kurulumu
ISO dosyasını download ettiğinizde veya mount ettiğinizde vCenter Server 7’nin 6.42 GB boyutunda olduğunu göreceksiniz. Önceki vCenter Server sürümleri ile karşılaştırdığınızda bu sürümün ISO boyutu bir hayli fazla olduğunu göreceksiniz. vCenter Server 7 ISO dosyasını download ettikten sonra Windows sunucumuza mount ediyoruz ve aşağıdaki path’e gidiyoruz.
D:\vcsa-ui-installer\win32
vCenter Server 7 Kurulumu
Yukarıda belirtmiş olduğum path’e gittikten sonra Installer isimli uygulamayı buluyoruz ve sağ click Run As Administrator butonu ile çalıştırıyoruz.
vCenter Server 7 Kurulumu
vCenter Server 7 kurulumunda karşımıza 4 adet seçenek çıkıyor. Biz burada Fresh bir kurulum yani yeni bir kurulum yapacağımız için Install butonu ile devam ediyoruz.
vCenter Server 7 Kurulumu
vCenter Server 7 Kurulumu Stage 1 ve Stage 2 olmak üzere iki aşamadan oluşuyor. Stage 1 ‘de ilk olarak vCenter Server deploy ediliyor. Stage 2 de ise SSO konfigurasonunu belirtiyoruz.
Next ile devam ediyoruz.
vCenter Server 7 Kurulumu
Kullanıcı sözleşmesini kabul ediyoruz ve Next ile devam ediyoruz.
vCenter Server 7 Kurulumu
vCenter Server Deployment Target bölümünde bu vCenter Server’in hangi ESXi veya vCenter Server’a deploy edileceğini belirtiyoruz.
ESXi host or vCenter Server name: vCenter Server Appliance’in hangi ESXi veya vCenter Server’a kurulacak ise onun bilgilerini yazmamız gerekiyor. Kurulumu başlattığınız bilgisyarın/sunucunun ESXi veya vCenter Server’a erişimi olduğundan emin olun.
HTTPS Port: Default olarak bırakıyoruz.
Username: ESXi veya vCenter Server’in username’ini belirtmeniz gerekiyor.
Password: ESXi veya vCenter Server’in password’unu belirtmeniz gerekiyor.
Tüm işlemleri tamamladıktan sonra Next butonu ile devam ediyoruz.
vCenter Server 7 Kurulumu
Bir önceki kurulumda burada vCenter Server Appliance yazarken artık VMware appliance yazısını buradan kaldırmış. Set up vCenter Server VM bölümünden vCenter Server 7’nin virtual machine ismini ve password’unu belirtiyoruz.
VM Name: vCenter Server ‘in virtual machine ismini belirtiyoruz. Inventory’de buraya yazacağınız ismi göreceksiniz.
Set root password: vCenter Server ‘in root password’unu belirtiyoruz.
Confirm root password: Yukarıda belirtmiş olduğumuz root password’unu tekrar yazıyoruz.
Next ile devam ediyoruz.
vCenter Server 7 Kurulumu
Select Deployment Size bölümünde deploy edilecek vCenter Server ‘in size’ini belirtiyoruz. Bu konu ile ilgili yukarıda zaten bilgi vermiştim.
vCenter Server içerisinde barındıracağımız ESXi ve virtual machine sayısına göre bize en uygun olan Deployment size’i seçiyoruz ve Next ile devam ediyoruz.
vCenter Server 7 Kurulumu
vCenter Server 7’nin barınacağı datastore’u seçiyoruz. Eğer vCenter Server virtual machine’inin üzerinde bulunan disk’lerin thin olarak oluşmasını istiyorsanız Enable Thin Disk Mode seçeneğini seçmelisiniz. Next ile devam ediyoruz.
vCenter Server 7 Kurulumu
Şimdi en önemli bölümlerden birine geldik. Configure Network Settings bölümünde deploy edeceğiniz vCenter Server 7’nin network ayarlarını belirtmeniz gerekiyor.
Network: Bu bölümden vCenter Server Appliance virtual machine’inin hangi virtual machine port group’da olacağını seçiyoruz.
IP version: IPv4 veya IPv6 seçeneklerinden birini seçebilirsiniz. Default olarak IPv4 gelecektir.
IP assignment: Bu bölümden vCenter Server sunucusunun static mi yoksa DHCP’den mi IP kullanacağını belirtebilirsiniz. Static vermeniz için için daha garanti bir çözüm olacaktır.
FQDN: FQDN bölümünden vCenter’ınızın FQDN’ini belirtmeniz gerekiyor. Burada dikkat etmeniz gereken birşey bulunuyor. Buraya belirteceğiniz FQDN’in DNS üzerinde düzgün birşekilde çözülüyor olması gerekiyor. Aksi halde erişim sorunlarınız ortaya çıkacaktır.
IP address: Bu bölümde vCenter Server ‘a vereceğimiz IP’yi yazıyoruz.
Subnet mask or prefix length: Bu bölümden vermiş olduğumuz IP’nin subnet bilgisini yazıyoruz.
Default gateway: Vermiş olduğumuz IP’nin gateway’ini belirtiyoruz.
DNS Server: FQDN bölümünde belirtmiş olduğunuz adres hangi DNS üzerinde çözülüyor ise o DNS’i buraya belirtmeniz gerekiyor.
Common ports:
vCenter Server ‘a HTTP ve HTTPS üzerinden eriştiğimzi default 80 ve 443 port’unu eğer değiştirmek istiyorsanız bu bölümden değiştirebilirsiniz. Ancak bunu değiştirdiğinizde troubleshooting açısından çeşitli zorluklar ile karşılaşacağınızı unutmayın.
Tüm gerekli konfigruasyonları yaptıktan sonra Next ile devam ediyoruz.
vCenter Server 7 Kurulumu
Yaptığımız işlemlerin kısa bir özetini görüyoruz ve Finish butonu ile deployment’i başlatıyoruz.
Gördüğünüz gibi Stage 1 tamamlandı. Continue butonu ile Stage 2’nin kurulumuna başlıyoruz.
vCenter Server 7 Kurulumu
Stage 1 tamamlandıktna sonra Continue butonuna bastığımızda otomatik olarak Stage 2 ‘ye geçecektir. Stage 2 ‘de vCenter Server konfigurasyonunu yapacağız. Next ile devam ediyoruz.
vCenter Server 7 Kurulumu
vCenter Server configuration bölümünde karşımıza 2 seçenek çıkıyor.
Time synchronization mode:
Synchronize time with the ESXi host: Periyodik saat senkronizasyonunu etkinleştirir ve VMware tools, Guest OS ile ESXi host’un saatinin aynı olmasını sağlar.
Synchronize time with NTP servers: Saati senkronize etmek için bir NTP sunucu kullanır. Bu seçeneği belirlerseniz virgülle ayrılmış NTP sunucularının adlarını veya IP adreslerini girmelisiniz.
SSH access: Bu seçeneği Enable seçtiğinizde vCenter Server ‘a deploy edildiğinde SSH ile erişebilirsiniz. Eğer disable seçerseniz deploy edildikten sonra tekrar enable duruma getirebilirsiniz.
Next ile devam ediyoruz.
vCenter Server 7 Kurulumu
vCenter Server’ı kurarken mutlaka bir Single Sign on domain’i oluşturmanızı veya var olan bir Single Sign On domain’ine join etmeniz gerekiyor.
SSO configuration bölümünde karşımıza 2 seçenek çıkıyor. Bunlar;
Create a new Single Sign-On domain: Yeni bir Single Sign On domain’i oluşturmak istiyorsanız bu seçeneği seçmelisiniz.
Single Sign-On domain name: vCenter Server kurulum sırasında kendisine özel bir domain oluşturulmasını ister. Bu internal bir domain’dir. Default olarak vSphere.local bırakmanızı tavsiye ederim.
Single Sign-On password: Single Sign-On domain’i için password belirtmeniz gerekiyor.
Join an existing vCenter Single Sign-On domain: Eğer var olan bir Single Sign On domain’ine vCenter Server’inizi member etmek istiyorsanız bu seçeneği seçebilirsiniz.
Create a new Singile Sign-On domain seçeneğini seçiyorum ve Next ile devam ediyorum.
vCenter Server 7 Kurulumu
VMware’in müşteri iyileştirme programına katılmak istermisiniz diye karşımıza bir ekran çıkıyor. Join checkbox’ına basarsanız iyileştirme programına katılmış olursunuz. Ben bu seçeneği seçmiyorum ve Next ile devam ediyorum.
vCenter Server 7 Kurulumu
Stage 2 bölümünde yapmış olduğumuz işlemlerin kısa bir özetini görüyoruz ve Finish ile gerekli konfigurasyonların yapılmasını sağlıyoruz.
Son olarak karşımıza bir uyarı geliyor. Eğer OK butonuna basarsanız artık kurulumu geri alamayacağınız belirtiliyor. Tüm işlemleri kontrol ettiğimiz için OK butonu ile devam ediyoruz.
Stage 2 tamamlandığına göre artık vCenter Server’ımıza bağlanabiliriz. Bunun için vCenter Server’a belirtmiş olduğunuz FQDN veya IP adresini kullanabilirsiniz. Zaten Stage 2 tamamlandıktan sonra da vCenter Server Getting Started Page bölümünden de bağlantıyı sağlayabilirsiniz. Close butonuna bastığımızda karşımıza vCenter Server login ekranı gelecektir.
Makalenin başında da belirtmiştim. vCenter Server 7 ile birlikte artık vSphere Web Client kullanılmıyor. Tüm işlemleri vSphere Client yani HTML 5 Client üzerinden gerçekleştiriyoruz. Launch vSphere Client (HTML5) butonuna basıyoruz.
Kurulum sırasında belirtmiş olduğumuz [email protected] account’u ile login oluyoruz.
vCenter Server 7 Kurulumu nu tamamladık. Bu aşamadan sonra Datacenter oluşturup, ESXi host’larınızı ekleyebilirsiniz.
Umarım faydalı olmuştur.
İyi çalışmalar.
#vcenter 7 kurulumu#vcenter nasıl kurulur#vcenter server 7 installation#vcenter server 7 kur#vcenter server eğitimi
0 notes
Text
For the past one week, I’ve been working on a centralized Logs management system for VMware vSphere and vCenter environment. Having searched on the web for a simple, better open-source solution for this, the ideal solution seemed to be Rsyslog collector. So I ended up installing Rsyslog server on CentOS 7 system and configuring it as a central logs server for vCenter Server Appliance(vCSA) logs and all logs generated by vSphere servers. In this guide, we will cover both installation/configuration of Rsyslog server and configuration of vCSA/vSphere to send logs to remote Rsysog server we configured. Setting up vSphere and vCenter Central Logs Management with Rsyslog Before we get started, let me state the assumptions here: You have installed CentOS 7 server; Debian based system should be fine Rsyslog is installed Your user account has sudo privileges If any of the above is not satisfied, make sure you have all set. When done, use steps below to install and configure Rsyslog server to receive logs from your VMware vSphere and vCenter infrastructure. Step 1: Update your system Let’s update our system packages to the latest releases: sudo yum update For Ubuntu, do the same with apt: sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get upgrade Reboot the system if possible for updates which require an update to take effect, e.g kernel updates: sudo reboot Step 2: Configure the Rsyslog server Both CentOS and Ubuntu/Debian systems come with rsyslog installed and running. We will need to create an additional configuration file for our VMware setup. For basic configuration of Rsyslog on Ubuntu/Debian, refer to How to Configure Rsyslog Centralized Log Server on Ubuntu 18.04 LTS The default configuration file is./etc/rsyslog.conf. Any additional configuration can be placed under the directory/etc/rsyslog.d/. Create a directory for VMware vSphere and vCSA appliance logs: $ sudo mkdir -p /data/logs/vcenter,esxi Then add the following configuration file to /etc/rsyslog.d/vmware.conf.This is a config for vSphere Infrastructure logging. It has templates which dictate where and how to store logs, match patterns, and log timestamp definition. # Provides TCP syslog reception $ModLoad imtcp #### Create Templates for Log parsing #### Log store is created folder previously template(name="TIMESTAMP" type="string" string="%timegenerated:8:25%||%HOSTNAME%||%syslogtag%||%msg%\n") template(name="ESXI" type="string" string="/data/logs/esxi/%fromhost-ip%/%$YEAR%-%$MONTH%/%$DAY%.%$MONTH%-messages.log") template(name="VCENTER" type="string" string="/data/logs/vcenter/%fromhost-ip%/%$YEAR%-%$MONTH%/%$DAY%.%$MONTH%-messages.log") #### Define remote logging RuleSet $RuleSet remote ### The following rule is created to store logs coming from vCenter with different parameters ### If log is coming from vcenter with IP 192.168.10.50 it will be stored using VCENTER template. ### Replace 192.168.10.50 with your vCSA IP address if $fromhost == '192.168.10.50' then *.* ?VCENTER else # Store all other logs using TIMESTAMP and ESXI templates. *.* ?ESXI;TIMESTAMP ### Tell rsyslog to listen TCP port 514. ### All events coming to this port will be parsed using remote RuleSet. $InputTCPServerBindRuleset remote $InputTCPServerRun 514 Here we defined three templates: TIMESTAMP: Used to format all logs coming from certain IP Address. This is to make logs more readable by having proper time formats. ESXI: This tells rsyslog to store logs from each host in a separate folder and logs from each day be stored in a folder corresponding to that day. Logs from vSphere hosts will be stored in /data/logs/esxi VCENTER: This tells rsyslog to store logs from a vCenter appliance in /data/logs/vcenterusing timestamp and structure similar to the one used on ESXI template. Restart rsyslog service after making the changes: sudo systemctl restart rsyslog Check status, it should be in running state: $ systemctl status rsyslog
● rsyslog.service - System Logging Service Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/rsyslog.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Thu 2018-08-02 11:54:03 EAT; 1min ago Docs: man:rsyslogd(8) Main PID: 12489 (rsyslogd) Tasks: 8 Memory: 7.6M CGroup: /system.slice/rsyslog.service └─12489 /usr/sbin/rsyslogd -n Aug 02 11:54:03 rsyslog.example.com systemd[1]: Starting System Logging Service... Aug 02 11:54:03 rsyslog.example.com rsyslogd[12489]: [origin software="rsyslogd" swVersion="8.24.0" x-pid="12489" x-info="http://www.r...] start Aug 02 11:54:03 rsyslog.example.com systemd[1]: Started System Logging Service. Hint: Some lines were ellipsized, use -l to show in full. Open Rsyslog firewall ports Rsyslog listens on port 514, we configured it to user TCP, open it using your firewalld administration tool. On Ubuntu / Debian with ufw: sudo ufw allow 514/tcp On CentOS 7: sudo firewall-cmd --add-port=514/tcp --permanent sudo firewall-cmd --reload Step 3: Configure vSphere hosts and vCSA Appliance The only pending piece is to configure vSphere and vCSA appliance to push logs to our rsyslog server. How to Configure vSphere remote Syslog Open your vCenter and navigate to: Hosts and Clusters > Select Host > Configure > Advanced System Settings > Edit on Filter box, search “syslog”. You should see “Syslog.global.logHost“. Fill rsyslog server address inside this box: tcp://192.168.10.35:514 If you want to configure both tcp and udp, separate them using a comma: tcp://192.168.10.35:514,udp://192.168.10.35:514 It should look like below: How to Configure vCenter (vCSA) remote Syslog For vCSA, configure remote rsyslog by opening vCSA administration UI: http://vCSA-IP:5480 This will give login dashboard: Enter username and password provided during installation. The initial default username is root, and the default password is vmware. Procedure: In the vCenter Server Appliance Management Interface, select Syslog. In the Forwarding Configuration section, click Configure if you have not configured any remote syslog hosts. Click Edit if you already have configured hosts. In the Create Forwarding Configuration page, enter the server address of the destination host. The maximum number of supported destination hosts is three. From the Protocol drop-down menu, select the protocol to use. In the Port text box, enter the port number to use for communication with the destination host. In the Create Forwarding Configuration pane, click Add to enter another remote syslog server. Click Save. Verify that the remote syslog server is receiving messages. In the Forwarding Configuration section, click Send Test Message. Verify on the remote syslog server that the test message was received. The new configuration settings are shown in the Forwarding Configuration section. If you go back to the rsyslog server, there should be two folders created under logs directory configured earlier: $ ls /data/logs/ esx vcenter $ ls /data/logs/vcenter/192.168.10.50/2018-08/02.08-messages.log /data/logs/vcenter/192.168.10.50/2018-08/02.08-messages.log And for ESXI hosts: $ file /data/logs/esx/192.168.10.31/2018-08/02.08-messages.log /data/logs/esx/192.168.10.31/2018-08/02.08-messages.log: ASCII text, with very long lines You can consider configuring log rotation for the same. $ cat /etc/logrotate.d/vmware /data/logs/esxi/*/*/*.log rotate 90 daily notifempty compress /data/logs/vcenter/*/*/*.log rotate 90 daily notifempty compress You now have a working rsyslog server for your vSphere Infrastructure. Have a happy logging.
0 notes
Text
Microsoft lync 2013 download for windows 7 64 bit

#MICROSOFT LYNC 2013 DOWNLOAD FOR WINDOWS 7 64 BIT PDF#
#MICROSOFT LYNC 2013 DOWNLOAD FOR WINDOWS 7 64 BIT INSTALL#
#MICROSOFT LYNC 2013 DOWNLOAD FOR WINDOWS 7 64 BIT 64 BIT#
#MICROSOFT LYNC 2013 DOWNLOAD FOR WINDOWS 7 64 BIT UPDATE#
#MICROSOFT LYNC 2013 DOWNLOAD FOR WINDOWS 7 64 BIT 32 BIT#
Or else, you can buy it from the below link. You can directly purchase a copy of Microsoft office 2013 from the Microsoft store.
#MICROSOFT LYNC 2013 DOWNLOAD FOR WINDOWS 7 64 BIT UPDATE#
You will receive every update and will always remain on the safe side. In this way, you don’t need to worry about any bugs or future updates. The best way to enjoy all office suite features is by using the official version of Microsoft Office 2013. Microsoft Office 2013 Download (Official)
Operating System: Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 8.1, Windows 10, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2012.
Display: Graphics hardware acceleration requires a DirectX10 graphics card and a 1024 x 576 or higher resolution monitor.
Memory (RAM): 1 GB RAM (32-bit) 2 GB RAM (64-bit).
Computer and processor: 1 GHz or faster x86- or 圆4-bit processor with SSE2 instruction set.
It got the ability to return to the last viewed or edited location in Word & Powerpoint.
Office 2013 supports the embedding of online photos with content from, , and Flickr.
Client endpoint: 1. Hardware that supports each of the required software components previously listed.
Flash Fill is now available in Microsoft Excel. The vCenter Server and ESXi hosts must be running vSphere 5.0 or later.
Microsoft word got improved text wrapping and track changes features.
#MICROSOFT LYNC 2013 DOWNLOAD FOR WINDOWS 7 64 BIT PDF#
You can now import PDF files in Microsoft Word.I believe you will like to see Excel 2013, PowerPoint 2013, Word 2013, Outlook, OneNote 2013, MS Access, Publisher, and Lync installed with Microsoft Office 2013 download.Įspecially the most common Office 2013 applications Word, Excel, PowerPoint and OneNote will please Office 2013 users. Office programs installed with Microsoft Office 2013
#MICROSOFT LYNC 2013 DOWNLOAD FOR WINDOWS 7 64 BIT INSTALL#
If you wonder which Office programs are installed when you download Office 2013 and install it on your computer, you can check the below Office 2013 program menu screenshot from a Windows 7 start menu. Professionalplus_en-us_x86.exe setup file size for 32bit Microsoft Office 2013 Professional Plus Preview is 625 MB Professionalplus_en-us_圆4.exe setup file size for 64bit Microsoft Office 2013 Professional Plus Preview is 704 MB You can activate Office 2013 by following the below process:Ĭlick on File tab Then click Account tab. Office 2013 activation will prevent warning messages about the product is unlicensed so will let you undisturbed while you are working using MS Office products. Only after Office 2013 installation is complete, you can provide Office 2013 product key which will automatically activate Office 2013 setup. Microsoft Office Professional Plus 2013 Preview setup is a straight-forward process and does not require user interaction after you start installing Office 2013. If you want to install 32-bit Office instead, please run the 32-bit setup.Īfter you register for the Office 2013 Preview, you can try Microsoft Office 2013 download for 64-bit setup files which will especially make Excel users happy with its increased memory capabilities based on the 64-bit operating system it will be running on.Īfter you decide MS Office 2013 edition you want to download, you can choose among available Office 2013 languages (English, Spanish and Japanese) Depois de aplicar esta atualização, o Lync 2013 será atualizado para o. Currently my new Lync server cannot share a desktop through a Lync 2013 client installed on a Windows 8 workstation. A página de download exibirá esta atualização conforme aplicável ao Lync 2013. Baixe a versão de 64 bits do pacote de atualização skype para negócios 2015 agora. Please uninstall all 32-bit Office programs, then re-try installing 64-bit Office. Baixe a versão de 32 bits do pacote de atualização skype para negócios 2015 agora. Microsoft Office Project Professional 2010 We can't install the 64-bit version of Office because we found the following 32-bit programs on your PC:
#MICROSOFT LYNC 2013 DOWNLOAD FOR WINDOWS 7 64 BIT 32 BIT#
Or you can uninstall previously installed 32 bit applications, and then install 圆4 Microsoft Office 2013 Professional Plus preview (beta) version. So if you have already installed Office products of 32 bit, then you can try free Microsoft Office 2013 download of 32-bit distribution binaries and install 32 bit Office applications. One important note to choose x86 or 圆4 versions of Microsoft Office 2013 for Office users is previously installed Office products require the same product architecture family for new Office 2013 Preview applications too.
#MICROSOFT LYNC 2013 DOWNLOAD FOR WINDOWS 7 64 BIT 64 BIT#
This Microsoft TechNet page will not only provide you required activation keys (Office 2013 product key) but also links to 32 bit and 64 bit binaries of Microsoft Office 2013 Professional Plus setup files. Then you will be redirected to TechNet Product Key Distribution for Office 2013 pages. If you follow this download link, it will request you to login with your Passport account.

0 notes
Text
Vmware vsphere 6.5 keygen torrent

Vmware vsphere 6.5 keygen torrent license key#
Vmware vsphere 6.5 keygen torrent pro#
Vmware vsphere 6.5 keygen torrent software#
Vmware vsphere 6.5 keygen torrent Pc#
Vmware vsphere 6.5 keygen torrent software#
In this manner, you can, for example, test software on multiple systems. VMware Player, you can run multiple ora’s on the same unit. You may able to publish, run, and view exclusive machines from the Workstation user interface. Furthermore, easily hook up to vCloud Air.
Vmware vsphere 6.5 keygen torrent Pc#
Seamlessly move and drop online machines in the middle of your PC as well as your internal cloud jogging vSphere, ESXi or another illustration of Workstation. It gives you to increase and range your exclusive machines in the cloud. VMware Workstation provides relationships to VMware vSphere and vCloud Air service.
Support for systems with multiple screens.
Intelligent download and installing a fresh version of the toolkit VMware Tools.
The automatic suspension system of the VM when the node is turned off.
Main Features of VMware Workstation 15 Keygen The advanced functions of the VMware Workstation 14 products provide users with a secure workplace. Predicated on this great experience, the VMware Workstation team has had the opportunity to regularly improve and improve our products over time, “said Dave Offer, VP of Product Marketing, VMware PERSON Processing. VMware has been hearing and giving an answer to the precise needs of builders, IT specialists and companies for more than 17 years. VMware Workstation Torrent facilitates hundreds of visitor. This program has a number of different qualities which make it a great software so that you can run another os’s inside Windows. VMware Player is without a doubt one of the better programs for creating and emulating online machines. As all users who ever before worked with online machines know, they are really stored on hard disks in the same way archives that may be activated and packed by wide selection of VMware software players, which VMware Player aspires to be the best one, light and having the ability to be used in virtually any situation.
Vmware vsphere 6.5 keygen torrent license key#
VMware Workstation License key enables you to launch any recently created exclusive machines on your pc – this makes tests and setting up different applications easy and safe. In cases like this, a digital machine (VM), including the VMware Workstation Player, pays to in which os can be installed and operate on the desktop. VMware Player has increased support for the Glass windows program, which can react both as a bunch so that as a guest operating system. VMware Workstation 15 License keygen freeload Compared to earlier versions, the utmost number of reinforced virtual systems was up to 20. A new feature is a simple Install, rendering it easy to perform exclusive machines on the latest Home windows and Linux personal computers. To put it simply, it simplifies the execution of other VMware products, such as Workstation Expert, Server, and ESX Server. However, for commercial use, a cost is claimed. The player is free software which allows online machines to be created and rotated. VMware has released Workstation Player, which is going to save.
Vmware vsphere 6.5 keygen torrent pro#
VMware Workstation Pro Crack will not only run current os’s but also as old as OR WINDOWS 7. Inside the network part, VMware Workstation now allows an individual to rename online systems, brings new network latency simulator (great for evaluating certain types of software) and support for observing the Ip on the electronic machine unit – with it isn’t essential to log into it for IP and Apple pc address visualization. The built-in wizard, now you can transfer the VMware vCenter Server Equipment virtual module, that allows you to control the VMware vSphere digital infrastructure. With a straightforward user interface, fantastic operating-system support and portability, IT professionals are now able to provide their users with even more standard enterprise desktops. VMware Workstation 16.2.0 is a desktop virtualization software which allows you to perform a number of os without rebooting on a single computer. Main Features of VMware Workstation 15 Keygen.VMware Workstation 15 License keygen freeload.VMware Workstation 16 Pro Crack Free Torrent 2020.

0 notes
Text
Esxi 6.5 keygen torrent

ESXI 6.5 KEYGEN TORRENT LICENSE KEY
ESXI 6.5 KEYGEN TORRENT CRACK SOFTWARE
ESXI 6.5 KEYGEN TORRENT KEY FREE
ESXI 6.5 KEYGEN TORRENT LICENSE NUMBER
ESXI 6.5 KEYGEN TORRENT DOWNLOAD
vRealize-Endpoint-Operations-Management-Agent-x86-64-linux-6.7.vRealize-Endpoint-Operations-Management-Agent-noarch-linux-6.7.0-7947327.rpm.vRealize-Endpoint-Operations-Management-Agent-noJRE-6.7.0-7947327.zip.vRealize-Endpoint-Operations-Management-Agent-noJRE-6.7.VMware-NSX-Manager-upgrade-bundle-6.4.Related posts: Vsphere 6 7 Tpm Trusted Platform Module Let's hope for smooth upgrades in the next couple of weeks. vSphere 6.5 had a long closed and open beta phase to hunt for bugs. With 614 days, the development time of vSphere 6.5 was over 20 month. However, vSphere 6.0 still had some serious issues. Since vSphere 6.0 VMware started to extend major release cycles. VMware vSphere Management Java SDK 6.5 for Workbench IS.VMware vSphere Virtual Disk Development Kit 6.5.VMware vSphere Command Line Interface 6.5.VMware vSphere Automation Java SDK 6.5 for Workbench IS.VMware vSphere Automation SDK 6.5 for.VMware vSphere Automation SDK 6.5 for Ruby.VMware vSphere Automation SDK 6.5 for REST.VMware vSphere Automation SDK 6.5 for Python.VMware vSphere Automation SDK 6.5 for Perl.VMware vSphere Automation SDK 6.5 for Java.VMware Virtual SAN Management SDK 6.5.0.VMware Open Virtualization Format Tool 4.2.0.VMware vRealize Operations Manager 6.4.VMware vRealize Log Insight 4.0.0 for NSX.VMware vSphere Management Assistant 6.5 (vMA).VMware vRealize Log Insight 4.0.0 for vCenter.VMware Virtual SAN Witness Appliance 6.5.VMware vSphere Hypervisor (ESXi) 6.5.0.Another way is to select the 'Create board outline' tool, left click on the first point on design area, right click and select 'Arc mode' from the submenu. I can't see the solder mask and solder paste for pads. Press 'OK' to apply changes and you'll get the board you need. The easiest way to create a circular board is to select 'Objects Board Points' from main menu then choose 'Create circular board' option and specify the board radius. Specify the opposite point of the circle then left click on first point to close the board outline.
ESXI 6.5 KEYGEN TORRENT DOWNLOAD
VMware vSphere 6.5 Release Notes and Download Links
Vsphere 6 7 Tpm Trusted Platform Module.
ESXI 6.5 KEYGEN TORRENT LICENSE KEY
Free Vmware Esxi 5.1 License Key Crack Download.
ESXI 6.5 KEYGEN TORRENT CRACK SOFTWARE
Free Vmware Esxi 5.1 License Key Crack Software.
But it wasn’t what I expected it only let’s you create a VM with 8vcpu to get more you need to buy a license I bought one for £580 that includes 3 hosts and 1 vcenter server.
ESXI 6.5 KEYGEN TORRENT LICENSE NUMBER
When you go onto the VMware website to download esxi 6.5 u1 it gives u a free license number to enter on the esxi web interface after you have installed it. VMware Player Crack 15.5.6 With Keygen Free 2020 Windows + Mac With many applications that range from a single educational instrument to a company tool for providing simplified expertise to conduct a corporate background on a BYO apparatus, Workstation Player frees the VMware vSphere hypervisor to provide a simple yet stable and secure. VMware player is publicly available on the current market and isn’t subject to any licensing or restrictions. Trade associations need to be paid permits to utilize Workstation Player. We encourage pupils and non-profit organizations to profit from this offering.
ESXI 6.5 KEYGEN TORRENT KEY FREE
VMware Player 15.5.6 2020 Crack & Key freeload.

0 notes
Text
Vmware vcenter converter standalone 5.5 2 download

Vmware vcenter converter standalone 5.5 2 download how to#
Vmware vcenter converter standalone 5.5 2 download software#
Vmware vcenter converter standalone 5.5 2 freeload#
Vmware vcenter converter standalone 5.5 2 download windows#
Support for DSA authentication for Linux conversionsĪs concerning the resolved issues, the release notes of VMware converter 5.5.1 standalone mentions those following fixes:.VMware Converter standalone adds those new features: It's a maintenance release which fixed several bugs, but with a bonus added a support for VMware VSAN. You can check out the release notes from this page. It's a build 1682692 and you can download it from here. The latest release of VMware Converter Standalone 5.5.1 is available since few days.
Vmware vcenter converter standalone 5.5 2 download software#
Virtual infrastructure monitoring software review.
Reviews – Virtualization Software and reviews, Disaster and backup recovery software reviews.
Videos – VMware Virtualization Videos, VMware ESXi Videos, ESXi 4.x, ESXi 5.x tips and videos.
Vmware vcenter converter standalone 5.5 2 freeload#
Free – Free virtualization utilities, ESXi Free, Monitoring and free backup utilities for ESXi and Hyper-V.VMware Workstation and other IT tutorials.
Vmware vcenter converter standalone 5.5 2 download how to#
How To – ESXi Tutorials, IT and virtualization tutorials, VMware ESXi 4.x, ESXi 5.x and VMware vSphere.
Desktop Virtualization – Desktop Virtualization, VMware Workstation, VMware Fusion, VMware Horizon View, tips and tutorials.
Backup – Virtualization Backup Solutions, VMware vSphere Backup and ESXi backup solutions.
Server Virtualization – VMware ESXi, ESXi Free Hypervizor, VMware vSphere Server Virtualization, VMware Cloud and Datacenter Virtualization.
Tips – VMware, Microsoft and General IT tips and definitions, What is this?, How this works?.
VMware vRealize Operations and vSAN Integration Workshop.
VMware vRealize Automation: Install, Configure, Manage.
VMware vRealize Operations for Administrators.
VMware vRealize Oprations: Install, Configure Manage.
VMware Site Recovery Manager: Install, Configure, Manage.
VMware Integrated Openstack: Install, Configure, Manage.
VMware Cloud on AWS: Deploy and Manage 2019.
VMware Workspace ONE: Advanced Integration.
VMware Horizon 7: Install, Configure, Manage.
VMware NSX-T Data Center: Troubleshooting and Operations.
VMware NSX-T Data Center: Install, Configure, Manage.
VMware vSphere: Optimize and Scale – NEW !!!.
VMware vSphere: Install, Configure, Manage – NEW !!!.
VMware vCenter Converter Standalone is a conversion utility to turn over saved virtual machines into VMware ones.
Handles many virtual machines including Microsoft.
Run simultaneous conversions to speed up virtual setup.
Convert existing virtual machines over to the VMware format.
VMware vCenter Converter Standalone Key Features: Monitor console conversations over local and remote locations. Convert more than one virtual machine at the same time to scale up a virtual machine hosted environment faster. Possible being seen as dominance software to take an increasing piece of the virtual machine market for themselves, this package can boost performance when switching from other unreliable virtual machine offerings by different software suppliers. Third party image formats can also be converted over to VMware virtual machines as well.
Vmware vcenter converter standalone 5.5 2 download windows#
VMware vCenter Converter Standalone is a converter that is capable of switching Windows or Linux physical machines over to VMware virtual machines.

0 notes
Text
Download vmware esxi 5.1 iso free

#Download vmware esxi 5.1 iso free how to#
#Download vmware esxi 5.1 iso free update#
#Download vmware esxi 5.1 iso free upgrade#
:)Īs you might already read in my article about the changes to the ESXi, there isn't any vRAM limitation on the free ESXi 5.1 but there is still the 2 physical CPU limit together with the 32Gb physical RAM limit. I'm writing it down here for my own bookmarking needs as well.
#Download vmware esxi 5.1 iso free update#
This article is meant to be for every user who don't uses vSphere update manager for this process. More advanced users can skip, because they'll probably know this method.
#Download vmware esxi 5.1 iso free upgrade#
I've already wrote about patching ESXi without vCenter, but this time the command used slightly differ, and here I'm showing you the the steps which needs to be accomplished to upgrade to the latest ESXi 5.1 version. If you're running the free version of ESXi 5.0 in your homelab or testing it at work, you might be wondering what's the easy way to upgrade existing ESXi 5.0 installation to the latest ESXi 5.1 without much effort and without breaking your existing installation, without re-installing everything. Virtual infrastructure monitoring software review. Reviews – Virtualization Software and reviews, Disaster and backup recovery software reviews.Videos – VMware Virtualization Videos, VMware ESXi Videos, ESXi 4.x, ESXi 5.x tips and videos.Free – Free virtualization utilities, ESXi Free, Monitoring and free backup utilities for ESXi and Hyper-V.VMware Workstation and other IT tutorials.
#Download vmware esxi 5.1 iso free how to#
How To – ESXi Tutorials, IT and virtualization tutorials, VMware ESXi 4.x, ESXi 5.x and VMware vSphere.
Desktop Virtualization – Desktop Virtualization, VMware Workstation, VMware Fusion, VMware Horizon View, tips and tutorials.
Backup – Virtualization Backup Solutions, VMware vSphere Backup and ESXi backup solutions.
Server Virtualization – VMware ESXi, ESXi Free Hypervizor, VMware vSphere Server Virtualization, VMware Cloud and Datacenter Virtualization.
Tips – VMware, Microsoft and General IT tips and definitions, What is this?, How this works?.
VMware vRealize Operations and vSAN Integration Workshop.
VMware vRealize Automation: Install, Configure, Manage.
VMware vRealize Operations for Administrators.
VMware vRealize Oprations: Install, Configure Manage.
VMware Site Recovery Manager: Install, Configure, Manage.
VMware Integrated Openstack: Install, Configure, Manage.
VMware Cloud on AWS: Deploy and Manage 2019.
VMware Workspace ONE: Advanced Integration.
VMware Horizon 7: Install, Configure, Manage.
VMware NSX-T Data Center: Troubleshooting and Operations.
VMware NSX-T Data Center: Install, Configure, Manage.
VMware vSphere: Optimize and Scale – NEW !!!.
VMware vSphere: Install, Configure, Manage – NEW !!!.

1 note
·
View note
Text
Vmware 7

Vmware 76719
Vmware 7.0.2
VMware Skyline Health Diagnostics for vSphere - FAQ Note: VMware withdrew ESXi602-BG, ESXi602-BG, and ESXi501-BG due to instability issues reported by Intel. For more information, see Intel Sightings in ESXi Bundled Microcode Patches for VMSA-2018-0004.
VMware vSphere 7.0 and TLS Protocol. In vSphere 7.0, TLS 1.2 is enabled by default. TLS 1.0 and TLS 1.1 are disabled by default. If you upgrade vCenter Server to 7.0 and that vCenter Server instance connects to ESXi hosts, other vCenter Server instances, or other services, you might encounter communication problems.
Vmware 76719
Jul 16, 2020 The new vCenter can simplify management and operations with new VMware features. Now vCenter 7 cannot be installed on a Windows machine. VMware vCenter 7 can be deployed only as a virtual appliance (VCSA – vCenter Server Appliance) based on a Photon OS (a Linux-based operating system maintained by VMware).
Register to download your 60 day trial
Explore vSphere for free for 60 Days.
Don't have an account yet? Register to start your free 60-day trial. Already have an account? Log in to start your free 60-day trial.
Installation and Configuration
vSphere delivers an efficient and secure hybrid cloud platform to help you get the best performance, availability and efficiency out of your infrastructure and applications from day one.
- A base hypervisor, vSphere ESXi, that is installed on every physical server for hosting virtual machines.
- One instance of a management server, vCenter Server, enables centralized management of multiple vSphere hosts.
Start your VMware vSphere evaluation with the following steps:
Resources
vSphere Documentation Product Information vSphere Central vSphere 7 Technical Blogs
Troubleshooting & Support
Learn basic tips and tricks for troubleshooting various components of VMware vSphere.
Other Resources
Buying VMware vSphere.
The rich capabilities of vSphere are packaged into multiple editions to fit the needs of any organization. VMware vSphere is available in English, German, Simplified Chinese, and Japanese.
Find out which product is best suited to your business needs:

One instance of VMware vCenter Server, sold separately, is required for VMware vSphere deployments
Buy Online
Purchase VMware vSphere from our online store.
Find a Reseller
Leverage the VMware Partner Network to help you purchase the vSphere products that fit your needs.
Contact VMware Sales
Contact us today and speak to a sales expert to discuss your business needs.
Please login or create an account to access VMware vSphere downloads
Connect Support
View the top articles related to troubleshooting and support for this product. Add keywords to narrow your search.
Relevant Keywords: Intro maker.
vSphere 7
The new generation of vSphere for existing enterprise apps. Available in two editions.
VMware vSphere 7, the new generation of vSphere, is now generally available. This major new release brings a massive improvement in the work experience of vSphere administrators, folks who are responsible for the security, performance, and resiliency of the infrastructure and applications that provide all the key services to their organizations.
Watch the vSphere 7 digital launch event for the executive view, a technical overview, and a customer perspective with the hosts of siliconANGLE’s theCUBE.
To deep dive into the new features in vSphere 7, please visit the vSphere Academyand the YouTube playlist for vSphere 7.
Major Release
The purpose of this major release from vSphere is two-fold. The first is to embed containers and Kubernetes into vSphere, unifying them with virtual machines as first class citizens. This enables all vSphere administrators to become Kubernetes administrators and easily deliver new services to their developers. More on this in part two of this blog post, when vSphere 7 with Kubernetes becomes available as part of VMware Cloud Foundation 4. If you’re interested in vSphere 7 with Kubernetes, please visit the VMware Cloud Foundation blog site to learn more.
The second purpose of this major release is to deliver an essential building block of the cloud operating model to vSphere admins for running existing enterprise applications with vSphere 7. vSphere 7 addresses key challenges faced by our vSphere admins in areas of lifecycle management, security, and performance and resiliency needed by business-critical applications, AI/ML applications and latency sensitive applications.
Lifecycle Management
vSphere admins spend a significant amount of time on the lifecycle management of infrastructure. Lifecycle management includes ensuring that their systems are up-to-date and that the latest firmware for the underlying compute, storage and networking are installed and working. It also includes installing patches provided by VMware and other industry vendors, as updates are released in response to security vulnerabilities and as enhancements are deployed. Upgrading to the latest vSphere software version often takes a dedicated amount of time too, since each host needs to be updated, and the current process involves manual steps to validate. A typical vCenter Server upgrade would include migrating external PSCs and the vCenter Server from Windows OS to a vCenter Server appliance. Upgrading vSphere clearly involved many different activities and tools that required significant planning.
vSphere 7 offers a much simpler software architecture with a single upgrade workflow. With vSphere 7, the only requirement is to upgrade vCenter Server; there is no need to upgrade other external components such as the external PSC (Platform Services Controller) or load balancers. This results in a more efficient upgrade process given the fewer nodes that need to be managed.
Also, vSphere 7 enables the upgrades of entire ESXi clusters (versus a single ESXi host at a time) using a desired state model with cluster image management. The desired state model of the upgrade validates each host’s configuration until it matches the desired state. This simplifies and automates the host upgrade significantly for the entire ESXi cluster, once customers have upgraded to vSphere 7. Note that customers would have to upgrade to vSphere 7 to take advantage of the desired state model for future upgrades.
Security
vSphere admins are frequently and deeply involved in security operations related to infrastructure. Implementing data privacy and security policies and performing periodic compliance validation becomes a joint responsibility of IT and security organizations. The problem is that there are many ways in the industry to implement security policies, including implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA). Life for vSphere admins is even more complicated because many customers already have MFA in their corporate identity management systems.
vSphere 7 solves this problem using Identity Federation, which means vCenter Server can integrate with an enterprise identity provider without involving the vAdmins and vCenter Server. This simplifies the vSphere Admin’s job and helps reduce compliance audit scope.
vSphere 7 also enables vSphere admins to protect the integrity of your virtual infrastructure with remote attestation by a trusted computing base. This capability is delivered by vSphere Trust Authority. With vSphere Trust Authority, vSphere admins conduct security checks on a few strongly trusted hosts, validating the operating system, firmware, credentials, etc. These trusted systems are then compared to other running systems, with any differences being identified, so they can be evaluated for security vulnerabilities.
Performance and Resiliency
Whether customers are running database applications that demand a large VM such as SAP HANA or Oracle back ends, or AI/ML applications using GPU resources, or latency sensitive applications that require granular access to timing information, the needs for large and high performing applications continues to grow.
vSphere 7 delivers massive improvements to Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS), vMotion, and Assignable Hardware to meet the needs of enterprise applications.
Vmware 7.0.2
Improved DRS – Now using a workload centric approach for efficient resource allocation and live migration of workloads, the improved DRS concentrates less on the ESXi host utilization and prioritizes the VM condition – think of it as how “happy” your virtual machine is. The VM DRS score is calculated every minute, allowing vSphere to provide a much more granular optimization of resources.
Large application vMotion – vSphere admins can extend vSphere’s vMotion capability to large workloads such as SAP HANA and Oracle back ends. Previously, these workloads necessitated a longer stun-time during the switchover phase. With vSphere 7 and the greatly improved vMotion logic to transfer only those pages that are desired by the workload, stun time is reduced drastically for large workloads.
Assignable Hardware – With vSphere 7, vSphere admins can provision efficient pools of accelerated hardware for AI/ML applications with supported GPUs. Assignable Hardware will now interact with DRS when that VM is powered on (initial placement) to find an ESXi host that has such a device available, claim that device, and register the VM to that host. If there is a host failure and vSphere HA kicks in, Assignable Hardware also allows for that VM to be restarted on a suitable host with the required hardware available.
Precision Time Protocol (PTP) – vSphere 7 delivers software timestamp based PTP support for applications that need millisecond-level time accuracy.
Next Steps
Now is the time to start planning your upgrade.
To learn about the upgrade process, pricing and packaging for vSphere 7 and upgrading your vSphere license keys, please visit the vSphere Upgrade Center. If you have questions, you can visit Resources in the Upgrade Center or contact VMware Support.
To learn more about the vSphere 7 release, please visit the key product resources onvSphere Central, vSphere 7 blog or vSphere Academy.
Also, remember that End of General Support (EOGS) for vSphere 6.0 occurred on March 12, 2020. Please read the 6.0 EOGS blog for more details and upgrade to vSphere 7 as soon as possible to take advantage of the new capabilities.
Thank you for helping us improve vSphere 7 by giving us feedback, and being open about the challenges you face in your operating environments. Please continue to provide feedback through all channels, including our user groups and the VMware Technology Network . You can learn also more about vSphere 7 through our VMUG webcast series and through the resources below. Thank you for your continued confidence in vSphere!
Key vSphere 7 upgrade resources:
Visit the vSphere 7 Upgrade Center
Visit the vSphere Central
Watch thevSphere 7 launch event to hear executive, technical, and customer perspectives on vSphere 7
Additional Information:
We are excited about vSphere 7 and what it means for our customers and the future. Watch the vSphere 7 Launch Event replay, an event designed for vSphere Admins, hosted by theCUBE. We will continue posting new technical and product information about vSphere 7 and vSphere with Kubernetes Monday through Thursdays into May 2020. Join us by following the blog directly using the RSS feed, on Facebook, and on Twitter. Thank you, and please stay safe.

0 notes
Text
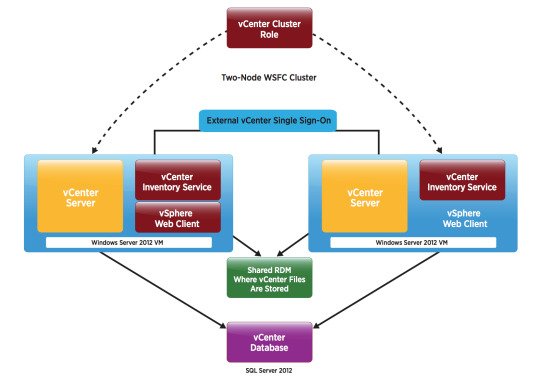
Vmware Vcenter Server 6.0

Vmware Vcenter Server 6.0 Crack
Vmware Vcenter Server 6.0 Windows 10
Vmware Vcenter Server 6.0 Download Free Trial
In previous post of this series, we’ve learnt about vCenter Server Architecture, such as its components, services, and Platform Services Controller (PSC). If you’ve missed previous posts of this series, you can find them here.
In this post, we’ll learn installing vCenter Server step-by-step in windows environment. When vCenter Server is installed, following services are also installed with it.
For complete guidance regarding vCenter Server installation and configuration, you can follow VMware vSphere 6.0 Part 2 – vCenter, Alarms and Templates course. In next post, we’ll see how vSphere Web Client works and used for managing and controlling vCenter Server. VMware's vCenter server appliance 6.0 has the same scalability numbers as the windows installable server. It seems that there is no reason to avoid the installation of vCenter appliance again. Buy one Microsoft windows server license less next time.I will not go through an installation guide since there are plenty of these published on the. Click Finish to complete the installation. Installing the VMWARE vCenter Server Appliance 6.0. Double Click the index.html file in the root of the DVD. Ensure pop up blockers to no block the Client Integration Plugin. Select Allow, so the VMware Client Integration Plug-In can access the operating system.
vCenter Server
vSphere Web Client (enables to connect to vCenter Server instance using web browser)
VMware Inventory Service (stores vCenter Server application and inventory data)
vSphere Auto Deploy (support tool that can provision many physical hosts with ESXi software)
vSphere ESXi Dump Collector (configure ESXi to dump the VMkernel memory to a network server, rather than to a disk)
vSphere Syslog Collector (support tool that provides a unified architecture for system and network logging)
vSphere Web Client directly communicates with vCenter Server, and vSphere Client is used to directly communicate with ESXi hosts. vCenter Server provides access to the ESXi hosts via an agent called vpxa.
Minimum Hardware Requirements for vCenter Server
Before installing and configuring vCenter Server, we should consider minimum hardware requirements. Following are the minimum hardware requirements. We’re installing vCenter Server in home-lab environment, so we’ll install it as embedded PSC with 2CPUs and 4GB RAM.
Let’s start the process:
Step 1: Download the vCenter Server ISO from VMware site. After downloading, mount it on CD/DVD drive
Step 2: Open the mounted path and double click the Autorun.exe to start the process.
Step 3: Select vCenter Server for Windows and click Install to begin the installation.
Vmware Vcenter Server 6.0 Crack
Step 4: Windows Installer preparing to install in process, click Next to install vCenter Server 6.0.0
Step 5: Accept the License Agreement and click Next
Step 6: Select Embedded Deployment and click Next
Vmware Vcenter Server 6.0 Windows 10
Step 7: Enter the System Name as FQDN and click Next
Step 8: Select Create New vCenter Single Sign-On domain, enter vCenter Single Sign-On password, Confirm password, Site name, and click Next
Step 9: Select Use Windows Local System Account and click Next
Vmware Vcenter Server 6.0 Download Free Trial
Step 10: Select Use an embedded database (vPostgres) and click Next
Step 11: Verify Configure Ports and click Next
Step 12: Leave Destination Dictionary default and click Next
Step 13: Review your settings and click Install
Step 14: vCenter Server installation process will start now, and will take some time to install.
Step 15: Installation process is completed, click Finish or Launch vSphere Web Client
vCenter Server installation is completed when you click Finish button. When you’ll click on Launch vSphere Web Client, it will launch vSphere Web Client. For complete guidance regarding vCenter Server installation and configuration, you can follow VMware vSphere 6.0 Part 2 – vCenter, Alarms and Templates course. In next post, we’ll see how vSphere Web Client works and used for managing and controlling vCenter Server.
I hope you’ve enjoyed reading this post, if you have any query or suggestion, please feel free to write in comments. Thanks a lot.
Author: Nisar Ahmad
Systems Engineer, double VCP6 (DCV & NV), 5 x vExpert 2017-21, and the owner of My Virtual Journey, with experience in managing a Datacenter environment using VMware and Microsoft Technologies. This blog mainly covers virtualization and cloud technologies but also covers some other technologies such as Cyber Security, Quantum Computing, etc.
VMware vCenter Converter Standalone 6.0 | 14 May 2015 | Build 2716716
Check periodically for additions and updates to these release notes.
What's in the Release Notes
These release notes cover the following topics:
Introduction to Converter Standalone
VMware vCenter Converter Standalone provides an easy-to-use solution to automate the process of creating VMware virtual machines from physical machines (running Windows and Linux), other virtual machine formats, and third-party image formats. Through an intuitive wizard-driven interface and a centralized management console, Converter Standalone can quickly and reliably convert multiple local and remote physical machines without any disruptions or downtime.
Benefits
Convert physical machines running Windows or Linux operating systems to VMware virtual machines quickly and without any disruption or downtime.
Convert third-party image or virtual machine formats such as Parallels Desktop, Symantec Backup Exec System Recovery, Norton Ghost, Acronis, StorageCraft, Microsoft Virtual Server or Virtual PC, and Microsoft Hyper-V Server virtual machines to VMware virtual machines.
Enable centralized management of remote conversions of multiple physical servers or virtual machines simultaneously.
Ensure conversion reliability through quiesced snapshots of the guest operating system on the source machine before data migration.
Enable non-disruptive conversions through hot cloning, with no source server downtime or reboot.
What's New
The VMware vCenter Converter Standalone 6.0 provides:
Support for virtual machine hardware version 11.
Compatibility with vSphere 6.0 and Workstation 11.
Support for additional guest operating systems: Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7, Ubuntu 14, CentOS 6-7, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows 8.1.
Support of pure IPv6 environments.
Proxy mode.
File-level cloning for volumes with ReFS file system.
Support for XFS file system.
Support for predictable network interface names.
VMware vCenter Converter Standalone 6.0 Support Notice
VMware vCenter Converter Standalone 6.0 is the last release of the product to support third-party backup images and virtual machines as sources for conversion. This capability will be discontinued in the next release. If you use this capability, you should start planning your transition. For the full list of the third-party backup images and virtual machines see Interoperability.
Installation Notes
You can download, install, and run VMware vCenter Converter Standalone in English only.
Users with limited rights cannot install Converter Standalone on Windows. You must log in as an administrator to install Converter Standalone.
Platforms
You can install VMware Converter Standalone 6.0 on the following platforms:
Windows Server 2003 R2 SP2 (32-bit and 64-bit)
Windows Vista SP2(32-bit and 64-bit)
Windows Server 2008 SP2 (32-bit and 64-bit)
Windows Server 2008 R2 (64-bit)
Windows 7 (32-bit and 64-bit)
Windows 8 (32-bit and 64-bit)
Windows 8.1 (32-bit and 64-bit)
Windows Server 2012 (64-bit)
Windows Server 2012 R2 (64-bit)
Interoperability
Converter Standalone 6.0 supports the following sources.
Physical machine running an operating system noted in Supported Guest Operating Systems
VMware Desktop products
Workstation 10.x and 11.0
Fusion 6.x and 7.0
Player 6.x and 7.0
VMware vCenter virtual machines
vSphere 6.0
vSphere 5.5
vSphere 5.1
vSphere 5.0
vSphere 4.1
vSphere 4.0
Third-party backup images and virtual machines - to be discontinued. See Support notice.
Acronis True Image Echo 9.1 and 9.5, and Acronis True Image Home 10 and 11 (.tib)
Symantec Backup Exec System Recovery (formerly LiveState Recovery) 6.5, 7.0, 8.0, and 8.5, and LiveState Recovery 3.0 and 6.0 (.sv2i format only)
Norton Ghost version 10.0, 12.0, and 14.0 (.sv2i format only)
Parallels Desktop 2.5, 3.0, and 4.0 (.pvs and .hdd). Compressed disks are not supported
Parallels Workstation 2.x (.pvs). Compressed disks are not supported. Parallels Virtuozzo Containers are not supported.
StorageCraft ShadowProtect Desktop, ShadowProtect Server, ShadowProtect Small Business Server (SBS), ShadowProtect IT Edition, versions 2.0, 2.5, 3.0, 3.1, and 3.2 (.spf)
The Microsoft VHD format for the following sources:
Microsoft Virtual PC 2004 and Microsoft Virtual PC 2007 (.vmc)
Microsoft Virtual Server 2005 and 2005 R2 (.vmc)
For conditions and limitations about converting Backup Exec System Recovery, ShadowProtect, and Consolidated Backup images, see the VMware vCenter Converter Standalone User's Guide.
Depending on the selected source, you can convert it to the following destinations.
VMware vCenter virtual machines
ESX 4.0 and 4.1
ESXi 4.0, 4.1, 5.0, 5.1, 5.5 and 6.0
vCenter Server 4.0, 4.1, 5.0, 5.1, 5.5 and 6.0
VMware Desktop virtual machines
VMware Workstation 10.x and 11.0
VMware Player 6.x and 7.0
VMware Fusion 6.x and 7.0
Earlier releases of Converter Standalone (versions 3.x, 4.x and 5.x) might not be compatible with VMware vSphere 6.x.
Supported Guest Operating Systems
Converter Standalone 6.0 supports the following guest operating systems:
Windows Server 2003 R2 SP2 (32-bit and 64-bit)
Windows Vista SP2 (32-bit and 64-bit)
Windows Server 2008 SP2 (32-bit and 64-bit)
Windows Server 2008 R2 (64-bit)
Windows 7 (32-bit and 64-bit)
Windows 8 (32-bit and 64-bit)
Windows 8.1 (32-bit and 64-bit)
Windows Server 2012 (64-bit)
Windows Server 2012 R2 (64-bit)
CentOS 6.x (32-bit and 64-bit)
CentOS 7.0 (64-bit)
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4.x (32-bit and 64-bit)
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5.x (32-bit and 64-bit)
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.x (32-bit and 64-bit)
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.x (64-bit)
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 9.x (32-bit and 64-bit)
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 10.x (32-bit and 64-bit)
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 11.x (32-bit and 64-bit)
Ubuntu 12.04 (32-bit and 64-bit)
Ubuntu 14.x (32-bit and 64-bit)
CAUTION: During cloning of powered on Linux machines, Converter Standalone 6.0 preserves the following source file systems on the destination: ext2, ext3, ext4, reiserfs, vfat, and xfs. All other source file systems are converted into ext3 or ext4 file systems on the destination virtual machine.
For more information about the operating systems supported by Converter Standalone and other system requirements, see the VMware vCenter Converter Standalone User's Guide.
Prior Releases of Converter Standalone
Features from prior releases of Converter Standalone are described in the release notes for each release. To view release notes for prior releases of Converter Standalone, click one of the following links:
Known Issues
The Converter Standalone 6.0 release contains the following known issues:
Installation
If the name of the Converter Standalone installation directory contains non-ASCII characters, you might experience conversion and configuration problems If the name of the Converter Standalone installation directory contains non-ASCII characters, the following issues might occur:
Conversion and configuration of Windows virtual machines might fail with an error message Unable to reconfigure destination virtual machine. In the vmware-converter-worker.log, this error generates a message similar to Error 3 (error restoring key: Unknown error 3 (0x3) (3)) restoring registry key C:ã—ã™ãŸã•ã‹ãn°...dataSKUNKWORKS_FILLER into... .
If you try to convert a Linux physical machine, you might receive an error message in the Convert Machine wizard Unable to obtain hardware information.
You must restart machines that run 64-bit Windows Vista or later before re-installing Converter Standalone If you uninstall Converter Standalone from a 64-bit Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, or Windows 7 machine and do not restart it, a subsequent Converter Standalone installation might fail with the following error message: Error 29144. Could not install service Vstor2 MntApi 1.0 Driver (shared). Please reboot and try to install again. Workaround: Restart the Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, or Windows 7 machine and try installing Converter Standalone again.
Converter Standalone installer removes Workstation 6.5.x remote agents without notification When you use Workstation 6.5.x to hot-clone a Windows source machine, Workstation deploys a remote Workstation agent on the source. If you choose to leave the remote agent on that source and then install Converter Standalone on the same machine, the Converter Standalone installer uninstalls that agent without any warning messages.
Users with limited rights cannot install Converter Standalone on Windows If you are logged in to Windows as a non-administrator user, the following error message is displayed while the InstallShield is extracting files for Converter Standalone installation: Unable to save file: C:WINDOWSInstaller The system cannot find the path specified. The error is displayed because limited users do not have the required write permissions. Workaround: Select the %TEMP% directory to extract the installation files:
Click OK in the error message. A Save As dialog box appears.
Browse to the Temp folder of the current user (for example, C:Documents and Settings'username'Local SettingsTemp) and click OK.
NOTE: You still need to log in as an administrator to install Converter Standalone.
You cannot install vCenter Converter 4.2.1 on the same machine where you have already installed Converter Standalone 6.0 If you install Converter Standalone 6.0 and then install vCenter Converter 4.2.1 server on the same machine, downloading the vCenter Converter 4.2.1 plug-in from vSphere Client fails. Workaround: First install vCenter Converter 4.2.1 and then install Converter Standalone 6.0.
General
Disk-based cloning of a powered off machine image to a virtual datastore destination might fail You might not be able to perform a disk-based cloning of a powered off machine image to a virtual datastore destination. The conversion might fail at 1% with a message Operation expirienced network error if the size of the source disk is not a number that is a multiple of a MB. Workaround: Use volume-based cloning, if the option is available.
Converter Standalone might display an incorrect version of the Windows operating system Converter Standalone might display incorrect operating system information for running machines or virtual machines with Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2 and later.
If the operating system is Windows 8.1, Windows 8 is displayed.
If the operating system is Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2012 is displayed.
Workaround: None. Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2 work as expected despite the incorrect operating system displayed.
Creation of virtual machine with thick destination disk type of certain size fails on VSAN datastore even if it seems to have enough space If you try to perform disk-based conversion with thick destination disk type of certain size on VSAN datastore, the creation of virtual machine might fail with the following error 'converter.fault.InsufficientManagedDiskSpace', even if it seems to have enough space. Workaround: Change the destination disk type to thin.
If you try to convert a source physical or virtual machine to a managed destination by using thick provisioned disks with large empty spaces on them, the conversion task might fail If you try to perform a disk-based cloning of a physical or virtual machine to a managed destination by using thick provisioned disks with large empty spaces on them, the conversion task might fail with an error message Unable to clone disk source_disk on the virtual machine virtual_machine_name. The following messages appear in the log file:
(03200 warning 'Default') (,0) (NFC ERROR) NfcNetTcpRead: bRead: -1 (03200 warning 'Default') (,0) (NFC ERROR) NfcNet_Recv: requested 264, recevied only 0 bytes (03200 warning 'Default') (,0) (NFC ERROR) NfcFile_Stream: Failed to get message from source (03200 warning 'Default') (,0) (NFC ERROR) NFC_NETWORK_ERROR
The destination ESX server must return an acknowledgement after each processed NFC write request. If the source sends a large block of zeroes that must be written it might take a long time for the ESX to return the acknowledgement. Thus, the Converter assumes that the operation has timed out and closes the connection, no matter that the ESX server is still writing to the target disk.
Workaround: Change the destination disk type to thin.
When converting hosted virtual machines with unpartitioned disks, you might not be able to obtain hardware information about the source When converting hosted virtual machines with unpartitioned disks, you might not be able to obtain hardware information about the source. In such case, the following error messages might appear in the worker log:
(01628 warning 'Default') Partition:Invalid sector magic number.
(01628 warning 'Default') ERROR: Failure during open: Reading disk signature
(01628 error 'Default') (BaseDiskSetComputer::DoOpen) OpenDisks failed, mntapi error: 32.
Workaround: Remove the unpartitioned disks from the conversion job.
A running P2V conversion job fails if you create a new conversion job for the same Windows source machine and use a different port to deploy the Converter Standalone agent If, while running a P2V conversion job, you start creating another conversion job for the same powered on Windows source machine, and specify a port for the connection, Converter Standalone deploys the Converter Standalone agent using the port you specified. If the connection port is different from the one that is being used for the already running conversion job, both jobs fail. The following error message appears in the Job summary tab for the first conversion job: FAILED: A general system error occurred: No connection could be made because the target machine actively refused it. The following error message appears in the Job summary tab for the second conversion job: FAILED: Unable to create a VSS snapshot of the source volume(s). Error code: 2147754774 (0x80042316).
You cannot copy running conversion or configuration jobs If you open the Copy As New wizard for a running configuration or conversion job when the source is a virtual machine or a backup image and you click Next, the wizard displays the error message Unable to obtain hardware information for the selected machine. Workaround: Wait for the job to complete before selecting Copy as New in its pop-up menu.
Linked Cloning of source images greater than 2GB to a network share that does not support large files fails Creating linked clones from source images that are larger than 2GB to a network share that does not support large files (for example, to a Linux SMB share) fails. Converter Standalone does not split the source files into smaller chunks. If the source is larger than the supported file size on the destination, the conversion tasks fails.
Creating a conversion job to convert a standalone VMware source with a VMDK file greater than 2GB from a network share that does not support large files, fails If you select a standalone virtual machine source with VMDK file greater than 2GB residing on a remote network location that does not support large files (for example, Linux SMB share), the following error message appears in the Converter wizard on clicking Next or View source details: Unable to obtain hardware information for the selected machine. Workaround: Map the network shared folder to the machine where Converter Standalone runs, and select the source from there.
Converter Standalone cannot detect the power state of VMware Workstation or other VMware hosted source virtual machines if they are located on a read-only network share If the source machine is a Workstation or another VMware hosted source and is located on a network share with read-only permissions, Converter Standalone cannot detect if the source is powered on or suspended. This might lead to data inconsistency on the destination machine if changes are made to the powered on source virtual machine during conversion. Workarounds:
Verify that the source virtual machine is powered off prior to conversion.
Provide write privileges to the network share where the source virtual machine resides.
Conversion jobs from and to ESX hosts that are not connected to vCenter Servers fail if the number of disks on the source machine is more than nine When converting a source machine that has more than nine disks, conversion fails with the following error in the log file: Error on logout (ignored): Operation timed out SSLStreamImpl::BIORead (3BBA4E8) timed out. The error is due to the limited number of NFC connections that can be established to ESX hosts that are not connected to vCenter Server instances. Workaround: Connect to the destination ESX host through a vCenter Server. In this case, the number of source disks is limited to 27 for ESX and to 23 for ESXi hosts.
Converting source volumes with unrecognized file systems might prevent the destination virtual machines from starting While you are setting up a volume-based cloning task in one of the Converter Standalone wizards, the volume name might be missing in some rows of the Source Volumes tab. This means that Converter Standalone does not recognize the file system on those volumes. The destination virtual machine that is created as a result of such a conversion task might fail to start up. Nevertheless, Converter Standalone copies the source volume data to the destination using block-level copying. Workaround: configure the destination virtual machine after the conversion.
Converting standalone VMware sources with a VMDK file greater than 2GB to a hosted destination that resides on a network share that does not support large files, fails If you select a standalone virtual machine source with VMDK file greater than 2GB and try to convert it to hosted destination residing on a remote network location that does not support large files (for example, Linux SMB or NFS share), the conversion job might fail with one of following error messages:
Unable to connect to the virtual disk
Remote server closed connection after 0 response bytes read
An error occurred during an operation on a virtual disk
If conversion is successful, the following error message related to the VMDK file might appear when you power on the destination virtual machine: Internal Inconsistency errors Workaround:
In the main application window of Converter Standalone, right-click the failed job and select Copy As New...
Go to the Options page and select Data to Copy.
In the Data to Copy pane, select the volumes to copy and click Advanced.
On the Destination layout tab, select Split not pre-allocated or Split pre-allocated as the destination disk type.
Click Next to view a summary of the conversion job.
On the Ready to Complete page, click Finish to resubmit the job.
Converter Standalone is unable to detect the system volume if it resides on a SCSI disk and IDE disks are present in the source machine On source machines with SCSI and IDE disks, Converter is unable to detect the system volume if the system volume resides on a SCSI disk. Converter only checks the first IDE disk in such configurations.
If the hardware configuration of the source machine is modified while the Conversion wizard is open, you need to restart the conversion wizard if you want to view correct source details Source machine details are retrieved per wizard session, as this is a time-consuming process. If some changes occur on the source machine (such as adding memory or hard drives) after this information is retrieved, the Conversion wizard does not show information about the changes. Workaround: Restart the conversion wizard.
Cloning a source that contains file system errors might result in a damaged virtual machine See Cloning a source that contains file system errors may result in a damaged copy (KB 1006689).
Timeout on SSL handshake when converting over a WAN link Converter Standalone does not support conversion over a WAN. When trying to perform a conversion over a WAN link, you might experience an SSL timeout because the timeout for SSL handshakes is two minutes. Workaround:
To avoid the two-minute handshake, perform a conversion to a hosted destination machine (for example, Workstation) in the same LAN.
Copy the temporary virtual machine and send it over the WAN to the remote site. If the intended destination is a Workstation virtual machine, this completes the process.
If the intended destination is ESX, import the Workstation virtual machine to the ESX server.
User Account Control (UAC) prevents installing Converter Standalone agent if you are not using the default Administrator account to connect to a powered on source machine If you are setting up a task to convert a powered on source machine that runs Windows Server 2008, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows Server 2012, or Windows 8 and you use a non-default Administrator account to log in to the source machine, the following error message might appear when you try to install Converter Standalone agent on the source machine: Insufficient permissions to connect to xxxxxxx. Here xxxxxxx is the IP address of the source machine. This is because Converter Standalone server cannot install Converter Standalone agent when UAC is enabled and you are logged in to the source as non-default Administrator user. Workaround: Disable the UAC on the source machine before you start the Conversion wizard. You can search the Microsoft Web site for procedures on disabling the UAC depending on the source operating system. For Windows Server 2012 and Windows 8, in addition to disabling UAC, you must perform the following steps:
In the Windows Start menu, type gpedit.msc. The Local Group Policy Editor opens.
Navigate to Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Local Policies > Security Options.
Disable the Run all administrators in Admin Approval Mode setting.
Restart.
The Reconfigure Virtual Machine wizard does not display correctly the vDS port group name When you reconfigure a virtual machine that uses dvSwitch and you navigate to the Network interface settings pane, the Network name text box does not display the name of the dvSwitch after the port group name. Only port group is displayed instead.
The reported network transfer rate might not be correct The reported network transfer rate might be higher than the actual one because of the inherent compression used by the network protocol. This does not affect the network throttling.
Adding a virtual machine to a domain might fail if you specify a fully qualified user name When configuring a virtual machine, you might not be able to add the virtual machine to a domain if you use a fully qualified user name (DOMAIN_NAMEUSER_NAME). Workaround: Specify the user name without including the domain name.
Conversion of a physical machine running Microsoft Windows XP or Windows Server 2003 with a BCD manager (Boot Manager for Windows Vista) and later might fail If you try to convert a physical machine with a BCD manager, the P2V conversion might fail in the following cases:
Microsoft Windows Vista or later is installed on the source physical machine, which is a dual-boot machine currently running Microsoft Windows XP or Windows Server 2003.
Microsoft Windows Vista or later is installed as a second operating system on the source physical machine and later is removed, but the BCD manager is left on the source machine.
Workaround 1: In case of a dual-boot machine conversion :
Boot the later version of Windows (Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, or Windows 7).
Perform a physical source conversion.
On the newly created virtual machine, boot a repair CD for the earlier version of Windows (Windows XP or Windows Server 2003).
Remove the BCD manager and revert the operating system to its compatible boot process.
Shut down the virtual machine and reconfigure it by using the Converter Standalone configuration wizard. Now you can boot the machine.
Workaround 2: In case of converting a source machine running Windows XP or Windows Server 2003 with a BCD manager:
On the source machine, boot a repair CD of the corresponding operating system.
Remove the BCD manager and revert the operating system to its compatible boot process.
For more information on how to repair BCD, see the Microsoft knowledge base article Windows no longer starts after you install an earlier version of the Windows operating system in a dual-boot configuration. Submitting a job might fail with The specified parameter was not correct:'info.owner'message If Converter Standalone is installed in a client-server mode and you have connected by using a username, which is the same as the computer name, submitting a job might fail with The specified parameter was not correct:'info.owner' message. Workaround: Connect by using a different user account with administrative rights. You might not be able to convert more than nine disks at once On ESX 3.5 and 4.0, conversion might fail if you try to convert more than nine disks. Workaround: Perform conversion in multiple steps to convert the disks in portions of up to nine. Then, attach all the disks to the target machine.
Windows Sources
If you convert a source machine with Windows 2008 and above operating system, some disk(s) may be offline or read-only If you convert a source machine with Windows 2008 and above operating system, some disk(s) in the destination VM may be offline or read-only. Workaround:
If the disk is offline, in the Disk Management console diskmgmt.msc, right-click the disk and select Online.
If the disk is read-only, run diskpart.exe with administrator's rights, and then run the following commands:
DISKPART> list disk Lists all disks and their status: online/offline.
DISKPART> select disk # Where '#' is the number of disk in offline state.
DISKPART> attribute disk clear readonly
DISKPART> online disk
Repeat steps 2-4 for every offline disk.
DISKPART> exit
Configuration of Windows virtual machines with multiple active partitions might not complete For Windows virtual machines with multiple active partitions, Converter Standalone might not recognize the boot partition and might not be able to complete the reconfiguration of the destination virtual machine. In such cases, after the conversion job is 96-98% complete, the conversion job status changes to Failed and an error message appears. For example: FAILED: Unable to find the system volume, reconfiguration is not possible. In the Worker/Agent log this issue is identified by the following statement: (#### warning 'Default') ERROR: (Mntapi_GetFirstBootDisk) more that *one* active volume found. Current active disk #0, another active disk #1. Workaround 1: Mark all non-boot active partitions on the destination machine as inactive and run configuration on the destination machine.
Boot into Windows Recovery Console on the destination machine.
Run diskpart.exe. The diskpart command prompt appears.
(Optional) To list the available disks, enter list disk.
Enter select disk <disk_number>.
(Optional) To list the partitions on the selected disk, enter list partition.
Enter select partition <partition_number>.
Enter inactive.
Repeat steps 4-7 to mark another partition as inactive.
Power off the destination machine.
Run Converter Standalone and configure the destination machine.
Workaround 2: Mark all non-boot active partitions on the source machine as inactive and attempt to run the conversion again.
On the source machine, run diskpart.exe. The diskpart command prompt appears.
(Optional) To list the available disks, enter list disk.
Enter select disk <disk_number>.
(Optional) To list the partitions on the selected disk, enter list partition.
Enter select partition <partition_number>.
Enter inactive.
Repeat steps 2-6 to mark another partition as inactive.
Run Converter Standalone and start the conversion again.
Conversion of a local powered on source machine fails at 1% If you select This local machine as a conversion source and a Converter Standalone agent from a previous Converter Standalone version is installed on the source machine, the conversion task fails at 1%. The following error message appears in the Status line of the Task progress tab: FAILED: Unable to create a VSS snapshot of the source volume(s). Error code: 127 (0x0000007F). This is because the Converter Standalone installer cannot upgrade previous versions of Converter Standalone agents. Workaround: Manually uninstall Converter Standalone agent from the source machine and create a new conversion task.
Converter Standalone worker process stops responding if you try to copy a configuration job during guest operating system customization If you right-click a running configuration job and select Copy As New while the destination machine is being customized, Converter Standalone worker process stops responding. Workaround: Wait for the configuration job to complete before you copy it.
Subsequent P2V conversions of remote source machines that run 64-bit Windows Vista or later might fail after a successful conversion If you convert successfully a remote source machine that runs 64-bit Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, or Windows 7 operating system and then try converting it again, the conversion fails with the error message Converter Standalone Agent installation failed on x.x.x.x Error code: 1603, where x.x.x.x is the IP address of the source machine. This error message might occur if automatic uninstall of remote Converter Standalone agent has been enabled during the first successful conversion. Workaround: Restart the remote source machine and try running the conversion task again.
Converter Standalone does not preserve disabled network adapters during conversion of physical machine sources that run on Windows During P2V conversion of Windows source machines, Converter Standalone does not detect disabled network adapters on the source and does not preserve them on the destination virtual machine. Workaround: On the Options page of the Converter Standalone wizard, click Networks to add network adapters to the destination virtual machine.
Microsoft Windows Vista reboots repeatedly after customization Providing wrong customization information might cause the destination virtual machine to reboot repeatedly if the source operating system is Microsoft Windows Vista. During conversion or configuration, if you choose to customize Microsoft Windows Vista and provide wrong customization information, for example an invalid serial key, the customized destination reboots repeatedly. This is a known issue with Microsoft Windows Vista. Workaround: Make sure that the provided customization information is valid.
Converter Standalone does not support cloning powered on Windows Server 2008 sources with FAT/FAT32 volume file system VSS under Windows Server 2008 does not support FAT/FAT32. Trying to convert a FAT/FAT32 volume causes the conversion task to fail. Workaround: Deselect all FAT/FAT32 volumes on the Options page of the Conversion wizard.
Converter Standalone remote agent does not notify the user about Converter 3.0.x or 4.0.x remote agents that have been installed on the source system during remote hot cloning process If Converter Standalone is converting a remote machine source that already has a remote agent from Converter version 3.0.x or 4.0.x, it uninstalls the old remote agent without issuing a notification or warning message. This prevents older Converter versions from converting this source machine later.
Previous Converter versions cannot convert source machines that have Converter Standalone 6.0 agent installed on them Converter Standalone 6.0 agent is deployed on the source machine during conversion. If Converter Standalone 6.0 agent is not uninstalled after the conversion, older Converter versions cannot deploy their agents on top of the newer Converter Standalone agent version. Therefore, you cannot use previous Converter versions to convert sources that have already been converted with Converter Standalone 6.0. Workaround: Uninstall Converter Standalone 6.0 agent before trying to convert the source with an older Converter version.
Stopping Converter Standalone processes during file-level cloning might cause the machine that runs the Converter Standalone server service to restart During file-level cloning of source systems that run Windows XP or Windows Server 2003, if any of the following Converter Standalone process is forcibly stopped, the machine on which the stopped process was running might automatically reboot.
VMware Converter Standalone Integrated Worker
VMware Converter Standalone Integrated Agent
This behavior is not consistent and depends on the Windows version and patch level.
Workaround: Do not stop any Converter Standalone services on the source machine during file-level cloning. For more information and hot fix, check the Microsoft site Error message when a Delayed Write Failure event is reported in Windows Server 2003: 'Stop 0x00000019 - BAD_POOL_HEADER' or 'Stop 0xCD PAGE_FAULT_BEYOND_END_OF_ALLOCATION'.
Converter Standalone does not change PIC HAL to APIC HAL during conversion of Windows source machines If the source to convert is running a Programmable Interrupt Controller (PIC) HAL, Converter Standalone does not change the PIC HAL to an Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller (APIC) HAL in the destination virtual machine. As a result, the destination virtual machine might not boot or might fail to perform as expected. To find out which HAL is running, go to Windows Device Manager and select Computer in the list of devices. If it displays Standard PC or Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) PC, you are running a PIC HAL. Workaround: VMware virtual machines are APIC computers. If your source computer is a PIC computer that runs a PIC HAL, you must update the HAL in the destination virtual machine to APIC HAL after the conversion. For more information on configuring the correct HAL, check the Microsoft Web site HAL options after Windows XP or Windows Server 2003 Setup. Note: Microsoft does not support running a PIC HAL on an APIC computer. If your source is an APIC computer running a PIC HAL, you must configure the correct HAL on the source machine before starting the conversion.
Owner name and organization are not displayed properly after customizing the guest operating system After customizing the guest operating system, Unicode characters used for owner name and organization on the Computer Information page do not appear the way they were set in the Conversion or the Configuration wizard. For all Windows operating systems except Windows Vista, customization parameters such as user name and organization must use characters only from the local encoding of the default user profile of the guest. For example, you can use Japanese characters for the user name only on a guest whose default user profile's local encoding is set to Japanese. These restrictions do not apply to Windows Vista guests because Windows Vista uses a UTF-8 encoded XML file to store the Microsoft sysprep parameters. Earlier versions of Windows use the sysprep.inf file, and the Microsoft Windows mini-setup process reads that file in the local encoding only. Workaround: Either avoid Unicode characters when assigning owner name and organization name for the destination virtual machine, or use the workaround described at: http://support.microsoft.com/kb/310441/.
Converter can convert FAT/FAT32 volumes during hot cloning only if the source machine has at least one NTFS volume For source machines running under Windows versions earlier than Windows Server 2008, VSS can take snapshots of FAT/FAT32 volumes only if the source machine has at least one NTFS volume. For all operating systems that support volume-based cloning, you need at least one NTFS volume for VSS to work.
Converter Standalone agent does not start automatically after reboot If the source machine starts up too slowly, Converter Standalone agent might not start automatically after the source machine is restarted. Workaround: Start the Converter Standalone agent manually:
Right-click My Computer and select Manage.
In the Computer Management window, select Services and Applications >Services on the left.
In the list on the right, double-click VMware Converter Standalone Agent.
Click Start to start the process.
Click Apply followed by OK.
The source virtual machine does not have the appropriate drivers The following error message appears in the log file when reconfiguration fails because the appropriate drivers are missing from the source operating system: Unable to find symmpi.sys in the specified CAB files This is usually observed in Windows Server 2003 SP1. Workaround:
Back up the virtual machine created during the failed conversion.
Attach the VMDK file containing the system folder to another Windows Server 2003 virtual machine.
Replace the WINDOWSDriver Cachei386driver.cab file in the destination virtual machine with a version of the driver.cab file that includes the missing driver from the helper virtual machine.
Detach the VMDK file from the helper virtual machine and run the Configure Machine wizard on the destination virtual machine.
Sysprep deletes drive letter mappings during customization If you choose customization options and the destination virtual machine fails at a Please Wait screen after the second sysprep reboot, you need to rerun the conversion task without customization. This issue occurs because of a problem with Microsoft sysprep, which deletes the drive letter mappings, preventing access to certain files.
You cannot import a Windows source with 'signature()' in the boot.ini file You cannot import a Window source with 'signature()' in the boot.ini file. If you import a Windows live source with 'signature()' in the boot.ini file, and try to reconfigure and convert it, the reconfiguration fails and this results in a conversion error. If you try to convert the source without reconfiguration, the conversion succeeds but the destination cannot boot. For more information on 'signature()' go to http://support.microsoft.com/kb/227704.
Linux Sources
Converted SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 10 machine might not have network connectivity If you convert a SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 10 machine, the converted virtual machine might not have network connectivity.
Workaround:
In the /etc/udev/rules.d/30-net_persistent_names.rules.d/30-net_persistent_names.rules file, comment out the lines that start with SUBSYSTEM and contain the old MAC addresses.
Check the /etc/sysconfig/network directory. If there is no ifcfg-eth0 file and there is a file of the form ifcfg-if-mac_address, rename it to ifcfg-eth0.
Restart the network service.
Converted powered on Linux machines cannot start up If you convert a powered on Linux machine that has a non-standard LVM filter saved in the /etc/lvm.conf file, the converted virtual machine might fail to start up. The following error message appears in the virtual machine console: Unable to access resume device (dev//) Workaround: Before the conversion, edit the filter in the lvm.conf file on the source Linux machine to allow all devices. For Red Hat Linux, the default value of the filter is ( 'a/.*/' ).
Linux P2V conversion fails in the beginning with the following error message: 'A general system error occured: <source_server_dns_name>: Connection closed by remote host' If the source machine sshd is configured to allow less than 3 unauthenticated connections, it may sever the converter connection. Workaround: Check MaxStartups in /etc/ssh/sshd_config and ensure it is either commented out or its first number is 3 or higher.
P2V conversions of SLES 9 sources cannot complete, if the root directory is located on an LVM disk When you select to convert a physical SLES 9 source, Converter Standalone cannot complete the conversion if the root directory is located on an LVM disk. After the conversion job is 99% complete, the job status changes to Failed and the following entry is added to the log: FAILED: An error occurred during the conversion: 'Failed to restore original lvm in initrd image: /usr/lib/vmware-converter/restoreLvmInInitrd.sh failed with return code: 1, and message: * Unpacking initrd image /mnt/p2v-src-root//boot/initrd cpio: unsupported cpio format, use newc or crc ERROR: Unable to unpack initrd image /mnt/p2v-src-root//boot/initrd ' Workaround: Convert the LVM disk to a basic disk.
On the Options page of the Conversion wizard, click Data to copy in the options list.
Click Advanced and select the Destination layout tab.
Select the volume that contains the root directory and click To basic.
Virtual machines cloned from SLES 11 SP1 sources to ESX/ESXi managed destinations boot in console mode After the conversion, the destination virtual machine cannot load the GNOME Display Manager and boots in console mode. The following warning message appears: GdmLocalIDisplayFactory: maximum number of X display failures reached: check X server log for errors. Workaround: Recreate the xorg.conf file.
X Server might fail to start in destination virtual machines converted from sources that run Linux When the destination virtual machine starts, X server might fail to start with an error Fatal X server Error. This is due to incompatibility issues between the display driver used in the Linux source and the display adapter of the destination VMware virtual machine. Workarounds:
Install VMware Tools on the destination virtual machine.
configure the X server on the destination virtual machine to change the refresh rate and the display resolution.
Linked cloning of standalone VMware sources to Linux SMB shared destination fails Linked cloning tasks of VMware standalone sources to SMB shared destinations that run on Linux fail with the following error: converter.fault.FileIOFault.
The number of LVM logical volumes per volume group is limited to 12 for powered on Linux sources During the conversion of powered on Linux machines, Converter Standalone converts LVM volume groups into new disks on the destination virtual machine. The number of LVM logical volumes on a source LVM volume group cannot exceed 12. Workaround: Move volumes out of the new disk to other destination disks:
On the Options page of the Conversion wizard, click Data to copy.
From the Data copy type drop-down menu, select Select Volumes to copy and click Advanced.
On the Destination layout tab, select a volume to move and click Move Up or Move Down until it is moved to the destination disk. You can move volumes between disks only if they are not Active /boot or System / volumes.
(Optional) To create a new destination disk, click Add Disk.
By default, the Linux P2V helper virtual machine is powered off when the conversion job finishes Workaround: Manually disable this option in the converter-worker.xml file.
On the machine where Converter Standalone server runs, browse to the converter-worker.xml file in the following location %ALLUSERSPROFILE%Application DataVMwareVMware Converter Standalone.
Open the converter-worker.xml file in a text editor and change the powerOffHelperVm flag from true to false.
To restart Converter Standalone worker: Reboot the system or open the Services section in the Microsoft Management Console, find the VMware Converter Worker service and restart it.
Note: Care should be taken when this option is enabled and the helper VM network is configured to use a static IP address. After the conversion, the helper VM retains the statically configured IP because it is still running. Thus any subsequent Linux P2V jobs cannot use the same static IP until this helper VM is powered off, or at least has its network interface disabled. Disabling the powerOffHelperVm flag is useful when the useSourcePasswordInHelperVm Converter Standalone worker flag is enabled. This allows users to log in to the helper virtual machine after conversion.
Source volumes on top of volume managers other than LVM are not recognized during conversion of powered on Linux machines Converter Standalone recognizes only managed source volumes that run on the LVM volume manager. Other volume managers, including but not limited to Veritas Volume Manager (VxVM), are not recognized.
Converter Standalone does not recognize source volumes that reside on Linux Software RAID configurations During cloning of powered on Linux machines, Converter Standalone does not recognize source volumes that are part of a Software RAID configuration (also referred to as multiple disk, or MD, configurations).
By default, Converter Standalone has a 20 minute timeout when waiting for the helper virtual machine to start up during Linux P2V conversion This might cause a Linux P2V conversion task to fail due to connection timeout. Workaround: Extend the timeout period (in milliseconds) by modifying the linuxP2VBootTimeout flag in the converter-worker.xml file.
On the machine where Converter Standalone server runs, browse to the converter-worker.xml file in the following location %ALLUSERSPROFILE%Application DataVMwareVMware Converter Standalone.
Open the converter-worker.xml file in a text editor and replace the default value for linuxP2VBootTimeout with the necessary timeout value in milliseconds. Note: The timeout value is measured in milliseconds. To specify the timeout in minutes, multiply the number of minutes by 60000 and use that value.
To restart Converter Standalone worker: Reboot the system or open the Services section in the Microsoft Management Console, find the VMware Converter Worker service and restart it.
Sparse files are not preserved during conversion of powered on source machines that run Linux By default, Converter Standalone does not preserve sparse files on the source machine during Linux P2V conversion. If you have large sparse files on the source, they are created as non-sparse on the destination virtual machine. This renders the used space on the destination file system larger than that on the source machine. This might also cause the conversion task to fail with a timeout error. Workaround: Manually enable preserving sparse files during Linux conversions by modifying the keepsake flag in the converter-worker.xml file.
On the machine where Converter Standalone server runs, browse to the converter-worker.xml file in the following location %ALLUSERSPROFILE%Application DataVMwareVMware Converter Standalone.
Open the converter-worker.xml file in a text editor and change the keepsake flag from false to true.
To restart Converter Standalone worker: Reboot the system or open the Services section in the Microsoft Management Console, find the VMware Converter Worker service and restart it.
Destination virtual machine might not boot if you change the disk controller type while converting a Linux virtual machine In Linux virtual machines, the root device can be defined using the block device name (such as /dev/sda1) in /boot/grub/grub.conf, /boot/grub/menu.lst, or /etc/fstab. If you change the disk controller type while converting the virtual machine, the destination virtual machine might not boot. This is because the root device now has a different name (for example, it might have been changed to /dev/hda1). Workaround: Configure the destination virtual machine manually. At the minimum, change the root device name to reflect its new name in the destination virtual machine. To make your system more robust, use the volume label or UUID instead of the block device name.
During conversion of powered on Linux machines, Converter Standalone does not recognize Linux source volumes if they are mapped directly on a hard disk Workaround: Linux source volumes that are not managed by LVM must be located in a partition so that Converter Standalone can recognize them during cloning of powered on Linux sources.
Linux P2V jobs on ESX 5.0 target hosts fail if the name of the virtual machine is not in ASCII symbols or in the Windows current system locale If the target host is ESX 5.0, the name of the virtual machine must be in ASCII or in the Windows current system locale, otherwise the helper machine cannot be connected and the Linux P2V conversion fails. Workaround: Before the conversion, enter the name of the virtual machine by using ASCII symbols. After the conversion is complete, you can rename the virtual machine.
Third-Party Formats
Virtual machines created from Acronis images that have dynamic volumes do not start up after the conversion Some Acronis True Image images of Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, or Windows 7 are not correctly configured and do not start up after the conversion. The problem occurs when the system or the active disk is located on a dynamic volume in the source. Workaround:
Create a new virtual machine using the vSphere Client.
Use the Acronis True Image software to restore the image inside the new virtual machine.
Limitations when converting third-party images You can use Converter Standalone to convert third-party virtual machines, system images, and backup images with the following limitations:
Backups of systems with dynamic disks are not supported (ShadowProtect and Backup Exec System Recovery).
All images for the backup of a machine must be in a single folder that contains no other images (ShadowProtect and Backup Exec System Recovery).
For incremental images, up to 16 incremental backups are supported (ShadowProtect and Backup Exec System Recovery).
Images of systems with logical volumes are not supported if the logical drive is also a system or active volume (only for ShadowProtect sources).
For volume-based cloning of Acronis and StorageCraft, all volumes in the disk before the active and system volumes must be backed up. For example, if a disk has 4 partitions, 1-4, with partition 2 as the active volume and partition 3 as the system volume, the backup must include volumes 1 through 3 (ShadowProtect and Backup Exec System Recovery).
Virtual machines from Macintosh versions of Virtual PC are not supported.
Older versions of VMware products have limited support of newer operating systems. For example, ESX 3.5 does not support Windows 7. The converted source operating system must be supported for the destination VMware platform. For a list of supported systems, see the Guest Operating System Installation Guide.
Separate backup images should be stored in separate folders Storing more than one third-party backup in a single folder results in a failed migration. Workaround: Place each backup in its own folder before using Converter Standalone to convert an image.
SDK Release Notes
Converter Standalone SDK 6.0
The VMware vCenter Converter Standalone API provides language-neutral interfaces to the Converter Standalone server management framework. The Converter Standalone SDK is a ZIP file that contains the following items.
Sample code demonstrating common use cases for programmatically managing Converter Standalone server. The sample code includes Java and C# source code files. See the respective Readme files (readme_java.htm and readme_dotnet.htm ) for information about building and using the samples.
The WSDL that defines the API available on Converter server.
Batch files and shell scripts to automate the process of generating client-side stubs, and for rebuilding the sample applications. For C# developers, the Microsoft Visual Studio project files (.sln) have been included.
Reference documentation, the VMware vCenter Converter Standalone API Reference Guide, which provides language-neutral descriptive information (object type definitions, properties, and method signatures, for example) for the VMware vCenter Converter Standalone API 6.0.
Obtaining the Software
You can obtain the Converter Standalone SDK 6.0 from here.
Supported Platforms
The Converter Standalone 6.0 SDK is tested only on the supported Windows platforms. See Platforms.

0 notes
Text
Want to install a Server / Virtual Machine from an ISO file on oVirt or RHEV Virtualization platform?. oVirt is a free and open-source virtualization solution for designed for running large-scale and mission critical workload on production environments. oVirt provides kernel-based virtual machine management for multi-node virtualization servers. The initial design was to be the best open source alternative to VMware vCenter. RHEV is a Red Hat Virtualization solution created from oVirt with few modifications in branding and additional features. With RHEV, you get support from Red Hat if you have an active subscription. So let’s see how you can create a new Virtual Machine / Server on oVirt or RHEV from an ISO file. Step 1: Upload ISO image to ISO library You should have created an ISO storage domain on RHEV/oVirt before doing ISO upload. To get the ISO location path, navigate to Storage > Storage Domains > iso_library > Path Get the Path then upload the ISO to the image directory. $ ls -1 /export/nfs/iso/d125a4b7-7c11-4957-a1f9-865a10fc9fc3/images/11111111-1111-1111-1111-111111111111/ CentOS-7-x86_64-Minimal-1810.iso rhel-8.0-x86_64-dvd.iso rhel-server-7.6-x86_64-dvd.iso Step 2: Create a new Virtual machine on RHEV / oVirt After ISO image upload is complete, go to Compute > Virtual Machines > New Add VM details such as CPU, Memory, OS, Network interface e.t.c. You can further change resources assigned to VM under “System” section. Under “Boot Options” section, attach your OS ISO image for installation. Start a VM after creation and open console with remote viewer application. The standard OS installation screen should show in the next screen. Follow the next installation prompts to complete installation of your operating system on RHEV / oVirt Virtualization platform.
0 notes
Text
Cpu running at 99 percent windows 10 無料ダウンロード.VMware vCenter Server Appliance 7.0 (VCSA)をデプロイしてみてみた
Cpu running at 99 percent windows 10 無料ダウンロード.Fix 99% or 100% High CPU Usage Issue in Windows 10 Fall Creators

Full solutions for fixing high CPU usage in Windows 10 Fall Creators.VMware vCenter Server Appliance (VCSA)をデプロイしてみてみた - Qiita
Sep 16, · Find the processes that are accounting for the majority of your CPU usage. Usually there will be only one that is nearly maxed out at %, though you may have a couple of different programs taking up 50% each. Many games and media editing programs will take % of your CPU while : M I'm Roshan V S, Windows expert and a Windows user like you. I appreciate you for providing details about the issue and we are happy to help you. Try the following methods: Method 1: Disable Superfetch 1. Open Taskmanager, click “More details,” then click “CPU” to order processes by how much CPU they’re using. 2 Nov 29, · タスクトレイでネコが走る「RunCat for Windows」の評価とレビュー、ダウンロードや使い方を解説します。本ソフトを起動するとタスクトレイにネコが表示され、CPUの負荷に応じてゆっくり走ったり速く走ったりするシンプルなソフトです。ネコが一生懸命走っているのを見ると、PCが頑張っている
Cpu running at 99 percent windows 10 無料ダウンロード.Windows 10 CPU Usage % - Microsoft Community
Mar 12, · Windows 10 PCのWindows通知設定が「CPU使用率%」を引きおこす可能性があるため、次に、Windows通知設定を変更して問題を修正してみましょう。 手順1:[スタート]ボタンをクリックし、[設定]をクリックしてWindows設定を開きます。Estimated Reading Time: 7 mins Jun 02, · Safe to set Maximum Processor State to 99%? Hello, just recently bought a Dell G7 15 Gaming Laptop (Intel i7 H with Nividia Geforce GTX with Max-Q) from the Memorial Day Sales. During extended gaming sessions I'm getting close to around 90 C according to HWMonitor on the CPU (GPU seems fine, peaking around C) May 12, · VMwareのホームページ へログインし、 [download]タブから'vSphere'を選択し、VCSAをダウンロードします. ① Download VMware vCenter Server ページ. ここでは、Get Free Trial (無償評価版)をクリック. ② Product Evaluation Center for VMware vSphere ページ. [Download vCenter Server for Linux
Tracy King updated on Aug 13, to Computer Instruction How-to Articles. Here are some solutions and methods that you can apply to fix high CPU usage error in Windows 10 Fall Creators:. Your computer gets slow after Windows 10 Fall Creators update? If your computer runs slower after installing Windows 10 Fall Creators, or CPU shows highly used in task manager, don't worry. Here in the below, you'll find quick fixes and complete methods to fully resolve the high CPU usage issue in Windows 10 Fall Creators and speed up your PC with simple clicks.
This fix can help you quickly end high CPU usage issue in Windows 10 Fall Creators when your PC becomes extremely slow or even get stuck with running programs:. When the C drive contains is full of junk files, or applications contain caches, the computer CPU will be overloaded. As a result, unexpected high CPU and disk usage issue will occur. Step 1. On EaseUS CleanGinus, click "Cleanup" and click "Scan" to start cleaning up the system and make your PC as good as new. Step 2. The software will scanning all over your computer to find idle data files that take a huge amount of disk space, you can select useless large files, system junk files and Windows invalid entries and click "Clean" to start system cleanup process.
Step 3. When the scan is complete, click "Done" to finish cleaning system junk files. Right-click on Start and select "Command Prompt Admin ", sign in with your administrator account;. Type: DISM. Restart PC after this and then CPU high usage or RAM high usage issue has been lowered down by then.
Go to "Services" tab and click "Open" services; 3. Navigate and locate Superfetch, right click on it and select "Properties"; 4. Click "Stop" to end the Superfetch service and click OK to confirm the change;. Note: One thing that you should know is that Registry Editor may clear and remove some useful files on your PC while running below clear command to fix high CPU usage issue in Windows 10 Fall Creators.
Therefore, please do remember to backup important files and data to an external storage device before you trying below tips. Find: "ClearPageFileAtShutDown" and set its value to 1 ; 4.
Restart the computer and then CUP high usage issue will be fixed. Download Windows 10 Builds Quick Fix External Hard Drive Access Denied Error. Store Download Support Live Chat. For Windows Data Recovery Wizard Free Download Data Recovery Wizard Pro Buy Try Data Recovery Wizard Technician Buy Try Partition Recovery Buy Try MS SQL Recovery Buy Try Exchange Recovery Buy Try Email Recovery Wizard Buy Try For Mac Data Recovery Wizard Free Download Data Recovery Wizard Pro Buy Try Data Recovery Wizard Technician Buy Try For iOS iPhone Data Recovery Free Download iPhone Data Recovery Pro Buy Try For Android Android Data Recovery Free Download Android Data Recovery Pro Buy Try Android Data Recovery App.
For Home Partition Master Free Download Partition Master Professional Buy Try For Business Partition Master Enterprise Buy Try. For Home Todo Backup Free Download Todo Backup Home Buy Try Todo Backup for Mac Buy Try For Business Todo Backup Enterprise Buy Try Central Management Backup Center Buy Try Central Management Console System Deploy Deploy Manager Buy Try.
PC Transfer Todo PCTrans Free Download Todo PCTrans Pro Buy Try Todo PCTrans Technician Buy Try Phone Transfer iPhone Data Transfer Free Download iPhone Data Transfer Pro Buy Try iPhone Data Transfer Free Download iPhone Data Transfer Pro Buy Try. Video Toolkit Video Editor Buy Try Video Downloader Buy Try Video Converter Buy Try Screen Recorder RecExperts for Windows Buy Try RecExperts for Mac Buy Try Audio Tools MakeMyAudio Buy Try.
Here are some solutions and methods that you can apply to fix high CPU usage error in Windows 10 Fall Creators: Quick Fix 1. End Task of running programs Quick Fix 2. Disable startup programs. In other words, Windows 10 Fall Creators)is end of services. To keep your OS and data safe, we suggest you update your computer to the latest Windows 10 version or the coming up version.
To install the latest Windows 10 update, click to Download Latest Windows 10 Update. If you need a full and complete solution, Method 1, 2 and 3 can be your best shot and you can give any one of them for a try now.
Was This Page Helpful? Follow us . Resources PC Data Recovery Mac Data Recovery Disk Partition Tips Data Backup Screen Recorder Phone Transfer. Partners Resellers Reseller Login Affiliates Support Center Contact Support Team.
Hot Products Data Recovery Wizard Partition Master Todo Backup Todo PCTrans MobiMover RecExperts United States English . ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
0 notes
Text
VCP-SEC 2021 2V0-81.20 Exam Questions
If you are going to appear for 2V0-81.20 Professional VMware Security exam to earn your VCP-SEC 2021 Certification. PassQuestion provides the best-designed quality Professional VMware Security 2V0-81.20 Exam Questions that can help you to pass VMware 2V0-81.20 exam with good grades.If you are using Professional VMware Security 2V0-81.20 Exam Questions, then you will be able to prepare for the VMware 2V0-81.20 exam in an easier way.Make sure that you are using up to date Professional VMware Security 2V0-81.20 Exam Questions so you can easily clear the VCP-SEC 2021 Certification 2V0-81.20 exam on the first shot.
Professional VMware Security exam (2V0-81.20)
Professional VMware Security exam tests a candidate's knowledge of VMware's security solutions and the candidate's ability to administer the security features and functions of NSX-T Data Center, Workspace ONE, and VMware Carbon Black Cloud. The Professional VMware Security exam (2V0-81.20) which leads to VMware Certified Professional – Security 2021 certification is a 70-item exam, with a passing score of 300 using a scaled scoring method. Candidates are given 130 minutes to complete the exam, which includes adequate time to complete the exam for non-native English speakers.
Exam Information
Exam Number: 2V0-81.20 Exam Language: English Associated Certification: VCP-SEC 2021 Duration: 130 minutes Number of Questions: 70 Questions Passing Score: 300 Format: Multiple Choice, Multiple Choice Multiple Selection, Drag and Drop, Matching
2V0-81.20 Exam Topics
Section 1 – Architecture and Technologies Section 2 – Products and Solutions Section 3 – Planning and Designing Section 4 – Installing, Configuring, and Setup Section 5 – Performance-tuning, Optimization, and Upgrades Section 6 – Troubleshooting and Repairing Section 7 – Administrative and Operational Tasks
View Online Professional VMware Security 2V0-81.20 Free Questions
Where in the NSX UI does an administrator deploy NSX Intelligence? A.Go to Plan & Troubleshoot > Configuration > ADD NSX INTELLIGENCE APPLIANCE B.Go to Security > Configuration > Appliances > ADD NSX INTELLIGENCE APPLIANCE C.Go to System > Configuration > Appliances > ADD NSX INTELLIGENCE APPLIANCE D.Go to Home > Configuration > Appliances > ADD NSX INTELLIGENCE APPLIANCE Answer: C
Users on iOS and Android devices are being prompted for their credentials when accessing an application protected by Workspace ONE Access. The current configuration includes: Workspace ONE UEM is integrated with Workspace ONE Access Workspace ONE UEM has a Certificate Authority configured Single sign-on has been enabled through device profiles What authentication method can be used to allow iOS and Android devices to launch an application without being prompted for credentials? A.TRUESSO B.Kerberos C.Mobile SSO D.Windows SSO E.OKTA Answer: C
An administrator has added a new ESXi host to a vCenter Server Cluster with NSX-T Data Center already working. The administrator installed NSX-T Data Center components in the new ESXi. When the administrator deploys a new VM in the host, connectivity tests good with ping, but SSH session traffic is erratic. The VDS and NSX-T Data Center configuration is the same as each ESXI in the Cluster, but only VMs in the new ESXI are having problems. What should the administrator do to address the problem? A.Verify VLAN connection in each physical uplink. B.Verify MTU configuration in each physical uplink. C.Change VDS MTU to 1500 in each physical uplink. D.Change VDS MTU to 2000 in each physical uplink. Answer: B
When creating a compliance policy in Workspace ONE UEM, which three of the following options are valid Notify actions? (Choose three.) A.Send SMS to Device B.Send Push Notification to Device C.Voice Call to User D.Send Email to User E.SMS to Manager Answer: ABD
What is the number of NSX managers that can be deployed in a NSX-T Data Center production environment? A.a single NSX Manager and three NSX Controllers B.a NSX Management Cluster of three Managers and a NSX Controllers Cluster of three Controllers C.a single NSX Management Cluster of three Managers which includes the NSX Controller function D.a single NSX Manager and a single NSX Controller Answer: B
0 notes
Text
Deep Dive Architecture Comparison of DaaS & VDI, Part 2
In part 1 of this blog series, I discussed the Horizon 7 architecture and a typical single-tenant deployment using Pods and Blocks. In this post I will discuss the Horizon DaaS platform architecture and how this offers massive scale for multiple tenants in a service provider environment.
Horizon DaaS Architecture
The fundamental difference with the Horizon DaaS platform is multi-tenancy architecture. There are no Connection or Security servers, but there are some commonalities. I mentioned Access Point previously, this was originally developed for Horizon Air, and is now a key component for both Horizon 7 and DaaS for remote access.
If you take a look at the diagram above you’ll see these key differences. Let’s start with the management appliances. There are five virtual appliances (OVA) used for Horizon DaaS; Service Provider, Tenant, Desktop Manager, Resource Manager and Access Point. When these appliances are deployed, they are always provisioned as an HA pair (master/slave), except for Access Point which is active/active across multiple appliances. No load-balancer is required, only for multiple Access Point appliances. The remaining virtual appliances use a virtual IP in the master/slave configuration. There is only a single OVA (template), and upon initial installation, the bootstrap process uses this template as a base for each of the virtual appliance types.
I’ve already introduced Access Point with the Horizon 7 architecture previously, but it’s worth mentioning that this is a recent addition. Previously with the original Desktone product and subsequent versions of Horizon DaaS platform, remote access was provided using dtRAM (Desktone Remote Access Manager). The dtRAM is also a virtual appliance (based on FreeBSD and pfSense) and still available, but I would now recommend using Access Point for the latest features.
Service Provider
The service provider has two different types of virtual appliance (HA pair); the Service Provider and Resource Manager.
The Service Provider appliance provides the Service Center portal where the provider can perform a number of activities including Desktop Model management, Tenant management, monitoring and discovery of infrastructure resources. This appliance also contains a Resource Manager service which targets and deploys other management virtual appliances. For example, when a Tenant Appliance pair is created, it’s name, networks, IP address, and so on, are stored in the FDB (Fabric Database). The Service Provider appliance then instructs the resource manager service to clone a tenant appliance.
Resource Manager
The Resource Manager virtual appliance communicates with the infrastructure (vCenter) to carry out desktop provisioning, and provides management of all desktops for tenants. Unlike Horizon 7 that can provision View Composer linked clones, Instant Clones or full clones, only full clones are currently supported with Horizon DaaS. Resources are assigned to tenants so they can consume compute, storage and network for virtual desktops.
It’s important to note that Resource Manager appliances are tied to the service provider, and not the tenant.
Tenant
The tenant also has two different types of virtual appliance (HA pair); Tenant and Desktop Manager virtual appliance.
The Tenant appliance provides a web-based UI (Enterprise Center) for both the tenant end-user and IT administrator. End-users can manage their own virtual desktops, and the administrator functions allow for creation and management of the tenant desktops.
Other tenant operations provided by Enterprise Center, include:
Domain registration
Gold pattern conversion
Desktop pool creation
AD user and group assignment to virtual desktops
The Tenant virtual appliance also contains a Desktop Manager component which brokers connections to tenant virtual desktops. Each Desktop Manager supports up to 5,000 virtual desktops. If more are required then a HA-pair of Desktop Manager virtual appliances can be deployed.
Desktop Manager
The Desktop Manager virtual appliance is the same as the Tenant appliance, but does not include the brokering or Enterprise Center portal. You can deploy Desktop Manager appliances to scale beyond the 5,000 virtual desktop limit.
Resources are assigned to the Desktop Manager for consumption by the tenant. In some cases you may have a vSphere cluster dedicated for 3D workloads with vDGA pass-through. These 3D specific resources would be dedicated to a Desktop Manager virtual appliance pair.
Each virtual desktop is installed with the DaaS Agent which sends heartbeats to the Desktop Manager in order to keep track of it’s state.
Networking
As shown in the above diagram, there are three networks associated with Horizon DaaS; Backbone Link Local network, Service Provider network, and tenant networks.
The Backbone Link Local network is a private network that is dedicated for all virtual appliances. Although the Tenant virtual appliances are connected to this network, there is no access from the tenant network.
The Service Provider management network provides access for service provider administration of the Service Provider appliances, and vSphere infrastructure.
The Tenant network (per tenant) is dedicated for virtual desktops. This also has IP connectivity to the tenants supporting infrastructure such as Active Directory, DNS, NTP, and file servers.
Horizon DaaS Terminology

Conclusion
VMware Horizon® is a family of desktop and application virtualization solutions that has matured significantly over the past few years. vCloud Air Network service providers can provide customers with either a managed Horizon 7 platform, or Desktop as a Service with Horizon DaaS.
Both Horizon 7 and Horizon DaaS offer virtual desktops and applications, and used in combination with App Volumes, applications can be delivered in near real-time to end-users.
Access Point provides remote access to both Horizon 7 and Horizon DaaS which provide many advantages to the service provider. With their active/active scalable deployment, and hardened Linux platform, service providers and customers can benefit from multiple authentication and access methods from any device and any location.
For both Horizon solutions, RDSH continues to be an attractive choice for delivering desktop or application sessions. These can either be presented to the user with the Horizon Client, or with integration with Workspace ONE and Identity Manager.
Finally, the vCloud Air Network is a global ecosystem of service providers that are uniquely positioned to supply modern enterprises with the ideal VMware-based solutions they need to grow their businesses. Built on the foundation of existing VMware technology, vCloud Air Network Service Providers deliver a seamless entry into the cloud. You can learn more about the vCloud Air Network, or search for a vCAN service provider here: http://vcloudproviders.vmware.com
0 notes
Text
Linux Engineer Job For 4-7 Year Exp In Hewlett Packard Enterprise Bengaluru / Bangalore, India - 3511431
Linux Engineer Job For 4-7 Year Exp In Hewlett Packard Enterprise Bengaluru / Bangalore, India – 3511431
4+ years of experience in managing Linux Engineer2+ years of Experience in Linux clust Install, administer and maintain hardware, system software, networking, accounts, and security measures on VMWare configuration Strong Knowledge in installing and configuring all flavors of ESXi and vCenter server. Diagnose and correct system issues, whether these be issues with correct operation or…

View On WordPress
0 notes